Will Employee–AI Collaboration Enhance Employees’ Proactive Behavior? A Study Based on the Conservation of Resources Theory
Abstract
1. Introduction
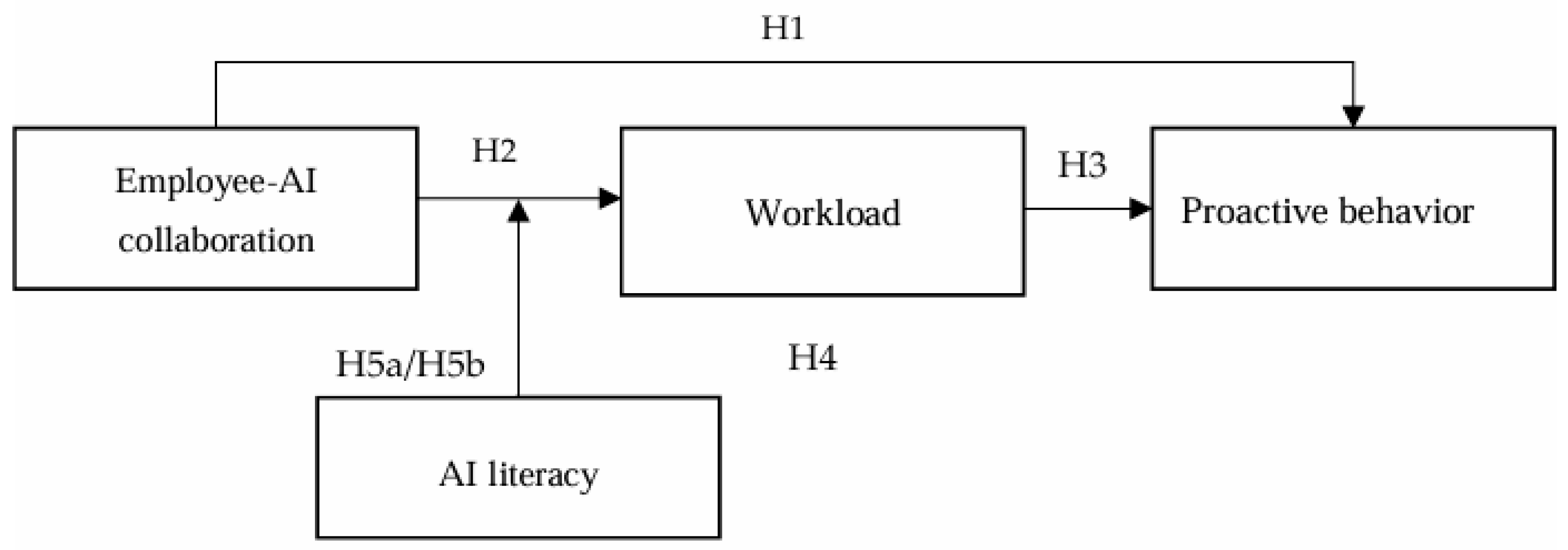
2. Theoretical Foundation and Research Hypotheses
2.1. Employee–AI Collaboration and Proactive Behavior
2.2. The Mediating Role of Workload
2.3. The Moderating Role of AI Literacy
3. Methodology
3.1. Procedure and Sample
3.2. Measurement
3.3. Analysis Strategy
4. Results
4.1. Common Method Bias Test
4.2. Descriptive Statistics Analysis
4.3. Confirmatory Factor Analysis
4.4. Hypothesis Testing
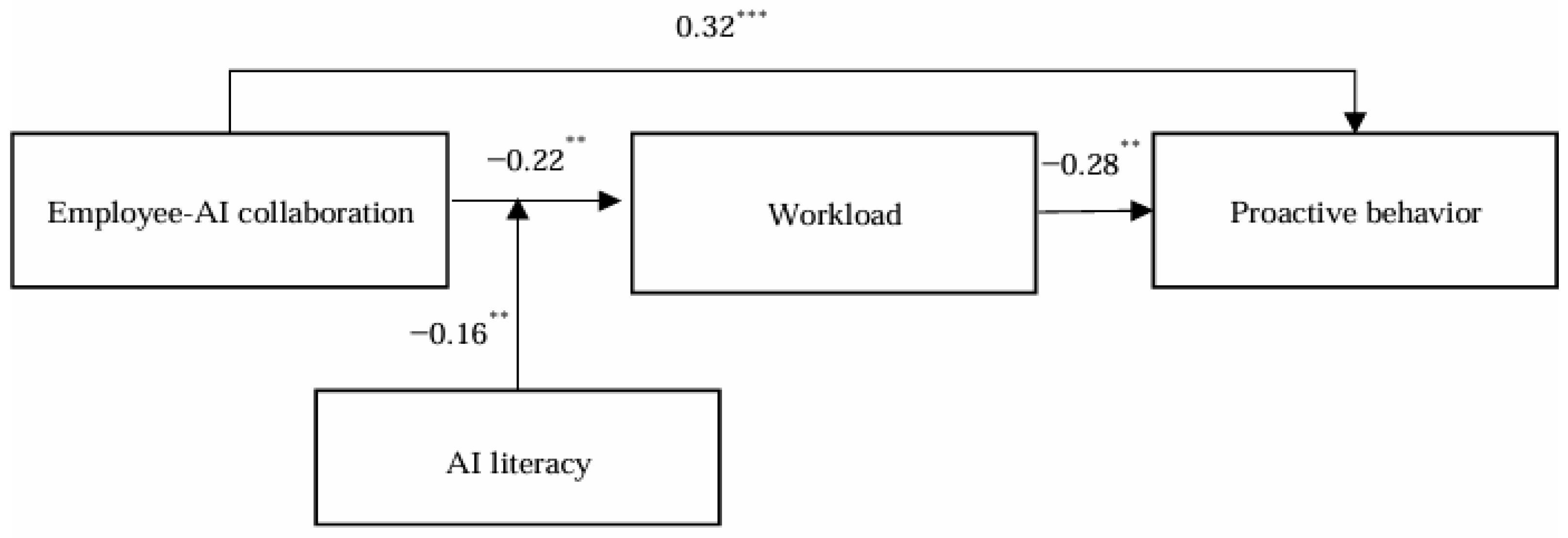
4.4.1. Direct Effect Test
4.4.2. Mediation Effect Test
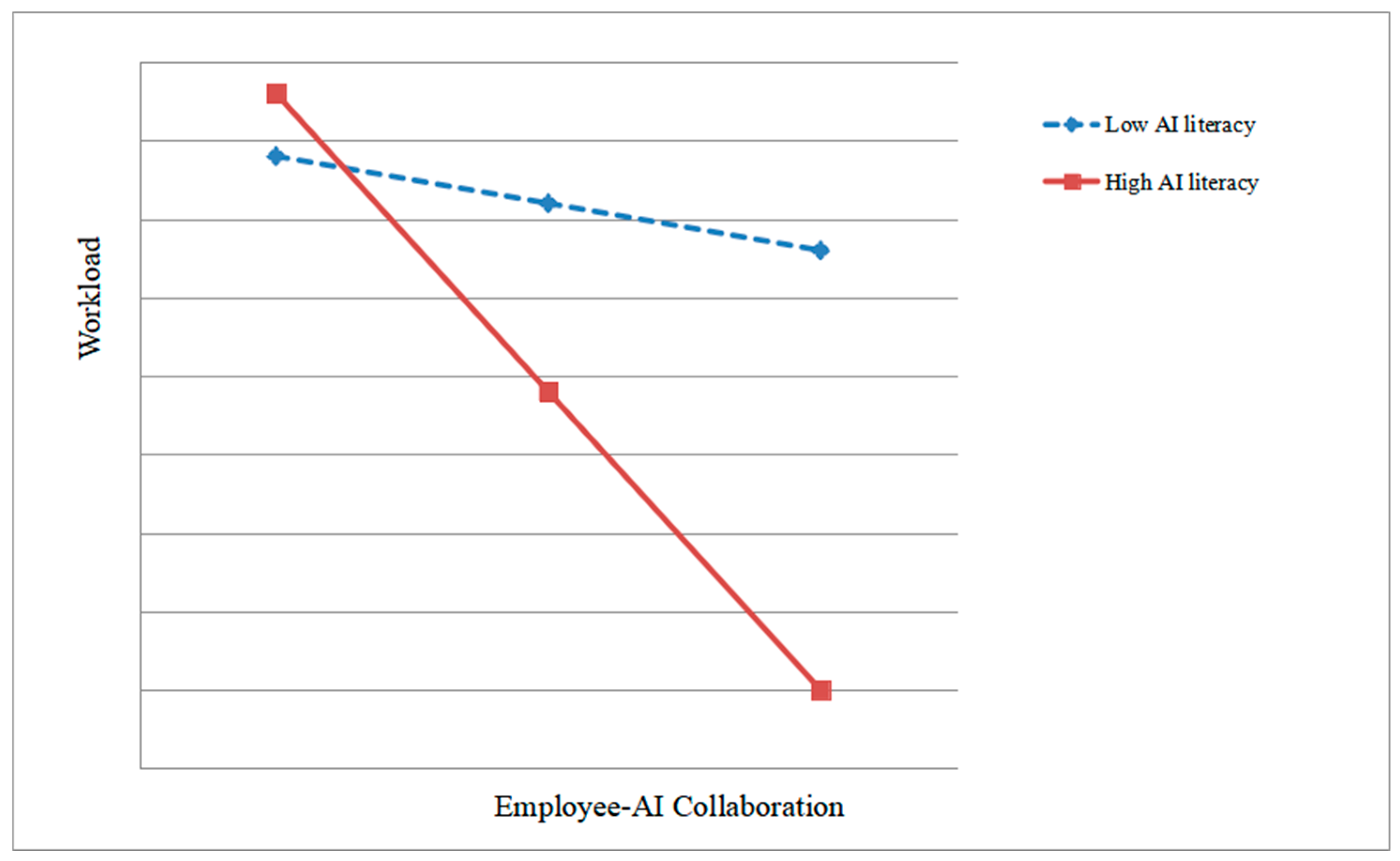
4.4.3. Moderation Effect Test
4.4.4. Moderated Mediation Effect Test
5. Discussion
5.1. Theoretical Contributions
5.2. Practical Contributions
5.3. Research Limitations and Future Research Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- Items of Employee–AI collaboration
- AI participates in my decision-making process.
- AI participates in my prediction process.
- AI participates in my problem-solving process.
- AI participates in my information identification and evaluation process.
- AI participates in my problems, opportunities, or risk recognition process.
- Items of Workload
- How often does your job require you to work very fast?
- How often does your job require you to work very hard?
- How often does your job leave you with little time to get things done?
- How often is there a great deal to be done?
- How often do you have to do more work than you can do well?
- Items of Proactive behavior
- At work, I would come up with new ideas for completing core tasks.
- I would actively seek out ways to improve how my work is done.
- I would initiate changes to make my job more efficient or effective.
- I would look for opportunities to take on responsibilities beyond my regular duties.
- Items of AI literacy
- I can distinguish between smart devices and non-smart devices.
- I know how AI technology can support work tasks and business processes.
- I can identify the AI technology used in the tools and platforms I use at work.
- I can skillfully use AI applications or products to support my work and improve performance.
- It is usually hard for me to learn to use a new AI application or product. (reverse scored)
- I use AI applications or products to enhance work efficiency and effectiveness.
- I can evaluate the capabilities and limitations of an AI application or product after using it for a while.
- I can choose proper solutions from various AI-driven tools or platforms available at work.
- I can select the most appropriate AI application or product for specific tasks in my job.
- I always comply with ethical principles when using AI applications or products in my work.
- I am always aware of privacy and information security issues when using AI applications or products.
- I am always alert to the potential misuse or abuse of AI technology in the workplace.
References
- Bai, J. Y., Huan, T. C. T., Leong, A. M. W., Luo, J. M., & Fan, D. X. (2025). Examining the influence of AI event strength on employee performance outcomes: Roles of AI rumination, AI-supported autonomy, and felt obligation for constructive change. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 126, 104111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankins, S., Ocampo, A. C., Marrone, M., Restubog, S. L. D., & Woo, S. E. (2024). A multilevel review of artificial intelligence in organizations: Implications for organizational behavior research and practice. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 45(2), 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basri, W. S. (2024). Enhancing AI auto efficacy: Role of AI knowledge, information source, behavioral intention and information & communications technology learning. Profesional de la Información, 33(3), e330325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørkelo, B., Einarsen, S., & Matthiesen, S. B. (2010). Predicting proactive behaviour at work: Exploring the role of personality as an antecedent of whistleblowing behaviour. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 83(2), 371–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowling, N. A., Alarcon, G. M., Bragg, C. B., & Hartman, M. J. (2015). A meta-analytic examination of the potential correlates and consequences of workload. Work & Stress, 29(2), 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, Á. A., Perer, A., & Hong, J. I. (2023). Improving human-AI collaboration with descriptions of AI behavior. Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction, 7(CSCW1), 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzarossa, M. C., Massari, L., & Tessera, D. (2016). Workload characterization: A survey revisited. ACM Computing Surveys, 48(3), 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardon, P., Fleischmann, C., Aritz, J., Logemann, M., & Heidewald, J. (2023). The challenges and opportunities of AI-assisted writing: Developing AI literacy for the AI age. Business and Professional Communication Quarterly, 86(3), 257–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, T. K. F., Ahmad, Z., Ismailov, M., & Sanusi, I. T. (2024). What are artificial intelligence literacy and competency? A comprehensive framework to support them. Computers and Education Open, 6, 100171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cu, M. K., Gamboa, V. L., Sy, J. J. A., Tan, S. M., & Ong, E. (2023, November 18). Humans + AI: Exploring the collaboration between AI and human labor in the workplace. 2023 9th International HCI and UX Conference in Indonesia (CHIuXiD) (pp. 35–40), Bali, Indonesia. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deci, E. L., Olafsen, A. H., & Ryan, R. M. (2017). Self-determination theory in work organizations: The state of a science. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 4(1), 19–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J., & Smith, A. P. (2017). The impact of workload and fatigue on performance. In G. Di Bucchianico, A. F. Rebelo, & S. P. S. Rajan (Eds.), Human mental workload: Models and applications (pp. 90–105). Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryer, D., & Payne, R. (1984). Proactive behaviour in unemployment: Findings and implications. Leisure Studies, 3(3), 273–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaba, D. M., & Lee, T. (1990). Measuring the workload of the anesthesiologist. Anesthesia & Analgesia, 71(4), 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopher, D., & Donchin, E. (1986). Workload: An examination of the concept. In K. R. Boff, L. Kaufman, & J. P. Thomas (Eds.), Handbook of perception and human performance (Vol. 2, pp. 1–49). Wiley. [Google Scholar]
- Guingrich, R. E., & Graziano, M. S. (2024). Ascribing consciousness to artificial intelligence: Human-AI interaction and its carry-over effects on human-human interaction. Frontiers in Psychology, 15, 1322781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, A. F. (2017). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression-based approach (2nd ed.). Guilford Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Heyder, T., & Posegga, O. (2021). Extending the foundations of AI literacy. In Proceedings of the 42nd International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS) (Vol. 9, pp. 1–9). Association for Information Systems. [Google Scholar]
- Hobfoll, S. E., & Shirom, A. (2000). Conservation of resources theory: Applications to stress and management in the workplace. In R. T. Golembiewski (Ed.), Handbook of organizational behavior (2nd ed., pp. 57–81). CRC Press. [Google Scholar]
- Hornberger, M., Bewersdorff, A., & Nerdel, C. (2023). What do university students know about artificial intelligence? Development and validation of an AI literacy test. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 5, 100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H., Yin, Z., Baruch, Y., & Yuan, Y. (2023). The impact of trust in AI on career sustainability: The role of employee–AI collaboration and protean career orientation. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 146, 103928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.-C., Korte, S.-M., Burton, S., Keskitalo, P., Turunen, T., Smith, D., Wang, L., Lee, J. C.-K., & Beaton, M. C. (2025). Artificial intelligence (AI) literacy: An argument for AI literacy in education. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 62, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosch, T., Karolus, J., Zagermann, J., Reiterer, H., Schmidt, A., & Woźniak, P. W. (2023). A survey on measuring cognitive workload in human-computer interaction. ACM Computing Surveys, 55(13s), 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-M., Liu, K.-X., Xie, J.-F., & Wu, H.-Y. (2024a). How does human-robot collaboration affect hotel employees’ proactive behavior? International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction. Advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-M., Wu, T.-J., Wu, Y. J., & Goh, M. (2023). Systematic literature review of human-machine collaboration in organizations using bibliometric analysis. Management Decision, 61(10), 2920–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-M., Zhang, L.-X., & Mao, M.-Y. (2025). How does human-AI interaction affect employees’ workplace procrastination? Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 212, 123951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-M., Zhang, R.-X., Wu, T.-J., & Mao, M. (2024b). How does work autonomy in human-robot collaboration affect hotel employees’ work and health outcomes? Role of job insecurity and person-job fit. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 117, 103654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintner, T. (2024). A systematic review of AI literacy scales. npj Science of Learning, 9(1), 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvi, R., Foroudi, P., & AmirDadbar, N. (2025). Dynamics of user engagement: AI mastery goal and the paradox mindset in AI-employee collaboration. International Journal of Information Management, 83, 102908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, B. W., Guay, R. P., Colbert, A. E., & Stewart, G. L. (2019). Proactive personality and proactive behaviour: Perspectives on person-situation interactions. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 92(1), 30–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D. T. K., Leung, J. K. L., Chu, K. W. S., & Qiao, M. S. (2021). AI literacy: Definition, teaching, evaluation and ethical issues. Proceedings of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 58(1), 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S. Y., Kuo, P. Y., Barbarin, A., Kaziunas, E., Chow, A., Singh, K., & Lasecki, W. S. (2019, November 9–13). Identifying challenges and opportunities in human-AI collaboration in healthcare. Companion Publication of the 2019 Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (pp. 506–510), Austin, TX, USA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perchik, J. D., Smith, A., Elkassem, A., Park, J., Rothenberg, S., Tanwar, M., Yi, P., Sturdivant, A., Tridandapani, S., & Sotoudeh, H. (2023). Artificial intelligence literacy: Developing a multi-institutional infrastructure for AI education. Academic Radiology, 30(7), 1472–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickup, L., Wilson, J. R., Norris, B. J., Mitchell, L., & Morrisroe, G. (2005). The Integrated Workload Scale (IWS): A new self-report tool to assess railway signaller workload. Applied Ergonomics, 36(6), 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinski, M., & Benlian, A. (2023, January 3–6). AI literacy: Towards measuring human competency in artificial intelligence. 56th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (pp. 165–174), Maui, HI, USA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinski, M., & Benlian, A. (2024). AI literacy for users: A comprehensive review and future research directions of learning methods, components, and effects. Computers in Human Behavior: Artificial Humans, 2(1), 100062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preacher, K. J., Rucker, D. D., & Hayes, A. F. (2007). Addressing moderated mediation hypotheses: Theory, methods, and prescriptions. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 42(1), 185–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverberi, C., Rigon, T., Solari, A., Hassan, C., Cherubini, P., & Cherubini, A. (2022). Experimental evidence of effective human-AI collaboration in medical decision-making. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 14952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salanova, M., & Schaufeli, W. B. (2008). A cross-national study of work engagement as a mediator between job resources and proactive behaviour. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 19(1), 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperandio, J. (1971). Variation of operator’s strategies and regulating effects on workload. Ergonomics, 14(5), 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J., Ng, D. T. K., & Chu, S. K. W. (2023). Artificial intelligence (AI) literacy in early childhood education: The challenges and opportunities. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 4, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, S. S. (2020). Rise of machine agency: A framework for studying the psychology of human-AI interaction (HAII). Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 25(1), 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timperley, H., & Robinson, V. (2000). Workload and the professional culture of teachers. Educational Management & Administration, 28(1), 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, T., Sawa, Y., Kim, Y., Urakami, J., Oura, H., & Seaborn, K. (2022, April 29–May 5). Trust in human-AI interaction: Scoping out models, measures, and methods. Extended Abstracts of the 2022 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 1–7), New Orleans, LA, USA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardanyan, A. (2022). Employee-AI augmented collaboration: A qualitative study of fashion designers and stylists. In Academy of management proceedings (Vol. 2022, No. 1, p. 18240). Academy of Management. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B., Rau, P.-L. P., & Yuan, T. (2023). Measuring user competence in using artificial intelligence: Validity and reliability of artificial intelligence literacy scale. Behaviour & Information Technology, 42(9), 1324–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D., Churchill, E., Maes, P., Fan, X., Shneiderman, B., Shi, Y., & Wang, Q. (2020, April 25–30). From human-human collaboration to Human-AI collaboration: Designing AI systems that can work together with people. Extended Abstracts of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 1–6), Honolulu, HI, USA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolley, A. W. (2024). Artificial intelligence and people at work. Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Business and Management. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T. J., Liang, Y., & Wang, Y. (2024). The buffering role of workplace mindfulness: How job insecurity of human-artificial intelligence collaboration impacts employees’ work–life-related outcomes. Journal of Business and Psychology, 39(6), 1395–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T. J., & Zhang, R. X. (2024). Exploring the impacts of intention towards human-robot collaboration on frontline hotel employees’ positive behavior: An integrative model. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 123, 103912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T. J., Zhang, R. X., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Navigating the human-artificial intelligence collaboration landscape: Impact on quality of work life and work engagement. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 62, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J., & Lu, W. (2022). Developing a human-organization-technology fit model for information technology adoption in organizations. Technology in Society, 70, 102010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z., Kong, H., Baruch, Y., Decosta, P. L. E., & Yuan, Y. (2024). Interactive effects of AI awareness and change-oriented leadership on employee-AI collaboration: The role of approach and avoidance motivation. Tourism Management, 105, 104966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H., Ye, L., Guo, M., & Deng, Y. (2025). Reflection or dependence: How AI awareness affects employees’ in-role and extra-role performance? Behavioral Sciences, 15(2), 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q., Tang, Y., Liu, Y., Liu, W., & Huang, Y. (2022, April 29–May 5). UX research on conversational human-AI interaction: A literature review of the ACM Digital Library. Proceedings of the 2022 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 1–24), New Orleans, LA, USA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X., Chen, C., Li, W., Yao, Y., Cai, F., Xu, J., & Qin, X. (2025). How do coworkers interpret employee AI usage: Coworkers’ perceived morality and helping as responses to employee AI usage. Human Resource Management. Advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Mean | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Gender | 1.34 | 0.56 | 1 | ||||||
| 2 Age | 27.34 | 2.56 | 0.12 | 1 | |||||
| 3 AI Literacy | 4.34 | 1.22 | 0.21 * | 0.31 ** | 1 | ||||
| 4 Employee–AI Collaboration | 4.45 | 1.59 | 0.13 | 0.23 * | 0.27 ** | 1 | |||
| 5 Workload | 5.01 | 1.51 | 0.31 ** | 0.23 * | −0.14 * | −0.21 ** | 1 | ||
| 6 Proactive Behavior | 4.45 | 1.32 | 0.22 * | 0.21 * | 0.22 * | 0.28 ** | −0.27 ** | 1 |
| Model | χ2/df | CFI | TLI | RMSEA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Four-factor model | 1.21 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.05 |
| Three-factor model (EAC + WL, PB, AL) | 7.34 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.16 |
| Two-factor model (EAC + WL + PB, AL) | 13.44 | 0.63 | 0.72 | 0.20 |
| Single-factor model (EAC + WL + PB + AL) | 16.89 | 0.49 | 0.44 | 0.29 |
| Moderator Variable | Effect | SE | Lower Limit of 95% Confidence Interval | Higher Limit of 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean − 1SD | 0.22 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.31 |
| Mean + 1SD | 0.01 | 0.36 | −0.06 | 0.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, C.; Zhao, X.; Guo, B.; Chen, N. Will Employee–AI Collaboration Enhance Employees’ Proactive Behavior? A Study Based on the Conservation of Resources Theory. Behav. Sci. 2025, 15, 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15050648
Sun C, Zhao X, Guo B, Chen N. Will Employee–AI Collaboration Enhance Employees’ Proactive Behavior? A Study Based on the Conservation of Resources Theory. Behavioral Sciences. 2025; 15(5):648. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15050648
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Chenxi, Xinan Zhao, Baorong Guo, and Ningning Chen. 2025. "Will Employee–AI Collaboration Enhance Employees’ Proactive Behavior? A Study Based on the Conservation of Resources Theory" Behavioral Sciences 15, no. 5: 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15050648
APA StyleSun, C., Zhao, X., Guo, B., & Chen, N. (2025). Will Employee–AI Collaboration Enhance Employees’ Proactive Behavior? A Study Based on the Conservation of Resources Theory. Behavioral Sciences, 15(5), 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15050648






