Abstract
This pilot study aimed to monitor the residential/office indoor, outdoor, and personal levels of ozone for people living, working, and commuting in Athens, Greece. Participants (16 persons) of this study worked at the same place. Passive sampling analysis results did not indicate any limit exceedance (Directive 2008/50/EC: 120 µg/m3, World Health Organization (WHO) Air Quality Guidelines 2005: 100 µg/m3). The highest “house-outdoor” concentration was noticed for participants living in the north suburbs of Athens, confirming the photochemical ozone formation at the northern parts of the basin during southwestern prevailing winds. The residential indoor to outdoor ratio (I/O) was found to be significantly lower than unity, underlying the outdoor originality of the pollutant. The highest “office-indoor” concentration was observed in a ground-level building, characterized by the extensive use of photocopy machines and printers. Personal ozone levels were positively correlated only with indoor-office concentrations. A clear correlation of personal ozone levels to the time spent by the individuals during moving/staying outdoors was observed. On the other hand, no correlation was observed when focusing only on commuting time, due to the fact that transit time includes both on-foot and in-vehicle time periods, therefore activities associated with increased exposure levels, but also with pollutants removal by recirculating air filtering systems, respectively.
1. Introduction
Air pollutants can be found everywhere, thus a certain level of human exposure is inevitable, whether a person is indoors or outdoors. Exposure to air pollution is largely determined by the concentration of air pollutants in the microenvironments where people spend their time, and the time they spend within them. However, personal exposure is more complex and does not only arise from pollutant concentrations in indoor and outdoor air [1]. In order to accurately quantify everyday human exposure, the impact of the individuals’ daily routine, activity, and mobility patterns should not be ignored.
Ozone is a prominent, highly reactive, secondary air pollutant, formed almost entirely from chemical reactions taking place within the atmosphere involving NOX and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) as precursors. Exposure to ground-level ozone has been associated with a variety of harmful health effects [2,3,4,5,6]. Excessive ozone in the air may result in the induction of respiratory symptoms (cough, throat irritation, chest tightness or discomfort, wheezing, shortness of breath) [7,8], while other researchers connected it with cardiovascular and respiratory mortality [9,10].
Evaluation of the relationship between ozone exposure and health effects has often been conducted by using the ozone concentrations from fixed site measurements [10,11,12,13]. This was particularly preferred for extended population studies, as well as for economic reasons. However, as these measurements do not take into account the existence of a personal cloud of each individual, they usually result in poor correlations of personal exposure with ambient concentrations [14,15,16,17,18]. These limitations were overtaken by the development of light-weight passive ozone samplers [19] for the assessment of personal exposure to O3, which have been used to a large extent since then [3,5,17,18,20,21,22,23,24,25], and still comprise a reliable [26] and cost-effective method.
Across Europe, the highest number of ozone exceedances occurs in the Southern/Mediterranean region, a region frequently characterized by high solar radiation intensity, where the transport of polluted air masses from Europe and other continents to the southern Europe/Mediterranean Basin favors photochemical O3 production [27,28]. To the best of our knowledge, relatively few studies have been conducted within this area; these studies include those by Bernard et al. [29] and Liard et al. [30] in France, by Cattaneo et al. [31] in Italy, and by Karakatsani et al. [3] as well as the RESPOZE study [6,20,23] in Greece.
This paper describes a pilot study which aimed to monitor the residential and office indoor, outdoor, and personal levels of ozone for people living, working, and commuting in Athens. Participants of this study worked at the same place and used a variety of means of transportation while commuting to/from work. Since epidemiological studies have shown that commuting in traffic is associated with adverse health effects [32,33,34], and ozone is a secondary by-product of traffic-related air pollutants, the participants’/commuters’ exposure to ozone was investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Study Design
The study was performed in the greater area of Athens basin, which has been characterized by documented high ozone levels, especially in non-traffic and suburban areas [4,35,36]. In particular, higher ozone concentration is observed in the northern and eastern parts of the basin, as a result of photochemical transformation processes involving precursor substances excessively produced in the densely populated city center and in the port area of Piraeus, the transport of which is aided by the frequent prevalence of southeasterly seabreeze mesoscale circulations [37].
Sixteen people working in the same place (National Center for Scientific Research Demokritos, situated in Aghia Paraskevi, Athens) participated in the study. Aghia Paraskevi, a northeastern suburb of Athens, is frequently characterized by high levels of ozone, often exceeding the European Union (EU) Directive 2008/50/EC standards [38]. Participants used one or more different means of transportation for commuting: bus, train, metro, suburban rail, car, and walking. According to the study design, for each volunteer, residential (indoor and outdoor), office (indoor and outdoor), and personal (breathing zone) concentration of ozone were measured for a period of five working days (~100 h), using passive sampling. The distribution of houses as well as the National Center for Scientific Reserch (NCSR) Demokritos locations are displayed in Figure 1.
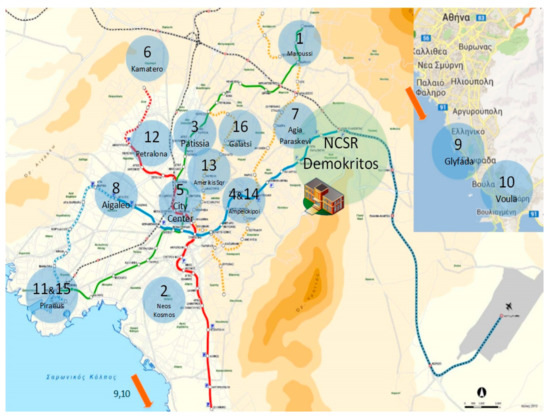
Figure 1.
Map of Athens city and suburbs. Participants’ code (1–16) and the areas of each residence are marked with a blue circle. Metro and train routes are marked with red, blue, and green lines. Bus route to/from NCSR Demokritos (green circle) is marked with a black dashed line.
Passive sampling was used for personal, indoor (house and office), and outdoor (house and office) measurements. Outdoor ozone concentration values obtained from the National Air Quality Monitoring network were also used for comparison purposes. The sampling was conducted concurrently for all the participants and lasted for five consecutive working days (29/10 to 2/11/2013). This allowed keeping the effect of meteorology constant across all comparisons, but also led to the main limitation of this study, which is the small sample of 16 participants. Outdoor offices’ sampling was conducted in five different locations in NCSR Demokritos; as it was expected, low differences among them were observed (SD < 10%).
For the measurement period, participants were requested to complete time activity diaries, recording 10-min intervals their moving status and whether they were outdoors, indoors (house, office, or elsewhere) or in transit (type of transport, time of waiting). In parallel, checklists including information on residential/office building characteristics (location, ventilation pattern, occupant activities) were filled in by all participants. Finally, temperature and relative humidity inside offices and houses were continuously monitored with HOBO data loggers (Onset Company, Cape Cod, MA, USA) Table 1 presents temperature, relative humidity, and average time (hours/day) of at least one open window (as recorded on questionnaires) for each participant.

Table 1.
Indoor and outdoor average temperature (T) and relative humidity (RH) and average time (hours/day) of at least one open window, recorded for each participant.
2.2. Sampling and Chemical Analysis
Radiello® passive samplers were used for indoor/outdoor/personal passive sampling of ozone for five days. At indoor locations, the samplers were placed in the center of each room, not closer than 1 m to the wall, at the height of the breathing zone of seated occupants, i.e., at approximately 110 cm; either on tables or other furniture. Heating sources, including the sun, were avoided. Outdoor sampling locations were chosen in order to be protected from meteorological parameters and to avoid significant point sources of pollution, such as building exhaust vents. Personal samples were placed at the breathing zone of the participants, who carried it throughout the sampling period. During sleeping hours, participants were asked to put the sampler nearby their bed.
The samples were extracted with freshly prepared 3-methyl-2-benzothiazolinone hydrazone hydrocloride (MBTH) solution 5 mg/mL, and were left to react for approximately 1 h with stirring from time to time. They were then were filtered through micropore filter, in strict accordance with the manufacturer’s protocol [39]. Absorbance was measured at 430 nm in a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (RAYLEIGH UV-1601, Beijing Beifen-Ruili Analytical Instrument (Group) Co., Ltd. (BFRL), Beijing, China). A six-point calibration curve was used for the quantification of ozone. Duplicate samples, for 10% of the passive samplers, were collected in order to test the quality of the sample analysis. The duplicate analysis gave a relative standard deviation (RSD) of 6%. Field blanks, one set per microenvironment, were also reserved in order to be able to assess contamination during sample handling in the field and facilitate blank correction and calculation of the detection limit. After exposure, the samples were stored in the dark, along with the blanks. Analysis was performed in less than a week and the blank correction of the samples was conducted. The reagents and solvents proposed by the passive sampler manufacturers [39] were used in all analytical procedures. The limit of detection was determined as three times the standard deviation of the average blank value and was found to be 0.1 μg/m3. Half detection limit was used as the concentration for samples in which ozone was not detected (<LOD, below limit of detection).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ozone Concentration Levels
The information gathered from the participants’ activity logbooks revealed that metro and bus were the most frequently used means of commuting, while the majority of the participants used two different ways to commute (Figure 2a,b).
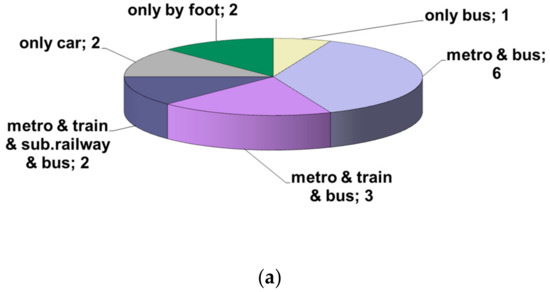
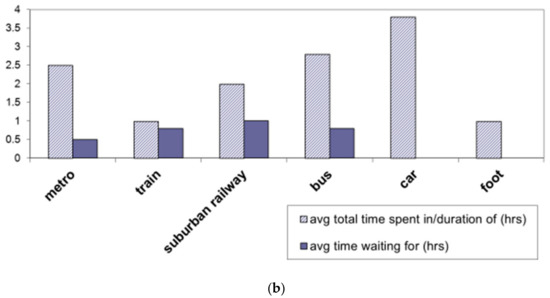
Figure 2.
Number of participants per commuting mode (a), average total time (h) spent in/during waiting for transit (b).
Personal, indoor, and outdoor sample analysis results did not indicate any limit exceedance (Directive 2008/50/EC: 120 µg/m3, WHO Air Quality Guidelines 2005: 100 µg/m3, for ambient air). Table 2 presents the statistics for personal, indoor, and outdoor ozone levels. The measured outdoor values (in NCSR Demokritos and residences’ areas) were well correlated to the five-day averaged value provided by the National Air Quality Monitoring network (r = 0.74, p < 0.05), while being comparable to those reported by Grivas et al. [23] for the city of Athens. The highest “house-outdoor” concentration was noticed for participants living mainly in the north suburbs of Athens (Figure 1: participants # 1, 7, 10, 16) while the lowest were noticed for participants living downtown (Figure 1: participants # 3, 5, 13). According to WHO (WHO air quality guidelines—global update 2005), ozone concentrations within the city itself are often lower than those in the surrounding countryside, as fresh nitric oxide emissions from traffic suppress high concentrations of ozone entering in air from the surrounding countryside. This was also depicted by the wind direction versus ozone concentration rose diagram presented in Figure 3 (data provided by the National Air Quality Monitoring and Hellenic National Meteorological service networks). As it seems, the prevailing wind had a southwestern origin (i.e. from the center of the city) and favored the photochemical ozone formation at the northern parts of the basin which comprises a frequent pattern for Attiki basin, especially during the warm season [37,40].

Table 2.
Ozone personal, indoor, and outdoor levels concentration levels during the sampling campaign.
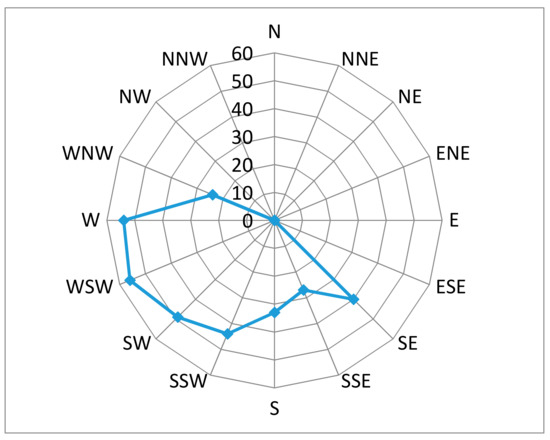
Figure 3.
Rose diagram of five-day averaged values of O3 (μg/m3) versus wind direction.
The highest “house-indoor” values were recorded for participants living at suburban areas in the basin (Figure 1: participants # 1, 7, 8, 16), while the lowest were recorded for all participants living in or close to the city center. In all cases, the residential indoor to outdoor ratio (I/O) was found to be significantly lower than unity (values ranging between 0.02 and 0.3), underlying the outdoor originality of the pollutant [41]. This outcome is amplified by the strong positive correlation (r = 0.83, p < 0.05) between residential indoor and outdoor concentration.
Although the outdoor levels inside the NCSR Demokritos campus did not present significant deviation (SD < 10%), the “office-indoor” concentration differed substantially among the different buildings/rooms. The highest “office-indoor” concentration (28.9 µg/m3) was observed in a ground-level building, occupied by offices with extended use of photocopy machines and printers (administration building). In this room, the I/O ratio (office-indoor/office-outdoor) was the highest one observed (0.8), while the ratio values for the other offices were significantly lower than unity (values ranging between 0.02 and 0.4). The presence of photocopying and printing equipment has been associated with ozone emissions and its health-related side-effects [42].
Personal ozone levels have been recorded to be significantly lower than the limit values. The comparison of personal ozone levels to those documented from other studies is constrained by a number of factors: method and uncertainty of sampling, different climatic conditions, season and period of sampling, participants’ activity pattern, etc. Nevertheless, the ratios of personal to residential-outdoor (0.14 ± 0.09) and personal to office-outdoor (0.1 ± 0.06) concentrations were similar to those found for Athens and Thessaloniki cities by Grivas et al. [23], or other cities worldwide [22,43,44] during fall. As Grivas et al. [23] underlined, the low ratio value reveals the large discrepancy between the two exposure metrics (personal versus ambient air) and thus the protective role of the indoor environment, due to the lack of indoor sources of ozone and the increased times spent indoors. Personal ozone levels were positively correlated (r = 0.5, p < 0.05) with indoor-office concentrations. In opposition, no correlation was reported between personal and residential indoor levels.
3.2. Effect of Participants’ Activity
The effect of the participants’ activity on personal ozone exposure was investigated. Table 3 presents the correlation between the personal levels of ozone (Cp) and time spent outdoors—including commuting time—(Tout), time spend indoors at home (Thome), time spent indoors at the office (Toffice), and time spent during commuting (Tcom). Statistically significant correlation (p < 0.05) was found in cases of Cp versus time spent outdoors and in the office (positive correlation) as well as versus time spent in the house (negative correlation). No significant correlation was found between Cp and time spent during commuting.

Table 3.
Pearson correlation coefficients between personal concentration (Cp) and Cp to outdoor concentration levels versus time fractions spent in each microenvironment.
Increased time spent outdoors is expected to be associated with higher personal to outdoor concentration ratios [45]. Indeed, in the present study, statistically significant positive correlations were observed between Cp to outdoor residential (Cp/Cores) and Cp to outdoor office (Cp/Coof) ratios versus time spent outdoors (Tout). The above findings indicate a clear correlation of the personal ozone levels to the time spent by the individuals during moving or staying outdoors. In opposition, no correlation was observed when focusing only on commuting time, due to the fact that transit time includes both on-foot and in-vehicle time periods. As Cattaneo et al. [31] remarked, while on-foot transit has been associated with increased personal concentrations characteristic of exposure in outdoor microenvironments, in-vehicle exposure in modern automobiles, with active air conditioning systems, has been reported to be minimal [46], due to ozone removal by recirculating air filtering systems.
Although six out of the 16 participants were smokers, 10 out of 16 reported passive smoking in home or/and office. A significant positive correlation (Table 3) was observed between personal ozone levels and time of exposure to environmental tobacco smoke (including passive smoking). This finding could support exposure-health effect studies, as it has been reported that heavy personal tobacco use may be an effect modifier for ozone-associated morbidity [47,48]. Finally, no correlation was found between indoor ozone levels and the duration of room windows being open, probably due to (a) the inaccuracy of the information from the participants regarding the ventilation pattern and (b) different periods of the day where windows were open in each house/office, consequently recording different outdoor ozone contributions due to its diurnal cycle.
4. Conclusions
This pilot study aimed to monitor the residential/office indoor, outdoor, and personal levels of ozone for people living, working, and commuting in Athens. The highest “house-outdoor” concentration was noticed for participants living in the north suburbs of Athens, confirming the photochemical ozone formation at the northern parts of the basin during southwestern prevailing winds. The indoor to outdoor ratio (I/O) was found to be significantly lower than unity, underlying the predominance of the outdoor originality of the pollutant. A clear correlation of personal ozone levels to the time spent by the individuals during moving/staying outdoors was observed. On the other hand, no correlation was observed when focusing only on commuting time, due to the fact that transit time includes both on-foot and in-vehicle time periods, activities associated with an increase in exposure levels as well as with pollutants removal by recirculating air filtering systems, respectively.
In general, although overall personal exposures were low and clearly below limit values, the time-activity pattern does matter in the actual levels, and thus, a person could lower exposure by changing their time-activity pattern. A further study including individuals’ exposure measurements for prolonged periods in parallel with detailed commuting route tracking (e.g., using the Global Positioning System—GPS) and comprehensive activity recording would support the connection of these results with human health effects in epidemiological studies aimed at improving quality of life.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank all the participants who participated in the study.
Author Contributions
Dikaia E. Saraga and Krystallia K. Kalimeri conceived and designed the experiments; Dikaia E. Saraga performed the experiments and Krystallia K. Kalimeri conducted the chemical analysis of the samples; Dikaia E. Saraga and Krystallia K. Kalimeri analyzed the data; John G. Bartzis contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; all authors contributed in writing the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Steinle, S.; Reis, S.; Sabel, C.E. Quantifying human exposure to air pollution-Moving from static monitoring to spatio-temporally resolved personal exposure assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 443, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annesi-Maesano, I.; Baiz, N.; Banerjee, S.; Rudnai, P.; Rive, S.; on behalf of the SINPHONIE Group. Indoor air quality and sources in schools and related health effects. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part. B 2013, 16, 491–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakatsani, A.; Kapitsimadis, F.; Pipikou, M.; Chalbot, M.C.; Kavouras, I.G.; Orphanidou, D.; Papiris, S.; Katsouyanni, K. Ambient air pollution and respiratory health effects in mail carriers. Environ. Res. 2010, 110, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassomenos, P.A.; Dimitriou, K.; Paschalidou, A.K. Human health damage caused by particulate matter PM10 and ozone in urban environments: The case of Athens, Greece. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 6933–6942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Aguilar, M.; Barraza-Villarreal, A.; Moreno-Macías, H.; Winer, A.M.; Cicero-Fernández, P.; Vélez-Márquez, M.G.D.; Cortez-Lugo, M.; Sienra-Monge, J.J.; Romieu, I. Assessment of personal exposure to ozone in asthmatic children residing in Mexico City. Salud Pública de México 2008, 50, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoli, E.; Dimakopoulou, K.; Evangelopoulos, D.; Rodopoulou, S.; Karakatsani, A.; Veneti, L.; Sionidou, M.; Tsolakoglou, I.; Krasanaki, I.; Grivas, G.; et al. Is daily exposure to ozone associated with respiratory morbidity and lung function in a representative sample of schoolchildren? Results from a panel study in Greece. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.P.; Krzyzanowski, M.; Koffi, B. Tropospheric Ozone in the European Union The Consolidated Report. Topic Report No. 8/1998. European Environment Agency, November 1998. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/TOP08-98/page001.html (accessed on 26 June 2017).
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Guidelines for Indoor Air Quality: Selected Pollutants; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; ISBN 978 92 890 0213 4. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, M.L.; McDermott, A.; Zeger, S.L.; Samet, J.M.; Dominici, F. Ozone and short-term mortality in 95 US urban communities, 1987–2000. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2004, 292, 2372–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Melly, S.; Schwartz, J. Modifiers of short-term effects of ozone on mortality in eastern Massachusetts—A case-crossover analysis at individual level. Environ. Health 2010, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Poon, R.; Chen, L.; Frescura, A.M.; Montuschi, P.; Ciabattoni, G.; Wheeler, A.; Dales, R. Acute effects of air pollution on pulmonary function, airway inflammation, and oxidative stress in asthmatic children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonnell, W.F.; Zenick, H.; Hayes, C.G. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s Ozone Epidemiology Research Program: A strategy for assessing the effects of ambient ozone exposure upon morbidity in exposed populations. Air Waste 1993, 43, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickmilder, M.; de Burbure, C.; Sylviane, C.; Xavier, D.; Alfred, B.; Alain, D. Increase of exhaled nitric oxide in children exposed to low levels of ambient ozone. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part. A 2007, 70, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauer, M.; Brook, J.R. Personal and Fixed-Site Ozone Measurements with a Passive Sampler. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1995, 45, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gall, E.T.; Chen, A.; Chang, V.W.C.; Nazaroff, W.W. Exposure to particulate matter and ozone of outdoor origin in Singapore. Build. Environ. 2015, 93, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Williams, R.; Pinto, J.P. Determinants of the associations between ambient concentrations and personal exposures to ambient PM2.5, NO2, and O3 during DEARS. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 63, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Yoda, Y.; Otani, N.; Kameda, T.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K.; Shima, M. Personal and Atmospheric Concentrations of Ozone in Southeastern Hyogo Prefecture, Japan. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 60, 962–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamsvfv, R.; Rappold, A.G.; Case, M.; Schmitt, M.; Stone, S.; Jones, P.; Thornburg, J.; Devlin, R.B. Multi-pollutant exposures in an asthmatic cohort. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutrakis, P.; Wolfson, J.M.; Bunyaviroch, A.; Froehlich, S.E.; Hirano, K.; Mulik, J.D. Measurement of ambient ozone using a nitrite-coated filter. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Dimakopoulou, K.; Grivas, G.; Samoli, E.; Rodopoulou, S.; Spyratos, D.; Papakosta, D.; Karakatsani, A.; Chaloulakou, A.; Katsouyanni, K. Determinants of personal exposure to ozone in school children. Results from a panel study in Greece. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geyh, A.S.; Roberts, P.T.; Lurmann, F.W.; Schoell, B.M.; Avol, E.L. Initial field evaluation of the Harvard active ozone sampler for personal ozone monitoring. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 1999, 9, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyh, A.S.; Xue, J.; Ozkaynak, H.; Spengler, J.D. The Harvard Southern California chronic ozone exposure study: Assessing ozone exposure of grade-school-age children in two southern California communities. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grivas, G.; Dimakopoulou, K.; Samoli, E.; Papakosta, D.; Karakatsani, A.; Katsouyanni, K.; Chaloulakou, A. Ozone exposure assessment for children in Greece: Results from the RESPOZE study. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Parkhurst, W.J.; Xue, J.; Ozkaynak, A.H.; Neuberg, D.; Spengler, J.D. Outdoor/Indoor/Personal ozone exposures of children in Nashville, Tennessee. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2004, 54, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.J.; Koutrakis, P.; Suh, H.H; Mulik, J.D.; Burton, R.M. Use of personal measurements for ozone exposure assessment: A pilot study. Environ. Health Perspect. 1993, 101, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.J.S.; Olson, M.P.; Allen, G.A.; Koutrakis, P.; McDonnell, W.F.; Gerrity, T.R. Evaluation of the Harvard ozone passive sampler on human subjects indoors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerasopoulos, E.; Kouvarakis, G.; Vrekoussis, M.; Donoussis, C.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Kanakidou, M. Photochemical ozone production in the eastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 3057–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofanelli, P.; Bonasoni, P. Background ozone in the southern Europe and Mediterranean area: Influence of the transport processes. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, N.L.; Gerber, M.J.; Astre, C.M.; Saintot, M.J. Ozone measurement with passive samplers: Validation and use for ozone pollution assessment in Montpellier, France. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liard, R.; Zureik, M.; Le Moullec, Y.; Soussan, D.; Glorian, M.; Grimfeld, A.; Neukirch, F. Use of personal passive samplers for measurement of NO2, NO, and O3 levels in panel studies. Environ. Res. 1999, 81, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaneo, A.; Taronna, M.; Garramone, G.; Peruzzo, C.; Schlitt, C.; Consonni, D.; Cavallo, D.M. Comparison between personal and individual exposure to urban air pollutants. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HEI Panel on the Health Effects of Traffic-Related Air Pollution. Traffic-Related Air Pollution: A Critical Review of the Literature on Emissions, Exposure, and Health Effects; HEI Special Report 17; Health Effects Institute: Boston, MA, USA, January 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Samoli, E.; Atkinson, R.W.; Analitis, A.; Fuller, G.W.; Green, D.C.; Mudway, L.; Anderson, H.R.; Kelly, F.J. Associations of short-term exposure to traffic-related air pollution with cardiovascular and respiratory hospital admissions in London, UK. Occup. Environ. Med. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, K.N.; Cavallari, J.M.; Hunt, M.J.O.; Lazo, M.; Molina, M.; Molina, L.; Holguin, F. Traffic-related air pollution exposures and changes in heart rate variability in Mexico City: A panel study. Environ. Health 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfetsos, A.; Vlachogiannis, D. An analysis of ozone variation in the greater Athens area using granger causality. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2013, 4, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroidis, I.; Ilia, M. Trends of NOx, NO2 and O3 concentrations at three different types of air quality monitoring stations in Athens, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 63, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, G.; Chaloulakou, A.; Kassomenos, P. An overview of the PM10 pollution problem, in the metropolitan area of Athens, Greece. Assessment of controlling factors and potential impact of long range transport. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 389, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pateraki, S.; Asimakopoulos, D.N.; Maggos, T.; Vasilakos, C. Particulate matter levels in a suburban Mediterranean area: Analysis of a 53-month long experimental campaign. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radiello® Diffusive Air Sampling Application—Ozone. Available online: http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/technical-documents/articles/analytical/radiello-air-sampler/ozone-applications.html (accessed on 28 June 2017).
- Vassilakos, C.; Saraga, D.; Maggos, T.; Michopoulos, J.; Pateraki, S.; Helmis, C.G. Temporal variations of PM25 in the ambient air of a suburban site in Athens, Greece. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 349, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Assimakopoulos, V.D.; Saraga, D.; Helmis, C.G.; Stathopoulou, O.I.; Halios, C.H. An experimental study of the indoor air quality in areas of different use. Glob. Nest J. 2008, 10, 192–200. [Google Scholar]
- Cacho, C.; Ventura Silva, G.; Martins, A.O.; Fernandes, E.O.; Saraga, D.E.; Dimitroulopoulou, C.; Bartzis, J.B.; Rembges, D.; Barrero-Moreno, J.; Kotzias, D. Air pollutants in office environments and emissions from electronic equipment: A review. Fresen. Environ. Bull. 2013, 22, 2488–2497. [Google Scholar]
- Pekey, H.; Pekey, B.; Arslanbas, D.; Bozkurt, Z.B.; Dogan, G.; Tuncel, G. Source apportionment of personal exposure to fine particulate matter and volatile organic compounds using positive matrix factorization. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, H.H.; Zanobetti, A. Exposure error masks the relationship between traffic-related air pollution and heart rate variability. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2010, 52, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, M.S.; Ramirez-Aguilar, M.; Meneses-Gonzalez, F.; Hernandez-Avila, M.; Geyh, A.S.; Sienra-Monge, J.J.; Romieu, I. Ozone exposure among Mexico City outdoor workers. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2013, 53, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.; Capel, J.; Ollison, W. Measurement of microenvironmental ozone concentrations in Durham, North Carolina, using a 2B technologies 205 federal equivalent method monitor and an interference-free 2B technologies 211 monitor. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2014, 64, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halios, C.H.; Assimakopoulos, V.D.; Helmis, C.G.; Flocas, H.A. Investigating cigarette smoke indoor pollution in a controlled environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 337, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassino, C.; Ito, K.; Bader, I.; Ciotoli, C.; Thurston, G.; Reibman, J. Cigarette smoking and ozone-associated emergency department use for asthma by adults in New York City. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).