Toxic Phytoplankton in Mussel Farms in the Gulf of Trieste, Adriatic Sea (Italy): A Preliminary Analysis of Long-Term Data (2001–2022) in Relation to Environmental Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Strategy and Analysis
2.3. Database Setting and Statistical Analysis
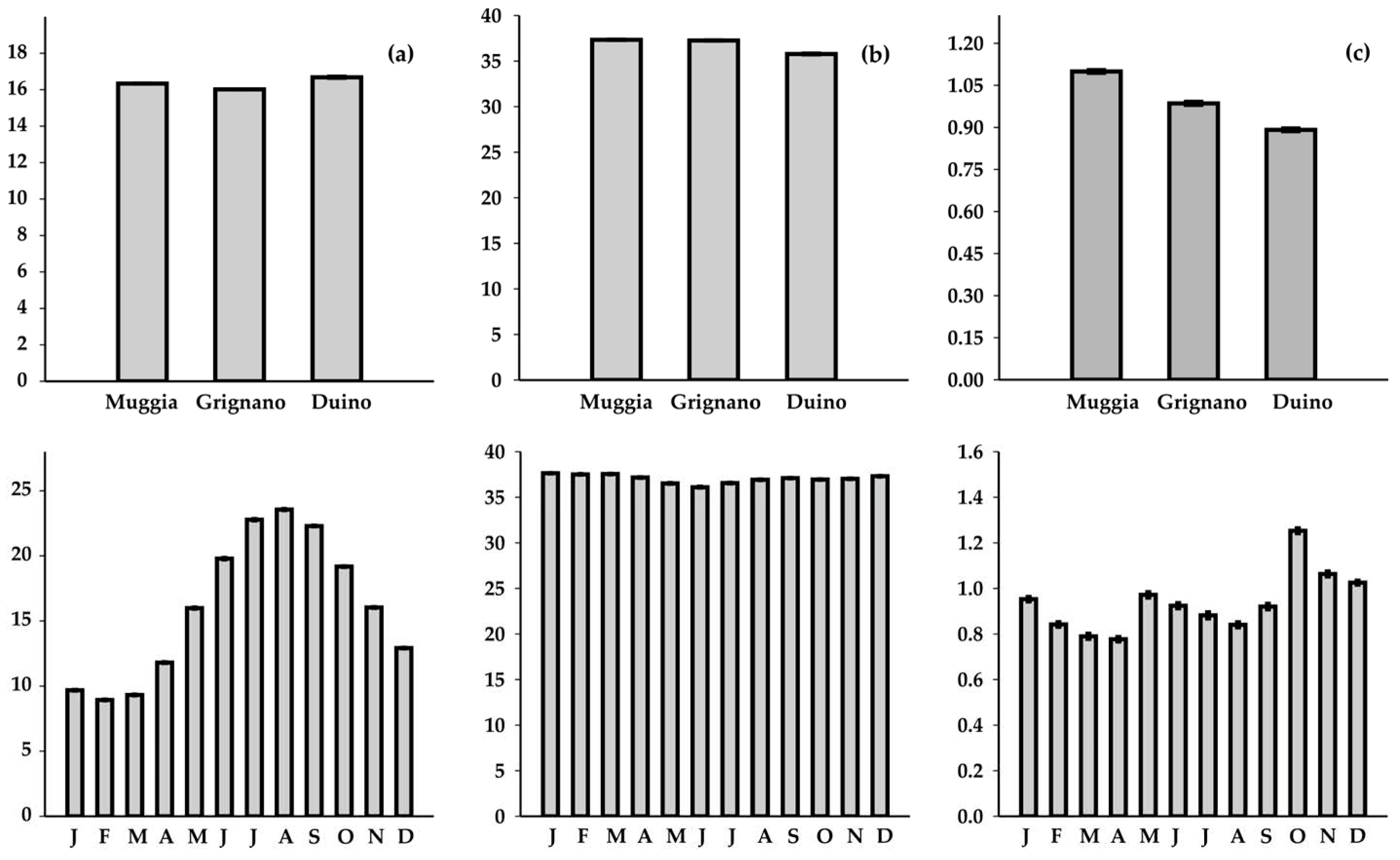
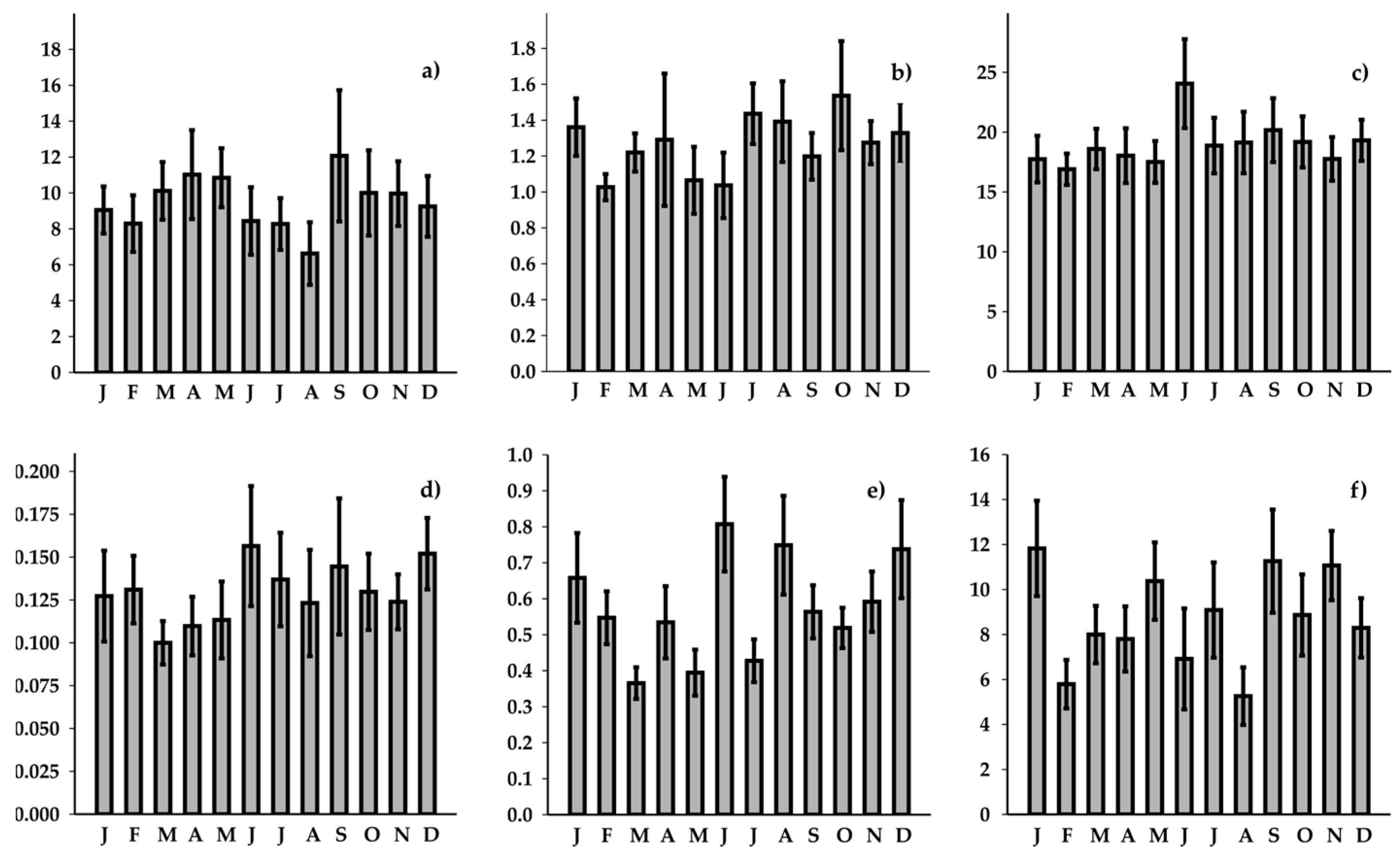
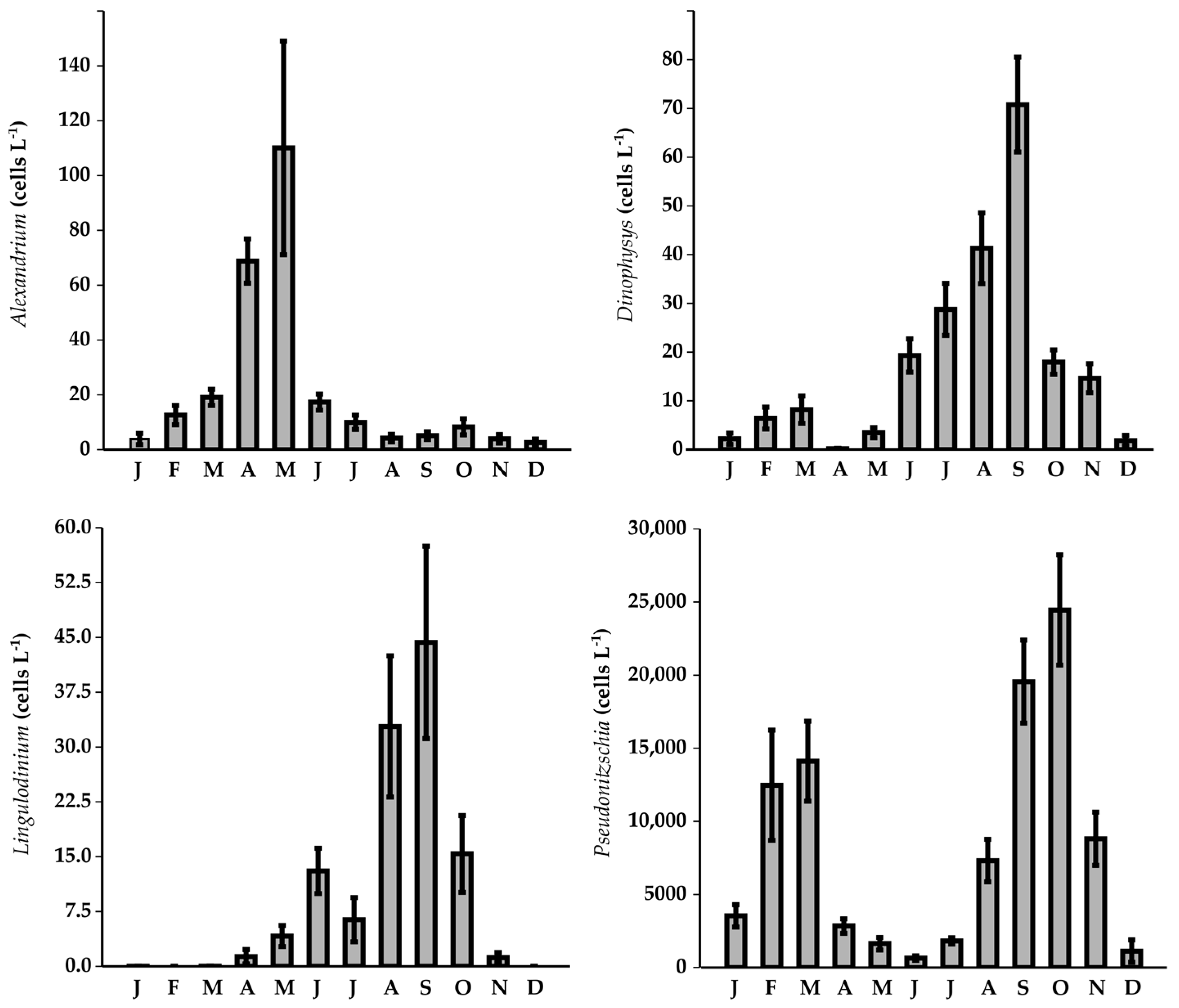
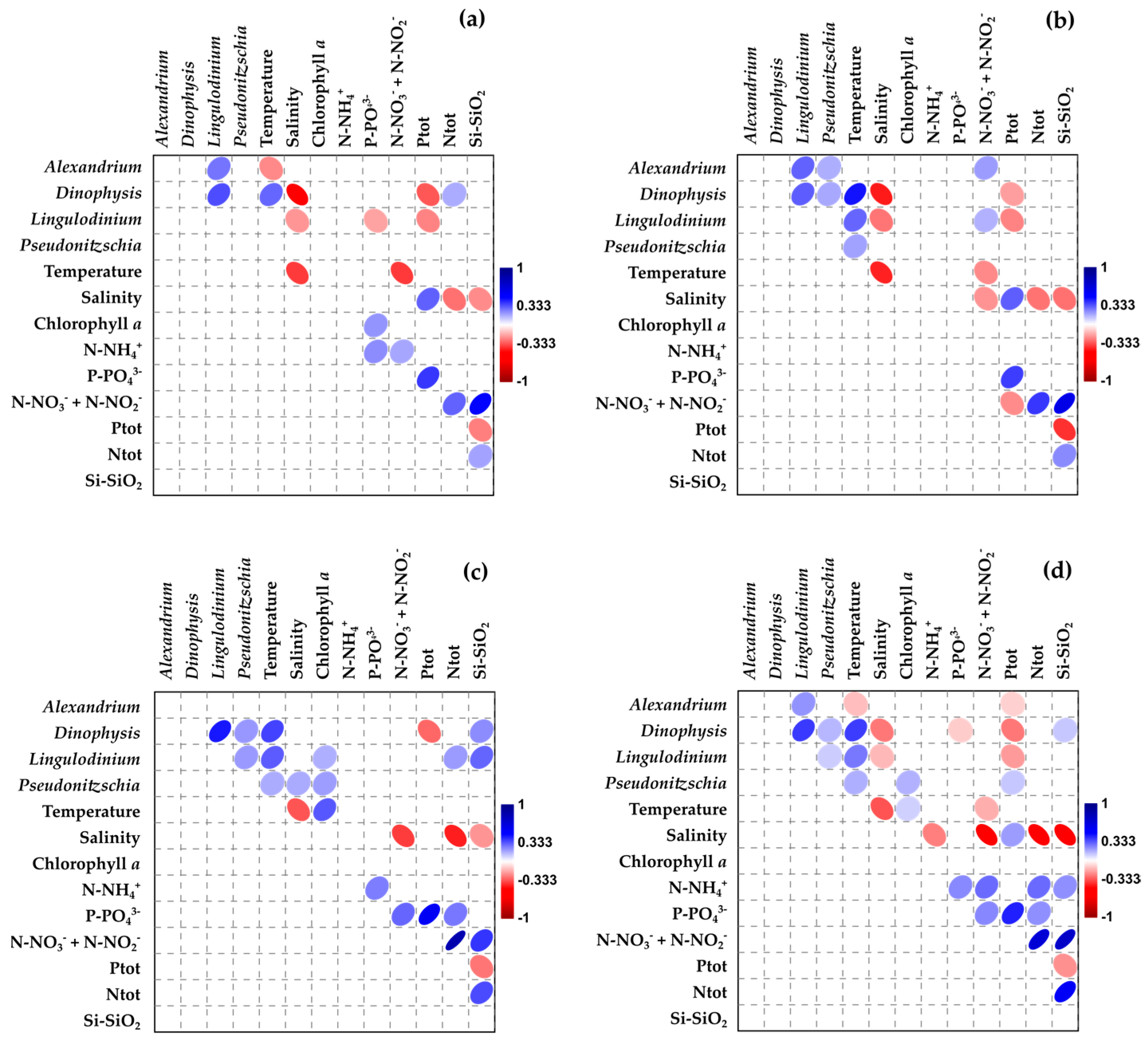
3. Results
3.1. Physico-Chemical Parameters
3.2. Nutrients
3.3. Toxic Phytoplankton
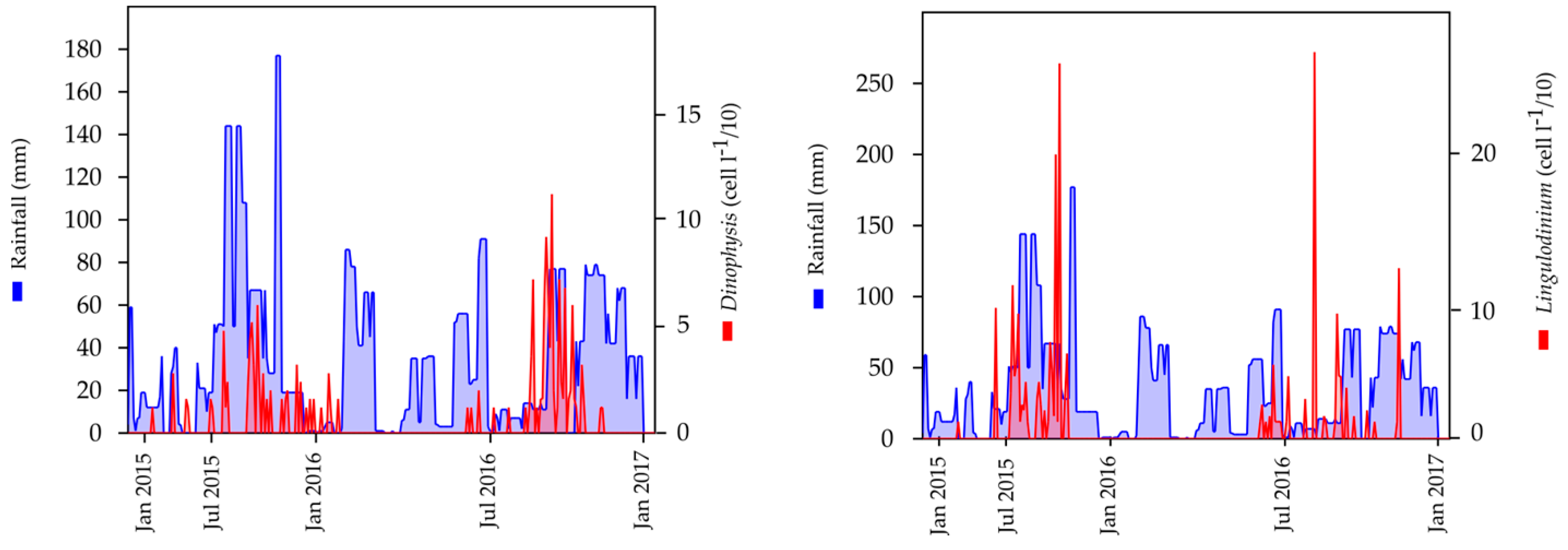
3.4. Analysis of Precipitation
3.5. Relationships Between Variables
4. Discussion
4.1. Physico-Chemical Parameters and Nutrients
4.2. Toxic Phytoplankton
4.3. Correlation of Toxic Phytoplankton with Physico-Chemical Parameters, Nutrients, and Rainfall
4.4. Toxic Phytoplankton and Sampling Techniques
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
- -
- Implementing continuous, in situ measurements (e.g., automated sensors for monitoring the temperature, salinity, chlorophyll a concentration, and turbidity) would enable the real-time detection of environmental shifts that precede bloom events;
- -
- Developing and calibrating hydrodynamic models integrated with phytoplankton dynamics can improve forecasts on bloom formation, spread, and persistence. The adoption of machine learning algorithms, particularly explainable models, should be further explored to enhance transparency and stakeholder confidence in early warning systems;
- -
- Long-term, cross-border collaboration in regard to data collection and the harmonisation of sampling protocols will be critical to ensure comparability and broader applicability of predictive tools;
- -
- Interdisciplinary studies that include economic risk assessments, especially for the aquaculture sector, can support evidence-based decision making and adaptive management under future climate scenarios.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lassus, P.; Chomérat, N.; Hess, P.; Nézan, E. Toxic and Harmful Microalgae of the World Ocean/Micro-Algues Toxiques et Nuisibles de l’océan Mondial; Manuals and guides/IOC; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2016; ISBN 978-87-990827-6-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hasle, G.R.; Syvertsen, E.E.; Steidinger, K.A.; Tangen, K.; Tomas, C.R. Identifying Marine Diatoms and Dinoflagellates; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Valbi, E.; Ricci, F.; Capellacci, S.; Casabianca, S.; Scardi, M.; Penna, A. A Model Predicting the PSP Toxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium Minutum Occurrence in the Coastal Waters of the NW Adriatic Sea. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- France, J.; Mozetič, P. Ecological Characterization of Toxic Phytoplankton Species (Dinophysis Spp., Dinophyceae) in Slovenian Mariculture Areas (Gulf of Trieste, Adriatic Sea) and the Implications for Monitoring. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 1504–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, B.; Daranas, A.H.; Norte, M.; Riobó, P.; Franco, J.M.; Fernández, J.J. Yessotoxins, a Group of Marine Polyether Toxins: An Overview. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 73–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, S.S.; Hubbard, K.A.; Lundholm, N.; Montresor, M.; Leaw, C.P. Pseudo-Nitzschia, Nitzschia, and Domoic Acid: New Research since 2011. Harmful Algae 2018, 79, 3–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.-W.; Pushparaj, S.S.C.; Muthu, M.; Gopal, J. Review of Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs) Causing Marine Fish Kills: Toxicity and Mitigation. Plants 2023, 12, 3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, S.; Brown, C.E.; Garcia Diaz, M.; O’Leary, H.; Solís, D. Non-Linear Impacts of Harmful Algae Blooms on the Coastal Tourism Economy. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, L. Clearance Rate Responses of Mediterranean Mussels, Mytilus Galloprovincialis, to Variations in the Flow, Water Temperature, Food Quality and Quantity. Aquat. Living Resour. 1999, 12, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curpan, A.-S.; Impellitteri, F.; Plavan, G.; Ciobica, A.; Faggio, C. Review: Mytilus Galloprovincialis: An Essential, Low-Cost Model Organism for the Impact of Xenobiotics on Oxidative Stress and Public Health. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 256, 109302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaku Canu, D.; Solidoro, C. Socio-Economic Analysis and Stakeholder Involvement: Mussel-Farming in the Gulf of Trieste. Mar. Policy 2014, 43, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solidoro, C.; Del Negro, P.; Mosetti, R.; De Walderstein, W.; Gomes Ferreira, J.; Zentilin, A.; Bricelj, A.; Beran, A.; Libralato, S.; Melaku Canu, D.; et al. Sostenibilità Della Mitilicoltura Triestina; Istituto Nazionale di Oceanografia e di Geofisica Sperimentale: Borgo Grotta Gigante, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2019/627 of 15 March 2019 Laying down Uniform Practical Arrangements for the Performance of Official Controls on Products of Animal Origin Intended for Human Consumption in Accordance with Regulation (EU) 2017/625 of the European Parliament and of the Council and Amending Commission Regulation (EC) No 2074/2005 as Regards Official Controls. Off. J. Eur. Union 2019, 131, 51–100. [Google Scholar]
- Henigman, U.; Mozetič, P.; Francé, J.; Knific, T.; Vadnjal, S.; Dolenc, J.; Kirbiš, A.; Biasizzo, M. Okadaic Acid as a Major Problem for the Seafood Safety (Mytilus Galloprovincialis) and the Dynamics of Toxic Phytoplankton in the Slovenian Coastal Sea (Gulf of Trieste, Adriatic Sea). Harmful Algae 2024, 135, 102632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karydis, M. Toxic Phytoplankton in Eutrophic Regional Seas: An Overview. Glob. NEST J. 2023, 25, 178–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M. Harmful Algae at the Complex Nexus of Eutrophication and Climate Change. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobler, C.J. Climate Change and Harmful Algal Blooms: Insights and Perspective. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heneash, A.M.M.; Tadrose, H.R.Z.; Hussein, M.M.A.; Hamdona, S.K.; Abdel-Aziz, N.; Gharib, S.M. Potential Effects of Abiotic Factors on the Abundance and Distribution of the Plankton in the Western Harbour, South-Eastern Mediterranean Sea, Egypt. Oceanologia 2015, 57, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakulovic, D.; Gvozdenovic, S.; Joksimovic, D.; Mandic, M.; Pestoric, B. Toxic and Potentially Toxic Phytoplankton in the Mussel and Fish Farms in the Transitional Area of Montenegrin Coast (South-Eastern Adriatic Sea). Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 17, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamvakis, A.; Tsirtsis, G.; Karydis, M.; Patsidis, K.; Kokkoris, G.D. Drivers of Harmful Algal Blooms in Coastal Areas of Eastern Mediterranean: A Machine Learning Methodological Approach. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2021, 18, 6484–6505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikoti, C.; Genitsaris, S. Review of Harmful Algal Blooms in the Coastal Mediterranean Sea, with a Focus on Greek Waters. Diversity 2021, 13, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karydis, M.; Kitsiou, D. Eutrophication and Environmental Policy in the Mediterranean Sea: A Review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 4931–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivotti, R.; Faganeli, J.; Malej, A. Eutrophication of Coastal Waters–Gulf of Trieste. Water Sci. Technol. 1986, 18, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, S.; Mistaro, A.; Sparnocchia, S.; Colugnati, L.; Bajt, O.; Toniatti, L. Anthropogenic Loads and Biogeochemical Role of Urea in the Gulf of Trieste. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malej, A.; Malacic, V. Factors Affecting Bottom Layer Oxygen Depletion in the Gulf of Trieste(Adriatic Sea). Ann. An. Istrske Mediter. Stud. (Hist. Nat.) 1995, 6, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Comici, C.; Bussani, A. Analysis of the River Isonzo Discharge (1998–2005). Boll. Geofis. Teor. Appl. 2007, 48, 435–454. [Google Scholar]
- Cozzi, S.; Giani, M. River Water and Nutrient Discharges in the Northern Adriatic Sea: Current Importance and Long Term Changes. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 1881–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, V.; Mozetic, P.; Malej, A. Overview of Eutrophication-Related Events and Other Irregular Episodes in Slovenian Sea (Gulf of Trieste, Adriatic Sea). In Annales: Series Historia Naturalis; Scientific and Research Center of the Republic of Slovenia: Koper, Slovenia, 2007; Volume 17, p. 197. [Google Scholar]
- Malej, A.; Mozetic, P.; Malacic, V.; Terzic, S.; Ahel, M. Phytoplankton Responses to Freshwater Inputs in a Small Semi-Enclosed Gulf (Gulf of Trieste, Adriatic Sea). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 120, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stravisi, F. Some Characteristics of the Circulation in the Gulf of Trieste. Thalass. Jugosl. 1983, 19, 355–363. [Google Scholar]
- Stravisi, F. The Vertical Structure Annual Cycle of the Mass Field Parameters in the Gulf of Trieste. Boll. Oceanogr. Teor. Appl. 1983, 3, 239–250. [Google Scholar]
- Boldrin, A.; Carniel, S.; Giani, M.; Marini, M.; Bernardi Aubry, F.; Campanelli, A.; Grilli, F.; Russo, A. Effects of Bora Wind on Physical and Biogeochemical Properties of Stratified Waters in the Northern Adriatic. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2009, 114, C08S92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, M.; Fernetti, M.; Busetti, M.; Ghribi, M.; Camerlenghi, A. Multicriteria GIS-Based Analysis for the Evaluation of the Vulnerability of the Marine Environment in the Gulf of Trieste (North-Eastern Adriatic Sea) for Sustainable Blue Economy and Maritime Spatial Planning. People Nat. 2023, 5, 2006–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giani, M.; Djakovac, T.; Degobbis, D.; Cozzi, S.; Solidoro, C.; Umani, S.F. Recent Changes in the Marine Ecosystems of the Northern Adriatic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 115, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malačič, V.; Celio, M.; Čermelj, B.; Bussani, A.; Comici, C. Interannual Evolution of Seasonal Thermohaline Properties in the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic) 1991–2003. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, 2005JC003267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama, J.C. The Simultaneous Analysis of Total Nitrogen and Total Phosphorus in Natural Waters. Mar. Chem. 1981, 10, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasshoff, K.; Kremling, K.; Ehrhardt, M. Methods of Seawater Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zingone, A.; Totti, C.; Sarno, D.; Cabrini, M.; Caroppo, C.; Giacobbe, M.; Lugliè, A.; Nuccio, C.; Socal, G. CAPITOLO 21. FITOPLANCTON: METODICHE DI ANALISI QUALI-QUAN-TITATIVA. In Metodologie di Studio del Plancton Marino; ISPRA: Rome, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Uthermöhl, H. On the Perfecting of Quantitative Phytoplankton Method. Int. Assoc. Theor. Appl. Limnol. Commun. 1958, 9, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, O.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Schlitzer, R.; Anderson, R.; Dodas, E.; Lohan, M.; Geibert, W.; Tagliabue, A.; Schlitzer, R.; Cullen, J.T.; Janssen, D.J.; Velazquez, S.; et al. UVicSPACE: Research & Learning Repository. Chem. Geol. 2018, 493, 210–223. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An Analysis of Variance Test for Normality (Complete Samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis; Pearson Education India: Noida, India, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Grubbs, F.E. Sample Criteria for Testing Outlying Observations; University of Michigan: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Press, W.; Teukolsky, S.; Vetterling, W.; Flannery, B. Numerical Recipes in C, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, R.O. Statistical Methods for Environmental Pollution Monitoring; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Redfield, A.C. The Biological Control of Chemical Factors in the Environment. Sci. Prog. 1960, 11, 150–170. [Google Scholar]
- Ragkos, A.; Skordos, D.; Koutouzidou, G.; Giantsis, I.A.; Delis, G.; Theodoridis, A. Socioeconomic Appraisal of an Early Prevention System against Toxic Conditions in Mussel Aquaculture. Animals 2022, 12, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socal, G.; Boldrin, A.; Bianchi, F.; Civitarese, G.; De Lazzari, A.; Rabitti, S.; Totti, C.; Turchetto, M.M. Nutrient, Particulate Matter and Phytoplankton Variability in the Photic Layer of the Otranto Strait. J. Mar. Syst. 1999, 20, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, L.; Sarno, D.; Procaccini, G.; Poletti, R.; Dahlmann, J.; Montresor, M. Toxic Pseudo-Nitzschia Multistriata (Bacillariophyceae) from the Gulf of Naples: Morphology, Toxin Analysis and Phylogenetic Relationships with Other Pseudo-Nitzschia Species. Eur. J. Phycol. 2002, 37, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga, I. Pseudo-Nitzschia Blooms in the Bay of Banyuls-Sur-Mer, Northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Diatom Res. 2006, 21, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosak, S.; Burić, Z.; Djakovac, T.; Viličić, D. Seasonal Distribution of Plankton Diatoms in Lim Bay, Northeastern Adriatic Sea. Acta Bot. Croat. 2009, 68, 351–365. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, M.L.; Trainer, V.L.; Smayda, T.J.; Karlson, B.S.O.; Trick, C.G.; Kudela, R.M.; Ishikawa, A.; Bernard, S.; Wulff, A.; Anderson, D.M.; et al. Harmful Algal Blooms and Climate Change: Learning from the Past and Present to Forecast the Future. Harmful Algae 2015, 49, 68–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botana, L.M. Toxicological Perspective on Climate Change: Aquatic Toxins. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2016, 29, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henson, S.A.; Cael, B.B.; Allen, S.R.; Dutkiewicz, S. Future Phytoplankton Diversity in a Changing Climate. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edullantes, B.; Low-Decarie, E.; Steinke, M.; Cameron, T. Comparison of Thermal Traits between Non-Toxic and Potentially Toxic Marine Phytoplankton: Implications to Their Responses to Ocean Warming. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2023, 562, 151883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcamo, J.; Olesen, J.E. Life in Europe Under Climate Change; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Marullo, S.; Artale, V.; Santoleri, R. The SST Multidecadal Variability in the Atlantic–Mediterranean Region and Its Relation to AMO. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 4385–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, A. Timescales, Dynamics, and Ecological Understanding. Ecology 2010, 91, 3471–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossarini, G.; Solidoro, C.; Umani, S.F. Dynamics of Biogeochemical Properties in Temperate Coastal Areas of Freshwater Influence: Lessons from the Northern Adriatic Sea (Gulf of Trieste). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 115, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, S.; Falconi, C.; Comici, C.; Čermelj, B.; Kovac, N.; Turk, V.; Giani, M. Recent Evolution of River Discharges in the Gulf of Trieste and Their Potential Response to Climate Changes and Anthropogenic Pressure. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 115, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchettin, D.; Traverso, P.; Tomasino, M. Po River Discharges: A Preliminary Analysis of a 200-Year Time Series. Clim. Change 2008, 89, 411–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solidoro, C.; Bastianini, M.; Bandelj, V.; Codermatz, R.; Cossarini, G.; Melaku Canu, D.; Ravagnan, E.; Salon, S.; Trevisani, S. Current State, Scales of Variability, and Trends of Biogeochemical Properties in the Northern Adriatic Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2009, 114, C07S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozetič, P.; Solidoro, C.; Cossarini, G.; Socal, G.; Precali, R.; Francé, J.; Bianchi, F.; De Vittor, C.; Smodlaka, N.; Fonda Umani, S. Recent Trends Towards Oligotrophication of the Northern Adriatic: Evidence from Chlorophyll a Time Series. Estuaries Coasts 2010, 33, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipizer, M.; De Vittor, C.; Falconi, C.; Comici, C.; Tamberlich, F.; Giani, M. Effects of Intense Physical and Biological Forcing Factors on CNP Pools in Coastal Waters (Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 115, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollenweider, R.; Giovanardi, F.; Montanari, G.; Rinaldi, A. Characterization of the Trophic Conditions of Marine Coastal Waters with Special Reference to the NW Adriatic Sea: Proposal for a Trophic Scale, Turbidity and Generalized Water Quality Index. Environmetrics Off. J. Int. Environmetrics Soc. 1998, 9, 329–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettine, M.; Casentini, B.; Fazi, S.; Giovanardi, F.; Pagnotta, R. A Revisitation of TRIX for Trophic Status Assessment in the Light of the European Water Framework Directive: Application to Italian Coastal Waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1413–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry, F.B.; Cossarini, G.; Acri, F.; Bastianini, M.; Bianchi, F.; Camatti, E.; De Lazzari, A.; Pugnetti, A.; Solidoro, C.; Socal, G. Plankton Communities in the Northern Adriatic Sea: Patterns and Changes over the Last 30 Years. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 115, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, S.; Cabrini, M.; Kralj, M.; De Vittor, C.; Celio, M.; Giani, M. Climatic and Anthropogenic Impacts on Environmental Conditions and Phytoplankton Community in the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic Sea). Water 2020, 12, 2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantoni, C.; Cozzi, S.; Pecchiar, I.; Cabrini, M.; Mozetič, P.; Catalano, G.; Umani, S.F. Short-Term Variability of Primary Production and Inorganic Nitrogen Uptake Related to the Environmental Conditions in a Shallow Coastal Area (Gulf of Trieste, N Adriatic Sea). Oceanol. Acta 2003, 26, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozetič, P.; Francé, J.; Kogovšek, T.; Talaber, I.; Malej, A. Plankton Trends and Community Changes in a Coastal Sea (Northern Adriatic): Bottom-up vs. Top-down Control in Relation to Environmental Drivers. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 115, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, S.; Reisenhofer, E.; Di Monte, L.; Cantoni, C.; Adami, G. Effect of Environmental Forcing on the Fate of Nutrients, Dissolved Organic Matter and Heavy Metals Released by a Coastal Wastewater Pipeline. Chem. Ecol. 2008, 24, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozetič, P.; Malačič, V.; Turk, V. A Case Study of Sewage Discharge in the Shallow Coastal Area of the Northern Adriatic Sea (Gulf of Trieste). Mar. Ecol. 2008, 29, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scroccaro, I.; Ostoich, M.; Umgiesser, G.; De Pascalis, F.; Colugnati, L.; Mattassi, G.; Vazzoler, M.; Cuomo, M. Submarine Wastewater Discharges: Dispersion Modelling in the Northern Adriatic Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2010, 17, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malej, A.; MozetiČ, P.; MalaČČ, V.; Turk, V. Response of Summer Phytoplankton to Episodic Meteorological Events (Gulf of Trieste, Adriatic Sea). Mar. Ecol. 1997, 18, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faganeli, J.; Ogrinc, N. Oxic–Anoxic Transition of Benthic Fluxes from the Coastal Marine Environment (Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea). Mar. Freshw. Res. 2009, 60, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Agustı, S.; Kennedy, H.; Vaqué, D. The Mediterranean Climate as a Template for Mediterranean Marine Ecosystems: The Example of the Northeast Spanish Littoral. Prog. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 245–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremare, A.; Amouroux, J.; Cauwet, G.; Charles, F.; Courties, C.; de Bovee, F.; Dinet, A.; Devenon, J.-L.; Durrieu de Madron, X.; Ferre, B.; et al. Effets d’une Forte Tempête Hivernale Sur Les Variables Physiques et Biologiques à Une Station Côtière Méditerranéenne. Oceanol. Acta 2003, 26, 407–419. [Google Scholar]
- De Vittor, C.; Paoli, A.; Umani, S.F. Dissolved Organic Carbon Variability in a Shallow Coastal Marine System (Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 78, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadayol, Ò.; Peters, F.; Marrasé, C.; Gasol, J.M.; Roldán, C.; Berdalet, E.; Massana, R.; Sabata, A. Episodic Meteorological and Nutrient-Load Events as Drivers of Coastal Planktonic Ecosystem Dynamics: A Time-Series Analysis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 381, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipizer, M.; Cozzi, S.; Catalano, G.; Falconi, C. Seasonal Fluctuations of DIN/DIP and DON/DOP Ratio in the Northern Adriatic Sea. Ann. Dell’istituto Super. Di Sanità 1999, 35, 383–388. [Google Scholar]
- Gismondi, M.; Giani, M.; Savelli, F.; Boldrin, A.; Rabitti, S. Particulate Organic Matter in the Northern and Central Adriatic. Chem. Ecol. 2002, 18, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucea, A.; Duarte, C.M.; Agustí, S.; Kennedy, H. Nutrient Dynamics and Ecosystem Metabolism in the Bay of Blanes (NW Mediterranean). Biogeochemistry 2005, 73, 303–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degobbis, D.; Precali, R.; Ivancic, I.; Smodlaka, N.; Fuks, D.; Kveder, S. Long-Term Changes in the Northern Adriatic Ecosystem Related to Anthropogenic Eutrophication. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 13, 495–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degobbis, D.; Precali, R.; Ferrari, C.R.; Djakovac, T.; Rinaldi, A.; Ivančić, I.; Gismondi, M.; Smodlaka, N. Changes in Nutrient Concentrations and Ratios during Mucilage Events in the Period 1999–2002. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 353, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozetic, P.; Umani, S.F.; Kamburska, L. Plankton Variability in the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic). Archo Oceanogr. Limnol. 2002, 23, 7–19. [Google Scholar]
- Viličić, D.; Marasović, I.; Mioković, D. Checklist of Phytoplankton in the Eastern Adriatic Sea. Acta Bot. Croat. 2002, 61, 57–91. [Google Scholar]
- Cabrini, M.; Fornasaro, D.; Cossarini, G.; Lipizer, M.; Virgilio, D. Phytoplankton Temporal Changes in a Coastal Northern Adriatic Site during the Last 25 Years. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 115, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistocchi, R.; Guerrini, F.; Pezzolesi, L.; Riccardi, M.; Vanucci, S.; Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Forino, M.; Fattorusso, E.; Tartaglione, L.; et al. Toxin Levels and Profiles in Microalgae from the North-Western Adriatic Sea—15 Years of Studies on Cultured Species. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 140–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerino, F.; Fornasaro, D.; Kralj, M.; Giani, M.; Cabrini, M. Phytoplankton Temporal Dynamics in the Coastal Waters of the North-Eastern Adriatic Sea (Mediterranean Sea) from 2010 to 2017. Nat. Conserv. 2019, 34, 343–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totti, C.; Romagnoli, T.; Accoroni, S.; Coluccelli, A.; Pellegrini, M.; Campanelli, A.; Grilli, F.; Marini, M. Phytoplankton Communities in the Northwestern Adriatic Sea: Interdecadal Variability over a 30-Years Period (1988–2016) and Relationships with Meteoclimatic Drivers. J. Mar. Syst. 2019, 193, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vascotto, I.; Mozetič, P.; Francé, J. Phytoplankton Time-Series in a LTER Site of the Adriatic Sea: Methodological Approach to Decipher Community Structure and Indicative Taxa. Water 2021, 13, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladan, Ž.N.; Matić, F.; Arapov, J.; Skejić, S.; Bužančić, M.; Bakrač, A.; Straka, M.; Dekneudt, Q.; Grbec, B.; Garber, R.; et al. The Relationship between Toxic Phytoplankton Species Occurrence and Environmental and Meteorological Factors along the Eastern Adriatic Coast. Harmful Algae 2020, 92, 101745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljubešić, Z.; Bosak, S.; Viličić, D.; Borojević, K.K.; Marić, D.; Godrijan, J.; Ujević, I.; Peharec, P.; Đakovac, T. Ecology and Taxonomy of Potentially Toxic Pseudo-Nitzschia Species in Lim Bay (North-Eastern Adriatic Sea). Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Round, F.E.; Crawford, R.M.; Mann, D.G. Diatoms: Biology and Morphology of the Genera; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Burkholder, J.M.; Glibert, P.M.; Skelton, H.M. Mixotrophy, a Major Mode of Nutrition for Harmful Algal Species in Eutrophic Waters. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonda, S.; Franco, P.; Ghirardelli, E.; Malej, A. Outline of Oceanography and the Plankton of the Adriatic Sea. In Marine Eutrophication and Population Dynamics, Proceedings of the 25th EMBS, İstanbul, Turkey, 18–20 August 1992; Colombo, G., Ferrari, I., Ceccarelli, V.U., Rossi, R., Eds.; Olsen & Olsen: Fredensborg, Denmark, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Godrijan, J.; Marić, D.; Tomažić, I.; Precali, R.; Pfannkuchen, M. Seasonal Phytoplankton Dynamics in the Coastal Waters of the North-Eastern Adriatic Sea. J. Sea Res. 2013, 77, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brush, M.J.; Mozetič, P.; Francé, J.; Aubry, F.B.; Djakovac, T.; Faganeli, J.; Harris, L.A.; Niesen, M. Phytoplankton Dynamics in a Changing Environment. In Coastal Ecosystems in Transition: A Comparative Analysis of the Northern Adriatic and Chesapeake Bay; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; pp. 49–74. [Google Scholar]
- Cabrini, M.; Cok, S.; Pecchiar, I. Dinamica e Struttura Del Fitoplancton Nella Fascia Costiera Del Golfo Di Trieste. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2000, 7, 850–853. [Google Scholar]
- Zingone, A.; Escalera, L.; Aligizaki, K.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Ismael, A.; Montresor, M.; Mozetič, P.; Taş, S.; Totti, C. Toxic Marine Microalgae and Noxious Blooms in the Mediterranean Sea: A Contribution to the Global HAB Status Report. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M. Harmful Algal Blooms and Eutrophication: Nutrient Sources, Composition, and Consequences. Estuaries 2002, 25, 704–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattenrath-Lehmann, T.K.; Marcoval, M.A.; Mittlesdorf, H.; Goleski, J.A.; Wang, Z.; Haynes, B.; Morton, S.L.; Gobler, C.J. Nitrogenous Nutrients Promote the Growth and Toxicity of Dinophysis Acuminata during Estuarine Bloom Events. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Smith, J.L.; Kulis, D.M.; Anderson, D.M. Role of Dissolved Nitrate and Phosphate in Isolates of Mesodinium Rubrum and Toxin-Producing Dinophysis Acuminata. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 75, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Portela, M.; Reguera, B.; Gago, J.; Le Gac, M.; Rodríguez, F. Uptake of Inorganic and Organic Nitrogen Sources by Dinophysis Acuminata and D. Acuta. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingues, R.B.; Lima, M.J. Unusual Red Tide of the Dinoflagellate Lingulodinium Polyedra during an Upwelling Event off the Algarve Coast (SW Iberia). Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 63, 102998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroppo, C.; Congestri, R.; Bracchini, L.; Albertano, P. On the Presence of Pseudo-Nitzschia Calliantha Lundholm, Moestrup et Hasle and Pseudo-Nitzschia Delicatissima (Cleve) Heiden in the Southern Adriatic Sea (Mediterranean Sea, Italy). J. Plankton Res. 2005, 27, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahraoui, I.; Grami, B.; Bates, S.S.; Bouchouicha, D.; Chikhaoui, M.A.; Mabrouk, H.H.; Hlaili, A.S. Response of Potentially Toxic Pseudo-Nitzschia (Bacillariophyceae) Populations and Domoic Acid to Environmental Conditions in a Eutrophied, SW Mediterranean Coastal Lagoon (Tunisia). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 102, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezinski, M.A. The Si: C: N Ratio of Marine Diatoms: Interspecific Variability and the Effect of Some Environmental Variables 1. J. Phycol. 1985, 21, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smayda, T.J. Harmful Algal Blooms: Their Ecophysiology and General Relevance to Phytoplankton Blooms in the Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1137–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krom, M.; Herut, B.; Mantoura, R. Nutrient Budget for the Eastern Mediterranean: Implications for Phosphorus Limitation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smayda, T.J. Turbulence, Watermass Stratification and Harmful Algal Blooms: An Alternative View and Frontal Zones as “Pelagic Seed Banks”. Harmful Algae 2002, 1, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, K.; Cembella, A.; Clarke, D.; Cusack, C.; Arneborg, L.; Karlson, B.; Liu, Y.; Naustvoll, L.; Siano, R.; Gran-Stadniczeñko, S.; et al. Apparent Biogeographical Trends in Alexandrium Blooms for Northern Europe: Identifying Links to Climate Change and Effective Adaptive Actions. Harmful Algae 2022, 119, 102335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninčević-Gladan, Ž.; Skejić, S.; Bužančić, M.; Marasović, I.; Arapov, J.; Ujević, I.; Bojanić, N.; Grbec, B.; Kušpilić, G.; Vidjak, O. Seasonal Variability in Dinophysis Spp. Abundances and Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning Outbreaks along the Eastern Adriatic Coast. Bot. Mar. 2008, 51, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatharis, S.; Danielidis, D.B.; Tsirtsis, G. Recurrent Pseudo-Nitzschia Calliantha (Bacillariophyceae) and Alexandrium Insuetum (Dinophyceae) Winter Blooms Induced by Agricultural Runoff. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalef, R. Life-Forms of Phytoplankton as Survival Alternatives in an Unstable Environment. Oceanol. Acta 1978, 1, 493–509. [Google Scholar]
- Weise, A.M.; Levasseur, M.; Saucier, F.J.; Senneville, S.; Bonneau, E.; Roy, S.; Sauvé, G.; Michaud, S.; Fauchot, J. The Link between Precipitation, River Runoff, and Blooms of the Toxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium Tamarense in the St. Lawrence. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 59, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.T.; Tester, P.A.; Lincoln, J.A.; Carlsson, P.; Granéli, E. Effects of N: P: Si Ratios and Zooplankton Grazing on Phytoplankton Communities in the Northern Adriatic Sea. III. Zooplankton Populations and Grazing. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1999, 18, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozetic, P.; Lipej, L. Phytoplankton-zooplankton Trophic Interactions along the Salinity Gradient (Gulf of Trieste). Rapp. De La Comm. Int. Pour L’exploration Sci. De La Mer Méditerranée 1998, 35, 468–469. [Google Scholar]
- Bill, B.D.; Moore, S.K.; Hay, L.R.; Anderson, D.M.; Trainer, V.L. Effects of Temperature and Salinity on the Growth of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) Isolates from the Salish Sea. J. Phycol. 2016, 52, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boivin-Rioux, A.; Starr, M.; Chassé, J.; Scarratt, M.; Perrie, W.; Long, Z. Predicting the Effects of Climate Change on the Occurrence of the Toxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium Catenella Along Canada’s East Coast. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 7, 608021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzidovšek, M.; Francé, J.; Podpečan, V.; Vadnjal, S.; Dolenc, J.; Mozetič, P. Explainable Machine Learning for Predicting Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning Events in the Adriatic Sea Using Long-Term Monitoring Data. Harmful Algae 2024, 139, 102728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tondelli, L.; Bettoso, N.; Blasutto, O.; Celio, M.; Acquavita, A. Toxic Phytoplankton in Mussel Farms in the Gulf of Trieste, Adriatic Sea (Italy): A Preliminary Analysis of Long-Term Data (2001–2022) in Relation to Environmental Conditions. Environments 2025, 12, 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050152
Tondelli L, Bettoso N, Blasutto O, Celio M, Acquavita A. Toxic Phytoplankton in Mussel Farms in the Gulf of Trieste, Adriatic Sea (Italy): A Preliminary Analysis of Long-Term Data (2001–2022) in Relation to Environmental Conditions. Environments. 2025; 12(5):152. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050152
Chicago/Turabian StyleTondelli, Lisa, Nicola Bettoso, Oriana Blasutto, Massimo Celio, and Alessandro Acquavita. 2025. "Toxic Phytoplankton in Mussel Farms in the Gulf of Trieste, Adriatic Sea (Italy): A Preliminary Analysis of Long-Term Data (2001–2022) in Relation to Environmental Conditions" Environments 12, no. 5: 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050152
APA StyleTondelli, L., Bettoso, N., Blasutto, O., Celio, M., & Acquavita, A. (2025). Toxic Phytoplankton in Mussel Farms in the Gulf of Trieste, Adriatic Sea (Italy): A Preliminary Analysis of Long-Term Data (2001–2022) in Relation to Environmental Conditions. Environments, 12(5), 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050152






