Polystyrene Nanoplastic Behavior and Toxicity on Crustacean Daphnia magna: Media Composition, Size, and Surface Charge Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design, Choice of NPLs, Natural Freshwaters, and Synthetic Media
2.2. Water Sampling and Characterization of the Water Quality Parameters
2.3. Characterization of NPLs’ Behavior in Natural Freshwaters and Synthetic Media
2.4. Exposure of D. magna to NPLs in Natural and Synthetic Freshwater
2.5. Data Treatment
3. Results and Discussion
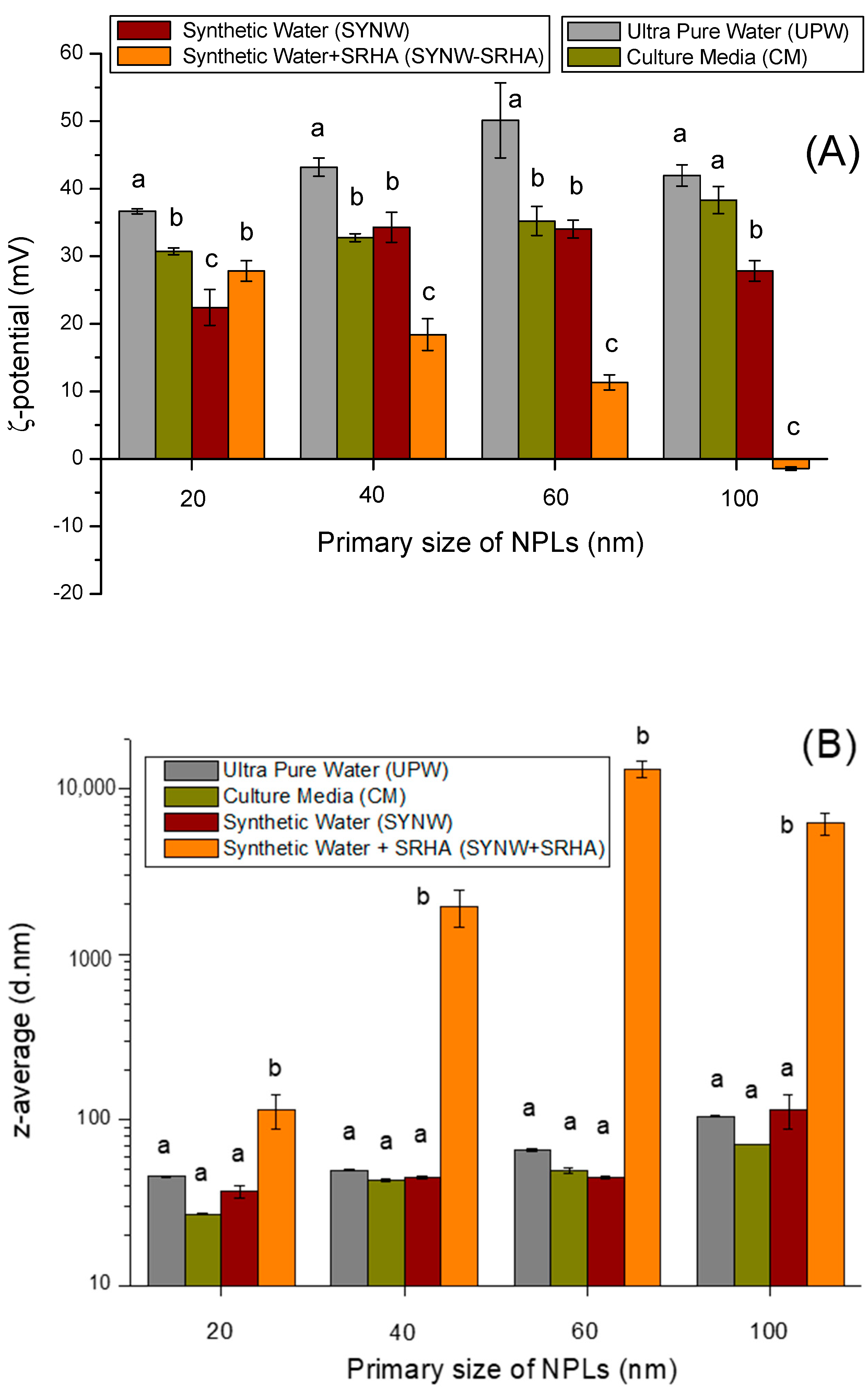
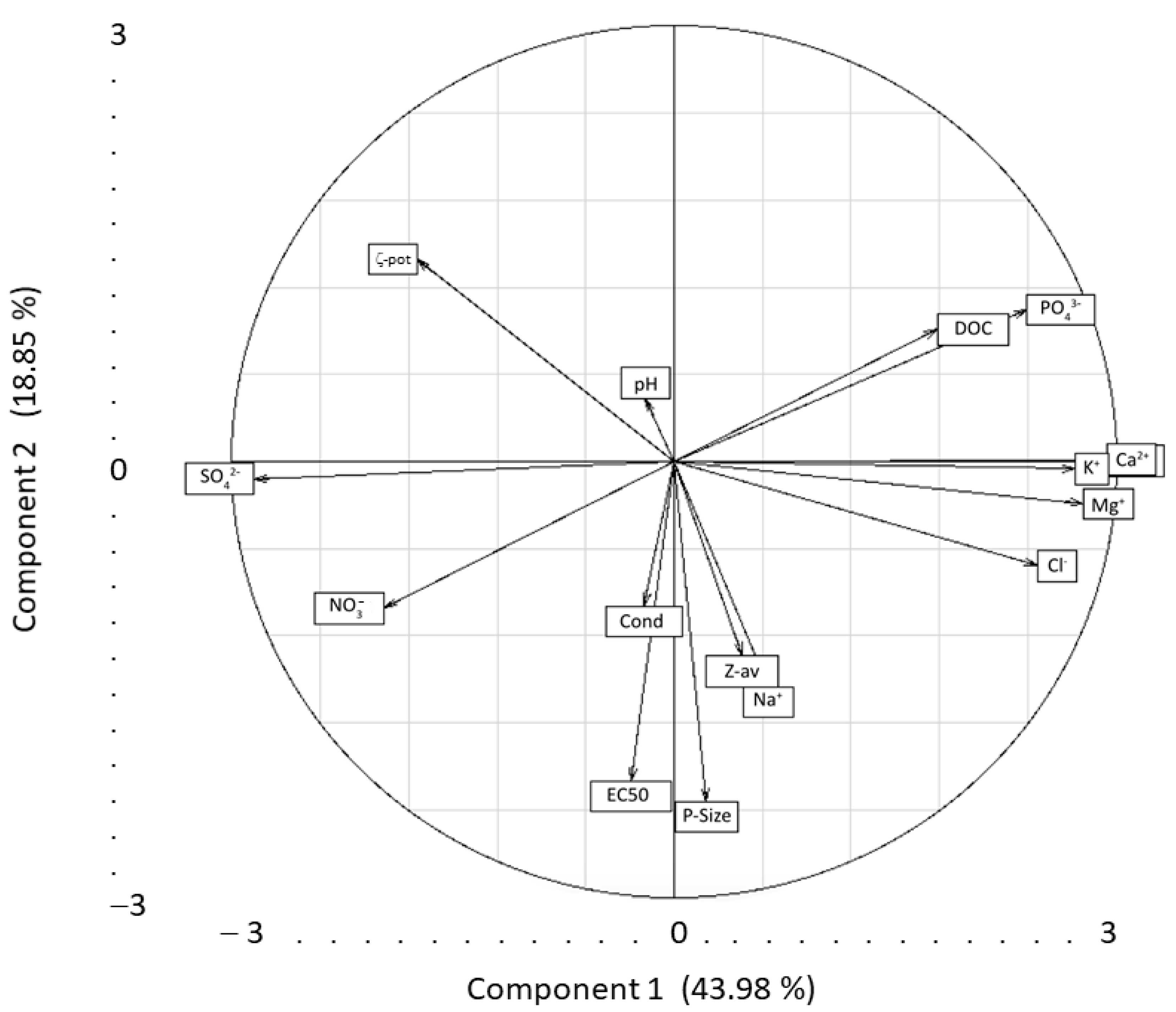
3.1. Behavior of NPLs in Synthetic Media and Freshwaters
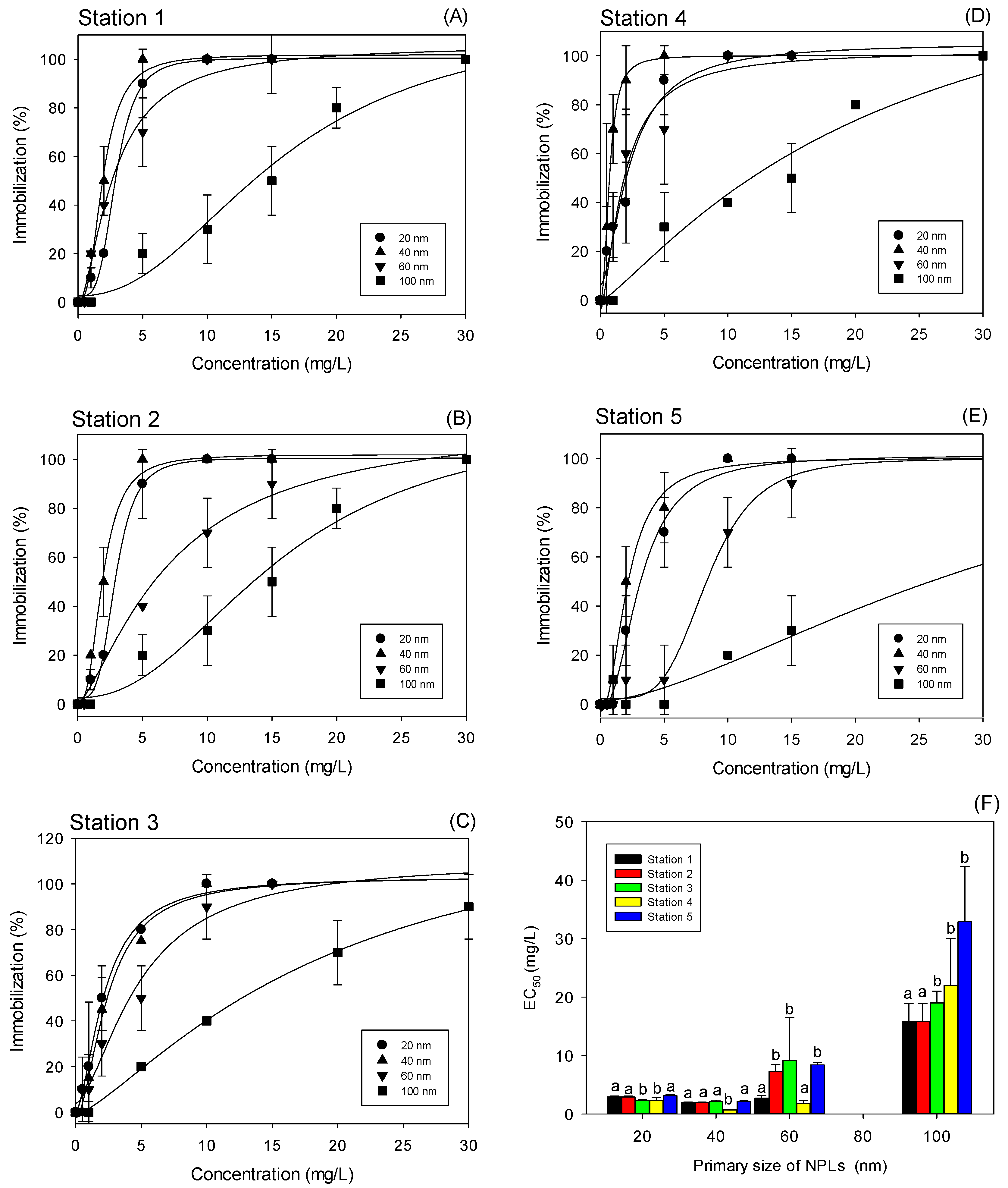
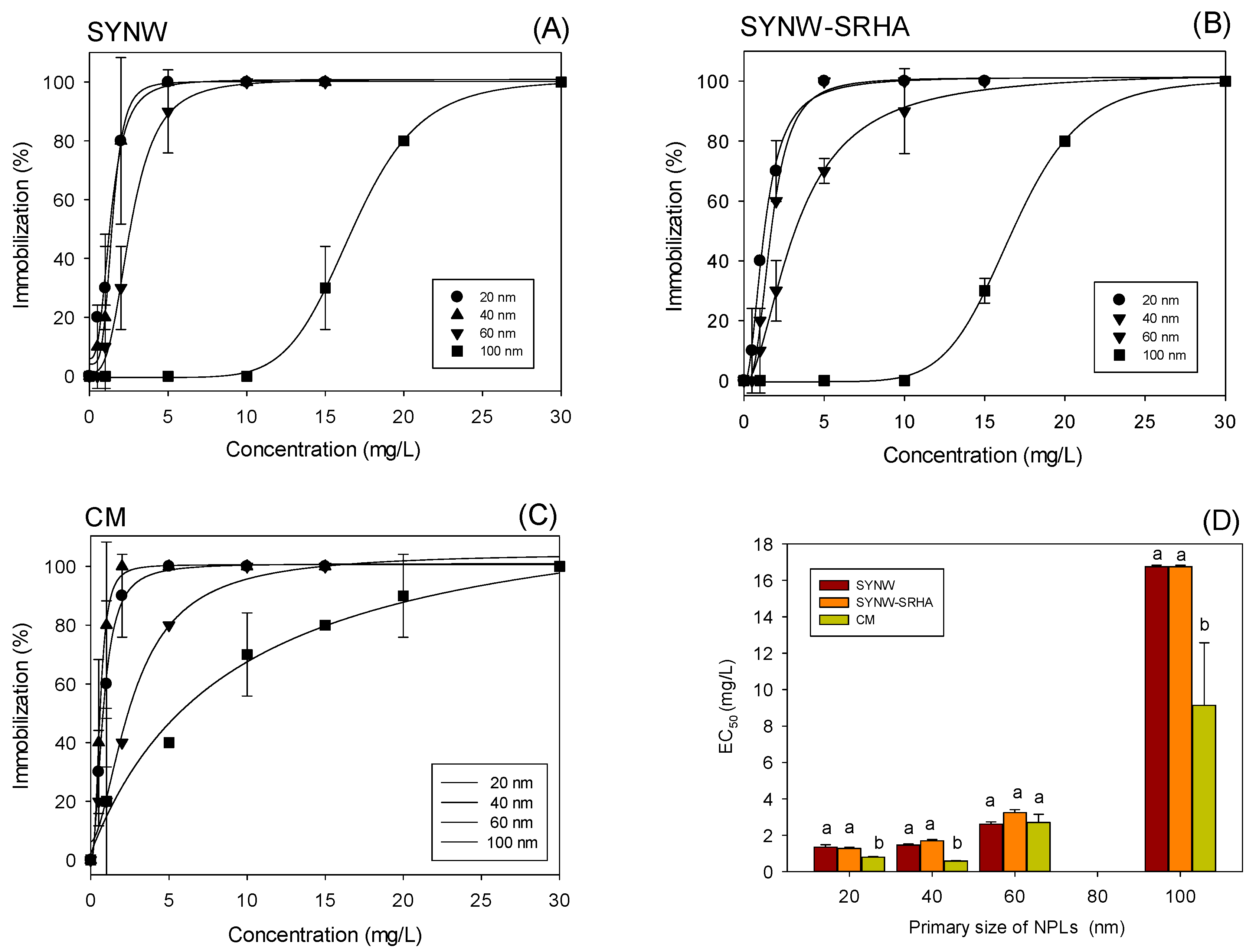
3.2. Effect of NPLs of Different Sizes on Crustacean Daphnia magna
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alimi, O.S.; Budarz, J.F.; Hernandez, L.M.; Tufenkji, N. Microplastics and nanoplastics in aquatic environments: Aggregation, deposition, and enhanced contaminant transport. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1704–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Moore, C.J.; vom Saal, F.S.; Swan, S.H. Plastics, the environment and human health: Current consensus and future trends. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2153–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chao, J.Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.C.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q. Research progress of nanoplastics in freshwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkola, A.; Krause, S.; Lynch, I.; Sambrook Smith, G.H.; Nel, H. Nano and microplastic interactions with freshwater biota—Current knowledge, challenges and future solutions. Environ. Int. 2021, 152, 106504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaylarde, C.C.; Baptista Neto, J.A.; da Fonseca, E.M. Nanoplastics in aquatic systems—Are they more hazardous than microplastics? Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 115950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, T.S.; Cole, M.; Lewis, C. Interactions of microplastic debris throughout the marine ecosystem. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 0116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, T.S.; Lewis, C.N. Marine microplastics spell big problems for future generations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eerkes-Medrano, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Aldridge, D.C. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review of the emerging threats, identification of knowledge gaps and prioritisation of research needs. Water Res. 2015, 75, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Scherer, C.; Alvarez-Muñoz, D.; Brennholt, N.; Bourrain, X.; Buchinger, S.; Fries, E.; Grosbois, C.; Klasmeier, J.; Marti, T.; et al. Microplastics in freshwater ecosystems: What we know and what we need to know. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2014, 26, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oriekhova, O.; Stoll, S. Heteroaggregation of nanoplastic particles in the presence of inorganic colloids and natural organic matter. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.; Wang, J. Interaction of nanoplastics with extracellular polymeric substances (eps) in the aquatic environment: A special reference to eco-corona formation and associated impacts. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, G.; Gabellieri, E.; Cioni, P.; Paccagnini, E.; Faleri, C.; Lupetti, P.; Corsi, I.; Morelli, E. Interplay between extracellular polymeric substances (eps) from a marine diatom and model nanoplastic through eco-corona formation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffle, J.; Wilkinson, K.J.; Stoll, S.; Filella, M.; Zhang, J. A generalized description of aquatic colloidal interactions: The three-colloidal component approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2887–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadare, O.O.; Wan, B.; Liu, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Guo, L.-H. Eco-corona vs. protein corona: Effects of humic substances on corona formation and nanoplastic particle toxicity in daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8001–8009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulido-Reyes, G.; Leganes, F.; Fernández-Piñas, F.; Rosal, R. Bio-nano interface and environment: A critical review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 3181–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, Y.; An, Y.J. Effects of micro- and nanoplastics on aquatic ecosystems: Current research trends and perspectives. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, H.; Besson, M.; Swarzenski, P.W.; Lecchini, D.; Metian, M. Effects of virgin micro- and nanoplastics on fish: Trends, meta-analysis, and perspectives. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 4733–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.J.; Perono, G.; Tommasi, F.; Pagano, G.; Oral, R.; Buric, P.; Kovacic, I.; Toscanesi, M.; Trifuoggi, M.; Lyons, D.M. Resolving the effects of environmental micro- and nanoplastics exposure in biota: A knowledge gap analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besseling, E.; Wang, B.; Lürling, M.; Koelmans, A.A. Nanoplastic affects growth of S. obliquus and reproduction of D. magna. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12336–12343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, A.M.; Hansen, B.H.; Frenzel, M.; Johnsen, H.; Altin, D. Uptake and toxicity of methylmethacrylate-based nanoplastic particles in aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casado, M.P.; Macken, A.; Byrne, H.J. Ecotoxicological assessment of silica and polystyrene nanoparticles assessed by a multitrophic test battery. Environ. Int. 2013, 51, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naha, P.C.; Casey, A.; Tenuta, T.; Lynch, I.; Dawson, K.A.; Byrne, H.J.; Davoren, M. Preparation, characterization of nipam and nipam/bam copolymer nanoparticles and their acute toxicity testing using an aquatic test battery. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 92, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nasser, F.; Lynch, I. Secreted protein eco-corona mediates uptake and impacts of polystyrene nanoparticles on daphnia magna. J. Proteom. 2016, 137, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rist, S.; Baun, A.; Hartmann, N.B. Ingestion of micro- and nanoplastics in daphnia magna—Quantification of body burdens and assessment of feeding rates and reproduction. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 228, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, W.; Jiang, R.; Hu, S.; Xiao, X.; Wu, J.; Wei, S.; Xiong, Y.; Ouyang, G. Investigating the toxicities of different functionalized polystyrene nanoplastics on daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, V.P.; Nogueira, D.J.; Vicentini, D.S.; Matias, W.G. Can the sonication of polystyrene nanoparticles alter the acute toxicity and swimming behavior results for daphnia magna? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 14192–14198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Li, Y.M.; Perez, E.; Jiang, Q.C.; Chen, Q.; Jiao, Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.L. Polystyrene nanoplastic induces oxidative stress, immune defense, and glycometabolism change in daphnia pulex: Application of transcriptome profiling in risk assessment of nanoplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, J.; Stoll, S.; Slaveykova, V.I. Influence of nanoplastic surface charge on eco-corona formation, aggregation and toxicity to freshwater zooplankton. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Jiang, R.; Lin, W.; Ouyang, G. Effect of salinity and humic acid on the aggregation and toxicity of polystyrene nanoplastics with different functional groups and charges. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Swan, S.H.; Moore, C.J.; vom Saal, F.S. Our plastic age. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1973–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nel, A.; Xia, T.; Mädler, L.; Li, N. Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 2006, 311, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, B.G.; Koizumi, K.; Chung, S.-Y.; Kodera, Y.; Kim, J.-O.; Saido, K. Global styrene oligomers monitoring as new chemical contamination from polystyrene plastic marine pollution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persoone, G.; Janssen, C.; De Coen, W. Cyst-based toxicity tests x: Comparison of the sensitivity of the acute daphnia magna test and two crustacean microbiotests for chemicals and wastes. Chemosphere 1994, 29, 2701–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lê, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. Factominer: An r package for multivariate analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 25, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramirez Arenas, L.; Ramseier Gentile, S.; Zimmermann, S.; Stoll, S. Coagulation of TiO2, CeO2 nanoparticles, and polystyrene nanoplastics in bottled mineral and surface waters. Effect of water properties, coagulant type, and dosage. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Chae, Y.; An, Y.J. Mixture toxicity of nickel and microplastics with different functional groups on daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12852–12858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkranz, P.; Chaudhry, Q.; Stone, V.; Fernandes, T.F. A comparison of nanoparticle and fine particle uptake by daphnia magna. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 2142–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehse, S.; Kloas, W.; Zarfl, C. Short-term exposure with high concentrations of pristine microplastic particles leads to immobilisation of daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pochelon, A.; Stoll, S.; Slaveykova, V.I. Polystyrene Nanoplastic Behavior and Toxicity on Crustacean Daphnia magna: Media Composition, Size, and Surface Charge Effects. Environments 2021, 8, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8100101
Pochelon A, Stoll S, Slaveykova VI. Polystyrene Nanoplastic Behavior and Toxicity on Crustacean Daphnia magna: Media Composition, Size, and Surface Charge Effects. Environments. 2021; 8(10):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8100101
Chicago/Turabian StylePochelon, Alexis, Serge Stoll, and Vera I. Slaveykova. 2021. "Polystyrene Nanoplastic Behavior and Toxicity on Crustacean Daphnia magna: Media Composition, Size, and Surface Charge Effects" Environments 8, no. 10: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8100101
APA StylePochelon, A., Stoll, S., & Slaveykova, V. I. (2021). Polystyrene Nanoplastic Behavior and Toxicity on Crustacean Daphnia magna: Media Composition, Size, and Surface Charge Effects. Environments, 8(10), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8100101






