Abstract
School-based intervention programs aiming to support adolescents with mental health problems, such as (school-related) stress and performance anxiety, show inconsistent results. In order to make intervention efforts more beneficial, it is crucial to investigate who is most (un)likely to benefit and under what circumstances. The current study aimed to identify whether problem severity, maladaptive perfectionism, and perceived parental pressure moderate the effectiveness of a school-based performance anxiety program, and if this depends on the level of program attendance. The final sample consisted of N = 196 adolescents (Mage = 14.12, SD = 0.79, with 53% females) who participated in a randomized controlled trial. ANCOVAs were conducted for two indicators of performance anxiety: test anxiety and fear of failure. The results demonstrated that for test anxiety, the program was only effective for adolescents with higher pretest levels. Moreover, in the subsample of adolescents with higher program attendance, the program was only effective for adolescents with higher self-criticism perfectionism, and larger effects were observed for adolescents with higher pretest test anxiety and socially prescribed perfectionism. Our findings demonstrate that even a short program can yield positive effects, particularly for adolescents with high program attendance and who experience high problem severity and maladaptive perfectionism.
1. Introduction
Adolescence is a period of remarkable transformations, characterized by the development of identity and social skills, a heightened sensitivity to stress, and an increased risk of developing mental health problems (Andersen & Teicher, 2008; Branje et al., 2021; Romeo, 2013). In addition, in today’s society, adolescents frequently experience elevated levels of stress and performance anxiety due to high expectations from themselves and others (Von der Embse et al., 2017). This contributes to their vulnerability of experiencing mental health issues (Jacobsen & Nørup, 2020), such as internalizing and externalizing problems and reduced wellbeing (Chappel et al., 2014; Snyder et al., 2017). Among the most salient negative stressors experienced by adolescents are stressors related to school, such as taking exams, keeping up with schoolwork, and failure in exams (Anniko et al., 2019; Núñez-Regueiro & Núñez-Regueiro, 2021). In the Netherlands, 27–47% of secondary school students experience school-related stress and pressure, and almost one in three secondary school students regularly or often experience pressure to meet their own or other people’s expectations (Boer et al., 2021; Kleinjan et al., 2020). Moreover, in the last two decades, there have been increases in school stress and pressure in higher-income European countries (Boer et al., 2021; Cosma et al., 2020, 2021; Stevens et al., 2018), as well as higher expectations from oneself or others (Curran & Hill, 2019), enlarging the need for supporting adolescents with school-related stress and performance anxiety.
In an effort to reach adolescents who can benefit from programs preventing (the escalation of) mental health problems, school-based intervention programs have been developed, including programs targeting stress management, social skills, and test anxiety. Systematic and meta-analytic reviews indicate moderate effectiveness of such school-based programs overall (de Mooij et al., 2020; Durlak et al., 2011; Soares & Woods, 2020; Van Loon et al., 2020); however, there are inconsistent effects across individual studies. In fact, meta-analyses demonstrate substantial heterogeneity in effects across studies, to which various factors seem to contribute, including the target group (Van Loon et al., 2020), dosage (de Mooij et al., 2020), and level of implementation (Durlak et al., 2011). Yet, individual studies examining the effectiveness of school-based programs often focus on the overall effectiveness rather than on moderators of effectiveness. This precludes obtaining an overview of who benefitted from the program and under what circumstances. Insight into the moderators of effectiveness of school-based intervention programs is important for various reasons (Brière et al., 2014). First, it can identify (groups of) individuals that are most likely or unlikely to benefit from a program, guiding which programs should be offered to specific groups. Second, it could help the development and implementation of intervention programs by revealing factors crucial for effectiveness, such as greater program adherence or attendance, which has previously been related to greater program gains (Yin et al., 2005). Finding no significant moderators of effectiveness is also informative, as this demonstrates that programs are effective for a diverse and broad group of individuals (Brière et al., 2014).
The current study aims to provide insight into the moderators of effectiveness of a school-based skills-training program for adolescents addressing performance anxiety, encompassing test anxiety, and fear of failure. As demonstrated with a randomized controlled trial (RCT), this program had a small overall effect on reducing adolescents’ test anxiety. Furthermore, for adolescents with high program attendance, i.e., adolescents who attended more than half of the sessions, the program had small effects on reducing test anxiety and fear of failure (Van Loon et al., 2023). The present study aims to extend our understanding of the effectiveness of this program by investigating the variation in program effectiveness across individuals. More specifically, this study investigated if program effectiveness is moderated by higher problem severity (i.e., higher pretest levels of performance anxiety), as well as higher expectations from oneself or from others, manifested as maladaptive perfectionism and parental pressure, and whether this depends on the level of program attendance.
Based on previous meta-analyses (Brière et al., 2014; Horowitz & Garber, 2006; Menting et al., 2013; Stice et al., 2009; Stice & Shaw, 2004; Van Loon et al., 2020), we hypothesized the effects of the performance anxiety program to be larger for adolescents with higher pretest performance anxiety (i.e., fear of failure and test anxiety). Because of high severity of problems at baseline, there is supposed to be more room for improvement and, thus, larger program effects in this group (Stice et al., 2009; Stice & Shaw, 2004). In addition, more severe symptoms or problems can result in more motivation for change or to learn (new) skills to deal with these symptoms (Stice et al., 2009; Stice & Shaw, 2004), as the participants are likely to experience problems related to their performance anxiety.
Perfectionism is considered to be a multidimensional cognitive process, defined as striving for flawlessness and the pursuit of excessively high standards for performance, combined with critical self-evaluation (Flett et al., 2016). Perfectionism can be conceptualized at both an intrapersonal and interpersonal levels, with several dimensions. These include self-oriented perfectionism (SOP), that is, perfectionistic standards directed by oneself and toward oneself (i.e., intrapersonal level), and socially prescribed perfectionism (SPP), which is the belief that others hold perfectionistic expectations and motives for oneself (i.e., interpersonal level; Flett et al., 2016). Additionally, SOP can be divided into SOP striving, that is, striving for high standards, and SOP critical, that is, self-criticism when one does not attain perfection and has excessive concern over mistakes (Flett et al., 2016). Socially prescribed perfectionism and self-criticism are considered as maladaptive, and therefore, the focus of this study, while striving for high personal standards, is considered an adaptive, healthy trait (Flett & Hewitt, 2002; O’Connor et al., 2010).
Several features of maladaptive perfectionism, such as procrastination, social disconnection (e.g., heightened rejection sensitivity; a view of the self as irrelevant to others), and high self-presentation (e.g., the need to appear perfect; the need to portray a flawless image) (Flett & Hewitt, 2002; Frost et al., 1990; Hewitt et al., 2020), might make it more difficult to benefit from interventions. For example, individuals who are hyper-vigilant to signs of rejection or have the tendency to try to cover up their perceived shortcomings might be hesitant to disclose important (intimate) information to a therapist or instructor, which may create problems with establishing a good working alliance with the therapist, negatively affecting the program outcome (Flett & Hewitt, 2002; Hewitt et al., 2020; Miller et al., 2017; Zuroff et al., 2000). Furthermore, individuals might procrastinate to perform a task or homework to avoid less-than-perfect performance (Frost et al., 1990), hindering program success. Previous reviews suggest that maladaptive perfectionism has a negative impact on program processes and outcomes (Morris & Lomax, 2014; Smith et al., 2022). To illustrate, one RCT of a group-based cognitive behavioral treatment (CBT) program for children at risk for anxiety and/or depression (8–11 years) showed that pre-treatment self-criticism was related to higher post-treatment depression scores (Nobel et al., 2012). Another RCT of a group-based CBT program for clinically anxious children (6–13 years) demonstrated that self-oriented perfectionism predicted higher levels of anxiety symptoms (Mitchell et al., 2013), whereas socially prescribed perfectionism was not related to depression or anxiety (Mitchell et al., 2013; Nobel et al., 2012). Yet another study of a universal school-based cognitive behavior prevention program for anxiety in children (9–12 years) revealed that high levels of perfectionism (both SOP and SPP) were associated with increased pre- to postintervention anxiety levels (Essau et al., 2012). Yet, these studies did not assess if perfectionism moderated program effectiveness. As maladaptive perfectionism is related with higher levels of mental health problems (Flett et al., 2016; Limburg et al., 2017; O’Connor et al., 2010), leaving more room for improvement or more motivation to change, it may also be that maladaptive perfectionism is associated with higher program effectiveness. Taken together, maladaptive perfectionism may either hinder or promote program effectiveness. As research on its role as a moderator is lacking, it is important for program development and implementation to clarify how maladaptive perfectionism impacts program effectiveness. Furthermore, investigating both the intrapersonal and interpersonal dimension of maladaptive perfectionism may clarify what aspect of maladaptive perfectionism is most relevant to program effectiveness and should, therefore, be taken into account. This might especially be important in adolescents, as adolescence is a developmental phase characterized by the formation of identity, seeking independence from parents and increasing peer influence (Branje et al., 2021; Brown, 2004).
Another potential moderator of program effectiveness is parental pressure, referring to the perception of high parental expectations and excessive parental criticism (Frost et al., 1990). Self-evaluations of performance are tied to assumptions about parental expectations, and failure to meet these expectations may lead to disapproval or potential loss of love and acceptance (Frost et al., 1990). Previous RCT research showed that some parenting behaviors, such as negative affect, low emotional warmth, and overinvolvement, are associated with less favorable CBT program outcomes in clinically anxious youth (6–18 years) (Creswell et al., 2008; Festen et al., 2013). These negative parenting styles might limit youth to develop coping skills and self-competence to deal with challenges, hindering program success (Festen et al., 2013). Therefore, it is expected that adolescents with higher perceived parental pressure benefit less from the performance anxiety program.
In sum, it is crucial to better understand individual characteristics that affect program effectiveness to optimize successful implementation and the tailoring and optimalization of programs to meet the specific needs of different (groups of) participants. The current study aims to identify whether problem severity (i.e., pretest levels of performance anxiety), maladaptive perfectionism (i.e., self-criticism and socially prescribed perfectionism), and perceived parental pressure moderate the effectiveness of a school-based skills-training program addressing skills to deal with performance anxiety and whether this depends on the level of program attendance. It is expected that adolescents with higher problem severity benefit more from the program. No clear hypotheses are formulated for maladaptive perfectionism, as the previous literature is inconsistent. Finally, it is expected that adolescents with higher parental pressure benefit less from the program. If some characteristics promote or hinder program effectiveness for adolescents in need, programs should be adapted to address the unique needs of these (groups of) individuals. Overall, identifying factors associated with program gains or failure may improve successful implementation.
2. Methods
2.1. Design and Procedure
Implementation and data collection occurred at nine secondary schools in one of the four largest city in the Netherlands between 2018 and 2021 (Van Loon et al., 2023). After a three-session psychoeducation program about stress (Vogelaar et al., 2024), the students could self-select into one of the skills-training programs offered at school, either a performance anxiety program or a social skills-training program (Van Loon et al., 2023). The current study only focuses on the performance anxiety program. An RCT was conducted for a school-based skills-training program addressing skills to deal with performance anxiety (Van Loon et al., 2023).
The students and parents received written information about the programs and research and provided active informed consent. The students were randomly allocated into the experimental or waitlist control group. Before (T1) and after (T2) the implementation of the skills-training programs, program outcomes were assessed for both groups. The present study is registered in the International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (Netherlands Trial Register, number NTR7680), is published as a study protocol (Van Loon et al., 2019), and the design is approved by the Ethical Committee Psychology of Leiden University (CEP18-1105/419; first submission was approved on 4 December 2018; two amendments have been approved at a later stage). The data collection started in February 2019. Overall effectiveness results are presented elsewhere (Van Loon et al., 2023).
2.2. Participants
A total of 211 students enrolled in the performance anxiety program, with N = 104 in the experimental group and N = 107 in the control group. A total of 15 participants dropped out of the study at T2 and were excluded from the analyses (N = 9 in the experimental group; N = 6 in the control group). Hence, the final sample consisted of N = 196 participants. The students were between 12 and 17 years old (Mage = 14.12, SD = 0.79, 53% females). At T1, the participants were in the first (15%), second (63%), third (13%), or fourth year (9%) of secondary school. The participants were practical–prevocational education students (33%), prevocational–senior general education students (28%), or senior general–preuniversity education students (39%). More than half of the participants had a Western ethnic identity (56%, e.g., Dutch); other participants had a mixed (Western–non-Western, 13%, e.g., Dutch–Turkish) or non-Western (31%, e.g., Moroccan) ethnic identity. Most participants were born in the Netherlands (84%) and lived with both of their parents (66%). The sample was representative for Dutch adolescents in terms of educational level and minority background (Van Loon et al., 2023).
2.3. Performance Anxiety Program
The performance anxiety programs were provided at school by trained professionals from three youth care organizations who had at least one year of experience with being a trainer and completed at least higher vocational education. The program, adjusted from existing programs, consisted of seven weekly sessions and was designed to fit the schedule of the schools (so a session could fit in one lesson of 45 min). The program consisted of psychoeducation and teaching cognitive coping strategies to deal with (school) pressure, in addition to relaxation techniques. The control group did not receive any training during the implementation of the skills-training programs in the experimental group. They received the program after completion of the assessment at T2 (approximately 8 weeks after the experimental group started the skills-training program). Regarding program integrity, on average, 90% of program assignments were implemented (Van Loon et al., 2023).
2.4. Instruments
2.4.1. Performance Anxiety
Test anxiety was assessed with the Spielberger Test Anxiety Inventory (TAI) (Spielberger, 1980; Van der Ploeg, 1984). The TAI consists of 20 items (e.g., “During tests I feel very tense”) rated on a 4-point scale ranging from 1 (almost never) to 4 (almost always). Previous research showed adequate validity and internal consistency (Van der Ploeg, 1984). Mean scores were computed, with higher scores reflecting more test anxiety. In the current sample, internal consistency is high at both timepoints (α = 0.93 at T1 and α = 0.89 at T2).
Fear of failure was assessed with the short form of the Performance Failure Appraisal Inventory (PFAI; Conroy et al., 2002). The PFAI consists of 5 items (e.g., “When I am failing, I am afraid that I might not have enough talent”) measured on a 5-point scale ranging from 1 (do not believe at all) to 5 (believe 100% of the time). Previous research showed adequate validity and internal consistency (Conroy et al., 2002). Mean scores were computed, with higher scores reflecting more fear of failure. In the current sample, internal consistency is high at both timepoints (α = 0.83 at T1 and α = 0.88 at T2).
2.4.2. Moderators
Problem severity was defined as the pretest (T1) level of performance anxiety, distinguishing the pretest level of test anxiety and pretest level of fear of failure.
Maladaptive perfectionism was assessed at T1 with the Child and Adolescent Perfectionism Scale (CAPS-14; O’Connor et al., 2009), translated into Dutch. The instrument consists of 14 items rated on a 5-point Likert scale ranging from 1 (false) to 5 (true). Two subscales of perfectionism were used: self-oriented critical perfectionism or self-criticism (SOP-C, four items; “I get mad at myself when I make a mistake”) and socially prescribed perfectionism (SPP, seven items; “Other people always expect me to be perfect”). Previous research showed good internal consistency (O’Connor et al., 2009). Mean scores were computed, with higher scores reflecting more maladaptive perfectionism. In the current sample, internal consistency is high for both subscales (α = 0.88 for SOP-C and α = 0.82 for SPP).
Perceived parental pressure was measured at T2 with the Multidimensional Inventory of Perfectionism in Sport (MIPS) with the subscale for perceived parental pressure (Stoeber et al., 2006). The subscale consists of eight items, including parental expectations (e.g., “My parents set extremely high standards for me”) and criticism (e.g., “My parents criticize everything I do not do perfectly”), rated on a 6-point scale of 1 (never) to 6 (always). Previous studies showed high internal consistency (above 0.92, Stoeber et al., 2006; Stoeber & Rambow, 2007). Mean scores were computed, with higher scores presenting more perceived parental pressure. The current sample has an excellent internal consistency of 0.94.
2.5. Data Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed with SPSS version 29. First, descriptive and correlation analyses (Pearson and point-biserial correlations) were performed for all study variables. Second, separate univariate analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) tests were conducted to determine the influence of the moderators (i.e., problem severity, self-criticism, socially prescribed perfectionism, and parental pressure) on the two indicators of performance anxiety, that is, test anxiety and fear of failure (N = 8 models). The models were tested in the full sample, using an intention-to-treat approach, as well as in a subsample of adolescents with higher program attendance (i.e., adolescents who attended four or more sessions (N = 46) (Van Loon et al., 2023). The post-test outcome measures (T2) were included as dependent variables, and the condition (i.e., experimental and control groups) was included as a fixed factor. The pretest outcome measures (T1) and gender were included as covariates in the analyses, as there were more females in the experimental group than in the control group (Van Loon et al., 2023). The moderators and interaction terms (moderator * condition) were added as additional factors to the ANCOVAs. In the models with problem severity (i.e., pretest test anxiety or fear of failure) as the moderator, only the interaction term was added. The moderators were centered around the mean. To interpret significant moderator effects, we divided the sample based on the median of the moderator variable and conducted separate ANCOVA tests on each subgroup. Cohen’s ds were calculated using an online effect size calculator (Psychometrica, n.d.) based on the η2. Small effect sizes were considered as d = 0.20, moderate effect sizes as d = 0.50, and large effect sizes as d = 0.80 (Cohen, 1988).
3. Results
3.1. Full Sample
Table 1 presents the means, SDs, and correlations for the study variables. Table 2 demonstrates the results of the moderator analyses in the full sample. For test anxiety, a small significant moderating effect was found for problem severity (F(1, 192) = 7.02; p = 0.01; d = 0.38). For participants with low levels of baseline test anxiety, the program was not effective (F(1, 97) = 0.34; p = 0.56), while participants with high levels of baseline test anxiety benefitted from the program (F(1, 91) = 8.20; p = 0.01; d = 0.60). Figure 1 demonstrates the moderating effect of problem severity. For test anxiety, self-criticism, socially prescribed perfectionism, and perceived parental pressure did not moderate program effectiveness. For fear of failure, problem severity, self-criticism, socially prescribed perfectionism, and perceived parental pressure did not moderate program effectiveness.

Table 1.
Correlations for the study variables of the full sample.

Table 2.
Results of the moderator analyses for test anxiety and fear of failure.
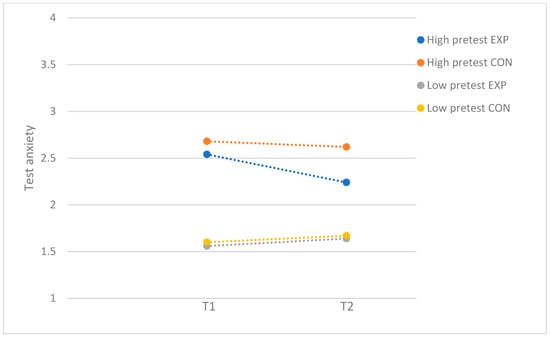
Figure 1.
Test anxiety: moderation by problem severity, with full sample. EXP = experimental group; CON = control group.
3.2. Subsample with Higher Program Attendance
Table 3 presents the results of the moderator analyses for participants with higher program attendance. For test anxiety, small significant moderating effects were found for problem severity (F(1, 142) = 6.48; p = 0.01; d = 0.43), self-criticism (F(1, 140) = 4.04; p = 0.05; d = 0.34), and socially prescribed perfectionism (F(1, 140) = 6.15; p = 0.01; d = 0.42). For problem severity, separate ANCOVAs in the subsamples with low (F(1, 68) = 2.71; p = 0.10) and high levels of baseline test anxiety (F(1, 69) = 0.52; p = 0.48) did not reveal program effectiveness in either of the samples. Even though there was no significant post hoc effect, the significant moderating effect of problem severity seems to be driven by adolescents with high baseline test anxiety. The findings demonstrated that the post-test levels in the experimental group were reduced for participants with high baseline test anxiety (T1: M = 2.61, SD = 0.42; T2: M = 2.28, SD = 0.54) while being slightly increased for participants with low baseline test anxiety (T1: M = 1.59, SD = 0.29; T2: M = 1.71, SD = 0.32; see Figure 2).

Table 3.
Results of the moderator analyses for test anxiety and fear of failure for participants who attended four or more sessions.
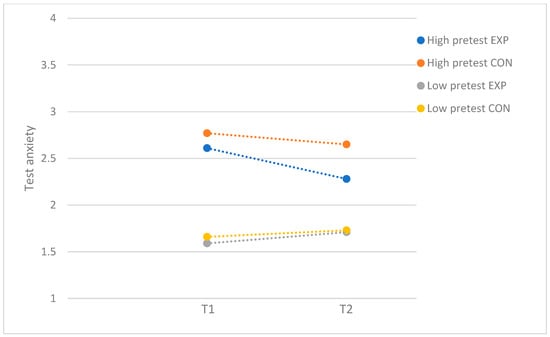
Figure 2.
Test anxiety: moderation by problem severity, with subsample of participants who attended more than half of the sessions. EXP = experimental group; CON = control group.
For self-criticism, the performance anxiety program resulted in a moderate reduction in test anxiety for participants with high levels of SOP-C (F(1, 73) = 5.03; p = 0.03; d = 0.52), whereas the program was not effective for participants with low levels of SOP-C (F(1, 61) = 0.17; p = 0.69). Figure 3 demonstrates the moderator effect for self-criticism. For socially prescribed perfectionism, there were no significant differences between the experimental and control group in the group of participants with low (F(1, 69) = 0.53; p = 0.47) and high levels of SPP (F(1, 65) = 0.47; p = 0.50). Even though there was no significant post hod effect, the significant moderating effect of SPP seem to be driven by adolescents with high levels of SPP, as the findings demonstrated that test anxiety was reduced for participants with high levels of SPP who attended the program (T1: M = 2.47, SD = 0.65; T2: M = 2.09, SD = 0.59) while staying relatively the same for participants with low levels of SPP (T1: M = 2.09, SD = 0.49; T2: M = 2.11, SD = 0.50) (see Figure 4).
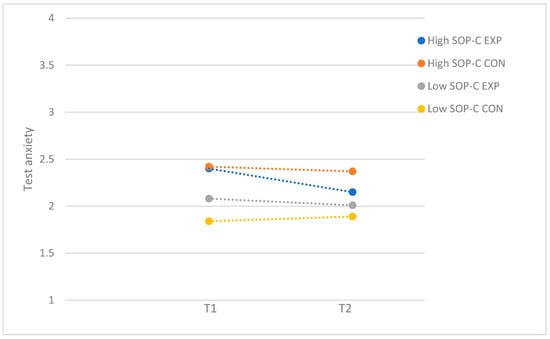
Figure 3.
Test anxiety: moderation by self-criticism perfectionism (SOP-C), with subsample of participants who attended more than half of the sessions. EXP = experimental group; CON = control group.
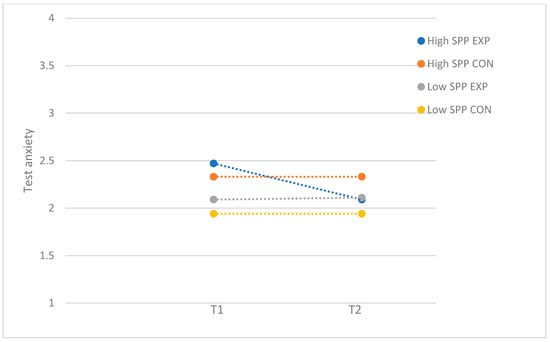
Figure 4.
Test anxiety: moderation by socially prescribed perfectionism (SPP), with subsample of participants who attended more than half of the sessions. EXP = experimental group; CON = control group.
For fear of failure, no moderator effects were found for problem severity, self-criticism, socially prescribed perfectionism, and perceived parental pressure.
4. Discussion
Given the increases in school stress and pressure over the last two decades (Boer et al., 2021; Cosma et al., 2020, 2021; Stevens et al., 2018), which are associated with negative mental health outcomes, it is necessary to support adolescents with school-related stress and performance anxiety, manifested as the fear of failure and test anxiety. Moreover, it is crucial for tailoring and optimizing of intervention programs to better understand which individuals are most likely or unlikely to benefit from such programs and which circumstances affect program effectiveness. Therefore, the current study aimed to identify whether problem severity, maladaptive perfectionism, and perceived parental pressure moderated the effectiveness of a school-based program addressing skills to deal with performance anxiety and whether the level of program attendance played a role. The results showed that for test anxiety, the program was only effective for adolescents with higher pretest levels. Furthermore, when program attendance was high, the program was only effective for adolescents with higher self-criticism, and larger effects were observed for adolescents with higher problem severity and socially prescribed perfectionism. Perceived parental pressure did not moderate program effectiveness and there were no significant moderator effects for fear of failure. Interestingly, moderation effects were only observed for test anxiety, not for the broader, more general form of performance anxiety: fear of failure. Test anxiety is school specific, while fear of failure is a broader construct and may manifest in various contexts beyond the academic environment, for instance, in sports, hobbies, or personal relationships. It is possible that the observed difference stems from the specific focus of the program and the immediate applicability to the academic context. The performance anxiety program focused on school-related stress and related coping skills and addressed scenarios related to the school context that are closely linked to (the measurements of) test anxiety and maladaptive perfectionism.
The finding that particularly adolescents with higher baseline test anxiety benefitted from the program is in line with previous research in adolescents (Brière et al., 2014; Horowitz & Garber, 2006; Menting et al., 2013; Stice et al., 2009; Stice & Shaw, 2004; Van Loon et al., 2020), highlighting that such programs have the potential to support adolescents who are at high risk or express a need for support in dealing with performance anxiety. Adolescents with higher problem severity are likely to be more motivated to engage in the program and have more to gain, which yields greater program benefits (Stice et al., 2009; Stice & Shaw, 2004). This suggests that these adolescents should be targeted for selective or indicated intervention programs to promote adolescent mental health. Moreover, it also advocates the use of screening methods at recruitment to select adolescents with high problem severity at baseline.
Most effects were found in the subsample of adolescents who attended more than half of the program. Unsurprisingly, these adolescents reported more needs at pretest (see Supplementary Table S1), confirming higher program engagement for those with higher problem severity and maladaptive perfectionism. At higher levels of program attendance and, therefore, more exposure to the program, it becomes apparent that adolescents with maladaptive perfectionism benefit (more) from the program. As maladaptive perfectionistic tendencies, such as procrastination, social disconnection, and a need to appear perfect might hinder youth to benefit from interventions, higher attendance allows for repeated exposure to coping strategies, more opportunities to practices these skills, and more time to build trust with the trainer(s), normalize experiences, and learn from peers. Alternatively, larger program effectiveness for adolescents with maladaptive perfectionism in this subsample might be related to higher problem severity, as these adolescents reported higher performance anxiety at baseline.
Our results indicate that higher maladaptive perfectionism, that is, self-criticism and socially prescribed perfectionism, is associated with larger program effects. This is in contrast with theoretical evidence that suggested that maladaptive perfectionism was related to less beneficial effects. These contrasting results might be related to the discussion of mostly (sub)clinical samples. Potentially, perfectionistic features may be more problematic in (sub)clinical samples, as these coincide with other mental health issues (e.g., obsessive-compulsive disorder, anxiety, and depression) and additional problematic behaviors, interfering with treatment and skill learning. For instance, clinical college student samples have reported higher levels of maladaptive perfectionism compared to non-clinical samples (Noble et al., 2017). It is possible that in our sample, the level of perfectionism was not extreme enough to prevent benefitting from the program. The focus of our performance anxiety program was on adolescents struggling with dealing with these problems, and since maladaptive perfectionism is strongly related to the fear of failure and test anxiety and may share some underlying mechanisms (Correia et al., 2018; Stricker et al., 2023), it is likely that the program worked better for adolescents with high levels of maladaptive perfectionism. Moreover, since maladaptive perfectionism is positively related with perceived stress and mental health problems (Flett et al., 2016; Limburg et al., 2017; O’Connor et al., 2010), it is possible that adolescents experiencing more problems at baseline are more motivated to engage in the program and have more to gain, yielding larger program effects (Stice et al., 2009; Stice & Shaw, 2004). Our results support this, as experiencing more test anxiety at baseline was positively associated with maladaptive perfectionism. These findings indicate that school-based performance anxiety programs are also beneficial for adolescents with high levels of maladaptive perfectionism. Both the intrapersonal (i.e., self-criticism) and interpersonal (i.e., socially prescribed perfectionism) dimensions of perfectionism seem to be relevant to program effectiveness.
Perceived parental pressure—consisting of high parental expectations and excessive parental criticism—did not influence program effectiveness, which contradicts earlier studies showing that negative parenting styles were associated with less favorable program outcomes in anxious youth (Creswell et al., 2008; Festen et al., 2013). However, these studies were conducted in younger samples and in youth with anxiety disorders (Creswell et al., 2008; Festen et al., 2013). First, it is possible that perceived parental pressure did not moderate program effectiveness in this age group, because adolescents have greater independence from parents than younger adolescents or children, which might make adolescents less susceptible to parental pressure. Additionally, this elevated independence in adolescence may create less opportunity for parents to impose high expectations and criticize their children. Indeed, recent research showed that perceived parental pressure was lower in older than younger athletes (Dunn et al., 2022). Second, it is likely that in clinical samples, problems are more complex or severe, making parents more involved and potentially exerting more pressure, hindering treatment effectiveness. Indeed, a previous study demonstrated that children with generalized anxiety disorder reported high levels of overprotection, parental pressure, and acute life events compared to non-patient school controls (Nordahl et al., 2010). Interestingly, socially prescribed perfectionism, i.e., the belief that others—not only parents—hold perfectionistic expectations, did affect program effectiveness. Possibly, adolescents’ sensitivity to peer norms might be a crucial factor to explain these divergent findings. As peers and friends become more important during adolescence, peer influence and pressure could have a significant role in adolescents’ attitudes and behavior (Brown, 2004) and, therefore, also in program effectiveness. Future research in this area is warranted. Even though our findings demonstrated that parental pressure did not influence program effectiveness, it does not mean that parents have no influence at all. Previous research showed that some parenting styles, such as negative affect and overinvolvement, influenced program outcomes (Creswell et al., 2008; Festen et al., 2013). Hence, future research should investigate different forms of parental influence on program effectiveness, including different parenting styles such as overprotection and behavioral control.
Strengths and Limitations
Despite the diverse and representative sample of Dutch adolescents in our study, with adolescents from various cultural backgrounds and educational levels, program implementation was disrupted by the COVID-19 pandemic (Van Loon et al., 2023). Some skills-training programs were postponed and restarted, which resulted in a lower program attendance and might have affected program implementation and outcome. However, program enrollment before or after the COVID-19 pandemic did not influence program effectiveness, suggesting that the COVID-19 pandemic had little impact (Van Loon et al., 2023).
We used a waitlist control design, so long-term follow-up was not possible. Future research should include follow-up assessments, as larger effects were found for follow-up compared to postintervention assessments for stress reduction interventions (Van Loon et al., 2020), and program gains were only found at follow-up for young adolescents after a cognitive behavioral prevention program (Essau et al., 2012). It might be that adolescents need to practice their newly learned skills in real-life settings in order for the program effects to unfold.
Another methodological limitation is the use of some of the questionnaires. We used the 14-item version of the CAPS (O’Connor et al., 2009), based on the original version (Flett et al., 2016), which has been shown to have acceptable reliability for use in general research for SPP, while SOP-C was only recommended for explorative research (Vicent et al., 2019). Nevertheless, in our sample the reliability was good for both maladaptive perfectionism subscales (>0.80). Furthermore, we measured perceived parental pressure at T2, which could have influenced the results. It is possible that parental pressure changed over time (from baseline to T2) as a result of the program. However, we expected that perceived parental pressure remained stable during the course of our study, as it has high temporal stability (O’Rourke et al., 2011), and parents were not actively involved in the program.
5. Conclusions and Implications
In conclusion, the current study examined moderators of effectiveness for a school-based performance anxiety program. Our findings demonstrate that even a short program of seven weekly 45 min sessions can reduce test anxiety in adolescents with higher problem severity and maladaptive perfectionism, especially when program attendance is high. As such, schools should be aware that low-threshold school-based programs have the potential to support adolescents in need, making it worthwhile to consider implementing such programs in the school setting. To optimize results, efforts should be made to motivate adolescents to attend and engage in such school-based intervention programs, as this allows them to benefit more.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/bs15040436/s1: Table S1. Means, standard deviations, and group differences between adolescents who attended less than four sessions (N = 49) and adolescents who attended four or more sessions (N = 46).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.W.G.v.L., H.E.C. and J.J.A.; Methodology, A.W.G.v.L., H.E.C. and J.J.A.; Formal analysis: A.W.G.v.L.; Investigation: A.W.G.v.L. and S.V.; Data curation: A.W.G.v.L.; Writing—original draft preparation: A.W.G.v.L., H.E.C. and J.J.A.; Writing—review and editing: A.W.G.v.L., H.E.C., J.J.A. and S.V.; Visualization: A.W.G.v.L.; Supervision: H.E.C. and J.J.A.; Project Administration: A.W.G.v.L.; Funding Acquisition: J.J.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by a grant from the Netherlands Organisation of Scientific Research (NWO), Grant Number 400.17.601, work package 3.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the independent Ethical Committee of Psychology of Leiden University (Number CEP18-1105/419, 4 December 2018). The study is registered in the International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (Number NTR7680, 12 December 2018).
Informed Consent Statement
Active informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests that are relevant to the content of this manuscript.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| RCT | Randomized controlled trial |
| SOP | Self-oriented perfectionism |
| SPP | Socially prescribed perfectionism |
| CBT | Cognitive behavioral therapy |
| SOP-C | Self-oriented critical perfectionism or self-criticism |
References
- Andersen, S. L., & Teicher, M. H. (2008). Stress, sensitive periods and maturational events in adolescent depression. Trends in Neurosciences, 31(4), 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anniko, M. K., Boersma, K., & Tillfors, M. (2019). Sources of stress and worry in the development of stress-related mental health problems: A longitudinal investigation from early-to mid-adolescence. Anxiety, Stress and Coping, 32(2), 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boer, M., van Dorsselaer, S., de Looze, M., de Roos, S., Brons, H., van den Eijnden, R., Monshouwer, K., Huijnk, W., ter Bogt, T., Vollebergh, W., & Stevens, G. (2021). HBSC 2021 Gezondheid en welzijn van jongeren in Nederland. Universiteit Utrecht. [Google Scholar]
- Branje, S., de Moor, E. L., Spitzer, J., & Becht, A. I. (2021). Dynamics of identity development in adolescence: A decade in review. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 31(4), 908–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brière, F. N., Rohde, P., Shaw, H., & Stice, E. (2014). Moderators of two indicated cognitive-behavioral depression prevention approaches for adolescents in a school-based effectiveness trial. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 53(1), 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B. B. (2004). Adolescents’ relationships with peers. In Handbook of adolescent psychology (pp. 363–394). John Wiley & Sons Inc. [Google Scholar]
- Chappel, A. M., Suldo, S. M., & Ogg, J. A. (2014). Associations between adolescents’ family stressors and life satisfaction. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 23(1), 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the social sciences. Erlbaum. [Google Scholar]
- Conroy, D. E., Willow, J. P., & Metzler, J. N. (2002). Multidimensional fear of failure measurement: The Performance Failure Appraisal Inventory. Journal of Applied Sport Psychology, 14, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, M. C., Rosado, A. F., & Serpa, S. (2018). Fear of failure and perfectionism in sport miedo a fallar y perfeccionismo en el deporte medo de falhar e perfeccionismo no desporto. Faculty of Human Kinetics, University of Lisbon, Portugal, 18, 161–172. [Google Scholar]
- Cosma, A., Stevens, G. W. J. M., Martin, G., Duinhof, E. L., Walsh, S. D., Garcia-Moya, I., Költő, A., Gobina, I., Canale, N., Catunda, C., Inchley, J., & de Looze, M. (2020). Cross-national time trends in adolescent mental well-being from 2002 to 2018 and the explanatory role of schoolwork pressure. Journal of Adolescent Health, 66(6), S50–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosma, A., Stevens, G. W. J. M., Vollebergh, W. A. M., & De Looze, M. (2021). Time trends in schoolwork pressure among Dutch adolescents, 2001–2017: Gender and educational differences. Scandinavian Journal of Public Health, 50, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, C., Willetts, L., Murray, L., Singhal, M., & Cooper, P. (2008). Treatment of child anxiety: An exploratory study of the role of maternal anxiety and behaviours in treatment outcome. Clinical Psychology and Psychotherapy, 15(1), 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, T., & Hill, A. P. (2019). Perfectionism is increasing over time: A meta-analysis of birth cohort differences from 1989 to 2016. Psychological Bulletin, 145(4), 410–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Mooij, B., Fekkes, M., Scholte, R. H. J., & Overbeek, G. (2020). Effective components of social skills training programs for children and adolescents in nonclinical samples: A multilevel meta-analysis. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 23(2), 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, J. G. H., Gotwals, J. K., Causgrove Dunn, J., & Lizmore, M. R. (2022). Perceived parental pressure and perceived coach pressure in adolescent and adult sport. Psychology of Sport and Exercise, 59, 102100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durlak, J. A., Weissberg, R. P., Dymnicki, A. B., Taylor, R. D., & Schellinger, K. B. (2011). The impact of enhancing students’ social and emotional learning: A meta-analysis of school-based universal interventions. Child Development, 82(1), 405–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essau, C. A., Conradt, J., Sasagawa, S., & Ollendick, T. H. (2012). Prevention of anxiety symptoms in children: Results from a universal school-based trial. Behavior Therapy, 43(2), 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festen, H., Hartman, C. A., Hogendoorn, S., de Haan, E., Prins, P. J. M., Reichart, C. G., Moorlag, H., & Nauta, M. H. (2013). Temperament and parenting predicting anxiety change in cognitive behavioral therapy: The role of mothers, fathers, and children. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 27(3), 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flett, G. L., & Hewitt, P. L. (2002). Perfectionism and maladjustment: An overview of theoretical, definitional, and treatment issues (pp. 5–31). American Psychological Association. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flett, G. L., Hewitt, P. L., Besser, A., Su, C., Vaillancourt, T., Boucher, D., Munro, Y., Davidson, L. A., & Gale, O. (2016). The Child–Adolescent Perfectionism Scale: Development, psychometric properties, and associations with stress, distress, and psychiatric symptos. Journal of Psychoeducational Assessment, 34(7), 634–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, R. O., Marten, P., Lahart, C., & Rosenblate, R. (1990). The dimensions of perfectionism. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 14(5), 449–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, P. L., Smith, M. M., Deng, X., Chen, C., Ko, A., Flett, G. L., & Patterson, R. J. (2020). The perniciousness of perfectionism in group therapy for depression: A test of the perfectionism social disconnection model. Psychotherapy, 57(2), 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, J. L., & Garber, J. (2006). The prevention of depressive symptoms in children and adolescents: A meta-analytic review. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 74(3), 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, B., & Nørup, I. (2020). Young people’s mental health: Exploring the gap between expectation and experience. Educational Research, 62(3), 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinjan, M., Pieper, I., Stevens, G., van de Klundert, N., Rombouts, M., Boer, M., & Lammers, J. (2020). Geluk onder druk? Onderzoek naar het mentaal welbevinden van jongeren in Nederland. UNICEF Netherlands. [Google Scholar]
- Limburg, K., Watson, H. J., Hagger, M. S., & Egan, S. J. (2017). The relationship between perfectionism and psychopathology: A meta-analysis. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 73(10), 1301–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menting, A. T. A., Orobio de Castro, B., & Matthys, W. (2013). Effectiveness of the incredible years parent training to modify disruptive and prosocial child behavior: A meta-analytic review. Clinical Psychology Review, 33(8), 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R., Hilsenroth, M. J., & Hewitt, P. L. (2017). Perfectionism and therapeutic alliance: A review of the clinical research. Research in Psychotherapy: Psychopathology, Process and Outcome, 20(1), 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J. H., Newall, C., Broeren, S., & Hudson, J. L. (2013). The role of perfectionism in cognitive behaviour therapy outcomes for clinically anxious children. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 51(9), 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, L., & Lomax, C. (2014). Review: Assessment, development, and treatment of childhood perfectionism: A systematic review. Child and Adolescent Mental Health, 19(4), 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobel, R., Manassis, K., & Wilansky-Traynor, P. (2012). The role of perfectionism in relation to an intervention to reduce anxious and depressive symptoms in children. Journal of Rational—Emotive and Cognitive—Behavior Therapy, 30(2), 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, C. M., Gnilka, P. B., Ashby, J. S., & McLaulin, S. E. (2017). Perfectionism, shame, and trichotillomania symptoms in clinical and nonclinical samples. Journal of Mental Health Counseling, 39(4), 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordahl, H. M., Wells, A., Olsson, C. A., & Bjerkeset, O. (2010). Association between abnormal psychosocial situations in childhood, generalized anxiety disorder and oppositional defiant disorder. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 44(9), 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Regueiro, F., & Núñez-Regueiro, S. (2021). Identifying salient stressors of adolescence: A systematic review and content analysis. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 50, 2533–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, R. C., Dixon, D., & Rasmussen, S. (2009). The structure and temporal stability of the Child and Adolescent Perfectionism Scale. Psychological Assessment, 21(3), 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, R. C., Rasmussen, S., & Hawton, K. (2010). Predicting depression, anxiety and self-harm in adolescents: The role of perfectionism and acute life stress. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 48(1), 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rourke, D. J., Smith, R. E., Smoll, F. L., & Cumming, S. P. (2011). Trait anxiety in young athletes as a function of parental pressure and motivational climate: Is parental pressure always harmful? Journal of Applied Sport Psychology, 23(4), 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psychometrica. (n.d.). Computation of effect sizes. Available online: https://www.psychometrica.de/effect_size.html (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Romeo, R. D. (2013). The teenage brain: The stress response and the adolescent brain. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 22(2), 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M. M., Sherry, S. B., Ge, S. Y. J., Hewitt, P. L., Flett, G. L., & Baggley, D. L. (2022). Multidimensional perfectionism turns 30: A review of known knowns and known unknowns. Canadian Psychology, 63(1), 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, H. R., Young, J. F., & Hankin, B. L. (2017). Chronic stress exposure and generation are related to the P-factor and externalizing specific psychopathology in youth. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 48(2), 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, D., & Woods, K. (2020). An international systematic literature review of test anxiety interventions 2011–2018. Pastoral Care in Education, 38(4), 311–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielberger, C. D. (1980). Test anxiety inventory: Sampler set: Manual, test scoring:” test attitude inventory”: Preliminary professional manual. Mind Garden. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, G., van Dorsselaer, S., Boer, M., De Roos, S., Duinhof, E., ter Bogt, T., van den Eijnden, R., Kuyper, L., Visser, D., Vollebergh, W., & de Looze, M. (2018). HBSC 2017: Gezondheid en welzijn van jongeren in Nederland. Utrecht University. [Google Scholar]
- Stice, E., & Shaw, H. (2004). Eating disorder prevention programs: A meta-analytic review. Psychological Bulletin, 130(2), 206–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stice, E., Shaw, H., Bohon, C., Marti, C. N., & Rohde, P. (2009). A meta-analytic review of depression prevention programs for children and adolescents: Factors that predict magnitude of intervention effects. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 77(3), 486–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeber, J., Otto, K., & Stoll, O. (2006). Multidimensional inventory of perfectionism in sport (MIPS): English version (Unpublised). School of Psychology, University of Kent. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/20524039.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Stoeber, J., & Rambow, A. (2007). Perfectionism in adolescent school students: Relations with motivation, achievement, and well-being. Personality and Individual Differences, 42(7), 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stricker, J., Schneider, M., & Preckel, F. (2023). Concurrent and predictive relations of multidimensional perfectionism with test anxiety in secondary school students. Anxiety, Stress and Coping, 36(2), 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Ploeg, H. M. (1984). The development and validation of the Dutch form of the test anxiety inventory. Applied Psychology, 33(2), 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, A. W. G., Creemers, H. E., Beumer, W. Y., Okorn, A., Vogelaar, S., Saab, N., Miers, A. C., Westenberg, P. M., & Asscher, J. J. (2020). Can schools reduce adolescent psychological stress? A multilevel meta-analysis of the effectiveness of school-based intervention programs. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 49, 1127–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Loon, A. W. G., Creemers, H. E., Vogelaar, S., Miers, A. C., Saab, N., Westenberg, P. M., & Asscher, J. J. (2023). The effectiveness of school-based skills-training programs reducing performance or social anxiety: Two randomized controlled trials. Child and Youth Care Forum, 52(6), 1323–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, A. W. G., Creemers, H. E., Vogelaar, S., Saab, N., Miers, A. C., Westenberg, P. M., & Asscher, J. J. (2019). The effectiveness of school-based skills-training programs promoting mental health in adolescents: A study protocol for a randomized controlled study. BMC Public Health, 19(1), 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicent, M., Rubio-aparicio, M., Sánchez-meca, J., & Gonzálvez, C. (2019). A reliability generalization meta-analysis of the child and adolescent perfectionism scale. Journal of Affective Disorders, 245, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelaar, S., Miers, A. C., Saab, N., Dusseldorp, E., van Loon, A. W. G., Creemers, H. E., Asscher, J. J., & Westenberg, P. M. (2024). Teaching Adolescents about stress using a universal school-based psychoeducation program: A cluster randomised controlled trial. School Mental Health, 16(2), 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von der Embse, N., Jester, D., Roy, D., & Post, J. (2017). Test anxiety effects, predictors, and correlates: A 30-year meta-analytic review. Journal of Affective Disorders, 227, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z., Moore, J. B., Johnson, M. H., Barbeau, P., Cavnar, M., Thornburg, J., & Gutin, B. (2005). The Medical College of Georgia FitKid Project: The relations between program attendance and changes in outcomes in year 1. International Journal of Obesity, 29, S40–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuroff, D. C., Blatt, S. J., Sotsky, S. M., Krupnick, J. L., Martin, D. J., Sanislow, C. A., & Simmens, S. (2000). Relation of therapeutic alliance and perfectionism to outcome in brief outpatient treatment of depression. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 68(1), 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).