Prefrontal Oxygenation in a Subjective Decision on a Situational Danger Assessment Task: Personality Traits and Decision-Making Styles Involvement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
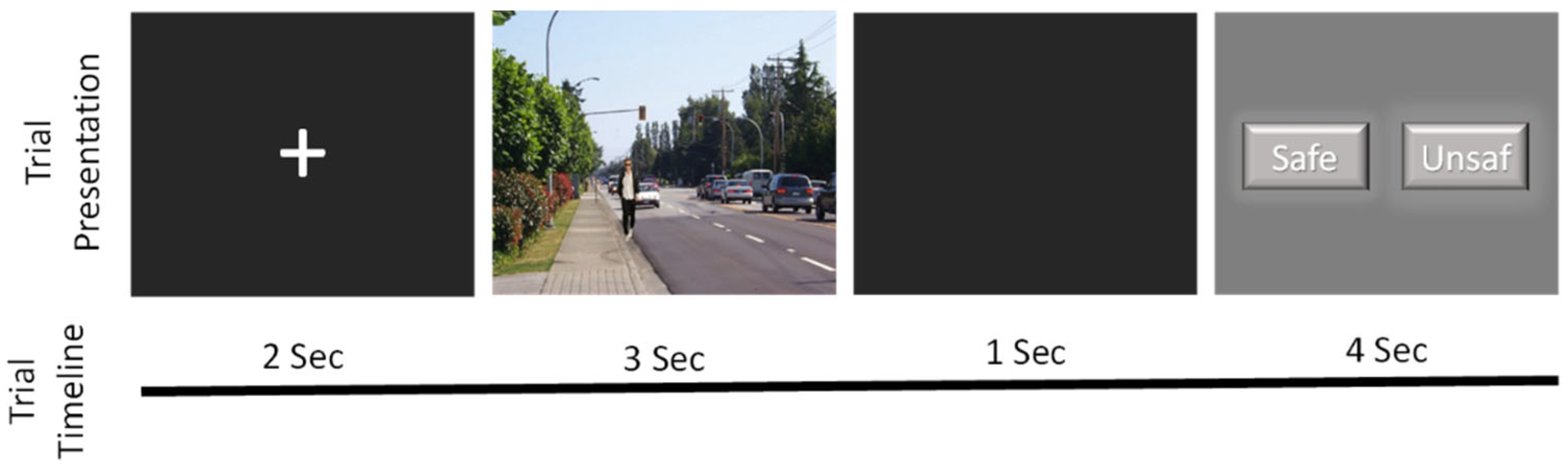
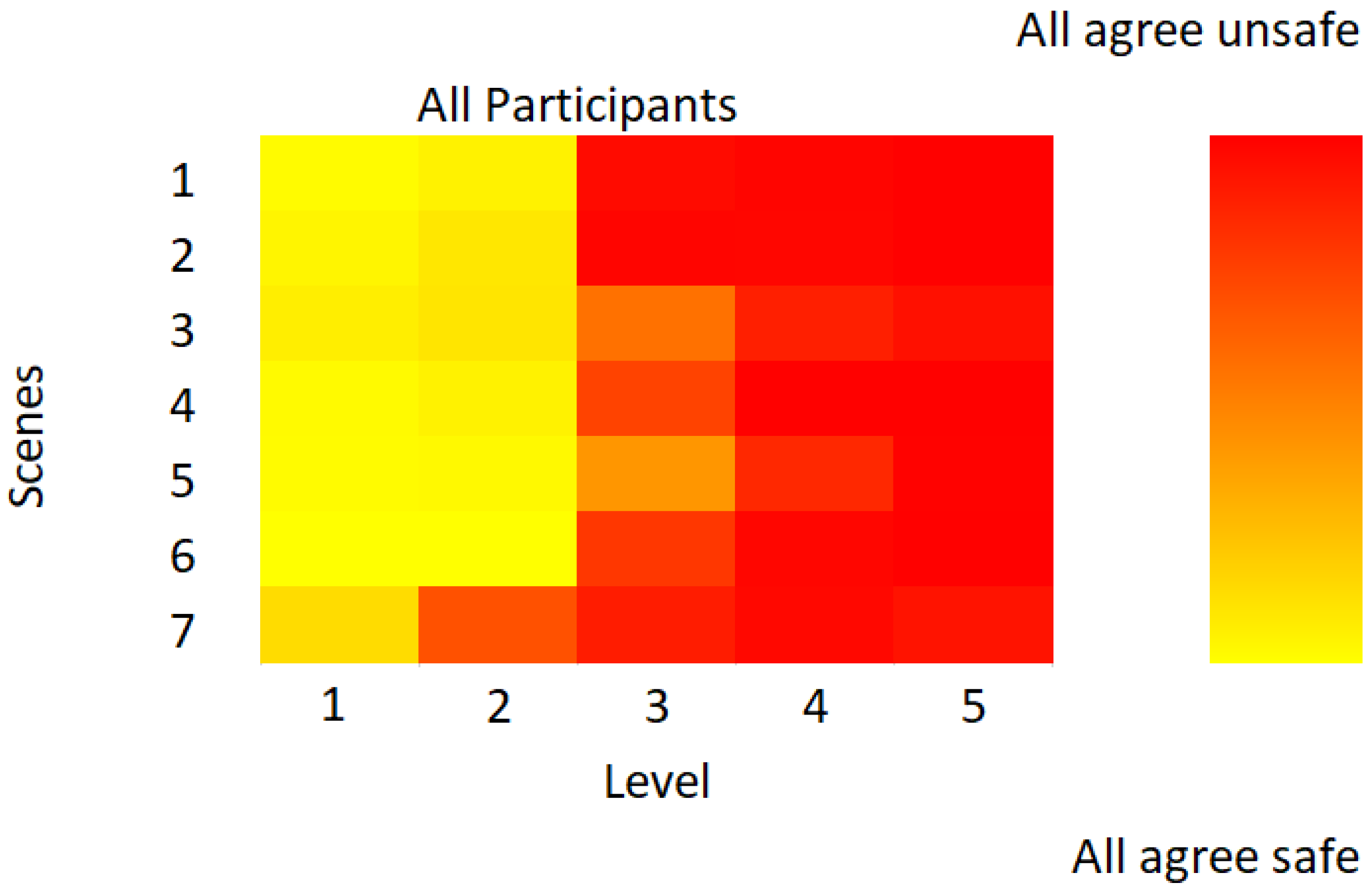
2.3. Behavioural Task: Subjective Situational Assessment
2.4. Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIR) Recording
2.5. Psychometric Measures
2.5.1. Zuckerman–Kuhlman–Aluja Personality Questionnaire Shortened Form
2.5.2. Melbourne Decision-Making Questionnaire (MDMQ)
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
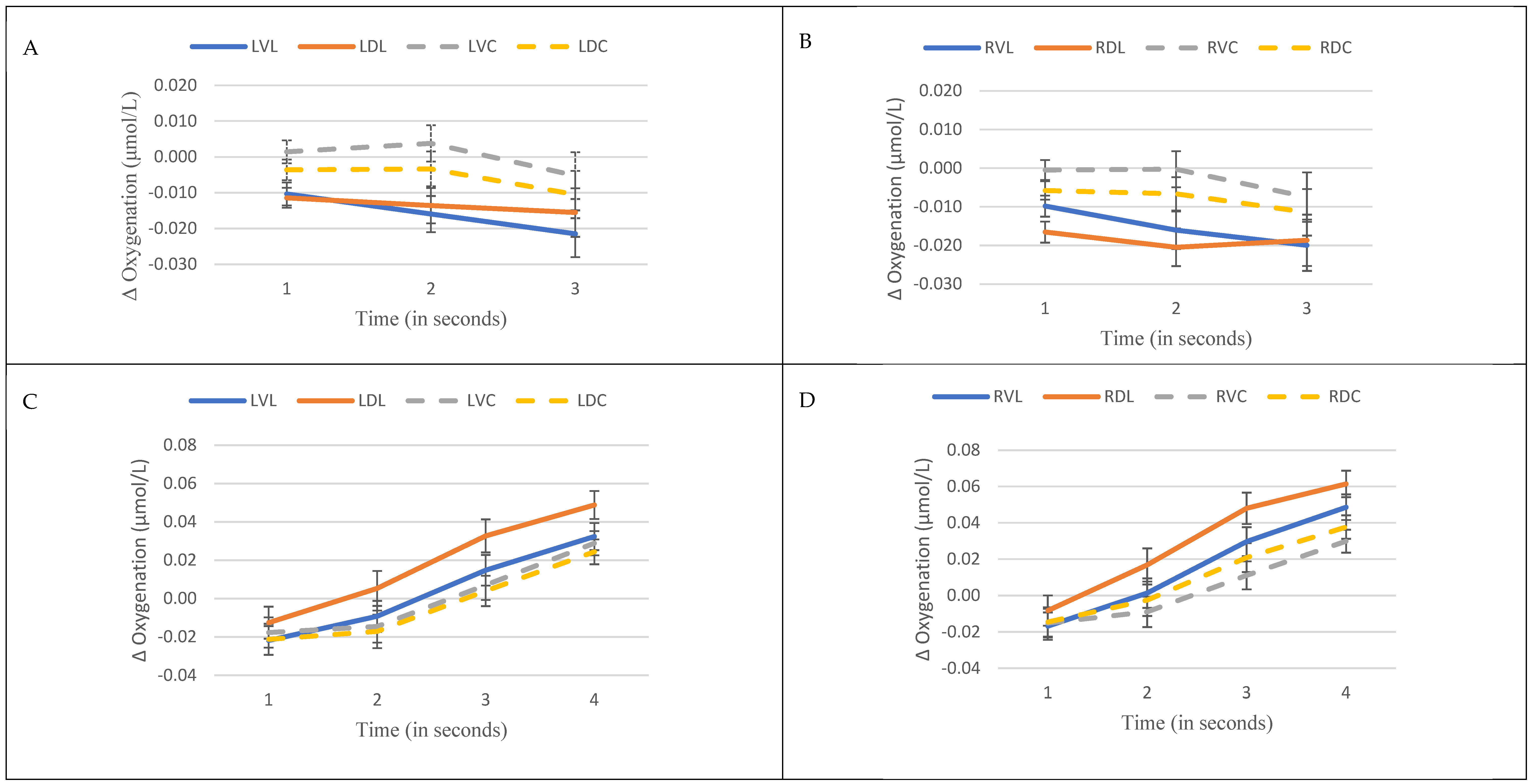
3.1. Prefrontal Oxygenation
3.2. Subgroup Analysis Based on ZKA-PQ and MDMQ Scores
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Acconito, C., Rovelli, K., & Angioletti, L. (2023). Neuroscience for a new concept of decision-making style. Neuropsychological Trends, 33, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluja, A., Balada, F., García, O., & García, L. F. (2024). Psychometric study of two decision-making measures: The melbourne decision-making questionnaire versus the general decision-making style questionnaire. Psychiatry International, 5(3), 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluja, A., Lucas, I., Blanch, A., García, O., & García, L. F. (2018). The Zuckerman-Kuhlman-Aluja personality questionnaire shortened form (ZKA-PQ/SF). Personality and Individual Differences, 134, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzate Saez De Heredia, R. A. S., Arocena, F. L., & Gárate, J. V. (2004). Decision-making patterns, conflict styles, and self-esteem. Psicothema, 16(1), 110–116. [Google Scholar]
- Ayaz, H., Shewokis, P. A., Curtin, A., Izzetoglu, M., Izzetoglu, K., & Onaral, B. (2011). Using MazeSuite and functional near infrared spectroscopy to study learning in spatial navigation. Journal of Visualized Experiments, 56, e3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balada, F., Lucas, I., Blanch, Á., Blanco, E., & Aluja, A. (2019). Neuroticism is associated with reduced oxygenation levels in the lateral prefrontal cortex following exposure to unpleasant images. Physiology & Behavior, 199, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltruschat, S., Cándido, A., Megías, A., Maldonado, A., & Catena, A. (2019). Risk proneness modulates the impact of impulsivity on brain functional connectivity. Human Brain Mapping, 41(4), 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barańczuk, U. (2019). The five factor model of personality and emotion regulation: A meta-analysis. Personality and Individual Differences, 139, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrash, J., Bruss, J., Anderson, S. W., Kuceyeski, A., Manzel, K., Tranel, D., & Boes, A. D. (2022). Lesions in different prefrontal sectors are associated with different types of acquired personality disturbances. Cortex, 147, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, A., & Van Der Linden, M. (2025). Decision-making and impulse control after frontal lobe injuries. Current Opinion in Neurology, 18(6), 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenstein, N. E., Schreuders, E., Peper, J. S., Crone, E. A., & van Duijvenvoorde, A. C. K. (2018). Individual differences in risk-taking tendencies modulate the neural processing of risky and ambiguous decision-making in adolescence. NeuroImage, 172, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutlee, C. G., & Huettel, S. A. (2012). The functional neuroanatomy of decision making: Prefrontal control of thought and action. Brain Research, 1428, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCoster, J., Iselin, A. M. R., & Gallucci, M. (2009). A conceptual and empirical examination of justifications for dichotomization. Psychological Methods, 14(4), 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domenech, P., & Koechlin, E. (2015). Executive control and decision-making in the prefrontal cortex. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 1, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Othman, R., El Othman, R., Hallit, R., Obeid, S., & Hallit, S. (2020). Personality traits, emotional intelligence and decision-making styles in Lebanese universities medical students. BMC Psychology, 8(1), 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecteau, S., Pascual-Leone, A., Zald, D. H., Liguori, P., Théoret, H., Boggio, P. S., & Fregni, F. (2007). Activation of prefrontal cortex by transcranial direct current stimulation reduces appetite for risk during ambiguous decision making. The Journal of Neuroscience, 27(23), 6212–6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellows, L. K. (2007). Advances in understanding ventromedial prefrontal function: The accountant joins the executive. Neurology, 68(13), 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, C. E., Poore, J. C., Krueger, F., Barbey, A. K., Solomon, J., & Grafman, J. (2014). The role of executive function and the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in the expression of neuroticism and conscientiousness. Social Neuroscience, 9(2), 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianotti, L. R., Knoch, D., Faber, P. L., Lehmann, D., Pascual-Marqui, R. D., Diezi, C., Schoch, C., Eisenegger, C., & Fehr, E. (2009). Tonic activity level in the right prefrontal cortex predicts individuals’ risk taking. Psychological Science, 20(1), 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon-Jones, E., & Gable, P. A. (2018). On the role of asymmetric frontal cortical activity in approach and withdrawal motivation: An updated review of the evidence. Psychophysiology, 55(1), e12879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heekeren, H. R., Marrett, S., Bandettini, P. A., & Ungerleider, L. G. (2004). A general mechanism for perceptual decision-making in the human brain. Nature, 431(7010), 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A. J., Hollinshead, M. O., Roffman, J. L., Smoller, J. W., & Buckner, R. L. (2016). Individual differences in cognitive control circuit anatomy link sensation seeking, impulsivity, and substance use. Journal of Neuroscience, 36(14), 4038–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, M., Grannan, B., Haroush, K., Moses, Z. B., Eskandar, E. N., Herrington, T., Patel, S., & Williams, Z. M. (2019). Dorsolateral prefrontal neurons mediate subjective decisions and their variation in humans. Nature Neuroscience, 22(6), 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keune, P. M., van der Heiden, L., Várkuti, B., Konicar, L., Veit, R., & Birbaumer, N. (2012). Prefrontal brain asymmetry and aggression in imprisoned violent offenders. Neuroscience Letters, 515(2), 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaleghi, A., Pirzad Jahromi, G., Zarafshan, H., Mostafavi, S. A., & Mohammadi, M. R. (2020). Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation of prefrontal cortex on risk-taking behavior. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 74(9), 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein-Flügge, M. C., Bongioanni, A., & Rushworth, M. F. (2022). Medial and orbital frontal cortex in decision-making and flexible behavior. Neuron, 110(17), 2743–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., Chen, R., Zhang, S., Turel, O., Bechara, A., Feng, T., Chen, H., & He, Q. (2019). Hemispheric mPFC asymmetry in decision making under ambiguity and risk: An fNIRS study. Behavioural Brain Research, 359, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, I., Balada, F., Blanco, E., & Aluja, A. (2019). Prefrontal cortex activity triggered by affective faces exposure and its relationship with neuroticism. Neuropsychologia, 132, 107146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, L., Burnett, P., Radford, M., & Ford, S. (1997). The melbourne decision making questionnaire: An instrument for measuring patterns for coping with decisional conflict. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Selva, J. M., Sánchez-Navarro, J. P., Bechara, A., & Román, F. (2006). Brain mechanisms involved in decision-making. Revista de Neurología, 42(7), 411–418. [Google Scholar]
- Molero-Chamizo, A., Riquel, R. M., Moriana, J. A., Nitsche, M. A., & Rivera-Urbina, G. N. (2019). Bilateral prefrontal cortex anodal tDCS effects on self-reported aggressiveness in imprisoned violent offenders. Neuroscience, 397, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morawetz, C., Mohr, P. N., Heekeren, H. R., & Bode, S. (2019). The effect of emotion regulation on risk-taking and decision-related activity in prefrontal cortex. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 14(10), 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsini, C. A., Heshmati, S. C., Garman, T. S., Wall, S. C., Bizon, J. L., & Setlow, B. (2018). Contributions of medial prefrontal cortex to decision making involving risk of punishment. Neuropharmacology, 139, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouerchefani, R., Ouerchefani, N., Allain, P., Ben Rejeb, M. R., & Le Gall, D. (2017). Contribution of different regions of the prefrontal cortex and lesion laterality to deficit of decision-making on the Iowa Gambling Task. Brain Cognition, 111, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panidi, K., Vorobiova, A. N., Feurra, M., & Klucharev, V. (2022). Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex plays causal role in probability weighting during risky choice. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 16115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Gómez, C., Vidal-Piñeiro, D., Clemente, I. C., Pascual-Leone, Á., & Bartrés-Faz, D. (2011). Down-regulation of negative emotional processing by transcranial direct current stimulation: Effects of personality characteristics. PLoS ONE, 6(7), e22812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psychology Software Tools, Inc. (2016). E-Prime 3.0 [Computer software]. Available online: https://support.pstnet.com/ (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Rodrigo, A. H., Ayaz, H., & Ruocco, A. C. (2016a). Examining the neural correlates of incidental facial emotion encoding within the prefrontal cortex using functional near-infrared spectroscopy. In D. Schmorrow, & C. Fidopiastis (Eds.), Foundations of augmented cognition: Neuroergonomics and operational neuroscience (Vol. 9743, pp. 102–112). Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, A. H., Di Domenico, S. I., Graves, B., Lam, J., Ayaz, H., Bagby, R. M., & Ruocco, A. C. (2016b). Linking trait-based phenotypes to prefrontal cortex activation during inhibitory control. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 11(1), 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolls, E. T., Wan, Z., Cheng, W., & Feng, J. (2022). Risk-taking in humans and the medial orbitofrontal cortex reward system. NeuroImage, 249, 118893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbloom, M. H., Schmahmann, J. D., & Price, B. H. (2012). The functional neuroanatomy of decision-making. The Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 24(3), 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sela, T., Kilim, A., & Lavidor, M. (2012). Transcranial alternating current stimulation increases risk-taking behavior in the balloon analog risk task. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, A., Miller, D., Feinstein, J. S., Goldberg, T. E., & Paulus, M. P. (2005). Left inferior prefrontal cortex activation during a semantic decision-making task predicts the degree of semantic organization. NeuroImage, 28(1), 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studer, B., Pedroni, A., & Rieskamp, J. (2013). Predicting risk-taking behavior from prefrontal resting-state activity and personality. PLoS ONE, 8(10), e76861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepanski, S. M., & Knight, R. T. (2014). Insights into human behavior from lesions to the prefrontal cortex. Neuron, 83(5), 1002–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, N., Wyres, M., Bollard, M., & Kneafsey, R. (2020). Use of functional near-infrared spectroscopy to evaluate cognitive change when using healthcare simulation tools. BMJ STEL, 6(6), 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbull, A., Wang, H. T., Murphy, C., Ho, N. S. P., Wang, X., Sormaz, M., Karapanagiotidis, T., Leech, R. M., Bernhardt, B., Margulies, D. S., & Smallwood, J. (2019). Left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex supports context-dependent prioritisation of off-task thought. Nature Communications, 10(1), 3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urieta, P., Aluja, A., Garcia, L. F., Balada, F., & Lacomba, E. (2021). Decision-making and the alternative five factor personality model: Exploring the role of personality traits, age, sex and social position. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 717705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urieta, P., Sorrel, M. A., Aluja, A., Balada, F., Lacomba, E., & García, L. F. (2022). Exploring the relationship between personality, decision-making styles, and problematic smartphone use. Current Psychology, 42(17), 14250–14267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Holstein, M., & Floresco, S. B. (2020). Dissociable roles for the ventral and dorsal medial prefrontal cortex in cue-guided risk/reward decision making. Neuropsychopharmacol, 45(4), 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volz, K. G., Schubotz, R. I., & von Cramon, D. Y. (2006). Decision-making and the frontal lobes. Current Opinion in Neurology, 19(4), 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Y., Zhang, J., Lu, F. M., Xiang, Y. T., & Yuan, Z. (2018). Neuroticism and conscientiousness respectively positively and negatively correlated with the network characteristic path length in dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex: A resting-state fNIRS study. Brain and Behavior, 8(9), e01074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X., Gao, M., Shi, J., Ye, H., & Chen, S. (2017). Modulating the activity of the DLPFC and OFC has distinct effects on risk and ambiguity decision-making: A tDCS study. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H., Chen, S., Huang, D., Wang, S., & Luo, J. (2015). Modulating activity in the prefrontal cortex changes decision-making for risky gains and losses: A transcranial direct current stimulation study. Behavioural Brain Research, 286, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W., Zhou, X., & Xia, L. X. (2019). Brain structures and functional connectivity associated with individual differences in trait proactive aggression. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Men | Women | Procrastination | Buck-Passing | Hypervigilance | Vigilance | Sensation Seeking | Neuroticism | Extraversion | Activity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Sd | Mean | Sd | t | p = | α | |||||||||
| Aggressiveness | 31.8 | 9.3 | 31.1 | 8.4 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.90 | 0.24 | 0.08 | 0.21 | −0.15 | 0.27 | 0.38 | −0.09 | 0.02 |
| Activity | 42.0 | 7.8 | 43.2 | 6.9 | −1.2 | 0.23 | 0.83 | −0.11 | −0.15 | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.18 | |
| Extraversion | 47.5 | 7.7 | 50.2 | 8.3 | −2.4 | 0.018 | 0.88 | −0.34 | −0.34 | −0.28 | 0.1 | 0.19 | −0.30 | ||
| Neuroticism | 33.5 | 9.1 | 35.9 | 9.8 | −1.8 | 0.081 | 0.91 | 0.55 | 0.47 | 0.66 | −0.13 | 0.02 | |||
| Sensation Seeking | 38.2 | 8.0 | 35.9 | 7.9 | 2.0 | 0.043 | 0.84 | 0.03 | −0.13 | −0.13 | −0.10 | ||||
| Vigilance | 9.6 | 2.2 | 10.2 | 1.9 | −2.1 | 0.039 | 0.77 | −0.16 | 0.21 | 0.04 | |||||
| Hypervigilance | 4.1 | 2.3 | 5.3 | 2.5 | −3.4 | 0.001 | 0.79 | 0.51 | 0.59 | ||||||
| Buck-Passing | 4.5 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 2.5 | −1.3 | 0.19 | 0.82 | 0.61 | |||||||
| Procrastination | 3.1 | 2.3 | 3.1 | 2.4 | −0.0 | 1.0 | 0.82 | ||||||||
| Effect | ZKA-PQ | MDMQ | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AG | AC | EX | NEU | SS | VIG | HYPER | BUCK-PAS | PROCR | ||||||||||
| F | p < | F | p < | F | p < | F | p < | F | p < | F | p < | F | p < | F | p < | F | p < | |
| Time | 2.3 | 0.059 | 0.88 | 0.47 | 0.85 | 0.50 | 1.86 | 0.12 | 1.48 | 0.21 | 2.72 | 0.029 | 2.31 | 0.058 | 1.29 | 0.27 | 1.72 | 0.14 |
| Level | 1.43 | 0.18 | 0.74 | 0.65 | 0.8 | 0.60 | 1.32 | 0.23 | 2.88 | 0.004 | 0.69 | 0.70 | 0.86 | 0.55 | 0.39 | 0.93 | 0.46 | 0.88 |
| Area | 0.73 | 0.75 | 1.32 | 0.19 | 0.9 | 0.56 | 0.6 | 0.87 | 1.63 | 0.069 | 0.78 | 0.69 | 0.7 | 0.78 | 1.06 | 0.39 | 1.76 | 0.042 |
| Level * Time | 1.09 | 0.37 | 0.76 | 0.73 | 0.8 | 0.69 | 1.84 | 0.025 | 1.83 | 0.026 | 0.33 | 0.99 | 1.31 | 0.19 | 1.6 | 0.067 | 1.01 | 0.45 |
| Time * Area | 0.81 | 0.74 | 1.28 | 0.16 | 0.93 | 0.57 | 0.45 | 0.99 | 1.32 | 0.13 | 0.87 | 0.66 | 0.75 | 0.82 | 0.73 | 0.85 | 1.16 | 0.26 |
| Level * Area | 0.96 | 0.56 | 1.18 | 0.19 | 1.13 | 0.26 | 1.01 | 0.46 | 1.38 | 0.045 | 0.91 | 0.66 | 1.15 | 0.22 | 1.01 | 0.46 | 0.78 | 0.87 |
| Level * Time * Area | 1.09 | 0.28 | 1.07 | 0.32 | 1.06 | 0.35 | 1.02 | 0.44 | 1.38 | 0.018 | 0.96 | 0.60 | 1.11 | 0.24 | 1.01 | 0.48 | 1.14 | 0.19 |
| Effect | ZKA-PQ | MDMQ | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AG | AC | EX | NEU | SS | VIG | HYPER | BUCK-PAS | PROCR | ||||||||||
| F | p < | F | p < | F | p < | F | p < | F | p < | F | p < | F | p < | F | p < | F | p < | |
| Time | 2.22 | 0.041 | 0.66 | 0.68 | 1.88 | 0.084 | 1.22 | 0.30 | 1.41 | 0.21 | 1.76 | 0.11 | 1.49 | 0.18 | 0.37 | 0.90 | 0.73 | 0.62 |
| Level | 1.27 | 0.26 | 1.11 | 0.36 | 1.01 | 0.43 | 1.49 | 0.16 | 1.45 | 0.18 | 0.45 | 0.89 | 0.8 | 0.60 | 0.85 | 0.56 | 0.63 | 0.76 |
| Area | 0.63 | 0.84 | 1.49 | 0.11 | 0.78 | 0.69 | 0.56 | 0.89 | 1.57 | 0.086 | 1.29 | 0.21 | 0.78 | 0.69 | 0.47 | 0.95 | 0.91 | 0.55 |
| Level * Time | 1.42 | 0.09 | 0.89 | 0.61 | 0.35 | 1.0 | 1.35 | 0.13 | 1.21 | 0.23 | 0.61 | 0.93 | 0.73 | 0.82 | 0.75 | 0.80 | 1.08 | 0.37 |
| Time * Area | 0.99 | 0.50 | 0.91 | 0.64 | 0.86 | 0.73 | 1.08 | 0.34 | 0.95 | 0.56 | 1.02 | 0.44 | 0.88 | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.91 | 0.76 | 0.86 |
| Level * Area | 1.31 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.48 | 1.03 | 0.42 | 1.06 | 0.36 | 1.14 | 0.25 | 1.02 | 0.45 | 1.05 | 0.39 | 0.94 | 0.61 | 1.32 | 0.072 |
| Level * Time * Area | 1.33 | 0.023 | 0.88 | 0.80 | 1.32 | 0.025 | 1.02 | 0.46 | 0.91 | 0.75 | 0.89 | 0.78 | 1.01 | 0.48 | 0.88 | 0.80 | 1.08 | 0.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balada, F.; Aymamí, N.; García, Ó.; García, L.F.; Aluja, A. Prefrontal Oxygenation in a Subjective Decision on a Situational Danger Assessment Task: Personality Traits and Decision-Making Styles Involvement. Behav. Sci. 2025, 15, 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15050647
Balada F, Aymamí N, García Ó, García LF, Aluja A. Prefrontal Oxygenation in a Subjective Decision on a Situational Danger Assessment Task: Personality Traits and Decision-Making Styles Involvement. Behavioral Sciences. 2025; 15(5):647. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15050647
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalada, Ferran, Neus Aymamí, Óscar García, Luis F. García, and Anton Aluja. 2025. "Prefrontal Oxygenation in a Subjective Decision on a Situational Danger Assessment Task: Personality Traits and Decision-Making Styles Involvement" Behavioral Sciences 15, no. 5: 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15050647
APA StyleBalada, F., Aymamí, N., García, Ó., García, L. F., & Aluja, A. (2025). Prefrontal Oxygenation in a Subjective Decision on a Situational Danger Assessment Task: Personality Traits and Decision-Making Styles Involvement. Behavioral Sciences, 15(5), 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15050647






