Deficiencies in Project Governance: An Analysis of Infrastructure Development Program
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work on Project Governance
- Active participation, which is the right decision at the right time;
- Contract fairness, meaning a rule of law to be enforced impartially;
- Transparency, where information must be freely available and implementation of the decisions must be according to the rules and regulations;
- Responsive decisions made must be implemented within a stipulated time period;
- Project monitoring and control in order to achieve strategic goals to meet and exceed the satisfaction of all the stakeholders;
- Equality between all involved parties, where all parties have the same opportunities to improve and maintain their own well-being;
- Effectiveness and efficiency through optimal utilization of resources and through sustainable utilization of natural resources; and;
- Accountability must be enforced through rule of law and transparency and should be in the form of public participation and user satisfaction.
Need of Project Governance for Infrastructural Planning in Pakistan
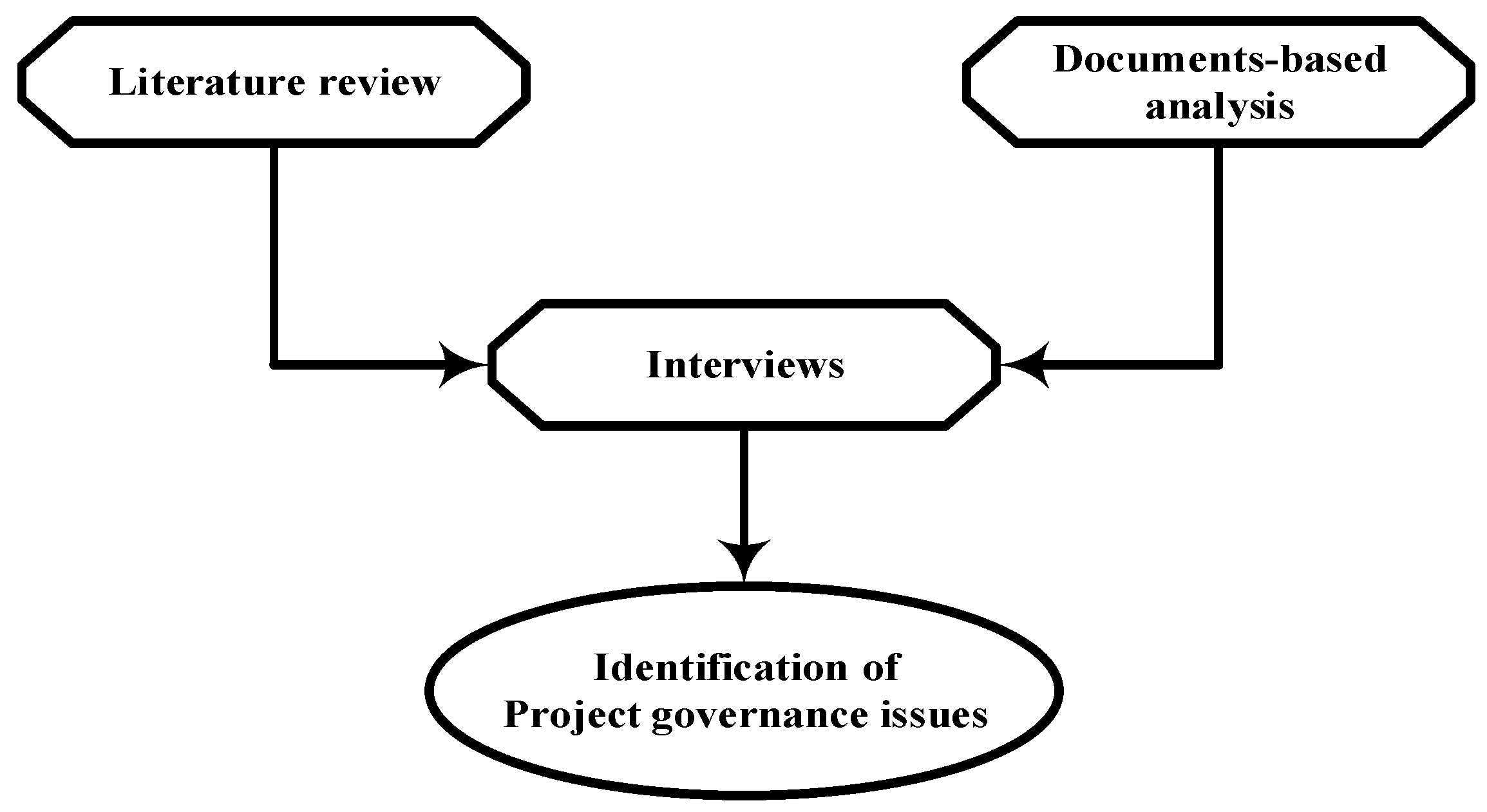
3. Method
3.1. Description of the Case Study Area
3.2. Case Study
3.3. Extraction of Data
- Literature review
- Official published reports and documents
- Published in the time span of 2009 to 2018
- Focused on the public infrastructure projects
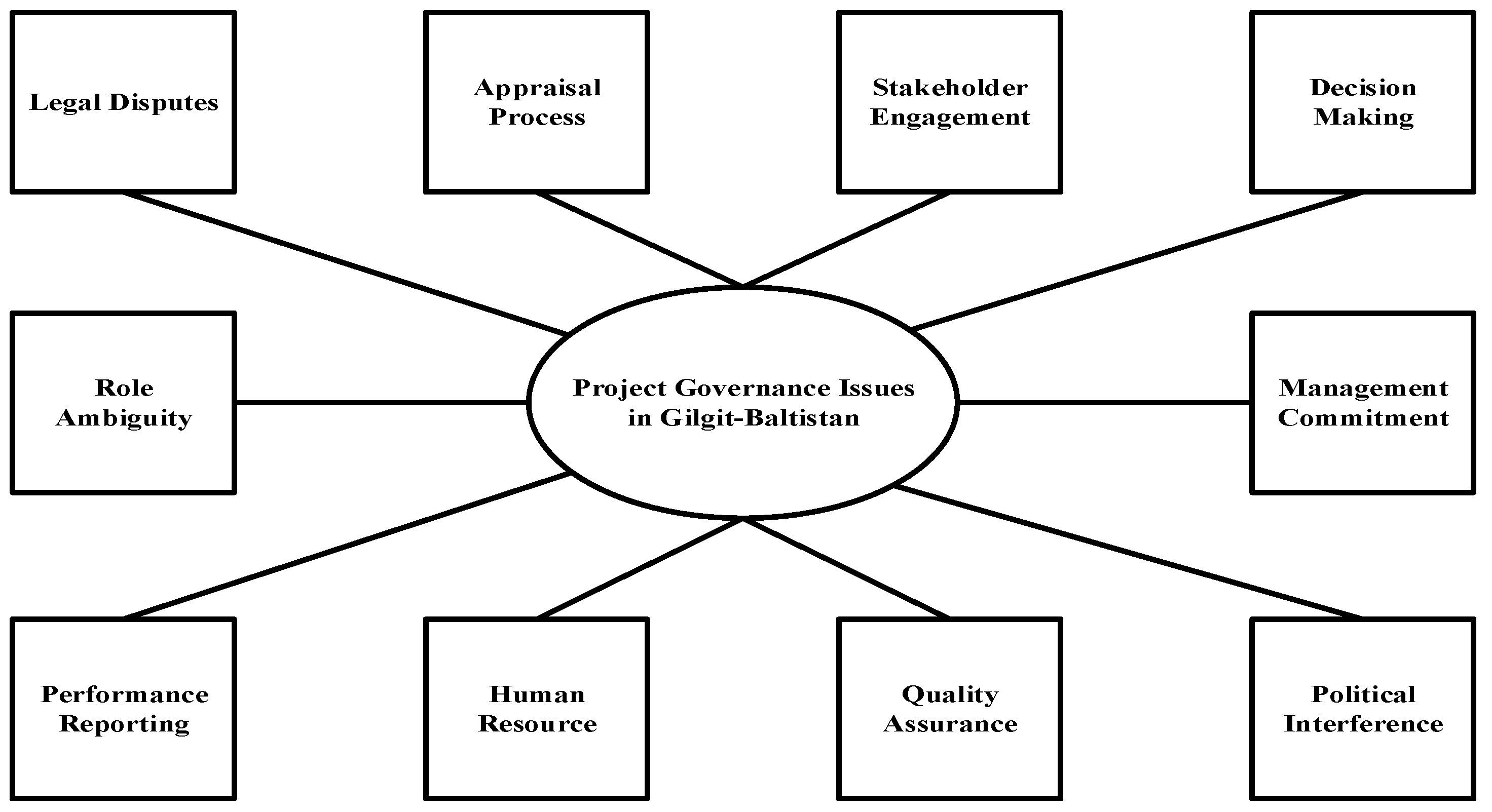
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Appraisal Process
4.2. Stakeholder Engagement
4.3. Decision-Making
4.4. Management Commitment
4.5. Political Interference
4.6. Quality Assurance
4.7. Human Resource
4.8. Performance Monitoring
4.9. Role Ambiguity
4.10. Legal Disputes
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Sector-Wise Projects | No. of Projects | Cost (PKR) Million |
|---|---|---|
Housing
| 12 | 713 |
Water and Power
| 22 | 2806 |
Natural resource management
| 9 | 312 |
Education
| 25 | 1096 |
Health
| 12 | 422 |
Transport and Communication
| 40 | 1393 |
Rural and Urban Development
| 6 | 217 |
| Total | 126 | 6959 |
References
- Abednego, Martinus P., and Stephen O. Ogunlana. 2006. Good project governance for proper risk allocation in public–private partnerships in Indonesia. International Journal of Project Management 24: 622–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Riaz M., and Noor Azmi bin Mohamad. 2014. Performance of project in public sector of pakistan: Developing a Framework for future Challenges. Serbian Project Management Journal 4: 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ahola, Tuomas, Inkeri Ruuska, Karlos Artto, and Jaakko Kujala. 2014. What is project governance and what are its origins? International Journal of Project Management 32: 1321–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, Nida, Rizwan U. Farooqui, and Syed M. Ahmed. 2008. Cost overrun factors in construction industry of Pakistan. Paper presented at First International Conference on Construction in Developing Countries (ICCIDC–I), Advancing and Integrating Construction Education, Karachi, Pakistan, August 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Bekker, Michiel C. 2015. Project Governance–the definition and leadership dilemma. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences 194: 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekker, Michiel Christiaan, and Herman Steyn. 2007. Defining ‘project governance’for large capital projects. Paper presented at AFRICON 2007, Windhoek, South Africa, September 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Brunet, Maude, and Monique Aubry. 2016. The three dimensions of a governance framework for major public projects. International Journal of Project Management 34: 1596–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burki, Shahid Javed. 2015. Historical dictionary of Pakistan. Lanham: Rowman & Littlefield. [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas, Ibsen Chivata, Hans Voordijk, and Geert Dewulf. 2017. Beyond theory: Towards a probabilistic causation model to support project governance in infrastructure projects. International Journal of Project Management 35: 432–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flyvbjerg, Bent, Nils Bruzelius, and Werner Rothengatter. 2003. Megaprojects and Risk: An Anatomy of Ambition. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Garland, Ross. 2009. Project Governance: A Practical Guide to Effective Project Decision Making. London: Kogan Page Publishers. [Google Scholar]
- Garvin, Michael J. 2009. Governance of PPP projects through contract provisions. Paper presented at Conference of Leadership and Management of Construction, Blacksburg, VA, USA, January 1. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. 2009. A typology of reviews: An analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal 26: 91–108. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Feng, Yan Chang-Richards, Suzanne Wilkinson, and Ti Cun Li. 2014. Effects of project governance structures on the management of risks in major infrastructure projects: A comparative analysis. International Journal of Project Management 32: 815–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, Sajad, Farman Karim, and Mir Nazeem. 2014. Monitoring Report of Development Projects. Skardu, Pakistan: Gilgit-Baltistan. [Google Scholar]
- Hellström, Magnus, Inkeri Ruuska, Kim Wikström, and Daniel Jåfs. 2013. Project governance and path creation in the early stages of Finnish nuclear power projects. International Journal of Project Management 31: 712–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelmbrekke, Hallgrim, Ole Jonny Klakegg, and Jardar Lohne. 2017. Governing value creation in construction project: A new model. International Journal of Managing Projects in Business 10: 60–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, Muhammad, and Mazlan Hassan. 2017. The Effect of Project Success on Corporate Reputation of the Public Sector Organizations in Pakistan. International Journal of Economics and Management 11: 815–32. [Google Scholar]
- Jonny Klakegg, Ole. 2009. Pursuing relevance and sustainability: Improvement strategies for major public projects. International Journal of Managing Projects in Business 2: 499–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanyane, Modimowabarwa Hendrick, and Kombi Sausi. 2015. Reviewing state-owned entities’ governance landscape in South Africa. African Journal of Business Ethics 9: 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazim, Muhammad, Rukhsana Perveen, Abid Zaidi, Rafiq Hussain, Nadia Fatima, and Sherzad Ali. 2015. Biodiversity of spiders (Arachnida: Araneae) fauna of Gilgit Baltistan Pakistan. International Journal of Fauna and Biological Studies 2: 77–79. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Asadullah, Ammar Hussain, Muhammad Waris, Ishak Ismail, and Muhammad Ilyas. 2018. Infrastructure project governance: An analysis of public sector project in northern Pakistan. Journal of Governance and Integrity 1: 120–34. [Google Scholar]
- Khattak, Muhammad Sajid, Usman Mustafa, and S. M. Shah. 2016. Mapping Project Management Competencies with Different Complexities for Improving Performance. Journal of Managerial Sciences 10: 206–17. [Google Scholar]
- Klakegg, Ole Jonny, Terry Williams, and Ole Morten Magnussen. 2007. Design of innovative government frameworks for major public investment projects: A comparative study of governance frameworks in UK and Norway. Paper presented at the IRNOP VIII Project Research Conference, September 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kochhar, Rahul. 1996. Explaining firm capital structure: The role of agency theory vs. transaction cost economics. Strategic Management Journal 17: 713–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, Raymond E., Witold J. Henisz, and Daniel Settel. 2009a. Defining and mitigating the governance challenges of infrastructure project development and delivery. Paper presented at 2009 Conference on Leadership and Management of Construction, Lake Tahoe, CA, USA, November 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Levitt, Raymond E., Witold J. Henisz, and Daniel Settel. 2009b. Defining and mitigating the governance challenges of infrastructure project development and delivery. Paper presented at Conference on Leadership and Management of Construction, Lake Tahoe, CA, USA, November 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lizarralde, G., C. Davidson, M. De Blois, and A. Pukteris. 2008. Building Abroad: Procurement of Construction and Reconstruction Projects in the International Context. Montreal: Building Abroad. [Google Scholar]
- Macheridis, Nikos. 2017. Governance of higher education–implementation of project governance. Tertiary Education and Management 23: 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, Stephen Keith, and Stephen Jonathan Whitty. 2015. Redefining governance: From confusion to certainty and clarity. International Journal of Managing Projects in Business 8: 755–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meso, Peter, Pratim Datta, and Victor Mbarika. 2006. Moderating information and communication technologies’ influences on socioeconomic development with good governance: A study of the developing countries. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology 57: 186–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meso, Peter, Philip Musa, Detmar Straub, and Victor Mbarika. 2009. Information infrastructure, governance, and socio-economic development in developing countries. European Journal of Information Systems 18: 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, Roger, and Serghei Floricel. 2000. Building governability into project structures. In The Strategic Management of Large Engineering Projects. Cambridge: MIT Press. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, Ralf, Li Zhai, and Anyu Wang. 2017. Governance and governmentality in projects: Profiles and relationships with success. International Journal of Project Management 35: 378–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, V. K., and Robert DeFillippi. 2012. The influence of strategic context on project management systems: A senior management perspective. In Project Governance. Berlin: Springer, pp. 3–45. [Google Scholar]
- Noor, Muhammad Ali, Malik MA Khalfan, and Tayyab Maqsood. 2012. Methods used to procure infrastructure projects in Pakistan: An overview. International Journal of Procurement Management 5: 733–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, Muhammad Ali, Malik M. A. Khalfan, and Tayyab Maqsood. 2013. The role of procurement practices in effective implementation of infrastructure projects in Pakistan. International Journal of Managing Projects in Business 6: 802–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunlana, Stephen O. 2010. Beyond the ‘iron triangle’: Stakeholder perception of key performance indicators (KPIs) for large-scale public sector development projects. International Journal of Project Management 28: 228–36. [Google Scholar]
- Patanakul, Peerasit, Young Hoon Kwak, Ofer Zwikael, and Min Liu. 2016. What impacts the performance of large-scale government projects? International Journal of Project Management 34: 452–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PC. 2010. Manual for Development Projects; Edited by Planning Commission of Pakistan. Islamabad: Planning Commission.
- Pinto, Jeffrey K. 2014. Project management, governance, and the normalization of deviance. International Journal of Project Management 32: 376–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PMI. 2013. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge: PMBOK Guide, 5th ed. Newton Square: Project Management Institute. [Google Scholar]
- PMI. 2016. Governance of Portfolios, Programs, and Projects: A Practice Guide. Newtown Square: Project Management Institute. [Google Scholar]
- Reside, Renato E., and Amado M Mendoza. 2010. Determinants of Outcomes of Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) in Infrastructure in Asia. Discussion paper. Quezon City: School of Economics, University of the Philippines Diliman. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes, Roderick Arthur William. 1996. The new governance: Governing without government. Political studies 44: 652–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, Jennifer. 2002. Using case studies in research. Management Research News 25: 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, Andreas, David Pauleen, and Sid Huff. 2012. KM governance: The mechanisms for guiding and controlling KM programs. Journal of Knowledge Management 16: 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Chandan. 2012. Determinants of PPP in infrastructure in developing economies. Transforming Government: People, Process and Policy 6: 149–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoker, Gerry. 1998. Governance as theory: Five propositions. International Social Science Journal 50: 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Too, Eric G., and Patrick Weaver. 2014. The management of project management: A conceptual framework for project governance. International Journal of Project Management 32: 1382–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unab, Wafa, and Muhammad Faheem A. Kundi. 2014. Review of project management (PM) practices in public infrastructure development organizations of Pakistan. Journal of Strategy and Performance Management 2: 144. [Google Scholar]
- Vaismoradi, Mojtaba, Hannele Turunen, and Terese Bondas. 2013. Content analysis and thematic analysis: Implications for conducting a qualitative descriptive study. Nursing & Health Sciences 15: 398–405. [Google Scholar]
- Waris, M., Khan Asadullah, Ismail Ishak, and Sitansu Panda. 2017. Project governance: A need for public sector infrastructure projects in Pakistan. Paper presented at FGIC 1st Conference on Governance & Integrity, "Innovation & Sustainability Through Governance" Yayasan Pahang, Kuantan, Malaysia, April 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, Oliver E. 1979. Transaction-cost economics: The governance of contractual relations. The Journal of Law and Economics 22: 233–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winch, Graham M. 2001. Governing the project process: A conceptual framework. Construction Management & Economics 19: 799–808. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. 2017. Social Analysis: Glossary of Key Terms. Available online: http://go.worldbank.org/HSXB13LCA0 (accessed on 5 June 2018).
- Xiang, Wenwen, Ying Li, and Yongyi Shou. 2013. An empirical study of critical success factors of project governance in China. Paper presented at 2013 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management (IEEM), Bangkok, Thailand, December 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Lin-lin, Yu Yang, Yi Hu, and Albert P. C. Chan. 2014. Understanding project stakeholders’ perceptions of public participation in China’s infrastructure and construction projects: Social effects, benefits, forms, and barriers. Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management 21: 224–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Robert K. 2017. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Li, Yanfei Xin, and Chaosheng Cheng. 2009. Understanding the value of project management from a stakeholder’s perspective: Case study of mega-project management. Project Management Journal 40: 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Zhao, Tuomas Ahola, Yun Le, and Jianxun Xie. 2017. Governmental governance of megaprojects: The case of EXPO 2010 Shanghai. Project Management Journal 48: 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwikael, Ofer, and John Smyrk. 2015. Project governance: Balancing control and trust in dealing with risk. International Journal of Project Management 33: 852–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sources | Focus of Study | Key investigations and Findings |
|---|---|---|
| (Zhai et al. 2017) | Governmental governance of mega projects | Encouraging accountability of the project leaders. Supporting cultural control. |
| (Cardenas et al. 2017) | Project governance of infrastructure projects | Project governance model for infrastructure projects. The model considers the project governance aspects, i.e., involvement of the contractor in the design and estimation of costs, procurement procedures, integration of the design and construction, the incentive and disincentive regimes, risk allocation, contract flexibility, and actions that allow the contracting party to maintain bargaining power during possible renegotiations. |
| (Müller et al. 2017) | Governance and governmentality of projects | Governance is a structural context, within which governmentality is implemented. Governance moderates the governmentality’s impact on the success. Successful projects tend to use standardized combinations of governance approaches. |
| (Hjelmbrekke et al. 2017) | Project governance as value addition in building projects | Aligning project output to the strategy of the organization. Governance is primarily about monitoring, leadership selection, incentives, and control systems. |
| (Brunet and Aubry 2016) | Governance framework for major public projects | There are three propositions on the governance dimensions, i.e., efficiency, legitimacy and accountability. |
| (Macheridis 2017) | Implementation of project governance | Processes and structures to govern multiple projects and to manage strategic objectives. |
| (Zwikael and Smyrk 2015) | Project governance-balancing control and trust in dealing with risk | Ethical decision-making and managerial action within an organization that is based on transparency, accountability, and defined roles. |
| (Xiang et al. 2013) | Critical Success Factors of Project Governance in China | Project governance is a framework for decision-making, including a series of structures, systems and processes, rules, and methods to support and complement the functional goals of project management. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, A.; Waris, M.; Ismail, I.; Sajid, M.R.; Ullah, M.; Usman, F. Deficiencies in Project Governance: An Analysis of Infrastructure Development Program. Adm. Sci. 2019, 9, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci9010009
Khan A, Waris M, Ismail I, Sajid MR, Ullah M, Usman F. Deficiencies in Project Governance: An Analysis of Infrastructure Development Program. Administrative Sciences. 2019; 9(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci9010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Asadullah, Muhammad Waris, Ishak Ismail, Mirza Rizwan Sajid, Mehfooz Ullah, and Faisal Usman. 2019. "Deficiencies in Project Governance: An Analysis of Infrastructure Development Program" Administrative Sciences 9, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci9010009
APA StyleKhan, A., Waris, M., Ismail, I., Sajid, M. R., Ullah, M., & Usman, F. (2019). Deficiencies in Project Governance: An Analysis of Infrastructure Development Program. Administrative Sciences, 9(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci9010009






