Abstract
Blockchain technology, while still challenged with key limitations, is a transformative Information and Communications Technology (ICT) that has changed our notion of trust. Improved efficiencies for agricultural sustainable development has been demonstrated when ICT-enabled farms have access to knowledge banks and other digital resources. UN FAO-recommended ICT e-agricultural infrastructure components are a confluence of ICT and blockchain technology requirements. When ICT e-agricultural systems with blockchain infrastructure are immutable and distributed ledger systems for record management, baseline agricultural environmental data integrity is safeguarded for those who participate in transparent data management. This paper reviewed blockchain-based concepts associated with ICT-based technology. Moreover, a model ICT e-agriculture system with a blockchain infrastructure is proposed for use at the local and regional scale. To determine context specific technical and social requirements of blockchain technology for ICT e-agriculture systems, an evaluation tool is presented. The proposed system and tool can be evaluated and applied to further developments of e-agriculture systems.
1. Introduction
Information and Communications Technology (ICT) is a precision agriculture technology [1]. In recent years, agricultural environmental monitoring initiatives have adopted a broad range of Information and Communications Technology (ICT)-based technologies such as the remote monitoring of farm conditions, and the remote control of farm equipment through smartphone applications [2,3,4,5,6,7]. Adil et al. [3], Bartlett et al. [4], and Yoshida et al. [6] applied ICT-based techniques in irrigation systems to enhance irrigation system and agricultural water management system efficiencies. Bartlett et al. [4] developed a smartphone application for users to access soil moisture deficit data and weather measurements through an online evapotranspiration-based irrigation scheduling tool. Jagannathan and Priyatharshini [5] developed an ICT-based system to observe soil moisture content, nutrient content, and the soil pH of agricultural areas. Jiang et al. [8] proposed a wireless sensor network (WSN) based algorithm with a novel dynamic converge cast tree algorithm (DCTA) in orchid greenhouses for achieving high-precision cultivation of orchids. Lin et al. [7] developed an ICT-based monitoring system to access the real-time risk of soil and irrigation water contamination in a pilot area for agricultural planning using a hierarchical management strategy. Yu et al. [9] developed a smartphone-based application as a crowdsourcing and human sensing tool to observe land conditions such as crop cover and growth. Perea et al. [10] developed an ICT-based system which offers agro-climatic data, soil data, and hydraulic system data to farmers in the irrigation scheduling of strawberry production.
The major purposes of agricultural environmental monitoring systems include supporting early warning systems, and measuring baseline data that policy makers and resources managers can use in planning [11]. Yet, bias is an ‘inherent human-related challenge’ [12] that propagates to group bias among groups of like-minded individuals. For example, stakeholders’ biases and preferences correlate highly with the mission of their represented organizations [13]. In a study about environmental and energy applications of Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis, Marttunen et al. [14] showed that the most important factor affecting objective prioritization biases are the people involved in the decision-making process. NGOs can also demonstrate bias by putting disproportionate focus on an issue relative to other comparable issues [15]. Dixon and Richards [16] explain why governments bias capital-intensive large agriculture systems to maximize inexpensive food supplies from rural agriculture to urban infrastructure, where the majority of elected officials’ constituents reside. By distributing database management among a greater number of actors, and making system wide data manipulation more difficult, baseline agricultural environmental data integrity is maintained--safeguarded from the biases or the fraudulent activity of any individual group of farmers, NGOs, stakeholders, consumers, and decision makers [17,18,19].
Since blockchain technology eliminates a single point of failure, increased data transparency and immutability will transform current economic organization and governance [20]. Blockchain competitiveness and cost-effectiveness are likely to increase following three laws: (1) Moore’s law, i.e., time required for data processing halves every 18 months; (2) Kryder’s Law, i.e., data storage halves every year; and (3) Nielsen’s Law, bandwidth doubles every two years [20,21]. Because blockchain can facilitate various transactions and processes as a democratizing framework for a system of distributed networks [22], ICT e-agriculture with a blockchain infrastructure is the evolutionary next step for current ICT enabled farm systems and e-agriculture schemes. While the internet allows us to share digitized information, the internet of things (IoT) yields much ICT data currently stored in databases or networked databases with centralized cloud computing architecture. With blockchain, however, agricultural and environmental monitoring data stored in a distributed cloud allows us to engineer trust and secure sustainable agricultural development with transparent data and ICT. In this way, blockchain technology is the foundation for democratized, automatic, and transparent data management [18]. ICT agricultural systems with blockchain infrastructures are therefore immutable and decentralized record management systems. Moreover, this immutability may revolutionize the way all biophysical resources are recorded and traced from source, to use, to reuse in large scale datasets [23], and may ensure government record and service integrity [24].
2. From ICT to Blockchain
In theory, communication technology is a centralizing force whereas information technology is a decentralizing force [25]. Yet, because ICT platforms comprise broadband network infrastructure, wireless sensors technologies, and mobile devices [7,26], ICT is a powerful tool to facilitate data collection, validation, access, exploration, and communication [27]. And because ICT-based systems permit various stakeholders to assemble and share data pertaining to the interests of any given project [11], it is a popular choice in many fields. Environmental monitoring, for example, can be accomplished with broadband network infrastructure, wireless technologies, and mobile devices [26]. Spatiotemporal integration of geographic information systems (GIS), remote sensing (RS), and global positioning systems (GPS) can be used for site-specific monitoring data related to environmental planning and management decision-making [7]. ICT systems with e-services are commonplace for monitoring soil data, irrigation water data, and smart city design projects for flood control [2,7,11]. Further, with social webs and miniaturized sensors, ICT-based technologies can promote citizen participation in environmental monitoring, a topic that has been studied for the last two decades [11,28]. In terms of the IoT and the numerous technologies used in an ICT e-agriculture, a major challenge of achieving a comprehensive secure ecosystem for IoT architecture can be undertaken with blockchain technology [29].
The legacy technology addressed in our work and discussed in the context of trust, is the centrally managed, centralized databases for storage of agricultural and environmental monitoring data. Legacy IT data management systems typically used for national level data present a ‘high cost single point of failure’ prone to cyber-attack, asynchronous inaccurate data [24], censorship [30], data distortion [19], and scientific misconduct [19]. Blockchain, however, has been described as a transformative ICT that may have far-reaching implications for governance, management, and decision-making [20]. Additionally, because it could eliminate the need for intermediaries [31,32], blockchain has changed our notion of trust requirements in centralized authorities [22]. Though blockchain is not predicted to be mainstream until 2025 and is still an ‘immature opportunity space’ (i.e., the blockchain technology market is estimated to grow from 210.2 million USD in 2016 to 2312.5 million USD by 2021 [33]), an industry call to action focused on smart water technology opportunities further recognizes that blockchain (and artificial intelligence) is the ‘backbone’ technology going forward [33]. Results of a literature search in the Web of Science database using the keyword, “blockchain” (Figure 1) reveals that blockchain technology is an interdisciplinary topic with little to nothing found in reference to agriculture.
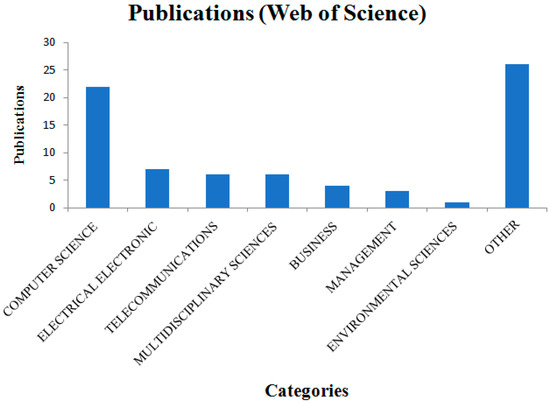
Figure 1.
Web of Science database literature search results for ‘blockchain’. Note: Category ‘Other’ does not include agriculture-related disciplines.
As the name implies, a blockchain is organized in a linear sequence of smaller encrypted datasets called ‘blocks’, which contain timestamped batches of transactions [34]. Each block contains a reference to its precedent block and an answer to a complex mathematical puzzle, which serves to validate the transactions it contains [34]. More specifically, it is a decentralized ledger system of transaction records, which is distributed across a network of computers or databases [34,35,36]. The technology has been widely applied, including for executing smart contracts, Ethereum; advancing scientific research, Gridcoin; authenticating digital identity, OneName; increasing supply chain transparency, Provenance; and increasing economic opportunities in developing nations [37,38,39,40]. Though there are several distributed database architectures that farms could likely organize with (e.g., peer network node data stores; distributed SQL data warehouses; Hadoop framework; NoSQL databases; NewSQL databases; and distributed ledgers), blockchain technology serves to ensure that all recorded data cannot be redacted from historical record. CouchDB (http://couchdb.apache.org/), for example, an immutable NoSQL database software with replication/synchronization capabilities for offline use, would be useful for remote sensing and mobilizing citizen science data/ farmer data captured with mobile devices. Yet, while distributed ledgers are in fact distributed databases with cryptography-based consensus maintenance mechanisms, and though distributed databases like CouchDB can provide immutability, blockchain technology can provide both of these two key features in addition to being ‘censorship resistant’ [41]. Furthermore, Ethereum blockchain technology can auto-execute programmed transactions (i.e., ‘smart contracts’) that are secure and censorship resistant [37].
3. Proponents of Change
3.1. Trust
An inherent feature of the blockchain technology is its redefining element of “trust”. Whether the technology is trust-less or trust-enabling, it ensures that Hobbes’ social contract is upheld even if (1) human nature is intrinsically self-interested or becomes self-interested and (2) the state, misrepresents the masses while representing the interests of corrupt politicians or powerful capitalists [42]. In their executive report for strategic investing, IBM researchers note that many centralized authorities who rely on ‘security through obscurity’ have the ability to gain access to data and the devices that collect this data whether or not management or authorization permissions were explicitly granted to them [22]. Currently, the majority of environmental monitoring data is stored on centralized servers managed by administrators who are trusted with data integrity, security, and access authorization [43]. Beyond being more vulnerable to data loss than distributed databases, centralized database administrators are a source of risk. Centralized database administrators may have their own agendas and vested interests which can affect data-related decisions [44]. Conflicts of interest may arise when these administrators require certain data to achieve their ends (e.g., for funding or political agenda alignment) but must manipulate data to obtain it. For example, Canada’s recent majority government made environmental data deletions [30]. Similarly, during the recent US presidential election, an international effort to download environmental data from the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) was undertaken [45,46].
Data distortion is not limited to political agendas. Environmental protection organizations have also delimited access, distorted, or deleted data thought to lessen its funding prospects [19]. Lacetera and Zirulia [19] note that individual scientists have actively engaged in fraudulent activities. A frequently cited cause for scientific misconduct is the increasing pressure for individual scientists and institutions to publish high-ranking research [47]. The validity of environmental research, however, remains questionable whenever perceived or real conflicts of interests exist [48]. The “March for Science” [49] (https://www.marchforscience.com) is a literal demonstration of the eroded trust between the US government and its scientific community, and a reaction to research censorship and disappearing datasets. Lewis [50] aptly summarizes why conflicts of interest are not conducive to public trust in the generalizable and observed relationship, ‘Government hires scientists to support its policies; industry hires them to support its business; and universities hire them to bring in grants that are handed out to support government policies and industry practices’. Yet, because of its trust element, blockchain is even identified as a driver of environmentally friendly social behavior. Since the technology can enable wealth creation through transparent and immutable property rights never before possessed, new land owners are motivated to maintain their property’s sustainability for their future families [51]. This behavior is facilitated, however, by removing the social requirement to trust and rely on centralized authority in order to engage in self-organization and collaboration. An extreme example of this is Bitnation, which offers ‘governance 2.0’ and views governments merely as governance service providers [42].
3.2. Information Intensive Farming
Governments recognize that blockchain technology provides ‘the framework for government to reduce fraud, corruption, error and the cost of paper-intensive processes…and to redefine the relationship between government and the citizen in terms of data sharing, transparency and trust.’ [24]. Gupta [52] cites examples of how governments can facilitate a transition to using blockchain technology and recommends that governments identify the ‘pain points’ in their national processes. For example, to address mortgage applications, trade finance, and digital identity issues specific to Hong Kong, the S.A.R. experimented with implementation of proof of concept projects resulting in white paper publications [53]. Yet, farming currently has the lowest ICT intensity of all economic sectors even though farming is nationally, both capital- and technology-intensive [22]. Just as ICTs have contributed to socio-economic growth in business sectors, improved agricultural efficiencies for farming communities to achieve food and job security has been demonstrated when ICT-enabled farms have access to knowledge banks and other digital resources [54]. Larsen et al. [55] proposed an ‘agricultural innovation system’ as a tool to analyze mechanisms and infrastructure required for building innovative food systems among scientists and farmers.
ICT-enabled farming systems referred to as ‘e-agriculture’ by the Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations (FAO), is one way that governments can implement ICT to increase market efficiencies, food safety and security, and reduce institutional risk from uncertainty, in addition to facilitate reaching Millennium Development Goals [56]. FAO and the International Telecommunication Union [54] piloted Asia-Pacific ICT studies to develop a guide for advancing a national e-agriculture strategy that consists of a vision, an action plan, and a monitoring and evaluation framework. Additionally, their proposed list of e-agricultural infrastructure components is a confluence of ICT and blockchain technology requirements. Though cross-sectoral leadership commitment is key to realizing the potential of ICT in agriculture, and formulating national e-agricultural priorities and objectives in a national e-agricultural vision is a vital first step [54], blockchain technology provides necessary infrastructure for e-agriculture.
It has been officially recognized that precision agriculture increases the national security threat levels for a nation’s agriculture sector by exposing it to data theft, hacking vulnerabilities, and to tactics used with ‘the intent to steal farm-level data in bulk’ [57]. Acharya and Acharya [58] cite risk scenarios associated with private sector agricultural technology such as Hydrobio (http://hydrobioars.com/) which uses satellite imagery to automate irrigation decisions and could be hacked resulting in economic loss and social instability when harvestable crop fields are flooded. Other corporations such as Blue River Technology (http://www.bluerivert.com/) which automates chemical spray schedules, John Deere (www.deere.com) which uses satellite position for auto-driving tractors, and Taranis (http://www.taranis.ag/) which uses remote sensing for farm disease management, could all fall prey to ‘agro-terrorism’. Monsanto’s Climate Corp created an ‘Internet of Farms’ with FieldView (https://climate.com/) where an integrated mesh network of farm sensors can increase productivity efficiencies. At the same time, however, since it is a centralized field management platform that gives data-driven insights to users, it is vulnerable to becoming a single point of failure for farms across the nation if hacked [58]. Blockchain technology with its cryptoeconomic security features would ensure that data and technological infrastructure such as a national level distributed database conforming to international agricultural standards and naming conventions would remain impenetrable to malicious attackers.
3.3. Model
Figure 2 is a proposed system model of an ICT e-agricultural system with a blockchain infrastructure in which water quality monitoring data is added to the blockchain. Data from a real-time water quality monitoring system is backed-up locally and is added to the blockchain when a provider node creates a new block. The water quality data is distributed over the network so that each miner node has a piece of the complete water quality data and no single node can access the data in its entirety. A query is also created for referencing purposes so that the provider node can later cross-reference the blockchained data with the backed-up data if needed. Miner nodes in the network contribute its hardware, electricity, and processing power to validate the chain resulting in a compilation of the complete water quality data, which is the reward for each node’s “work”. At each node, a water quality monitoring API facilitates system operations. Structured Query Language (SQL) data queries can be used for data upload/download and as a graphical user interface by record management applications. Though a backed-up version of the complete water quality data is stored off-chain and locally, a database gatekeeper’s (or administrator’s) access to the database requires issuance of encryption and decryption keys based on their permission levels which are also stored on the blockchain. An alternative to this, though not depicted in Figure 2, is to create a permissioned blockchain where only pre-approved nodes are granted read-only access to the ledger of complete water quality data.

Figure 2.
Information Communication Technology (ICT) e-agriculture system model with blockchain infrastructure for use at a local and regional scale.
While ICT e-agriculture enhances farmers’ access to agricultural services and high quality data, improves traceability, and validates compliance with international standards [54], the data remains unsecured. An ICT e-agriculture with a blockchain infrastructure can ensure immutability of this data and a way to spatially and temporally trace current (and historical) agricultural data as agricultural products move from their production sources to the consumer. An ICT e-agriculture cannot only support information exchange across the agricultural sector at a local scale, it can also facilitate international exchanges [54]. By eliminating data manipulation risk when integrating data into existing databases, a nation’s ICT e-agriculture system with a blockchain infrastructure can increase its likelihood of export to international markets since compliance with international standards becomes a transparent and undisputed matter. Further, an ICT e-agriculture with a block chain infrastructure is a way to diversify current agricultural management practices in a way that engages the public through ownership of the agricultural production process, even if only to voice feedback as market demand for high quality and verifiably certified standards-compliant products.
Elements of individual farm systems can further benefit from blockchain technology. For example, in Taiwan, there are 17 Farmland Irrigation Associations that attend to the sustainable development of agriculture by modernizing paddy field conservation management approaches since farmland irrigation development has direct and indirect contributions to the environment, agricultural production, and rural livelihood [59]. These associations each operate as a ‘public juridical person’, the members of which are appointed by local government. When data derived from this type of “other knowledge source” is integrated and published on the blockchain, it becomes longitudinal, archival information from which can be compiled histories of irrigation canals to include construction and maintenance planning information. ICT e-agriculture enables access to agricultural services and facilitates capacity-building and empowerment [54]. The blockchain infrastructure’s added values of data immutability and transparency further facilitate public contribution to irrigation matters previously not considered public because of hierarchical management structures. For an irrigation association working with a particular farm, ICT e-agriculture with blockchain infrastructure can be a bridging mechanism to increase public support of water resource use improvement efforts, and to increase the association’s contribution to society so that water is not a limiting factor in sustainable agricultural development.
4. Evaluation Tool
Re-contextualized and adapted from Suichies’ [60] visual summation of Greenspan’s [61] cautionary article for businesses considering embarking on an infrastructure transformation, Figure 3 is a proposed tool that can be used by experts to determine if there is a need for blockchain technology in spite of its limitations and with respect to agricultural environmental data management. Experts can quickly make a dual assessment such that if a need for a bridging mechanism of potential gaps in IT infrastructure exist, blockchain technology is recommended as an enabling environment for ICT in agriculture. Namely, to determine if centralized databases are sufficient for their technical requirements. Similarly, if gaps in knowledge flows among cross-sectoral stakeholders exist and potential systemic-wide bias and/or opaqueness in national processes and agricultural environmental data management persist, blockchain technology is recommended. Figure 3 then also assists experts to decide if trust in a centralized system is suitable for their social requirements in the context of agricultural environmental data management. Based on the flowchart outcomes, blockchain-based approaches may hold potential for enhancing agricultural environmental monitoring and data management, and achieving sustainable agricultural development with ICT.
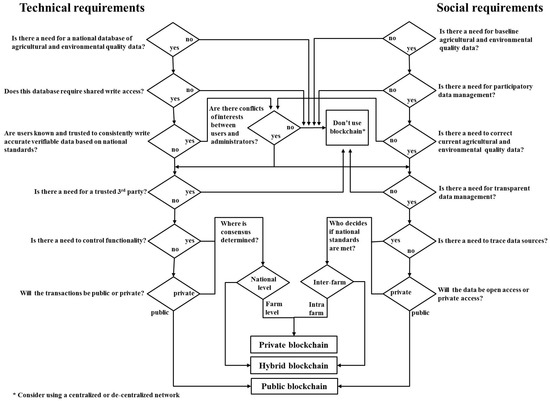
Figure 3.
Evaluation tool to determine blockchain suitability for technical and social requirements of ICT e-agriculture systems. Re-contextualized and adapted from Suichies [60].
5. Key Limitations
Scalability remains the all-inclusive and fundamental problem within a Nakamoto-consensus blockchain network [62]. While it is generally understood that as a network gains users, the network itself gains value, the issue of scaling is unresolved [63]. Blockchain protocols face serious scalability obstacles [62,64] since transaction processing rates are limited by block size and block interval such that larger block sizes improve throughput while slowing propagation within the network and, minimizing block intervals reduces latency while degrading system stability with increased branching [62].
At the core of the problem of reducing blocktime is the issue of security since the faster the blocktime, the more centralization of processing is needed. This tradeoff is such that fast processing time, maximum decentralization, and minimal system overhead (i.e., consensus messages per second) are in direct conflict [65]. That is, time (in seconds) until block finality when multiplied with the ‘overhead’ must be greater than or equal to the number of decentralized validators (i.e., miners) available if incentives for node aggregation in the same data center is to be avoided, thereby maximizing decentralization [65]. Ethereum, “blockchain 2.0”, achieves its security and blocktime goals using cryptoeconomics (i.e., cryptography and economic incentives) which will ultimately change network security protocols from proof of work to proof of stake. The risk of centralization for faster blocktime can be mitigated then, using randomizing determinants, and sharding whereby every user on the chain interacts with only a small portion of the chain and execution is parallelized and split across all nodes [65]. Most protocols in academia use an honest majority security model which has yet to resolve the issue of a malicious minority percent of the validators that can permanently stall the finalization process by publishing a block with missing data. Ethereum network solutions will likely be found in random sampling and erasure codes [65], i.e., ‘security through transparency’ [22].
Currently, blockchain networks will always be slower than centralized databases because of three additional processes per transaction it undertakes: cryptographic verification, consensus mechanisms, redundancy [66]. The tradeoff, however, is that blockchain networks are more robust than centralized databases which rely on expensive infrastructure, such as backup systems, that come online as needed. In the event of a natural disaster, for example, a centralized database may fail when its primary and backup servers are compromised. Similar to ad hoc networking which will not fail unless every node is taken offline [67] a blockchain network structure, however, is dynamic.
6. Conclusions
Environmental monitoring data sharing is essential for environmental monitoring and management, as well as agricultural environment management and monitoring for food safety. This paper argues that an ICT e-agriculture with a blockchain infrastructure is the next step in the evolution of ICT e-agriculture. ICT’s contribution to digital democratization has progressed from trusted closed and centralized networks, to open access centralized cloud computing, and now to blockchain distributed networks that do not require public trust in a centralized authority. E-agriculture can increase economic efficiencies, food safety, and reduce uncertainty risk while achieving sustainable agricultural development. When ICT e-agricultural systems with blockchain infrastructures are immutable and decentralized record management systems, baseline agricultural environmental data is safeguarded for farmers, NGOs, stakeholders, consumers, and decision makers who participate in transparent data management. In conjunction with this paper, the authors have introduced a prototype of an ICT e-agricultural system with blockchain infrastructure for national-level application using GCOIN [68] protocol, an open-source software similar to an improved Bitcoin that utilizes a multi-token architecture, a multi-tier permission system, and improved mining difficulty. GCOIN can also run on operating systems such as Ubuntu or Fedora and uses a cryptographic protocol in C++ on a ×86 server for its decentralized consensus algorithms based on non-uniform and non-linear Proof of Work (PoW) to execute smart contracts, operating as an effective distributed ledger [68]. Currently, the prototype ICT e-agriculture infrastructure, built at National Taiwan University, compiles national-level water quality data from irrigation water monitoring data collected by remote sensors at various farm locations throughout Taiwan into the GCOIN blockchain system instead of a centralized database. A user interface is used to visualize the system and its operation. Further development and incorporation of agricultural data on local weather, energy use, pesticide use, soil quality, farm production costs, and biodiversity conservation efforts are required.
Though centralized databases may be suitable for current agriculture environmental data management programs within ICT e-agriculture systems, technical and social needs can change. An evaluation tool for a dual-assessment of technical and social requirements is presented, as is a model system of a blockchain network of ICT e-agriculture systems for implementation at the local and regional scale. Blockchain technology, while still challenged with key limitations, will become ubiquitous as the fast pace of technological advancement proceeds. Future work on the implementation of blockchain technology in real-world e-agriculture case studies or current agricultural environmental monitoring systems, such as our prototype, may further elucidate the feasibility of applying this technology in environmental data and agricultural monitoring initiatives and national ICT e-agriculture in general.
Acknowledgments
This study has been funded by the Council of Agriculture, Taiwan.
Author Contributions
The scope of this study was developed by Yu-Pin Lin, Joy Petway, Johnathen Anthony, and Hussnain Mukhtar. The first manuscript draft was written by Yu-Pin Lin, Johnathen Anthony, Joy Petway and Hussnain Mukhtar and was substantially revised by Yu-Pin Lin, Joy Petway, Johnathen Anthony, Hussnain Mukhtar, Cheng-Fu Chou, Shih-Wei Liao, and Yi-Fong Ho. The authors would like to thank Dr. Wan-Yu Lien for helping the paper formatting.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gebbers, R.; Adamchuk, V.I. Precision agriculture and food security. Science 2010, 327, 828–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, A.Z.; Islam, N.; Shaikh, Z.A. A review of wireless sensors and networks’ applications in agriculture. Comput. Stand. Interfaces 2014, 36, 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Adil, A.; Badarla, V.; Plappally, A.K.; Bhandari, R.; Sankhla, P.C. Development of affordable ICT solutions for water conservation in agriculture. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Communication Systems and Networks (COMSNETS), Bangalore, India, 6–10 January 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett, A.C.; Andales, A.A.; Arabi, M.; Bauder, T.A. A smartphone app to extend use of a cloud-based irrigation scheduling tool. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 111, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, S.; Priyatharshini, R. In Smart farming system using sensors for agricultural task automation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Technological Innovation in ICT for Agriculture and Rural Development (TIAR), Chennai, India, 10–12 July 2015; pp. 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, K.; Tanaka, K.; Hariya, R.; Azechi, I.; Iida, T.; Maeda, S.; Kuroda, H. Contribution of ict monitoring system in agricultural water management and environmental conservation. In Serviceology for Designing the Future; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; pp. 359–369. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.P.; Chang, T.K.; Fan, C.; Anthony, J.; Petway, J.R.; Lien, W.Y.; Liang, C.P.; Ho, Y.F. Applications of information and communication technology for improvements of water and soil monitoring and assessments in agricultural areas—A case study in the taoyuan irrigation district. Environments 2017, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.A.; Wang, C.H.; Liao, M.S.; Zheng, X.Y.; Liu, J.H.; Chuang, C.L.; Hung, C.L.; Chen, C.P. A wireless sensor network-based monitoring system with dynamic convergecast tree algorithm for precision cultivation management in orchid greenhouses. Precis. Agric. 2016, 17, 766–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.Y.; Shi, Y.; Tang, H.J.; Yang, P.; Xie, A.K.; Liu, B.; Wu, W.B. eFarm: A tool for better observing agricultural land systems. Sensors 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perea, R.G.; Garcia, I.F.; Arroyo, M.M.; Diaz, J.A.R.; Poyato, E.C.; Montesinos, P. Multiplatform application for precision irrigation scheduling in strawberries. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 183, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, C.; Fonseca, A. New approaches to environmental monitoring: The use of ICT to explore volunteered geographic information. GeoJournal 2008, 72, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gipp, B.; Breitinger, C.; Meuschke, N.; Beel, J. CryptSubmit: Introducing Securely Timestamped Manuscript Submission and Peer Review Feedback using the Blockchain. Available online: https://www.gipp.com/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/gipp2017b.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2017).
- Collier, Z.A.; Bates, M.E.; Wood, M.D.; Linkov, I. Stakeholder engagement in dredged material management decisions. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 496, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marttunen, M.; Belton, V.; Lienert, J. Are objectives hierarchy related biases observed in practice? A meta-analysis of environmental and energy applications of multi-criteria decision analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NGO Monitor. Amnesty International: Failed Methodology, Corruption, and Anti-Israel Bias. 2015. Available online: http://www.ngo-monitor.org/books/amnesty_international_failed_methodology_corruption_and_anti_israel_bias/ (accessed on 2 June 2017).
- Dixon, J.; Richards, C. On food security and alternative food networks: Understanding and performing food security in the context of urban bias. Agric. Hum. Values 2016, 33, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejesus, R.M.; Little, B.B.; Lovell, A.C. Using data mining to detect crop insurance fraud: Is there a role for social scientists? J. Financ. Crime 2005, 12, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yan, J.; Zhang, K.Z. Blockchain-based sharing services: What blockchain technology can contribute to smart cities. Financ. Innov. 2016, 2, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacetera, N.; Zirulia, L. The economics of scientific misconduct. J. Law Econ. Organ. 2011, 27, 568–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, S.; De Filippi, P.; Potts, J. Economics of Blockchain. 2016. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2744751 (accessed on 10 May 2017).
- Wiles, N. The Radical Potential of Blockchain Technology. 2015. Available online: https://www.meetup.com/London-Futurists/events/221734513/ (accessed on 10 May 2017).
- IBM Corporation. Device Democracy: Saving the Future of the Internet of Things. 2015. Available online: http://www-01.ibm.com/common/ssi/cgi-bin/ssialias?htmlfid=GBE03620USEN (accessed on 29 April 2017).
- Nobre, C.A.; Sampaio, G.; Borma, L.S.; Castilla-Rubio, J.C.; Silva, J.S.; Cardoso, M. Land-use and climate change risks in the amazon and the need of a novel sustainable development paradigm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10759–10768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walport, M. Distributed Ledger Technology: Blackett Review. 2016. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/distributed-ledger-technology-blackett-review (accessed on 10 May 2017).
- Bloom, N.; Garicano, L.; Sadun, R.; Van Reenen, J. The distinct effects of information technology and communication technology on firm organization. Manag. Sci. 2014, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreopoulou, Z. Green informatics: Ict for green and sustainability. Agrárinformatika J. Agric. Inform. 2012, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, C.; Fonseca, A.; Camara, A.; Ferreira, F. Promoting the use of environmental data collected by concerned citizens through information and communication technologies. J. Environ. Manag. 2004, 71, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.P.; Deng, D.P.; Lin, W.C.; Lemmens, R.; Crossman, N.D.; Henle, K.; Schmeller, D.S. Uncertainty analysis of crowd-sourced and professionally collected field data used in species distribution models of taiwanese moths. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 181, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banafa, A. IoT and Blockchain Convergence: Benefits and Challenges. 10 January 2017. Available online: http://iot.ieee.org/newsletter/january-2017/iot-and-blockchain-convergence-benefits-and-challenges.html (accessed on 19 May 2017).
- MacNeil, R. Canadian environmental policy under conservative majority rule. Environ. Polit. 2014, 23, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansiti, M.; Lakhani, K.R. The truth about blockchain. Harvard Bus. Rev. 2017, 95, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Back, A.; Corallo, M.; Dashjr, L.; Friedenbach, M.; Maxwell, G.; Miller, A.; Poelstra, A.; Timón, J.; Wuille, P. Enabling Blockchain Innovations with Pegged Sidechains. 2014. Available online: http://www.opensciencereview.com/papers/123/enablingblockchain-innovations-with-pegged-sidechains (accessed on 10 May 2017).
- DNV GL AS. Global Opportunity Report 2017. Available online: http://www.globalopportunitynetwork.org/the-2017-global-opportunity-report.pdf (accessed on 19 May 2017).
- Pazaitis, A.; De Filippi, P.; Kostakis, V. Blockchain and Value Systems in the Sharing Economy: The Illustrative Case of Backfeed. 2017. Available online: https://blog.p2pfoundation.net/blockchain-value-systems-sharing-economy-illustrative-case-backfeed/2017/06/16 (accessed on 10 May 2017).
- Wright, A.; De Filippi, P. Decentralized Blockchain Technology and the Rise of Lex Cryptographia. 2015. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2580664 (accessed on 10 May 2017).
- Sutherland, W.J.; Barnard, P.; Broad, S.; Clout, M.; Connor, B.; Cote, I.M.; Dicks, L.V.; Doran, H.; Entwistle, A.C.; Fleishman, E.; et al. A 2017 horizon scan of emerging issues for global conservation and biological diversity. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2017, 32, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, G. Ethereum: A Secure Decentralised Generalised Transaction Ledger. Ethereum Proj. Yellow Paper, 2014. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/ac15/ea808ef3b17ad754f91d3a00fedc8f96b929.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2017).
- Swan, M. Blockchain thinking: The brain as a DAC (decentralized autonomous organization). In Proceedings of the Texas Bitcoin Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 27–29 March 2015; pp. 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Sanchez, P.; Zafar, M.B.; Kate, A. Listening to whispers of ripple: Linking wallets and deanonymizing transactions in the ripple network. Proc. Priv. Enhanc. Technol. 2016, 2016, 436–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilkington, M. Blockchain technology: Principles and applications. In Research Handbook on Digital Transformations; Edward Elgar: Cheltenham, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Meunier, S. Blockchain Technology—A Very Special Kind of Distributed Database. 29 December 2016. Available online: https://medium.com/@sbmeunier/blockchain-technology-a-very-special-kind-of-distributed-database-e63d00781118 (accessed on 2 June 2017).
- Scott, B. How Can Cryptocurrency and Blockchain Technology Play a Role in Building Social and Solidarity Finance? Unrisd Working Paper. 2016. Available online: http://www.unrisd.org/brett-scott (accessed on 10 May 2017).
- Özsu, M.T.; Valduriez, P. Principles of Distributed Database Systems; Springer Science & Business Media: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shulman, A.; Co-founder, C. How to Mitigate the Most Significant Database Vulnerabilities. Top Ten Database Security Threats. 2006. Available online: http://schell.com/Top_Ten_Database_Threats.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2017).
- Schlanger, Z. Rogue Scientists Race to Save Climate Data from Trump. Available online: https://www.wired.com/2017/01/rogue-scientists-race-save-climate-data-trump/ (accessed on 17 January 2017).
- Malakoff, D.; Cornwall, W. Trump team targets key climate metric. Science 2016, 354, 1364–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.S.; Riske-Morris, M.; Diaz, S.R. Causal factors implicated in research misconduct: Evidence from ori case files. Sci. Eng. Ethics. 2007, 13, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohr, J.R.; McCoy, K.A. Preserving environmental health and scientific credibility: A practical guide to reducing conflicts of interest. Conserv. Lett. 2010, 3, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March for Science. Available online: https://www.marchforscience.com (accessed on 16 April 2017).
- Lewis, D.L. Science for sale: How the us government uses powerful corporations and leading universities to support government policies. In Silence Top Scientists, Jeopardize Our Health, and Protect Corporate Profiles; Skyhorse Publishing Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Forbes, S. How Bitcoin will End World Poverty. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/steveforbes/2015/04/02/how-bitcoin-will-end-world-poverty/2/#211bf31452fc (accessed on 16 April 2017).
- Gupta, V. Building the Hyperconnected Future on Blockchains. World Government Summit, 2017. Available online: http://internetofagreements.com/files/WorldGovernmentSummit-Dubai2017.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2017).
- Hong Kong Monetary Authority. Whitepaper on Distributed Ledger Technology. 2017. Available online: http://www.hkma.gov.hk/media/eng/doc/key-functions/finanical-infrastructure/Whitepaper_On_Distributed_Ledger_Technology.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2017).
- The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; International Telecommunication Union. 2E-Agriculture Strategy Guide Piloted in Asia-Pacific Countries; The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; International Telecommunication Union: Bangkok, Thailand, 2016; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-i5564e.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2017).
- Larsen, K.; Kim, R.; Theus, F. Agribusiness and Innovation Systems in Africa. World Bank Publications, 2009. Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/2643 (accessed on 10 May 2017).
- World Summit on the Information Society. Available online: http://www.itu.int/net/wsis/index.html (accessed on 16 April 2017).
- United States Federal Bureau of Investigation. Smart Farming May Increase Cyber Targeting Against US Food and Agriculture Sector. 2016. Available online: https://publicintelligence.net/fbi-smart-farm-hacking/ (accessed on 2 June 2017).
- Acharya, A.P.; Acharya, A. Cyberterrorism and Biotechnology. Foreign Affairs, 2017. Available online: https://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/world/2017-06-01/cyberterrorism-and-biotechnology (accessed on 2 June 2017).
- Department of Engineering and Irrigation. Council of Agriculture, Executive Yuan Website. Available online: http://doie.coa.gov.tw/english/about-us.asp (accessed on 5 May 2017).
- Suichies, B. Why Blockchain Must Die in 2016. Available online: https://medium.com/@bsuichies/why-blockchain-must-die-in-2016-e992774c03b4 (accessed on 13 April 2017).
- Greenspan, G. Avoiding the Pointless Blockchain Project. Available online: http://www.multichain.com/blog/2015/11/avoiding-pointless-blockchain-project/ (accessed on 14 April 2017).
- Eyal, I.; Gencer, A.E.; Sirer, E.G.; Van Renesse, R. Bitcoin-ng: A scalable blockchain protocol. In Proceedings of the 13th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (NSDI 16), Santa Clara, CA, USA, 16–18 March 2016; pp. 45–59. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo, P. Mike Hearn: Bitcoin Farewell Post was no ‘Banker Conspiracy’. Available online: http://www.coindesk.com/mike-hearn-bitcoin-post-banker-conspiracy/ (accessed on 9 May 2017).
- Sompolinsky, Y.; Zohar, A. Accelerating Bitcoin’s Transaction Processing: Fast Money Grows on Trees, not Chains. 2013. Available online: https://www.smithandcrown.com/open-research/accelerating-bitcoins-transaction-processing-fast-money-grows-on-trees-not-chains/ (accessed on 10 May 2017).
- Buterin, V. Problems in cryptoeconomic research. In Hard Problems in Cryptoeconomics; Taipei Ethereum Event: Taipei, Taiwan, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan, G. Blockchains vs Centralized Databases. Available online: http://www.multichain.com/blog/2016/03/blockchains-vs-centralized-databases/ (accessed on 22 April 2017).
- De Filippi, P. It’s Time to Take Mesh Networks Seriously (and not Just for the Reasons you Think). Available online: https://www.wired.com/2014/01/its-time-to-take-mesh-networks-seriously-and-not-just-for-the-reasons-you-think/ (accessed on 22 April 2017).
- Gcoin. Available online: http://g-coin.org/index.html (accessed on 10 May 2017).
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).