Genotoxic Effects of Water in Aquatic Ecosystems with Varying Cyanobacterial Abundance Assessed Using the Allium Test
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microcosm Organization
2.2. Cyanobacteria Analysis
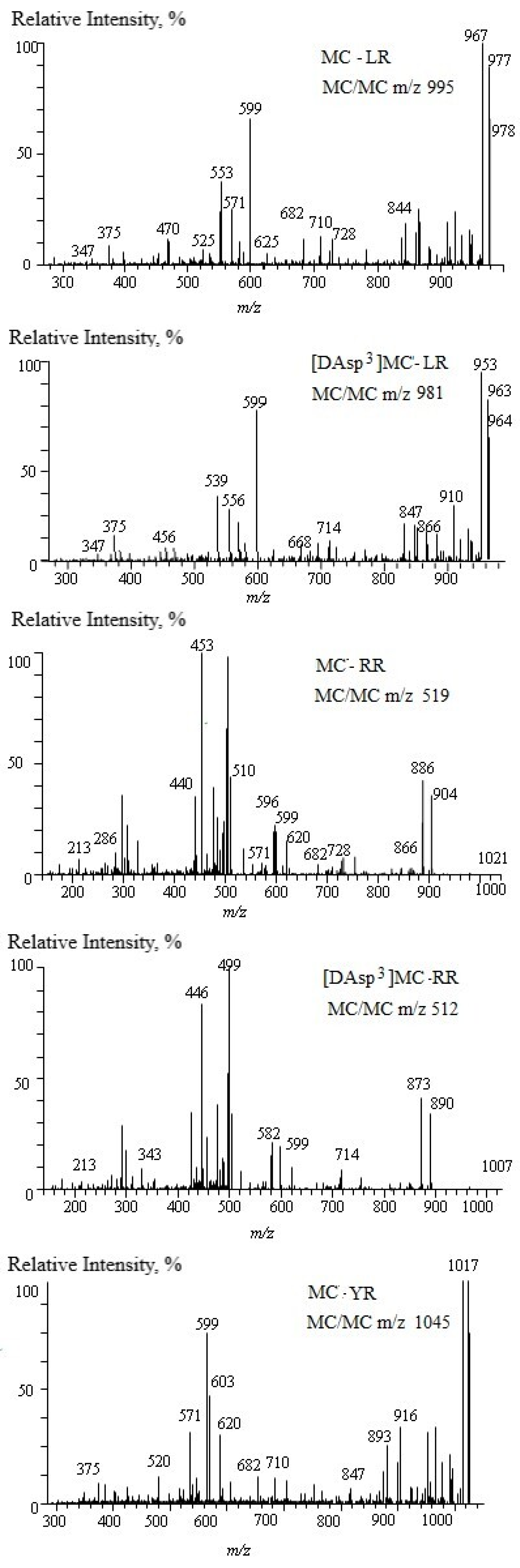
2.3. MCs Analysis
2.4. Allium Cepa Test
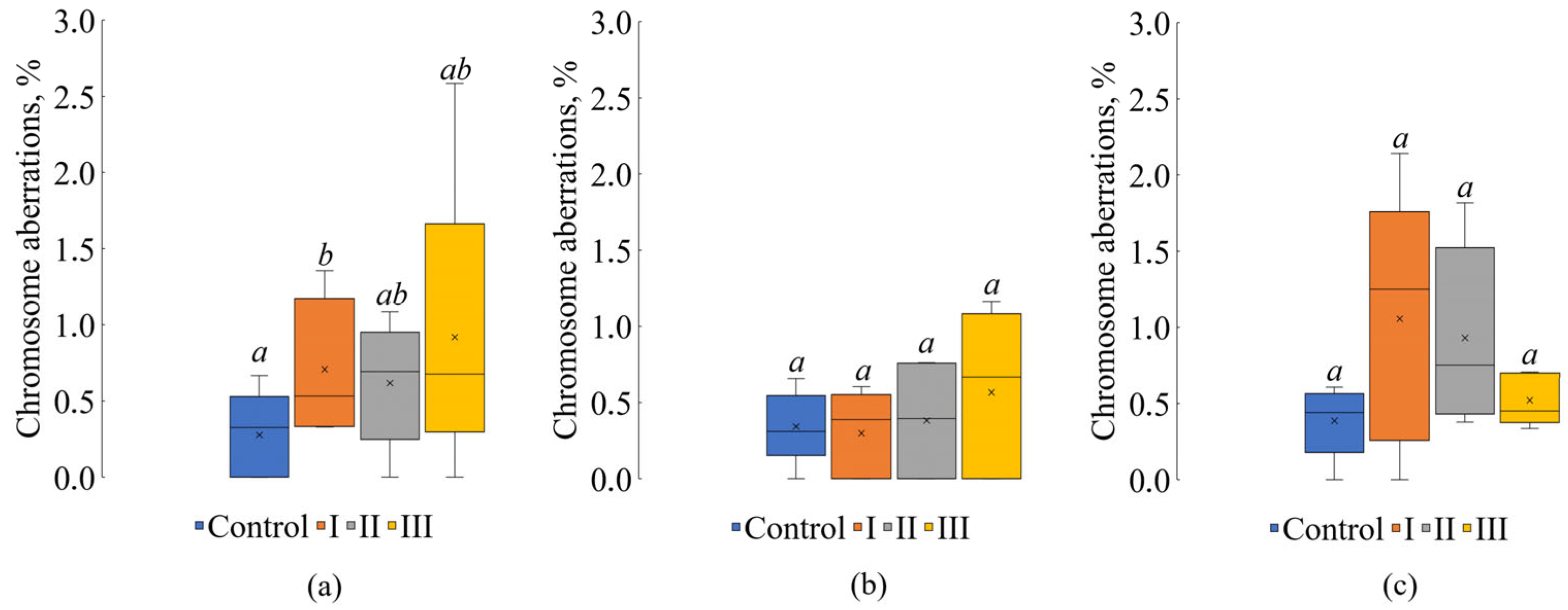
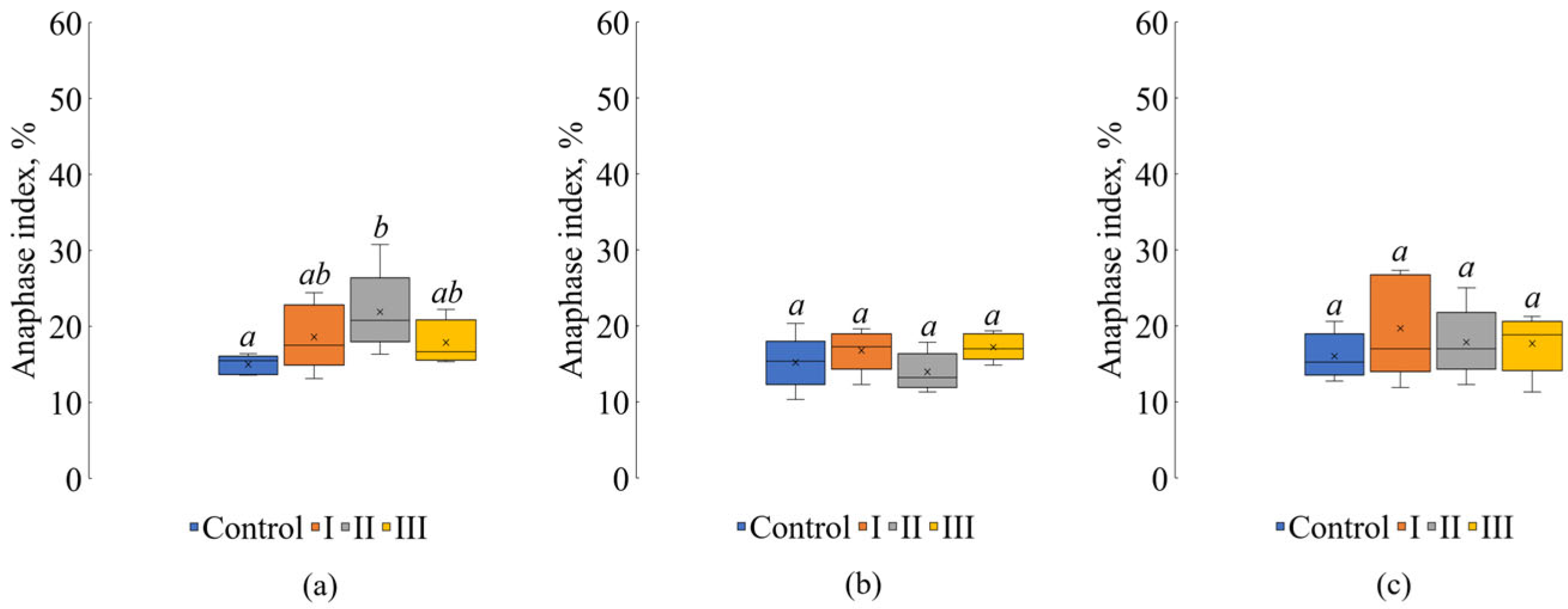
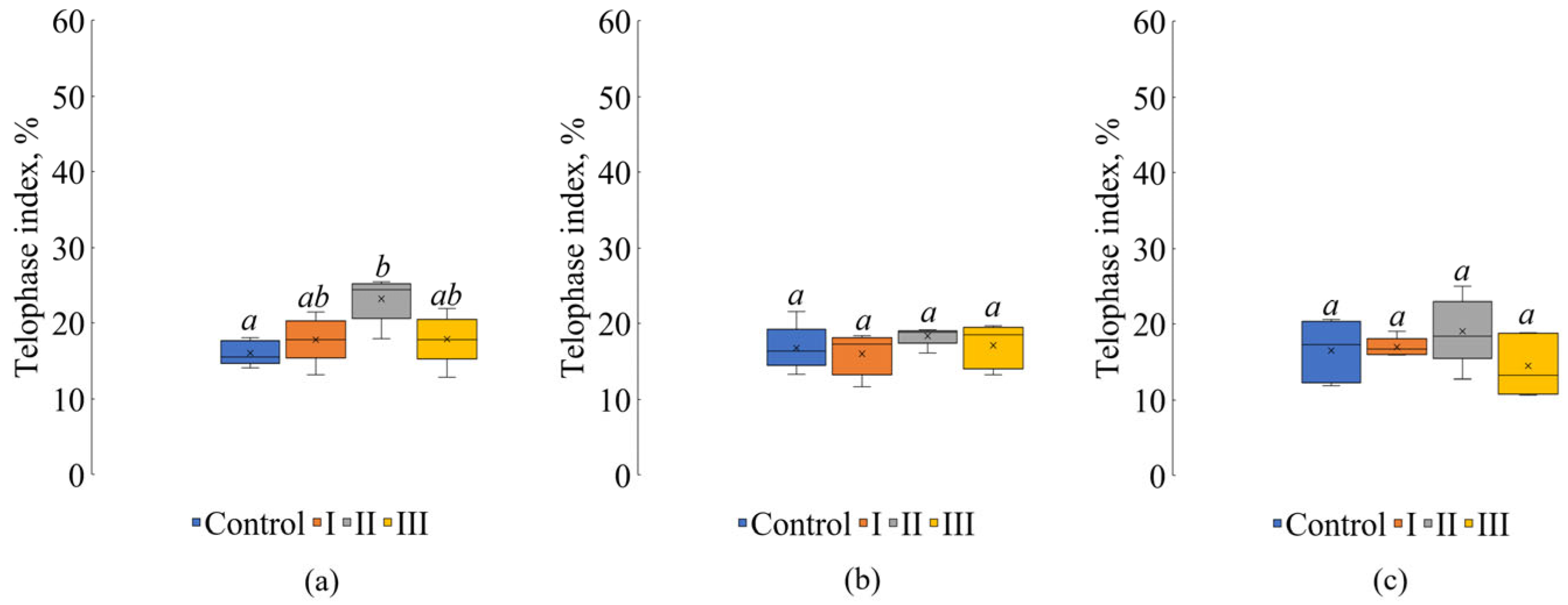
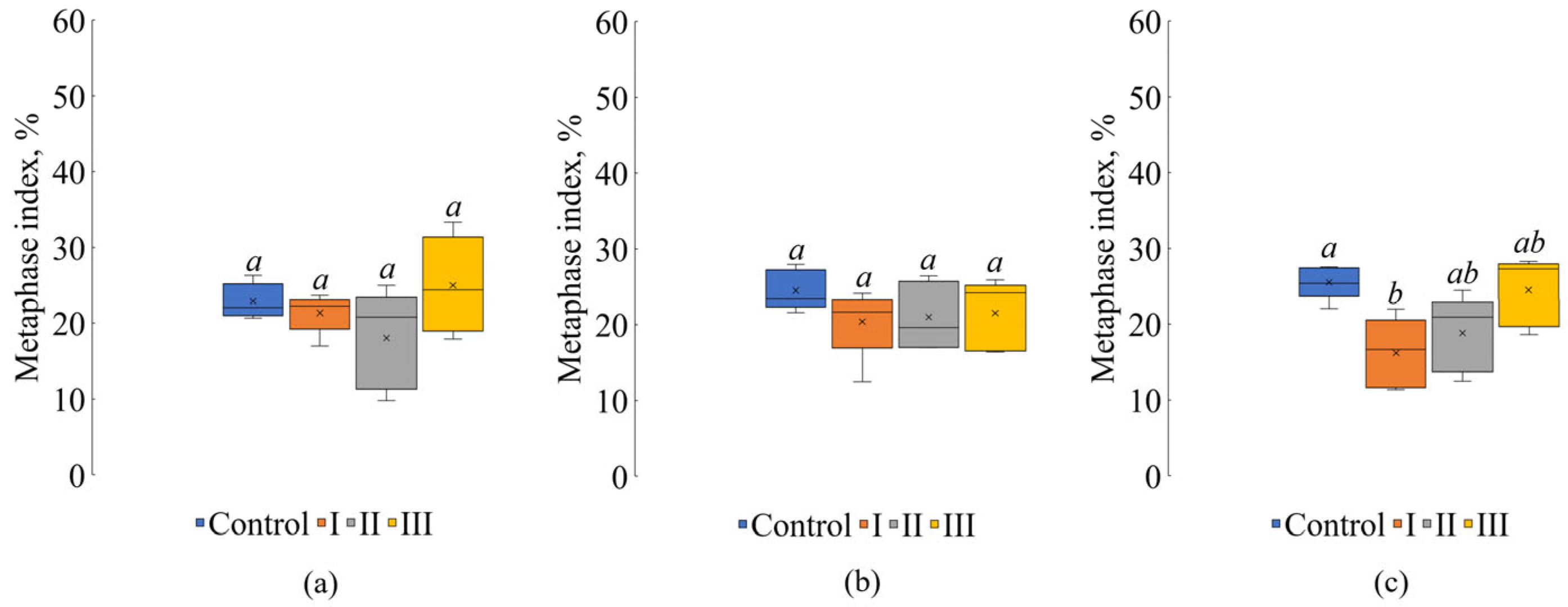
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Wood, R. Acute animal and human poisonings from cyanotoxin exposure—A review of the literature. Environ. Int. 2016, 91, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, F.M.; Manganelli, M.; Vichi, S.; Stefanelli, M.; Scardala, S.; Testai, E.; Funari, E. Cyanotoxins: Producing organisms, occurrence, toxicity, mechanism of action and human health toxicological risk evaluation. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 1049–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svircev, Z.; Drobac, D.; Tokodi, N.; Mijovic, B.; Codd, G.; Meriluoto, J. Toxicology of microcystins with reference to cases of human intoxications and epidemiological investigations of exposures to cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 621–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorova, N.A.; Kuz, N.V.; Sinitsyna, O.O. Materials for the substantiation of the hygienic standard of microcystin-LR in water of water objects. Hyg. Sanit. 2018, 97, 1046–1052. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Lam, P.K.S.; Shaw, G.R.; Wickramasinghe, W. Genotoxicity investigation of a cyanobacterial toxin, cylindrospermopsin. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1499–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Quijada, L.; Hercog, K.; Štampar, M.; Filipič, M.; Cameán, A.M.; Jos, Á.; Žegura, B. Genotoxic effects of cylindrospermopsin, microcystin-LR and their binary mixture in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cell line. Toxins 2020, 12, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, M.; Gao, X.; Giesy, J.P.; Cui, Y.; Yang, L.; Kong, Z. Genotoxicity of crude extracts of cyanobacteria from Taihu Lake on carp (Cyprinus carpio). Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierosławska, A.; Rymuszka, A. Cylindrospermopsin induces oxidative stress and genotoxic effects in the fish CLC cell line. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žegura, B.; Straser, A.; Filipič, M. Genotoxicity and potential carcinogenicity of cyanobacterial toxins—A review. Mutat. Res. 2011, 727, 16–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaïcha, N.; Miles, C.O.; Beach, D.G.; Labidi, Z.; Djabri, A.; Benayache, N.Y.; Nguyen-Quang, T. Structural diversity, characterization and toxicology of microcystins. Toxins 2019, 11, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vankova, D.; Pasheva, M.; Kiselova-Kaneva, Y.; Ivanov, D.; Ivanova, D. Mechanisms of cyanotoxin toxicity—carcinogenicity, anticancer potential, and clinical toxicology. In Medical Toxicology; Pınar, E., Tomohisa, O., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žegura, B. An overview of the mechanisms of microcystin-LR genotoxicity and potential carcinogenicity. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1042–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankiewicz, J.; Walter, Z.; Tarczynska, M.; Palyvoda, O.; Wojtysiak-Staniaszczyk, M.; Zalewski, M. Genotoxicity of cyanobacterial extracts containing microcystins from Polish water reservoirs as determined by SOS chromotest and comet assay. Environ. Toxicol. 2002, 17, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughinghouse, H.D., IV; Prá, D.; Silva-Stenico, M.E.; Rieger, A.; Frescura, V.D.-S.; Fiore, M.F.; Tedesco, S.B. Biomonitoring genotoxicity and cytotoxicity of Microcystis aeruginosa (Chroococcales, Cyanobacteria) using the Allium cepa test. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 432, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierosławska, A.; Rymuszka, A. Assessment of the potential genotoxic and proapoptotic impact of selected cyanotoxins on fish leukocytes. Centr. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 38, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Ingested nitrate and nitrite, and cyanobacterial peptide toxins. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2010; Volume 94, pp. 1–412. [Google Scholar]
- Plata-Calzado, C.; Prieto, A.I.; Cameán, A.M.; Jos, Á. Analytical Methods for Anatoxin-a Determination: A Review. Toxins 2024, 16, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawankar, S.; Masten, S.J.; Lahr, R.H. Review of the Occurrence, Treatment Technologies, and Detection Methods for Saxitoxins in Freshwaters. J. Water Health 2024, 22, 1472–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaram, R.; Newton, A.R.; Lee, A.; Herber, S.; El-Khouri, A.; Chafin, J. A Review of Microcystin and Nodularin Toxins Derived from Freshwater Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms and Their Impact on Human Health. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2024, 16, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, K.A.; Fadul, J.C.; Fiore, M.F.; Pinto, E. A systematic review on guanitoxin: General characteristics and ecological risks. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baunach, M.; Guljamow, A.; Miguel-Gordo, M.; Dittmann, E. Harnessing the potential: Advances in cyanobacterial natural product research and biotechnology. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2024, 41, 347–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugumanova, G.; Ponomarev, E.D.; Askarova, S.; Fasler-Kan, E.; Barteneva, N.S. Freshwater cyanobacterial toxins, cyanopeptides and neurodegenerative diseases. Toxins 2023, 15, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humpage, A.R.; Fontaine, F.; Froscio, S.; Burcham, P.; Falconer, I.R. Cylindrospermopsin genotoxicity and cytotoxicity: Role of cytochrome P-450 and oxidative stress. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2005, 68, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hercog, K.; Maisanaba, S.; Filipič, M.; Jos, Á.; Cameán, A.M.; Žegura, B. Genotoxic potential of the binary mixture of cyanotoxins microcystin–LR and cylindrospermopsin. Chemosphere 2017, 189, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosrovyan, A.; Avalyan, R.; Atoyants, A.; Aghajanyan, E.; Hambaryan, L.; Aroutiounian, R.; Gabrielyan, B. Tradescantia-based test systems can be used for the evaluation of the toxic potential of harmful algal blooms. Water 2023, 15, 2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Máthé, C.; Bóka, K.; Kónya, Z.; Erdődi, F.; Vasas, G.; Freytag, C.; Garda, T. Microcystin-LR, a cyanotoxin, modulates division of higher plant chloroplasts through protein phosphatase inhibition and affects cyanobacterial division. Chemosphere 2024, 358, 142125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhász, G.P.; Kéki, S.; Dékány-Adamoczky, A.; Freytag, C.; Vasas, G.; Máthé, C.; Garda, T. Microcystin-LR, a cyanobacterial toxin, induces changes in the organization of membrane compartments in Arabidopsis. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunsche, L.; Vicari, T.; Calado, S.L.M.; Wojciechowski, J.; Magalhães, V.F.; Assis, H.C.S.; Leme, D.M.; Cestari, M.M. Genotoxicity detected during cyanobacteria bloom in a water supply reservoir. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Contam. 2020, 15, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiskesjö, G. The Allium test as a standard in environmental monitoring. Hereditas 1985, 102, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leme, M.D.; Marin-Morales, M.A. Allium cepa test in environmental monitoring: A review on its application. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2009, 10, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonciu, E.; Firbas, P.; Fontanetti, C.S.; Wusheng, J.; Karaismailoğlu, M.C.; Liu, D.; Menicucci, F.; Popescu, A.; Pesnya, D.S.; Romanovsky, A.V.; et al. An evaluation for the standardization of the Allium cepa test as cytotoxicity and genotoxicity assay. Caryologia 2018, 71, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, J.S.; Codd, G.A. Co-occurrence of cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins with other environmental health hazards: Impacts and implications. Toxins 2020, 12, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesnya, D.S.; Kurbatova, S.A.; Sharov, A.N.; Chernova, E.N.; Yershov, I.Y.; Shurganova, G.V.; Vodeneeva, E.L. Genotoxicity of natural water during the mass development of cyanobacteria evaluated by the Allium test method. Toxins 2022, 14, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamplona-Silva, M.T.; Gonçalves, L.C.; Marin-Morales, M.A. Genetic toxicity of water contaminated by microcystins collected during a cyanobacteria bloom. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 166, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.R.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Boyer, G.L. The fate of microcystins in the environment and challenges for monitoring. Toxins 2014, 6, 3354–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medvedeva, N.G.; Zaytseva, T.B.; Kuzikova, I.L.; Chernova, E.N. Microcystin-LR biodestruction by autochthonous microbiota of different water bodies in the Northwest of Russia. Biol. Bull. 2023, 50, 1376–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painefilú, J.C.; González, C.; Krock, B.; Bieczynski, F.; Luquet, C.M. Microcystin-LR Sensitizes the Oncorhynchus mykiss Intestinal Epithelium and Interacts with Paralytic Shellfish Toxins to Alter Oxidative Balance. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2024, 485, 116891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa, M.G.; Cascajosa-Lira, A.; Prieto, A.I.; Gutiérrez-Praena, D.; Vasconcelos, V.; Jos, A.; Cameán, A.M. Cytotoxic Effects and Oxidative Stress Produced by a Cyanobacterial Cylindrospermopsin Producer Extract versus a Cylindrospermopsin Non-Producing Extract on the Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cell Line. Toxins 2023, 15, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gao, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yang, R.; Geng, R.; Li, R.; Yu, G. Comparative Toxicology of Algal Cell Extracts and Pure Cyanotoxins: Insights into Toxic Effects and Mechanisms of Harmful Cyanobacteria Raphidiopsis raciborskii. Harmful Algae 2024, 135, 102635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chang, X.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Pu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. Exudates of Microcystis aeruginosa on Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Responses in Gills of Sinocyclocheilus grahami. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 280, 116587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falfushynska, H.; Kasianchuk, N.; Siemens, E.; Henao, E.; Rzymski, P. A Review of Common Cyanotoxins and Their Effects on Fish. Toxics 2023, 11, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Chen, X.; Hu, J.; Chang, X.; Qian, Y. Adverse Effects of Microcystis aeruginosa Exudates on the Filtration, Digestion, and Reproduction Organs of the Benthic Bivalve Corbicula fluminea. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrand, H.; Dürselen, C.-D.; Kirschtel, D.; Pollingher, U.; Zohary, T. Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernova, E.; Russkikh, I.; Voyakina, E.; Zhakovskaya, Z. Occurrence of microcystins and anatoxin-a in eutrophic lakes of Saint Petersburg, Northwestern Russia. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2016, 45, 466–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujvárosi, A.Z.; Hercog, K.; Riba, M.; Gonda, S.; Filipič, M.; Vasas, G.; Žegura, B. The cyanobacterial oligopeptides microginins induce DNA damage in the human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cell line. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varriale, F.; Tartaglione, L.; Zervou, S.-K.; Miles, C.O.; Mazur-Marzec, H.; Triantis, T.M.; Kaloudis, T.; Hiskia, A.; Dell’Aversano, C. Untargeted and targeted LC–MS and data processing workflow for the comprehensive analysis of oligopeptides from cyanobacteria. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 137012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, K.; DesRochers, N.; Renaud, J.B.; Sumarah, M.W.; McMullin, D.R. Metabolomics Reveals Strain-Specific Cyanopeptide Profiles and Their Production Dynamics in Microcystis aeruginosa and M. flos-aquae. Toxins 2023, 15, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervou, S.-K.; Hammoud, N.A.; Godin, S.; Hiskia, A.; Szpunar, J.; Lobinski, R. Detection of Secondary Cyanobacterial Metabolites Using LC-HRMS in Lake Karaoun. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thukral, M.; Allen, A.E.; Petras, D. Progress and Challenges in Exploring Aquatic Microbial Communities Using Non-Targeted Metabolomics. ISME J. 2023, 17, 2147–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.B.; Médice, R.V.; Jacinavicius, F.R.; Pinto, E.; Crnkovic, C.M. Metabolomics Applied to Cyanobacterial Toxins and Natural Products. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2023, 1439, 21–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X. Current research scenario for biological effect of exogenous factors on microcystin synthesis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 26190–26201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westrick, J.A.; Szlag, D.C.; Southwell, B.J.; Sinclair, J. A review of cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins removal/inactivation in drinking water treatment. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thawabteh, A.M.; Naseef, H.A.; Karaman, D.; Bufo, S.A.; Scrano, L.; Karaman, R. Understanding the risks of diffusion of cyanobacteria toxins in rivers, lakes, and potable water. Toxins 2023, 15, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, I.-S.; Zimba, P.V. Cyanobacterial bioactive metabolites—A review of their chemistry and biology. Harmful Algae 2019, 83, 42–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faltermann, S.; Zucchi, S.; Kohler, E.; Blom, J.F.; Pernthaler, J.; Fent, K. Molecular effects of the cyanobacterial toxin cyanopeptolin (CP1020) occurring in algal blooms: Global transcriptome analysis in zebrafish embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 149, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowska, N.; Szeląg-Wasielewska, E. Toxic picoplanktonic cyanobacteria—Review. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1497–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earnshaw, C.D.; McMullin, D.R. Cyanopeptolins and anabaenopeptins are the dominant cyanopeptides from Planktothrix strains collected in Canadian lakes. Toxins 2024, 16, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, K.M.; Wright, E.J.; Beach, D.G.; McCarron, P. Multi-class cyanobacterial toxin analysis using hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1738, 465483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacinavicius, F.R.; Campos, T.G.V.; Passos, L.S.; Pinto, E.; Geraldes, V. A Rapid LC–MS/MS Method for Multi-Class Identification and Quantification of Cyanotoxins. Toxicon 2023, 234, 107282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirks, C.; Cappelli, P.; Blomqvist, M.; Ekroth, S.; Johansson, M.; Persson, M.; Drakare, S.; Pekar, H.; Zuberovic Muratovic, A. Cyanotoxin occurrence and diversity in 98 cyanobacterial blooms from Swedish lakes and the Baltic Sea. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Haffar, M.; Fajloun, Z.; Azar, S.; Sabatier, J.-M.; Abi Khattar, Z. Lesser-known cyanotoxins: A comprehensive review of their health and environmental impacts. Toxins 2024, 16, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyak, Y.M.; Polyak, M.S. The role of cyanotoxins in human and animal pathology (a review). J. Microbiol. Epidemiol. Immunobiol. 2022, 99, 231–243. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandberg, A. Literature Review of the Toxicity of Naturally Occurring Cyanotoxins of Drinking Water Relevance; Swedish Agricultural University (SLU): Uppsala, Sweden, 2024; Available online: https://stud.epsilon.slu.se/20120/1/zandberg-a-20240624.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2025).





| Treatment | Sampling Date | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Day 21 | Day 42 | |
| Control | 0.10 ± 0.001 | 0.003 ± 0.001 | 0 |
| I | 57.74 ± 6.10 | 0.33 ± 0.10 | 0.029 ± 0.005 |
| II | 20.28 ± 1.79 | 0.15 ± 0.02 | 0.01 ± 0.002 |
| III | 9.01 ± 0.62 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.003 ± 0.001 |
| Congener | Sampling Day | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 21 | 42 | |||||||
| Treatment | |||||||||
| I | II | III | I | II | III | I | II | III | |
| [D-Asp3]MC-LR | 0.029 ± 0.004 | 0.009 ± 0.002 | - * | - | 0.015 ± 0.003 | 0.009 ± 0.002 | - | - | - |
| MC-LR | 0.127 ± 0.015 | 0.033 ± 0.007 | 0.005 ± 0.001 | 0.006 ± 0.001 | 0.141 ± 0.038 | 0.060 ± 0.014 | - | - | - |
| [D-Asp3]MC-RR | 0.298 ± 0.069 | 0.062 ± 0.012 | 0.006 ± 0.001 | 0.015 ± 0.003 | 0.157 ± 0.032 | 0.080 ± 0.017 | - | 0.013 ± 0.003 | - |
| [D-Asp3]MC-YR | 0.005 ± 0.001 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.005 ± 0.001 | - |
| MC-RR | 0.135 ± 0.024 | 0.029 ± 0.006 | 0.005 ± 0.001 | 0.012 ± 0.002 | 0.134 ± 0.033 | 0.054 ± 0.011 | - | - | - |
| MC-YR | 0.014 ± 0.003 | 0.005 ± 0.001 | - | - | 0.005 ± 0.001 | - | - | 0.007 ± 0.002 | - |
| Total MCs | 0.608 ± 0.116 | 0.138 ± 0.028 | 0.016 ± 0.003 | 0.033 ± 0.006 | 0.452 ± 0.107 | 0.203 ± 0.044 | - | 0.025 ± 0.006 | - |
| Congener | Sampling Day | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 21 | 42 | |||||||
| Treatment | |||||||||
| I | II | III | I | II | III | I | II | III | |
| [D-Asp3]MC-LR | 0.010 ± 0.003 | 0.080 ± 0.015 | 0.036 ± 0.007 | - * | 0.006 ± 0.001 | 0.004 ± 0.001 | - | - | - |
| MC-LR | 0.043 ± 0.009 | 0.322 ± 0.111 | 0.157 ± 0.024 | 0.028 ± 0.006 | 0.092 ± 0.014 | 0.029 ± 0.005 | - | 0.028 ± 0.008 | - |
| [D-Asp3]MC-RR | 0.218 ± 0.057 | 1.700 ± 0.362 | 0.782 ± 0.161 | 0.082 ± 0.014 | 0.067 ± 0.011 | 0.052 ± 0.011 | - | - | - |
| [D-Asp3]MC-YR | 0.004 ± 0.001 | 0.026 ± 0.006 | 0.016 ± 0.002 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| MC-RR | 0.062 ± 0.011 | 0.568 ± 0.121 | 0.281 ± 0.062 | 0.016 ± 0.002 | 0.036 ± 0.007 | 0.008 ± 0.002 | - | - | - |
| MC-YR | 0.008 ± 0.002 | 0.049 ± 0.013 | 0.023 ± 0.004 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 0.011 ± 0.002 | - | - | - | - |
| Total MCs | 0.345 ± 0.083 | 2.745 ± 0.628 | 1.295 ± 0.260 | 0.128 ± 0.023 | 0.212 ± 0.035 | 0.093 ± 0.019 | - | 0.028 ± 0.008 | - |
| Treatment | Sampling Date | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Day 21 | Day 42 | |
| Control | 23.6 ± 0.4 | 19.6 ± 0.5 | 25.8 ± 1.2 |
| I | 11.9 * ± 0.4 | 17.9 ± 0.4 | 17.6 * ± 1.0 |
| II | 17.2 * ± 0.5 | 19.1 ± 0.4 | 17.2 * ± 1.2 |
| III | 16.9 * ± 0.7 | 16.1 * ± 0.4 | 24.5 ± 1.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kurbatova, S.; Pesnya, D.; Sharov, A.; Yershov, I.; Chernova, E.; Fedorov, R.; Semadeni, I.; Shurganova, G. Genotoxic Effects of Water in Aquatic Ecosystems with Varying Cyanobacterial Abundance Assessed Using the Allium Test. Environments 2025, 12, 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12090321
Kurbatova S, Pesnya D, Sharov A, Yershov I, Chernova E, Fedorov R, Semadeni I, Shurganova G. Genotoxic Effects of Water in Aquatic Ecosystems with Varying Cyanobacterial Abundance Assessed Using the Allium Test. Environments. 2025; 12(9):321. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12090321
Chicago/Turabian StyleKurbatova, Svetlana, Dmitry Pesnya, Andrey Sharov, Igor Yershov, Ekaterina Chernova, Roman Fedorov, Ivan Semadeni, and Galina Shurganova. 2025. "Genotoxic Effects of Water in Aquatic Ecosystems with Varying Cyanobacterial Abundance Assessed Using the Allium Test" Environments 12, no. 9: 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12090321
APA StyleKurbatova, S., Pesnya, D., Sharov, A., Yershov, I., Chernova, E., Fedorov, R., Semadeni, I., & Shurganova, G. (2025). Genotoxic Effects of Water in Aquatic Ecosystems with Varying Cyanobacterial Abundance Assessed Using the Allium Test. Environments, 12(9), 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12090321








