Investigation of Lexical and Inflectional Verb Production and Comprehension in French-Speaking Teenagers with Developmental Language Disorders (DLDs)
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Verb Inflection Production and Comprehension Deficits in Preschool-Aged Children with DLD
1.2. Verb Inflection Deficits in Grade-School-Aged Children and Teenagers with DLD
1.3. Effects of Verb Argument Structure Properties in DLD
1.4. Accounts of Verb Production and Comprehension Deficits in DLD
1.5. The Present Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.1.1. Participants with DLD
2.1.2. Control Participants
2.2. Tasks and Stimuli
2.2.1. Action Naming
2.2.2. Sentence Production and Comprehension Tasks
2.3. Procedure
Response Coding
3. Results
3.1. Action Naming
3.1.1. Target Verb Production
3.1.2. Non-Target Response Analysis for Verb Production
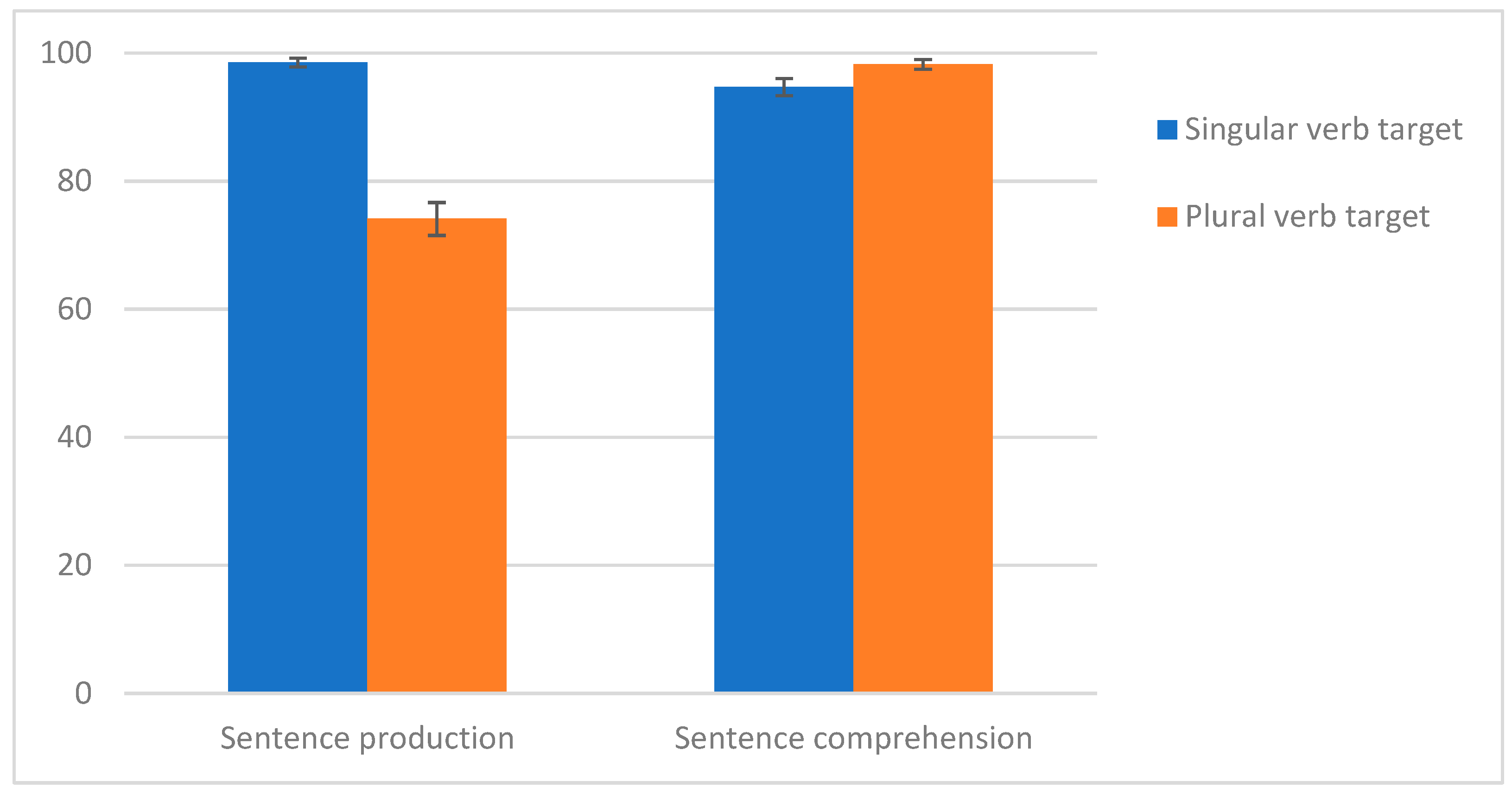
3.2. Sentence Production
3.2.1. Target Sentence Production
3.2.2. Non-Target Response Analysis for Sentence Production
3.3. Sentence Comprehension
3.3.1. Target Sentence Comprehension
3.3.2. Error Analysis for Sentence Comprehension
3.4. Additional Analyses on Argument Structure and Subject–Verb Agreement Effects Across Tasks
3.4.1. Argument Structure Effects Across Action Naming and Sentence Production Tasks
3.4.2. Subject–Verb Agreement Effects Across Sentence Comprehension and Production Tasks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| French Verb | Infinitive | Regularity (I/R) | 3ps Present Singular/Plural | δ | Frequency | AOA |
| Intransitive | ||||||
| dormir ‘to sleep’ | [dɔʁmiʁ] | I | [dɔʁ/dɔʁm] | 2 | 463.61 | 500 |
| partir ‘to leave’ | [paʁtsiʁ] | I | [pɑʁ/paʁt] | 2 | 1086.61 | – |
| cuire ‘to cook’ | [kɥiʁ] | I | [kɥi/kɥi:z] | 1 | 115.24 | 500 |
| rougir ‘to blush’ | [ʁuʒiʁ] | R | [ʁuʒi/ ʁuʒɪs] | 2 | 56.11 | – |
| grandir ‘to grow’ | [gʁãdziʁ] | R | [gʁãdzi/ gʁãdzɪs] | 2 | 117.21 | – |
| courir ‘to run’ | [kuʁiʁ] | I | [kuʁ] | 2 | 545.72 | 16 |
| rire ‘to laugh’ | [ʁiʁ] | I | [ʁi] | 1 | 612.34 | 500 |
| pleurer ‘to cry’ | [plœʁe] | R | [plœʁ] | 2 | 374.55 | 16 |
| nager ‘to swim’ | [nɑʒe] | R | [nɑʒ] | 2 | 162.51 | 27 |
| tomber ‘to fall’ | [tɔ̃be] | R | [tɔ̃b] | 2 | 871.87 | 27 |
| 1.8 (0.42) | 440.60 (347.17) | |||||
| Transitive | ||||||
| remplir ‘to fill’ | [ʁãpliʁ] | R | [ʁãpli/ ʁãplɪs] | 2 | 111.22 | 500 |
| sentir ‘to smell’ | [sãtsiʁ] | I | [sã/sãt] | 2 | 236.81 | 500 |
| lire ‘to read’ | [liʁ] | I | [li/li:z] | 1 | 1757.45 | 26 |
| mordre ‘to bite’ | [mɔʁdʁ] | I | [mɔ:ʁ/ mɔʁd] | 1 | 88.51 | 500 |
| construire ‘to build’ | [kɔ̃strɥiʁ] | I | [kɔ̃strɥi/ kɔ̃strɥi:z] | 2 | 144.2S6 | 500 |
| manger ‘to eat’ | [mãʒe] | R | [mãʒ] | 2 | 1468.30 | 11 |
| prendre ‘to take’ | [pʁãdʁ] | I | [pʁã/pʁɛn] | 1 | 1656.39 | 15 |
| couper ‘to cut’ | [kupe] | R | [kup] | 2 | 316.91 | 25 |
| cacher ‘to hide’ | [kaʃe] | R | [kaʃ] | 2 | 463.46 | 29 |
| détruire ‘to destroy’ | [detʁɥiʁ] | I | [detʁɥi/ detʁɥi:z] | 2 | 13.56 | – |
| 1.7 (0.48) | 625.74 (706.07) | |||||
| Ditransitive | ||||||
| lire/raconter ‘to read/tell’ | [liʁ] | I | [li/li:z] | 1 | 1757.45 | 26 |
| vendre ‘to sell’ | [vãdʁ] | I | [vã/vãd] | 1 | 198.76 | – |
| voler ‘to steal’ | [vɔle] | R | [vɔl] | 2 | 488.96 | 500 |
| lancer ‘to throw’ | [lãse] | R | [lãs] | 2 | 194.83 | 13 |
| donner ‘to give’ | [dɔne] | R | [dɔn] | 2 | 1230.13 | 21 |
| offrir ‘to offer’ | [ɔfriʁ] | I | [ɔfr] | 2 | 126.56 | – |
| dire ‘to tell’ | [dziʁ] | I | [dzi/dzi:z] | 1 | 5949.40 | 500 |
| apporter ‘to bring’ | [apɔʁrte] | R | [apɔʁrt] | 3 | 313.84 | 26 |
| brosser ‘to brush’ | [brɔse] | R | [brɔs] | 2 | 22.37 | 15 |
| laver ‘to wash’ | [lave] | R | [lav] | 2 | 407.14 | 28 |
| 1.8 (0.63) | 1068.94 (1800.26) | |||||
| Kruskal–Wallis test a | H(2) = 0.32, p = 0.85 | H(2) = 0.23, p = 0.89 | H(2) = 0.32, p = 0.85 | |||
| Notes: Frequencies are from the Manulex database. AOA, Age of Acquisition. Numbers in bold correspond to the month that the verb emerged or is acquired by children based on Trudeau et al. (2008). AOA of 500 corresponds to verbs that are listed as part of the first 500 words of French-speaking children in Quebec (Bergeron & Henry, 1994). Missing values are identified with a –. a Statistical analyses were performed between the 3 verb types using Kruskal–Wallis tests; no significant differences were found between the number of regular/irregular verbs nor between their number of syllables or verb frequencies. | ||||||
Appendix B
| Response Types | Total | Mean | Median | Range |
| DLD group | ||||
| Instransitive verbs | ||||
| Verb substitution (same ArgStr) | 15 (11) | 0.88 | 1 | 0–3 |
| Verb substitution (diff. ArgStr) | 3 (3) | 0.18 | 0 | 0–1 |
| Lexical category change | 5 (5) | 0.29 | 0 | 0–1 |
| Transitive verbs | ||||
| Verb substitution (same AgStr) | 32 (14) | 2.00 | 2 | 0–4 |
| Verb substitution (diff. ArgStr) | 13 (13) | 0.76 | 1 | 0–1 |
| Lexical category change | 2 (2) | 0.12 | 0 | 0–1 |
| Ditransitive verbs | ||||
| Verb substitution (same AgStr) | 87 (17) | 5.12 | 5 | 4–6 |
| Verb substitution (diff. ArgStr) | 18 (16) | 1.06 | 1 | 0–2 |
| Lexical category change | 5 (4) | 0.29 | 0 | 0–2 |
| TL group | ||||
| Instransitive verbs | ||||
| Verb substitution (same ArgStr) | 17 (13) | 1 | 1 | 0–3 |
| Verb substitution (diff. ArgStr) | 3 (3) | 0.18 | 0 | 0–1 |
| Lexical category change | 2 (2) | 0.12 | 0 | 0–1 |
| Transitive verbs | ||||
| Verb substitution (same AgStr) | 26 (14) | 1.53 | 1 | 0–4 |
| Verb substitution (diff. ArgStr) | 15 (14) | 0.88 | 1 | 0–2 |
| Lexical category change | – | – | – | – |
| Ditransitive verbs | ||||
| Verb substitution (same AgStr) | 80 (17) | 4.71 | 5 | 2–6 |
| Verb substitution (diff. ArgStr) | 20 (13) | 1.18 | 1 | 0–4 |
| Lexical category change | – | – | – | – |
| 1 | A second model with group as a simple factor was not significantly different from this one (AIC = 233.4, BIC = 248.8, log likelihood = −1127, nb. of observations = 345); however, no differences were found between groups in follow-up analyses on error patterns. |
| 2 | Other idiosyncratic error types were one unintelligible response provided by a participant with DLD, and one overregularization (mordre [mɔʁd(ʁ)] → *mordir [mɔʁdiʁ] ‘to bite’), by a TL participant. |
| 3 | Other unique error types by participants with DLD were one lexical category change (le poulet rôtit ‘the chicken roasts’ → deux dindes au feu de bois ‘two turkeys at the wood fire’), and one overregularization (sentit /sɛãti/ -> *senta /sɛãta/ ‘smelled’). One TL participant omitted a subject and one omitted one answer. |
References
- Abdalla, F., & Crago, M. (2008). Verb morphology deficits in Arabic-speaking children with specific language impairment. Applied Psycholinguistics, 29(2), 315–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu, L., Sanz-Torrent, M., Olmos, J. G., & MacWhinney, B. (2013). The formulation of argument structure in SLI: An eye-movement study. Clinical Linguistics & Phonetics, 27(2), 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balthazar, C. H., Ebbels, S., & Zwitserlood, R. (2020). Explicit grammatical intervention for developmental language disorder: Three approaches. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 51(2), 226–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, D., Mächler, M., Bolker, B., & Walker, S. (2015). Fitting linear mixed-effects models USINGLME4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67(1), 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, A.-M., & Henry, F. (1994). GIRAFE: Guide d’intervention en réadaptation auditive: Formule de l’enfant. Grilles d’intervention. Méridien. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Bishop, D. V. M. (1994). Grammatical errors in specific language impairment: Competence or performance limitations? Applied Psycholinguistics, 15(4), 507–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D. V. M. (2014). Problems with tense marking in children with specific language impairment: Not how but when. Philisophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 369, 20120401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D. V. M., Snowling, M. J., Thompson, P. A., Greenhalgh, T., & The CATALISE-2 Consortium. (2017). Phase 2 of CATALISE: A multinational and multidisciplinary Delphi consensus study of problems with language development: Terminology. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 58(10), 1068–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, E., Vasić, N., & de Jong, J. (2014). Production and processing of subject–verb agreement in monolingual Dutch children with specific language impairment. Journal of Speech Language, and Hearing Research, 57(3), 952–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolini, U., Caselli, M. C., Deevy, P., & Leonard, L. B. (2002). Specific language impairment in Italian: The first steps in the search for a clinical marker. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders, 37(2), 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolini, U., Leonard, L. B., & Caselli, M. C. (1998). Specific language impairment in Italian and English: Evaluating alternative accounts of grammatical deficits. Language and Cognitive Processes, 13(1), 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, E., & Munzel, U. (2000). The nonparametric Behrens-Fisher Problem: Asymptotic theory and a small-sample approximation. Biometrical Journal, 42(1), 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clahsen, H. (1989). The grammatical characterization of developmental dysphasia. Linguistics, 27(5), 897–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clahsen, H., Bartke, S., & Göllner, S. (1997). Formal features in impaired grammars: A comparison of English and German SLI children. Journal of Neurolinguistics, 10(2–3), 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsi, P. M. (1972). Human memory and the medial temporal region of the brain [Unpublished doctoral thesis, McGill University]. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Courteau, É., Loignon, G., Steinhauer, K., & Royle, P. (2023). Identifying linguistic markers of French-speaking teenagers with developmental language disorder: Which tasks matter? Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 66(1), 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courteau, É., Royle, P., & Steinhauer, K. (2024). Number agreement processing in adolescents with and without developmental language disorder (DLD): Evidence from event-related brain potentials. Scientific Reports, 13, 22836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, T. A., Katz, J. S., & Robinson, J. L. (2016). Delayed match-to-sample in working memory: A BrainMap meta-analysis. Biological Psychology, 120, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, J., & Fletcher, P. (2014). Argument structure and specific language impairment: Retrospect and prospect. In J. Hoeksema, & D. Gilbers (Eds.), Black book: A festschrift in honor of Frans Zwarts. University of Groningen. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Dromi, E., Leonard, L. B., & Shteiman, M. (1993). The grammatical morphology of Hebrew-speaking children with specific language impairment: Some competing hypotheses. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 36(4), 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duinmeijer, I. (2013). Persistent problems in SLI: Which grammatical problems remain when children grow older? Linguistics in Amsterdam, 6, 28–48. [Google Scholar]
- Duinmeijer, I. (2017). Persistent grammatical differences in specific language impairment. rule learning or rule implementation? [Doctoral dissertation, University of Amsterdam]. LOT, Netherlands Graduate School. Available online: https://dare.uva.nl/search?identifier=2d891cea-6719-482c-b386-6b69ec848112 (accessed on 2 September 2025).[Green Version]
- Ebbels, S. H. (2014). Introducing the SLI debate. International Journal of Language and Communication Disorders, 49(4), 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbels, S. H., van der Lely, H. K., & Dockrell, J. E. (2007). Intervention for verb argument structure in children with persistent SLI: A randomized control trial. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 50(5), 1330–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elin Thordardottir, E. T., & Weismer, S. E. (2002). Verb argument structure weakness in specific language impairment in relation to age and utterance length. Clinical Linguistics & Phonetics, 16(4), 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J., & Weisberg, S. (2011). An {R} companion to applied regression (2nd ed.). Sage. Available online: http://socserv.socsci.mcmaster.ca/jfox/Books/Companion (accessed on 2 September 2025).[Green Version]
- Franck, J., Cronel-Ohayon, S., Chillier, L., Frauenfelder, U. H., Hamann, C., Rizzi, L., & Zesiger, P. (2004). Normal and pathological development of subject-verb agreement in speech production: A study on French children. Journal of Neurolinguistics, 17(2–3), 147–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopnik, M. (1990). Feature blindness: A case study. Language Acquisition, 1(2), 139–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grela, B. G., & Leonard, L. B. (2000). The influence of argument-structure complexity on the use of auxiliary verbs by children with SLI. Journal of Speech and Language Hearing Research, 43(5), 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güven, S., & Leonard, L. B. (2023). Verb morphology in Turkish-speaking children with and without DLD: The role of morphophonology. Clinical Linguistics & Phonetics, 37(1), 99–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, P. (2010). Older Dutch children with specific language impairment: Constructing an error profile [Master’s thesis, University of Amsterdam]. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Jakubowicz, C. (2003). Computational complexity and the acquisition of functional categories by French-speaking shildren with SLI. Linguistics, 41(2), 175–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresh, S. (2008). L’acquisition et le traitement de la morphologie du participe passé en français [Master’s thesis, UQÀM]. Available online: https://archipel.uqam.ca/1740 (accessed on 24 October 2020).[Green Version]
- Kunnari, S., Savinainen-Makkonen, T., Leonard, L. B., Makinen, L., Tolonen, A.-K., Luotonen, M., & Leinonen, E. K. (2011). Children with specific language impairment in Finnish: The use of tense and agreement inflections. Journal of Child Language, 38(5), 999–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalioti, M., Stavrakaki, S., Manouilidou, C., & Talli, I. (2016). Subject–verb agreement and verbal short-term memory: A perspective from Greek children with specific language impairment. First Language, 36(3), 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, A.-L., Quémart, P., Magis, D., & Maillart, C. (2014). The sentence repetition task: A powerful diagnostic tool for French children with specific language impairment. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 35(12), 3423–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenth, R. V. (2016). Least-squares means: The R package lsmeans. Journal of Statistical Software, 69(3), 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, L. B. (1989). Language learnability and specific language impairment in children. Applied Psycholinguistics, 10, 179–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, L. B. (2014). Specific language impairment across languages. Child Development Perspectives, 8(1), 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, L. B., Bortolini, U., Caselli, M. C., McGregor, K. K., & Sabbadini, L. (1992). Morphological deficits in children with specific language impairment: The status of features in the underlying grammar. Language Acquisition, 2(2), 151–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lété, B., Sprenger-Charolles, L., & Colé, P. (2004). MANULEX: A grade-level lexical database from French elementary-school readers. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers, 36, 156–166. [Google Scholar]
- Lukács, Á, Leonard, L. B., Kas, B., & Pléh, C. (2009). The use of tense and agreement by Hungarian-speaking children with language impairment. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 52(1), 98–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinis, T. (2011). On the nature and cause of specific language impairment: A view from sentence processing and infant research. Lingua, 121(3), 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, M. L. (2012). Interrater reliability: The kappa statistic. Biochemia Medica, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C. A., Leonard, L. B., & Finneran, D. (2008). Grammaticality judgements in adolescents with and without language impairment. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders, 43(3), 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscati, V., Rizzi, L., Vottari, I., Chilosi, A. M., Salvadorini, R., & Guasti, M. T. (2020). Morphosyntactic weaknesses in developmental language disorder: The role of structure and agreement configurations. Journal of Child Language, 47(5), 909–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- New, B., Pallier, C., Ferrand, L., & Matos, R. (2001). Une base de données lexicales du français contemporain sur internet: Lexique™//a lexical database for contemporary French: Lexique™. L’année Psychologique, 101(3), 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, J., & Crago, M. (2001). The morphosyntax of specific language impairment in French: An extended optional default account. Language Acquisition, 9(4), 269–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, J., Crago, M., & Genesee, F. (2005). Domain-general versus domain-specific accounts of specific language impairment: Evidence from bilingual children’s acquisition of object pronouns. Language Acquisition: A Journal of Developmental Linguistics, 13(1), 33–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Leroux, A. T. (2005). Number problems in children. In C. Gurski (Ed.), Proceedings of the 2005 Canadian linguistic association annual conference. University of Western Ontario. Available online: https://cla-acl.ca/pdfs/actes-2005/Perez-Leroux.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2025).[Green Version]
- Pizzioli, F., & Schelstraete, M.-A. (2008). The argument-structure complexity effect in children with specific language impairment: Evidence from the use of grammatical morphemes in French. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 51(3), 706–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poll, G. H., Miller, C. A., & van Hell, J. G. (2016). Sentence repetition accuracy in adults with developmental language impairment: Interactions of participant capacities and sentence structures. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 59(2), 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourquié, M. (2015). fLEX: Multilingual assessment of inflectional and lexical processing [Software, Intellectual Property 2016-01-88]. Basque Government. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Pourquié, M., Lacroix, H., & Kartushina, N. (2019). Investigating vulnerabilities in grammatical processing of bilinguals: Insights from Basque-Spanish adults and children. Linguistic Approaches to Bilingualism, 9(4–5), 600–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, M. L., & Bode, J. V. (1993). GAPS in the verb lexicons of children with specific language impairment. First Language, 13(37, Pt. 1), 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, M. L., Noll, K. R., & Grimm, H. (1997). An extended optional infinitive stage in German-speaking children with specific language impairment. Language Acquisition, 6(4), 255–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, M. L., Wexler, K., & Cleave, P. (1995). Specific Language Impairment as a Period of Extended Optional Infinitive. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research, 38, 850–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, T., & van Hout, R. (2015). The t test and beyond: Recommendations for testing the central tendencies of two independent samples in research on speech, language and hearing pathology. Journal of Communication Disorders, 58, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, Y., & Royle, P. (1999). Uninflected structure in familial language impairment: Evidence from French. Folia Phoniatrica et Logopaedica, 51(1–2), 70–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royle, P. (2007). Variable effects of morphology and frequency on inflection patterns of French preschoolers. The Mental Lexicon Journal, 2(1), 103–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royle, P., & Elin Thordardottir, E. T. (2008). Elicitation of the passe compose in French preschoolers with and without specific language impairment. Applied Psycholinguistics, 29(3), 341–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royle, P., St-Denis, A., Mazzocca, P., & Marquis, A. (2018). Insensitivity to verb conjugation patterns in French children with SLI. Clinical Linguistics & Phonetics, 32(2), 128–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secord, W. A., Wiig, E., Boulianne, L., Semel, E., & Labelle, M. (2009). Évaluation clinique des notions langagières fondamentales®—Version pour francophones du Canada (CELF® CDN-F). The Psychological Corporation; Pearson Assessment Inc. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Spoelman, M., & Bol, G. W. (2012). The use of subject-verb agreement and verb argument structure in monolingual and bilingual children with specific language impairment. Clinical Linguistics & Phonetics, 26(4), 357–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrakaki, S., Chrysomallis, M.-A., & Petraki, E. (2011). Subject-verb agreement, object clitics and wh-questions in bilingual French-Greek SLI: The case-study of a French-Greek-speaking child with SLI. Clinical Linguistics & Phonetics, 25(5), 339–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudeau, N., Sutton, A., Frank, I., Poulin-Dubois, D., Denault, J., & Sylvestre, A. (2008). Les inventaires MacArthur-Bates du développement de la communication (IMDC): Manuel technique et guide de l’utilisateur. Available online: https://eoa.umontreal.ca/agora-des-professionnels/ressources/inventaires-macarthur-bates-imbdc/ (accessed on 18 July 2011).[Green Version]
- Ullman, M. T., Earle, F. S., Walenski, M., & Janacsek, K. (2020). The neurocognition of developmental disorders of language. Annual Review of Psychology, 71(1), 389–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullman, M. T., & Pierpont, E. I. (2005). Specific language impairment is not specific to language: The procedural deficit hypothesis. Cortex, 41(3), 399–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Lely, H. K. J., & Battell, J. (2003). Wh-movement in children with grammatical DLD: A test of the RDDR Hypothesis. Language, 79(1), 153–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerman, F., duinmeijer, I., & Orgassa, A. (2011). Effecten van sli op nederlandse congruentie. Nederlandse Taalkunde, 16(1), 30–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| DLD Group (N = 17) | TL Group (N = 17) | Brunner–Munzel Tests | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | tbm | p-Value | CLES | |
| Age | 14.06 | 0.68 | 12.76 | 1.49 | 13.77 | <0.001 | 0.79 |
| School | 7.53 | 0.51 | 6.59 | 1.50 | 7.43 | <0.001 | 0.72 |
| Sent Rec | 54.69 | 7.82 | 69.69 | 8.88 | 43.02 | <0.0001 | 0.90 |
| Word Rec | 24.0 | 22.37 | 66.71 | 22.60 | 9.20 | <0.0001 | 0.08 |
| Corsi–F | 5.56 | 1.55 | 5.94 | 1.44 | 0.60 | 0.55 | 0.44 |
| Corsi–B | 4.94 | 1.06 | 5.94 | 1.68 | 2.10 | 0.04 | 0.31 |
| DMTS–1s | 0.88 | 0.10 | 0.92 | 0.07 | 1.24 | 0.22 | 0.37 |
| DMTS–5s | 0.84 | 0.13 | 0.87 | 0.09 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.44 |
| SV Agreement | Transitivity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Example | Sg | Pl | In | Tr | Di |
| 1 | Le monsieur/Il part [ilpaʁ] ‘The man/He leaves’ |  |  | |||
| 2 | Les messieurs/Ils partent [ilpaʁt] ‘The men/They leave’ |  |  | |||
| 3 | Le chien/Il mord [ilmɔʁ] l’os ‘The dog/He bites the bone’ |  |  | |||
| 4 | Les chiens/Ils mordent [ilmoʁd] l’os ‘The dogs/They bite the bone’ |  |  | |||
| 5 | L’enfant lance la balle au chien. The child throws the ball to the dog |  |  | |||
| Task | Type of Error | Code |
|---|---|---|
| 2 & 3 | Substitution with another lexical category (e.g., secret ‘secret’ for parler/dire ‘speak/say’) | 0 |
| 2 & 3 | Unintelligible or inexistent word | 0 |
| 2 & 3 | Substitution with a verb of same transitivity (e.g., lire ‘read to’ for parler/dire ‘speak/say to’) | 1 |
| 2 & 3 | Substitution with a verb of different transitivity (e.g., chuchoter ‘whisper’ for parler/dire ‘speak/say’) | 1 |
| 3 | Substitution with an uninflected verb (e.g., dormir ‘to sleep’ for ils dorment ‘they sleep’) | 0 |
| 3 | Subject omission (e.g., _ construit la maison ‘_ builds the house’) | 0 |
| 3 | Over-regularisation (e.g., senté [sãte] for senti [sãtsi] ’smelled’) | 0 |
| 3 | Direct object omission (e.g., les deux gars sentent_ ‘the two boys smell _’) | 1 |
| 3 | Use of a different tense (e.g., perfect past: s’est endormi ‘fell asleep’). | 1 |
| 3 | Substitution with a progressive form (e.g., en train de dire ‘in the process of saying’ = ‘is saying’) | 1 |
| 3 & 4 | Verb agreement error (e.g., grandit [grãdzi] ‘grows’ for grandissent [grãdzis] ‘grow’) | 0 |
| 3 & 4 | Lexical error (e.g., image of nage ‘(he) swims’ for grandit ‘(he) grows’) | 0 |
| 3 & 4 | Mixed error (e.g., image of nagent ‘(they) swim’ for grandit ‘(he) grows’) | 0 |
| Response Types | Total | Mean | Median | Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instransitive verbs | ||||
| Verb substitution (same ArgStr) | 32 (24) | 0.94 | 1 | 0–3 |
| Verb substitution (diff. ArgStr) | 6 (6) | 0.18 | 0 | 0–1 |
| Lexical category change | 7 (7) | 0.21 | 0 | 0–1 |
| Transitive verbs | ||||
| Verb substitution (same AgStr) | 58 (29) | 1.71 | 1.5 | 0–4 |
| Verb substitution (diff. ArgStr) | 28 (27) | 0.82 | 1 | 0–2 |
| Lexical category change | 2 (2) | 0.06 | 0 | 0–1 |
| Ditransitive verbs | ||||
| Verb substitution (same AgStr) | 167 (34) | 4.91 | 5 | 2–6 |
| Verb substitution (diff. ArgStr) | 38 (29) | 1.12 | 1 | 0–4 |
| Lexical category change | 5 (4) | 0.15 | 0 | 0–2 |
| Estimate | Std. | Error | z | Pr (>|z|) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept: TL froup, singular verbs | 5.6358 | 0.4918 | 11.460 | <0.000001 |
| Group: DLD | −2.0661 | 0.4217 | −4.900 | <0.000001 |
| cAGE | −0.6165 | 0.2699 | −2.284 | =0.0224 |
| Plural verbs | −1.5586 | 0.3041 | −5.126 | <0.000001 |
| Singular | Plural | |
|---|---|---|
| TL Group | 100 (0) | 92.36 (0.27) |
| DLD Group | 97.06 (0.17) | 55.88 (0.50) |
| Response Types | Total | Mean | Median | Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLD Group | ||||
| Verb substitution (same ArgStr) | 40 (16) | 2.35 | 1 | 0–4 |
| Verb substitution (different ArgStr) | 30 (14) | 1.76 | 2 | 0–4 |
| Progressive tense | 11 (8) | 0.65 | 0 | 0–2 |
| Verb number agreement | 75 (16) | 4.41 | 4 | 0–9 |
| Direct object omission | 5 (4) | 0.29 | 0 | 0–2 |
| Indirect object omission | 6 (6) | 0.35 | 0 | 0–1 |
| Uninflected verb a | 5 (1) | |||
| Other tense a | 5 (4) | 0.29 | 0 | 0–2 |
| TL Group | ||||
| Verb substitution (same ArgStr) | 47 (17) | 2.76 | 3 | 1–6 |
| Verb substitution (different AgStr) | 24 (13) | 1.41 | 1 | 0–4 |
| Progressive tense | 13 (9) | 0.76 | 1 | 0–2 |
| Verb number agreement | 13 (8) | 0.76 | 0 | 0–3 |
| Direct object omission | 2 (1) | |||
| Indirect object omission | 2 (1) |
| Estimate | Std. | Error | z | Pr (>|z|) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept: TL group, singular | 5.1335 | 0.8306 | 6.180 | <0.000001 |
| Group: DLD | −2.5420 | 0.7765 | −3.274 | =0.00106 |
| Number: plural | 1.233 | 0.6336 | 1.946 | =0.05161 |
| Response types a Only Evidenced in Participants with DLD | Total | Mean | Median | Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLD group | ||||
| Inflectional distractor | 19 (12) | 1.12 | 1 | 0–5 |
| Lexical distractor a | 2 (2) | 0.12 | 0 | 0–1 |
| Mixed distractor a | 1 (1) | |||
| TD group | ||||
| Inflectional Distractor | 1 (1) | 0.06 | 0 | 0–1 |
| Estimate | Std. | Error | z | Pr (>|z|) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept: TL group, singular, Task 3 sentence production | 9.8010 | 1.0548 | 9.292 | <0.000001 |
| Task4: comprehension | −6.2069 | 1.2079 | −5.139 | <0.000001 |
| Group: DLD | −2.4602 | 0.3779 | −6.510 | <0.000001 |
| Number: Task 4 | 4.7827 | 0.7406 | 6.458 | <0.000001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pourquié, M.; Courteau, E.; Duquette, A.-S.; Royle, P. Investigation of Lexical and Inflectional Verb Production and Comprehension in French-Speaking Teenagers with Developmental Language Disorders (DLDs). Behav. Sci. 2025, 15, 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15091252
Pourquié M, Courteau E, Duquette A-S, Royle P. Investigation of Lexical and Inflectional Verb Production and Comprehension in French-Speaking Teenagers with Developmental Language Disorders (DLDs). Behavioral Sciences. 2025; 15(9):1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15091252
Chicago/Turabian StylePourquié, Marie, Emilie Courteau, Ann-Sophie Duquette, and Phaedra Royle. 2025. "Investigation of Lexical and Inflectional Verb Production and Comprehension in French-Speaking Teenagers with Developmental Language Disorders (DLDs)" Behavioral Sciences 15, no. 9: 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15091252
APA StylePourquié, M., Courteau, E., Duquette, A.-S., & Royle, P. (2025). Investigation of Lexical and Inflectional Verb Production and Comprehension in French-Speaking Teenagers with Developmental Language Disorders (DLDs). Behavioral Sciences, 15(9), 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15091252






