Featured Application
Authors are encouraged to provide a concise description of the specific application or a potential application of the work. This section is not mandatory.
Abstract
A growing body of literature shows that the transverse relaxation times of the placenta change during pregnancy and may be an early indicator of disease. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of pregnant women is not, however, currently used frequently despite this evidence. One significant barrier to adoption is the cost of undertaking an MRI scan and the over utilization of existing equipment. Low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) offers a low-cost alternative, capable of measuring transverse relaxation in a single point in space. Ultrasound imaging (US) is routinely used at several points during pregnancy but is not capable of early detection of pre-eclampsia, for example. It does, however, provide a technique that is capable of locating the placenta with ease. In combination with a single point low-field measurement, localised with ultrasound imaging allows access to this exciting technique without the need for an expensive traditional MRI. In this work, we present a unilateral system (NMR CAPIBarA), operating at a magnetic field of only 18mT, which measures transverse relaxation times at distances from its surface equivalent to the positioning of a human placenta. Data are presented to characterise the system using relation time standards covering the full transverse relaxation time range relevant for the developing placenta, which are also measured on a 1.5 T clinical MRI scanner.
1. Introduction
The average cost for a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan has been suggested to be in excess of $2500 [1]. In comparison to the average cost of an ultrasound at $263 [2], from a cost perspective alone it is unsurprising that the routine monitoring of placental health is undertaken throughout a pregnancy using ultrasound. Routine ultrasound, however, reveals little about many diseases of the placenta until they have progressed. MRI is generally thought to be safe after the end of the first trimester. As early as 1998 [3], it had been reported that the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) relaxation parameter, known as the transverse relaxation time of the placenta decreases through pregnancy. Furthermore, for cases of pre-eclampsia this value fell below the ‘healthy’ trend line with other later studies confirming these findings [4,5,6]. Ultrasound scans have become routine during pregnancy in many countries around the world, as they are affordable in most hospitals and can be purchased in some quantity in an average obstetrics department. If a simple add-on to the ultrasound could be developed to provide a measure of the transverse relaxation time of the placenta, then it should be possible to provide an early prediction of mothers at high risk of pre-eclampsia who could be more closely monitored.
Unilateral magnetic resonance systems, often termed inside-out, usually use an array of permanent magnets to generate a uniform magnetic field, satisfying the requirements of a magnetic resonance experiment, some distance away from a surface. The earliest unilateral systems were designed for well logging, and consequently much of the technology was not published in the academic literature [7]. The introduction of unilateral systems to the mainstream came in the late 1990’s with the development of the NMR-MoUSE [8,9]. This bench top system had a magnet array that produced a uniform magnetic field parallel to, and a few mm away from, the surface of the device. Paired with a radio frequency (RF) surface coil, MR is performed in the small region where an RF field and static magnetic fields overlap approximately perpendicularly. This is known as the sensitive volume.
The NMR-MoUSE has been a commercial product for nearly two decades and has evolved into a suite of instruments offering different distances of sensitive regions above the surface from 2 mm with 5 μM resolution for the PM2 up to 25 mm away with 100 μM resolution for the PM25 [10]. Medical applications of this unilateral system have been appearing in the literature, including profiling of human skin [11], articular cartilage [12], bone volume–to–total volume ratio [13], T1-based mammographic density [14] and T2-based mammographic density [15].
In our work, we report the development of a low-field unilateral system, which we call the NMR CAPIBarA-Clinical Assessment of Patients Implemented with Bar magnet Arrays (because it is like a very large NMR-MoUSE), which operates at a magnetic field of only 18 mT. The instrument is capable of measuring transverse relaxation times over the range of values presented in the literature for the developing placenta and at a distance sufficiently far away to reach an anterior placenta for an average pregnancy.
2. Materials and Methods
In an article by Dabaghyan et al. [16], the authors presented a unilateral magnet design which, like the NMR MoUSE, provides a B0 parallel with the surface of the magnet. Their magnet was constructed from two rectangular arrays of 240 small NdFeB magnets, around 400 mm between centers with a saddle point at around 80 mm above the magnet surface and with a field strength at this point of 10 mT (note that this is more than an order of magnitude smaller than the 0.25 T and above of the profile NMR-MoUSE family). Their system was designed to measure the NMR signal from the lung (a notoriously challenging tissue to MRI), and required a target volume of the order of 30 cm3. This was achieved using a short solenoid coil of height and radius 5 cm placed in the midpoint of the array.
Using a similar design with a smaller number of larger magnet blocks, we achieved a field with a sensitive volume that can be easily maneuvered to remotely interrogate the placenta. Each half of our magnet consists of a 5 by 2 50 × 50 × 25 mm N52 Neodymium Magnet (first4magnets.com F335-N52-R) array, as shown schematically in Figure 1, and produces a sensitive volume of 18 mT at 76 mm above the magnet surface in the center. The magnets are held in place with laser cut acrylic sheets. Figure 2a shows the side view of the magnet with a plastic model (Pregnant Women Model AS30591, anatomystuff.co.uk) to aid visualization. Figure 2b shows the top view of the magnet array.
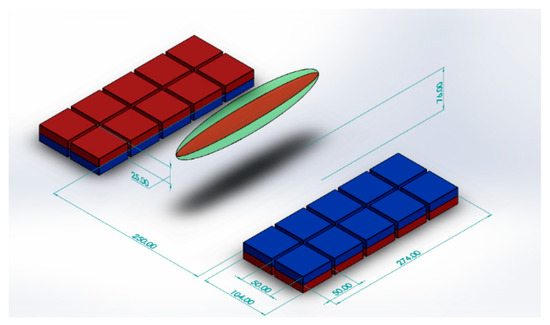
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of magnet array showing position of the ‘sweet spot’.
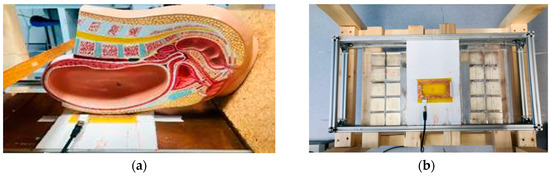
Figure 2.
(a) Side view of the magnets and coil with a pregnancy model showing positioning and (b) top view of the magnets (with copper sheet removed) and coil with the copper sheets removed from above the magnets.
Unlike Dabaghyan et al. [16], who made use of a solenoid to interrogate a large sample volume, a planar coil was produced using a milled 75 μm FR4 Printed Circuit Board (PCB) with 5 turns at a line width of 2 mm, with 1mm spacing between tracks, inner and outer coil lengths of 82 mm and 105 mm, respectively, and inner and outer coil widths of 40 mm and 67 mm, respectively, with an epoxy resin coating applied post-production. The coil is also visible in Figure 2b. Note that this type of PCB coil must have a suitable coating material, in our case epoxy resin, for effective matching of permittivity to ensure sufficient performance. To provide an intermediate between the CAPIBarA system and the MRI scanner, a solenoid coil, encompassing the sensitive volume of the magnet, was also tested. A solenoid minimises two of the primary issues of surface coils, filling factor (how much of the sensitive volume of the coil is filled with sample), and the amount of sample in inhomogeneous RF fields. The 20 mm diameter by 20 mm length solenoid comprised three layers of 30 turns of Litz wire. The Litz wire had 81 strands of 0.04 mm diameter copper wrapped in silk giving an overall wire diameter of 0.67 mm. During operation, the magnets are covered in copper sheets to minimise the interaction of the magnets with the RF coil.
A schematic diagram of the MR electronics is shown in Figure 3. A commercial magnetic resonance console (Radioprocessor, SpinCore, Gainesville, FL, USA) is controlled using an in-house MATLAB GUI (Mathworks, MA) to produce the Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill (CPMG) pulse sequence [17] used to determine the effective transvers relaxation time. The output of the Spincore was amplified (BT00500, Tomco, Stepney, Australia) and fed to the input of a duplexer (custom built transcoupler, nmr-service.de, Germany) that operates from 0.7 to 1 MHz. The resulting MR signal was amplified using a pair of ZFL-500LN amplifiers (MiniCircuits, Brooklyn, NY, USA) with a 1 MHz low pass filter (EF508, Thorlabs, Newton, NJ, USA) either side of the second pre-amplifier.
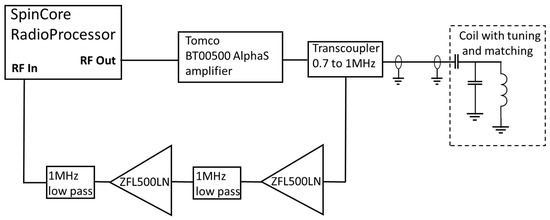
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of the NMR electronics.
Coarse tuning and matching was accomplished using AVX high-voltage capacitors, with the fine tuning being achieved by changing the length of the coaxial cable between the duplexer and the capacitors. A series of silicone oils (Schumacer Racing, Northampton, UK) of different viscosities from 300 cP to 30,000 cP were used to give samples of different effective transverse relaxation times. A clinical MRI scanner (1.5 T MAGNETOM Avanto, Siemens, Erlangen, Germany) was used to provide a reference value to demonstrate the suitability of this system to replace high-field clinical imaging.
The effective transverse relaxation time, T2eff, is most commonly measured by the CPMG pulse sequence [17] where an RF excitation pulse tips the magnetization by 90° into the transverse plane where the phase becomes scrambled due to molecular interactions. After, a delay τ an RF pulse is applied, which flips the magnetization by 180°, causing an effective rewinding of the phase generating a so-called spin echo τ later. This process is repeated to produce a train of echoes with an exponential envelope of time constant T2eff. In very homogeneous field, the decay of T2eff is minimal since there is little loss of phase coherence due to Brownian motion through field gradients. However, for less homogeneous magnetic fields this results in a parameter that is highly dependent on diffusion, field gradient magnitude, and the echo time (which is equal to 2τ). An alternative method reported in [18] measures the integral of the echoes as a function of increasing echo times (TE) to avoid a contribution from molecular diffusion; however, such an approach is too lengthy for clinical applications of inhomogeneous low-field systems such as this. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is improved by undertaking this experiment and averaging the results, and the signal is averaged linearly, whilst the noise scales with the square root of the number of averages; hence, the SNR is dependent on .
The value of T2eff is then calculated by determining the modulus of the real and imaginary components of the spin echoes before taking the integral of each of the echoes (to improve SNR); a monoexponential is then fitted to the timecourse of the decay using a Levenberg Marquardt least squares minimization revealing T2eff as the time constant of the decay. In our case, this is undertaken within the previously mentioned custom MATLAB (Mathworks, Natick, MA, USA) GUI used to run the console.
Figure 4 shows the data for 5000 cP silicon oil from a CPMG sequence using the solenoid coil on the CAPIBarA system. The MR signal acquired from 256 averages of a CPMG experiment with RF pulse durations is set to 5 μs for a frequency of 804.25 kHz. The signal is acquired with a dwell time of 10 μs for 8 points over the center of 250 echoes that are 800 μs apart. Each average is collected with a repetition time of 1200 ms, giving a total experimental time of 5 min.
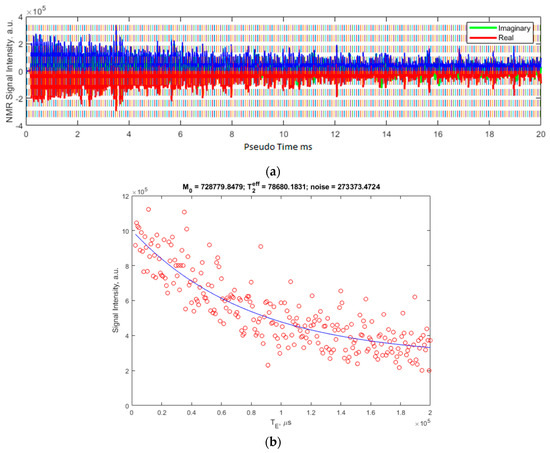
Figure 4.
(a) shows the raw signal as collected using the MATLAB GUI. The blue overlay is the modulus of the real (red) and imaginary (green, mostly overlaid) channels of the acquisition. (b) shows the resulting integrals of these echoes in red and the fit to this data, the parameters of which are shown above the plot. The T2eff is shown in microseconds.
For the planar coil, the CPMG sequence parameters are similar except for the pulse duration, which is increased to 67.5 μs for a frequency of 764 Khz; the dwell time is increased to 25 μs and the number of averages is increased to 1536, giving a total experiment time of 30 min.
The size of the sensitive volume is dependent on several parameters, including the transmission bandwidth, receiver chain bandwidth (which in turn is dependent on the acquisition time) and the homogeneity of the magnetic field. The more homogeneous the field, the larger this volume will be, whilst shorter dwell times and shorter transmit pulses will also increase the size of this volume. The narrowest bandwidth of these will dictate the overall bandwidth of the measurement. In this case, the RF pulse is limiting and excites a bandwidth of 50 kHz for the solenoid and 3.7 kHz for the planar coil. This corresponds to 1.2 mT and 88 Μt, respectively. The volume over which the magnet is homogenous to these values is determined using a homebuilt 3 axis magnetometer based on CYL8405 (ChenYang Gmbh, Finsing, Germany). The sensitive volumes were found to be 209 mm3 and 60 mm3, respectively. Graphical approximations of these volumes are shown as the green and red ellipsoids, respectively, on Figure 1.
3. Results
Figure 4a shows the resulting echo train as collected by the CPMG sequence discussed in the previous section. The integral of the echoes is then calculated and plotted along with the resulting fit in Figure 4b.
A range of silicone oils are tested on the high-field MRI system utilizing a similar CPMG pulse sequence with imaging. An image is produced for each of the echo times, collecting a total of 16 images, the first of which is shown in Figure 5a. A region covering the center of each of the samples is then selected and the same region averaged in each of the 16 images. This provides similar data to that shown in Figure 4b but with fewer points owing to software limitations. The exponential time constant is once again T2eff, which is shown as a function of viscosity in Figure 5b.
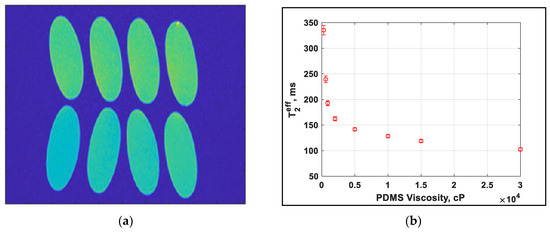
Figure 5.
(a) Image of the final echo of the echo image from MRI showing the range of values experienced. Viscosity in cP is labelled (b) dependence of T2eff on the PDMS viscosity.
The values as determined for the T2eff from the CAPIBarA are plotted against those from the MRI in Figure 6 and show a correlation between 0.4 and 0.5 that, importantly, is linear, thus demonstrating that this system works over the range of values needed to make useful predictions of placental health.
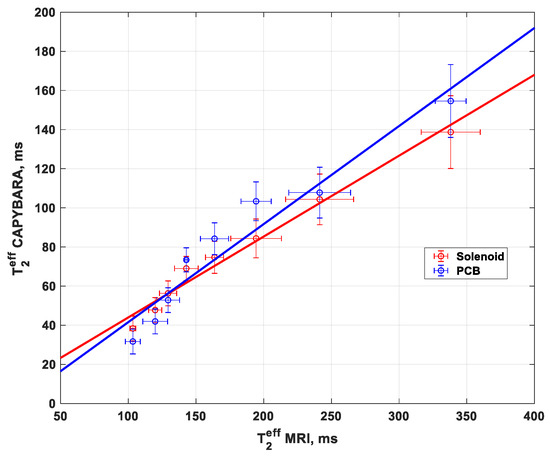
Figure 6.
T2eff measurements using solenoid and PCB coil with a unilateral system (NMR CAPIBarA) compared to the clinical MRI T2eff measurement.
4. Discussion
It can be seen from the data in Figure 4 that there is significant scatter of the data points around the fit owing to thermal, background and system noise. The nature and in particular the symmetry of this noise is such that it is not detrimental to the fit and is included as a baseline offset. Furthermore, the ability to collect a number of spin echoes per experiment without impacting on the repetition time of the experiment allows for a sufficiently high density of data points to allow for a good level of confidence in the fit parameters. The homogeneity of the system yields a prolate ellipsoid with its major axis along the gap between the magnets, which is to be expected. The transmit efficiency is the limiting factor in the sensitive volume, which may, however, be an advantage for practical uses of the system yielding a small sensitive spot that is well visualised in concurrent modalities such as ultrasound imaging. At present, the system is only capable of reaching anterior placentae although there is evidence in the literature to suggest that there is an increased risk of placental disease with such placement [19]. In order to reach a posterior placenta, the additional thickness presented by the spine must be overcome. This will require greater spacing between the pair of magnet arrays, which will produce a corresponding drop of field strength that will require additional averaging or more efficient RF coil designs. It may be desirable in such a case to have variable spacing between the pair of magnet arrays, such that the depth can be optimised for each measurement (although this brings with it the complication of needing to vary the tuning between experiments).
5. Conclusions
We have demonstrated a system that is capable of measuring the values of T2eff over the range that has been shown in the literature to be representative of diseased placentae. These measurements have been undertaken at a depth that is relevant to an anterior placenta but is not sufficiently deep to reach a posterior placenta at this time. The ability to co-locate the MR sensitive volume, by utilizing routine ultrasound imaging, provides potential access to a new diagnostic technique that is capable of early detection of placental diseases such as pre-eclampsia and may allow for more appropriate monitoring and treatment of expectant mothers who are at heightened risk. The current measurement time of 30 min for the planar coil is longer than acceptable for a routine scan in a clinical environment, but the 5-min scan for the solenoid suggests that there is scope for improving the depth of the measurement to reach a posterior placenta despite the loss of SNR that increased depth brings. Furthermore, the homogeneity of the magnet, and the large potential measurement volume, facilitates a range of viable measurement locations within the magnet volume. It is anticipated that with adjustments to the designs of the magnet array and RF coil, or possibly by introducing shaped, adiabatic or chirp pulses, it should be possible to undertake ultrasound co-located MR measurements of placental health in vivo using this low-cost system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and Methodology, R.H.M. and M.I.N.; Software, R.H.M.; Magnet array development, C.L.T. and N.K.A.; Investigation N.K.A.; Electronics, M.I.N., N.K.A. and R.H.M; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, M.I.N.; Writing—Review and Editing, R.H.M., C.L.T. and N.K.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
N.K.A gratefully acknowledges the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research (MOHESR) in the United Arab Emirates for funding and the Dubai Health Authority (DHA) for study leave.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Glover, L. Why Does an MRI Cost So Darn Much? 2014. Available online: http://money.com/money/2995166/why-does-mri-cost-so-much/ (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Dean, R. Expecting? How much does an ultrasound cost? 2014. Available online: https://blog.bernardbenefits.com/bid/196963/expecting-how-much-does-an-ultrasound-cost (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Gowland, P.A.; Freeman, A.; Issa, B.; Boulby, P.; Duncan, K.R.; Baker, P.N.; Bowtell, R.W.; Johnson, I.R.; Worthington, B.S. In vivo relaxation time measurements in the human placenta using echo planar imaging at 0.5 T. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1998, 16, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.; Morris, D.M.; Baker, P.N.; Crocker, I.P.; Gowland, P.A.; Parker, G.J.; Sibley, C.P. Magnetic resonance imaging relaxation time measurements of the placenta at 1.5 T. Placenta 2011, 32, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameyama, N.K.; Kido, A.; Himoto, Y.; Moribata, Y.; Minamiguchi, S.; Konishi, I.; Togashi, K. What is the most suitable MR signal index for quantitative evaluation of placental function using Half-Fourier acquisition single-shot turbo spin-echo compared with T2-relaxation time? Acta Radiol. 2017, 59, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siding, M.; Peters, D.A.; Frokjaer, J.B.; Christiansen, O.B.; Petersen, A.; Uldbjerg, N.; Sorensen, A. Placental magnetic resonance imaging T2 * measurements in normal pregnancies and in those complicated by fetal growth restriction. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 6, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinberg, R.L.; Jackson, J.A. An Introduction to the History of NMR Well Logging. Concepts Magn. Reson. 2001, 13, 340–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidmann, G.; Savelsberg, R.; Blumle, P.; Blumich, B. The NMR MoUSE, a mobile universal surface explorer. J. Magn. Reson. A 1996, 122, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumich, B.; Blumler, P.; Eidmann, G.; Guthausen, A.; Haken, R.; Schmitz, U.; Saito, K.; Zimmer, G. The NMR-mouse: Construction, excitation, and applications. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1998, 16, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NMR-MOUSE. Available online: magritek.com/products/nmr-mouse/ (accessed on 16 October 2019).
- Van Landeghem, M.; Danieli, E.; Perlo, J.; Blümich, B.; Casanova, F. Low-gradient single-sided NMR sensor for one-shot profiling of human skin. J. Magn. Reson. 2012, 215, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rössler, E.; Mattea, C.; Stapf, S. Feasibility of high-resolution one-dimensional relaxation imaging at low magnetic field using a singlesided NMR scanner applied to articular cartilage. J. Magn. Reson. 2015, 251, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brizi, L.; Barbieri, M.; Baruffaldi, F.; Bortolotti, V.; Fersini, F.; Liu, H.; d’Eurydice, M.N.; Obruchkov, S.; Zong, F.; Galvosas, P.; et al. Bone volume–to–total volume ratio measured in trabecular bone by single-sided NMR devices. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tourell, M.C.; Ali, T.S.; Hugo, H.J.; Pyke, C.; Yang, S.; Lloyd, T.; Thompson, E.W.; Momot, K.I. T1-based sensing of mammographic density using single-sided portable NMR. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 80, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, T.S.; Tourell, M.C.; Hugo, H.J.; Pyke, C.; Yang, S.; Lloyd, T.; Thompson, E.W.; Momot, K.I. Transverse relaxation-based assessment of mammographic density and breast tissue composition by single-sided portable NMRe. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 82, 1199–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabaghyan, M.; Muradyan, I.; Hrovat, A.; Butler, J.; Frederick, E.; Zhou, F.; Kyriazis, A.; Hardin, C.; Patz, S.; Hrovat, M. A portable single-sided magnet system for remote NMR measurements of pulmonary function. NMR Biomed. 2014, 27, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meiboom, S.; Gill, D. Modified spin-echo method for measuring nuclear relaxation times. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1958, 29, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henoumont, C.C.; Laurent, S.; Vander Elst, L. How to perform accurate and reliable measurements of longitudinal and transverse relaxation times of MRI contrast media in aqueous solutions. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2009, 4, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zia, S. Placental Location and Pregnancy Outcome. J. Turk. Ger. Gynecol. Assoc. 2013, 14, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).