Assessing the Spectrum of Internet Use in a Healthy Sample: Altered Psychological States and Intact Brain Responses to an Equiprobable Go/NoGo Task
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. The Equiprobable Auditory Go/NoGo Task
2.3. EEG Recording and Processing
2.4. ERP Components
2.5. Questionnaires
2.5.1. The Nine-Item Problematic Internet Use Questionnaire (PIUQ-9)
2.5.2. The Dimensions of Problematic Internet Use (DPIU)
2.5.3. The Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI)
2.5.4. Beck’s Depression Inventory (BDI-II)
2.5.5. The Clark–Beck Obsessive–Compulsive Inventory (CBOCI)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants’ Data
3.2. Behavioral Results
PIU Questionnaires and Behavioral Responses
3.3. PIU Questionnaires and Psychological Measures
Correlation Between PIU Questionnaires and Psychological Questionnaires
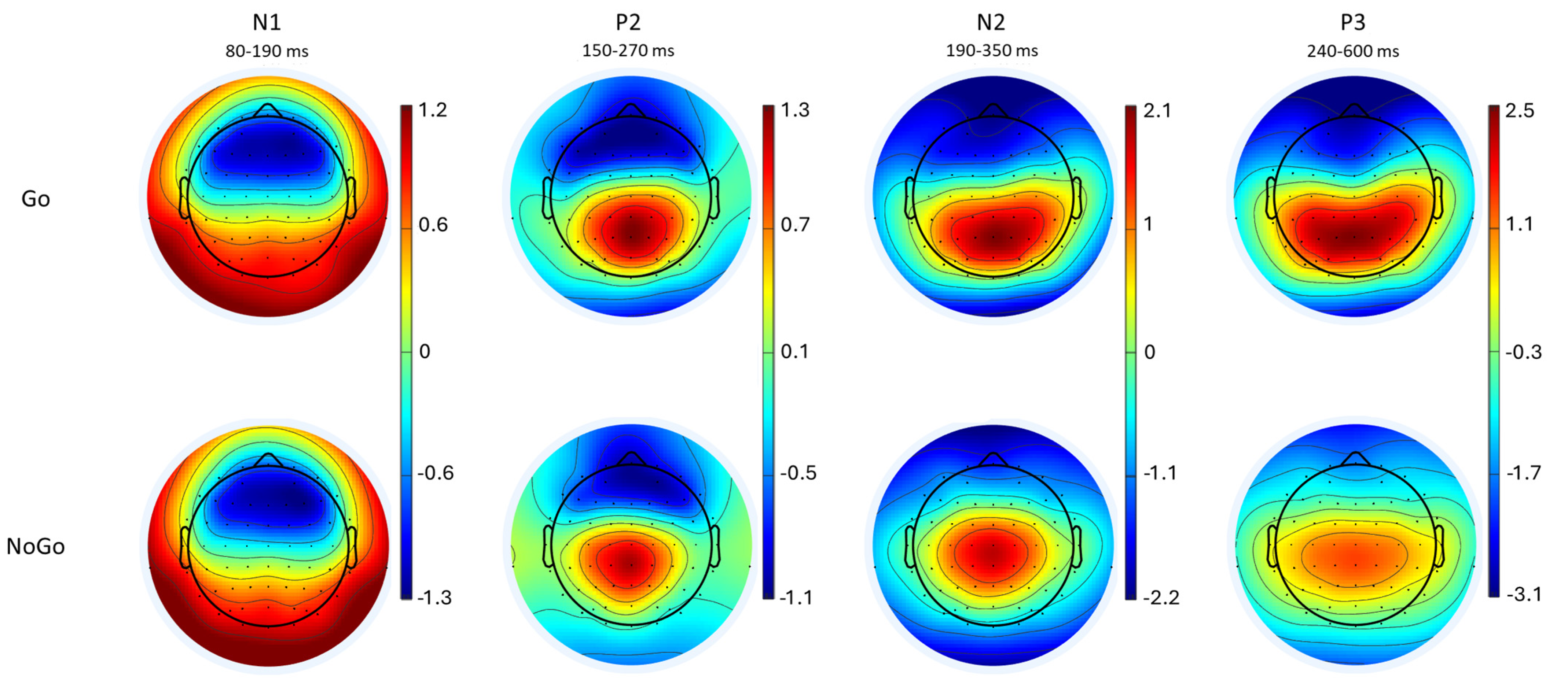
3.4. ERP Results
3.4.1. PIU Questionnaires and ERP Components in Go Condition
3.4.2. PIU Questionnaires and ERP Components in NoGo Condition
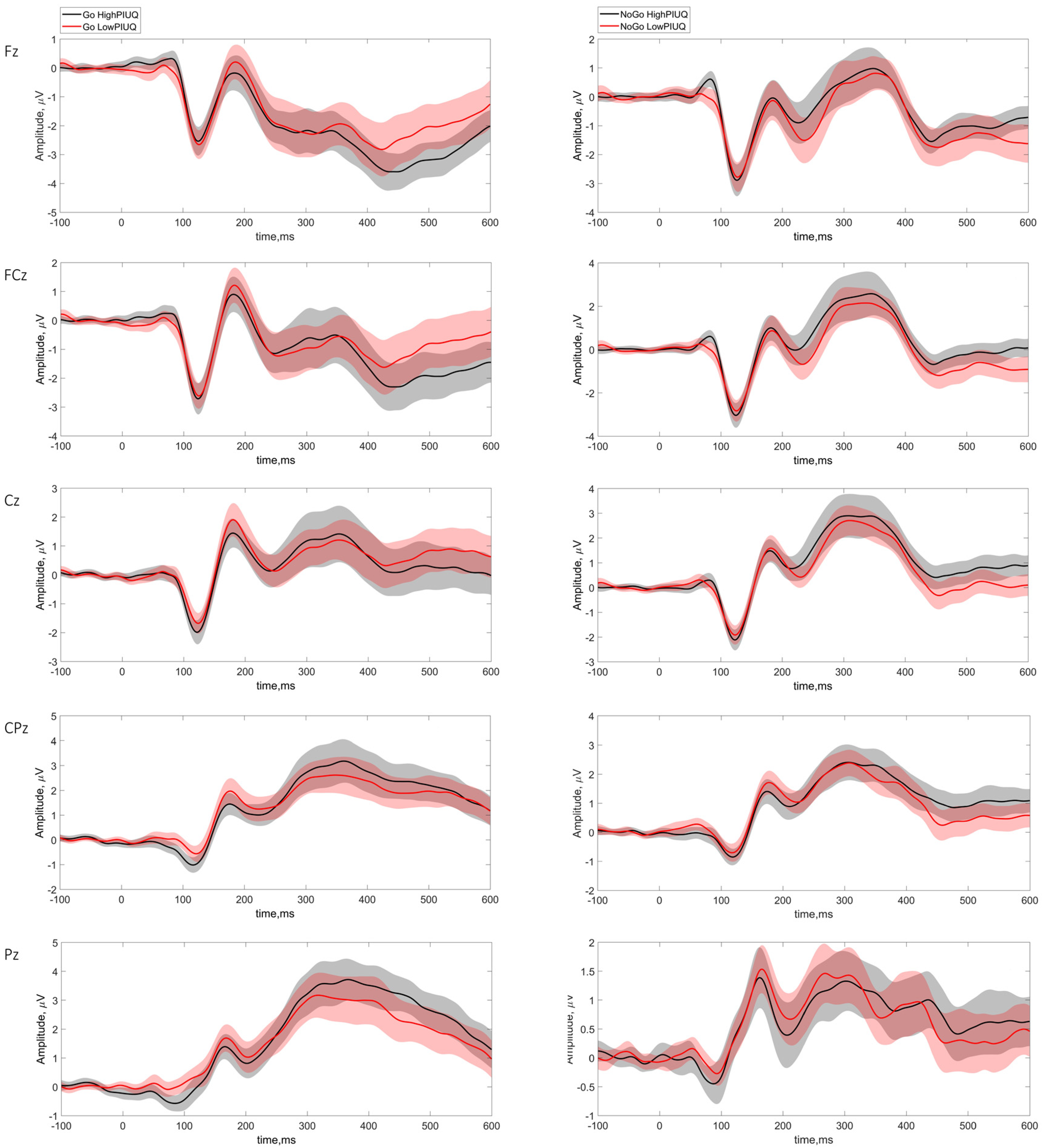
3.4.3. Low vs. High Engagement in PIU
4. Discussion
4.1. Behavioral Level
4.2. Psychological Level
4.3. Neurophysiological Level
4.3.1. Early Sensory Processing (N1 and P2)
4.3.2. Response Monitoring and Inhibition (N2 and P3)
4.3.3. High vs. Low PIU Comparison
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PIU | Problematic Internet Use |
| ERP | Event-Related Potential |
References
- American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). American Psychiatric Association. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E. L., Steen, E., & Stavropoulos, V. (2017). Internet use and problematic internet use: A systematic review of longitudinal research trends in adolescence and emergent adulthood. International Journal of Adolescence and Youth, 22(4), 430–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreassen, C. S., Griffiths, M. D., Gjertsen, S. R., Krossbakken, E., Kvam, S., & Pallesen, S. (2013). The relationships between behavioral addictions and the five-factor model of personality. Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 2(2), 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, R. J., & De Blasio, F. M. (2013). Sequential processing in the equiprobable auditory Go/NoGo task: A temporal PCA study. International Journal of Psychophysiology: Official Journal of the International Organization of Psychophysiology, 89(1), 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, R. J., De Blasio, F. M., & Cave, A. E. (2016). Sequential processing in young and older adults in the equiprobable auditory Go/NoGo task. Clinical Neurophysiology, 127(5), 2273–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, R. J., Johnstone, S. J., Clarke, A. R., Rushby, J. A., Brown, C. R., & McKenzie, D. N. (2007). Caffeine effects on ERPs and performance in an auditory Go/NoGo task. Clinical Neurophysiology, 118(12), 2692–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A. T., Epstein, N., Brown, G., & Steer, R. A. (1988). An inventory for measuring clinical anxiety: Psychometric properties. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 56(6), 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A. T., Steer, R. A., & Brown, G. K. (1996). BDI-II: Beck depression inventory manual (2nd ed.). Psychological Corporation. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 57(1), 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beppi, C., Violante, I. R., Hampshire, A., Grossman, N., & Sandrone, S. (2020). Patterns of focal- and large-scale synchronization in cognitive control and inhibition: A review. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 14, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, M., Wegmann, E., Stark, R., Müller, A., Wölfling, K., Robbins, T. W., & Potenza, M. N. (2019). The Interaction of Person-Affect-Cognition-Execution (I-PACE) model for addictive behaviors: Update, generalization to addictive behaviors beyond internet-use disorders, and specification of the process character of addictive behaviors. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 104, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevers, D., & Noël, X. (2013). Pathological gambling and the loss of willpower: A neurocognitive perspective. Socioaffective Neuroscience & Psychology, 3, 21592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkauskas, J., Király, O., Demetrovics, Z., Podlipskyte, A., & Steibliene, V. (2020). Psychometric Properties of the Nine-Item Problematic Internet Use Questionnaire (PIUQ-9) in a Lithuanian Sample of Students. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 11, 565769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L., Zhou, H., Gu, Y., Wang, S., Wang, J., Tian, L., Zhu, H., & Zhou, Z. (2018). The neural correlates of implicit cognitive bias toward internet-related cues in internet addiction: An ERP study. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 9, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, D. A., Antony, M., Beck, A. T., Swinson, R., & Steer, R. A. (2005). Screening for obsessive and compulsive symptoms: Validation of the clark-beck obsessive-compulsive inventory. Psychological Assessment, 17, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colrain, I. M., Sullivan, E. V., Ford, J. M., Mathalon, D. H., McPherson, S.-L., Roach, B. J., Crowley, K. E., & Pfefferbaum, A. (2011). Frontally mediated inhibitory processing and white matter microstructure: Age and alcoholism effects. Psychopharmacology, 213(4), 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, K. E., & Colrain, I. M. (2004). A review of the evidence for P2 being an independent component process: Age, sleep and modality. Clinical Neurophysiology: Official Journal of the International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology, 115(4), 732–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, A., & Makeig, S. (2004). EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G., Lu, Q., Zhou, H., & Zhao, X. (2010). Impulse inhibition in people with Internet addiction disorder: Electrophysiological evidence from a Go/NoGo study. Neuroscience Letters, 485(2), 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkers, F. C. L., & van Boxtel, G. J. M. (2004). The N2 in go/no-go tasks reflects conflict monitoring not response inhibition. Brain and Cognition, 56(2), 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enriquez-Geppert, S., Konrad, C., Pantev, C., & Huster, R. J. (2010). Conflict and inhibition differentially affect the N200/P300 complex in a combined go/nogo and stop-signal task. NeuroImage, 51(2), 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D. E., Park, J. Y., Maxfield, N., & Drobes, D. J. (2009). Neurocognitive variation in smoking behavior and withdrawal: Genetic and affective moderators. Genes, Brain, and Behavior, 8(1), 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M., Pourrahimi, A. M., Poormohammad, A., Sardari, S., Rajizadeh, M. A., Mazhari, S., & Pourkand, D. (2024). Video game addiction is associated with early stage of inhibitory control problems: An event-related potential study using cued Go/NoGo task. Addiction Biology, 29(4), e13391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feher, A., Fejes, E., Kapus, K., Jancsak, C., Nagy, G. D., Horvath, L., Tibold, A., & Feher, G. (2023). The association of problematic usage of the internet with burnout, depression, insomnia, and quality of life among Hungarian high school students. Frontiers in Public Health, 11, 1167308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillmore, M. T., & Rush, C. R. (2002). Impaired inhibitory control of behavior in chronic cocaine users. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 66(3), 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fineberg, N. A., Menchón, J. M., Hall, N., Dell’Osso, B., Brand, M., Potenza, M. N., Chamberlain, S. R., Cirnigliaro, G., Lochner, C., Billieux, J., Demetrovics, Z., Rumpf, H. J., Müller, A., Castro-Calvo, J., Hollander, E., Burkauskas, J., Grünblatt, E., Walitza, S., Corazza, O., … Zohar, J. (2022). Advances in problematic usage of the internet research—A narrative review by experts from the European network for problematic usage of the internet. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 118, 152346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, J. (2020). ERP markers of auditory Go/NoGo processing. University of Wollongong thesis collection 2017. Available online: https://ro.uow.edu.au/theses1/1010 (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- Fogarty, J. S., Barry, R. J., De Blasio, F. M., & Steiner, G. Z. (2018). ERP components and behavior in the auditory equiprobable go/no-go task: Inhibition in young adults. Psychophysiology, 55(7), e13065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, J. S., Barry, R. J., & Steiner, G. Z. (2020). Auditory stimulus- and response-locked ERP components and behavior. Psychophysiology, 57(5), e13538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Batista, Z. E., Guerra-Peña, K., Cano-Vindel, A., Herrera-Martínez, S. X., & Medrano, L. A. (2018). Validity and reliability of the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II) in general and hospital population of Dominican Republic. PLoS ONE, 13(6), e0199750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L., Ge, X., & Xu, Y. (2011). P300 change and cognitive behavioral therapy in subjects with Internet addiction disorder: A 3-month follow-up study. Neural Regeneration Research, 6(26), 2037–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, M. D. (2014). Internet addiction disorder and internet gaming disorder are not the same. Journal of Addiction Research & Therapy, 5(4), e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griskova-Bulanova, I., Griksiene, R., Voicikas, A., & Ruksenas, O. (2016). Go and NoGo: Modulation of electrophysiological correlates by female sex steroid hormones. Psychopharmacology, 233(13), 2607–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, W., Schmeichel, B. J., & Baddeley, A. D. (2012). Executive functions and self-regulation. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 16(3), 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IBM SPSS. (n.d.). (v29.0.2.0) [Computer software]. IBM SPSS. [Google Scholar]
- Ioannidis, K., Hook, R., Goudriaan, A. E., Vlies, S., Fineberg, N. A., Grant, J. E., & Chamberlain, S. R. (2019). Cognitive deficits in problematic internet use: Meta-analysis of 40 studies. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 215(5), 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JASP Team. (2024). JASP (version 0.18.3) [Computer software]. Available online: https://jasp-stats.org/ (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Jentsch, J. D., & Pennington, Z. T. (2014). Reward, Interrupted: Inhibitory Control and Its Relevance to Addictions. Neuropharmacology, 76, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joos, K., Gilles, A., Van de Heyning, P., De Ridder, D., & Vanneste, S. (2014). From sensation to percept: The neural signature of auditory event-related potentials. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 42, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashif, S., Pandey, S., & Warriach, Z. I. (2021). Neurophysiological markers of internet gaming disorder: A Literature review of electroencephalography studies. Cureus, 13(9), e17866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M., Lee, T., Choi, J., Kwak, Y., Hwang, W., Kim, T., Lee, J., Lim, J., Park, M., Kim, Y., Kim, S., Kim, D., Kwon, J., Kim, M., Lee, T. H., Choi, J.-S., Kwak, Y. B., Hwang, W. J., Kim, T., … Kwon, J. S. (2017). Neurophysiological correlates of altered response inhibition in internet gaming disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder: Perspectives from impulsivity and compulsivity. Scientific Reports, 7, 41742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Király, O., Griffiths, M. D., Urbán, R., Farkas, J., Kökönyei, G., Elekes, Z., Tamás, D., & Demetrovics, Z. (2014). Problematic internet use and problematic online gaming are not the same: Findings from a large nationally representative adolescent sample. Cyberpsychology, Behavior and Social Networking, 17(12), 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koronczai, B., Urbán, R., Kökönyei, G., Paksi, B., Papp, K., Kun, B., Arnold, P., Kállai, J., & Demetrovics, Z. (2011). Confirmation of the three-factor model of problematic internet use on off-line adolescent and adult samples. Cyberpsychology, Behavior and Social Networking, 14(11), 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuss, D. J., & Lopez-Fernandez, O. (2016). Internet addiction and problematic Internet use: A systematic review of clinical research. World Journal of Psychiatry, 6(1), 143–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y., & Kang, H.-B. (2014). EEG and ERP based degree of internet game addiction analysis. Journal of Korea Multimedia Society, 17, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littel, M., van den Berg, I., Luijten, M., van Rooij, A. J., Keemink, L., & Franken, I. H. A. (2012). Error processing and response inhibition in excessive computer game players: An event-related potential study. Addiction Biology, 17(5), 934–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melynyte, S., Ruksenas, O., & Griskova-Bulanova, I. (2017). Sex differences in equiprobable auditory Go/NoGo task: Effects on N2 and P3. Experimental Brain Research, 235, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Microsoft Corporation. (2018). [Computer software]. Microsoft Corporation. [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwenhuis, S., Yeung, N., & Cohen, J. D. (2004). Stimulus modality, perceptual overlap, and the go/no-go N2. Psychophysiology, 41(1), 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noroozi, F., Hassanipour, S., Eftekharian, F., Eisapareh, K., & Kaveh, M. H. (2021). Internet addiction effect on quality of life: A systematic review and meta-analysis. The Scientific World Journal, 2556679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A. K., Kamarajan, C., Manz, N., Chorlian, D. B., Stimus, A., & Porjesz, B. (2016). Delta, theta, and alpha event-related oscillations in alcoholics during Go/NoGo task: Neurocognitive deficits in execution, inhibition, and attention processing. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry, 65, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M., Choi, J.-S., Park, S. M., Lee, J.-Y., Jung, H. Y., Sohn, B. K., Kim, S. N., Kim, D. J., & Kwon, J. S. (2016). Dysfunctional information processing during an auditory event-related potential task in individuals with Internet gaming disorder. Translational Psychiatry, 6(1), 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M., Jung, M. H., Lee, J., Choi, A. R., Chung, S. J., Kim, B., Kim, D. J., & Choi, J.-S. (2020). Neurophysiological and cognitive correlates of error processing deficits in internet gaming disorder. Cerebral Cortex, 30(9), 4914–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M., Kim, Y. J., Kim, D. J., & Choi, J.-S. (2017a). Differential neurophysiological correlates of information processing in Internet gaming disorder and alcohol use disorder measured by event-related potentials. Scientific Reports, 7(1). Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-017-09679-z (accessed on 28 June 2024). [CrossRef]
- Park, M., Kim, Y., Kim, D., Choi, J., Park, M., Kim, Y. J., Kim, D. J., & Choi, J.-S. (2017b). Sustained dysfunctional information processing in patients with Internet gaming disorder 6-month follow-up ERP study. Medicine, 96(36), e7995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, F., Pernier, J., Bertrand, O., & Echallier, J. F. (1989). Spherical splines for scalp potential and current density mapping. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 72(2), 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosyan, A., & Statista. (2024). Topic: Internet usage worldwide. Statista. Available online: https://www.statista.com/topics/1145/internet-usage-worldwide/ (accessed on 13 March 2024).
- Porjesz, B., & Begleiter, H. (2003). Alcoholism and human electrophysiology. Alcohol Research & Health: The Journal of the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, 27(2), 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Ramey, T., & Regier, P. S. (2019). Cognitive impairment in substance use disorders. CNS Spectrums, 24(1), 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randall, W. M., & Smith, J. L. (2011). Conflict and inhibition in the cued-Go/NoGo task. Clinical Neurophysiology: Official Journal of the International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology, 122(12), 2400–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, T., & Clark, L. (2015). Behavioral addictions. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 30, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schou Andreassen, C., Billieux, J., Griffiths, M. D., Kuss, D. J., Demetrovics, Z., Mazzoni, E., & Pallesen, S. (2016). The relationship between addictive use of social media and video games and symptoms of psychiatric disorders: A large-scale cross-sectional study. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors: Journal of the Society of Psychologists in Addictive Behaviors, 30(2), 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokhadze, E., Stewart, C., Hollifield, M., & Tasman, A. (2008). Event-related potential study of executive dysfunctions in a speeded reaction task in cocaine addiction. Journal of Neurotherapy, 12(4), 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinella, M. (2002). Correlations between orbitofrontal dysfunction and tobacco smoking. Addiction Biology, 7(4), 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista Research Department. (n.d.). Global: Internet users 2014–2029. Statista. Available online: https://www.statista.com/forecasts/1146844/internet-users-in-the-world (accessed on 13 March 2024).
- Tomé, D., Barbosa, F., Nowak, K., & Marques-Teixeira, J. (2015). The development of the N1 and N2 components in auditory oddball paradigms: A systematic review with narrative analysis and suggested normative values. Journal of Neural Transmission, 122(3), 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ameringen, M., Simpson, W., Patterson, B., Turna, J., & Khalesi, Z. (2018). Internet addiction or psychopathology in disguise? Results from a survey of college-aged internet users. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 28(6), 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-P., & Gorenstein, C. (2013). Psychometric properties of the Beck Depression Inventory-II: A comprehensive review. Revista Brasileira De Psiquiatria, 35(4), 416–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winstanley, C. A., Eagle, D. M., & Robbins, T. W. (2006). Behavioral models of impulsivity in relation to ADHD: Translation between clinical and preclinical studies. Clinical Psychology Review, 26(4), 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. (2015). Public health implications of excessive use of the internet, computers, smartphones and similar electronic devices: Meeting report, main meeting hall, foundation for promotion of cancer research, national cancer research centre, Tokyo, Japan, 27–29 August 2014. World Health Organization. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/184264 (accessed on 23 April 2024).
- Yao, Y.-W., Wang, L.-J., Yip, S. W., Chen, P.-R., Li, S., Xu, J., Zhang, J.-T., Deng, L.-Y., Liu, Q.-X., & Fang, X.-Y. (2015). Impaired decision-making under risk is associated with gaming-specific inhibition deficits among college students with Internet gaming disorder. Psychiatry Research, 229(1), 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J., Yuan, K., Feng, D., Cheng, J., Li, Y., Cai, C., Bi, Y., Sha, S., Shen, X., Zhang, B., Xue, T., Qin, W., Yu, D., Lu, X., & Tian, J. (2016). Inhibition control impairments in adolescent smokers: Electrophysiological evidence from a Go/NoGo study. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 10(2), 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H., Zhao, X., Li, N., Wang, M., & Zhou, P. (2009). Effect of excessive Internet use on the time–frequency characteristic of EEG. Progress in Natural Science, 19(10), 1383–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J., Abdullah, M. F. I. L., & Mansor, N. S. (2024). EEG components of inhibitory control ability in internet gaming disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Brain and Behavior, 14(1), e3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z., Li, C., & Zhu, H. (2013). An error-related negativity potential investigation of response monitoring function in individuals with internet addiction disorder. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 7, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z., Yuan, G., Yao, J., Li, C., & Cheng, Z. (2010). An event-related potential investigation of deficient inhibitory control in individuals with pathological Internet use. Acta Neuropsychiatrica, 22(5), 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Valid (n) | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| PIUQ9 | 133 | 19.85 ± 5.32 |
| DPIU_total score | 119 | 25.97 ± 18.8 |
| DPIU_Entertainment and Video Streaming | 83 | 9.99 ± 4.5 |
| DPIU_Social Media | 84 | 9.55 ± 4.33 |
| DPIU_Gaming | 30 | 12.27 ± 5.36 |
| DPIU_Messaging | 33 | 13.3 ± 5.26 |
| DPIU_Dating Apps | 9 | 6.78 ± 3.866 |
| DPIU_Sexual Content | 14 | 10.5 ± 4.18 |
| DPIU_Online Shopping | 18 | 8.39 ± 3.9 |
| DPIU_Information Search | 22 | 13.32 ± 3.82 |
| BAI | 132 | 31.71 ± 7.64 |
| BDI | 129 | 10.72 ± 8.95 |
| CBOCI | 132 | 19.49 ± 11.67 |
| CBOCI_obsessions | 132 | 11.99 ± 6.93 |
| CBOCI_compulsions | 133 | 7.54 ± 5.91 |
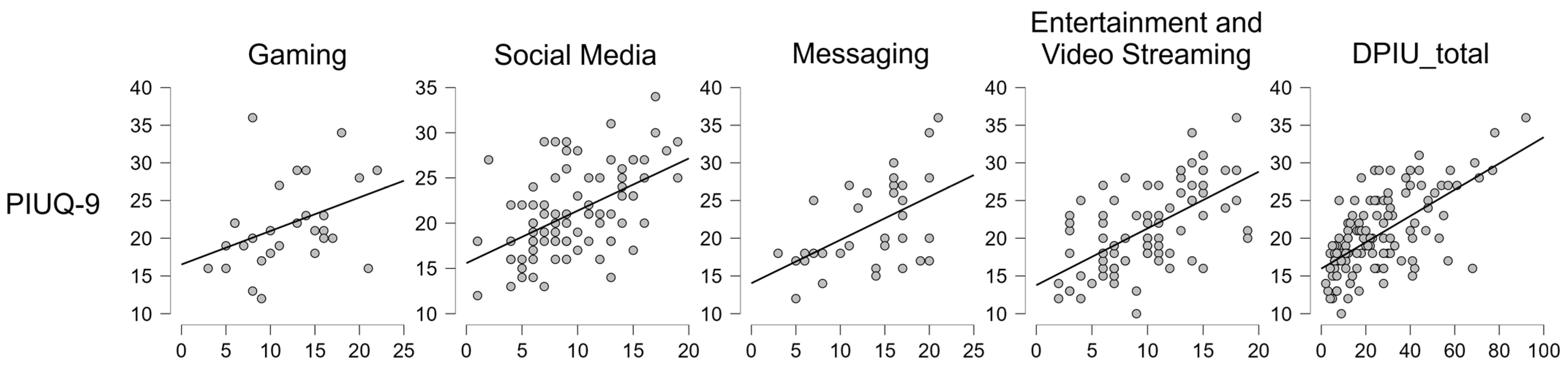
| Variable | PIUQ-9 | Gaming | Social Media | Messaging | Entertainment and Video Streaming | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaming | Spearman’s rho | 0.426 * | — | |||
| p-value | 0.019 | — | ||||
| N | 30 | — | ||||
| Social Media | Spearman’s rho | 0.512 * | 0.487 * | — | ||
| p-value | <0.001 | 0.029 | — | |||
| N | 84 | 20 | — | |||
| Messaging | Spearman’s rho | 0.472 * | 0.43 | 0.644 * | — | |
| p-value | 0.005 | 0.288 | <0.001 | — | ||
| N | 33 | 8 | 27 | — | ||
| Entertainment and Video Streaming | Spearman’s rho | 0.603 * | 0.326 | 0.453 * | 0.758 * | — |
| p-value | <0.001 | 0.129 | <0.001 | <0.001 | — | |
| N | 83 | 23 | 56 | 22 | — | |
| DPIU_total | Spearman’s rho | 0.585 * | 0.392 * | 0.59 * | 0.781 * | 0.622 * |
| p-value | <0.001 | 0.032 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| N | 119 | 30 | 84 | 33 | 83 | |
| Go Condition | NoGo Condition | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrode | N1 | N2 | P2 | P3 | N1 | N2 | P2 | P3 |
| Amplitudes | ||||||||
| Fz | −2.49 ± 1.4 | −2.86 ± 2.25 | 0.25 ± 1.69 | −1.1 ± 2.19 | −2.62 ± 1.49 | −1.53 ± 1.9 | 0.28 ± 1.8 | 1.55 ± 1.99 |
| FCz | −2.48 ± 1.33 | −1.78 ± 2.11 | 1.1 ± 1.75 | 0.17 ± 2.52 | −2.57 ± 1.4 | −0.66 ± 1.78 | 1.08 ± 1.77 | 3.06 ± 2.43 |
| Cz | −1.7 ± 1.06 | −0.38 ± 1.67 | 1.64 ± 1.57 | 1.79 ± 2.5 | −1.75 ± 1.06 | 0.22 ± 1.36 | 1.5 ± 1.42 | 3.48 ± 2.19 |
| CPz | −0.85 ± 0.87 | 0.64 ± 1.47 | 1.76 ± 1.31 | 3.33 ± 2.36 | −0.85 ± 0.9 | 0.6 ± 1.24 | 1.68 ± 1.24 | 2.95 ± 1.66 |
| Pz | −0.51 ± 0.87 | 0.67 ± 1.5 | 1.64 ± 1.25 | 4.03 ± 2.31 | −0.54 ± 0.85 | 0.15 ± 1.44 | 0.15 ± 1.44 | 2.19 ± 1.5 |
| Latencies | ||||||||
| Fz | 127.12 ± 12.23 | 280.39 ± 43.06 | 191.13 ± 19.99 | 366.25 ± 68.7 | 128.44 ± 15.41 | 248.54 ± 34.93 | 189.74 ± 28.32 | 339.57 ± 41.2 |
| FCz | 125.25 ± 9.4 | 263.71 ± 33.35 | 188.13 ± 17.47 | 340.19 ± 42.83 | 126.03 ± 10.49 | 240.08 ± 31.15 | 188.32 ± 22.96 | 332.07 ± 40.74 |
| Cz | 123.37 ± 11.58 | 259.44 ± 35.4 | 189.8 ± 21.78 | 352.71 ± 53.42 | 124.24 ± 8.257 | 235 ± 31.96 | 184.79 ± 17.72 | 328.24 ± 43.26 |
| CPz | 115.07 ± 18.73 | 242.3 ± 37.25 | 189.14 ± 24.52 | 362.07 ± 61.45 | 117.18 ± 16.63 | 237.34 ± 38.36 | 189.9 ± 29.83 | 334.85 ± 53.62 |
| Pz | 97.12 ± 23.67 | 224.05 ± 35.94 | 173.57 ± 28.81 | 362.52 ± 60.31 | 99.81 ± 27.271 | 239.94 ± 42.87 | 182.9 ± 30.957 | 350.18 ± 63 |
| Variable | U | p | Effect Size | SE Effect Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIUQ9 | 1330 | <0.001 * | 1 | 0.135 |
| BAI | 997 | <0.001 * | −0.544 | 0.136 |
| BDI | 891 | 0.003 * | −0.417 | 0.137 |
| CBOCI | 1040 | <0.001 * | −0.565 | 0.135 |
| CBOCI obsessions | 975.5 | <0.001 * | −0.467 | 0.135 |
| CBOCI compulsions | 1034 | <0.001 * | −0.555 | 0.135 |
| Variable | U | p | Effect Size | SE Effect Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correct_Go | 617 | 0.571 | 0.072 | 0.135 |
| Correct_NoGo | 734 | 0.436 | −0.104 | 0.135 |
| GO_RT | 766 | 0.267 | −0.152 | 0.135 |
| Amplitudes | Latencies | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrode Site | Component | U | p | Effect Size | SE Effect Size | U | p | Effect Size | SE Effect Size |
| Go Condition | |||||||||
| Fz | N1 | 709 | 0.633 | 0.066 | 0.135 | 676.5 | 0.903 | 0.017 | 0.135 |
| N2 | 634 | 0.738 | −0.047 | 0.135 | 574.5 | 0.32 | −0.136 | 0.135 | |
| P2 | 625 | 0.665 | −0.06 | 0.135 | 604 | 0.504 | −0.092 | 0.135 | |
| P3 | 580 | 0.353 | −0.128 | 0.135 | 467 | 0.029 | −0.298 | 0.135 | |
| FCz | N1 | 652 | 0.891 | −0.02 | 0.135 | 616.5 | 0.596 | −0.073 | 0.135 |
| N2 | 622 | 0.641 | −0.065 | 0.135 | 727.5 | 0.494 | 0.094 | 0.135 | |
| P2 | 626 | 0.673 | −0.059 | 0.135 | 635.5 | 0.749 | −0.044 | 0.135 | |
| P3 | 634 | 0.738 | −0.047 | 0.135 | 556.5 | 0.233 | −0.163 | 0.135 | |
| Cz | N1 | 551 | 0.211 | −0.171 | 0.135 | 560.5 | 0.251 | −0.157 | 0.135 |
| N2 | 652 | 0.891 | −0.02 | 0.135 | 730.5 | 0.473 | 0.098 | 0.135 | |
| P2 | 586 | 0.388 | −0.119 | 0.135 | 734 | 0.449 | 0.104 | 0.135 | |
| P3 | 682 | 0.856 | 0.026 | 0.135 | 738.5 | 0.42 | 0.111 | 0.135 | |
| CPz | N1 | 515 | 0.099 | −0.226 | 0.135 | 551.5 | 0.212 | −0.171 | 0.135 |
| N2 | 713 | 0.602 | 0.072 | 0.135 | 624 | 0.655 | −0.062 | 0.135 | |
| P2 | 542 | 0.177 | −0.185 | 0.135 | 678 | 0.89 | 0.02 | 0.135 | |
| P3 | 753 | 0.336 | 0.132 | 0.135 | 707.5 | 0.643 | 0.064 | 0.135 | |
| Pz | N1 | 440 | 0.013 | −0.338 | 0.135 | 587.5 | 0.395 | −0.117 | 0.135 |
| N2 | 665 | 1 | 0 | 0.135 | 498 | 0.066 | −0.251 | 0.135 | |
| P2 | 578 | 0.342 | −0.131 | 0.135 | 623.5 | 0.65 | −0.062 | 0.135 | |
| P3 | 741 | 0.407 | 0.114 | 0.135 | 706 | 0.655 | 0.062 | 0.135 | |
| NoGo condition | |||||||||
| Fz | N1 | 644 | 0.822 | −0.032 | 0.135 | 689 | 0.795 | 0.036 | 0.135 |
| N2 | 709 | 0.633 | 0.066 | 0.135 | 685.5 | 0.825 | 0.031 | 0.135 | |
| P2 | 659 | 0.952 | −0.009 | 0.135 | 720.5 | 0.544 | 0.083 | 0.135 | |
| P3 | 708 | 0.641 | 0.065 | 0.135 | 742 | 0.398 | 0.116 | 0.135 | |
| FCz | N1 | 649 | 0.865 | −0.024 | 0.135 | 626.5 | 0.675 | −0.058 | 0.135 |
| N2 | 716 | 0.579 | 0.077 | 0.135 | 709.5 | 0.627 | 0.067 | 0.135 | |
| P2 | 719 | 0.557 | 0.081 | 0.135 | 720.5 | 0.544 | 0.083 | 0.135 | |
| P3 | 669 | 0.969 | 0.006 | 0.135 | 692.5 | 0.766 | 0.041 | 0.135 | |
| Cz | N1 | 646 | 0.839 | −0.029 | 0.135 | 594 | 0.436 | −0.107 | 0.135 |
| N2 | 664 | 0.996 | −0.002 | 0.135 | 664 | 0.996 | −0.002 | 0.135 | |
| P2 | 659 | 0.952 | −0.009 | 0.135 | 680 | 0.873 | 0.023 | 0.135 | |
| P3 | 697 | 0.73 | 0.048 | 0.135 | 673 | 0.934 | 0.012 | 0.135 | |
| CPz | N1 | 619 | 0.617 | −0.069 | 0.135 | 672.5 | 0.938 | 0.011 | 0.135 |
| N2 | 575 | 0.325 | −0.135 | 0.135 | 683 | 0.847 | 0.027 | 0.135 | |
| P2 | 622 | 0.641 | −0.065 | 0.135 | 675.5 | 0.912 | 0.016 | 0.135 | |
| P3 | 662 | 0.978 | −0.005 | 0.135 | 813 | 0.103 | 0.223 | 0.135 | |
| Pz | N1 | 632 | 0.721 | −0.05 | 0.135 | 773.5 | 0.231 | 0.163 | 0.135 |
| N2 | 578 | 0.342 | −0.131 | 0.135 | 794 | 0.156 | 0.194 | 0.135 | |
| P2 | 588 | 0.401 | −0.116 | 0.135 | 654.5 | 0.912 | −0.016 | 0.135 | |
| P3 | 603 | 0.499 | −0.093 | 0.135 | 752.5 | 0.337 | 0.132 | 0.135 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simkute, D.; Tarailis, P.; Pipinis, E.; Griskova-Bulanova, I. Assessing the Spectrum of Internet Use in a Healthy Sample: Altered Psychological States and Intact Brain Responses to an Equiprobable Go/NoGo Task. Behav. Sci. 2025, 15, 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15050579
Simkute D, Tarailis P, Pipinis E, Griskova-Bulanova I. Assessing the Spectrum of Internet Use in a Healthy Sample: Altered Psychological States and Intact Brain Responses to an Equiprobable Go/NoGo Task. Behavioral Sciences. 2025; 15(5):579. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15050579
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimkute, Dovile, Povilas Tarailis, Evaldas Pipinis, and Inga Griskova-Bulanova. 2025. "Assessing the Spectrum of Internet Use in a Healthy Sample: Altered Psychological States and Intact Brain Responses to an Equiprobable Go/NoGo Task" Behavioral Sciences 15, no. 5: 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15050579
APA StyleSimkute, D., Tarailis, P., Pipinis, E., & Griskova-Bulanova, I. (2025). Assessing the Spectrum of Internet Use in a Healthy Sample: Altered Psychological States and Intact Brain Responses to an Equiprobable Go/NoGo Task. Behavioral Sciences, 15(5), 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15050579







