Assessment of Non-Anthropogenic Addition of Uric Acid to a Water Treatment Wetlands
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
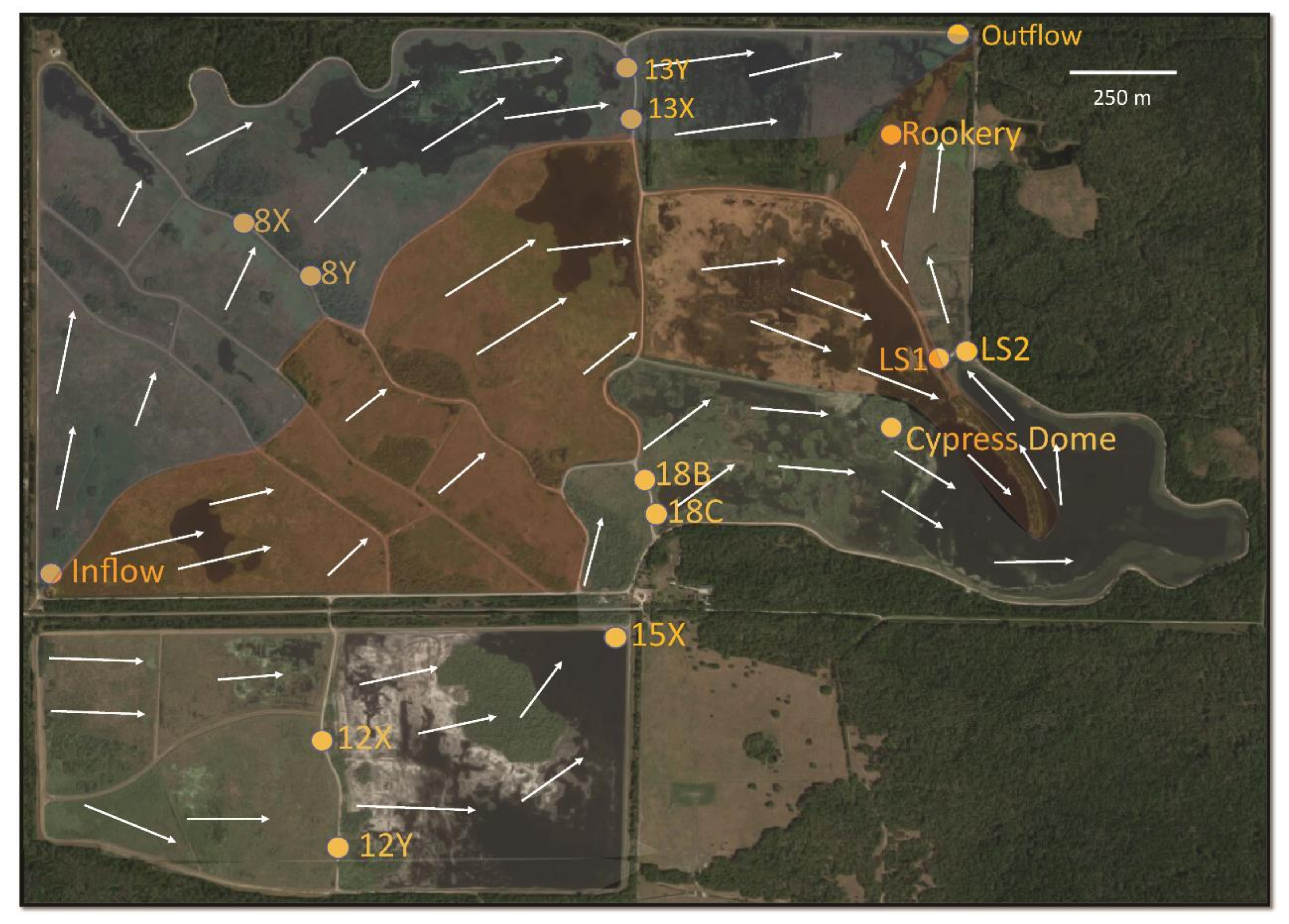
2.1. Structure of the Park and Sampling
2.2. Uric Acid Chemical Analysis
2.3. Instrumentation
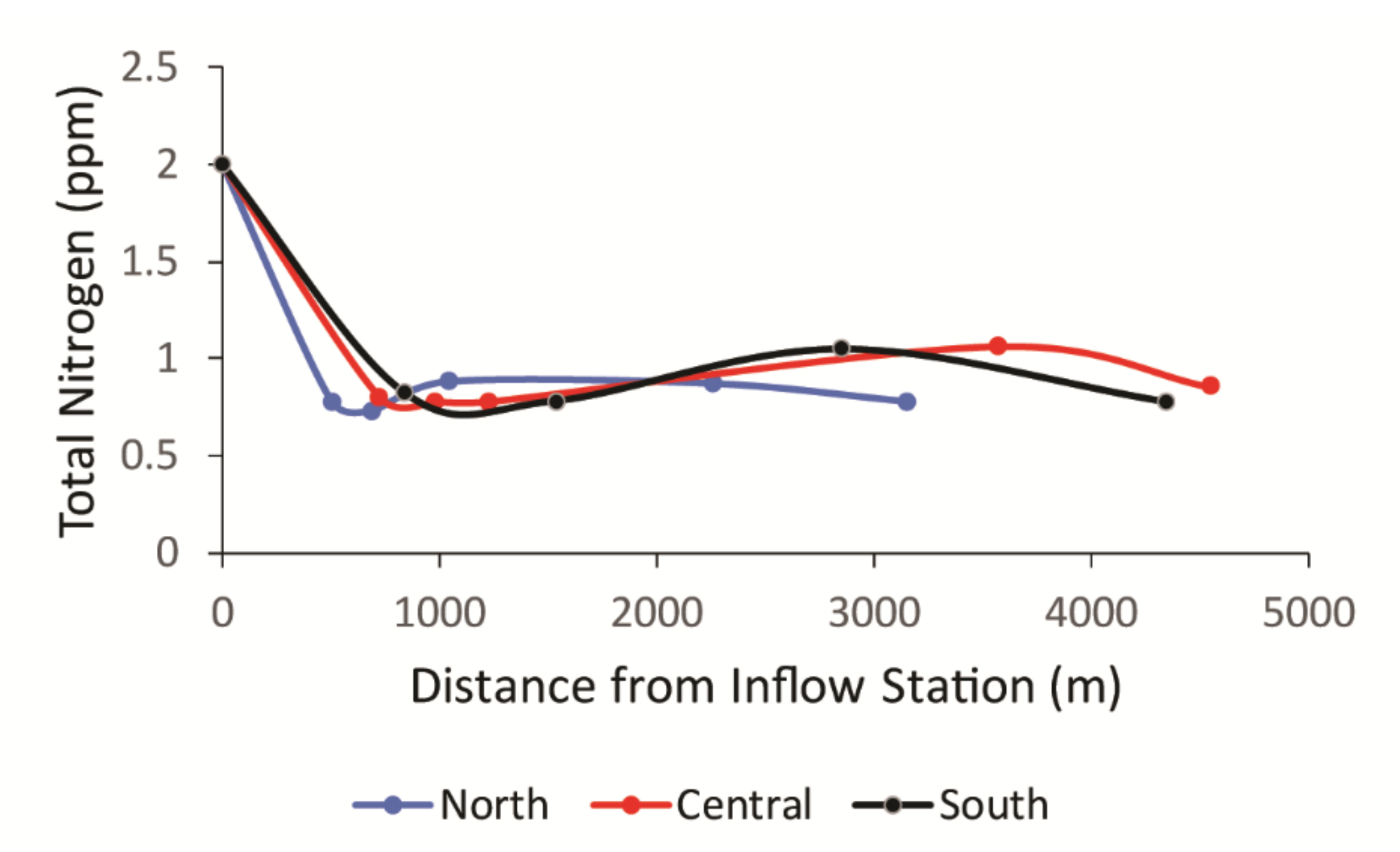
3. Results
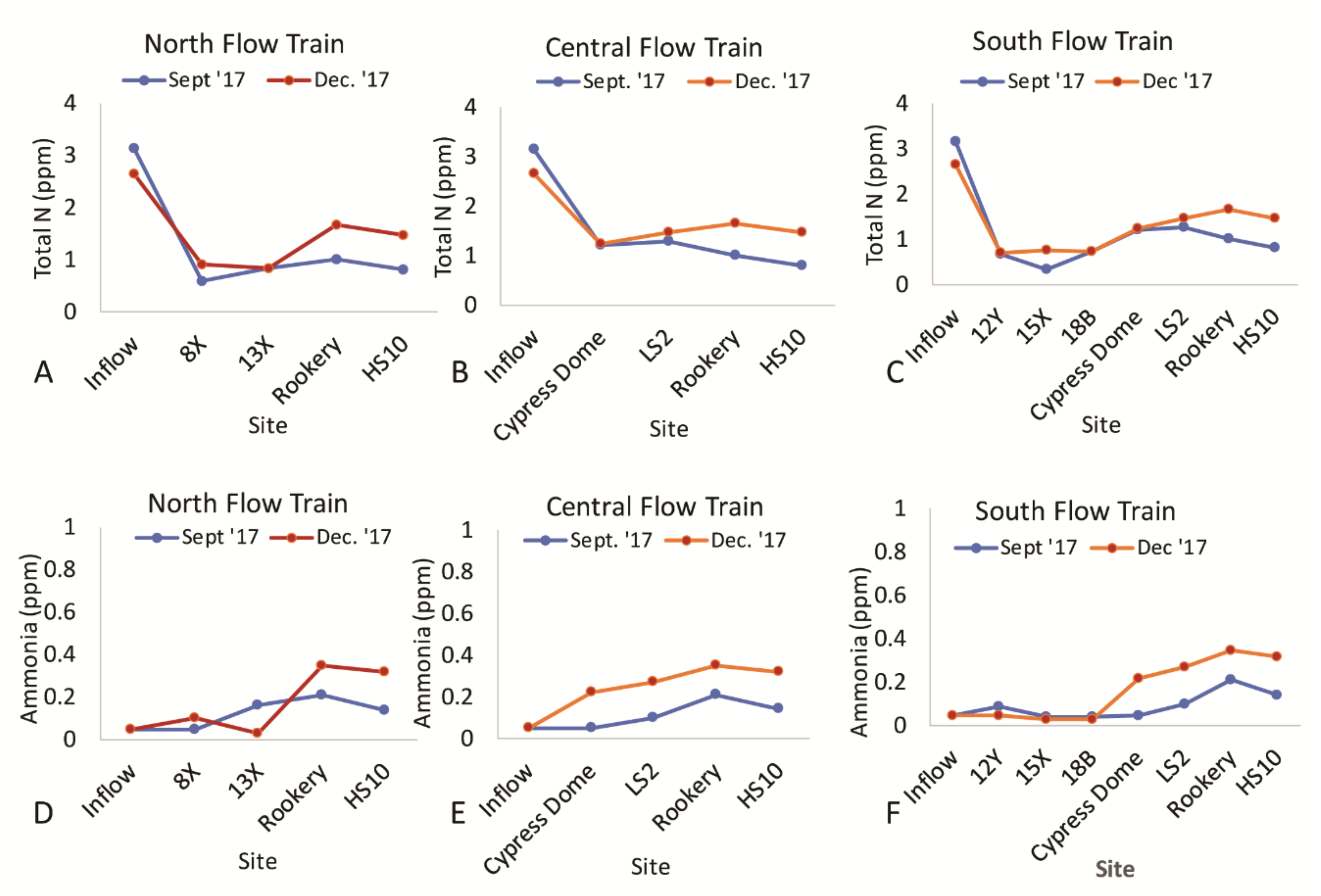
3.1. Uric Acid Concentrations
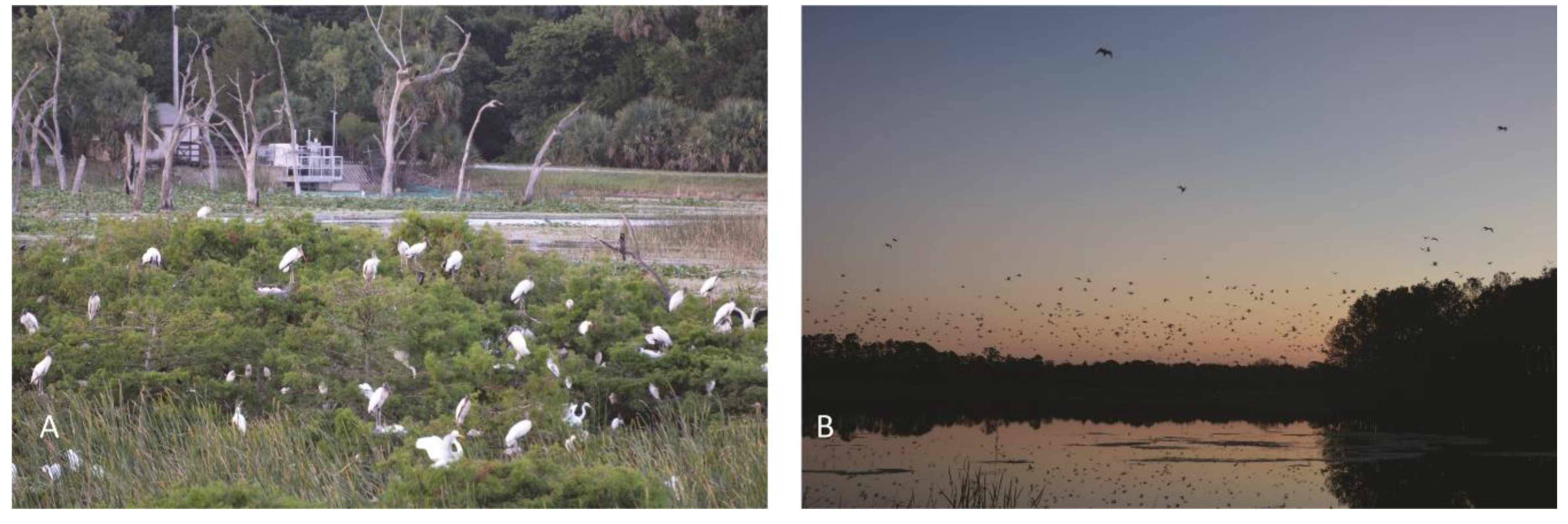
3.2. Animal UA Analysis and Bird Population
4. Discussion
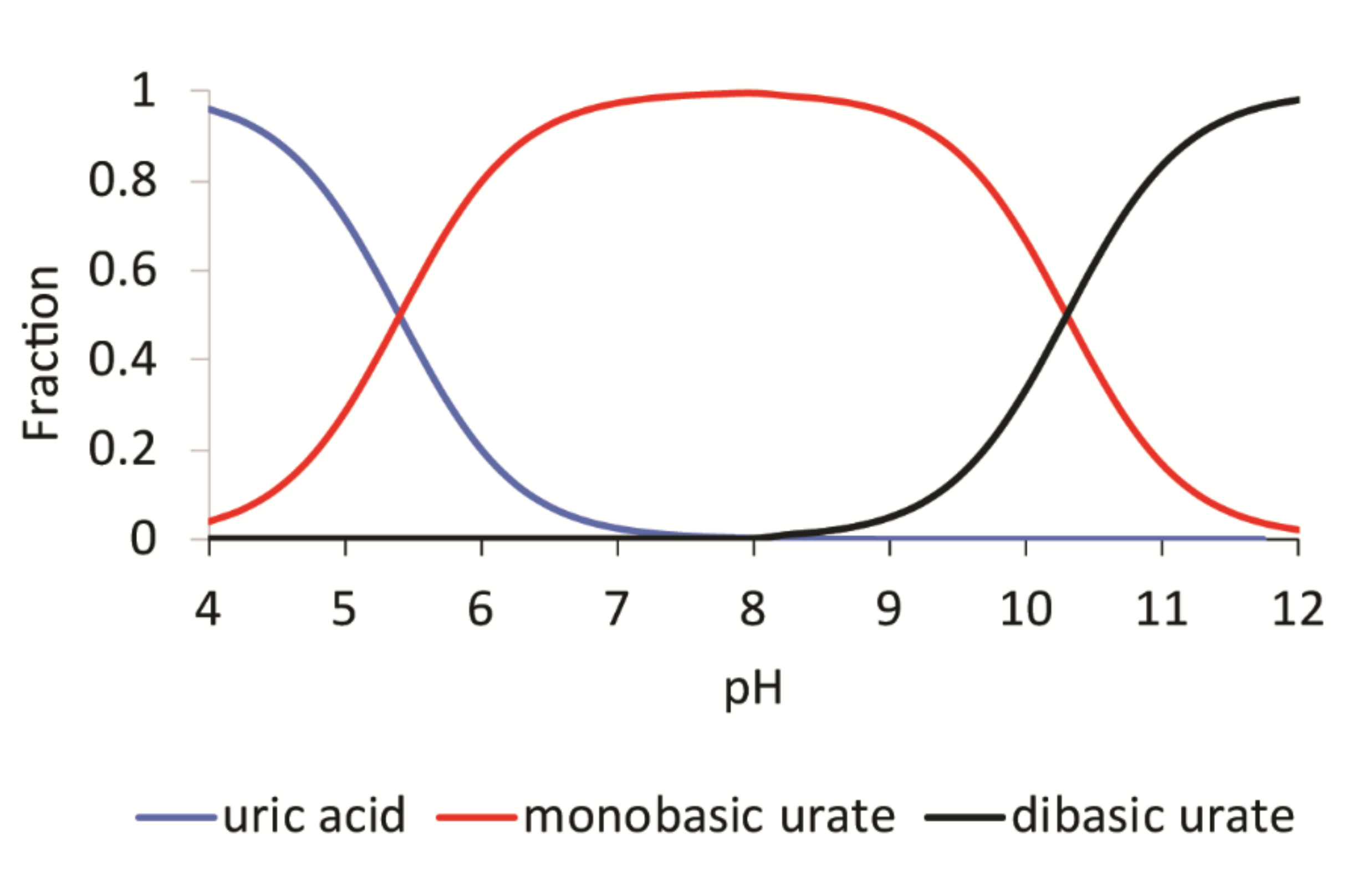
4.1. Uric Acid Solubility
4.2. Uric Acid Degradation
4.3. Nutrient Balance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kadlec, R.H.; Wallace, S. Treatment Wetlands, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- D’Angelo, E.M.; Reddy, K.R. Regulators of heterotrophic microbial potentials in wetland soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 815–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.R.; Reddy, K.R.; Majer-Newman, J. Hydrologic and Vegetation Effects on Water Column Phosphorus in Wetland Mesocosms. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 1242–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaune, R.D.; Pezeshki, S.R. The Role of Soil Organic Carbon in Maintaining Surface Elevation in Rapidly Subsiding U.S. Gulf of Mexico Coastal Marshes. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 3, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.R.; Reddy, K.R. Influence of Selected Inorganic Electron Acceptors on Organic Nitrogen Mineralization in Everglades Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, J.G.; Burford, M.; Olley, J.; Udy, J. Phosphorus Sorption in Soils and Sediments: Implications for Phosphate Supply to a Subtropical River in Southeast Queensland. Autralia Biogeochem. 2011, 102, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, R.K.; Frederick, B.; Haven, R.C.; Lothrop, T.L.; Skene, E.; Oyler, A.R.; Allman, W.P. Wetland Treatment Systems: A Case History; Report No.: EPA832-R-93_005; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Winter Park, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Jawitz, J.W. Hydralic Analysis of Cell-Network Treatment Wetlands. J. Hydrol. 2006, 330, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.R.; Gardner, L.M.; Sees, M.; Corstange, R. The Short-Term Effects of Prescribed Burning on Biomass Removal and the Release of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in a Treatment Wetland. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 2386–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heider, E.C.; Valenti, D.; Long, R.L.; Garbou, A.; Rex, M.; Harper, J.K. Quantifying Sucralose in a Water-Treatment Wetlands: Service-Learning in the Analytical Chemistry Laboratory. J. Chem. Educ. 2018, 95, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazzina, I.; Folli, C.; Secchi, A.; Berni, R.; Percudani, R. Completing the Uric Acid Degradation Pathway Through Phylogenetic Comparison of Whole Genomes. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, N.M.A.; Lynch, V.M.; Clarke, J.A. A re-evaluation of the chemical composition of avian urinary excreta. J. Ornithol. 2020, 161, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, J.; Bunch, R.L. Uric Acid as a Pollution Indicator. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1965, 37, 1444–1446. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, I.; Yoo, K.; Wee, G.N.; No, J.H.; Park, J.; Min, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Leea, T.K. Short-term Effects of Great Cormorant Droppings on Water Quality and Microbial Community of an Artificial Agricultural Reservoir. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gere, G.; Andrikovics, S. Effects of waterfowl on water quality. Hydrobiologia 1992, 243, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H. The Determination of Uric Acid in Human Blood. J. Biol. Chem. 1945, 158, 601–608. [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama, N. A Direct Colorimetric Determination of Uric Acid in Serum and Urine with Uricase-Catalse System. Clin. Chim. Acta. 1971, 31, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbán, J.; Andreu, Y.; Almenara, M.J.; de Marcos, S.; Castillo, J. Direct Determination of Uric Acid in Serum by a Fluorimetric-Enzymatic Method Based on Uricase. Talanta 2001, 54, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, L.S. Habitat Quality Assessment of Two Wetland Treatment Systems; Report, No.: EPA/600/R-93/222; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, W.R.; Khalaf, A. Solubility of Uric Acid and Monosodium Urate. Med. Biol. Eng. 1972, 10, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, B.A.; Jurinak, J.J. Estimation of Acitivity Coefficients from the Electrical Conductivity of Natural Aquatic Systems and Soil Extracts. Soil Sci. 1973, 116, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogels, G.D.; Van der Drift, C. Degradation of purines and pyrimidines by microorganisms. Bacteriol. Rev. 1976, 40, 403–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouf, M.A.; Lomprey, R.F., Jr. Degradation of Uric Acid by Certain Aerobic Bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 1968, 96, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, J.C.; Barker, H.A. Purine Fermentaion by Clostritium Cylindrosporum II. Purine Transformations. J. Biol. Chem. 1956, 218, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Easterly, O. Wetlands Reclamation Project: From Experiment to Success; City of Orlando Booklet: Orlando, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, A.; Borad, C.K. Effects of Waterbirds on Water Quality. Hydrobiologia 2001, 464, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, S.; Bauer, S.; Klaassen, M. Quantification of Allochthonous Nutrient Input into Freshwater Bodies by Herbivorous Waterbirds. Freshwater Biol. 2008, 53, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




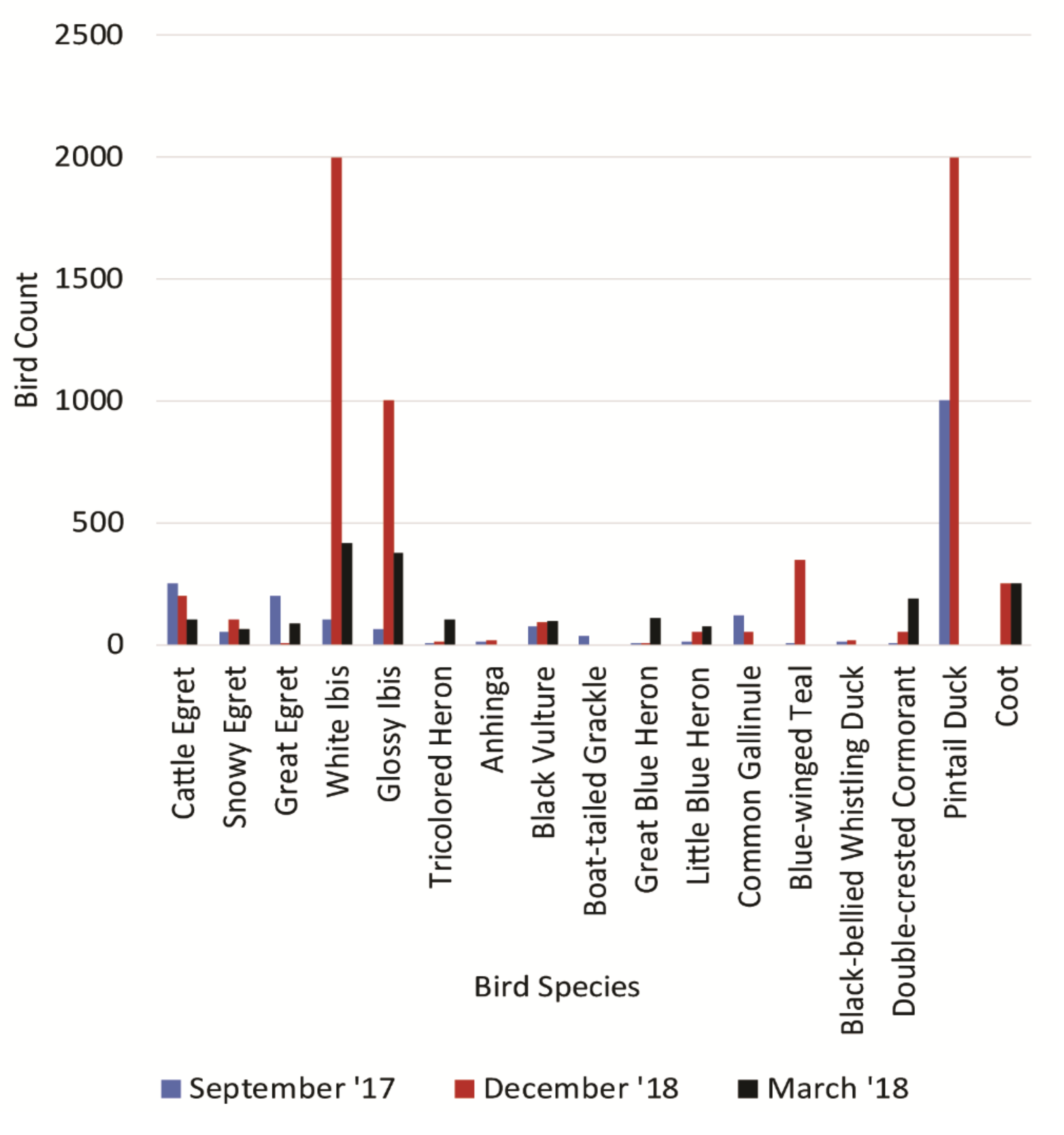
| Date | GE | SE | WI | GB | GI | LB | TH | BH | WS | CE | Total | Density Birds/ha |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oct 1991 * | 107 | 88 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 30 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 267 | 0.54 |
| Dec 1991 * | 10 | 33 | 0 | 10 | 15 | 8 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 77 | 0.04 |
| Feb 1992 * | 42 | 11 | 59 | 11 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 129 | 0.26 |
| Mar 1992 * | 16 | 3 | 106 | 8 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 138 | 0.28 |
| Apr 1992 * | 38 | 26 | 35 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 130 | 0.26 |
| May 1992 * | 18 | 4 | 9 | 8 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 55 | 0.11 |
| Sept 2017 | 200 | 50 | 100 | 4 | 65 | 10 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 250 | 686 | 1.37 |
| Dec 2017 | 8 | 100 | 2000 | 8 | 1000 | 50 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 200 | 3376 | 6.77 |
| Mar 2018 | 83 | 62 | 415 | 109 | 374 | 72 | 103 | 0 | 0 | 103 | 1321 | 2.65 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Welch, J.; Simmons, V.; Meléndez, E.; Sees, M.; Gold, Y.; Heider, E.C. Assessment of Non-Anthropogenic Addition of Uric Acid to a Water Treatment Wetlands. Environments 2020, 7, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7080060
Welch J, Simmons V, Meléndez E, Sees M, Gold Y, Heider EC. Assessment of Non-Anthropogenic Addition of Uric Acid to a Water Treatment Wetlands. Environments. 2020; 7(8):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7080060
Chicago/Turabian StyleWelch, Joseph, Vanessa Simmons, Eduardo Meléndez, Mark Sees, Yolanda Gold, and Emily C. Heider. 2020. "Assessment of Non-Anthropogenic Addition of Uric Acid to a Water Treatment Wetlands" Environments 7, no. 8: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7080060
APA StyleWelch, J., Simmons, V., Meléndez, E., Sees, M., Gold, Y., & Heider, E. C. (2020). Assessment of Non-Anthropogenic Addition of Uric Acid to a Water Treatment Wetlands. Environments, 7(8), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7080060





