Toxic Leadership and Job Satisfaction in the Middle Eastern Education Sector: The Influence of Organizational Culture and Trust
Abstract
1. Introduction
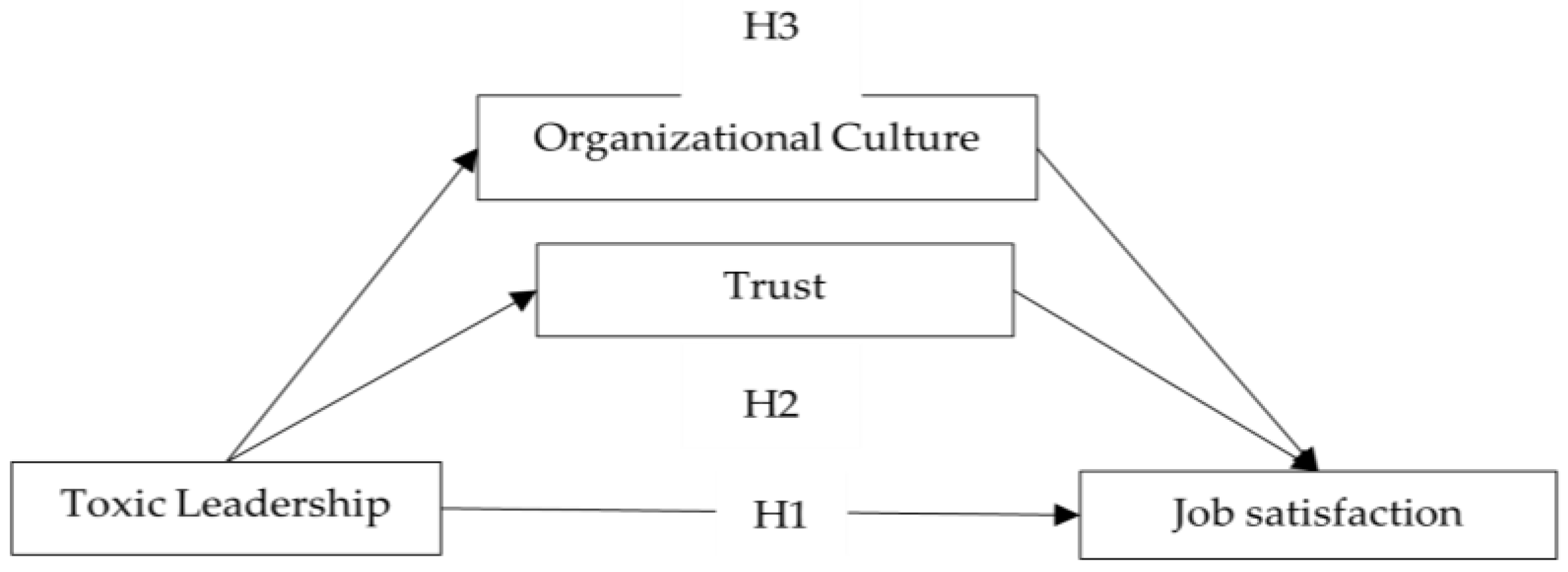
2. Hypotheses and Theories
2.1. Toxic Leadership and Job Satisfaction
2.2. Trust in Leader
2.3. Organizational Culture
3. Research Design
3.1. Methodology and Criteria
3.2. Respondents’ Profile
3.3. Measurements
3.4. Research Model
4. Analysis and Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Theoretical Implications
7. Practical Implications
8. Limitations and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adler, R. H. (2022). Trustworthiness in qualitative research. Journal of Human Lactation, 38(4), 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agha, S. (2021). Mental well-being and association of the four factors coping structure model: A perspective of people living in lockdown during COVID-19. Ethics, Medicine and Public Health, 16, 100605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M. A. O., Zhang, J., Fouad, A. S., Mousa, K., & Nour, H. M. (2024). The dark side of leadership: How toxic leadership fuels counterproductive work behaviors through organizational cynicism and injustice. Sustainability, 17(1), 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akca, M. (2017). The impact of toxic leadership on intention to leave of employees. International Journal of Economics, Business and Management Research, 1(4), 285–298. [Google Scholar]
- Alanezi, F. (2021). Toxic leadership and organizational performance: A study of public organizations in Saudi Arabia. International Journal of Public Leadership, 17(2), 153–169. [Google Scholar]
- Alanezi, A. (2024). Toxic leadership behaviours of school principals: A qualitative study. Educational Studies, 50(6), 1200–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayoubi, M. M., Al Shobaki, M. J., & Abu-Naser, S. S. (2020). Strategic leadership practices and their relationship to improving the quality of educational service in Palestinian Universities. International Journal of Business Marketing and Management (IJBMM), 5(3), 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Al Zaabi, H. H., Abu Elanain, H. M., & Ajmal, M. M. (2018). Impact of toxic leadership on work outcomes: An empirical study of public banks in the UAE. International Journal of Public Sector Performance Management, 4(3), 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubrey, D. W. (2012). The effect of toxic leadership. ARMY WAR COLL CARLISLE BARRACKS PA. [Google Scholar]
- Babatunde, M. M. O., & Nurudeen, O. R. U. N. B. O. N. (2020). Influence of toxic leadership behaviour on teachers’ diligence and productivity in Lagos State Senior Secondary Schools, Nigeria. International Journal of Education and Evaluation, 6(2), 36–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bajada, C., & Shashnov, M. (2019). The effects of economic development and the evolution of social institutions on the level of corruption: Comparing the Asia-Pacific with other regional blocs. Asia Pacific Business Review, 25(4), 470–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. (1977). Social learning theory. Prentice-Hall. [Google Scholar]
- Bandura, A. (1989). Human agency in social cognitive theory. American Psychologist, 44(9), 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskan, G. A. (2020). Academic bullying in higher education: A literature review. International Journal of Educational Administration and Policy Studies, 12(1), 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Behery, M., Al-Nasser, A. D., Jabeen, F., & El Rawas, A. S. (2018). Toxic leadership and organizational citizenship behavior: A mediation effect of followers’ trust and commitment in the middle East. International Journal of Business & Society, 19(3), 793–815. [Google Scholar]
- Behery, M., Arafeh, L., & Al-Nasser, A. (2019). Employees’ perception of organizational health and workplace bullying in higher education: The mediating role of organizational commitment. International Journal of Organizational Analysis, 27(5), 1191–1211. [Google Scholar]
- Bellou, V., & Dimou, M. (2022). The impact of destructive leadership on public servants’ performance: The mediating role of leader-member exchange, perceived organizational support and job satisfaction. International Journal of Public Administration, 45(9), 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, D., & Bubb, S. (2021). Leadership for wellbeing. In School leadership and education system reform (p. 143). Bloomsbury Academic. [Google Scholar]
- Brouwers, M., & Paltu, A. (2020). Toxic leadership: Effects on job satisfaction, commitment, turnover intention and organisational culture within the South African manufacturing industry. SA Journal of Human Resource Management, 18(1), 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Brower, H. H., Schoorman, F. D., & Tan, H. H. (2000). A model of relational leadership: The integration of trust and leader–member exchange. The Leadership Quarterly, 11(2), 227–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, J. P., & Hoobler, J. M. (2011). Aggressive reactions to abusive supervision: The role of interactional justice and narcissism. Scandinavian Journal of Psychology, 52(4), 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byman, D. (2002). Keeping the peace: Lasting solutions to ethnic conflicts. JHU Press. [Google Scholar]
- Casula, M., Rangarajan, N., & Shields, P. (2021). The potential of working hypotheses for deductive exploratory research. Quality & Quantity, 55(5), 1703–1725. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, A., Oswald, A., & Warr, P. (1996). Is job satisfaction U-shaped in age? Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 69(1), 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, M., Walter, G., & Horsfall, J. (2013). Toxic leadership: Lessons for mental health nurses. Issues in Mental Health Nursing, 34(9), 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darko, A., Chan, A. P., Adabre, M. A., Edwards, D. J., Hosseini, M. R., & Ameyaw, E. E. (2020). Artificial intelligence in the AEC industry: Scientometric analysis and visualization of research activities. Automation in Construction, 112, 103081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawadi, S., Shrestha, S., & Giri, R. A. (2021). Mixed-methods research: A discussion on its types, challenges, and criticisms. Journal of Practical Studies in Education, 2(2), 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantopoulos, A., Sarstedt, M., Fuchs, C., Wilczynski, P., & Kaiser, S. (2012). Guidelines for choosing between multi-item and single-item scales for construct measurement: A predictive validity perspective. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 40(3), 434–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, T. K., & Henseler, J. (2015). Consistent partial least squares path modeling. MIS Quarterly, 39(2), 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorfman, P. W. (1996). International and cross-cultural leadership research. Handbook for International Management Research, 2, 504–518. [Google Scholar]
- EL Telyani, A., Farmanesh, P., & Zargar, P. (2022). An examination of the relationship between levels diversity-organizational performance: Does innovative culture matter? SAGE Open, 12(1), 21582440211067244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emirie, T. B., & Mengistu Gebremeskel, M. (2024). The prevalence and effect of destructive leadership behavior on teachers’ organizational commitment in the post-COVID-19 period: A case study of secondary schools in Amhara Regional State. Cogent Education, 11(1), 2392426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdal, N., & Budak, O. (2021). The mediating role of organizational trust in the effect of toxic leadership on job satisfaction. International Journal of Research in Business and Social Science (2147-4478), 10(3), 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, A., Shaw, B., Murray, J., & Branch, S. (2015). Destructive leadership: Causes, consequences and countermeasures. Organizational Dynamics, 44(4), 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahie, D. (2019). The lived experience of toxic leadership in Irish higher education. International Journal of Workplace Health Management, 13, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, S., & Sprigg, C. A. (2014). Culture of silence: The impact of workplace bullying. Industrial and Commercial Training, 46(7), 355–359. [Google Scholar]
- Farmanesh, P., & Zargar, P. (2021). Trust in leader as a psychological factor on employee and organizational outcome. IntechOpen. [Google Scholar]
- Firing, K., Thorkelsdóttir, R. B., & Chemi, T. (2022). The Theatre of War: Leader development between personal identity and person-in-role. Culture and Organization, 8(3–4), 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, K. N. (2011). Academic bullying: A barrier to tenure and promotion for African-American faculty. Florida Journal of Educational Administration & Policy, 4(1), 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie, N. A., & Mann, L. (2004). Transformational leadership and shared values: The building blocks of trust. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 19(6), 588–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, A. (2006). High toxicity leadership: Borderline personality disorder and the dysfunctional organization. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 21(8), 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göçen, A. (2021). Ethical leadership in educational organizations: A cross-cultural study. Turkish Journal of Education, 10(1), 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graen, G. B., & Uhl-Bien, M. (1995). Relationship-based approach to leadership: Development of leader-member exchange (LMX) theory over 25 years: Applying a multi-level multi-domain perspective. The Leadership Quarterly, 6(2), 219–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J. E. (2014). Toxic leadership in educational organizations. Education Leadership Review, 15(1), 18–33. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2019). Multivariate data analysis (8th ed.). Cengage Learning. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J. F., Jr., Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C. M., & Gudergan, S. P. (2017). Advanced issues in partial least squares structural equation modeling. Sage Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Harley, B., & Cornelissen, J. (2022). Rigor with or without templates? The pursuit of methodological rigor in qualitative research. Organizational Research Methods, 25(2), 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A., & Jones, M. (2018). The dark side of leadership and management. School Leadership & Management, 38(5), 475–477. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, P., Harris, K. J., Gillis, W. E., & Martinko, M. J. (2021). Abusive supervision and the entrapment of employees: A self-regulatory perspective. Journal of Business Ethics, 170(3), 567–582. [Google Scholar]
- Hattab, S., Wirawan, H., Salam, R., Daswati, D., & Niswaty, R. (2022). The effect of toxic leadership on turnover intention and counterproductive work behaviour in Indonesia public organisations. International Journal of Public Sector Management, 35(3), 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2017). Using partial least squares path modeling in international advertising research: Basic concepts and recent issues. In S. Okazaki (Ed.), Handbook of research on international advertising (pp. 252–276). Edward Elgar Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., & Sinkovics, R. R. (2009). The use of partial least squares path modeling in international marketing. In New challenges to international marketing. Emerald Group Publishing Limited. [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock, M. J. (2015). The Relationship between toxic leadership, organizational citizenship, and turnover behaviors among San Diego nonprofit paid staff. University of San Diego. [Google Scholar]
- Hobfoll, S. E. (1989). Conservation of resources: A new attempt at conceptualizing stress. American Psychologist, 44(3), 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobfoll, S. E. (2011). Conservation of resource caravans and engaged settings. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 84(1), 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbouri, F. (2023). The role of leadership in fueling ethnic divisions: The case of Iraq. Washington State University. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A. M. (2006). Culture, identity, and motivation: The historical anthropology of a family firm. Culture and Organization, 12(2), 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jöreskog, K. G. (1971). Simultaneous factor analysis in several populations. Psychometrika, 36(4), 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N. A. (2021). Determinants of proactive work behavior of employees during the COVID-19 crisis. European Journal of Psychology Open, 80(1–2), 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasawneh, S., Abu-Alruz, J., Oliemat, A., Hailat, S., & Bataineh, O. (2024). Toxic leadership in higher education: A typology of behaviours. Research in Post-Compulsory Education, 29(3), 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawand, C., & Zargar, S. M. (2022). Workplace bullying and employee silence: The mediating role of psychological safety. International Journal of Organizational Analysis, 30(6), 1249–1265. [Google Scholar]
- Kilic, M., & Günsel, A. (2019). The dark side of the leadership: The effects of toxic leaders on employees. European Journal of Social Sciences, 2(2), 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, A. C., Matthews, S. H., & Leavitt, K. (2021). The effect of toxic work environments on employee unethical behavior. Journal of Management, 47(6), 1377–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Koltz, R. L., Moser, C. M., & Martinez, M. A. (2021). Addressing workplace bullying in academia: Developing a proactive and reflective approach. Journal of Leadership Education, 20(1), 160–173. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, I., Anjam, M., & Zaman, U. (2022). Hell is empty, and all the devils are here: Nexus between toxic leadership, crisis communication, and resilience in COVID-19 tourism. Sustainability, 14(17), 10825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrague, L. J., Nwafor, C. E., & Tsaras, K. (2020). Influence of toxic and transformational leadership practices on nurses’ job satisfaction, job stress, absenteeism and turnover intention: A cross-sectional study. Journal of Nursing Management, 28(5), 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguda, E. (2021). Toxic leadership: Managing its poisonous effects on employees and organizational outcomes. In The Palgrave handbook of workplace well-being (pp. 969–999). Palgrave Macmillan. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P., Yin, K., Shi, J., Damen, T. G., & Taris, T. W. (2023). Are bad leaders indeed bad for employees? A meta-analysis of longitudinal studies between destructive leadership and employee outcomes. Journal of Business Ethics, 191(2), 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liden, R. C., Sparrowe, R. T., & Wayne, S. J. (1997). Leader-member exchange theory: The past and potential for the future. The Academy of Management Review, 22, 47–72. [Google Scholar]
- Lipman-Blumen, J. (2006). The allure of toxic leaders: Why we follow destructive bosses and corrupt politicians--and how we can survive them. Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Mackey, J. D., Ellen, B. P., III, McAllister, C. P., & Alexander, K. C. (2021). The dark side of leadership: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis of destructive leadership research. Journal of Business Research, 132, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlangu, V. P. (2014). The effects of toxic leadership on teaching and learning in South African township schools. Journal of Social Sciences, 38(3), 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, K., O’Neill, O., & Lei, X. (2018). Toxic leadership and the masculinity contest culture: How “win or die” cultures breed abusive leadership. Journal of Social Issues, 74(3), 500–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, D. M., & Meredith, J. R. (1993). Conducting case study research in operations management. Journal of Operations Management, 11(3), 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y., Tan, J., & Li, J. (2017). Abusive supervision by academic supervisors and postgraduate research students’ creativity: The mediating role of leader–member exchange and intrinsic motivation. International Journal of Leadership in Education, 20(5), 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergen, A., & Ozbilgin, M. F. (2021). Understanding the followers of toxic leaders: Toxic illusion and personal uncertainty. International Journal of Management Reviews, 23(1), 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosevic, I., Maric, S., & Lončar, D. (2020). Defeating the toxic boss: The nature of toxic leadership and the role of followers. Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies, 27(2), 117–137. [Google Scholar]
- Nyhan, R. C., & Marlowe, H. A., Jr. (1997). Development and psychometric properties of the organizational trust inventory. Evaluation Review, 21(5), 614–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oden, J., Ward, W. L., & Raisingani, M. (2019). Treatment of pediatric obesity: Past and present approaches to diet and exercise. Global Perspectives on Childhood Obesity, 2, 387–397. [Google Scholar]
- Orunbon, N. O., Lawal, R. O., Isaac-Philips, M. M., & Salaudeen, R. I. (2022). Toxic leadership, teachers’ job satisfaction and organisational commitment in lagos state tertiary institutions, Nigeria. Journal of Educational Sciences, 6(1), 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, A., Hogan, R., & Kaiser, R. B. (2007). The toxic triangle: Destructive leaders, susceptible followers, and conducive environments. The Leadership Quarterly, 18(3), 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, T. C. (2001). Competitive advantage: Logical and philosophical considerations. Strategic Management Journal, 22(9), 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, J. M., Fischman, G. E., & Berliner, D. C. (2016). Rebooting the debate: How media coverage of school choice misrepresents the evidence. National Education Policy Center. [Google Scholar]
- Rasool, S. F., Maqbool, R., Samma, M., Zhao, Y., & Anjum, A. (2019). Positioning depression as a critical factor in creating a toxic workplace environment for diminishing worker productivity. Sustainability, 11(9), 2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, S. F., Wang, M., Zhang, Y., & Samma, M. (2020). Sustainable work performance: The roles of workplace violence and occupational stress. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(3), 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousseau, D. M., Sitkin, S. B., Burt, R. S., & Camerer, C. (1998). Not so different after all: A cross-discipline view of trust. Academy of Management Review, 23(3), 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, F., Malik, M. I., & Qureshi, S. S. (2021). Toxic leadership and its impact on work engagement: A mediating role of self-efficacy. Current Psychology, 40, 6287–6295. [Google Scholar]
- Scandura, T. A., & Pellegrini, E. K. (2008). Trust and leader—Member exchange: A closer look at relational vulnerability. Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies, 15(2), 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Schilling, J., Schuh, S. C., & Wirth, M. (2022). The dark side of leadership: A meta-analysis of destructive leadership and its outcomes. The Leadership Quarterly, 33(4), 101583. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, A. A. (2008). Development and validation of the toxic leadership scale. University of Maryland. [Google Scholar]
- Schmiedel, T., Recker, J., & vom Brocke, J. (2020). The relation between BPM culture, BPM methods, and process performance: Evidence from quantitative field studies. Information & Management, 57(2), 103175. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, I. S. (2012). Human rights journalism. In Advances in reporting humanitarian interventions, basingsto e. Palgrave Macmillan. [Google Scholar]
- Simard, K., & Parent-Lamarche, A. (2022). Abusive leadership, psychological well-being, and intention to quit during the COVID-19 pandemic: A moderated mediation analysis among Quebec’s healthcare system workers. International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health, 95(2), 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N., Sengupta, S., & Dev, S. (2018). Toxic leadership: The most menacing form of leadership. In Dark sides of organizational behavior and leadership (pp. 147–164). Intechopen. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, N., & Fredricks-Lowman, I. (2020). Conflict in the workplace: A 10-year review of toxic leadership in higher education. International Journal of Leadership in Education, 23(5), 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousan, A., Farmanesh, P., & Zargar, P. (2022). The effect of surface acting on job stress and cognitive weariness among healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic: Exploring the role of sense of community. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, P. E. (1985). Measurement of human service staff satisfaction: Development of the Job Satisfaction Survey. American Journal of Community Psychology, 13(6), 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, H., & Ding, D. (2022). Toxic leadership and its impact on employee performance: The mediating role of psychological safety. Journal of Business Research, 144, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavanti, M. (2011). Managing toxic leaders: Dysfunctional patterns in organizational leadership and how to deal with them. Human Resource Management, 2011, 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Telyani, A. E., Farmanesh, P., & Zargar, P. (2021). The impact of COVID-19 Instigated changes on loneliness of teachers and motivation–engagement of students: A psychological analysis of education sector. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepper, B. J., & Duffy, M. K. (2002). Abusive supervision, downward hostility, and subordinate resistance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 87(5), 897–904. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, D. A. (2010). The truth about mentoring minorities: Race matters. Harvard Business Review, 88(4), 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Thoroughgood, C. N., Sawyer, K. B., Padilla, A., & Lunsford, L. (2018). Destructive leadership: A critique of leader-centric perspectives and toward a more holistic definition. Journal of Business Ethics, 151, 627–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, W. G. (1988). Organizational culture in higher education: Defining the essentials. The Journal of Higher Education, 59(1), 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twale, D. J., & De Luca, B. M. (2008). Faculty incivility: The rise of the academic bully culture and what to do about it. Jossey-Bass. [Google Scholar]
- Uysal, H. T. (2019). The mediation role of toxic leadership in the effect of job stress on job satisfaction. International Journal of Business, 24(1), 55–73. [Google Scholar]
- Whicker, M. L. (1996). Toxic leaders: When organizations go bad. Praeger. [Google Scholar]
- Winn, G. L., & Dykes, A. C. (2019). Identifying toxic leadership and building worker resilience. Professional Safety, 64(3), 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Witzel, M. (2022). Post-pandemic leadership. Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Yaghi, A., & Yaghi, M. (2021). Evaluating organizational hypocrisy within universities as toxic leadership behavior. Public Integrity, 23(4), 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakhem, N. B., Farmanesh, P., Zargar, P., & Kassar, A. (2022). Wellbeing during a pandemic: An empirical research examining autonomy, work-family conflict and informational support among SME employees. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 890265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zargar, P., Sousan, A., & Farmanesh, P. (2019). Does trust in leader mediate the servant leadership style–job satisfaction relationship? Management Science Letters, 9(13), 2253–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. J., Chen, Y. Q., & Sun, H. (2015). Emotional intelligence, conflict management styles, and innovation performance: An empirical study of Chinese employees. International Journal of Conflict Management, 26(4), 450–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H., Peng, Z., Han, Y., Sheard, G., & Hudson, A. (2013). Psychological mechanism linking abusive supervision and compulsory citizenship behavior: A moderated mediation study. The Journal of Psychology, 147(2), 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y., Lin, J., Liu, X., Gao, S., Yang, F., & Xu, H. (2021). Validity and reliability of the toxic leadership behaviors of nurse managers scale among Chinese nurses. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 1363792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Factors | Dimensions | Indicators | Outer Loadings | Alpha | Rho A | CR | AVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toxic Leadership | Self-promoting | SP1 | 0.724 | 0.809 | 0.831 | 0.824 | 0.635 |
| SP2 | 0.816 | ||||||
| SP3 | 0.902 | ||||||
| Abusive | AB1 | 0.826 | 0.749 | 0.811 | 0.753 | 0.704 | |
| AB2 | 0.808 | ||||||
| AB3 | 0.813 | ||||||
| Unpredictable | UNP1 | 0.851 | 0.707 | 0.736 | 0.737 | 0.708 | |
| UNP2 | 0.728 | ||||||
| UNP3 | 0.811 | ||||||
| Narcissistic | NRC1 | 0.789 | 0.788 | 0.771 | 0.813 | 0.767 | |
| NRC2 | 0.746 | ||||||
| NRC3 | 0.795 | ||||||
| Controlling | CNT1 | 0.803 | 0.821 | 0.765 | 0.794 | 0.745 | |
| CNT2 | 0.819 | ||||||
| CNT3 | 0.744 | ||||||
| Job Satisfaction | — | JS1 | 0.843 | 0.873 | 0.842 | 0.866 | 0.732 |
| JS2 | 0.827 | ||||||
| JS3 | 0.874 | ||||||
| JS4 | 0.746 | ||||||
| Trust in the Leader | — | TR1 | 0.886 | 0.890 | 0.938 | 0.856 | 0.575 |
| TR2 | 0.808 | ||||||
| TR3 | 0.803 | ||||||
| TR4 | 0.723 | ||||||
| Organizational Culture | Environment | ENV1 | 0.850 | 0.806 | 0.911 | 0.845 | 0.582 |
| ENV2 | 0.841 | ||||||
| ENV3 | 0.823 | ||||||
| Mission | MS1 | 0.823 | 0.802 | 0.830 | 0.841 | 0.721 | |
| MS2 | 0.845 | ||||||
| MS3 | 0.757 | ||||||
| Socialization | SC1 | 0.887 | 0.771 | 0.757 | 0.720 | 0.678 | |
| SC2 | 0.890 | ||||||
| SC3 | 0.703 | ||||||
| Information | INF1 | 0.765 | 0.783 | 0.766 | 0.813 | 0.731 | |
| INF2 | 0.744 | ||||||
| INF3 | 0.823 | ||||||
| Strategy | STR1 | 0.794 | 0.794 | 0.740 | 0.822 | 0.714 | |
| STR2 | 0.772 | ||||||
| STR3 | 0.809 |
| SP | AB | UNP | NRC | JS | TR | ENV | MS | SC | INF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP | ||||||||||
| AB | 0.708 | |||||||||
| UNP | 0.488 | 0.534 | ||||||||
| NRC | 0.706 | 0.635 | 0.734 | |||||||
| JS | 0.631 | 0.713 | 0.665 | 0.722 | ||||||
| TR | 0.701 | 0.485 | 0.673 | 0.722 | 0.801 | |||||
| ENV | 0.711 | 0.702 | 0.701 | 0.724 | 0.724 | 0.746 | ||||
| MS | 0.466 | 0.564 | 0.560 | 0.622 | 0.701 | 0.7012 | 0.722 | |||
| SC | 0.512 | 0.544 | 0.598 | 0.578 | 0.598 | 0.588 | 0.611 | 0.628 | ||
| INF | 0.537 | 0.613 | 0.633 | 0.649 | 0.612 | 0.671 | 0.622 | 0.637 | 0.677 | |
| STR | 0.628 | 0.698 | 0.648 | 0.670 | 0.703 | 0.720 | 0.733 | 0.711 | 0.702 | 0.719 |
| Construct | Items | Convergent Validity | Weights | VIF | t-Statistics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TL | Self-promoting | 0.722 | 0.373 | 1.860 | 4.105 |
| Abusive | 0.371 | 1.761 | 4.041 | ||
| Unpredictable | 0.518 | 2.232 | 5.052 | ||
| Narcissistic | 0.388 | 1.798 | 4.127 | ||
| Controlling | 0.314 | 1.716 | 4.198 | ||
| OC | Environment | 0.717 | 0.413 | 1.924 | 5.337 |
| Mission | 0.404 | 2.012 | 5.459 | ||
| Socialization | 0.387 | 1.903 | 5.349 | ||
| Information | 0.408 | 1.874 | 5.364 | ||
| Strategy | 0.411 | 2.019 | 5.297 |
| Effects | Relations | β | t-Statistics | Ƒ2 | Decision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct | |||||
| H1 | TX → JS | −0.312 | −5.229 *** | 0.102 | Supported |
| Mediation | |||||
| H2 | TX →TR → JS | −0.343 | −2.348 * | 0.108 | Supported |
| H3 | TX → OC → JS | −0.361 | −3.689 * | 0.112 | Supported |
| Control Variables | |||||
| Gender → JS | 0.132 | 2.514 * | |||
| Age → JS | 0.119 | 2.132 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassanein, F.R.; Mohammadi, S.; Zargar, P. Toxic Leadership and Job Satisfaction in the Middle Eastern Education Sector: The Influence of Organizational Culture and Trust. Adm. Sci. 2025, 15, 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci15050171
Hassanein FR, Mohammadi S, Zargar P. Toxic Leadership and Job Satisfaction in the Middle Eastern Education Sector: The Influence of Organizational Culture and Trust. Administrative Sciences. 2025; 15(5):171. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci15050171
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassanein, Fida Ragheb, Samaneh Mohammadi, and Pouya Zargar. 2025. "Toxic Leadership and Job Satisfaction in the Middle Eastern Education Sector: The Influence of Organizational Culture and Trust" Administrative Sciences 15, no. 5: 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci15050171
APA StyleHassanein, F. R., Mohammadi, S., & Zargar, P. (2025). Toxic Leadership and Job Satisfaction in the Middle Eastern Education Sector: The Influence of Organizational Culture and Trust. Administrative Sciences, 15(5), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci15050171







