Environmental Stressors of Mozambique Soil Quality
Abstract
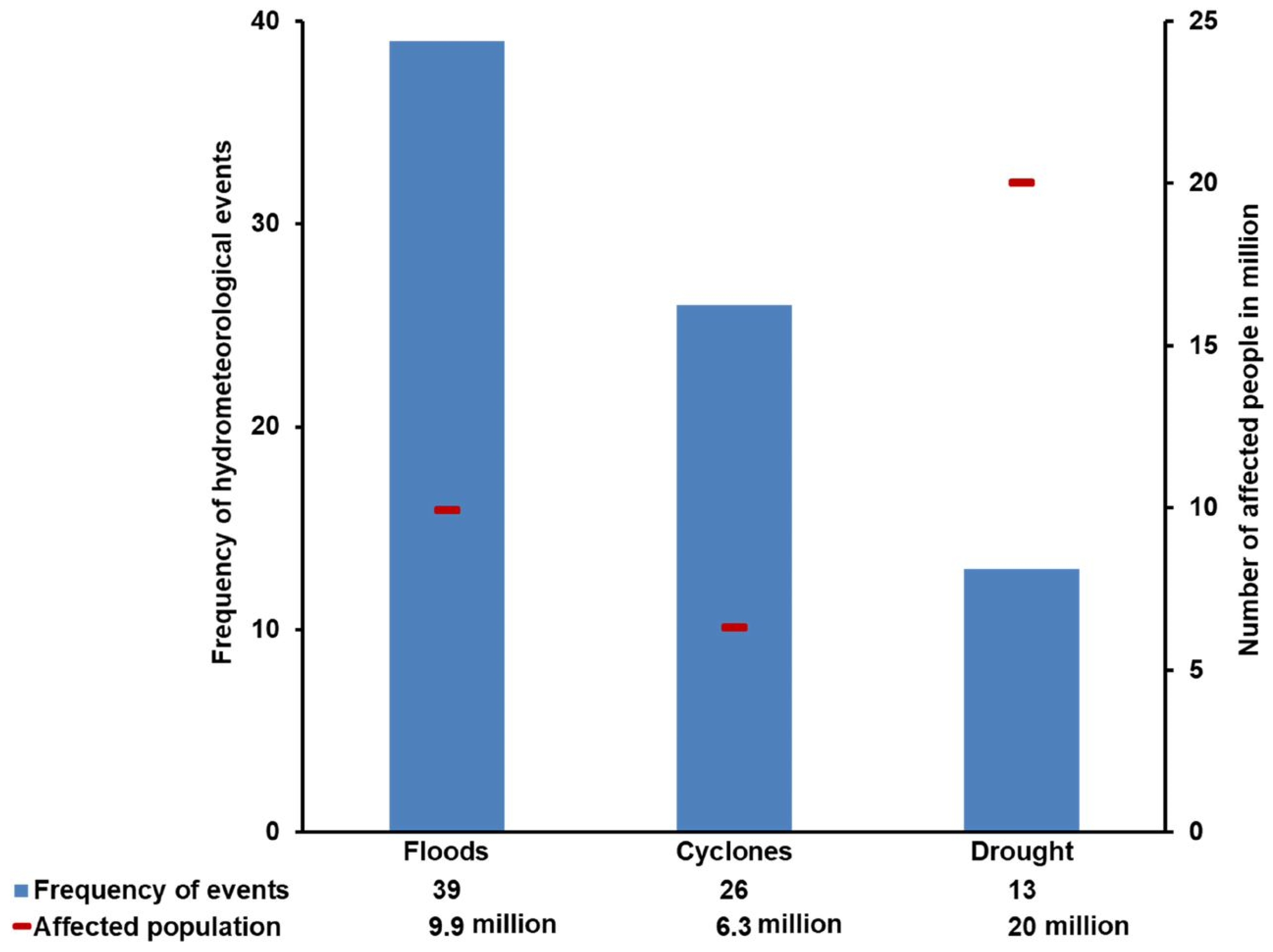
1. Introduction
2. Soil Fertility
3. Deforestation
3.1. Agriculture
3.2. Timber Harvesting
3.3. Charcoal Production
3.4. Uncontrolled Fires
4. Mining
5. Solid Wastes
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Report: Voluntary National Review of Agenda 2030 for Sustainable Development, Mozambique. VNR2020—Voluntary National Report: Our Commitment to Sustainable Development for All. 2020. Available online: https://planipolis.iiep.unesco.org/en/2020/voluntary-national-review-agenda-2030-sustainable-development (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- World Food Programme. Mozambique Annual Country Report 2022—Country Strategic Plan 2022–2026. 2022. Available online: https://www.wfp.org/operations/mz02-mozambique-country-strategic-plan-2022-2026 (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- The UN Refugee Agency. Annual Results Report 2022 Mozambique. UNHCR, 3 of May, 2023. Available online: www.unhcr.org (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Human Development Report 2023/2024. Breaking the Gridlock. Reimagining Cooperation in a Polarized World; United Nations Development Programme: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. Urban Population (% of total population)—Mozambique. 2022. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.URB.TOTL.IN.ZS?locations=MZ (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- United States Census Bureau. Available online: https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/international-programs/data/population-vulnerability/mozambique.html (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Folmer, E.C.R.; Geurts, P.M.H.; Francisco, J.R. Assessment of soil fertility depletion in Mozambique. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1998, 71, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, V.P. Plantation designs in northern Mozambique: Development, struggles and (re)compositions facing the ProSAVANA program. Tapuya: Latin American Science. Technol. Soc. 2023, 6, 2252122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, M.J.; Quentala, L.; Dias, R.; Ramalho, E.; Fernandes, J.; Milisse, D.; Manhiça, V.; Ussene, U.; Cune, G.R.; Daudi, E.X.; et al. Geochemical characterisation of soil of Beira city, Mozambique: Geogenic origin and relation with land cover. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 187, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marassiro, M.J.; Romarco de Oliveira, M.L.; Pereira, G.P. Family farming in Mozambique: Characteristics and challenges. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 10, e22110615682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianciullo, S.; Attorre, F.; Trezza, F.R.; Rezende, M.; Ntumi, C.; Campira, J.; Munjovo, E.T.; Timane, R.D.; Riccardi, T.; Malatesta, L. Analysis of land cover dynamics in Mozambique (2001–2016). Rend. Lincei. Sci. Fis. E Nat. 2023, 34, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugabe, V.A.; Gudo, E.S.; Inlamea, O.F.; Kitron, U.; Ribeiro, G.S. Natural disasters, population displacement and health emergencies: Multiple public health threats in Mozambique. BMJ Glob. Health 2021, 6, e006778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, B.; Candeias, C.; Rocha, F. Soil Risk Assessment in the Surrounding Area of Hulene-B Waste Dump, Maputo (Mozambique). Geosciences 2022, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaal, A.; Sultan, M.; Abotalib, A.Z.; Bedair, M.; Krishnamurthy, R.V.; Elhebiry, M. Emerging mercury and methylmercury contamination from new artisanal and small-scale gold mining along the Nile Valley, Egypt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 52514–52534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuenberger, A.; Winkler, M.S.; Cambaco, O.; Cossa, H.; Kihwele, F.; Lyatuu, I.; Zabre, H.R.; Farnham, A.; Macete, E.; Munguambe, K. Health impacts of industrial mining on surrounding communities: Local perspectives from three sub-Saharan African countries. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bey, A.; Meyfroidt, P. Improved land monitoring to assess large-scale tree plantation expansion and trajectories in Northern Mozambique. Environ. Res. Commun. 2021, 3, 115009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temudo, M.P.; Silva, J.M.N. Agriculture and forest cover changes in post-war Mozambique. J. Land Use Sci. 2012, 7, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedano, F.; Silva, J.A.; Machoco, R.; Meque, C.H.; Sitoe, A.; Ribeiro, N.; Anderson, K.; Ombe, Z.A.; Baule, S.H.; Tucker, C.J. The impact of charcoal production on forest degradation: A case study in Tete, Mozambique. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 094020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maria, R.M.; Yost, R. A Survey of Soil Fertility Status of Four Agroecological Zones of Mozambique. Soil Sci. 2006, 171, 902–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Varennes, A. Produtividade dos Solos e Ambiente; Escolar Editora: Lisboa, Portugal, 2003; ISBN 972-592-156-9. [Google Scholar]
- Stoorvogel, J.J.; Smaling, E.M.A. Assessment of Soil Nutrient Depletion in Sub-Saharan Africa: 1983–2000; The Winand Staring Centre: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1990; Report 28, 4 Volumes; Volume 1, ISSN 0924-3062. [Google Scholar]
- Chichongue, O.; van Tol, J.; Ceronio, G.; Preez, C.D. Effects of Tillage Systems and Cropping Patterns on Soil Physical Properties in Mozambique. Agriculture 2020, 10, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muatendauafa, A.S.R.; Francisco, A.; Zuarica, F.J.E.; Alface, L.A.; João, X.S. Importance of Conservation Agriculture in Soil Preservation in Vanduzi District in Mozambique. RECIMA21-Rev. Científica Multidiscip. 2023, 4, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Serrani, D.; Cocco, S.; Cardelli, V.; D’Ottavio, P.; Rafael, R.B.A.; Feniasse, D.; Vilanculos, A.; Fernández-Marcos, M.L.; Giosué, C.; Tittarelli, F.; et al. Soil fertility in slash and burn agricultural systems in central Mozambique. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 322, 116031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokura, W.; Matimele, H.; Smit, J.; Hoffman, M.T. Long- term changes in forest cover in a global biodiversity hotspot in southern Mozambique’, Bothalia 2020, 50, a1. 50. [CrossRef]
- Ryan, C.M.; Berry, N.J.; Joshi, N. Quantifying the causes of deforestation and degradation and creating transparent REDD+ baselines: A method and case study from central Mozambique. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 53, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosário, N.M. Agronegócio em Moçambique: Uma breve análise da situação de estrangerização do agronegócio. Soc. E Territ.–Natal 2019, 31, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaehringer, J.G.; Atumane, A.; Berger, S.; Eckert, S. Large-scale agricultural investments trigger direct and indirect land use change: New evidence from the Nacala corridor, Mozambique. J. Land Use Sci. 2018, 13, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhantumbo, I.; Salomão, A. Biofuels, Land Access and Rural Livelihoods in Mozambique; International Institute for Environment and Development (IIED): London, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-1-84369-744-2. [Google Scholar]
- Mozambique: Chimanimani Organic Coffee Project with 1600 Farmers to be Largest Plantation. Available online: https://clubofmozambique.com/news/mozambique-chimanimani-organic-coffee-project-with-1600-farmers-to-be-largest-plantation-photos-210098/ (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- MADER. Inquérito Agrário Integrado 2020: Marco Estatístico. República de Moçambique. Ministério da Agricultura e Desenvolvimento Rural. Direção de Planificação e Políticas. Moçambique. 2021. Available online: https://www.agricultura.gov.mz/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/MADER_Inquerito_Agrario_2020.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Serra, C.M.; Dondeyne, S.; Durang, T. (Coordenadores) O Meio Ambiente em Moçambique: Notas Para Reflexão Sobre Notas Para Reflexão Sobrea Situação Actual e os Desafios Para o Futuro a Situação Actual e os Desafios Para o Futuro. Grupo Ambiente—Parceiros de Cooperação. Maputo, Moçambique Maputo, Moçambique. Junho 2013. Available online: https://biblioteca.biofund.org.mz/biblioteca_virtual/o-meio-ambiente-em-mocambique-notas-para-reflexao-sobre-a-situacao-actual-e-os-desafios-para-o-futuro/ (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Bruna, N. Land of Plenty, Land of Misery: Synergetic Resource Grabbing in Mozambique. Land 2019, 8, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land of Plenty, Land of But a Few. Available online: https://terradealguns.divergente.pt/en/ (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Marzoli, A. Inventário Florestal Nacional. Projecto de Avaliação Integrada das Florestas de Moçambique (AIFM); DNTF: Maputo, Mozambique, 2007; Available online: https://biblioteca.biofund.org.mz/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/1548752956-F226.National%20Forest%20Inventory_Mozambique.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Joaquim-Meque, E.; Lousada, J.; Liberato, M.L.R.; Fonseca, T.F. Forest in Mozambique: Actual Distribution of Tree Species and Potential Threats. Land 2023, 12, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Forest Watch. Available online: https://www.globalforestwatch.org/dashboards/country/MOZ/?category=forest-change&lang=en&location=WyJjb3VudHJ5IiwiTU9aIl0%3D&map=eyJjYW5Cb3VuZCI6dHJ1ZX0%3D (accessed on 19 January 2024).
- Garcia, M.F.R.; Bandeira, R.R.; Lise, F. Influências ambientais na qualidade de vida em Moçambique. Rev. Eletrônica Acolhendo A Alf. Nos Países De Língua Port. 2009, III, 69–93. [Google Scholar]
- Lukumbuzya, K.; Sianga, C. Overview of the Timber Trade in East and Southern Africa: National Perspectives and Regional Trade Linkages; TRAFFIC and WWF; TRAFFIC: Cambridge, UK, 2017; 53p. [Google Scholar]
- Mbanze, A.A.; Shuangao, W.; Mudekwed, J.; Dias, C.R.; Sitoe, A. The rise and fall of plantation forestry in northern Mozambique. Trees For. People 2022, 10, 100343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woollen, E.; Ryan, C.M.; Baumert, S.; Vollmer, F.; Grundy, I.; Fisher, J.; Fernando, J.; Luz, A.; Ribeiro, N.; Lisboa, S.N. Charcoal production in the Mopane woodlands of Mozambique: What are the trade-offs with other ecosystem services? Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2016, 371, 20150315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffer, L.J. Indigenous fire use to manage savanna landscapes in southern Mozambique. Fire Ecol. 2010, 6, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamane, M.; Zorrilla-Miras, P.; Verweij, P.; Sitoe, A.; Ryan, C.; Patenaude, G.; Grundy, I.; Nhantumbo, I.; Metzger, M.; Ribeiro, N.; et al. Understanding Land Use, Land Cover and Woodland-Based Ecosystem Services Change, Mabalane, Mozambique. Energy Environ. Res. 2017, 7, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, B.A.; Robinson, C.A. Are agroecosystems sustainable in semiarid regions? Adv. Agron. 1997, 60, 191–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, S.; O’Keefe, P.; Sill, M. The Southern African Environment: Profiles of the SADC Countries; Earthscan: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781853831713. [Google Scholar]
- Certini, G.; Moya, D.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Mastrolonardo, G. The impact of fire on soil-dwelling biota: A review. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 488, 118989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwadialor, I.J. Minimizing the impact of mining activities for sustainable mined-out area conservation in Nigeria. FUTY J. Environ. 2011, 6, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raso, E.F.; Savaio, S.S.; Mulima, E.P. Impact of artisanal gold mining on agricultural soils: Case of the district of Manica, Mozambique. Rev. Verde 2022, 17, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondeyne, S.; Ndunguru, E.; Rafael, P.; Bannerman, J. Artisanal mining in central Mozambique: Policy and environmental issues of concern. Resour. Policy 2009, 34, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujere, N.; Isidro, M. Impacts of Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining on Water Quality in Mozambique and Zimbabwe. In Impact of Water Pollution on Human Health and Environmental Sustainability; McKeown, A.E., Bugyi, G., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2016; Chapter 5; pp. 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilson, G.; Mondlane, S.; Hilson, A.; Arnall, A.; Laing, T. Formalizing artisanal and small-scale mining in Mozambique: Concerns, priorities and challenges. Resour. Policy 2021, 71, 102001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondeyne, S.; Ndunguru, E. Artisanal gold mining and rural development policies in Mozambique: Perspectives for the future. Futures 2014, 62, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júnior, A.; Ibraimo, M.; Mosca, J. Exploração artesanal de ouro em Manica. Obs. Meio Rural 2016, 38, 1–20. Available online: https://omrmz.org/observador/or-38-exploracao-artesanal-de-ouro-em-manica/ (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Macie, A.E.A.; Bacci, D.C. Coal Mining at Moatize, Tete Province, Northwest of Mozambique: A Socio Environmental Analysis. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2017, 6, 433–442. [Google Scholar]
- Marove, C.A.; Sotozono, R.; Tangviroon, P.; Tabelin, C.B.; Igarashi, T. Assessment of soil, sediment and water contaminations around open-pit coal mines in Moatize, Tete province, Mozambique. Environ. Adv. 2022, 8, 100215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gani, A.H.A.; Aderoju, O.M.; Dias, A.G.; Monjane, A.A.R. Improving the attitude and reaction towards municipal solid waste management in Mozambique. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 247, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallwey, J.; Hettiarachchi, H.; Hulsmann, S. Challenges and opportunities in municipal solid waste management in Mozambique: A review in the light of nexus thinking. AIMS Environ. Sci. 2017, 4, 621–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tvedten, I.; Candiracci, S. “Flooding our eyes with rubbish”: Urban waste management in Maputo, Mozambique. Environ. Urban. 2018, 30, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tas, A.; Belon, A. A Comprehensive Review of the Municipal Solid Waste Sector in Mozambique: Background Documentation for the Formulation of Nationally Appropriate Mitigation Actions in the Waste Sector in Mozambique; Carbon Africa Limited: Maputo, Nairobi, 2014; Available online: www.carbonafrica.co.ke (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Ferrari, K.; Gamberini, R.; Rimini, B. The waste hierarchy: A strategic, tactical and operational approach for developing countries: The case study of Mozambique. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan 2016, 11, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, F.; Vinti, G.; Vaccari, M. Appropriate solid waste management system in Quelimane (Mozambique): Study and design of a small-scale center for plastic sorting with wastewater treatment. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2022, 4, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pereira, M.J.S.L.; Esteves da Silva, J. Environmental Stressors of Mozambique Soil Quality. Environments 2024, 11, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11060125
Pereira MJSL, Esteves da Silva J. Environmental Stressors of Mozambique Soil Quality. Environments. 2024; 11(6):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11060125
Chicago/Turabian StylePereira, Mario J. S. L., and Joaquim Esteves da Silva. 2024. "Environmental Stressors of Mozambique Soil Quality" Environments 11, no. 6: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11060125
APA StylePereira, M. J. S. L., & Esteves da Silva, J. (2024). Environmental Stressors of Mozambique Soil Quality. Environments, 11(6), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11060125





