Abstract
Globally, little is known about the dispersal of microplastics (MP) and anthropogenic particles (AP) via atmospheric deposition (AD) into water bodies. Correlating AD to the large number of MP in estuaries is challenging but an important first step toward reducing this form of pollution. A previously published model of the surface waters of the Indian River Lagoon (IRL, east central coast of Florida, USA) estimated it contained 1.4 trillion microplastics. To determine if AD could produce this much plastic deposition, we deployed passive AD collectors throughout a 145 km2 area at three site types with assistance from citizen scientists. We predicted that the rate of deposition of MP and AP would be greatest in residential areas, intermediate within a national park, and lowest on intertidal oyster reefs. Moreover, we predicted Florida’s wet season and individual rain events would increase deposition based on the published literature. Over 14 months, deposition averaged 1224 MP/m2/d; extrapolated, this yields 1.1 trillion MP for the lagoon-wide total deposition estimate (95% CI: 0.86–1.39 trillion MP). This value suggests that AD may represent an important pathway for MP to enter this estuary. More MP were deposited during rain events and in the wet season, with no differences among sites. Overall, our results provide important data for understanding AD of MP and AP in estuaries.
Keywords:
microplastics; Indian River Lagoon; Mosquito Lagoon; Florida; precipitation; rain; air pollution 1. Introduction
Plastics are ubiquitous pollutants and a serious global environmental challenge. Plastic production is expected to grow by 2–3 times by 2050 [1]. With this increase comes an increase in plastic pollution entering Earth’s aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. Lau et al. [2] predicted that 710 million metric tons of plastic waste will enter these systems by 2040. Microplastics (MP, size: 1 µm–5 mm) and nanoplastics (size: <1 µm) are directly manufactured or indirectly produced by the breakdown of larger plastic items. MP pollution has been reported in every studied ocean, estuary, lagoon, and bay, as well as in the tissues of hundreds of species of aquatic vertebrates and invertebrates, with bioaccumulation reaching multiple trophic levels [3,4]. While scientists are making steady progress in quantifying MP abundances in these diverse aquatic systems as well as understanding the impacts of plastic on organisms (e.g., mortality, cytotoxicity, neurotoxicity, genotoxicity [5]), it is still unclear how MPs are transported everywhere on this planet. Contributors to macro- through nanoplastic pollution in aquatic systems include ship overspill, container wash-off, coastal plastic production facilities, inefficient wastewater treatment, stormwater runoff and litter [6,7] as well as land-based activities, including agriculture and construction [8]. In recent years, MP researchers have also begun looking skyward. Dris et al. [9] first reported MP in dust samples in Paris. Awareness of the potential long-distance dispersal of MP by the popular media greatly increased in 2019 when Allen & colleagues [10] published an article on MP accumulations in the remote French Pyrenees Mountains. Averaged over 5 months, they found 249 fragments, 73 films, and 44 fibers/m2/d. With no local sources of MP, they attributed their results to atmospheric wet and dry deposition.
Over the past decade, studies on atmospheric deposition of MP in urban, suburban, rural and remote locations have greatly increased; polymer identification results suggest both long and short distance transport is involved [11,12]. Most atmospheric-derived plastics are fibers or fragments [13,14]. Precipitation has been positively correlated with increased MP deposition as particles can adhere to water droplets [12,15,16,17] when either MP sampling of water bodies or AD sampling was performed. For example, Hitchcock [15] reported a 40-fold increase in MP from surface water sampling during storm events in the Cooks River estuary, Australia. Yuan et al. [12] tracked the long-term impacts of rain on atmospheric deposition in a large Chinese city and reported significant washout effects of MP by rain from the atmosphere, with light rain having the highest MP washout effect. Likewise, Szewc et al. [18] found twice the amount of MP deposition in wet versus dry seasons in coastal Poland.
Atmospheric particulate matter represents a complex mixture of plastic and anthropogenic particles [19]. Some, but not all, AD studies report anthropogenic particle densities and rates of deposition when quantifying MP deposition. Anthropogenic particles (AP) are primarily fibers that are often released during textile production from human-modified natural materials. These include modified cellulose (e.g., rayon) as well as natural textiles (wool, cotton, silk) that have been dyed or chemically processed [13]. Concerns regarding these materials have traditionally been limited, as natural materials are expected to break down over time. This concern may be changing based on studies that focus on any persistent additives rather than on only the raw organic materials.
There is urgency in understanding the AD of plastics from the standpoint of human health [20]. Ingestion and inhalation are considered the two primary pathways for human exposure to MP and nanoplastics, with adults intaking 74,000 to 121,000 particles per year [21]. Another study reported 320,000 MP per year in humans [22]. Differences between these and other results were likely associated with the study location and sampling protocols [23]. Food and drinking water, as well as food/beverage containers, are all well-known sources of MP [23]. Interestingly, shellfish are considered one of the greatest sources of dietary exposure to MP at a global scale [20]. Many ingested MP, but few nanoplastics, are thought to be excreted [23]. This was confirmed by MP in human stool samples [24]. With inhalation, studies have reported up to 30,000,000 MP inhaled annually by humans, with indoor atmospheres responsible for significantly higher densities of MP than outdoors [23]. Quantification of AD rates has ranged from high densities (3261 MP/m2/d in urban megacities [25]) to low values in remote locations (coastal Victoria Land, Antarctica: 1.7 MP/m2/d [26] and remote Canadian wilderness: 7 MP/m2/d [13]). Once an MP enters a human body, transport throughout the body is theoretically possible [23]. Nihart et al. [27], for example, isolated 3345 µg/g of plastic in an adult human brain for a total of 10 g of plastic per brain. To date, documented medical issues associated with plastics have focused on lung diseases of textile workers [20]. More research on this field is urgently needed, as the data on plastics in human tissues is well documented, but the effects remain understudied [19].
Studies of AD generally follow one of two methodologies. Scientists can use automated collection devices that collect wind versus precipitation samples on separate filters that are retrieved at times appropriate and possible based on the deployment location. For example, in the Pyrenees Mountains, the research team deployed two monitoring devices that were ~6 km away from the closest village [10]. Filter collections were scheduled monthly, but in reality, had to coincide with favorable weather. Additional limitations of the use of automated collectors include cost, permits for deployment locations, and maintenance, all of which lead to deploying a limited number of devices. Moreover, data collectors require technical training for filter collections and repairs. Passive AD collectors represent the second methodology and are designed to be inexpensive, easy to transport, and provide wide spatial coverage due to temporary placements, so large numbers can be deployed in new locations on each sampling day. Non-plastic (glass, steel), AD collection devices with top openings that have a way to trap particles that enter the container are popular [28]. To determine efficacy, open-top containers were compared to bottles with attached funnels; both were similarly effective at capturing and retaining AD MP [29]. Passive collectors represent a way to facilitate contributions by large numbers of citizen scientists.
Citizen science can greatly increase the scope of MP data collection, both spatially and temporally [30]. Trained citizen scientists have been used to collect MP on beaches worldwide, allowing researchers to study the geographic variation in MP levels across a larger scale than would otherwise be possible [31]. Citizen science data collection can either take place over long time periods or may be set to take place in multiple locations in a “blitz” style, in which all volunteers collect data during the same time frame. The blitz method allows for simultaneous data collection throughout a large area, which can help identify “hotspots” [32,33]. Moreover, by collecting data outdoors in their own backyard or favorite community public spaces, residents gain a personal connection (also known as “sense of place”) and thus may be more likely to make personal stewardship actions [34].
Our research focused on understanding the rate of deposition of MP and AP in the Indian River Lagoon (IRL), FL, USA. A recent publication calculated that there were 1.4 trillion MP in the surface waters of this estuarine system [30]. Hence, our primary goal was to determine if AD could account for this value. We collected samples in three distinct areas on and adjacent to Mosquito Lagoon (ML, northern IRL): (1) within federally protected Canaveral National Seashore that includes part of ML within its boundaries; (2) on intertidal oyster reefs within ML; and (3) outdoors in residential areas near ML shorelines. Within each site type, we determined rates of deposition for MP and AP, and we compared MP and AP accumulations in rain versus wind samples. Moreover, we determined polymer compositions of MP to better understand plastic pollution in the area. Citizen science was integral to both the sample collection and laboratory sample processing.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
The Indian River Lagoon (IRL) is an estuarine system that spans 40% (251 km) of the eastern coast of central Florida, extending from Ponce de Leon Inlet in the north to Jupiter Inlet in the south (Figure 1). The IRL is a shallow (mean depth: 1.22 m), bar-built lagoon with limited water exchange through 5 inlets [35]. Saltwater influx comes from the Atlantic Ocean inlets, while freshwater is predominantly from rainfall, discharge, and runoff [35]. There are three interconnected estuarine bodies—the Indian River, Banana River, and Mosquito Lagoon. Shorelines include both protected areas (Canaveral National Seashore, Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge) and urbanized cities. The IRL hosts an EPA National Estuary Program and is additionally classified as an Estuary of National Significance [35]. The region experiences wet and dry seasons, with the annual wet season running from 29 May to 14 October [36]. The wet season and the annual hurricane season partially overlap (NOAA Hurricane Season: 1 June–30 November [37]). During the peak of hurricane season, water levels within many regions of the IRL can exceed 1 m above the levels for the rest of the calendar year due to a combination of rain and wind direction [30,38].
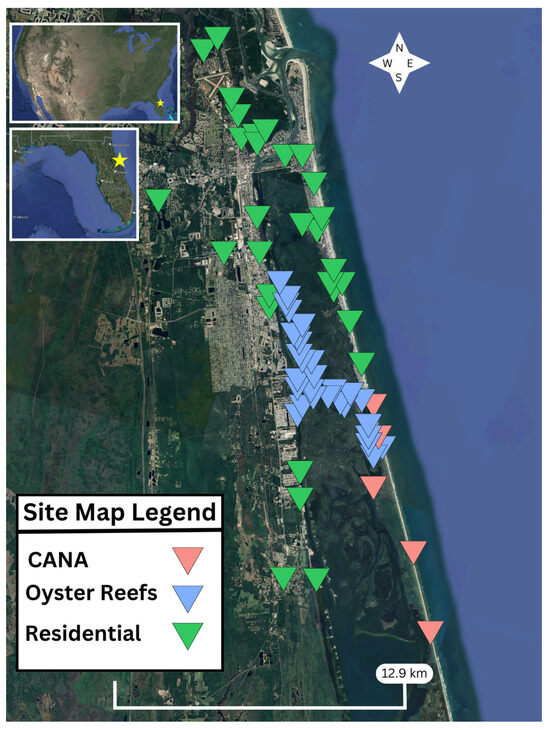
Figure 1.
Map of Florida, USA, with a focus on Mosquito Lagoon, including all study locations.
The IRL was classified as an MP “hotspot” by Walters et al. [30], with a mean density of 1.5 MP/L lagoon-wide, and because 44% of the surface water samples contained plastic. Based on the volume of water in the IRL [39], this translates into 1.4 trillion MP [30]. This research team had positive experiences with citizen science, with 84 trained citizens participating in water sampling and filtering for a total of 1600 h. Busch et al. [40] followed up their study by examining MP abundance associated with 30 IRL stormwater outfalls that were sampled monthly for 12 months. While there was no difference in MP abundances between closed culverts and open drainage channels, there were (1) more MP around outfalls, (2) more stormwater MP found in the fall months during the wet, hurricane season, and (3) stormwater MP were smaller in dimensions than the lagoon-wide average [40]. In total, 72 individuals (1042 volunteer hours) were critical to completing stormwater MP water sampling in the IRL. We focused our current research on understanding AD in the northernmost IRL basin called Mosquito Lagoon. Salinity in ML varies from 22.6 to 45.2 ppt, and annual temperatures range from 4 to 33 °C [41]. Water in ML is primarily moved by the wind rather than by tides in this enclosed, poorly drained estuary [39,42]. ML has long residence times with a 50% exchange of water taking 200–300 days in ML compared to one week in the southern lagoon or one tidal cycle near inlets [39,43].
Mosquito Lagoon is a very popular location for outdoor recreation, especially boat-based fishing and ecotourism [44]. In addition to IRL-wide surface water and stormwater data collections, MP research on IRL fauna has documented high MP abundances in all studied organisms. This includes studies on the filter-feeding eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica, Gmelin, 1791) (2.3 MP/adult oyster) [30], the mud crab Panopeus herbstii (Milne-Edwards, 1834; internal tissues: 4.2 MP + AP/adult crab; external entanglement: 20.3 MP + AP) [45], the endosymbiotic pea crab Zaops ostreum (Say, 1817) that resides among bivalve gills (internal tissues: 0.5 MP + AP/adult crab; external entanglement: 0.1 MP + AP/adult crab) [46], and the osprey Pandion haliaetus (Linnaeus, 1758) with 19.3 MP/bird [47].
2.2. Sample Collection
We collected AD data over 14 months at three unique site types (Figure 1). This included: (1) residential areas ≤5 km from the shorelines of Mosquito Lagoon in the cities of New Smyrna Beach and Edgewater and the town of Oak Hill. Citizen scientists were recruited for residential (outside their homes or nearby green spaces) collection help via flyers, social media, and a regional television news story. To compare residential areas to a potentially less-disturbed environment, (2) five collection locations were permitted on land within Canaveral National Seashore (CANA), spanning 10.4 km. All were accessible by car or on foot. Two were along the shoreline of ML (separated by 7.0 km), while the other three were adjacent to parking lots that could hold between 12 and 85 vehicles, and were a mean of 0.21 km (range: 0.02–0.54 km) from Mosquito Lagoon’s shoreline. (3) The third selected site type was intertidal oyster reefs in ML that were physically separate from any shoreline (i.e., patch reefs) and were only accessible by boat. Sampled oyster reefs were spread over 10.4 km. Reef collections only occurred at low tide when the oysters were exposed and when the boating conditions were safe. This was considered the least accessible of the 3 site types.
Passive AD collectors were deployed in groups of 3 (distance between jars was ~ 10 cm) at all site types. Collectors were 0.95 L (32-oz) Ball® wide-mouth glass canning jars (Rubbermaid, Inc., Atlanta, GA, USA) (height: 16.8 cm, diameter of top opening: 7.6 cm) that were kept closed with a steel lid and screw cap when not deployed. Jars and lids were previously triple-rinsed with 0.45-µm filtered, deionized (DI) water to remove contamination. After cleaning, 10 mL of 0.45-µm filtered, DI water was added to each collector to trap particles that entered the jars. A waterproof label was affixed to each collector to record all relevant information (site location, date, start and end times, precipitation/no precipitation, collector’s name) with a permanent marker.
Samples were collected on haphazard dates between 14 May 2024 and 25 July 2025 based on the availability of the citizen scientists/researchers. We acknowledge that allowing participants to choose their own sampling schedule could result in temporal biases in the data collection. Jars were placed in open areas that were away from any overhanging vegetation, as well as away from built structures, on a 45 × 14 × 1.5 cm wooden platform (oyster reefs excluded) so that any ground cover plants would not interfere with collections. Citizen scientists were instructed to wear only natural fibers when participating. Once the label information was recorded and the jars were arranged, the individual would remove the lids from the jars (~10 s/jar) and move away quickly to avoid contaminating the samples. Jar lids were wrapped in aluminum foil to protect them from contamination during collections. After approximately three hours, the lids were re-secured on the jars (Figure 2). Data was analyzed as particles per minute, so the 3 h timing was a guide and based on pilot studies in the area. If a rain event occurred while the jars were deployed, the samples were marked as “rain”; if no rain occurred, the samples were marked as “wind”. A local non-profit, Marine Discovery Center, assisted with the distribution and return of AD jars from the citizen scientists.
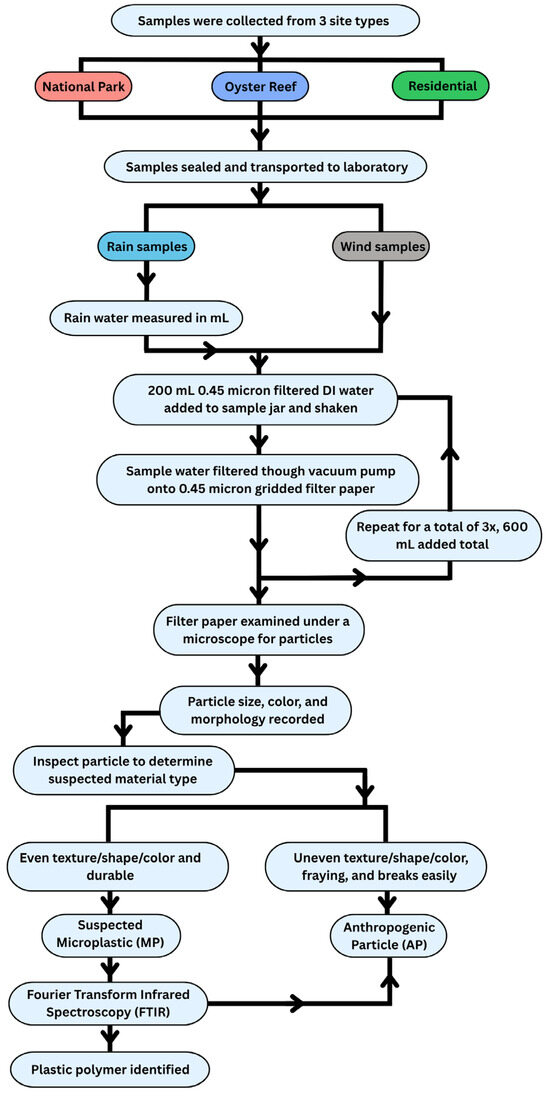
Figure 2.
Flow chart of sample collection and processing.
2.3. Laboratory Processing
2.3.1. Minimizing Contamination
To limit MP contamination throughout processing, standard protocols were followed [19]. All researchers wore 100% natural fiber clothing, and room air was filtered to 0.3 µm. All sample jars and all filtration units, forceps, and Petri dishes were triple-rinsed prior to each use with 0.45-µm DI water. While microscopy was underway, five “blanks” were placed around each microscope to account for any indoor aerial contamination. Each blank Petri dish contained a 0.45 µm filter to which 2 mL of filtered water was added to dampen the filter and promote potential particle capture. These dishes were open to the environment throughout the duration of microscopy. Once microscopy of a jar or group of jars was completed, MP plus AP from each blank dish were recorded, and a contamination rate per minute was calculated [48]. For more technical laboratory processing, a team of university student volunteers (also considered citizen scientists) assisted with filtering, microscopy, and polymer identification. With these citizen scientists, we followed training and QA/QC protocols used by other MP researchers [30]. Individuals were trained over multiple days with direct supervision (minimum: 3 training sessions). Once the supervisor and the individual were confident in their filtering and microscopy, the volunteer worked independently. If the individual or supervisor was not confident in the training’s success over time, then the individual was removed from data processing. Finally, a minimum of 10% of all samples were re-checked by project leaders. With this protocol, there were no issues with inaccurate processing during our study.
2.3.2. Processing “Wind” Versus “Rain” Samples
In the laboratory, 200 mL of 0.45-µm filtered DI water was added to each “wind” collector, and the jar was closed and shaken to collect any particles that adhered to the glass. This water was filtered through a gridded (3 mm2), 0.45-µm filter paper using a GAST® vacuum pum (Gast Manufacturing, Inc., Benton Harbor, MI, USA). This process was repeated 2 more times for a total of three rinses per jar and a total of 600 mL of filtered DI water. Filters were next placed in a washed and labeled Petri dish for microscopy. For “rain samples”, an additional step was included at the start to visually infer rainfall by recording the volume of rainwater in each collector in mL using a glass graduated cylinder. Rainfall amounts can be very patchy in this region, especially during summer “sea breeze collision” storms, so this method was used rather than relying on rainfall gauges at the closest airport. We acknowledge that this value might be an overestimate of total rainwater, as all passive collectors started with 10 mL of filtered water. However, some undetermined amount of evaporation occurred during the deployment of jars. No jars with no accumulated precipitation were dry at the end of the ~3 h deployment, so water was available throughout deployments to trap MP and AP. All samples were examined under a Leica EZ4 microscope (Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany) at 20–40× magnification to allow observation of particles as small as 4–10 µm. Data recorded for each particle were particle type (fiber, fragment, film, foam, bead, pellet), size (mm), color using a printed color guide, and suspected composition (microplastic or anthropogenic particle).
2.4. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Methods
We used Attenuated Total Reflection Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) on ~25% of the samples that were initially classified as “suspected MP” during visual analysis with a Shimadzu IRSpirit-T spectrometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) and Bruker Alpha-II FTIR spectrometer (Bruker, MA, USA). A random number generator was used to select among all samples that contained suspected MP. Suspected plastics were scanned in the 400 cm−1 to 4000 cm−1 range. Spectra were matched with a qualitative approach, in which the acquired spectra were compared against reference spectra from the KnowItAll FTIR Spectral Database Collection™.
Each spectrum was baseline-corrected and smoothed using a Savitzky–Golay filter with an average of 3 prior to library matching. Only responses that had a 70% or higher match with the standards database were deemed reliable and categorized as plastic. The matching score was derived from the Euclidean distance between the sample and the reference spectra, representing a nonlinear metric, as variations in environmental or instrumental conditions can influence the similarity value. A small percentage of particles were degraded and are reported as “unidentified plastic”. The remainder of the samples examined via FTIR matched the category of “cellulose/modified cellulose”. This included a variety of types of anthropogenically modified cellulose (e.g., rayon, microfibrillated cellulose). These particles were moved to the AP category for all of our analyses. For the remainder of the samples that were not processed, we inferred that the same ratio of plastics/non-plastics would result, as the FTIR-processed samples were randomly selected. We did not undertake repeated analyses of FTIR samples to quantify any error associated with this percentage.
2.5. Data Analysis
All statistical analyses were conducted using RStudio version 4.4.1, and each analysis was performed separately for MP and AP [49]. For models with multiple predictors, the “dredge” function from the MuMIn package was used to perform AIC-based model selection to systematically evaluate potential models [50]. Random effects for collection set ID (to account for nested sampling design) and individual site (to account for repeated measures across locations) were included in all models. All generalized linear mixed-effects models (GLMMs) were fitted using the glmmTMB package (version 1.1.10), and all models with a gamma distribution used a log link function [51]. Effect sizes for categorical predictors are reported relative to the reference levels: rain (sample type), dry (season), and CANA (site type). Pairwise comparisons were conducted using Tukey’s method via the emmeans package, which computes contrasts and confidence intervals on the model’s link scale (log scale for gamma models) [52].
Model assumptions were assessed visually using residual and diagnostic plots, and no major violations were detected. Additionally, overdispersion was evaluated for all Poisson models using diagnostic tools, such as the “check overdispersion” function from the performance package, and all models showed acceptable fit with no substantial overdispersion observed [53].
2.5.1. AD Density Comparisons
To analyze MP and AP abundance, GLMMs with a gamma distribution were fitted. Particle density per jar (particles/m2/min) adjusted by FTIR results was used as the response variable. Fixed effects included site type (CANA, oyster reefs, residential), sample type (rain or wind), season (wet or dry), and distance to lagoon (km).
To evaluate whether irregular sampling timing introduced temporal bias, a separate GLMM using a gamma distribution was fitted. The model included sampling date and sampling start time as fixed effects. This analysis was conducted independently of the main models to assess whether sampling date or time of day significantly influenced MP or AP density.
2.5.2. AD Particle Type Comparisons
To assess particle type distributions, MP and AP particle type (fiber, fragment, film, foam, bead, pellet) abundances were compared by site type and sample type. Due to the rarity of certain particle types, particles with low counts were grouped into an “Other” category; for MP, beads, foams, and pellets were combined, and for AP, beads, pellets, and films were combined. The count of each particle type was used as the response variable in separate GLMMs with Poisson distributions, with site type and sample type included as fixed effects.
2.5.3. AD Particle Size Comparisons
Particle size (mm) was modeled using linear mixed-effects models (LMMs) with the “lmer” function in the lme4 package (version 1.1-35.5) [54]. Because raw particle size distributions were highly right-skewed, sizes were log-transformed prior to modeling to improve normality and stabilize variance. This transformation was verified by visualizing size distributions before and after log transformation (Figure 3). Fixed effects included site type, sample type, season, and distance to the lagoon (km).
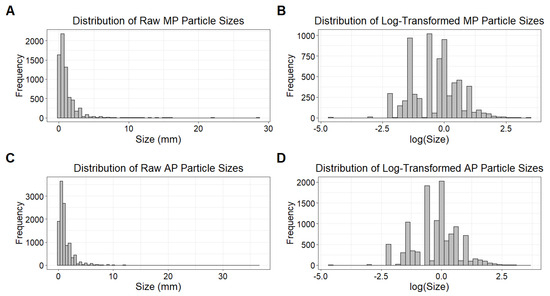
Figure 3.
Size distribution of MP (n = 6853) and AP (n = 11,380) particles before and after log transformation. (A,C) Distribution of raw particle sizes (mm), showing a highly right-skewed pattern. (B,D) Distribution of log-transformed particle sizes, which are approximately symmetric and suitable for linear mixed-effects modeling assumptions.
2.5.4. AD Particle Color Diversity and Abundance Comparisons
Particle color diversity was quantified using Shannon’s diversity index calculated per jar for both MP and AP using the “diversity” function from the vegan package and modeled using GLMMs with a gamma distribution [55]. Fixed effects included site type, sample type, season, and distance to lagoon (km). Additionally, the abundance of each particle color was modeled separately using GLMMs with Poisson distributions, with site type and sample type included as fixed effects. A separate model was fitted for each color using an iterative approach. For the color abundance models, light blue, royal blue, and navy blue were combined into one category (blue) to increase sample size and simplify interpretation.
3. Results
3.1. Data Summary
A total of 6853 MP and 11,380 AP were collected in the 1401 passive deposition jars, with 76% and 93% of jars containing deposited MP and AP, respectively. Overall, there was a mean (±S.D.) of 0.85 (±2.21) MP/m2/min (range: 0–39) and 3.42 (±3.55) AP/m2/min (range: 0–36). Twenty-five percent of collections contained rainwater. In total, sample collections occurred 191 times in CANA, 96 times on intertidal oyster reefs, and 180 times at residential sites led by citizen scientists. Residential site collections included 27 private homes, 2 elementary schools, and 6 city/county parks. Thirty citizen scientists participated in these collections (498 volunteer h), and 31 university students additionally contributed 822 h toward deployments, filtering, microscopy, and FTIR analyses. We are confident in the quality of the collected residential citizen science data. Our only surprise for this participatory research project was that many residents declined to participate because they were concerned about the difficulty of the request and the independence it provided (i.e., volunteers selected their times and locations). With student volunteers, only two were removed from participating during the training process. Indoor aerial contamination rates associated with laboratory processing were very low, with an average contamination rate per minute of 0.002 for MP and 0.014 for all particles. Average exposure time for blanks was ~37 min. Following examples in the published literature [48], no contamination correction factor was included in the data analysis as the contamination rate was so low.
With MP deposition, the majority were fibers (74.0%), fragments (14.2%), and films (11.2%). The remaining categories were foam (0.5%) and beads/pellets (0.1%). For the AP, 96.0% of particles were fibers, with the remaining particles being fragments (3.5%), films (0.4%), and beads/pellets (0.1%). The mean length (±S.D.) of an MP was 1.08 (±1.32) mm with a range in lengths from 0.01 to 28.5 mm. The mean length of AP was 1.20 (±1.38) mm with a range of 0.01–36.5 mm.
The three dominant colors of the 6853 MP accounted for 81.2% of the particles. When the three site types were considered, clear (overall mean: 53.0%, range: 48.4–58.0%), black (overall mean: 13.0%, range: 4.8–26.2%), and light blue (overall mean: 15.2%, range: 11.6–20.7%) dominated. The most color variation among site types was observed with black MP, with the fewest on oyster reefs and the most from residential locations. MP colors that each equaled less than 1% of the total were brown, red, orange, green, and purple.
Of the 11,380 anthropogenic particles, the colors were more equally distributed than with MP. With AP, the top three colors were clear (27.8%), royal blue (14.3%), and gray (12.5%), with residential sites having the largest percentage of clear particles and the lowest percentage of royal blue and gray particles. AP colors that were each less than 1% of the total included white (0.4%), brown (0.8%), and green (0.8%).
3.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Results
A flow diagram describes the process of FTIR sampling: total particles → visually suspected MPs → FTIR subset (~25% of total selected with a random number generator, n = 408) → confirmed plastics or reclassified as AP (modified cellulose) (Figure 2). After this process was complete, the MP and AP counts were normalized to equal 100%. Of the FTIR-documented plastics, four plastic types contributed over 70% of the total. These polymers were polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polypropylene (PP), polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), and nylon (Table 1).

Table 1.
Material composition of microplastics processed using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) (n = 220).
3.3. AD Densities: Modeling and Comparisons Among Treatments
Oyster reef collectors with precipitation were limited (n = 6) due to safety precautions associated with small watercraft and the high winds plus thunder/lightning associated with Florida rainstorms. The small sample size of this treatment may have impacted the results. Distance to the lagoon was removed from the final MP density model based on AIC optimization (χ2 = 97.57, df = 6, p < 0.001). There were no significant differences in MP density among the three site types (p > 0.600 for all pairwise comparisons) (Figure 4). More MP was deposited in rain than wind (β = −0.3278, 95% CI: [−0.729, 0.012], p = 0.058) as well as in the wet season versus the dry season (β = 0.761, 95% CI: [0.430, 1.090], p < 0.001).
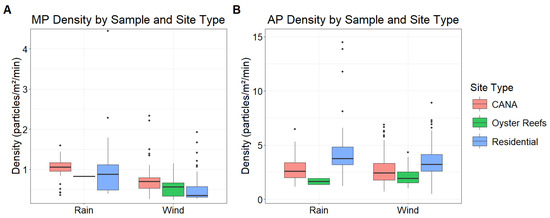
Figure 4.
Microplastic and anthropogenic particle densities compared by the 3 site types (Canaveral National Seashore = CANA, Oyster Reefs, Residential) and rain versus wind collections based on GLMM outputs (MP n = 6853, AP n = 11,380). There were no significant differences in MP density among site types (GLMM: p > 0.660 for all comparisons), while more MP were found in rain than wind samples (GLMM: p = 0.058). With AP, there were no significant differences among site types (GLMM: p > 0.100 for all comparisons) nor between rain and wind samples (GLMM: p = 0.230).
Different patterns were observed for AP deposition (χ2 = 336.63, df = 7, p < 0.001). Particle densities were, on average, 3–4× greater than the MP densities for the same samples (Figure 4). Rain and wind samples had similar AP densities (β = −0.1092, 95% CI: [−0.2875, 0.0692], p = 0.230), but AP densities were lower in the wet season than in the dry season (β = −0.2098, 95% CI: [−0.375, −0.045], p = 0.013). There were no differences in AP densities among the three site types (p > 0.100 for all pairwise comparisons), but locations closer to the IRL had significantly more AP (β = −0.2313, 95% CI: [−0.401, −0.062], p = 0.007).
Sampling date was initially a significant predictor of MP density (χ2 = 14.72, df = 1, p < 0.001). However, when season was included in the model, date was no longer significant (p = 0.843), indicating that seasonal classification adequately captured temporal variation. Sampling start time was not significant in either model. These results suggest that while sampling was not evenly distributed across time, the inclusion of season and random effects in the main models sufficiently accounts for temporal irregularity
3.4. AD Particle Types: Modeling and Comparisons Among Treatments
Distance to the lagoon was removed from the final MP model based on AIC optimization (χ2 = 43.03, df = 4, p < 0.001) but was retained in the AP model (χ2 = 13.72, df = 5, p = 0.018). Fibers were the dominant MP type (74.0%), and there was more fiber deposition in rain than in wind (β = −0.3682, 95% CI: [−0.606, −0.130], p = 0.002) (Table 2). Fragment and film deposition did not vary between wind and rain samples (p = 0.890 and p = 0.812, respectively). Across site types, fiber deposition was significantly higher at CANA sites compared to both oyster reefs (β = 0.667, 95% CI: [0.237, 1.097], p = 0.001) and residential sites (β = 0.566, CI: [0.168, 0.965], p = 0.003), while oyster reefs and residential sites did not differ (β = −0.191, 95% CI: [−0.484, 0.283], p = 0.812).

Table 2.
Types of microplastics and anthropogenic particles found by site type (CANA, oyster reefs, residential) and by sample type (rain, wind) (MP n = 6853, AP n = 11,380).
For AP, no significant differences in particle type deposition were found between rain and wind samples (p > 0.350 for all comparisons). Across site types, fiber deposition was highest in residential areas, intermediate at CANA sites, and lowest at oyster reefs (Table 2). Pairwise comparisons confirmed significantly more AP fibers at residential sites compared to both CANA (β = −0.220, 95% CI: [−0.492, 0.051], p = 0.001) and oyster reefs (β = −0.451, 95% CI: [−0.700, −0.202], p < 0.001), and more fibers at CANA than at oyster reefs (β = 0.230, 95% CI: [−0.069, 0.530], p = 0.021). No significant differences among site types were found for AP fragments or particles in the “Other” category (foams and film particles) (p > 0.200 for all comparisons).
3.5. AD Particle Dimensions: Modeling and Comparisons Among Treatments
For MP, particle size was strongly affected by season, with the wet season having significantly larger particles than the dry season (β = 0.461, 95% CI: [0.328, 0.587], p < 0.001; Figure 5). There was, however, no effect of wind versus rain on the size of MP (β = 0.007, 95% CI: [−0.115, 0.135], p = 0.910). MP sizes did not differ between residential and CANA sites (β = 0.055, 95% CI: [−0.219, 0.330], p = 0.884) but were significantly smaller at oyster reef sites compared to both residential (β = −0.2466, 95% CI: [−0.467, −0.026], p = 0.024) and CANA sites (β = 0.302, 95% CI: [0.025, 0.579], p = 0.029). As with the MP, AP were larger in the wet season (β = 0.132, 95% CI: [0.029, 0.235], p = 0.013) with no effect of single rain events on AP size (β = 0.017, 95% CI: [−0.093, 0.126], p = 0.769) (Figure 5). AP were also significantly smaller at oyster reefs than at both CANA (β = 0.331, 95% CI: [0.178, 0.484], p < 0.001) and residential sites (β = −0.426, 95% CI: [−0.596, −0.256], p < 0.001). In contrast, particle size did not differ between CANA and residential sites (β = −0.095, 95% CI: [−0.236, 0.046], p = 0.252). Moreover, AP particle size decreased with increasing distance from the IRL (β = −0.116, 95% CI: [−0.230, −0.001], p = 0.049).
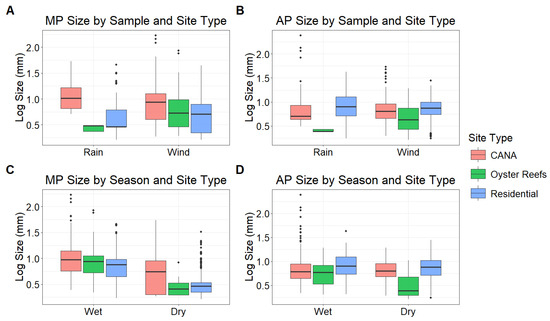
Figure 5.
Microplastic and anthropogenic particle sizes compared by the 3 site types (Canaveral National Seashore = CANA, Oyster Reefs, Residential) and rain versus wind collections based on LMM outputs (MP n = 6853, AP n = 11,380). The size of MP (LMM: p < 0.001) and AP (LMM: p = 0.013) was larger during the wet season, with no effect of wind versus rain (MP LMM: p = 0.910, AP LMM: p = 0.769). MP (LMM: p = 0.024) and AP (LMM: p < 0.001) size was smaller on oyster reefs than at other locations.
3.6. AD Particle Colors: Modeling and Comparisons Among Treatments
Color comparisons were made in two different ways for the suite of all possible colors of MP and AP (Figure 6). First, we compared the total diversity of colors. For both the MP (χ2 = 22.42, df = 3, p < 0.001) and AP (χ2 = 6.95, df = 3, p = 0.074) color diversity analyses, distance to the lagoon (km) and sample type were dropped during model selection. Shannon diversity of MP colors was significantly higher in the wet season compared to the dry season (β = 0.5982, 95% CI: [0.257, 0.940], p = 0.009). Among site types, CANA sites had significantly higher color diversity than oyster reef sites (β = 0.549, 95% CI: [0.047, 1.050], p = 0.028). Residential sites did not differ significantly from either CANA (β = 0.188, 95% CI: [−0.252, 0.629], p = 0.575) or oyster reefs (β = −0.360, 95% CI: [−0.870, 0.149], p = 0.222; Figure 6). None of the tested predictors, site type, or season, had a significant effect on the diversity of AP particle colors. Pairwise comparisons among site types were all non-significant (p > 0.120), and the full model did not significantly improve fit over the null model (χ2 = 6.95, df = 3, p = 0.074).
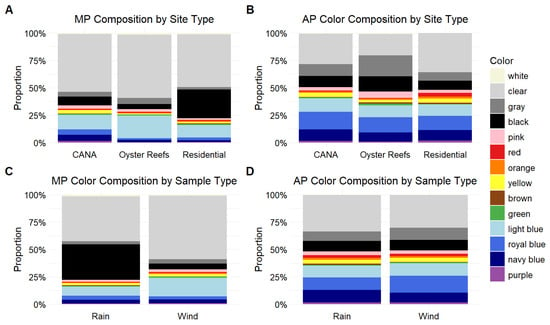
Figure 6.
Proportion of microplastic and anthropogenic particles by color found across the 3 site types (Canaveral National Seashore = CANA, Oyster Reefs, Residential) and sample types (rain versus wind) (MP n = 6853, AP n = 11,380). With MP, there were no significant differences among site types or sample types (GLMM: p > 0.097 for all colors). With AP, there were no significant differences between sample types (GLMM: p > 0.096 for all colors), but color differed between site types, with blue (GLMM: p ≤ 0.003) and clear (GLMM: p ≤ 0.001) particles more abundant at CANA and residential sites.
With MP color abundance, there were no significant differences among colors between the 3 site types or sample type (rain, wind) (p > 0.097 for all colors) (Figure 6). With AP color abundance, there were no significant differences in any color between sample types (p > 0.096 for all colors). However, there were AP site type differences with the color blue more abundant at CANA than at oyster reefs (β = 1.51, 95% CI: [1.19–2.27], p = 0.003) and at residential sites compared to oyster reefs (β = 1.58, 95% CI: [1.79–3.06], p < 0.001). Similarly, clear AP was more abundant at CANA (β = 1.22, 95% CI: [1.22–1.77], p = 0.001) and residential sites (β = 1.55, 95% CI: [1.55–2.27], p < 0.001) than at oyster reefs.
4. Discussion
Plastic and AP are important contaminants in Florida’s Indian River Lagoon, and we documented that both enter the IRL via atmospheric deposition. Individual rain events and the wet season significantly increased AD of MP in this region. We collected a total of 6853 MP and 11,380 anthropogenic particles over the course of our 14-month project that covered 145 km2, including 88 km2 directly over IRL waters. The overall deposition rate for MP in the northern IRL was 1224 MP/m2/d, with a 95% confidence interval of 945–1521 MP/m2/day based on replicated sample sets. If this rate is extrapolated to include the entire Indian River Lagoon (914.3 km2 of surface waters), this equates to an estimated 1.1 trillion MP lagoon-wide, with a 95% CI of 0.86–1.39 trillion MP. Based on a previous lagoon-wide annual finding of 1.5 MP/L in surface water, Walters et al. [30] inferred that there should be 1.4 trillion MP for the entire IRL. While MP entering the IRL via stormwater outfalls was not sufficient to reach this total [40], atmospheric deposition of MP closely aligned with the predicted total. The annual wet season is important in understanding AD in central Florida. It runs from 29 May to 14 October [36]. During the wet season, MP deposition increased while AP deposition decreased. Mean lengths of AP were 0.12 mm longer than MP at 1.20 and 1.08 mm, respectively, and the deposition lengths of both MP and AP were significantly larger during the wet season. In two previous IRL-wide studies that focused on temporal patterns of MP in surface waters, MP loads were also higher in fall/winter seasons (September–February) than in other seasons [30,40]. Multiple hurricanes impacted Florida’s east coast during these studies.
Rain increased MP deposition rates, but not deposition rates of AP in our study. Similarly to our results, many studies from around the globe found more MP deposition during precipitation events [12,25,56]. For example, Hitchcock [15] found MP abundances in the highly urbanized Cooks River estuary in Australia were 40-fold higher than average during a large storm event (79 mm of precipitation within 48 h). There are multiple explanations for this increase. First, when rain contacts the Earth’s surface, its pounding on hard surfaces can mobilize plastics held in the sediment, road paint, tire fragments, and litter, as well as MP previously deposited by AD [15]. MP may then be resuspended into the atmosphere or washed to new locations via rainwater flow. A second way that rain can mobilize MP is by causing wastewater treatment systems to overflow [57]. Third, rain can mobilize MP contained in clouds [12]. Researchers have determined that most MPs are released at the “first flush” at the beginning of a rain event [58,59,60]. Yuan et al. [12] suggested that atmospheric MP can be removed from the atmosphere with great efficiency, and that light rain (<2.5 mm/h) had a better washout effect than moderate rain (2.5–10 mm/h) or heavy rain (10–50 mm/h). Yuan et al. [12] further suggested that this is due to the association of light rain with lower horizontal winds that disperse particles, the relative dimensions of MP versus raindrops, and the enhancement of MP and raindrop aggregations. Rain samples were analyzed separately from wind samples to evaluate the effect of rainfall volume (mL) on MP and AP density. Rainfall volume was used as a predictor in GLMMs with gamma distributions, with particle density per collector (particles/m2/min), adjusted by FTIR results, as the response variable (χ2 = 334.03, df = 1, p < 0.001). The majority of individual rainfall totals fell within the light or moderate categories. However, when rainfall volume was used as a predictor in the GLMMs, there was no positive correlation between rainwater volume and deposition for either MP (β = 0.0024, 95% CI: [−0.0012, 0.0650], p = 0.185) or AP (β = −0.0013, 95% CI: [−0.0031, 0.0005], p = 0.165).
We are currently living in the “age of plastics” due to our extensive use of plastics for many applications [61]. Plastics in ocean waters and in marine organisms have been a concern since the 1960s, when first reported in the stomachs of seabirds [62]. Plastics were first described as components of the global waters around 50 years ago, including the Sargasso Sea [63], Atlantic Ocean [64], Pacific Ocean [65], North Sea [66], and Southern Ocean [67]. Likewise, hitchhiking on plastics by fouling organisms (e.g., bryozoans, barnacles) was suggested as a dispersal mechanism to lead to new invasions [68]. Foamed plastics (polystyrene) were common in these early publications, matched 5% of our FTIR samples, and were exclusively found in CANA during the summer of 2024. The history of polystyrene dates back to 1839, with commercial applications entering markets in the 1950s [69]. Polystyrene was widely adopted because it is very inexpensive to produce as well as lightweight, sterile, chemically stable, and effective for insulation and flotation [69]. Small beads of polystyrene are warmed and then squeezed together to create the desired shape. While single-use polystyrene food containers are now banned in many locations, larger polystyrene items remain popular. When these products break down, the polystyrene beads are released and later found in our atmosphere and throughout our oceans. Another important polymer was polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which matched 17.7% of our FTIR samples. Overall, 62% of PTFE was from residential collectors, and 33% was recorded on oyster reefs. Moreover, 95% of PTFE particles were associated with wind samples. Invented in 1938, PTFE has numerous applications, including anti-friction coatings and medical devices; non-stick coatings for cookware (e.g., Teflon™); and water resistance for fabrics (e.g., Gore-Tex™) [70]. PTFE use continues to expand despite its and some chemicals used to produce it being listed as persistent organic pollutants [70]. Polypropylene (19.1% match with our samples) and PVC (2.0% match) are expected to be the most widely used plastics in 2050, the former for construction and automobile industry, and the latter for medical and laboratory applications, food containers, consumer goods, and textiles [70].
Most plastics end up in landfills, incineration plants, or are disposed of improperly [71]. Dokl et al. [71] predict that 69% of plastic waste will be landfilled in the USA in 2050, compared to 16% in the EU. The closest landfill to our study area was 12.4 km to the west of ML. Thus, any landfill-generated MP would have to have traveled a minimum of that distance, suggesting at least medium-distance transport. In CANA, it is possible to regularly observe improper disposal of beach trash, especially “single use” items. Large items that do not fit in the provided garbage receptacles are propped up against the bins located at boat ramps and beach boardwalks. These items include many types of plastic—polystyrene coolers, polystyrene and PE beach toys, and pop-up tents and beach chairs that include plastic fabrics (LJW, pers. obs.). To determine if there was a positive correlation in the daily number of park visitors to MP deposition, we compared MP densities to the number of cars that entered the north district of CANA [72]. CANA visitors in our study area ranged from a low of 534 cars/d in September 2024 to a high of 1490 cars/d in July 2025. Using a gamma distribution GLMM with particle density as the response variable, the density of CANA MP was not correlated with visitor numbers (p = 0.115). Similarly, AP density was not related to visitor numbers (p = 0.362). This suggests that short-distance dispersal within CANA was not a primary source of MP or AP within the park.
Our value of 1224 MP/m2/d in and around Mosquito Lagoon was one of the highest reported rates for AD, while the population numbers for the three communities in the study area were relatively low, with a total of 58,362 residents (New Smyrna Beach: 32,655 residents; Edgewater: 23,506 residents; Oak Hill: 2201 residents) [73]. Tourism in the study region is, however, significant, with Volusia County hosting 10.6 million visitors in 2022 [74]. Most high MP deposition rates are correlated with high population densities [25]. Higher MP deposition rates have been recorded in Shanghai (population: 30.5 million), China (3261/m2/d) [25]. Additional highly urbanized areas with high AD densities include central London (9.8 million residents, 771/m2/d [75]), Dongguan, China (7.8 million residents, 228/m2/d [28]), and Hamburg, Germany (1.8 million residents; 212/m2/d [76]) [73]. Some remote wilderness sites averaged higher than expected AD rates with 132 MP/m2/d (multiple national parks in the USA [17]), and the remote Pyrenees Mountain (366 MP/m2/d [10]). While remote, these two areas do have urban population centers within ~100 km. Other remote areas report very low rates of MP deposition: Antarctica (1.7 MP/m2/d) and Canadian wilderness (7 MP/m2/d) [13,26]. These locations do not have urban populations within 100 km. To classify a site as an MP “hotspot”, it is first necessary to define a hotspot. With four orders of magnitude reported for MP deposition per square meter per day in the published literature, we suggest that a location should be called a hotspot if it receives over 1000 MP/m2/d, moderate if it receives 100–999 MP/m2/d, and low if AD densities are below 100 MP/m2/d. Thus, our study areas of Mosquito Lagoon would be classified as an MP hotspot despite its surrounding low population density, but high annual tourism numbers.
Comparing published studies on IRL oysters and water to the current AD study of the IRL provided interesting results. Previously collected data on the intertidal oyster Crassostrea virginica throughout the IRL found an average of 2.26 MP per adult individual (2.43 MP/g tissue weight), and 70% of these 1402 oysters contained MP [48]. Crassostrea virginica excreted an average of 1 MP/h in feces, and 1 MP every 2 h in pseudo-feces (mucus-bound particles that never enter the oyster’s digestive tract). Size was correlated to MP retention; larger oysters were less efficient at egesting MP, and the larger the MP, the more likely it was retained in the tissues of C. virginica [48]. The mean length (±S.D.) of MP in IRL oysters was 2.8 ± 0.1 mm with a range of 0.1–35.0 mm [30]. The mean length of IRL MP associated with AD in this study was 1.08 mm, which is less than half the IRL MP. This suggests either selective filtering by the oysters or that only larger particles are located in an oyster’s filtration zone. In the IRL, fibers dominated in oyster tissue (95.0%) and water (95.6%) [30]. For this AD study, 74% of the MP were fibers. This difference, combined with smaller MP in AD, potentially reflects mobilization and resuspension of small fibers back into the atmosphere. Black was the most common fiber color in oysters and IRL water, while it was second to clear fibers in AD MP. PET was the most abundant polymer in IRL water and in C. virginica (50 and 56% of MP, respectively, followed by PP (26% and 13%), and PS (3% and 3%). In our AD MP study, PET was likewise the most abundant polymer (22.3% match), followed by PP (20.0%). AD of polystyrene matched at 5%. If plastic particles are primarily introduced to this lagoon from atmospheric deposition, then intertidal filter-feeding organisms such as oysters should feed as soon as the tide rises enough to allow feeding. That is when newly deposited MP particles should be mobilized. When submerged, C. virginica in this region filters approximately 60 L of water per day [77], and there are reports that this species can filter at different rates, with a 3-fold difference in filtration rate, especially when newly submerged by the tide [78]. At low tide, the oysters in ML are completely exposed, and their valves are closed. During these hours (~12 h/d), all particles would land on the shells or adjacent sediment. If the MP is buoyant, then as the tidal water starts to cover the oyster valves, the newly deposited particles would float to the surface at the same time the oysters are most actively feeding. PP and PE are considered buoyant MP, while denser plastics like PVC would sink [79]. Further research is needed to understand the relationship between AD, tides, and feeding in C. virginica to determine if selective foraging is occurring.
A number of variables may limit the accuracy of the reported AD values and modeling results. First, open-top passive deposition collectors may underestimate actual particle numbers. Used by us for the ease of deployment, especially by citizen scientists, and their cost-effectiveness that allows large numbers of collectors to be simultaneously deployed, an unknown number of particles may have entered a collector and then become resuspended and exited the collector without ever being trapped by the fluid. We acknowledge that such particle loss is an important concern for all open-top passive collectors, but this would result in an underestimate of MP and AP, making our results conservative. Moreover, Knobloch et al. [29] compared the efficacy of open-top samplers (glass beakers) to narrow-mouth glass bottles with attached funnels that provided identical diameter openings. MP collection numbers were similar for both types of collectors when deployed during rainy/dry periods in New Zealand; these authors concluded that both passive collector types are suitable for AD studies, and the open-top beakers may provide easier entrance for some particle types. A second concern is unquantified evaporation of the trapper fluid during the collection period. We acknowledge this concern that could also result in underestimating MP and AP numbers. However, in pilot tests run to determine an appropriate water volume for the passive collectors, there was always water present in the collectors after 4 h deployments when 10 mL of filtered water was added prior to deployment. A third concern relates to extrapolating AD particles collected on land to values for an estuary. Recent studies have documented that open-water areas may release MP from surface waters back into the atmosphere via particles attached to rain or wind-generated marine aerosols [80]. Additionally, these authors report that while saltwater environments are generally considered sinks for MP, upwelling and other conditions that mix surface and deeper waters can return MP to surface waters. Again, we acknowledge the importance of such fluxes and encourage more research to better understand these processes, especially in shallow estuaries such as the IRL.
Most AD research suggests that a combination of short- and long-distance transport is important in AD at a single location at a single time period. The ratio of long versus short distance movements depends on many factors, including particle shapes and sizes, densities, settling velocities, meteorological conditions, and topographical complexity of the study and surrounding areas [80]. For example, Illuminati et al. [26] suggested their MP deposition results in passive samplers in Antarctica were the result of both long and short-distance dispersal, with the latter associated with passing vessels and research stations. In our study area, the New Smyrna Beach Municipal Airport reports that the prevailing winds are from the north-northwest to northeast from October to February each year, while between March and September, the prevailing winds are from the east to southeast; average wind speeds were 16.4 kph, and gusts averaged 36.7 kph [81]. These values suggest that transport over land occurs during colder, dryer months while transport over the Atlantic Ocean dominates during the warmer, wetter months. Along the length of the 251 km IRL, the elevation of natural areas is similar and does not exceed 10 m [35]. Only structures created by humans change the topography of this region and include Native American shell middens, landfills, high-rise apartments and condominiums, and rocket assembly buildings associated with Kennedy Space Center and adjacent private space companies. Additionally, 24 bridges that cross over the lagoon alter the landscape and add unknown amounts of pollution to the IRL each year. No large textile or plastic manufacturing plants exist adjacent to the IRL. Tourism is the dominant industry, and this may contribute to the reported textile-related microplastic polymers (PP, PTFE, nylon, polyester). PET and polystyrene, especially as single-use containers, may also be tourism-related. Commercial industries and military bases adjacent to the IRL may also increase the abundance of specific polymers that are deposited in the IRL. In the region, there are multiple maritime manufacturers, aquaculture facilities, construction companies, and a large federal and private aerospace/aviation industry [35]. The space industry may additionally increase AD particle numbers during launches. In addition to increased tourism, rockets use diverse propellants that release particles in the “ground clouds” and “vapor trails” during take-offs [82]. There were 93 rocket launches in 2024 [83] that released HCl, alumina, black carbon soot, among other compounds, upon take-off [82].
5. Conclusions
We consider the Indian River Lagoon along the east, central coast of Florida to be an MP hotspot with a lagoon-wide average of 1.5 MP/L in surface water and an inferred 1.4 trillion MP lagoon-wide [30]. Our goal with this research was to determine if atmospheric deposition could account for this density of MP, and the answer was yes, AD may represent an important pathway for MP to enter this estuary. With 0.85 MP/m2/min or 1224 MP/m2/d, we estimated deposition of 1.1 trillion MP (95% CI: 0.86–1.39 trillion MP/d) via AD lagoon-wide. Additional MP may arrive via stormwater, septic and wastewater treatment plants, boats, litter, and businesses. MP will leave the lagoon by winds that cause resuspension into the atmosphere or washing up on shorelines, while heavier MP particles will sink to the bottom of the estuary, where they will be buried or consumed by lagoon fauna. We predicted residential collection locations would have the greatest density of MP and AP based on human population density, but this was not the case as all site types were similar in MP abundances. Overall, our results show that atmospheric deposition of particles is an important mechanism of particle transport and that plastics really do rain down in this region. For the safety of all organisms, including humans, in and around the IRL that may inhale or consume plastic particles, it is imperative that we create pathways to reduce and eventually eliminate plastic pollution. It is likewise imperative that more studies are conducted to understand AD around the globe, and especially to understand the polymer impacts on vertebrates and invertebrates.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.J.W., M.S. and P.S.; Methodology, L.J.W., M.S., P.S., F.J. and L.Z.; Formal Analysis, T.B. and F.J.; Investigation, L.J.W., M.S., P.S. and F.J.; Resources, L.J.W. and L.Z.; Data Curation, T.B., M.S. and F.J.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, L.J.W.; Writing—Review and Editing, M.S., P.S., T.B., F.J. and L.Z.; Visualization, T.B. and M.S.; Supervision, L.J.W. and L.Z.; Project Administration, L.J.W.; Funding Acquisition, L.J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Indian River Lagoon National Estuary Program (#IRL-2024SG-06) and the Biology Department at the University of Central Florida.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be publicly available within 6 months of publication on the UCF STARS Digital Repository.
Acknowledgments
We thank A. Frey, and the Marine Discovery Center in New Smyrna Beach for facilitating the citizen science aspect of this project, and Canaveral National Seashore for providing access to sites. We also thank S. Kim and C. Grove for FTIR processing support, and many University of Central Florida students for field and laboratory support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gould, R. Rethinking the Future of Plastic. 2022. Available online: https://www.iso.org/news/ref2792-1.html. (accessed on 27 September 2025).
- Lau, W.W.Y.; Shiran, Y.; Bailey, R.M.; Cook, E.; Stuchtey, M.R.; Koskella, J.; Velis, C.A.; Godfrey, L.; Boucher, J.; Murphy, M.B.; et al. Evaluating scenarios toward zero plastic pollution. Science 2020, 369, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.; Thompson, R.; Galloway, T. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajith, N.; Arumugam, S.; Parthasarathy, S.; Manupoori, S.; Janakiraman, S. Global distribution of microplastics and it impact on marine environment—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 25970–25986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSa, L.C.; Oliveira, M.; Ribeiro, F.; Rocha, T.L.; Bishop, K. Studies of the effects of microplastics on aquatic organisms: What do we know and where should we focus our efforts in the future? Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.; Friot, D. Primary Microplastics in the Oceans: A Global Evaluation of Sources; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: https://portals.iucn.org/library/sites/library/files/documents/2017-002-En.pdf (accessed on 28 September 2025).
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derraik, J.G.B. The pollution of the marine environment by plastic debris: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Saad, M.; Mirande, C.; Tassin, B. Synthetic fibers in atmospheric fallout: A source of microplastics in the environment? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 104, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Phoenix, V.; Le Roux, G.; Durántez Jiménez, P.; Simonneau, A.; Binet, S.; Galop, D. Atmospheric transport and deposition of microplastics in a remote mountain catchment. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Gao, T.; Sillanpää, M. Atmospheric microplastics: A review on current status and perspectives. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 203, 103118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Pei, C.; Li, H.; Lin, L.; Liu, S.; Hou, R.; Liao, R.; Xu, X. Atmospheric microplastics at a southern China metropolis: Occurrence, deposition flux, exposure risk and washout effect of rainfall. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, B.; Aherne, J.; Paterson, A.M.; Yao, H.; McConnell, C. Atmospheric deposition of anthropogenic particles and microplastics in south-central Ontario, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xu, A.; Shi, M.; Su, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; She, Z.; Xing, X.; Qi, S. Atmospheric deposition is an important pathway for inputting microplastics: Insight into the spatiotemporal distribution and deposition flux in a mega city. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 341, 123012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchcock, J.N. Storm events as key moments of microplastic contamination in aquatic ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Nie, Z.; Meng, Y.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y.; Chai, G. Influence of meteorological conditions on atmospheric microplastic transport and deposition. Environ. Res. 2025, 65, 120460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahney, J.; Hallerud, M.; Heim, E.; Hahnenberger, M.; Sukumaran, S. Plastic rain in protected areas of the United States. Science 2020, 368, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewc, K.; Graca, B.; Dolega, A. Atmospheric deposition of microplastics in the coastal zone: Characteristics and relationship with meteorological factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Gouin, T.; Koelmans, A.A.; Scheuermann, L. Development of screen criteria for microplastic particles in air and atmospheric deposition: Critical review and applicability towards assessing human exposure. Microplastic Nanoplastics 2021, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Kelly, F.J. Plastic and human health: A micro issue? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6634–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, K.D.; Covernton, G.A.; Davies, H.L.; Dower, J.F.; Juanes, F.; Dudas, S.E. Human consumption of microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7068–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, N.H.M.; Kooi, M.; Diepens, N.J.; Koelmans, A.A. Lifetime accumulation of microplastic in children and adults. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 5084–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, J. Micro(nano)plastics in the human body: Sources, occurrences, fates, and health risks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 3065–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabl, P.; Koppel, S.; Konigshofer, P.; Bucsics, T.; Trauner, M.; Reiberger, T.; Leibmann, B. Detection of various microplastics in human stool. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Duan, Y.; Han, X.; Sun, X.; Munyaneza, J.; Ma, J.; Xiu, G. Atmospheric deposition of microplastics in the megalopolis (Shanghai) during rainy season: Characteristics, influence factors, and source. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illuminati, S.; Notarstefano, V.; Tinari, C.; Fanelli, M.; Girolametti, F.; Ajdini, B.; Scarchilli, C.; Ciardini, V.; Iaccarino, A.; Giorgini, E.; et al. Microplastics in bulk atmospheric deposition along the coastal region of Victoria Land, Antarctica. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 175221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihart, A.J.; Garcia, M.A.; El Hayek, E.; Liu, R.; Olewine, M.; Kingston, J.D.; Castillo, E.F.; Gullapalli, R.R.; Howard, T.; Bleske, B.; et al. Bioaccumulation of microplastics in decedent human brains. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Tan, Z.; Zhan, Z.; Tan, X.; Chen, Q. Characteristic of microplastics in the atmospheric fallout from Dongguan city, China: Preliminary research and first evidence. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 24928–24935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobloch, E.; Ruffell, H.; Aves, A.; Pantos, O.; Gaw, S.; Revell, L.E. Comparison of deposition sampling methods to collect airborne microplastics in Christchurch, New Zealand. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, L.; Craig, C.; Dark, E.; Wayles, J.; Encomio, V.; Coldren, G.; Sailor-Tynes, T.; Fox, D.; Zhai, L. Quantifying spatial and temporal trends of microplastic pollution in surface water and in the eastern oyster Crassostrea virginica for a dynamic Florida estuary. Environments 2022, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosker, T.; Behrens, P.; Vijver, M.G. Determining global distribution of microplastics by combining citizen science and in-depth case studies. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolok, A.; Schoenfuss, H.; Propper, C.; Vail, T. Empowering citizen scientists: The strength of many in monitoring biologically active environmental contaminants. BioScience 2011, 61, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Muenich, R.; Peel, S.; Bowling, L.; Haas, M.; Turco, R.; Frankenberger, J.; Chaubey, I. The Wabash sampling blitz: A study on the effectiveness of citizen science. Citiz. Sci. Theory Pract. 2016, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hawthorne, T.L.; Toohy, K.R.; Yang, B.; Graham, L.; Lorenzo, E.M.; Torres, H.; McDonald, M.; Rivera, F.; Bouck, K.; Walters, L.J. Mapping emotional attachment as a measure of sense of place to identify coastal restoration priority areas. Appl. Geogr. 2022, 138, 102608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRLNEP One Lagoon Website. Available online: https://onelagoon.org/ (accessed on 27 September 2025).
- Lascody, R. The Onset of the Wet and Dry Seasons in East Central Florida—A Subtropical Wet-Dry Climate? 2002. Available online: https://www.weather.gov/media/mlb/climate/wetdryseason.pdf (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- NOAA AOML Website. Available online: https://www.aoml.noaa.gov/ (accessed on 27 September 2025).
- USGS Website. Available online: https://waterdata.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 27 September 2025).
- Smith, N.P. Tidal and nontidal flushing of Florida’s Indian River Lagoon. Estuaries 1993, 16, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, S.J.; Craig, C.A.; Wayles, J.; Sailor-Tynes, T.; Dark, E.; Sweat, L.H.; Fox, D.W.; Zhai, L.; Walters, L.J. Contribution of stormwater outfalls to microplastic pollution in a subtropical estuary using data collected with the assistance of citizen scientists. Environments 2023, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phlips, E.; Badylak, S.; Lasi, M.; Chamberlain, R.; Green, W.; Hall, L.; Hart, J.; Lockwood, J.; Miller, J.; Morriz, L.; et al. From red tides to green and brown tides: Bloom dynamics in a restricted subtropical lagoon under shifting climatic conditions. Estuaries Coasts 2015, 38, 886–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaPointe, B.E.; Herren, L.E.; Debortoli, D.; Vogel, M.A. Evidence of sewage-driven eutrophication and harmful algal blooms in Florida’s Indian River Lagoon. Harmful Algae 2015, 43, 82–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.P. Transport pathways through southern Indian River Lagoon. Fla. Sci. 2016, 79, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, L.J.; Sacks, P.; Campbell, D. Boating impacts and boat-wake resilient restoration of the eastern oyster Crassostrea virginica in Mosquito Lagoon, Florida, USA. Fla. Sci. 2021, 84, 173–199. [Google Scholar]
- Waite, H.R.; Donnelly, M.J.; Walters, L.J. Quantity and types of microplastics in the organic tissues of the eastern oyster Crassostrea virginica and the Atlantic mud crab Panopeus herbstii from a Florida estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, L.J.; Busch, S.J.; Vermeulen, S.; Craig, C.A. Entanglement and ingestion of microfibers by the pea crab Zaops ostrreum, an endosymbiont of the eastern oyster Crassostrea virginica. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 201, 116251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlin, J.; Donnelly, M.; Walters, L. Microplastic accumulation in the gastrointestinal tracts in birds of prey in central Florida, USA. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 264, 114633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, C.; Fox, D.; Zhai, L.; Walters, L. In-situ microplastic egestion efficiency of the eastern oyster Crassostrea virginica. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 178, 113653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posit Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R. Posit Software, PBC, Boston, MA. Available online: http://www.posit.co/ (accessed on 17 July 2025).
- Bartoń, K. MuMIn: Multi-Model Inference. R Package Version 1.48.11. 2025. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=MuMIn (accessed on 26 September 2025).
- Brooks, M.E.; Kristensen, K.; Benthem, K.J.; Magnusson, A.; Berg, C.W.; Nielsen, A.; Skaug, H.J.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.M. GlmmTMB balances speed and flexibility among packages for zero-inflated generalized linear mixed modeling. R J. 2017, 9, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenth, R. Emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, Aka Least-Squares Means. R Package Version 1.11.2-80003. 2025. Available online: https://rvlenth.github.io/emmeans/ (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Lüdecke, D.; Ben-Shachar, M.S.; Patil, I.; Waggoner, P.; Makowski, D. Performance: An R package for assessment, comparison and testing of statistical models. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.; Blanchet, F.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, R.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.; Szoecs, E.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.6-8. 2024. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- Sun, J.; Peng, Z.; Zhu, Z.-R.; Weng, F.; Dai, X.; Ni, B.-J. The atmospheric microplastics deposition contributes to microplastic pollution in urban waters. Water Res. 2022, 225, 119116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendall, L.S.; Sewell, M.A. Contributing to marine pollution by washing your face: Microplastics in facial cleansers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, T.; Park, Y.; Lim, B.; Kim, S.; Chae, M.-Y.; Chun, C.-H. Effect of the first-flush phenomenon on the quantification of microplastics in rainwater. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 187, 114559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Feng, Q.; Wang, J. Mini-review of microplastics in the atmosphere and their risks to humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Bang, K.W.; Ketchum, L.H., Jr.; Choe, J.S.; Yu, M.J. First flush analysis of urban storm runoff. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 293, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Moore, C.J.; vom Saal, F.S.; Swan, S.H. Plastics, the environment and human health: Concurrent consensus and future trends. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, B364, 2153–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.R. Rubber bands in a puffin’s stomach. Br. Birds 1960, 53, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, E.J.; Smith, K.L. Plastic on the Sargasso Sea surface. Science 1972, 175, 1240–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colton, J.B.; Knapp, F.D.; Burns, B.R. Plastic particles in surface waters of the northwestern Atlantic. Science 1974, 185, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venrick, E.L.; Bakman, T.W.; Bartram, W.C.; Platt, C.J.; Thornhill, M.S.; Yates, R.E. Man-made objects on the surface of the central North Pacific Ocean. Nature 1973, 241, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, T.R.; Dixon, T.J. Marine litter surveillance. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1983, 12, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, M.R.; Kirk, R.M.; Mabin, M.C.G. Pelagic tar, oil, plastics and other litter in surface waters of the New Zealand sector of the Southern Ocean, and on Ross Dependency shores. N. Z. Antarct. Rec. 1984, 6, 12–28. [Google Scholar]
- Winston, J.E. Drift plastic—An expanding niche for a marine invertebrate? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1982, 13, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastic Today Website. Available online: https://plasticstoday.com/ (accessed on 27 September 2025).
- Advancing Physics Website. Available online: https://www.aps.org/ (accessed on 27 September 2025).
- Dokl, M.; Copot, A.; Krajnc, D.; Van Fan, Y.; Vujanovic, A.; Aviso, K.B.; Tan, R.R.; Kravanja, Z.; Cucek, L. Global projections of plastic use, end-of-life fate and potential changes in consumption, reduction, recycling and replacement with bioplastics. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 51, 498–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Park Service Stats Website. Available online: https://irma.nps.gov/stats/ (accessed on 27 September 2025).
- World Population Review Website. Available online: https://worldpopulationreview.com/ (accessed on 27 September 2025).
- Daytona Regional Chamber of Commerce Website. Available online: https://DaytonaChamber.com/ (accessed on 28 September 2025).
- Wright, S.L.; Ulke, J.; Font, A.; Chan, K.L.A.; Kelly, F.J. Atmospheric deposition in an urban environment and an evaluation of transport. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.; Fischer, E.K. Microplastic abundance in atmospheric deposition within the metropolitan area of Hamburg, Germany. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galimany, E.; Lunt, J.; Freeman, C.J.; Reed, S.; Segura-Garcia, I.; Paul, V.J. Feeding behavior of eastern oysters Crassostrea virginica and hard clams Mercenaria mercenaria in shallow estuaries. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 567, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, E.; Hofmann, E.; Klinck, J.; Ray, S. Modeling Oyster populations: I. A commentary on filtration rate: Is faster always better? J. Shellfish Res. 1992, 11, 387–398. [Google Scholar]
- Chubarenko, I.; Bagaev, A.; Zobkov, M.; Esiukova, E. On some physical and dynamical properties of microplastic particles in marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 108, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Moss, K.; Le Roux, G.; Phoenix, V.R.; Sonke, J.E. Examination of the ocean as a source for atmospheric microplastics. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WindFinder Website. Available online: https://www.windfinder.com/windstatistics/new_smyrna_beach (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Ryan, R.G.; Marais, E.A.; Balhatchet, C.J.; Eastham, S.D. Impact of rocket launch and space debris air pollutant emissions on stratospheric ozone and global climate. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocketlaunch.org Website. Available online: https://rocketlaunch.org/ (accessed on 20 October 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).