Abstract
Reactive barriers, such as denitrifying bioreactors, have been identified as a clean-up option for nutrient-laden agriculture runoff. Here we tested a 20 m long, 3.75 m wide and 2.2 m deep woodchip bioreactor receiving tile drainage water from a 5.2 ha field site, aiming at testing the hydraulic functioning of a dual-inlet system and quantifying its impact on nutrient loads (nitrogen, reactive phosphorus, organic carbon) in a region with a drainage season taking place in the hydrological winter (November to April). The hydraulic conditions in the dual-inlet bioreactor system developed differently than expected; asymmetric flow rates led to long average hydraulic retention times and a highly dispersed residence time distribution, which was revealed by a bromide tracer test. With a nitrate load reduction of 51 to 90% over three drainage seasons, the woodchip bioreactor proved at the same time to be very effective under the winter conditions of northeastern Germany. The bioreactor turned from an orthophosphate source in the first year of operation into an orthophosphate sink in the second and third year, which was not expected because of anoxic conditions (favorable for denitrification) prevailing within the woodchips. Besides an efficient nutrient retention, the woodchip bioreactor contributed to the total organic carbon load of receiving waters, which impairs the overall positive role of bioreactors within intensively agriculturally used landscapes. We consider this promising low-maintenance biotechnology particularly suitable for single drainage pipes with high discharge and high nitrate concentrations.
1. Introduction
The nitrogen load of agricultural tile drainage water can contribute to eutrophication of surface waters, particularly in naturally nitrogen-limited aquatic ecosystems [1,2]. The tile drainage water represents an accelerated runoff component from agricultural fields, which can transport high amounts of nitrate (NO3−). The total export of nitrogen from field sites via the tile drainage pathway is a function of both the fertilization regime and the specific hydrological situation of a given year. More recently, it could be shown that discharge intensity overrides fertilization effects [3]. Even in years with little or no fertilizer application, nitrogen export rates might be high because of long-term nitrogen accumulation in the soil and high-volume fluxes. In order to overcome the dependence of nutrient export from agricultural land from the hydrological regime, constructed wetlands for the treatment of nitrate-laden tile drainage water have been proposed [4]. In case of limited available space, a denitrifying bioreactor, a rather technical variant, which falls into the category of reactive barriers, may be an option. It consists of an artificial ditch filled with organic substrates (e.g., woodchips) through which the drainage water is passed before it discharges to the surface water. The anoxic and carbon-enriched conditions in the bioreactor favor the occurrence of the microbially mediated denitrification converting nitrate to the non-hazardous dinitrogen gas (N2). Due to the environmentally problematic intermediate products nitrite (NO2−), nitric oxide (NO) and nitrous oxide (N2O), the completion of the denitrification process is an important factor for the bioreactor’s positive performance, which furthermore depends on its impact on other water quality-relevant substances. The main concern lies on phosphorus and (organic) carbon, for which increased concentrations have been observed in the outflow of bioreactors [5,6] and which can also lead to eutrophication and oxygen deficiency in surface waters. The nitrate removal efficiency depends on different factors such as hydraulic retention time (HRT), nitrate and dissolved oxygen (DO) load and temperature [7,8,9]. The HRT depends on the hydraulic performance of the bioreactor, which can be evaluated with the help of tracer tests [10,11]. The field study presented here aimed at testing the operability of a woodchip bioreactor under northeastern German climatic conditions where discharge is limited to the winter season. The specific objectives were to evaluate (i) the hydraulic performance and possible hydraulic anomalies due to two inlets and (ii) the integrative impact of the system on nutrient loads (nitrogen (N), reactive phosphorus (o-PO4-P), organic carbon (OC)) heading towards the surface water. Three years of operation provided the database that was analyzed to examine the objectives.
2. Materials and Methods
The woodchip bioreactor was installed at the edge of a systematically tile-drained field site (Figure 1a) at the brook “Saaler Bach” in Wiepkenhagen (Germany) in fall 2017. Two adjacent drainage pipes with a catchment of 2.9 ha (inlet 1) and 2.3 ha (inlet 2) were selected to load the facility with the help of diversion shafts (Figure 1c). The woodchip bioreactor was sized according to [12], envisaging an inflow of 12.5 m3 d−1 for each inlet (total inflow 25 m3 d−1) and a minimum theoretical (also termed “nominal”) hydraulic retention time tn of 0.5 days, which is defined as
with Vsat as the saturated bioreactor volume, n as the porosity of the woodchips (generally estimated to be 0.7 [13]) and Q as the flow rate in the bioreactor. The trapezoidal bioreactor, filled with woodchips with a particle size of the main fraction of 5.6 to 31.5 mm, has a length of 20 m, a depth of 2.20 m and a width at the bottom of 1.00 m and at the top on the level of the ground surface of 3.75 m (Figure 1b). The outlet is located in the middle of the bioreactor (Figure 1c) at a height of 0.6 m and ensures a minimum Vsat of 16.5 m3 and a minimum tn of ~0.5 days. During drainage season, the water level rises up to the level of the bypass pipes at a height of 1.8 m (≈40 cm below ground surface), which were installed to carry overflow caused by heavy rainfalls, resulting in a maximum Vsat of 76.5 m3. The water level in the system is measured manually every 1–2 weeks with an electric contact gauge, while the inflow at inlet 1 and the outflow are monitored continuously (15 min time interval) with an electromagnetic flow meter (WATERFLUX 3070 C). Two daily mixed water samples per week are taken by an automatic ISCO sampler (ISCO 6712 portable sampler, Teledyne ISCO, Lincoln, CA, USA) at inlet 1 and the outlet and analyzed after 0.45 µm filtration for NO3− and NO2− with ion chromatography. The nitrate removal efficiency NRE (%) for a complete drainage season and the daily nitrate removal rate NRR (g m−3 d−1) were calculated from the NO3−-N loads in the inflow (NO3Nin) and outflow (NO3Nout):
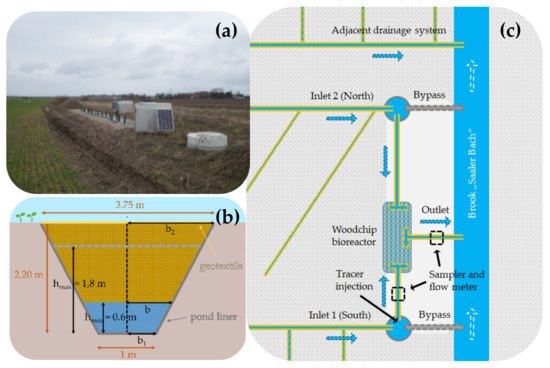
Figure 1.
(a) Photo of the woodchip bioreactor in March 2019 with the diversion shaft of inlet 1 in the front. (b) Trapezoidal cross section of the woodchip bioreactor. The saturated volume Vsat for a certain water level h can be calculated using the parameter b, which can be derived from linear interpolation between b2 and b1. (c) Schematic site overview of the woodchip bioreactor and the connected subsurface drainage system (drainage pipes ~1.6 m below ground surface). Blue arrows indicate envisaged direction of water flow.
Further water quality parameters are monitored weekly, such as total organic carbon (TOC), total bound nitrogen (TNb), i.e., all organic and inorganic nitrogen compounds except N2, and orthophosphate (PO43−), with a TOC/TNb-analyzer and a photometer. Organically bound nitrogen (Norg) is determined as the difference between TNb and (NO3−-N + NO2−-N), since ammonium (NH4+) concentrations turned out to be negligible in the system. Furthermore, on-site air temperature, as well as water temperature and redox potential at the bottom of the woodchip bioreactor, is constantly monitored (15 min time interval). Redox potential values are corrected to the standard hydrogen potential E0.
To get a deeper insight into the hydraulics of the system and the residence time of NO3−, a tracer test with potassium bromide (KBr) was carried out in the drainage season 2019/2020 during quasi-stationary low-flow conditions (Q ≈ 4.5 m3 d−1). For this purpose, 1121 g KBr (=750 g Br−) was dissolved in 5 L water and poured in inlet 1 of the woodchip bioreactor (Figure 1c). At the outlet, water samples were collected every 4 h for days 1–4, every 6 h for days 5–9, every 12 h for days 10–14 and every 24–72 h for days 15–40 and analyzed for Br− with ion chromatography to monitor the complete residence time distribution (RTD). The measured concentrations were reduced by the natural Br− background concentration of 0.305 mg L−1. With the help of the mean tracer residence time tmean (d), the accuracy of the previously calculated tn can be verified [10]:
with Ci as the Br−-concentration in the i-th sample, ∆ti as the respective sampling interval and ti as the appearance time. If the complete saturated bioreactor volume is hydraulically active (no stagnant zones) and no retardation of bromide occurs, tmean should be equal to tn [11]. The water level during the tracer test was ~1.55 m, resulting in a Vsat of 61 m3 for the complete bioreactor. Since the tracer was injected in inlet 1 and the outlet is located in the middle of the bioreactor, approximately half of the bioreactor (30.5 m3) was expected to be hydraulically involved in the tracer transport. Several parameters have been proposed to evaluate the hydraulic performance of the bioreactor such as the hydraulic efficiency λ, the short-circuiting indicator S and the Morrill Dispersion Index MDI [10]:
with tp as the peak appearance time (d) and t10, t16, t50 and t90 as the appearance time (d) of 10, 16, 50 and 90% of the cumulative tracer mass. Generally, hydraulic conditions similar to plug-flow (i.e., without considerable preferential flow or dispersion) are considered well-suited for the functioning of the bioreactor. Thus, parameter values of λ > 0.75, S ≈ 1 and MDI < 2 are classified as ideal [10,11].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydraulic Conditions in the Woodchip Bioreactor
Out of the three monitored drainage seasons, the seasons 2017/2018 and 2019/2020 are considered typical with generated run-off from November to April, while the drainage season 2018/2019 with run-off from February to April represents a special case due to the extreme dryness in the year 2018 (Figure 2). The hydraulic conditions in the woodchip bioreactor differed from the envisaged flow conditions, i.e., symmetric inflow from two sides to the outlet in the middle of the bioreactor. The inlet 2 did not contribute to the flow rate due to an unknown hydraulic connection to the neighboring drainage system, which was not visible on the available drainage system map. This led to the discharge of the run-off of inlet 2 towards the neighboring drainage system, where thus more drainage water was discharged than previously observed. The outflow at the outlet consisted almost exclusively of inflow via inlet 1, which facilitated the calculation of the nitrate balance of system but led ultimately to an oversizing of the bioreactor. To make sure a woodchip bioreactor works hydraulically as planned, it is recommended to choose a single inlet with high inflow and high nitrate concentrations to load the bioreactor. If multiple inlets are envisaged, the distance to the neighboring drainage pipe should be as high as possible to reduce the risk of an unknown subsurface hydraulic connection. The woodchip bioreactor causes back pressure in the drainage system, which can lead to changes in the flow pattern. Furthermore, control elements such as gate valves on critical spots could be included to allow subsequent and easy adjustments to the hydraulic system.
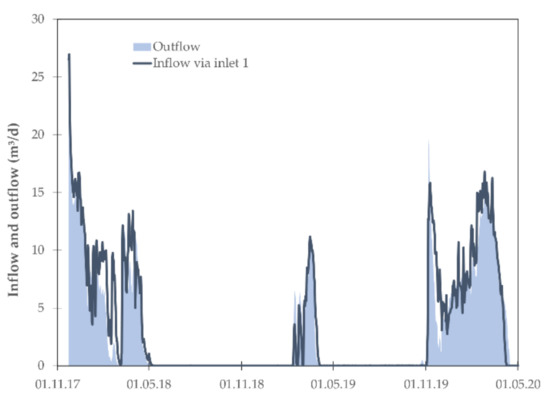
Figure 2.
Inflow and outflow of the woodchip bioreactor for the drainage seasons 2017 to 2020. For the inflow, only the southern inlet 1 (see Figure 1c) was monitored.
The RTD (Figure 3) of the tracer test resulted in a tmean of 6.75 days, indicating that more volume of the bioreactor was involved in the tracer flow from inlet 1 than expected, since an active flow volume of half of the bioreactor would have led to a tn of 4.75 days. Here, we assumed tn = tmean resulting in a saturated volume of 43.4 m3 corresponding to 71% of the saturated bioreactor volume, which was, in turn, used as best estimate for the normalization of the RTD (Figure 3) and tn calculation (Table 1), accepting inaccuracies regarding the effective porosity of the woodchips. The tracer recovery at the outlet was 61%, which is low even for a field study and suggests, to some degree, an interference of the northern inlet and the connected drainage system with the tracer test.
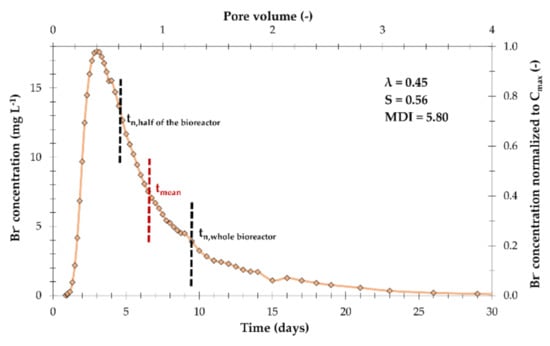
Figure 3.
Residence time distribution (RTD) and hydraulic performance parameters determined by 2019. For the calculation of pore volume, 71% of the saturated bioreactor volume was taken into account. The Br− concentrations were normalized to the maximum measured concentration (17.65 mg L−1).

Table 1.
Average (upper section) and sum (lower section) parameters of the woodchip bioreactor for drainage seasons 2017 to 2020 (~November till April).
Under the monitored low-flow conditions, the minimum residence time for Br− (thus, for NO3−) was ~24 h, which is even longer than the commonly recommended tn for sizing a woodchip bioreactor [12]. The latest increased bromide concentrations in the outlet were observed after ~30 days, which shows that the residence time of NO3− can vary enormously. The shape of the RTD is very similar to previous tracer studies [10,11] with a steep increase at the beginning, a subsequent peak at ~0.5 PV and a less steep decrease with tailing. The wide range of the RTD clearly shows that the bioreactor did not act as a plug-flow reactor (MDI >> 2). As stated for constructed wetlands by [14], a woodchip bioreactor will never show ideal plug-flow because the pore network of the woodchip will always cause a considerable hydrodynamic dispersion of the solute front, as can be observed in soils [15]. The plug-flow oriented target range of the performance parameters was derived for reactor types such as disinfection or sedimentation beds [16], which do not have sediment filling and require the absolute fulfilment of tn to function properly. It does not seem realistic to apply the same standards to a woodchip bioreactor and thus a poor hydraulic performance may not necessarily imply a poor nitrate removal performance. For the evaluation of the hydraulic performance, the parameters, which purely target at preferential flow (e.g., S or λ), should be preferred compared to parameters, which also target at dispersion (e.g., MDI). In this case, the resulting S-value of 0.56 indicates moderate short-circuiting in the third drainage season; it is likely that some pore water regions in the woodchips are more mobile than others (caused for example by local compaction or bio-clogging) and this might also change further over time as the woodchips are being decomposed, which in turn leads to a change of the pore network and the saturated hydraulic conductivity [17]. In this particular case, the minimum residence time due to short-circuiting was still sufficiently long for the nitrate removal, but for bioreactors with shorter tn, the replacement of the woodchips after several years might be more necessary due to hydraulic malfunctions than due to carbon-supply limitations [17].
3.2. Impact of the Woodchip Bioreactor on Nutrient Loads (N, o-PO4-P, OC)
With values from 51 to 90% (Table 1), the nitrate removal efficiency of the woodchip bioreactor was very high despite average water temperatures only slightly higher than the minimum of ~2 °C and far from the optimum (25–35 °C) for denitrification [9]. This finding is consistent with previous studies that woodchip bioreactors still remove some nitrate at low temperatures [18,19]. Lower average air temperatures show that temperature amplitudes were mitigated in the bioreactor due to an insulation effect caused by the depth of the bioreactor and the covering geotextile, so that temporary sub-zero air temperatures did not bring nitrate removal to a standstill. Extra heat might also be generated by the anaerobic decomposition processes as it was observed in systems such as waste landfills [20]. The positive average redox potential at inlet 1 indicates the continuous inflow of high energy-providing electron acceptors, such as O2 and NO3−, and is in the redox range, in which denitrification generally occurs (~+231 mV [9]). The negative average redox potential at inlet 2 is clearly below the redox range of denitrification and reflects the inlet’s hydraulic malfunctioning, i.e., no inflow of nitrate-laden drainage water.
It is likely that the high average HRT (tn ≥ 3.1 days) compensated the effect of low temperatures on the nitrate removal efficiency. The average NRRs (0.75–2.31 g m−3 d−1) are in the lower range of previously observed removal rates [5,7], because the NRR is normalized to Vsat (see Equation (3)), which in this case was sized for a higher flow rate than ultimately achieved. Yet no statement about the temporal development of the nitrate removal rate is possible, since the lower NRR in 2019/2020 is related to lower NO3− concentrations in the inflow (Table 1). The high HRT did not prevent the release of NO2− in the first drainage season, which indicates an incomplete denitrification. In the first month of operation, NO2−-N concentrations up to 10.8 mg L−1 were observed in the outflow and dropped afterwards to <0.005 mg L−1; in the following drainage seasons NO2−-N concentrations were also increased in the first month, but never exceeded 0.6 mg L−1 and were of minor importance for the overall N balance (see Figure 4b for drainage season 2019/2020). This coincides with remaining NO3−-N concentrations in the outflow in the first month, which did not reoccur during the rest of the drainage season. It seems that in this initial stage with high inflow and high NO3−-N concentrations (Figure 4a), denitrification was incomplete. During the remaining months, the denitrification was complete and only Norg was released from the woodchip bioreactor. However, compared to TOC, the release potential of the bioreactor for Norg is low due to the high C/N ratio (>200 [17]) of the woodchips. In the drainage season 2019/2020, the Norg-load in the outflow was only increased by 4% compared to the inflow, while for TOC an increase of 45.6% was observed.
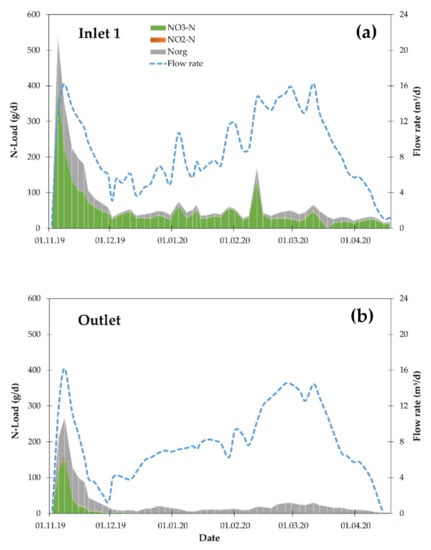
Figure 4.
N-Loads in the (a) inflow at inlet 1 and (b) outflow of the woodchip bioreactor in the drainage season 2019/2020. White vertical lines illustrate the sampling interval.
The decomposition of the woodchips leads to the release of organic and inorganic decomposition products [5,6]. During the first drainage season after installation of the woodchip bioreactor TOC and PO43− emissions were very high, but in case of TOC the release was lessened in the following drainage seasons (Table 1). A possible reason is the decrease in easily and quickly degradable organic compounds within the woodchip matrix. For the PO43− the concentrations were considerably increased (up to 4 mg L−1 compared to up to a maximum of 0.28 mg L−1 in the inflow) right after putting the bioreactor into service, but afterwards the woodchip bioreactor acted as a sink for PO43−—possibly due to consumption of PO43− by microorganisms [9]. The substance release in following drainage seasons is expected to be similar to drainage season 2019/2020 (Figure 5), which would corroborate the overall positive environmental effect of the system and support the suggestion by [21] to use weathered woodchips as filling material to prevent the strong substance release in the first drainage season.
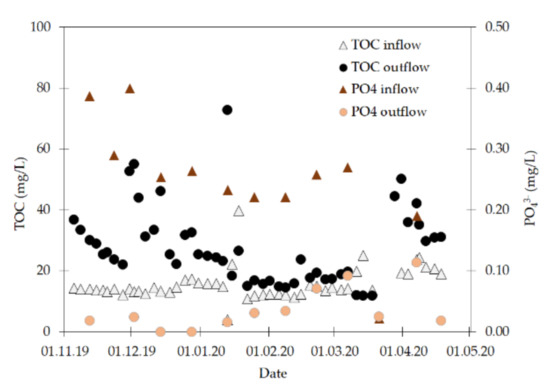
Figure 5.
Total organic carbon (TOC) and orthophosphate (PO43−) concentrations in the inflow and outflow of the woodchip bioreactor in drainage season 2019/2020.
4. Conclusions
In this study, a high nitrate removal efficiency was obtained with a woodchip bioreactor for agricultural drainage water in northeastern Germany indicating the usability of this measure type in regions with drainage seasons in the hydrologic wintertime. Although temperatures did range near the minimum temperature required for denitrification, it seems that a longer hydraulic retention time can compensate low temperature effects. Hydraulic retention times were longer than envisaged due to a hydraulic malfunction of the second inlet, which is why more precaution needs to be taken regarding subsurface flow conditions in the drainage pipe system for multiple-inlet bioreactors than in the case of a single-inlet bioreactor. The residence time distribution resulting from a tracer test showed a dispersed shape with a minimum residence time still sufficient for a complete nitrate removal, although short-circuiting parameters indicate moderate preferential flow in the 3-year-old woodchips. Negative environmental impact due to nitrite (NO2−), total organic carbon (TOC) and orthophosphate (PO43−) release was observed in the first month after installation of the woodchip bioreactor. In the following drainage seasons, the bioreactor turned into a sink for orthophosphate and the TOC and nitrite release faded.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.L. and L.G.; field work, L.G.; formal analysis, L.G.; writing—original draft preparation, L.G.; writing—review and editing, L.G., H.L. and B.L.; funding acquisition, B.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was conducted within the agricultural European Innovation Partnership (EIP-Agri) project “Drainfit” funded by the development program for the rural area of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania 2014–2020 with the support of the European Union and the State of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, represented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Environment. We acknowledge financial support for the article processing charge (APC) by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and University of Rostock within the funding programme Open Access Publishing.
Acknowledgments
We thank the LMS Agrarberatung GmbH for the project coordination and the good collaboration during the implementation of the woodchip bioreactor. We also thank J. Tatzelt for supervising and sampling in the initial stage of the bioreactor and the LUFA Rostock for water sample analysis. Furthermore, we thank the agricultural enterprise Müller for providing the farmland in Wiepkenhagen as study site.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Carpenter, S.R.; Caraco, N.F.; Correll, D.L.; Howarth, R.W.; Sharpley, A.N.; Smith, V.H. Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, R.W.; Sharpley, A.; Walker, D. Sources of nutrient pollution to coastal waters in the United States: Implications for achieving coastal water quality goals. Estuaries 2002, 25, 656–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauwe, A.; Kahle, P.; Tiemeyer, B.; Lennartz, B. Hydrology is the key factor for nitrogen export from tile-drained catchments under consistent land-management. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacic, D.A.; David, M.B.; Gentry, L.E.; Starks, K.M.; Cooke, R.A. Effectiveness of Constructed Wetlands in Reducing Nitrogen and Phosphorus Export from Agricultural Tile Drainage. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 1262–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.B.; Gentry, L.E.; Cooke, R.A.; Herbstritt, S.M. Temperature and Substrate Control Woodchip Bioreactor Performance in Reducing Tile Nitrate Loads in East-Central Illinois. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoover, N.L.; Bhandari, A.; Soupir, M.L.; Moorman, T.B. Woodchip Denitrification Bioreactors: Impact of Temperature and Hydraulic Retention Time on Nitrate Removal. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christianson, L.E.; Bhandari, A.; Helmers, M.J.; Kult, K.J.; Sutphin, T. Performance Evaluation of Four Field-Scale Agricultural Drainage Denitrification Bioreactors in Iowa. Trans. Asabe 2012, 55, 2163–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleimeier, C.; Liu, H.; Rezanezhad, F.; Lennartz, B. Nitrate Attenuation in Degraded Peat Soil-Based Constructed Wetlands. Water 2018, 10, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivett, M.O.; Buss, S.R.; Morgan, P.; Smith, J.W.N.; Bemment, C.D. Nitrate attenuation in groundwater: A review of biogeochemical controlling processes. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4215–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christianson, L.; Helmers, M.; Bhandari, A.; Moorman, T. Internal hydraulics of an agricultural drainage denitrification bioreactor. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 52, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghane, E.; Feyereisen, G.W.; Rosen, C.J. Efficacy of bromide tracers for evaluating the hydraulics of denitrification beds treating agricultural drainage water. J. Hydrol. 2019, 574, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, L.; Christianson, R.; Helmers, M.; Pederson, C.; Bhandari, A. Modeling and Calibration of Drainage Denitrification Bioreactor Design Criteria. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2013, 139, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, L.; Castelló, A.; Christianson, R.; Helmers, M.; Bhandari, A. Technical Note: Hydraulic Property Determination of Denitrifying Bioreactor Fill Media. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2010, 26, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headley, T.R.; Kadlec, R.H. Conducting hydraulic tracer studies of constructed wetlands: A practical guide. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2007, 7, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillel, D. Environmental Soil Physics; AP Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998; ISBN 9780123485250. [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf and Eddy Inc. Wastewater Engineering. Treatment and Resource Recovery, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2014; ISBN 9781259010798. [Google Scholar]
- Christianson, L.; Feyereisen, G.W.; Hay, C.; Tschirner, U.W.; Kult, K.; Wickramarathne, N.M.; Hoover, N.; Soupir, M.L. Denitrifying Bioreactor Woodchip Recharge: Media Properties after Nine Years. Trans. ASABE 2020, 63, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welander, U.; Mattiasson, B. Denitrification at low temperatures using a suspended carrier biofilm process. Water Res. 2003, 37, 2394–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyereisen, G.W.; Moorman, T.B.; Christianson, L.E.; Venterea, R.T.; Coulter, J.A.; Tschirner, U.W. Performance of Agricultural Residue Media in Laboratory Denitrifying Bioreactors at Low Temperatures. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Z.; Sun, M.; Ducoste, J.J.; Benson, C.H.; Luettich, S.; Castaldi, M.J.; Barlaz, M.A. Heat Generation and Accumulation in Municipal Solid Waste Landfills. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12434–12442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soupir, M.L.; Hoover, N.L.; Moorman, T.B.; Law, J.Y.; Bearson, B.L. Impact of temperature and hydraulic retention time on pathogen and nutrient removal in woodchip bioreactors. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 112, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).