Drivers of Mercury Accumulation in Juvenile Antarctic Krill, Epipelagic Fish and Adélie Penguins in Different Regions of the Southern Ocean
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mercury and Methylmercury in the Southern Ocean
3. The Bioconcentration of Mercury in Phytoplankton and Its Transfer to Grazing Zooplankton
4. Higher Contents of Total Mercury and Methylmercury in Juvenile Krill than in Adult Krill
| Location | Maturity/Sex | tHg | MeHg | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| South Orkney Islands | Juvenile | 71 ± 23 | 8 ± 3 | [31] |
| Female | 54 ± 18 | 8 ± 2 | ||
| Male | 48 ± 11 | 8 ± 3 | ||
| South Georgia Island | Juvenile | 14 ± 5 | 8 ± 2 | [31] |
| Female | 6 ± 2 | 2 ± 0.2 | ||
| Male | 7 ± 2 | 3 ± 0.1 | ||
| Antarctic Polar Front | Juvenile | 17 ± 6 | 5 ± 1 | [31] |
| West of Anvers Island (Coastal) | Juvenile | 19.4 ± 13.6 | 1.38 ± 0.89 | [29] |
| Adult | 8.06 ± 1.84 | 0.74 ± 0.53 | ||
| West Antarctic Peninsula Sea Ice Edge (Shelf) | Juvenile | 7.25 ± 1.20 | 1.07 ± 0.25 | [29] |
| Adult | 4.47 ± 1.12 | 1.03 ± 0.24 | ||
| Sea Ice Edge (Slope) | Juvenile | 7.88 ± 7.81 | 1.82 ± 0.47 | |
| Adult | 2.20 ± 0.52 | 0.13 ± 0.06 | ||
| West Antarctic Peninsula | Juvenile | 34 * | 3.25 * | [54] |
| Female | 18 * | 2.01 * | ||
| Male | 18 * | 2.01 * | ||
| N/W Weddell Sea | All specimens | (19–56) 32 | [55] | |
| Ross Sea (Offshore) | All specimens | 77 ± 26 | [14] | |
| Ross Sea/Marguerite Bay/Livingston Island | All specimens | 25 ± 2 | [56] | |
| King George Island | All specimens | 18 ± 5 | [57] | |
| Livingston Island | All specimens | 7 ± 8 | [18] |
5. Plankton Regional Distribution and Mercury Accumulation in Cryopelagic and Epipelagic Fish
6. Adélie Penguins as Biomonitors of the Circumpolar Availability of Mercury
- -
- Within the same marine area, P. adeliae feathers often have lower Hg concentrations than those of other penguin species or flying seabirds, which are likely to feed in deeper waters on organisms of higher trophic levels;
- -
- The mean Hg content of Adélie chick feathers is usually lower than that of adult feathers (0.22 ± 0.08 and 0.49 ± 0.23 µg g−1 dry wt, respectively);
- -
- Overall, differences in the Hg contents between the sexes were not statistically significant;
- -
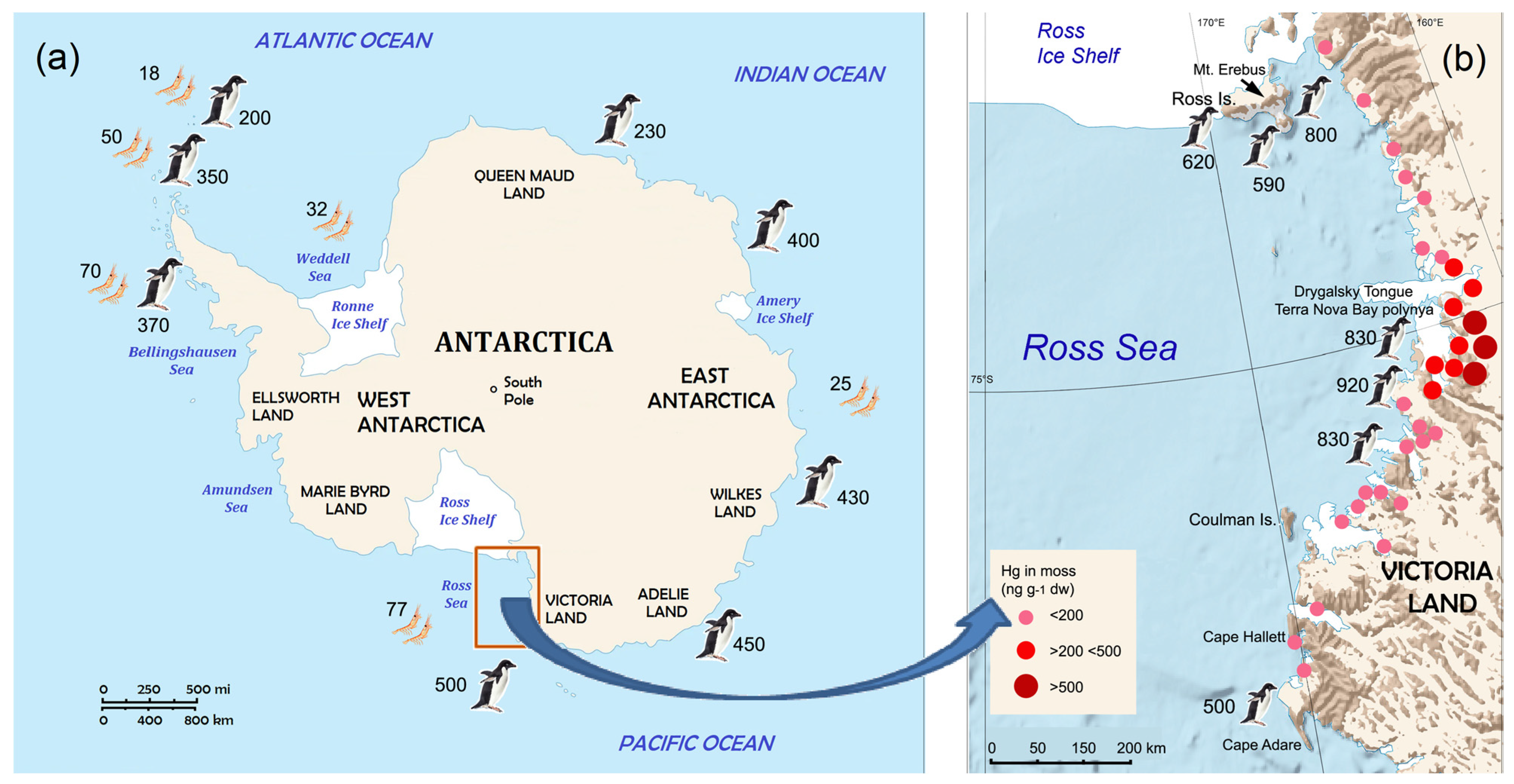
- Samples from East Antarctica had Hg concentrations intermediate between the low values in the Maritime and western Antarctic Peninsula and the highest values in the Ross Sea (Figure 1);
- -
- The highest Hg bioaccumulation in penguins from the Ross Sea was probably due to possible natural sources of Hg and higher fish consumption compared to the other colonies with a krill-dominated diet [22].
7. The Enhanced Bioaccumulation of Hg in the Ross Sea Food Webs
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMDEs | Atmospheric mercury depletion events |
| iHg | Inorganic mercury |
| MeHg | Monomethylmercury |
| tHg | Total mercury |
References
- CCMALR. Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources. Convention Area. 2018. Available online: https://www.ccamlr.org/en/organisation/convention-area (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Rogers, A.D.; Frinault, B.A.V.; Barnes, D.K.A.; Bindoff, N.L.; Downie, R.; Ducklow, H.W.; Friedlaender, A.S.; Hart, T.; Hill, S.L.; Hofmann, E.; et al. Antarctic future: An assessment of climate-driven changes in ecosystem structure, function, and service provisioning in the Southern Ocean. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2020, 12, 87–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargagli, R. Antarctic Ecosystems: Environmental Contamination, Climate Change, and Human Impact; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bargagli, R.; Rota, E. Environmental contamination and climate change in Antarctic ecosystems: An updated overview. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2024, 3, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.; Lu, H.; White, I.; King, J.C.; Phillips, T.; Hosking, J.S.; Bracegirdle, T.J.; Marshall, G.J.; Mulvaney, R.; Deb, P. Absence of 21st century warming on Antarctic Peninsula consistent with natural variability. Nature 2016, 535, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risebrough, R.W.; Rieche, P.; Peakall, D.B.; Herman, S.G.; Kirven, M.N. Polychlorinated biphenyls in the global ecosystem. Nature 1968, 220, 1098–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suttie, E.D.; Wolff, E.W. The local deposition of heavy metal emissions from point sources in Antarctica. Atmos. Environ. 1993, 27, 1833–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargagli, R. Environmental contamination in Antarctic ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herath, I.K.; Ma, H.; Bargagli, R.; Hu, Y.; Hirabayashi, M.; Motoyama, H.; Shi, G. Sources and distribution of trace elements in surface snow from coastal Zhongshan Station to Dome A (East Antarctica). Atmos. Environ. 2024, 331, 120583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, W.; Engstrom, D.R.; Mason, R.P.; Nater, E.A. The case for atmospheric mercury contamination in remote areas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargagli, R.; Monaci, F.; Bucci, C. Environmental biogeochemistry of mercury in Antarctic ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wania, F.; MacKay, D. Tracking the distribution of persistent organic pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 390A–396A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.A.; Schneider, L.; Fostier, A.H.; Guerrero, S.; Davée Guimarães, J.R.; Labuschagne, C.; Leaner, J.J.; Martin, L.G.; Mason, R.P.; Somerset, V.; et al. A synthesis of mercury research in the Southern Hemisphere, part 2: Anthropogenic perturbations. Ambio 2023, 52, 918–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargagli, R.; Monaci, F.; Sanchez-Hernandez, J.C.; Cateni, D. Biomagnification of mercury in an Antarctic marine coastal food web. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1998, 169, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarzynowska, M.; Saniewska, D.; Fudala, K.; Wilman, B.; Balazy, P.; Plońska, P.; Saniewski, M. Mercury and methylmercury in birds and marine mammals inhabiting the coastal zone of the two King George Island’s bays: Admiralty and King George Bay (maritime Antarctic). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 193, 115237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtson Nash, S.M.; Casa, M.V.; Kawaguchi, S.; Staniland, I.; Bjerregaard, P. Mercury levels in humpback whales, and other Southern Ocean marine megafauna. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seco, J.; Aparício, S.; Brierley, A.S.; Bustamante, P.; Ceia, F.R.; Coelho, J.P.; Philips, R.A.; Saunders, R.A.; Fielding, S.; Gregory, S.; et al. Mercury biomagnification in a Southern Ocean food web. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 275, 116620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, R.S.; Guímaro, H.R.; Bustamante, P.; Seco, J.; Chipev, N.; Fragão, J.; Tavares, S.; Ceia, F.R.; Pereira, M.E.; Barbosa, A.; et al. Mercury biomagnification in an Antarctic food web of the Antarctic Peninsula. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 304, 119199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, W.F.; Bustamante, P.; Ramirez, F.; Forero, M.G.; Phillips, R.A. Mercury concentrations in feathers of albatrosses and large petrels at South Georgia: Contemporary patterns and comparisons with past decades. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2024, 86, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasso, R.L.; Chiaradia, A.; Polito, M.J.; Rey, A.R.; Emslie, S.D. A comprehensive assessment of mercury exposure in penguin populations throughout the Southern Hemisphere: Using trophic calculations to identify sources of population-level variation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 97, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilcher, N.; Gaw, S.; Eisert, R.; Horton, T.W.; Gornley, A.M.; Cole, T.L.; Lyver, P.O.B. Latitudinal, sex and inter-specific differences in mercury and other trace metal concentrations in Adélie and Emperor penguins in the Ross Sea, Antarctica. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 154, 111047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusset, F.; Bustamante, P.; Carravieri, A.; Bertin, C.; Brasso, R.; Corsi, I.; Dunn, M.; Emmerson, L.; Guillou, G.; Hart, T.; et al. Circumpolar assessment of mercury contamination: The Adélie penguin as bioindicator of Antarctic marine ecosystems. Ecotoxicology 2023, 32, 1024–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, M.; Rossell, L.; Julià, L.; Giménez, J.; Sanpera, C.; Coll, M.; Bustamante, P.; Ramírez, F. Assessing mercury contamination in Southern Hemisphere marine ecosystems: The role of penguins as effective bioindicators. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 343, 123159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, W.F.; Ibañez, A.; Bustamante, P.; Carneiro, A.; Bearhop, S.; Cherel, Y.; Mariano-Jelicich, R.; McGill, R.A.R.; Montalti, D.; Votier, S.C.; et al. Spatial and sex differences in mercury contamination of skuas in the Southern Ocean. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 297, 118841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Wu, P.; Liu, H.; Lin, L.; Li, D.; Hu, J.; et al. Elevated methylmercury in Antarctic surface seawater: The role of phytoplankton mass and sea ice. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Fisher, N.S. Methylmercury uptake by diverse marine phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 1626–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesán-Onrubia, J.A.; Heimbürger-Boavida, L.-E.; Dufour, A.; Harmelin-Vivien, M.; García-Arévalo, I.; Knoery, J.; Thomas, B.; Carlotti, F.; Tedetti, M.; Bănaru, D. Bioconcentration, bioaccumulation and biomagnification of mercury in plankton of the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 194, 115439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargagli, R.; Rota, E. Mercury biogeochemistry and biomagnification in the Mediterranean Sea: Current knowledge and future prospects in the context of climate change. Coasts 2024, 4, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontag, P.T.; Steinberg, D.K.; Reinfelder, J.R. Patterns of total mercury and methylmercury bioaccumulation in Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) along the West Antarctic Peninsula. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korejwo, E.; Panasiuk, A.; Wawrzynek-Borejko, J.; Jędruch, A.; Bełdowski, J.; Paturej, A.; Bełdowska, M. Mercury concentrations in Antarctic zooplankton with a focus on the krill species, Euphausia superba. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seco, J.; Xavier, J.C.; Coelho, J.P.; Pereira, B.; Tarling, G.; Pardal, M.A.; Bustamante, P.; Stowasser, G.; Brierley, A.S.; Pereira, M.E. Spatial variability in total and organic mercury levels in Antarctic krill Euphausia superba across the Scotia Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapowicz, J.; Szumińska, D.; Szopińska, M.; Polkowska, Ż. The influence of global climate change on the environmental fate of anthropogenic pollution released from permafrost: Part I, case study of Antarctica. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 1534–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumhardt, K.M.; Long, M.C.; Sylvester, Z.T.; Petrik, C.M. Climate drivers of Southern Ocean phytoplankton community composition and potential impacts on higher trophic levels. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 916140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomalla, S.J.; Nicholson, S.-A.; Ryan-Keogh, T.J.; Smith, M.E. Widespread changes in Southern Ocean phytoplankton blooms linked to climate drivers. Nat. Clim. Change 2023, 13, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slemr, F.; Martin, L.; Labuschagne, C.; Mkololo, T.; Angot, H.; Magand, O.; Dommergue, A.; Garat, P.; Ramonet, M.; Bieser, J. Atmospheric mercury in the Southern Hemisphere—Part 1: Trend and inter-annual variations in atmospheric mercury at Cape Point, South Africa in 2007-2017, and on Amsterdam Island in 2012–2017. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 7683–7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unagar, A.; Hashmi, A.; Tiwari, A.K.; Jawak, S.D.; Desai, B.; Urba, A.; Qureshi, A. Coast of Eastern Antarctica as the source of atmospheric mercury during austral summer. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.E.; Angot, H.; Selin, N.E.; Gallée, H.; Sprovieri, F.; Pirrone, N.; Helmig, D.; Savarino, J.; Magand, O.; Dommergue, A. Understanding mercury oxidation and air-snow exchange on the East Antarctic Plateau: A modeling study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 15825–15840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargagli, R. Atmospheric chemistry of mercury in Antarctica and the role of cryptogams to assess deposition patterns in coastal ice-free areas. Chemosphere 2016, 163, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargagli, R.; Agnorelli, C.; Borghini, F.; Monaci, F. Enhanced deposition and bioaccumulation of mercury in Antarctic terrestrial ecosystems facing a coastal polynya. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8150–8155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, F. Enhanced daytime atmospheric mercury in the marine boundary layer in the Southern Ocean. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gworek, B.; Bemowska-Kałabun, O.; Kijeńska, M.; Wrzosek-Jakubowska, J. Mercury in Marine and Oceanic Waters—A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossa, D.; Heimbürger, L.-E.; Lannuzel, D.; Rintoul, S.R.; Butler, E.C.V.; Bowie, A.R.; Averty, B.; Watson, R.J.; Remenyi, T. Mercury in the Southern Ocean. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 4037–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerentorp-Mastromonaco, M.G.; Gårdfeldt, K.; Assmann, K.M.; Langer, S.; Delali, T.; Shlyapnikov, Y.M.; Zivkovic, I.; Horvat, M. Speciation of mercury in the waters of the Weddell, Amundsen and Ross Seas (Southern Ocean). Mar. Chem. 2017, 193, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canário, J.; Santos-Echeandia, J.; Padeiro, A.; Amaro, E.; Strass, V.; Klaas, C.; Hopperna, M.; Ossebaar, S.; Koch, B.P.; Laglera, L.M. Mercury and methylmercury in the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean. Deep-Sea Res. II 2017, 138, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnell, O.; Watras, C.J. Microbial mercury methylation in aquatic environments: A critical review of published field and laboratory studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnherr, I.; St. Louis, V.L.; Hintelmann, H.; Kirk, J.L. Methylation of inorganic mercury in polar marine waters. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, L.C.; Blum, J.D.; Johnson, M.W.; Umhau, B.P.; Popp, B.N.; Washburn, S.J.; Drazen, J.C.; Benitez-Nelson, C.R.; Hannides, C.C.S.; Close, H.G.; et al. Mercury cycling in the North Pacific subtropical gyre as revealed by mercury stable isotope ratios. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2019, 33, 777–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gionfriddo, C.M.; Tate, M.T.; Wick, R.R.; Schultz, M.B.; Zemla, A.; Thelen, M.P.; Schofield, R.; Krabbenhoft, D.P.; Holt, K.E.; Moreau, J.W. Microbial mercury methylation in Antarctic sea ice. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villar, E.; Cabrol, L.; Heimbürger-Boavida, L.-E. Widespread microbial mercury methylation genes in the global ocean. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2020, 12, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangoni, O.; Saggiomo, V.; Bolinesi, F.; Margiotta, F.; Budillon, G.; Cotroneo, Y.; Misic, C.; Rivaro, P.; Saggiomo, M. Phytoplankton blooms during austral summer in the Ross Sea, Antarctica: Driving factors and trophic implications. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, M.; et al. Distributions of nutrients, trace metals, phytoplankton composition, and elemental consumption in the Ross and Amundsen Seas. Mar. Chem. 2024, 265–266, 104436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Hugo, M.A.; Vernet, M.; Martinson, D.; Smith, R.; Iannuzzi, R. Variability on phytoplankton size structure in the western Antarctic Peninsula (1997–2006). Deep Res. Part II 2008, 55, 2106–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberman, K.L.; Ross, R.M.; Quetin, L.B. Diet of the Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba Dana): II. Selective grazing in mixed phytoplankton assemblages. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 283, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer-Locarnini, S.J.; Presley, B.J. Trace element concentrations in Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba. Polar Biol. 1995, 15, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzoeva, N.; Tereshchenko, N.; Paraskiv, A.; Proskurnin, V.; Stetsiuk, A.; Korotkov, A. Metals and metalloids in Antarctic krill and water in deep Weddell Sea areas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 178, 113624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroli, S.; Senofonte, O.; Caimi, S.; Pucci, P.; Pauwels, J.; Kramer, G.N. A pilot study for the preparation of a new Reference Material based on Antarctic krill. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1998, 360, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipro, C.V.Z.; Montone, R.C.; Bustamante, P. Mercury in the ecosystem of Admiralty Bay, King George Island, Antarctica: Occurrence and trophic distribution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargagli, R.; Battisti, E.; Focardi, S.; Formichi, P. Preliminary data on environmental distribution of mercury in northern Victoria Land. Antarct. Sci. 1993, 5, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, J.A.; Steinberg, D.K.; Nardelli, S.C.; Schofield, O. Omnivorous summer feeding by juvenile Antarctic krill in coastal waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2024, 69, 874–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissinotto, R.; Mayzaud, P.; Labat, J.-P.; Razouls, S. Grazing dynamics of Euphausia spinifera in the region of the Subtropical Convergence and the Agulhas Front. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimbürger, L.-E.; Cossa, D.; Marty, J.-C.; Migon, C.; Averty, B.; Dufour, A.; Ras, J. Methyl mercury distributions in relation to the presence of nano- and picophytoplankton in an oceanic water column (Ligurian Sea, North-western Mediterranean). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 5549–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B. The overwintering of Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, from an ecophysiological perspective. Polar Biol. 2012, 35, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Atkinson, A.; Pakhomov, E.A.; Hill, S.L.; Racault, M.-F. Massive circumpolar biomass of Southern Ocean zooplankton: Implications for food web structure, carbon export, and marine spatial planning. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2022, 67, 2516–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasso, R.L.; Lang, J.; Jones, C.D.; Polito, M.J. Ontogenetic niche expansion influences mercury exposure in the Antarctic silverfish Pleuragramma antarcticum. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 504, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmastroni, S.; Fattorini, N.; Pezzo, F.; Focardi, S. Gone fishing: Adélie penguin site-specific foraging and breeding performance. Antarct. Sci. 2020, 32, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutte, A.; Cherel, Y.; Churlaud, C.; Ponthus, J.-P.; Massé, G.; Bustamante, P. Trace elements in Antarctic fish species and the influences of foraging habitats and dietary habits on mercury levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjahrul, M. Studies on the level of heavy metal in the Antarctic fish. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2014, 3, 138–141. [Google Scholar]
- Polito, M.J.; Brasso, R.L.; Trivelpiece, W.Z.; Karnovsky, N.; Patterson, W.P.; Emslie, S.D. Different foraging strategies influence mercury (Hg) exposure in an Antarctic penguin community. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintle, N.J.P.; Sleadd, I.M.; Gundersen, D.T.; Kohl, K.; Buckley, B.A. Total mercury in six Notothenioid fishes. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 95, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cresson, P.; Travers-Trolet, M.; Rouquette, M.; Timmerman, C.-A.; Giraldo, C.; Lefebvre, S.; Ernande, B. Underestimation of chemical contamination in marine fish muscle tissue can be reduced by considering variable wet:dry weight ratios. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 123, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargagli, R.; Rota, E. Mediterranean marine mammals: Possible future trends and threats due to mercury contamination and interactions with other environmental stressors. Animals 2024, 14, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew, D.J. The CCAMLR ecosystem monitoring programme. Antarct. Sci. 1997, 9, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Mesa, M.; Eastman, J.T.; Vacchi, M. The role of notothenioid fish in the food web of the Ross Sea shelf waters: A review. Polar Biol. 2004, 27, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CCAMLR. Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources. Conservation measure 91-05 (2016), Ross Sea Region Marine Protected Area. 2016. Available online: https://cm.ccamlr.org/en/measure-91-05-2016 (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Ainley, D.G. The Adélie Penguin: Bellwether of Climate Change; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Gal, J.-K.; Lee, B.-Y.; Son, W.-J.; Jung, J.-W.; La, H.-S.; Shin, K.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Ha, S.-Y. Regional differences in the diets of Adélie and Emperor penguins in the Ross Sea, Antarctica. Animals 2021, 11, 2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacchi, M.; DeVries, A.L.; Evans, C.W.; Bottaro, M.; Ghigliotti, L.; Cutroneo, L.; Pisano, E. A nursery area for the Antarctic silverfish Pleuragramma antarcticum at Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea): First estimate of distribution and abundance of eggs and larvae under the seasonal sea-ice. Polar Biol. 2012, 35, 1573–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Location | Fish Species | tHg Muscle | tHg Whole Fish | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ross Sea | Pleuragramma antarcticum | 120 ± 70 a | 80 ± 35 a | [64] |
| Adélie Land | Pl. antarcticum | 65 ± 9 | [66] | |
| King George Is. | Pl. antarcticum | 40 ± 10 a | [68] | |
| Syowa Station | Pagothenia borchgrevinki | 26 ± 10 | 13 ± 4 | [67] |
| Adélie Land | P. borchgrevinki | 67 ± 40 | [66] | |
| Ross Sea | P. borchgrevinki | 605 ± 166 a | [69] | |
| Adélie Land | Trematomus newnesi | 79 ± 24 | [66] | |
| Ross Sea | T. newnesi | 545 ± 101 | [69] | |
| Ross Sea | T. newnesi | 290 ± 240 | [14] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bargagli, R.; Rota, E. Drivers of Mercury Accumulation in Juvenile Antarctic Krill, Epipelagic Fish and Adélie Penguins in Different Regions of the Southern Ocean. Environments 2025, 12, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060180
Bargagli R, Rota E. Drivers of Mercury Accumulation in Juvenile Antarctic Krill, Epipelagic Fish and Adélie Penguins in Different Regions of the Southern Ocean. Environments. 2025; 12(6):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060180
Chicago/Turabian StyleBargagli, Roberto, and Emilia Rota. 2025. "Drivers of Mercury Accumulation in Juvenile Antarctic Krill, Epipelagic Fish and Adélie Penguins in Different Regions of the Southern Ocean" Environments 12, no. 6: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060180
APA StyleBargagli, R., & Rota, E. (2025). Drivers of Mercury Accumulation in Juvenile Antarctic Krill, Epipelagic Fish and Adélie Penguins in Different Regions of the Southern Ocean. Environments, 12(6), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060180






