Developments in Molecular Level Characterization of Naphthenic Acid Fraction Compounds Degradation in a Constructed Wetland Treatment System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Oil Sand Process-Affected Waters
2.2. Constructed Wetland Treatment Systems
2.3. Sample Preparation and Extraction
2.4. Analysis of NAFCs
2.5. PCA, Kendrick Plot, and van Krevelen Plot Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
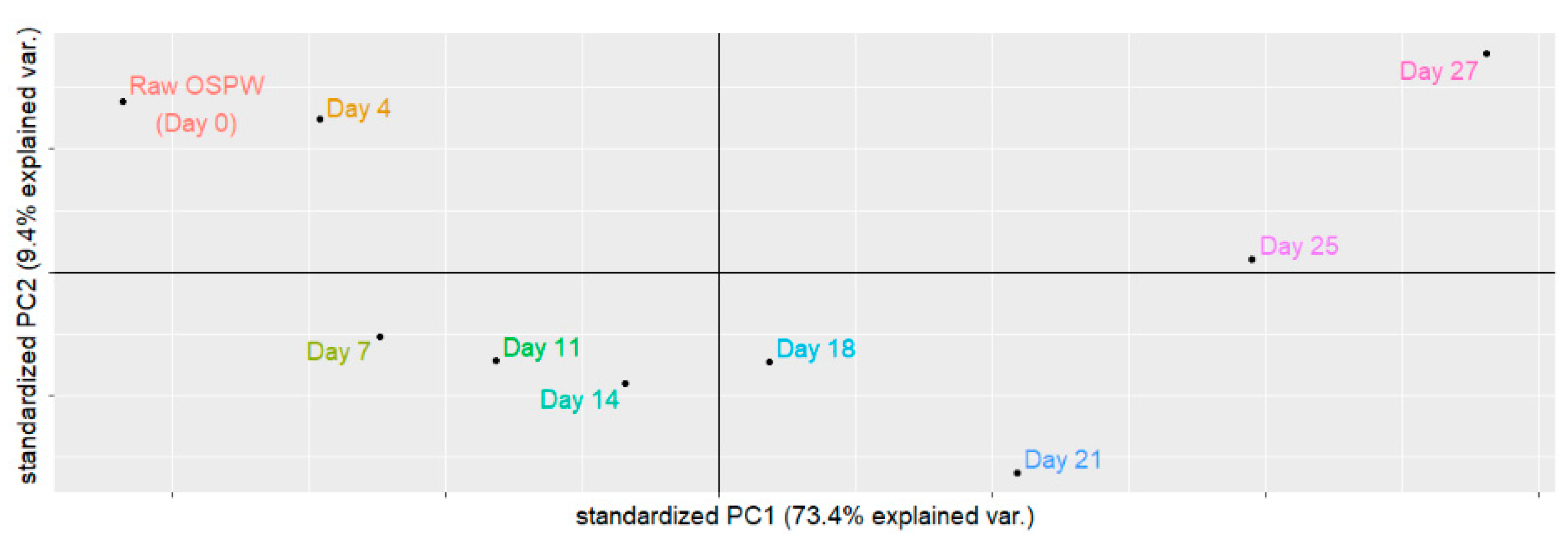
3.1. Principal Component Analysis
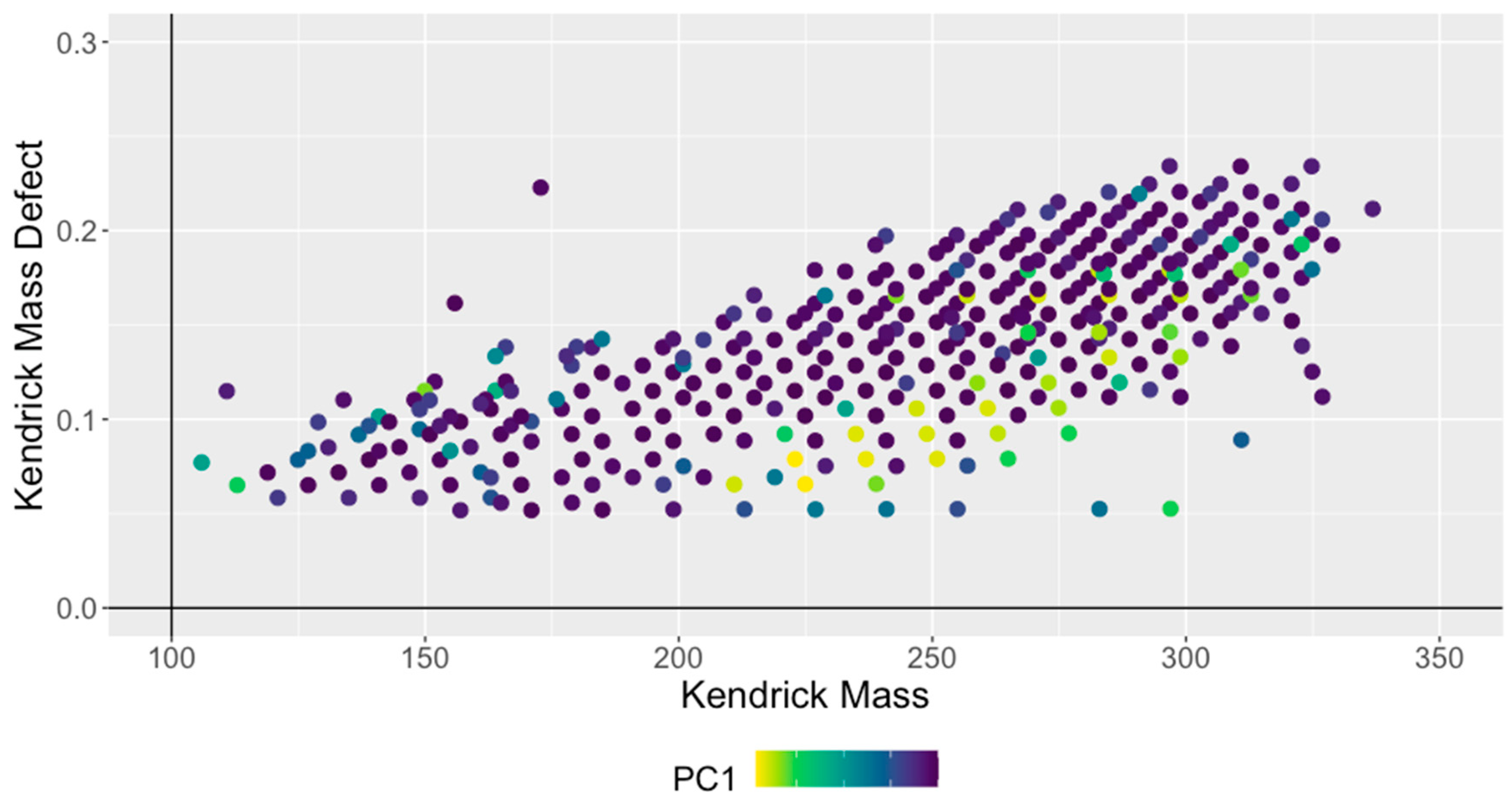
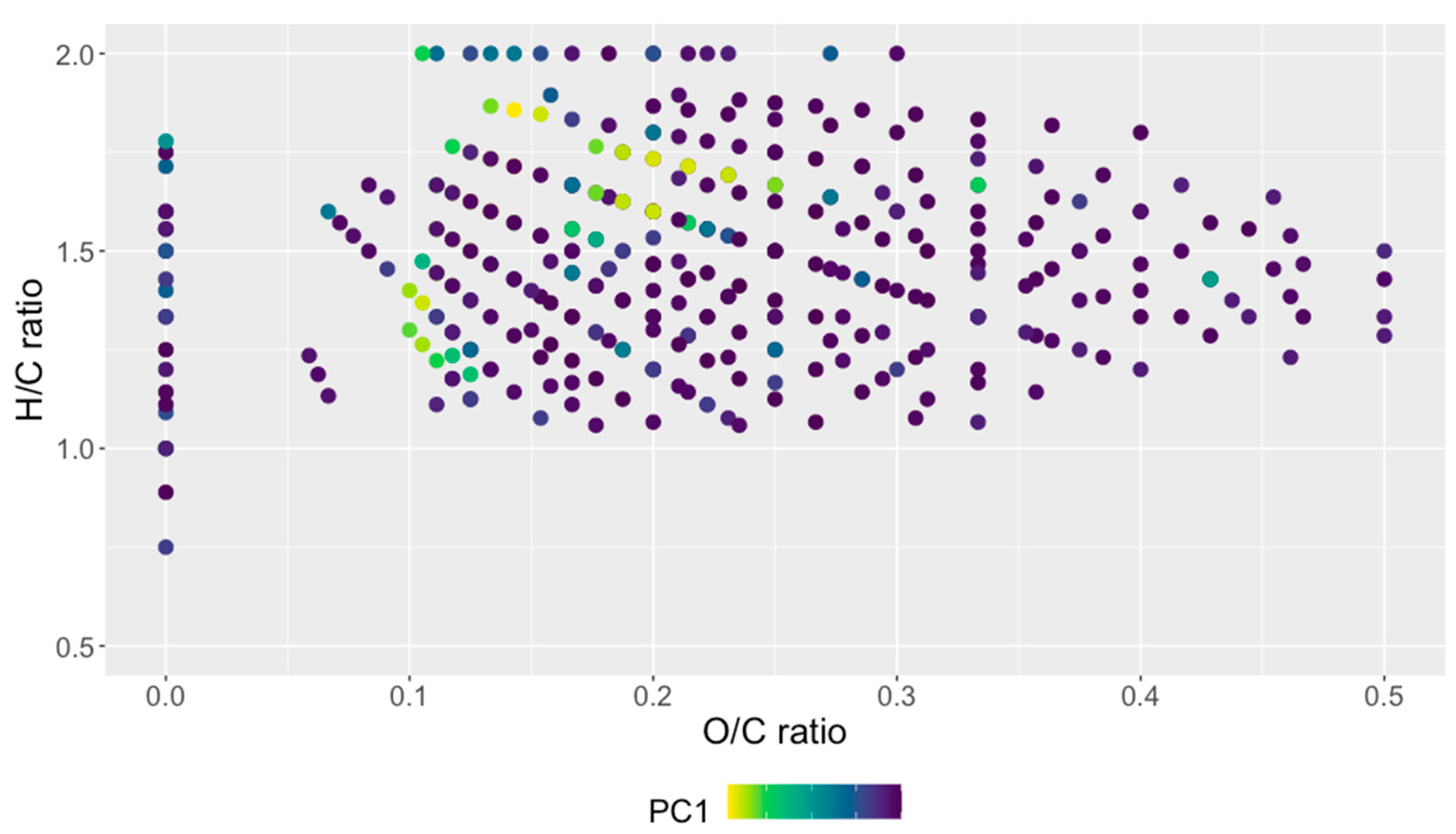
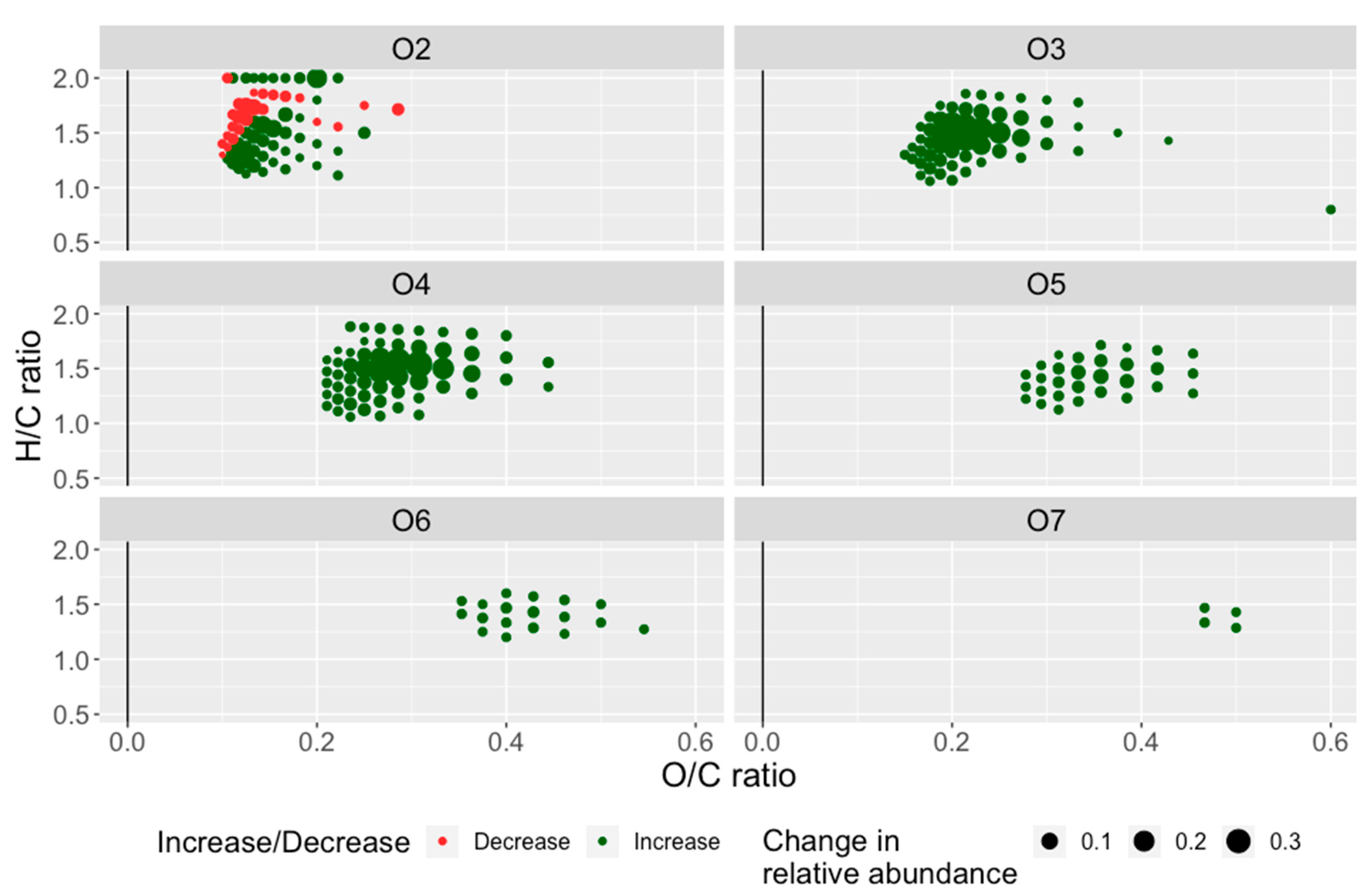
3.2. Interpretation of Kendrick and van Krevelen Plots
3.3. Heteroatom Class Distribution
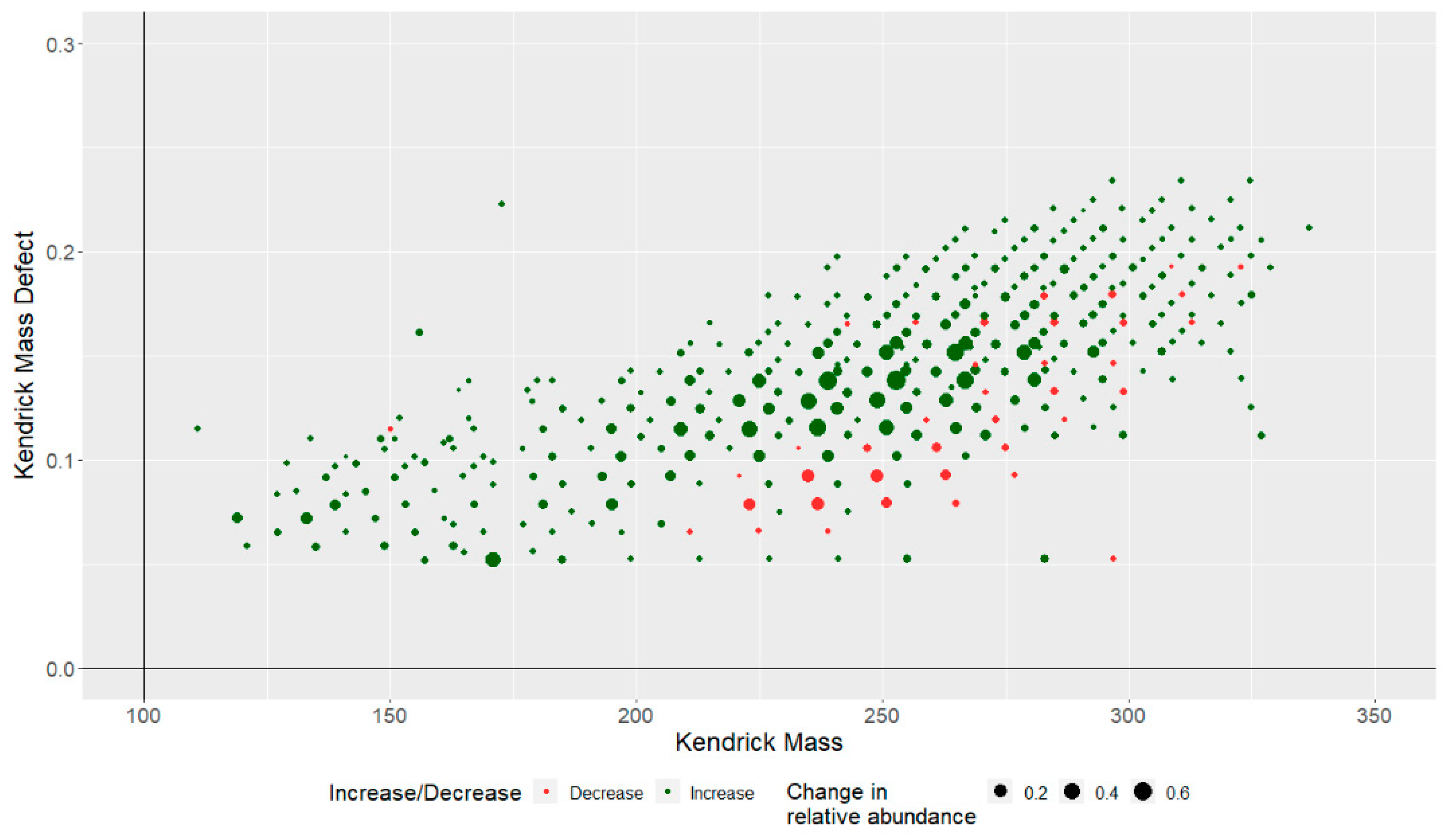
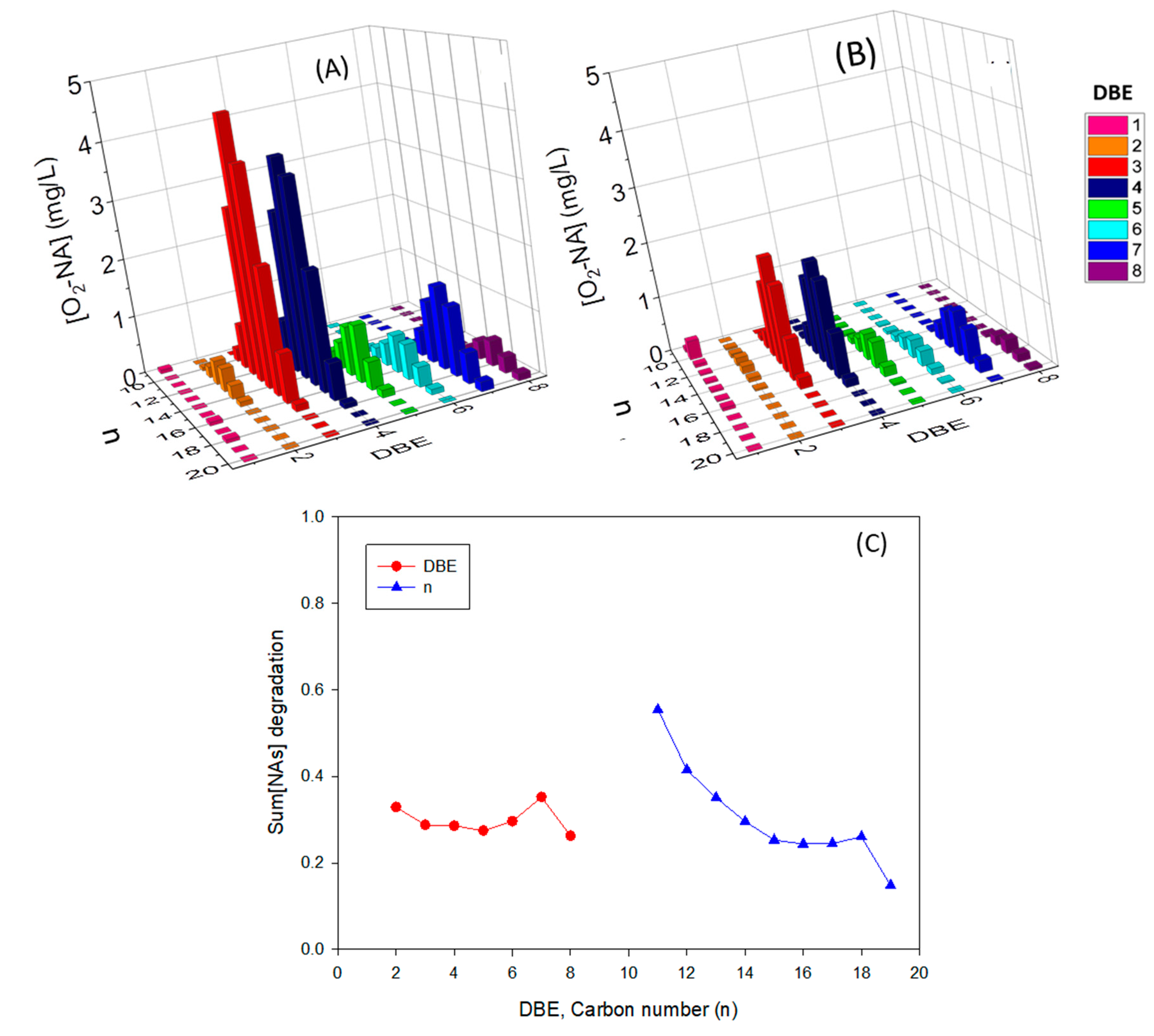
3.4. Degradation of Individual NA Species
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pramanik, S. Review of biological processes in oil sands: A feasible solution for tailings water treatment. Environ. Rev. 2016, 24, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalrhman, A.S.; Zhang, Y.; Arslan, M.; Gamal El-Din, M. Low-current electro-oxidation enhanced the biodegradation of the recalcitrant naphthenic acids in oil sands process water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madison, B.N.; Reynolds, J.; Halliwell, L.; Leshuk, T.; Gu, F.; Peru, K.M.; Headley, J.V.; Orihel, D.M. Can the toxicity of naphthenic acids in oil sands process-affected water be mitigated by a green photocatalytic method? FACETS 2020, 5, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marentette, J.R.; Sarty, K.; Cowie, A.M.; Frank, R.A.; Hewitt, L.M.; Parrott, J.L.; Martyniuk, C.J. Molecular responses of Walleye (Sander vitreus) embryos to naphthenic acid fraction components extracted from fresh oil sands process-affected water. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 182, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Villagomez, J.M.; Vázquez-Martínez, J.; Ramírez-Chávez, E.; Molina-Torres, J.; Trudeau, V.L. Profiling low molecular weight organic compounds from naphthenic acids, acid extractable organic mixtures, and oil sands process-affected water by SPME-GC-EIMS. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiseman, S.B.; Anderson, J.C.; Liber, K.; Giesy, J.P. Endocrine disruption and oxidative stress in larvae of Chironomus dilutus following short-term exposure to fresh or aged oil sands process-affected water. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 142, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaluddin, M.; Zwiazek, J.J. Naphthenic acids inhibit root water transport, gas exchange and leaf growth in aspen (Populus tremuloides) seedlings. Tree Physiol. 2002, 22, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, S.A.; Headley, J.V.; Peru, K.M.; Germida, J.J. Phytotoxicity of oil sands naphthenic acids and dissipation from systems planted with emergent aquatic macrophytes. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2008, 43, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaffey, A.; Dubé, M. Review of the composition and toxicity of oil sands process-affected water. Environ. Rev. 2017, 25, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headley, J.v.; Barrow, M.P.; Peru, K.M.; Fahlman, B.; Frank, R.A.; Bickerton, G.; McMaster, M.E.; Parrott, J.; Hewitt, L.M. Preliminary fingerprinting of Athabasca oil sands polar organics in environmental samples using electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 1899–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewer, D.M.; Young, R.F.; Whittal, R.M.; Fedorak, P.M. Naphthenic acids and other acid-extractables in water samples from Alberta: What is being measured? Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5997–6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Headley, J.V.; Peru, K.M.; Mohamed, M.H.; Frank, R.A.; Martin, J.W.; Hazewinkel, R.R.O.; Humphries, D.; Gurprasad, N.P.; Hewitt, L.M.; Muir, D.C.G.; et al. Chemical fingerprinting of naphthenic acids and oil sands process waters-A review of analytical methods for environmental samples. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2013, 48, 1145–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyakas, A.; Han, J.; Peru, K.M.; Headley, J.V.; Borchers, C.H. Comprehensive analysis of oil sands processed water by direct-infusion fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry with and without offline UHPLC sample prefractionation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4471–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Fu, L.; Stafford, J.; Belosevic, M.; Gamal El-Din, M. The toxicity of oil sands process-affected water (OSPW): A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 1785–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Patterson, J.; Arslan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Gamal El-Din, M. Biofiltration of oil sands process water in fixed-bed biofilm reactors shapes microbial community structure for enhanced degradation of naphthenic acids. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshref, M.N.A.; Ibrahim, M.D.; Huang, R.; Yang, L.; How, Z.T.; Klamerth, N.; Chelme-Ayala, P.; Hughes, S.A.; Brown, C.; Mahaffey, A.; et al. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy as a surrogate tool for the quantification of naphthenic acids in oil sands process water and groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, J.H.; Castle, J.W. Constructed wetland systems for efficient and effective treatment of contaminated waters for reuse. Environ. Geosci. 2008, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haakensen, M. Key Aspects for Successful Design and Implementation of Passive Water Treatment Systems. J. Environ. Solut. Oilgasand Min. 2015, 1, 59–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foote, L. Threshold considerations and wetland reclamation in Alberta’s mineable oil sands. Ecol. Soc. 2012, 17, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQueen, A.D.; Hendrikse, M.; Gaspari, D.P.; Kinley, C.M.; Rodgers, J.H.; Castle, J.W. Performance of a hybrid pilot-scale constructed wetland system for treating oil sands process-affected water from the Athabasca oil sands. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrikse, M.; Gaspari, D.P.; McQueen, A.D.; Kinley, C.M.; Calomeni, A.J.; Geer, T.D.; Simair, M.C.; Peru, K.M.; Headley, J.V.; Rodgers, J.H.; et al. Treatment of oil sands process-affected waters using a pilot-scale hybrid constructed wetland. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 115, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiti, T.M.; Tezel, U.; Pavlostathis, S.G. Effect of alkyl side chain location and cyclicity on the aerobic biotransformation of naphthenic acids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7909–7917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, D.T.; Warren, L.A.; McCarry, B.E.; Slater, G.F. Profiling of individual naphthenic acids at a composite tailings reclamation fen by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toor, N.S.; Franz, E.D.; Fedorak, P.M.; MacKinnon, M.D.; Liber, K. Degradation and aquatic toxicity of naphthenic acids in oil sands process-affected waters using simulated wetlands. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, N.S.; Han, X.; Franz, E.; Mackinnon, M.D.; Martin, J.W.; Liber, K. Selective biodegradation of naphthenic acids and a probable link between mixture profiles and aquatic toxicity. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 2207–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, H.A.; Morandi, G.D.; Jones, P.D.; Wiseman, S.B.; Giesy, J.P. Comparison of the Effects of Extraction Techniques on Mass Spectrometry Profiles of Dissolved Organic Compounds in Oil Sand Process-Affected Water. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 7001–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headley, J.V.; Peru, K.M.; Barrow, M.P. Advances in mass spectrometric characterization of naphthenic acids fraction compounds in oil sands environmental samples and crude oil-A review. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2016, 35, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Chen, Y.; Gamal El-Din, M. Silver-Ion Solid Phase Extraction Separation of Classical, Aromatic, Oxidized, and Heteroatomic Naphthenic Acids from Oil Sands Process-Affected Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6433–6441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headley, J.V.; Peru, K.M.; Janfada, A.; Fahlman, B.; Gu, C.; Hassan, S. Characterization of oil sands acids in plant tissue using Orbitrap ultra-high resolution mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanipour, S.; Hooshyari, M.; Baz-Lomba, J.A.; Reid, M.J.; Casale, M.; Thomas, K.V. The effect of extraction methodology on the recovery and distribution of naphthenic acids of oilfield produced water. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 1416–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Lillico, D.; How, Z.T.; Huang, R.; Belosevic, M.; Stafford, J.; Gamal El-Din, M. Separation of oil sands process water organics and inorganics and examination of their acute toxicity using standard in-vitro bioassays. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bataineh, M.; Scott, A.C.; Fedorak, P.M.; Martin, J.W. Capillary HPLC/QTOF-MS for characterizing complex naphthenic acid mixtures and their microbial transformation. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 8354–8361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagné, F.; André, C.; Turcotte, P.; Gagnon, C.; Sherry, J.; Talbot, A. A comparative toxicogenomic investigation of oil sand water and processed water in rainbow trout hepatocytes. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 65, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, H.A.; Saunders, D.M.V.; Al-Mousa, A.; Alcorn, J.; Pereira, A.S.; Martin, J.W.; Giesy, J.P.; Wiseman, S.B. Inhibition of ABC transport proteins by oil sands process affected water. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 170, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajaero, C.; McMartin, D.W.; Peru, K.M.; Bailey, J.; Haakensen, M.; Friesen, V.; Martz, R.; Hughes, S.A.; Brown, C.; Chen, H.; et al. Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry Characterization of Athabasca Oil Sand Process-Affected Waters Incubated in the Presence of Wetland Plants. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajaero, C.; Peru, K.M.; Simair, M.; Friesen, V.; O’Sullivan, G.; Hughes, S.A.; McMartin, D.W.; Headley, J.V. Fate and behavior of oil sands naphthenic acids in a pilot-scale treatment wetland as characterized by negative-ion electrospray ionization Orbitrap mass spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simair, M.C.; Parrott, J.L.; Le Roux, M.; Gupta, V.; Frank, R.A.; Peru, K.M.; Ajaero, C.; McMartin, D.W.; Headley, J.V. Treatment of oil sands process affected waters by constructed wetlands: Evaluation of designs and plant types by multiple lines of evidence. (under review).
- McQueen, A.D.; Kinley, C.M.; Hendrikse, M.; Gaspari, D.P.; Calomeni, A.J.; Iwinski, K.J.; Castle, J.W.; Haakensen, M.C.; Peru, K.M.; Headley, J.V.; et al. A risk-based approach for identifying constituents of concern in oil sands process-affected water from the Athabasca Oil Sands region. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beebe, D.A.; Castle, J.W.; Molz, F.J.; Rodgers, J.H. Effects of evapotranspiration on treatment performance in constructed wetlands: Experimental studies and modeling. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 71, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.H.; Wilson, L.D.; Shah, J.R.; Bailey, J.; Peru, K.M.; Headley, J.V. A novel solid-state fractionation of naphthenic acid fraction components from oil sands process-affected water. Chemosphere 2015, 136, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, V.G. Book review: Gplot2-Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis (2nd Edition). J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 77, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vince, Q.V. Software. Available online: http://www.vince.vu/software/ (accessed on 3 August 2020).
- R: The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 3 August 2020).
- Demeter, M.A.; Lemire, J.A.; Yue, G.; Ceri, H.; Turner, R.J. Culturing oil sands microbes as mixed species communities enhances ex situ model naphthenic acid degradation. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, J.T.; Toran, L.; Edlund, A.; Metcalf, J.L.; Lauber, C.; Knight, R. Uncovering the Horseshoe Effect in Microbial Analyses. mSystems 2017, 2, e00166-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughey, C.A.; Hendrickson, C.L.; Rodgers, R.P.; Marshall, A.G.; Qian, K. Kendrick mass defect spectrum: A compact visual analysis for ultrahigh-resolution broadband mass spectra. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 4676–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Chen, Y.; Meshref, M.N.A.; Chelme-Ayala, P.; Dong, S.; Ibrahim, M.D.; Wang, C.; Klamerth, N.; Hughes, S.A.; Headley, J.V.; et al. Characterization and determination of naphthenic acids species in oil sands process-affected water and groundwater from oil sands development area of Alberta, Canada. Water Res. 2018, 128, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; MacKinnon, M.D.; Martin, J.W. Estimating the in situ biodegradation of naphthenic acids in oil sands process waters by HPLC/HRMS. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Scott, A.C.; Fedorak, P.M.; Bataineh, M.; Martin, J.W. Influence of molecular structure on the biodegradability of naphthenic acids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 1290–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahad, J.M.E.; Pakdel, H.; Savard, M.M.; Calderhead, A.I.; Gammon, P.R.; Rivera, A.; Peru, K.M.; Headley, J.V. Characterization and quantification of mining-related “naphthenic acids” in groundwater near a major oil sands tailings pond. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5023–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, M.P.; Peru, K.M.; McMartin, D.W.; Headley, J.V. Effects of Extraction pH on the Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry Profiles of Athabasca Oil Sands Process Water. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 3615–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gamal El-Din, M. Dynamics of naphthenic acids and microbial community structures in a membrane bioreactor treating oil sands process-affected water: Impacts of supplemented inorganic nitrogen and hydraulic retention time. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 17670–17681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Shi, Y.; Xue, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gamal El-Din, M.; Liu, Y. Comparison of biomass from integrated fixed-film activated sludge (IFAS), moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) and membrane bioreactor (MBR) treating recalcitrant organics: Importance of attached biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 326, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostettler, F.D.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cao, W.; Bekins, B.A.; Rostad, C.E.; Kulpa, C.F.; Laursen, A. Forensic fingerprinting of oil-spill hydrocarbons in a methanogenic environment-Mandan, ND and Bemidji, MN. Environ. Forensics 2007, 8, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubot, W.; MacKinnon, M.D.; Chelme-Ayala, P.; Smith, D.W.; Gamal El-Din, M. Petroleum coke adsorption as a water management option for oil sands process-affected water. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 427, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, J.R.; Govers, H.A.J. Quantitative structure-activity relationships for biodegradation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1990, 19, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Chelme-Ayala, P.; Perez-Estrada, L.; Garcia-Garcia, E.; Pun, J.; Martin, J.W.; Belosevic, M.; Gamal El-Din, M. Impact of ozonation on naphthenic acids speciation and toxicity of oil sands process-affected water to vibrio fischeri and mammalian immune system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6518–6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, S.A.; Huang, R.; Mahaffey, A.; Chelme-Ayala, P.; Klamerth, N.; Meshref, M.N.A.; Ibrahim, M.D.; Brown, C.; Peru, K.M.; Headley, J.V.; et al. Comparison of methods for determination of total oil sands-derived naphthenic acids in water samples. Chemosphere 2017, 187, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Ramsay, B.A.; Wang, J.; Ramsay, J. Toxicity and composition profiles of solid phase extracts of oil sands process-affected water. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, J.S.; Mackinnon, M.D.; Fedorak, P.M. Aerobic Biodegradation of Two Commercial Naphthenic Acids Preparations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| NAFCs | Abundance (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Untreated OSPW | Treated OSPW | |
| O2-NA | 56.1 | 29.0 |
| O3-NAs | 16.1 | 25.2 |
| O4-NAs | 16.7 | 28.3 |
| O5-NAs | 1.9 | 4.0 |
| O6-NAs | 0.4 | 0.8 |
| Total Ox-NAs (3 ≤ x ≤ 6) | 35.1 | 57.4 |
| SO2 | 0.2 | 4.9 |
| SO3 | 5.1 | 2.0 |
| SO4 | 2.7 | 3.2 |
| SO5 | 0.31 | 1.1 |
| Total SOx (2 ≤ x ≤ 5) | 8.3 | 11.2 |
| Total NOx | 0.4 | 0.6 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ajaero, C.; Meulen, I.V.; Simair, M.C.; le Roux, M.; Parrott, J.; Peru, K.M.; McMartin, D.W.; Headley, J.V. Developments in Molecular Level Characterization of Naphthenic Acid Fraction Compounds Degradation in a Constructed Wetland Treatment System. Environments 2020, 7, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7100089
Ajaero C, Meulen IV, Simair MC, le Roux M, Parrott J, Peru KM, McMartin DW, Headley JV. Developments in Molecular Level Characterization of Naphthenic Acid Fraction Compounds Degradation in a Constructed Wetland Treatment System. Environments. 2020; 7(10):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7100089
Chicago/Turabian StyleAjaero, Chukwuemeka, Ian Vander Meulen, Monique C. Simair, Mignon le Roux, Joanne Parrott, Kerry M. Peru, Dena W. McMartin, and John V. Headley. 2020. "Developments in Molecular Level Characterization of Naphthenic Acid Fraction Compounds Degradation in a Constructed Wetland Treatment System" Environments 7, no. 10: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7100089
APA StyleAjaero, C., Meulen, I. V., Simair, M. C., le Roux, M., Parrott, J., Peru, K. M., McMartin, D. W., & Headley, J. V. (2020). Developments in Molecular Level Characterization of Naphthenic Acid Fraction Compounds Degradation in a Constructed Wetland Treatment System. Environments, 7(10), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7100089






