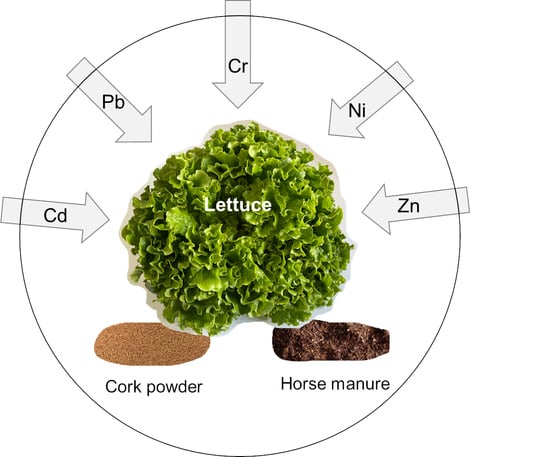
Comparison between a Traditional (Horse Manure) and a Non-Conventional (Cork Powder) Organic Residue in the Uptake of Potentially Toxic Elements by Lettuce in Contaminated Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Contamination, Soil Amendment and Plant Production
2.2. Plant Determinations
2.3. Quality Assurance
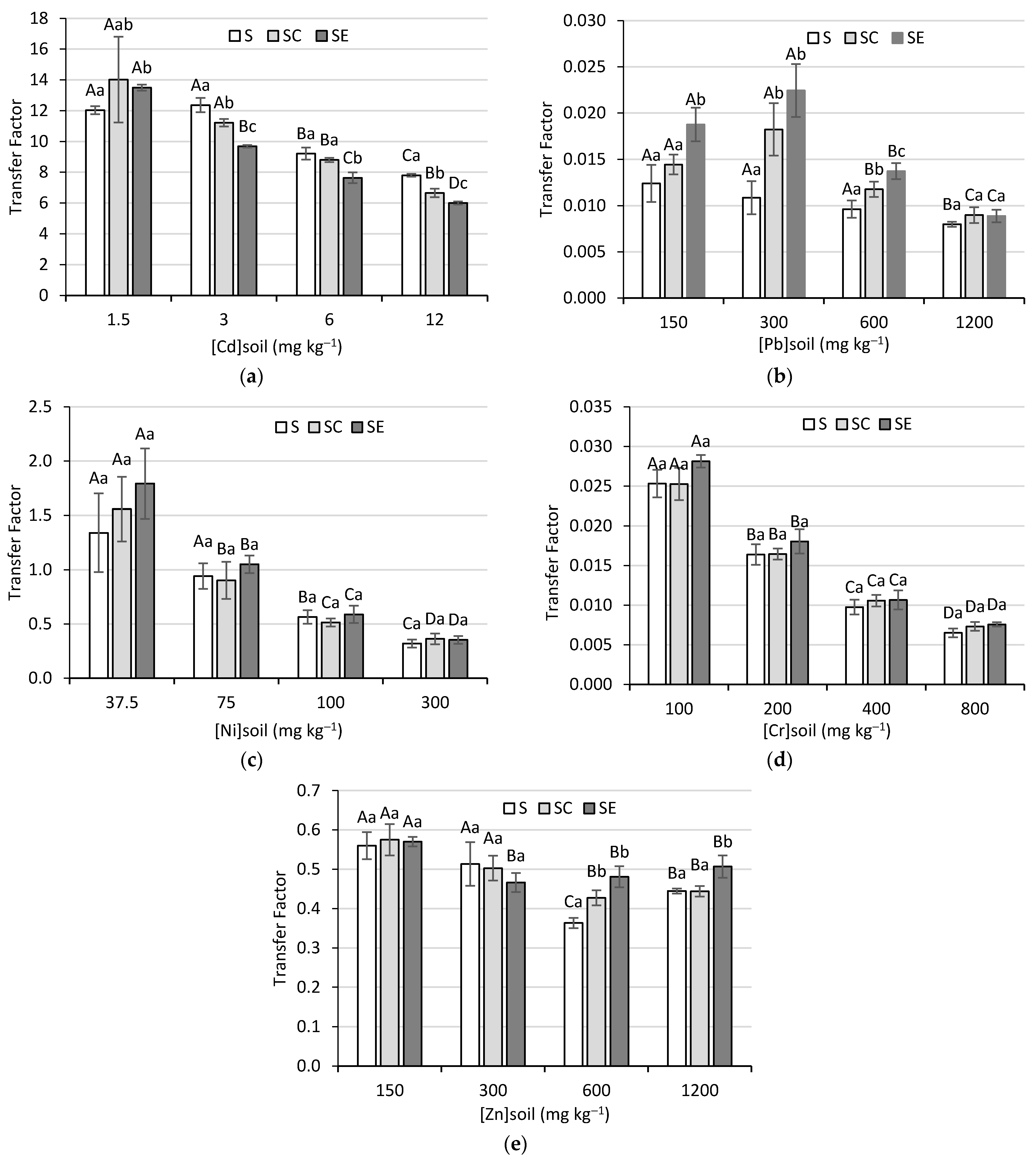
2.4. Transfer Factor (TF)
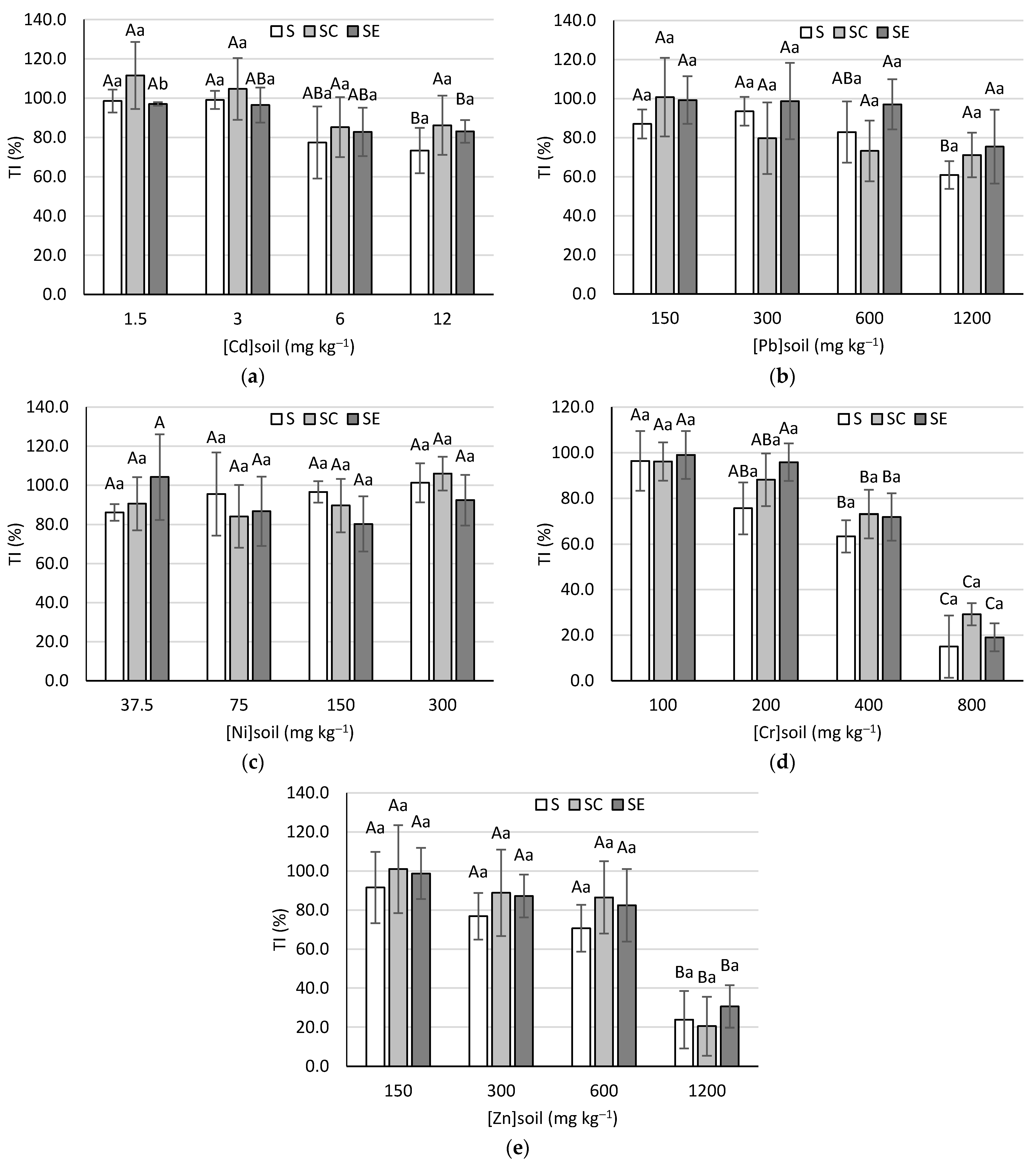
2.5. Tolerance Index (TI)
2.6. Statistical Treatment
3. Results and Discussion
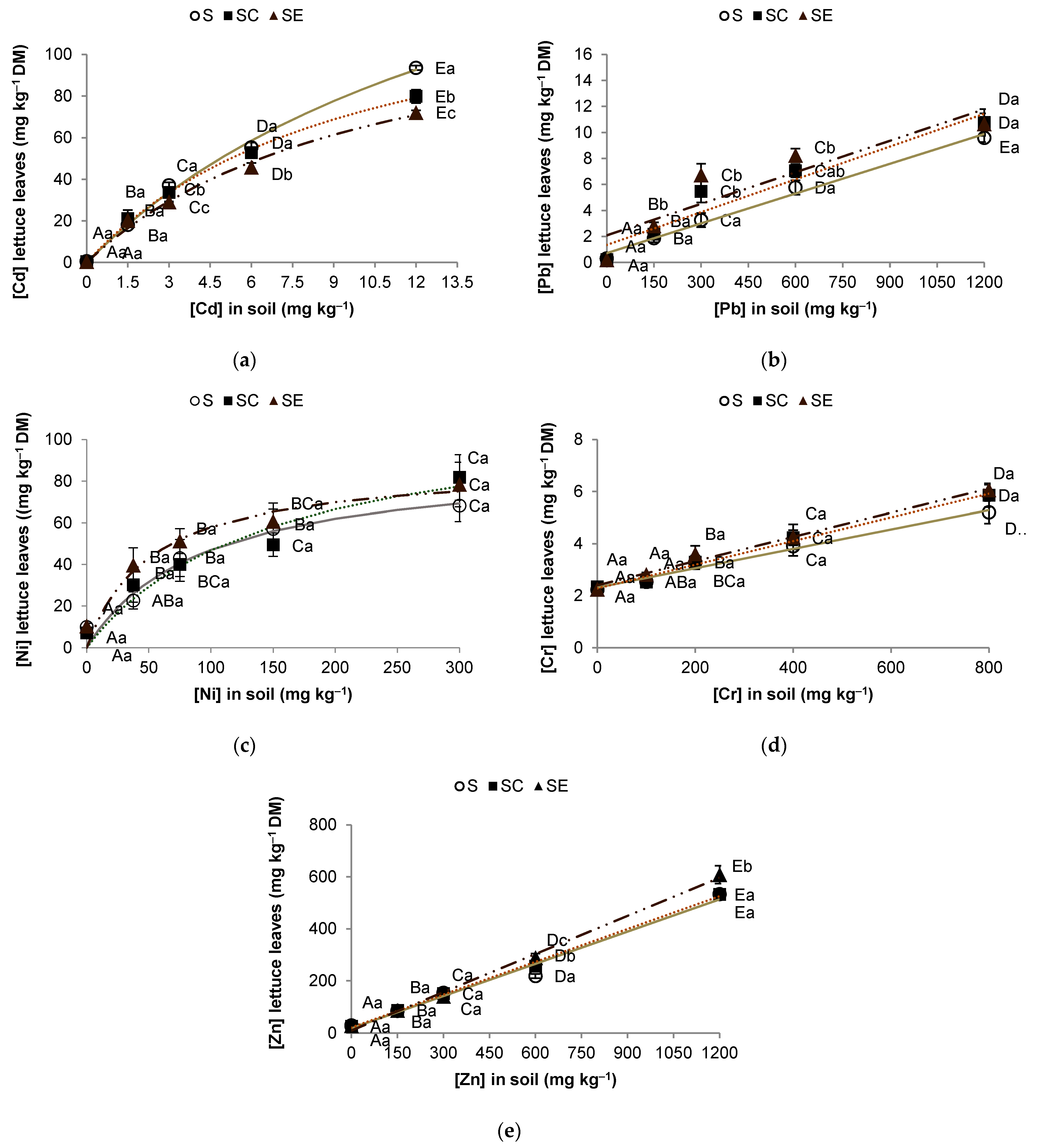
3.1. PTE Uptake Behavior in Lettuce
3.2. PTE Accumulation
3.3. Evaluation of Vegetable Contamination
3.4. Transfer Factor
3.5. Tolerance Index
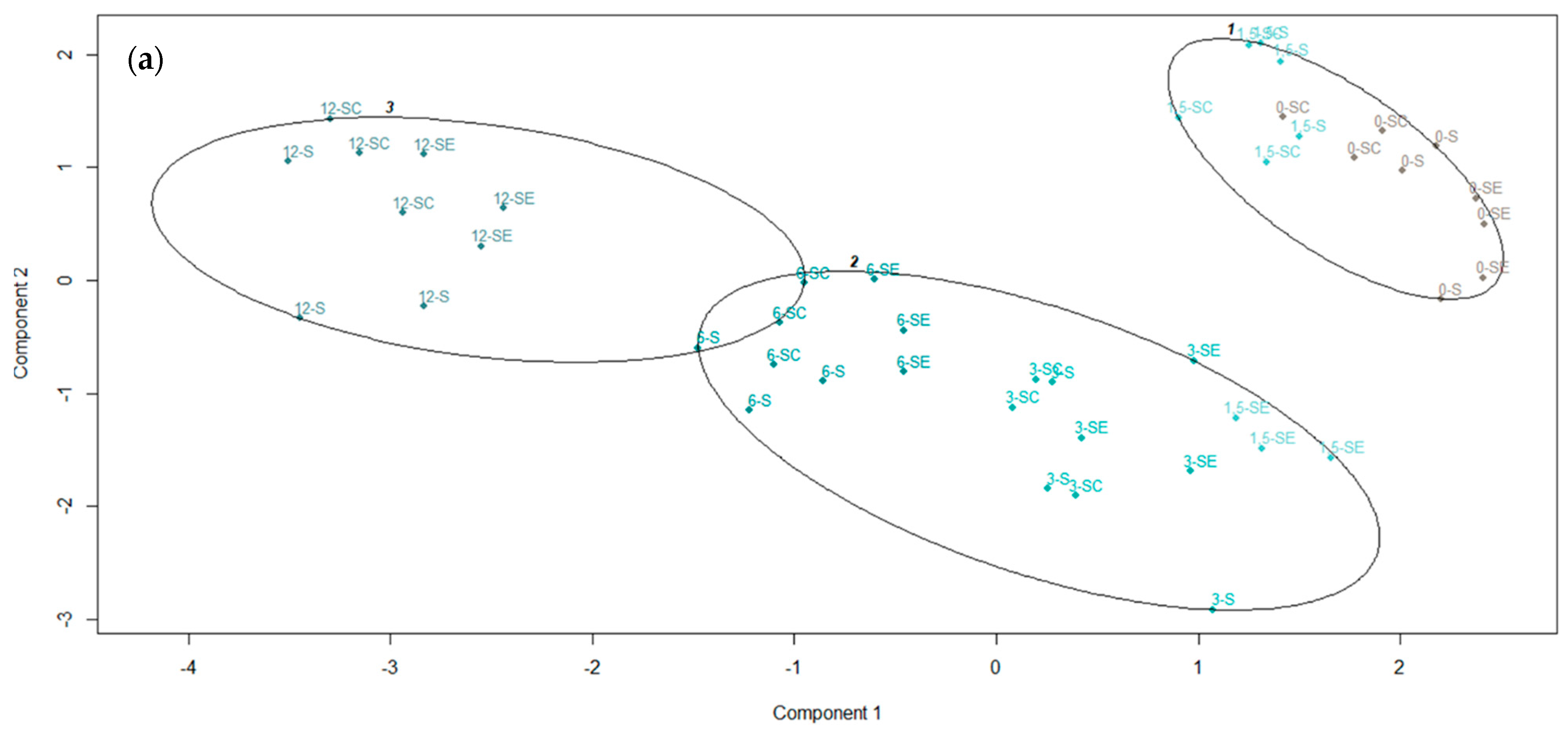
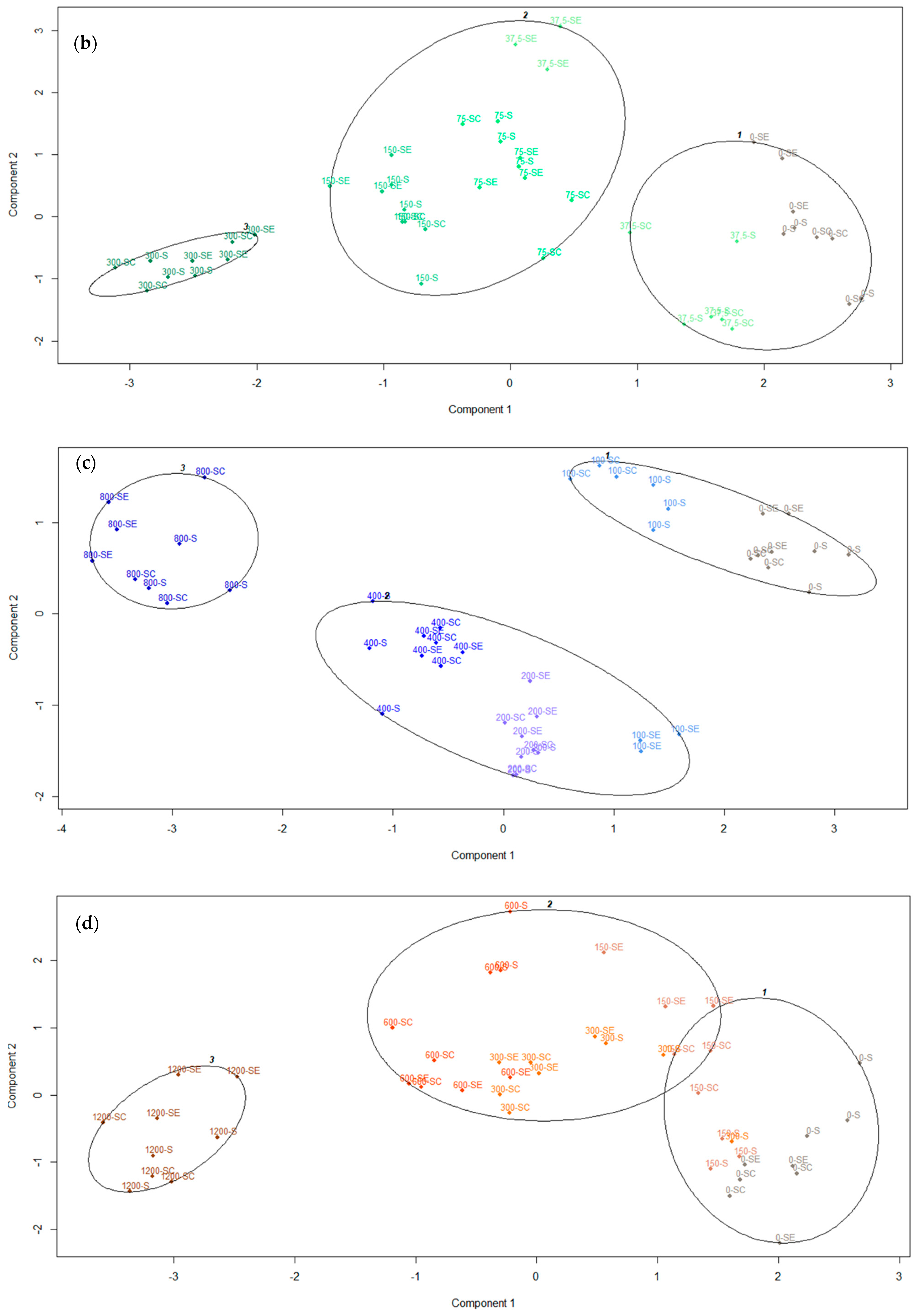
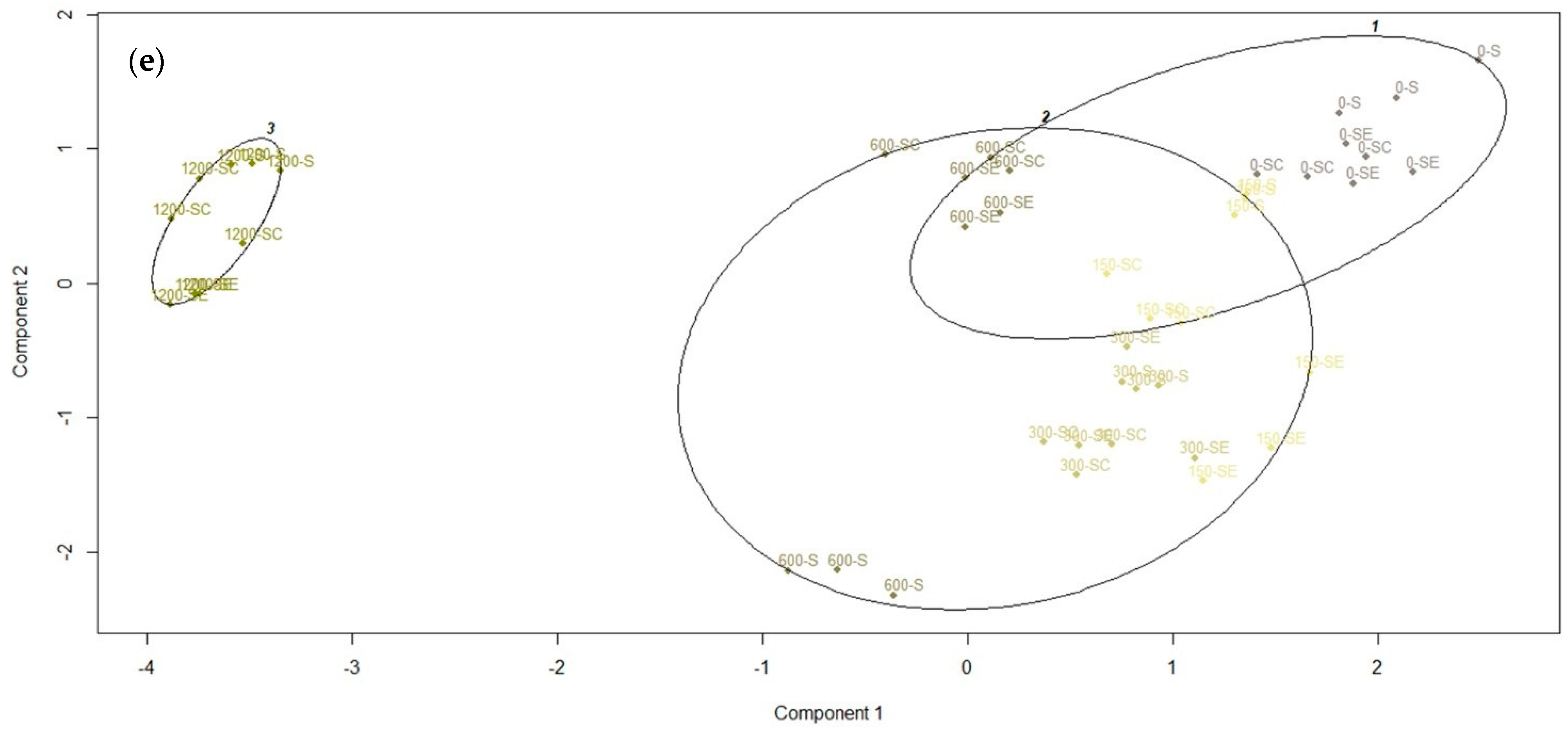
3.6. Cluster Analysis
3.7. Pratical Implications of This Work
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alloway, B.J. Heavy Metals in Soils, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 22. [Google Scholar]
- Tóth, G.; Hermann, T.; Szatmári, G.; Pásztor, L. Maps of heavy metals in the soils of the European Union and proposed priority areas for detailed assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, J.E.; Boyd, R.S.; Rajakaruna, N. Transfer of heavy metals through terrestrial food webs: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, S.; Ma, J.F. Toxic Heavy Metal and Metalloid Accumulation in Crop Plants and Foods. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2016, 67, 489–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagajyoti, P.C.; Lee, K.D.; Sreekanth, T.V.M. Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2010, 8, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertani, A.; Mietto, A.; Borin, M.; Nardi, S. Chromium in Agricultural Soils and Crops: A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente Solos Contaminados-Guia Técnico. 2019. Available online: https://sniambgeoviewer.apambiente.pt/GeoDocs/geoportaldocs/AtQualSolos/Guia_Tecnico_Valores%20de%20Referencia_2019_01.pdf (accessed on 8 March 2021).
- Canadian Ministry of the Environment. Soil, Ground Water and Sediment Standards for Use under Part XV.1 of the Environmental Protection Act. in 2011; Canadian Ministry of the Environment: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shanker, A.K.; Cervantes, C.; Loza-Tavera, H.; Avudainayagam, S. Chromium toxicity in plants. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Shamshad, S.; Rafiq, M.; Khalid, S.; Bibi, I.; Niazi, N.K.; Dumat, C.; Rashid, M.I. Chromium speciation, bioavailability, uptake, toxicity and detoxification in soil-plant system: A review. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 513–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Huang, D.; Liu, J. Functions and Toxicity of Nickel in Plants: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. Clean Soil Air Water 2009, 37, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, M.; Fariduddin, Q.; Hayat, S.; Ahmad, A. Nickel: An Overview of Uptake, Essentiality and Toxicity in Plants. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 86, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Temmerman, L.; Vanongeval, L.; Boon, W.; Hoenig, M.; Geypens, M. Heavy Metal Content of Arable Soils in Northern Belgium. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 148, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadley, M.R.; White, P.J.; Hammond, J.P.; Zelko, I.; Lux, A. Zinc in plants. New Phytol. 2007, 173, 677–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alloway, B. Zinc in Soils and Crop Nutrition, 2nd ed.; IZA: Brussels, Belgium; IFA: Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sofo, A.; Moreira, I.; Gattullo, C.E.; Martins, L.L.; Mourato, M. Antioxidant responses of edible and model plant species subjected to subtoxic zinc concentrations. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 49, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degryse, F.; Smolders, E.; Merckx, R. Labile Cd Complexes Increase Cd Availability to Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Adrees, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Tsang, D.C.; Zia-Ur-Rehman, M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Rinklebe, J.; Tack, F.M.; Ok, Y.S. A critical review on effects, tolerance mechanisms and management of cadmium in vegetables. Chemosphere 2017, 182, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Dong, Z.; Wijayawardena, M.; Liu, Y.; Naidu, R.; Semple, K. Measurement of soil lead bioavailability and influence of soil types and properties: A review. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Pinelli, E.; Dumat, C. Review of Pb availability and toxicity to plants in relation with metal speciation; role of synthetic and natural organic ligands. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 219–220, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datko-Williams, L.; Wilkie, A.; Richmond-Bryant, J. Analysis of U.S. soil lead (Pb) studies from 1970 to 2012. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468-469, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Khan, S.; Khan, A.; Alam, M. Soil contamination with cadmium, consequences and remediation using organic amendments. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1591–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, M.; Agrawal, M. Effects of red mud addition in soil fertilized with cowdung manure on growth performance and metal accumulations in Brassica juncea cultivars Kranti and Pusa Bold. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2019, 50, 1214–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.; Baretta, D.; Becegato, V.A.; Almeida, V.D.C.; Paulino, A.T. Copper/Zinc Bioaccumulation and the Effect of Phytotoxicity on the Growth of Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) in Non-contaminated, Metal-Contaminated and Swine Manure-Enriched Soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, P.; Rodrigues, D.; Mourinha, C.; Palma, P.; De Varennes, A.; Cruz, N.; Tarelho, L.A.; Rodrigues, S. Use of wastes from the pulp and paper industry for the remediation of soils degraded by mining activities: Chemical, biochemical and ecotoxicological effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigua, G.C.; Novak, J.M.; Watts, D.W.; Ippolito, J.A.; Ducey, T.F.; Johnson, M.G.; Spokas, K.A. Phytostabilization of Zn and Cd in Mine Soil Using Corn in Combination with Biochars and Manure-Based Compost. Environments 2019, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiwei, Q.; De Varennes, A.; Martins, L.L.; Mourato, M.; Cardoso, A.; Mota, A.M.; Pinto, A.; Gonçalves, M. Improvement in soil and sorghum health following the application of polyacrylate polymers to a Cd-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pintor, A.M.; Ferreira, C.I.; Pereira, J.C.; Correia, P.; Silva, S.P.; Vilar, V.J.; Botelho, C.M.; Boaventura, R.A. Use of cork powder and granules for the adsorption of pollutants: A review. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3152–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peijnenburg, W.; Baerselman, R.; De Groot, A.; Jager, T.; Leenders, D.; Posthuma, L.; Van Veen, R. Quantification of Metal Bioavailability for Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) in Field Soils. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 39, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAOTDR, Ministério do Ambiente, do Ordenamento do Território e do Desenvolvimento Regional. Decreto-Lei No. 276/2009. 2009. Available online: https://data.dre.pt/eli/dec-lei/276/2009/10/02/p/dre/pt/html (accessed on 8 March 2021).
- Ribeiro, D.M.; Scanlon, T.; Kilminster, T.; Martins, C.F.; Greeff, J.; Milton, J.; Oldham, C.; Freire, J.P.B.; Mourato, M.P.; De Almeida, A.M. Mineral profiling of muscle and hepatic tissues of Australian Merino, Damara and Dorper lambs: Effect of weight loss. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 104, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossato, L.; Macfarlane, J.; Whittaker, M.; Pudmenzky, A.; Doley, D.; Schmidt, S.; Monteiro, M. Metal-binding particles alleviate lead and zinc toxicity during seed germination of metallophyte grass Astrebla lappacea. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, D.A. Analysis and Approach: K-Means and K-Medoids Data Mining Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 5th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Computing & Communication Technologies, Panipat, India, 5 November 2011; Choudhary, R.K., Verma, M., Saini, S., Eds.; pp. 274–279. [Google Scholar]
- Stritsis, C.; Claassen, N. Cadmium uptake kinetics and plants factors of shoot Cd concentration. Plant Soil 2013, 367, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, L.; Chang, A.C.; Wu, L.; Kwon, S.-I.; Bottoms, R. Modeling uptake kinetics of cadmium by field-grown lettuce. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivelli, A.R.; Puschenreiter, M.; De Maria, S. Assessment of cadmium uptake and nutrient content in sunflower plants grown under Cd stress. Plant Soil Environ. 2014, 60, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Cai, P.; Liang, W.; Huang, Q. Immobilization and phytotoxicity of Cd in contaminated soil amended with chicken manure compost. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, R.; Escolar, Á.; Bernal, M.P. Heavy metals fractionation and organic matter mineralisation in contaminated calcareous soil amended with organic materials. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1894–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Jeong Choi, Y.; Kim, J.-G. In situ stabilization of cadmium-, lead-, and zinc-contaminated soil using various amendments. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Gu, C.; Tao, T.; Chen, G.; Shan, Y. Straw incorporation increases solubility and uptake of cadmium by rice plants. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Plant Soil Sci. 2013, 63, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, F.R.; Mourato, M.P.; Sales, J.R.; Fangueiro, D.; Martins, L.L. Effect of Cattle Slurry on the Growth of Spinach Plants in Cd-contaminated Soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2020, 51, 1370–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubar, N.; Carvalho, J.R.; Correia, M.N. Heavy metals biosorption on cork biomass: Effect of the pre-treatment. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 238, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, R.; Bharagava, R.; Yadav, S.; Mohan, D. Accumulation and distribution of toxic metals in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and Indian mustard (Brassica campestris L.) irrigated with distillery and tannery effluents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 1514–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noulas, C.; Tziouvalekas, M.; Karyotis, T. Zinc in soils, water and food crops. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 49, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, M.; McDonald, L.M. Metal Uptake in Plants and Health Risk Assessments in Metal-Contaminated Smelter Soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karak, T.; Paul, R.K.; Sonar, I.; Sanyal, S.; Ahmed, K.Z.; Boruah, R.K.; Das, D.K.; Dutta, A.K. Chromium in soil and tea (Camellia sinensis L.) infusion: Does soil amendment with municipal solid waste compost make sense? Food Res. Int. 2014, 64, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Brar, M.S.; Malhi, S.S. Decontamination of Chromium by Farm Yard Manure Application in Spinach Grown in Two Texturally Different Cr-Contaminated Soils. J. Plant Nutr. 2007, 30, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malandrino, M.; Abollino, O.; Buoso, S.; Giacomino, A.; La Gioia, C.; Mentasti, E. Accumulation of heavy metals from contaminated soil to plants and evaluation of soil remediation by vermiculite. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, M.B.; Simon, T.; Tam, G.; Wharton, S. Lead and Arsenic Uptake by Leafy Vegetables Grown on Contaminated Soils: Effects of Mineral and Organic Amendments. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 224, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, S.M.; Antoniadis, V.; Kwon, E.E.; Biswas, J.K.; Wang, H.; Ok, Y.S.; Rinklebe, J. Biosolids application affects the competitive sorption and lability of cadmium, copper, nickel, lead, and zinc in fluvial and calcareous soils. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 39, 1365–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Xu, J.; Brookes, P.C. Effects of inorganic and organic amendments on the uptake of lead and trace elements by Brassica chinensis grown in an acidic red soil. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EC). No 1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 49, L173/6. [Google Scholar]
- Gaw, S.K.; Kim, N.D.; Northcott, G.L.; Wilkins, A.L.; Robinson, G. Uptake of ΣDDT, Arsenic, Cadmium, Copper, and Lead by Lettuce and Radish Grown in Contaminated Horticultural Soils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6584–6593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markert, B. Establishing of ‘Reference Plant’ for inorganic characterization of different plant species by chemical fingerprinting. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1992, 64, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, H.; Marschner, P. Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: London, UK; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2012; Chapter XV; 651p. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, N.R.; Young, S.D.; Tye, A.M.; Breward, N.; Bailey, E.H. Does returning sites of historic peri-urban waste disposal to vegetable production pose a risk to human health?—A case study near Manchester, UK. Soil Use Manag. 2012, 28, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, F.C.; Albuuerque, A.M.; Almeida, A.C.; Silveira, P.B.; Filho, C.A.; Hazin, C.A.; Honorato, E.V. Heavy metals deposited in the culture of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) by the influence of vehicular traffic in Pernambuco, Brazil. Food Chem. 2017, 215, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Lu, C.; Tariq, M.; Xiao, Q.; Zhang, W.; Huang, K.; Lu, Q.; Lin, K.; Liu, Z. The response and tolerance mechanisms of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) exposed to nickel in a spiked soil system. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM); Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.; Leblanc, J.-C.; et al. Update of the risk assessment of nickel in food and drinking water. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. GEMS/Food Regional Diets: Regional per Capita Consumption of Raw and Semi-Processed Agricultural Commodities/Prepared by the Global Environment Monitoring System/Food Contamination Monitoring and Assessment Programme (GEMS/Food), Rev. ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Adamo, P.; Iavazzo, P.; Albanese, S.; Agrelli, D.; De Vivo, B.; Lima, A. Bioavailability and soil-to-plant transfer factors as indicators of potentially toxic element contamination in agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 500–501, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). Scientific Opinion on the risks to public health related to the presence of chromium in food and drinking water. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3595. [Google Scholar]
- Scientific Committee on Food Opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food on the Tolerable Upper Intake Level of Zinc; European Commission, Health Consumer Protection Directorate-General: Brussels, Belgium, 2003.
- Baldwin, K.R.; Shelton, J.E. Availability of heavy metals in compost-amended soil. Bioresour. Technol. 1999, 69, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.; Wang, X.; Naveed, M.; Mustafa, A.; Ashraf, S.; Samreen, T.; Nadeem, S.; Jamil, M. Biochar Mediated-Alleviation of Chromium Stress and Growth Improvement of Different Maize Cultivars in Tannery Polluted Soils. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dala-Paula, B.M.; Custódio, F.B.; Knupp, E.A.; Palmieri, H.E.; Silva, J.B.B.; Glória, M.B.A. Cadmium, copper and lead levels in different cultivars of lettuce and soil from urban agriculture. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Rehman, S.; Khan, A.Z.; Khan, M.A.; Shah, M.T. Soil and vegetables enrichment with heavy metals from geological sources in Gilgit, northern Pakistan. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, G.; Li, X. Heavy metal contamination in soils and vegetables near an e-waste processing site, south China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Qiao, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and vegetables from wastewater irrigated area, Beijing-Tianjin city cluster, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, W.; Ye, Z.; Lan, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wong, M. Lead, zinc and copper accumulation and tolerance in populations of Paspalum distichum and Cynodon dactylon. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 120, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity (1:2) (mS cm−1) | 0.10 ± 0.02 | |
| pH (H2O) (1:2.5) | 6.9 ± 0.1 | |
| Organic matter (g kg−1) | 13.6 ± 0.2 | |
| Extractable P (mg kg−1) | 73.8 ± 5.2 | |
| Extractable K (mg kg−1) | 57.5 ± 4.4 | |
| Ammoniacal nitrogen (N-NH4) (mg kg−1) | 2.35 ± 0.15 | |
| Nitric nitrogen (N-NO3) (mg kg−1) | <1.0 | |
| Extractable micronutrients (mg kg−1) | Fe | 31.1 ± 1.9 |
| Cu | 4.8 ± 0.2 | |
| Zn | 1.4 ± 0.1 | |
| Mn | 35.2 ± 2.0 |
| PTE | Mass Fractions (mg kg−1) | Applied Form | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| non essential | Cd | 0 | 1.5 | 3 | 6 | 12 | CdCl2.5/2 H2O |
| Cr | 0 | 100 | 200 | 400 | 800 | CrCl3.6H2O | |
| Pb | 0 | 150 | 300 | 600 | 1200 | Pb(NO3)2 | |
| essential | Ni | 0 | 37.5 | 75 | 150 | 300 | NiCl2.6H2O |
| Zn | 0 | 150 | 300 | 600 | 1200 | ZnSO4.7H2O | |
| Hyperbolic Model | ||||
| PTE | Treatment | Cmax | KM | R2 |
| Cd | S | 222.3 ± 35.4 | 16.8 ± 4.0 | 0.9955 |
| SC | 143.9 ± 9.9 | 9.8 ± 1.2 | 0.9980 | |
| SE | 133.5 ± 18.4 | 10.6 ± 2.5 | 0.9926 | |
| Ni | S | 90.8 ± 15.2 | 93.1 ± 39.7 | 0.9476 |
| SC | 115.2 ± 28.4 | 146.0 ± 77.3 | 0.9351 | |
| SE | 88.2 ± 11.7 | 52.1 ± 22.5 | 0.9419 | |
| Linear model | ||||
| PTE | Treatment | m | b | R2 |
| Cr | S | 0.0037 ± 0.0003 | 2.313 ± 0.132 | 0.9826 |
| SC | 0.0045 ± 0.0003 | 2.288 ± 0.104 | 0.9906 | |
| SE | 0.0046 ± 0.0003 | 2.404 ± 0.128 | 0.9877 | |
| Pb | S | 0.0076 ± 0.0005 | 0.719 ± 0.288 | 0.9897 |
| SC | 0.0084 ± 0.0014 | 1.349 ± 0.845 | 0.9282 | |
| SE | 0.0081 ± 0.0021 | 2.087 ± 1.269 | 0.8343 | |
| Zn | S | 0.41 ± 0.03 | 17.6 ± 20.4 | 0.9812 |
| SC | 0.42 ± 0.01 | 21.1 ± 7.2 | 0.9977 | |
| SE | 0.49 ± 0.02 | 9.9 ± 11.7 | 0.9955 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreira, I.; Leitão, I.; Mourato, M.P.; Martins, L.L. Comparison between a Traditional (Horse Manure) and a Non-Conventional (Cork Powder) Organic Residue in the Uptake of Potentially Toxic Elements by Lettuce in Contaminated Soils. Environments 2021, 8, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8050045
Moreira I, Leitão I, Mourato MP, Martins LL. Comparison between a Traditional (Horse Manure) and a Non-Conventional (Cork Powder) Organic Residue in the Uptake of Potentially Toxic Elements by Lettuce in Contaminated Soils. Environments. 2021; 8(5):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8050045
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreira, Inês, Inês Leitão, Miguel P. Mourato, and Luisa L. Martins. 2021. "Comparison between a Traditional (Horse Manure) and a Non-Conventional (Cork Powder) Organic Residue in the Uptake of Potentially Toxic Elements by Lettuce in Contaminated Soils" Environments 8, no. 5: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8050045
APA StyleMoreira, I., Leitão, I., Mourato, M. P., & Martins, L. L. (2021). Comparison between a Traditional (Horse Manure) and a Non-Conventional (Cork Powder) Organic Residue in the Uptake of Potentially Toxic Elements by Lettuce in Contaminated Soils. Environments, 8(5), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8050045