Morphospecies Abundance of Above-Ground Invertebrates in Agricultural Systems under Glyphosate and Microplastics in South-Eastern Mexico
Abstract
:1. Introduction
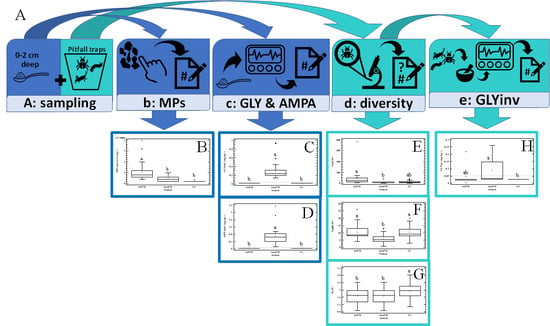
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Plot Selection
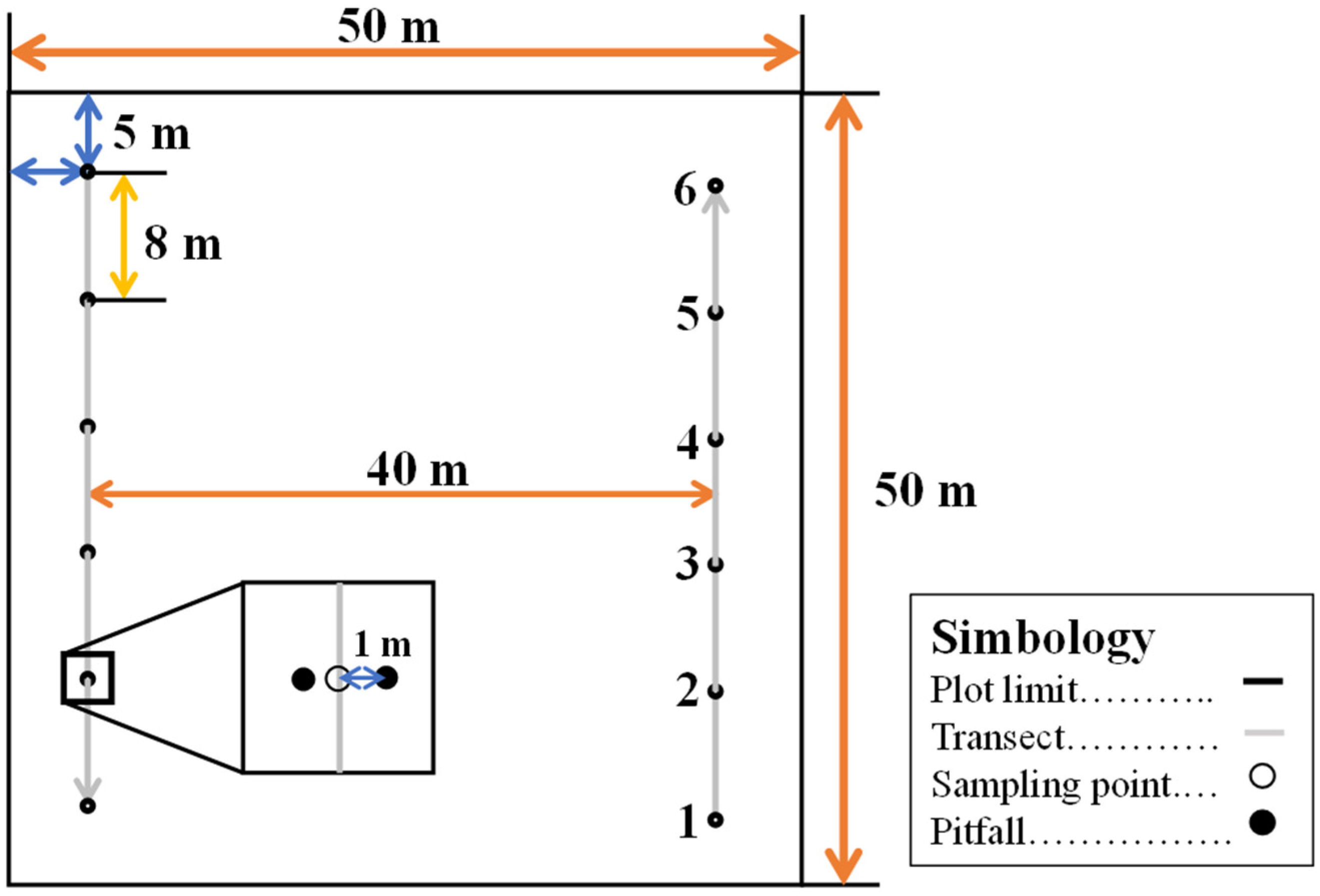
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Soil Glyphosate and AMPA Analysis
2.5. Glyphosate Analysis in Above-Ground Dwellers’ Tissue
2.6. Soil Microplastic Quantification
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
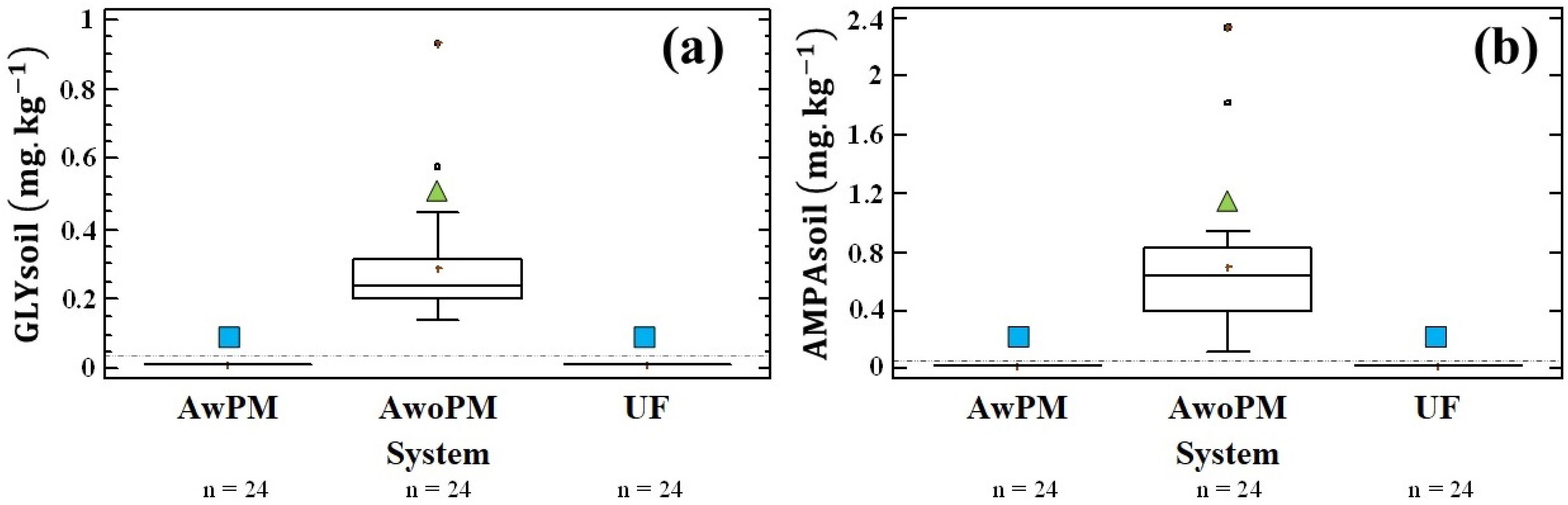
3.1. Glyphosate and AMPA in Soils
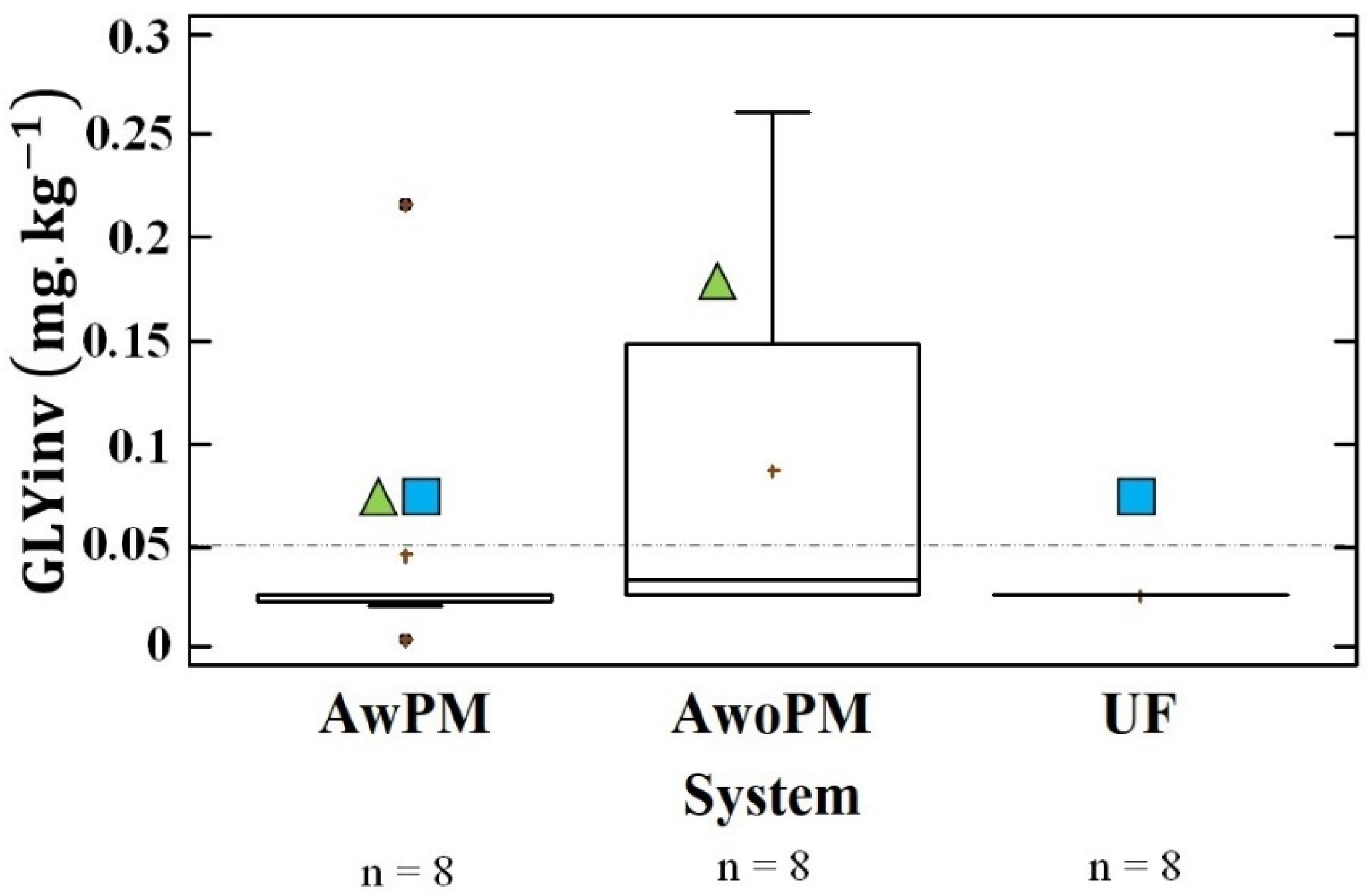
3.2. Glyphosate in Above-Ground Dwellers’ Tissue
3.3. Microplastics in Soil
3.4. Above-Ground Dweller Communities in the Presence of Soil GLY, AMPA and MPs
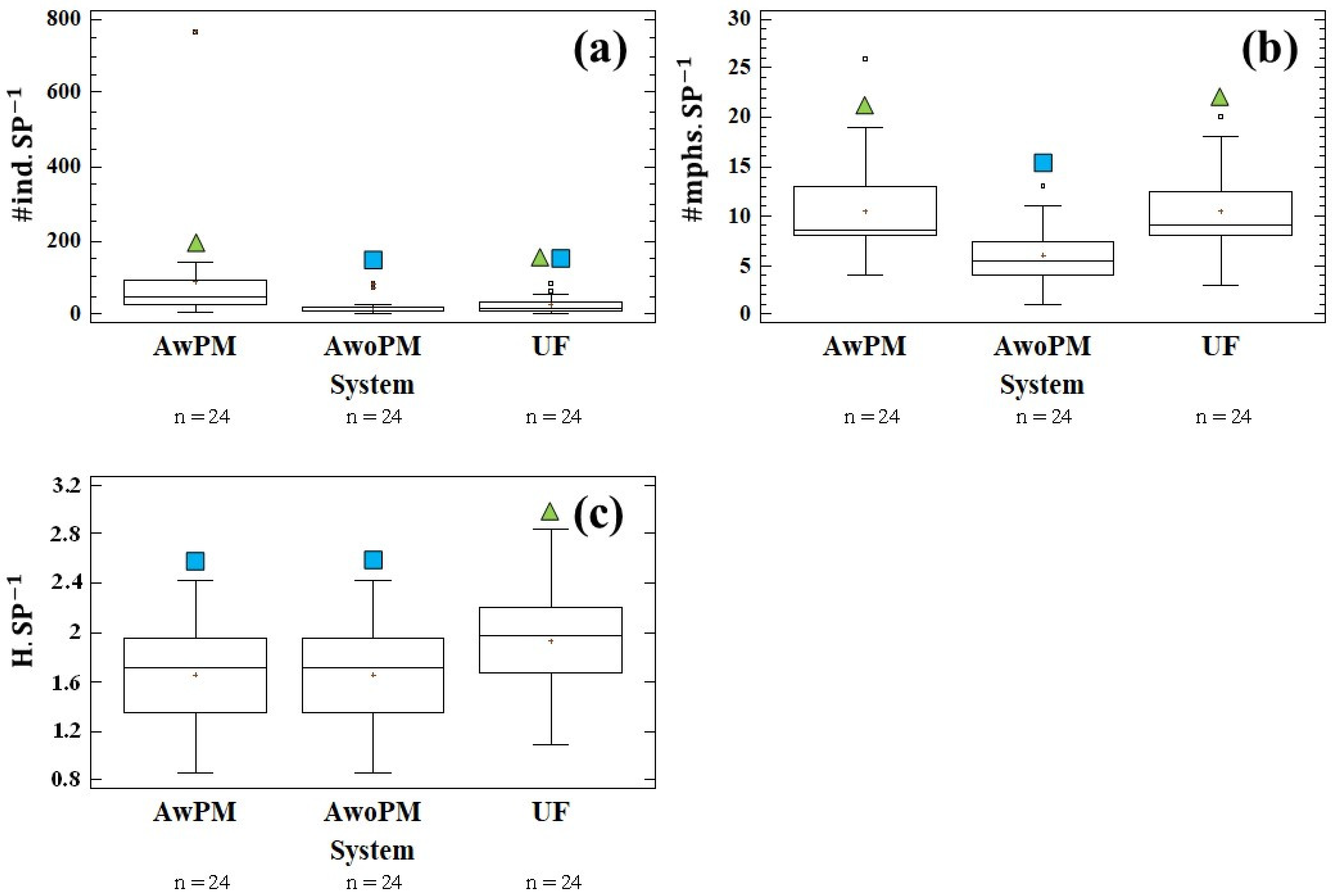
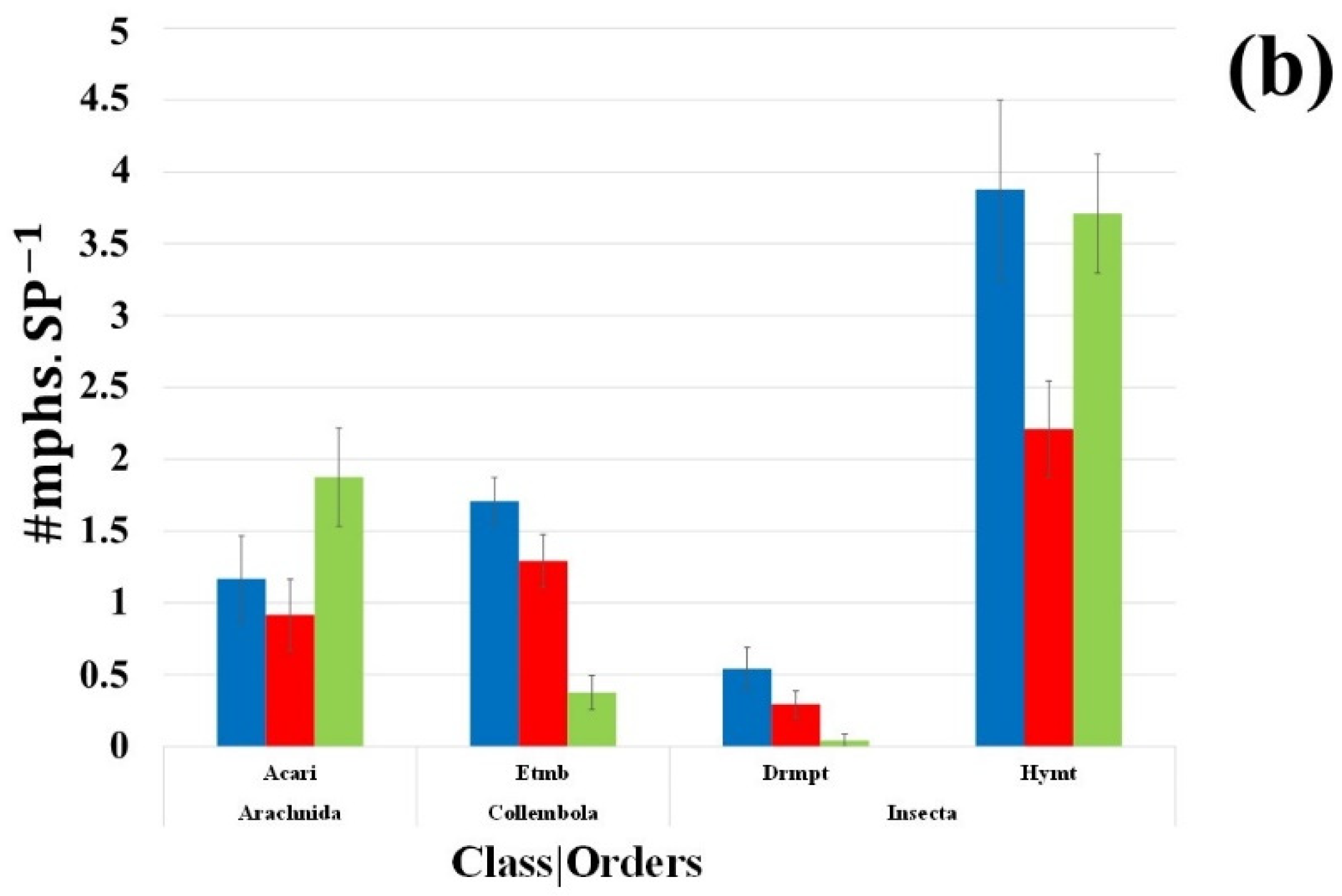
3.4.1. Numbers of Individual Above-Ground Dwellers per Order
3.4.2. Above-Ground Dwellers’ Morphospecies per Order
4. Discussion
4.1. GLY, AMPA and MP Presence in Soil
| Taxonomic Group | Exposure Concentration of GLY | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Araneae (Alpaida veniliae) | Coated preys (Musca domestica) with 192 mg (48% GLY) L−1 analytical grade acetone. | Negative effect on prey consumption, web construction, fecundity, fertility and progeny development time. | Benamú et al. [53] |
| (Pardosa milvina) | 12 and 7.68 g L−1 distilled water | Females attracted fewer males, as males were less able to detect and/or react to female signals. | Griesinger et al. [54] |
| (Tigrosa helluo, Pardosa milvina) | Exposure to filter paper immersed in a solution with 12 g L−1 distilled water | Tigrosa subdued the cricketers more quickly and with fewer lunges than Pardosa. | Rittman et al. [55] |
| (Hogna cf. bivittata) | Exposure to filter paper immersed in a solution with 280 mg L−1 distilled water | Consumption of caterpillars (Anticarsia gemmatalis) but especially ants (Acromyrmex sp.) decreased. | Lacava et al. [24] |
| Araneae (Pardosa agricola) and Carabidae (Poecilus cupreus) | Exposure to filter paper immersed in a solution (1:25) with 19.2 mg L−1 distilled water. | It seems harmless to Pardosa but it slowed down the translational movement of Poecilus. | Michalková et al. [56] |
| Araneae (Pardosa milvina, Hogna helluo) and Carabidae (Scarites quadriceps) | 12 g L−1 distilled water | Depending on topical, contact or combined exposure, translational (Pardosa) or seasonal (Hogna and Scarites) movement decreased, to the extent that prolonged exposure increased mortality (Pardosa). | Evans et al. [57] |
| Gastrropoda (Pseudosuccinea columella) | 0.1, 1 and 10 mg L−1 distilled water | Increase in amino acids as GLY concentration increases (alanine, glycine, glutamic acid, serine and threomine). | Tate et al. [25] |
| Hymenoptera (Apis mellifera) | 0–3.7 mg L−1 | It reduced sensitivity to nectar and affected associative learning. However, no effect was found on foraging behavior. | Herbert et al. [49] |
| - | 2.5, 5 and 10 mg L−1 | It affected the cognitive abilities needed to retrieve and integrate spatial information for a successful return to the hive. | Balbuena et al. [26] |
| - | 1.25, 2.5 and 5 ng bee−1 | β-carotene and retinaldehyde decreased with increasing GLY dose, implying increased oxidative stress. | Helmer et al. [58] |
| (Melipona quadrifasciata) | 3 µL of GLY dissolved in 10 µL of water | It killed all larvae after only a few days of exposure. | Eler et al. [27] |
| Oligochaeta (Eisenia fetida) | 0.2 and 0.8 mg kg−1 soil | Direct relationship with concentration, decreased weight and reproduction. | Yasmin et al. [59] |
| (Lumbriculus variegatus) | 0.05, 0.1, 0.5 and 5 mg L−1 | The Roundup Ultra formulation caused greater oxidative stress than pure GLY, even at non-toxic levels. | Contardo-Jara et al. [28] |
| Plastic Type | Plastic Mulch | MPs Concentration | Depth | Crop | Soil Type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PE, PP | NO | 153 (20–325) * items kg−1 | 0–5 cm | Rice | ND | Kim et al. [60] |
| PE, PET, | YES | 65 (10–265) items kg−1 | Pepper and cabbage | |||
| PP, PS | NO | 310 (75–7630) items kg−1 (in greenhouse) | Tomatoes, cucumbers and eggplants (in greenhouse) | |||
| PE, PET, PP | NO | 2110 (215–3315) items kg−1 (out of greenhouse) | ||||
| Biodegradable polylactic acid | NO | 320–12,560 items kg−1 | 0–20 cm | Rice | ND | Chen et al. [65] |
| ND | YES | 12,050 (7100–26,630 particles kg−1) 26,070 (13,470–42,960 particles kg−1) | 0–5 cm | Lettuce | Nitisol Gleysol | Zhang and Liu [62] |
| NO | 14,440 (8180–18,100 particles kg−1) | Indigenous trees | ||||
| PE, PMMA, PP, PS, PVC | NO | 0.34 ± 0.36 ** particles kg−1 | 0–5 cm | Wheat, barley, lucerne, triticale, white mustard, and corn | Entisol and Vertisol | Piehl et al. [63] |
| PP, PE, PA, PET, PVC, PC, ABS, PMMA y PS | YES | 78 ± 12.91 items kg−1 | 0–3 cm | Vegetables | ND | Liu et al. [61] |
4.2. Presence and Origin of GLY in Above-Ground Dwellers’ Tissue
4.3. Above-Ground Invertebrates in the Presence of Soil GLY and MPs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tibbett, M.; Fraser, T.D.; Duddigan, S. Identifying Potential Threats to Soil Biodiversity. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagner, M.; Mikola, J.; Saloniemi, I.; Saikkonen, K.; Helander, M. Effects of a Glyphosate-Based Herbicide on Soil Animal Trophic Groups and Associated Ecosystem Functioning in a Northern Agricultural Field. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maran, A.M.; Weintraub, M.N.; Pelini, S.L. Does Stimulating Ground Arthropods Enhance Nutrient Cycling in Conventionally Managed Corn Fields? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 297, 106934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.M. Antología Toxicológica de Glifosato +1000: Evidencias Científicas Publicadas Sobre Los Impactos Del Glifosato En La Salud, Ambiente y Biodiversidad. Available online: https://semillasdeidentidad.org/es/articulos/de-1000-evidencias-cientificas-publicadas-sobre-los-impactos-del-glifosato-en-la-salud-ambiente-y-biodiversidad (accessed on 28 September 2020).
- Yang, X.; Lwanga, E.H.; Bemani, A.; Gertsen, H.; Salanki, T.; Guo, X.; Fu, H.; Xue, S.; Ritsema, C.; Geissen, V. Biogenic Transport of Glyphosate in the Presence of LDPE Microplastics: A Mesocosm Experiment. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.J.; Huang, X.P.; Xiang, L.; Wang, Y.Z.; Li, Y.W.; Li, H.; Cai, Q.Y.; Mo, C.H.; Wong, M.H. Source, Migration and Toxicology of Microplastics in Soil. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmel, J.; Albert, J.; Kurtz, M.P.; Muñoz, K. Plasticulture Changes Soil Invertebrate Assemblages of Strawberry Fields and Decreases Diversity and Soil Microbial Activity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 124, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, F.; la Cecilia, D.; Tang, F.H.M.; McBratney, A. The Global Environmental Hazard of Glyphosate Use. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Alimentación y la Agricultura División de Estadística. Plaguicidas Uso. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/es/#data/RP (accessed on 28 September 2020).
- Sistema de Información Arancelaria Vía Internet. Fracción 2931.90.19 Sal Isopropilamonica de N(fosfonometil)Glicina. Sal de Glifosato. Available online: http://www.economia-snci.gob.mx/ (accessed on 28 September 2020).
- Battaglin, W.A.; Meyer, M.T.; Kuivila, K.M.; Dietze, J.E. Glyphosate and Its Degradation Product AMPA Occur Frequently and Widely in U.S. Soils, Surface Water, Groundwater, and Precipitation. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Montanarella, L.; Jones, A.; Fernández-Ugalde, O.; Mol, H.G.J.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Distribution of Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid (AMPA) in Agricultural Topsoils of the European Union. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jia, W.; Yan, C.; Wang, J. Agricultural Plastic Mulching as a Source of Microplastics in the Terrestrial Environment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, Z.; Wollmann, C.; Schaefer, M.; Buchmann, C.; David, J.; Tröger, J.; Muñoz, K.; Frör, O.; Schaumann, G.E. Plastic Mulching in Agriculture. Trading Short-Term Agronomic Benefits for Long-Term Soil Degradation? Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 690–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briassoulis, D.; Hiskakis, M.; Tserotas, P. Combined Effect of UVA Radiation and Agrochemicals on the Durability of Agricultural Multilayer Films. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 154, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E.L.; Huerta Lwanga, E.; Eldridge, S.M.; Johnston, P.; Hu, H.W.; Geissen, V.; Chen, D. An Overview of Microplastic and Nanoplastic Pollution in Agroecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duis, K.; Coors, A. Microplastics in the Aquatic and Terrestrial Environment: Sources (with a Specific Focus on Personal Care Products), Fate and Effects. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corradini, F.; Casado, F.; Leiva, V.; Huerta-Lwanga, E.; Geissen, V. Microplastics Occurrence and Frequency in Soils under Different Land Uses on a Regional Scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, N.; Aqeel, M.; Noman, A. Microplastics Could Be a Threat to Plants in Terrestrial Systems Directly or Indirectly. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Xiong, X.; He, M.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Gupta, J.; Khan, E.; Harrad, S.; Hou, D.; Sik, Y.; Bolan, N.S. Microplastics as Pollutants in Agricultural Soils. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruimin, Q.; Jones, D.L.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q.; Changrong, Y. Behavior of Microplastics and Plastic Film Residues in the Soil Environment: A Critical Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changrong, Y.; Wenqing, H.; Turner, N.C.; Enke, L.; Qin, L.; Shuang, L. Plastic-Film Mulch in Chinese Agriculture: Importance and Problems. World Agric. 2014, 4, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; Hu, W.; Qin, X.; Ma, X.; Yan, C.; Wang, H. The Status and Distribution Characteristics of Residual Mulching Film in Xinjiang, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 2639–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lacava, M.; García, L.F.; Viera, C.; Michalko, R. The Pest-Specific Effects of Glyphosate on Functional Response of a Wolf Spider. Chemosphere 2021, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, T.M.; Jackson, R.N.; Christian, F.A. Effects of Glyphosate and Dalapon on Total Free Amino Acid Profiles of Pseudosuccinea Columella Snails. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 64, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balbuena, M.S.; Tison, L.; Hahn, M.; Greggers, U.; Menzel, R.; Farina, W.M. Effects of Sublethal Doses of Glyphosate on Honeybee Navigation. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 2799–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eler Seide, V.; Cupertino Bernardes, R.; Guedes Pereira, E.J.; Pereira Lima, M.A. Glyphosate Is Lethal and Cry Toxins Alter the Development of the Stingless Bee Melipona quadrifasciata. Envionmental Pollut. 2018, 243, 1854–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contardo-Jara, V.; Klingelmann, E.; Wiegand, C. Bioaccumulation of Glyphosate and Its Formulation Roundup Ultra in Lumbriculus variegatus and Its Effects on Biotransformation and Antioxidant Enzymes. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, S.O. Glyphosate: Environmental Fate and Impact. Weed Sci. 2020, 68, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Datta, S.; Wani, A.B.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Romero, R.; Singh, J. Glyphosate Uptake, Translocation, Resistance Emergence in Crops, Analytical Monitoring, Toxicity and Degradation: A Review; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Bento, C.P.M.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Xue, S.; Lwanga, E.H.; Zomer, P.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Influence of Microplastic Addition on Glyphosate Decay and Soil Microbial Activities in Chinese Loess Soil. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Yang, X.; Pelaez, A.M.; Huerta Lwanga, E.; Beriot, N.; Gertsen, H.; Garbeva, P.; Geissen, V. Macro- and Micro- Plastics in Soil-Plant System: Effects of Plastic Mulch Film Residues on Wheat (Triticum Aestivum) Growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos Zapata, G.J.; Mendoza Vega, J. La Biodiversidad En Campeche: Estudio de Estado, 1st ed.; Villalobos-Zapata, G.J., Mendoza Vega, J., Eds.; Comisión Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad: Mexico City, Mexico, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía. Prontuario de Información Geográfica Municipal de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos: Campeche. Available online: http://www3.inegi.org.mx/contenidos/app/mexicocifras/datos_geograficos/04/04002.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2018).
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía. Guía para la Interpretación de Cartografía Climatológica. Available online: http://internet.contenidos.inegi.org.mx/contenidos/productos/prod_serv/contenidos/espanol/bvinegi/productos/historicos/1329/702825231781/702825231781_1.pdf (accessed on 28 March 2021).
- Comisión Nacional del Agua. Estaciones Climatológicas, Datos de la Estación 4063: EDZNA II. Available online: http://smn.conagua.gob.mx/tools/RESOURCES/Normales5110/NORMAL04063.TXT (accessed on 8 August 2018).
- Comisión Nacional del Agua. Estaciones Climatológicas, Datos de la Estación 4058: NOH YAXCHE. Available online: http://smn.conagua.gob.mx/tools/RESOURCES/Normales5110/NORMAL04058.TXT (accessed on 8 August 2018).
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Developmet. Guidance Document for Conducting Pesticide Terrestrial Field Dissipation Studies. Available online: http://www.oecd.org/officialdocuments/publicdisplaydocumentpdf/?cote=ENV/JM/MONO(2016)6&docLanguage=En (accessed on 31 July 2018).
- Environmental Protection Agency. Soil Sampling-Standard Operating Procedure ENV 3.13; Environmental Protection Agency: New York, NY, USA, 1997.
- Siewers, J.; Schirmel, J.; Buchholz, S. The Efficiency of Pitfall Traps as a Method of Sampling Epigeal Arthropods in Litter Rich Forest Habitats. Eur. J. Entomol. 2014, 111, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCravy, K.W. A Review of Sampling and Monitoring Methods for Beneficial Arthropods in Agroecosystems. Multidiscip. Digit. Publ. Inst. 2018, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheli, G.H.; Corley, J.C. Efficient Sampling of Ground-Dwelling Arthropods Using Pitfall Traps in Arid Steppes. Neotrop. Entomol. 2010, 39, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burch, J.B.; Cruz-Reyes, A. Clave Genérica Para La Identificación de Gastrópodos de Agua Dulce En México. México; Instituto de Biología, UNAM: Mexico City, Mexico, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Comisión Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad. Catálogo de Autoridades Taxonómicas de Especies de Flora y Fauna con Distribución en México. Available online: https://www.snib.mx/taxonomia/descarga/ (accessed on 10 January 2021).
- Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Bento, C.P.M.; Xue, S.; Gai, L.; van Dam, R.; Mol, H.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Short-Term Transport of Glyphosate with Erosion in Chinese Loess Soil—A Flume Experiment. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger, M.; Schledorn, P.; Schrödl, W.; Hoppe, H.-W.; Lutz, W.; Shehata, A.A. Detection of Glyphosate Residues in Animals and Humans. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2014, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douros, D.L.; Gaines, K.F.; Novak, J.M. Atrazine and Glyphosate Dynamics in a Lotic Ecosystem: The Common Snapping Turtle as a Sentinel Species. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Gertsen, H.; Peters, P.; Salánki, T.; Geissen, V. A Simple Method for the Extraction and Identification of Light Density Microplastics from Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 1056–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herbert, L.T.; Vázquez, D.E.; Arenas, A.; Farina, W.M. Effects of Field-Realistic Doses of Glyphosate on Honeybee Appetitive Behaviour. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 3457–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arregui, M.C.; Lenardón, A.; Sanchez, D.; Maitre, M.I.; Scotta, R.; Enrique, S. Monitoring Glyphosate Residues in Transgenic Glyphosate-Resistant Soybean. Pest Manag. Sci. 2004, 60, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bento, C.P.M.; van der Hoeven, S.; Yang, X.; Riksen, M.M.J.P.M.; Mol, H.G.J.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Dynamics of Glyphosate and AMPA in the Soil Surface Layer of Glyphosate-Resistant Crop Cultivations in the Loess Pampas of Argentina. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Bento, C.P.M.; Meng, L.; van Dam, R.; Mol, H.; Liu, G.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Decay Characteristics and Erosion-Related Transport of Glyphosate in Chinese Loess Soil under Field Conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 530–531, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benamú, M.A.; Schneider, M.I.; Sánchez, N.E. Effects of the Herbicide Glyphosate on Biological Attributes of Alpaida Veniliae (Araneae, Araneidae), in Laboratory. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesinger, L.M.; Evans, S.C.; Rypstra, A.L. Effects of a Glyphosate-Based Herbicide on Mate Location in a Wolf Spider That Inhabits Agroecosystems. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1461–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rittman, S.; Wrinn, K.M.; Evans, S.C.; Webb, A.W.; Rypstra, A.L. Glyphosate-Based Herbicide Has Contrasting Effects on Prey Capture by Two Co-Occurring Wolf Spider Species. J. Chem. Ecol. 2013, 39, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalková, V.; Pekár, S. How Glyphosate Altered the Behaviour of Agrobiont Spiders (Araneae: Lycosidae) and Beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Biol. Control 2009, 51, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.C.; Shaw, E.M.; Rypstra, A.L. Exposure to a Glyphosate-Based Herbicide Affects Agrobiont Predatory Arthropod Behaviour and Long-Term Survival. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmer, S.H.; Kerbaol, A.; Aras, P.; Jumarie, C.; Boily, M. Effects of Realistic Doses of Atrazine, Metolachlor, and Glyphosate on Lipid Peroxidation and Diet-Derived Antioxidants in Caged Honey Bees (Apis Mellifera). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 8010–8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasmin, S.; D’Souza, D. Effect of Pesticides on the Reproductive Output of Eisenia Fetida. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 79, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, H.; Lee, H.J. Abundance and Characteristics of Microplastics in Soils with Different Agricultural Practices: Importance of Sources with Internal Origin and Environmental Fate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Lu, S.; Song, Y.; Lei, L.; Hu, J.; Lv, W.; Zhou, W.; Cao, C.; Shi, H.; Yang, X.; et al. Microplastic and Mesoplastic Pollution in Farmland Soils in Suburbs of Shanghai, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.S.; Liu, Y.F. The Distribution of Microplastics in Soil Aggregate Fractions in Southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piehl, S.; Leibner, A.; Löder, M.G.J.; Dris, R.; Bogner, C.; Laforsch, C. Identification and Quantification of Macro- and Microplastics on an Agricultural Farmland. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezaei, M.; Riksen, M.J.P.M.; Sirjani, E.; Sameni, A.; Geissen, V. Wind Erosion as a Driver for Transport of Light Density Microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Peng, Y.; Xiao, L. Mixing Effect of Polylactic Acid Microplastic and Straw Residue on Soil Property and Ecological Function. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, F.; Simcik, M.F.; Capel, P.D. Occurrence and Fate of the Herbicide Glyphosate and Its Degradate Aminomethylphosphonic Acid in the Atmosphere. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicini, J.L.; Jensen, P.K.; Young, B.M.; Swarthout, J.T. Residues of Glyphosate in Food and Dietary Exposure. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 5226–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N.K.; Dörfler, U.; Welzl, G.; Munch, J.C.; Schroll, R.; Suhadolc, M. Large Variation in Glyphosate Mineralization in 21 Different Agricultural Soils Explained by Soil Properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.M. Cycling in Ecosystems Invertebrate-Mediated Transport Processes in Soils. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1988, 24, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jänsch, S.; Frampton, G.K.; Römbke, J.; Van Den Brink, P.J.; Scott-Fordsmand, J.J. Effects of Pesticides on Soil Invertebrates in Model Ecosystem and Field Studies: A Review and Comparison with Laboratory Toxicity Data. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 2490–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida Tapia, A. Evolución y Situación Actual de La Agricultura Protegida En México. Available online: https://www.berger.ca/es/recursos-para-los-productores/tips-y-consejos-practicos/estado-actual-la-agricultura-protegida-mexico/ (accessed on 28 September 2020).
- Chanatásig-Vaca, C.I.; Huerta Lwanga, E.; Rojas Fernández, P.; Ponce-Mendoza, A.; Mendoza Vega, J.; Morón Ríos, A.; Van der Wal, H.; Dzib-Castillo, B.B. Efecto Del Uso de Suelo En Las Hormigas (Formicidae: Hymenoptera) de Tikinmul, Campeche, México. Acta Zoológica Mexicana 2011, 27, 441–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, G.K.; Jänsch, S.; Scott-Fordsmand, J.J.; Römbke, J.; Van den Brink, P.J. Effects of Pesticides on Soil Invertebrates in Laboratory Studies: A Review and Analysis Using Species Sensitivity Distributions. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 2490–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comité International des PLastiques en Agriculture. Plasticulture: Definition. Available online: http://cipa-plasticulture.com/ (accessed on 28 March 2018).
- Centro de Investigación en Química Aplicada. Plásticos en la Agricultura. Available online: http://www.ciqa.mx/index.php/departamentos/19-plasticos-en-la-agricultura (accessed on 17 August 2017).
- Servicio de Información Agroalimentaria y Pesquera. Datos Abiertos: Superficie Cubierta y Número de Instalaciones de Agricultura Protegida SIAP. Available online: http://infosiap.siap.gob.mx/gobmx/datosAbiertos.php (accessed on 28 March 2018).
- Addison, P.; Baauw, A.H.; Groenewald, G.A. An Initial Investigation of the Effects of Mulch Layers on Soil-Dwelling Arthropod Assemblages in Vineyards. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2013, 34, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miñarro, M.; Espadaler, X.; Melero, V.X.; Suárez-Álvarez, V. Organic versus Conventional Management in an Apple Orchard: Effects of Fertilization and Tree-Row Management on Ground-Dwelling Predaceous Arthropods. Agric. For. Entomol. 2009, 11, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuovinen, T.; Kikas, A.; Tolonen, T.; Kivijärvi, P. Organic Mulches vs. Black Plastic in Organic Strawberry: Does It Make a Difference for Ground Beetles (Col., Carabidae)? J. Appl. Entomol. 2006, 130, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderland, K.D. The Diet of Some Predatory Arthropods in Cereal Crops. J. Appl. Ecol. 1975, 12, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Bi, Q.-F.; Xiang, Q.; Chen, Q.-L.; Christie, P.; Ke, X.; Wu, L.-H.; Zhu, Y.-G. Trophic Predator-Prey Relationships Promote Transport of Microplastics Compared with the Single Hypoaspis Aculeifer and Folsomia Candida. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orpet, R.J.; Goldberger, J.R.; Crowder, D.W.; Jones, V.P. Field Evidence and Grower Perceptions on the Roles of an Omnivore, European Earwig, in Apple Orchards. Biol. Control 2019, 132, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeu-Dalmau, C.; Piñol, J.; Espadaler, X. Friend or Foe? The Role of Earwigs in a Mediterranean Organic Citrus Orchard. Biol. Control 2012, 63, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, K.; de Sytske, W.; Helsen, H. Feeding Pattern during the Nesting Phase of the European Earwig Forficula Auricularia. Available online: https://edepot.wur.nl/400560 (accessed on 25 July 2020).
- Thompson, R.C.; Swan, S.H.; Moore, C.J.; Vom Saal, F.S. Our Plastic Age. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1973–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uribe-Hernández, R.; Juárez-Méndez, C.H.; De Montes Oca, M.A.; Palacios-Vargas, J.G.; Cutz-Pool, L.; Mejía-Recarmier, B.E. Collembola (Hexapoda) as Quality Bioindicators of the Hydrocarburans Polluted Soils in Southestern Mexico. Rev. Mex. Biodivers. 2010, 81, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, D.; Chen, Q.L.; An, X.L.; Yang, X.R.; Christie, P.; Ke, X.; Wu, L.H.; Zhu, Y.G. Exposure of Soil Collembolans to Microplastics Perturbs Their Gut Microbiota and Alters Their Isotopic Composition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 116, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.; Zhu, D.; Qiao, M. Effects of Polyethylene Microplastics on the Gut Microbial Community, Reproduction and Avoidance Behaviors of the Soil Springtail, Folsomia Candida. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| System | Characteristics | Glyphosate Application |
|---|---|---|
| AwPM (agriculture with plastic mulch) | AwPM1: Active cultivation of Cucurbita pepo pepo, using plastic mulch since 2016. Drip irrigation since November 2018, use of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) plastic film but no mulch during sampling. Use of fungicide (Benzimidazole, Boscalid, Carbendazim, Chlorothalonil, Pyraclostrobin), herbicide (Glyphosate) and insecticide (Imidacloprid). | Application by tractor in November 2018 (1.5 L 150 L−1 of water per hectare) and some sporadic applications (2–3 backpacks, each backpack = 200 cm3 20 L−1 of water per hectare) mainly on the periphery and patches of grass between bushes. |
| AwPM2: Freshly laid crop of Carica papaya, using mulch since 1998. Use of LDPE plastic film but no mulch during sampling. Use of acaricide (Abamectin, Etoxazole), fungicide (Thiophanate methyl, Boscalid, Carbendazim) and herbicide (Glyphosate). | Before planting papayas in 2016. Fumigation with 1 L 200 L−1 of water per hectare. | |
| AwoPM (agriculture without plastic mulch) | Both plots had dormant cultivation of Glycine max. Mennonite management. Use of herbicide (Glyphosate) and other unrecorded pesticides. | At the end of June and July, as well as in September 2018. Each spraying with 1 L 200 L−1 of water per hectare. |
| UF (Natural unmanaged farming) | UF1: Unmanaged secondary forest in regeneration since 1980. | No glyphosate application. |
| UF2: Vegetation not exploited since late 1970s within Archaeological Zone of Edzná. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Gutiérrez, E.; Rendón-von Osten, J.; Escalona-Segura, G.; Mendoza-Vega, J.; Dzul-Caamal, R.; Posthumus, S.; Vastenhouw, R.; Yang, X.; Geissen, V.; Huerta-Lwanga, E. Morphospecies Abundance of Above-Ground Invertebrates in Agricultural Systems under Glyphosate and Microplastics in South-Eastern Mexico. Environments 2021, 8, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110130
Hernández-Gutiérrez E, Rendón-von Osten J, Escalona-Segura G, Mendoza-Vega J, Dzul-Caamal R, Posthumus S, Vastenhouw R, Yang X, Geissen V, Huerta-Lwanga E. Morphospecies Abundance of Above-Ground Invertebrates in Agricultural Systems under Glyphosate and Microplastics in South-Eastern Mexico. Environments. 2021; 8(11):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110130
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Gutiérrez, Edilberto, Jaime Rendón-von Osten, Griselda Escalona-Segura, Jorge Mendoza-Vega, Ricardo Dzul-Caamal, Sita Posthumus, Rianne Vastenhouw, Xiaomei Yang, Violette Geissen, and Esperanza Huerta-Lwanga. 2021. "Morphospecies Abundance of Above-Ground Invertebrates in Agricultural Systems under Glyphosate and Microplastics in South-Eastern Mexico" Environments 8, no. 11: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110130
APA StyleHernández-Gutiérrez, E., Rendón-von Osten, J., Escalona-Segura, G., Mendoza-Vega, J., Dzul-Caamal, R., Posthumus, S., Vastenhouw, R., Yang, X., Geissen, V., & Huerta-Lwanga, E. (2021). Morphospecies Abundance of Above-Ground Invertebrates in Agricultural Systems under Glyphosate and Microplastics in South-Eastern Mexico. Environments, 8(11), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110130