Video Game Skills across Diverse Genres and Cognitive Functioning in Early Adulthood: Verbal and Visuospatial Short-Term and Working Memory, Hand–Eye Coordination, and Empathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Effects of Video Games on Cognitive and Affective Elements
1.2. Aims of This Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Materials
2.2.1. Gaming Skill Questionnaire (GSQ)
2.2.2. Digit Span Test (DST)
2.2.3. Corsi Block Test (CBT)
2.2.4. Deary–Liewald Reaction Time Task (DLRTT)
2.2.5. Empathy Quotient Questionnaire (EQ)
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Regression Analysis Process
- Single-Predictor Models: Initially, separate models were developed for each predictor to identify the most effective variable based on performance.
- Dyadic Predictor Models: Subsequently, models incorporating two predictors were constructed, consistently including the most effective variable from the single-predictor models. The performance of these dyadic models was then evaluated and compared to the Single-Predictor models to ascertain the most effective combination.
- Incremental Model Development: This iterative approach involved adding a predictor in each phase and comparing the performance of increasingly complex models. The process continued until the inclusion of new variables no longer significantly improved the models’ performance. The optimal model was determined when a simpler model from an earlier phase demonstrated superior performance compared to a more complex model from a later phase. This ensured the final model was robust and accurately reflected the most influential variables identified in the study.
2.4.2. One-Way ANOVA Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Correlations
3.2. Regressions
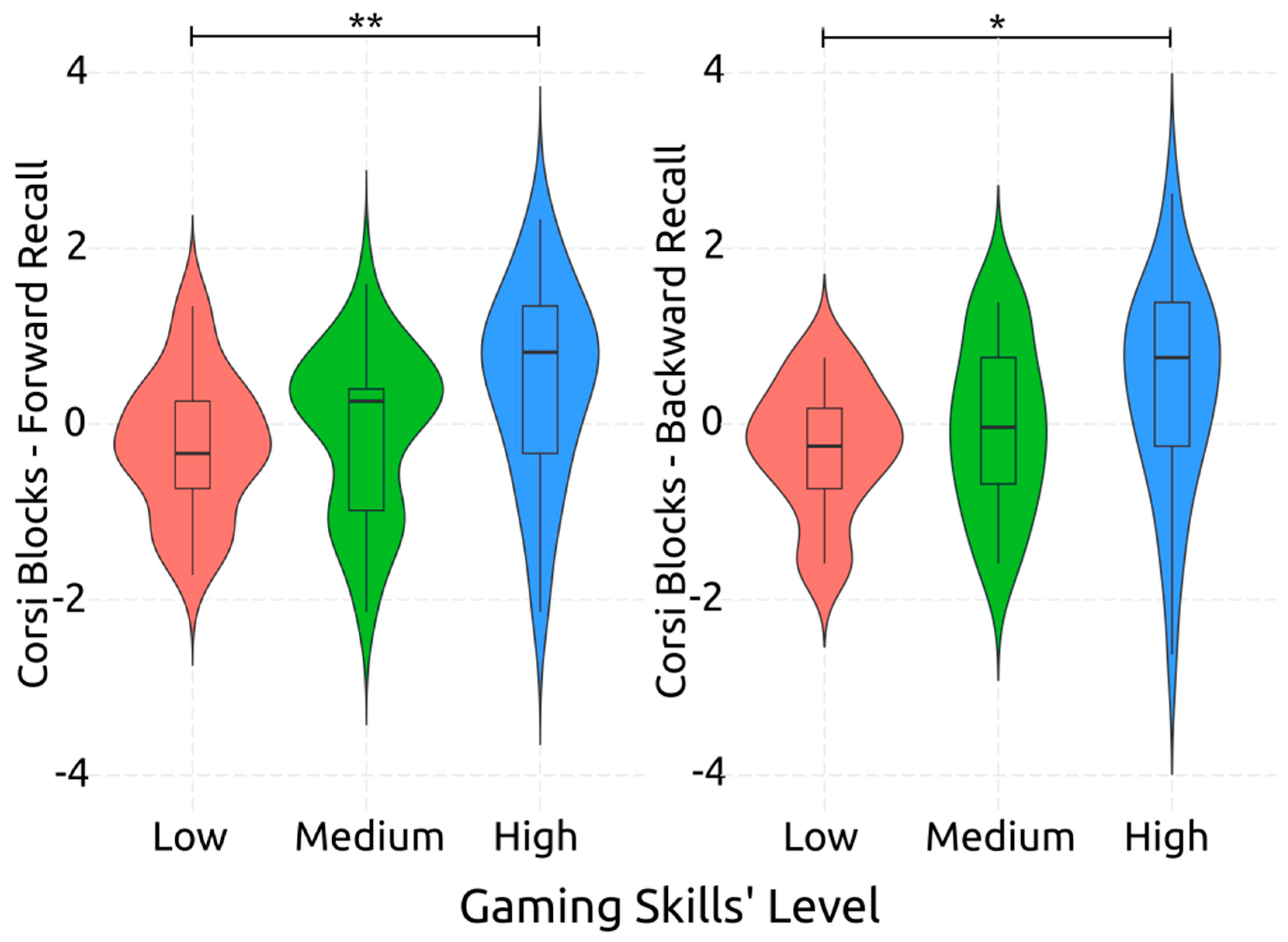
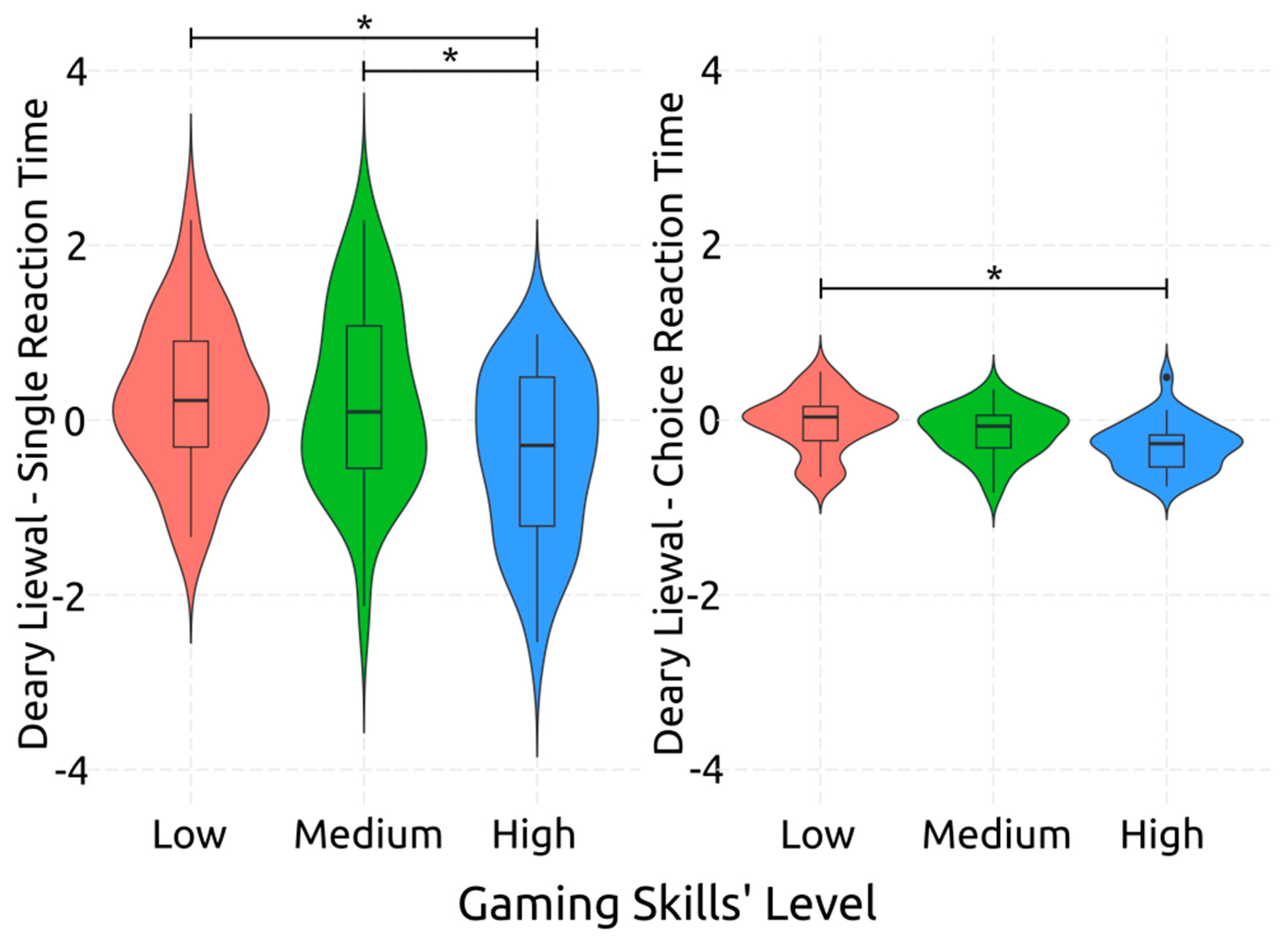
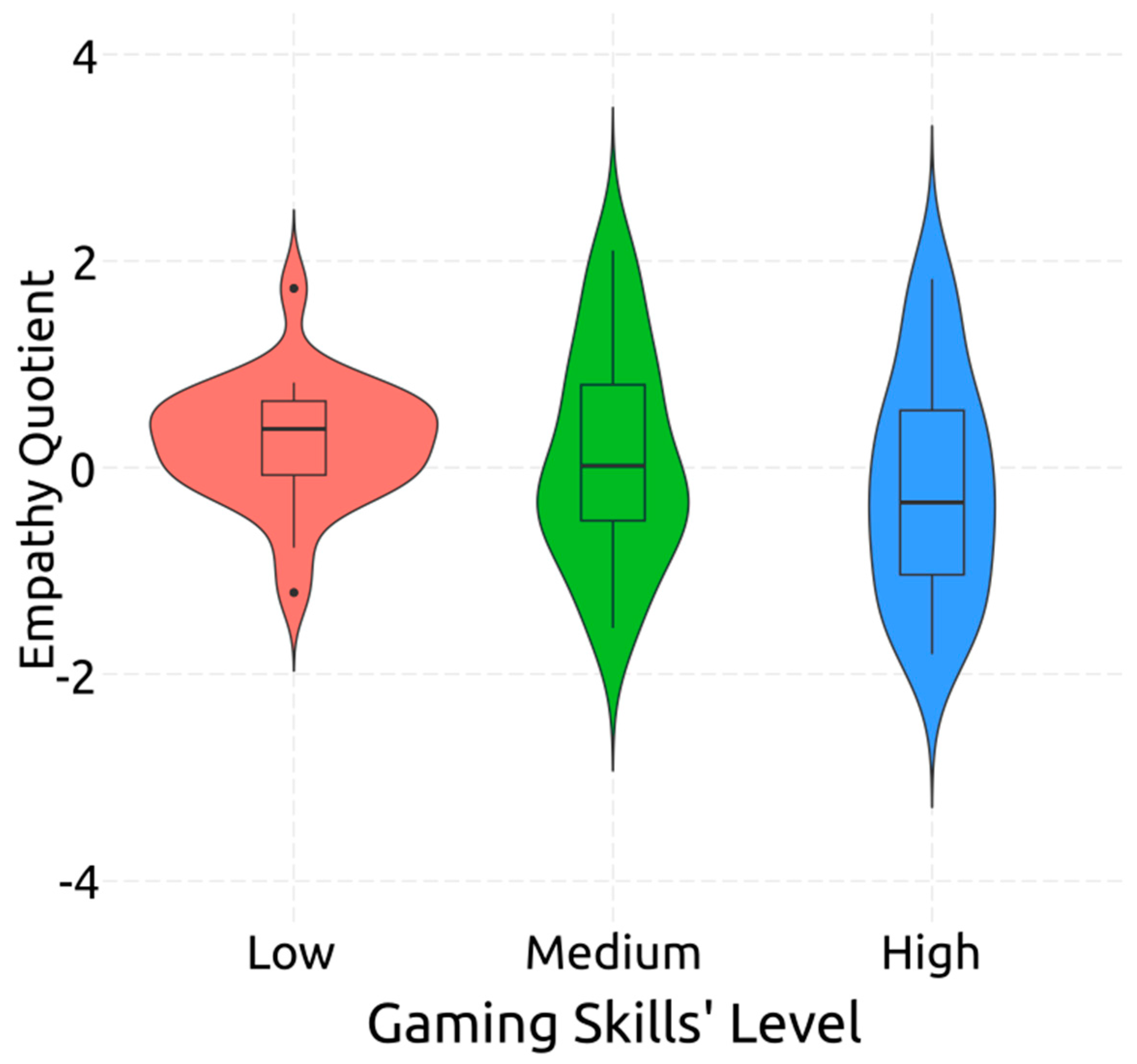
3.3. ANOVA
4. Discussion
4.1. Gaming Skill Level, Cognitive Functions, and Empathy
4.1.1. Verbal Short-Term Memory
4.1.2. Verbal Working Memory
4.1.3. Visuospatial Short-Term Memory
4.1.4. Visuospatial Working Memory
4.1.5. Psychomotor Speed
4.1.6. Attentional Speed
4.1.7. Empathy
4.2. Diverse Video Game Genres and Cognition
4.2.1. FPS & Action Games
4.2.2. Puzzle Games
4.3. Limitations and Future Studies
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, D.; Yee, N.; Caplan, S.E. Who Plays, How Much, and Why? Debunking the Stereotypical Gamer Profile. J. Comput.-Mediat. Commun. 2008, 13, 993–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entertainment Software Association 2024 Essential Facts about the U.S. Video Game Industry. Available online: https://www.theesa.com/resources/essential-facts-about-the-us-video-game-industry/2024-data/ (accessed on 12 July 2024).
- Lopez-Fernandez, O.; Williams, A.J.; Griffiths, M.D.; Kuss, D.J. Female Gaming, Gaming Addiction, and the Role of Women Within Gaming Culture: A Narrative Literature Review. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, B.; Stopfer, J.M.; Müller, K.W.; Beutel, M.E.; Egloff, B. Personality and Video Gaming: Comparing Regular Gamers, Non-Gamers, and Gaming Addicts and Differentiating between Game Genres. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 55, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granic, I.; Lobel, A.; Engels, R.C.M.E. The Benefits of Playing Video Games. Am. Psychol. 2014, 69, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, G.; Huo, Y.; Kelly, S.; Leung, J.; Tisdale, C.; Gullo, M. The Impact of eSports and Online Video Gaming on Lifestyle Behaviours in Youth: A Systematic Review. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2022, 126, 106974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro Pereira, A.; Costa, J.A.; Verhagen, E.; Figueiredo, P.; Brito, J. Associations Between Esports Participation and Health: A Scoping Review. Sports Med. 2022, 52, 2039–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaffas, A.A. An Operational Study of Video Games’ Genres. Int. J. Interact. Mob. Technol. IJIM 2020, 14, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, J.; Katchabaw, M.; Mercer, R.E. A Methodological Approach to Identifying and Quantifying Video Game Difficulty Factors. Entertain. Comput. 2014, 5, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apperley, T.H. Genre and Game Studies: Toward a Critical Approach to Video Game Genres. Simul. Gaming 2006, 37, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, G.; Green, S. The Changing Face of Video Games and Video Gamers: Future Directions in the Scientific Study of Video Game Play and Cognitive Performance. J. Cogn. Enhanc. 2017, 1, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, D.A. The Multiple Dimensions of Video Game Effects: Video Game Effects. Child Dev. Perspect. 2011, 5, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavelier, D.; Achtman, R.L.; Mani, M.; Föcker, J. Neural Bases of Selective Attention in Action Video Game Players. Percept. Learn. Mech. Manif. 2012, 61, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lövdén, M.; Fratiglioni, L.; Glymour, M.M.; Lindenberger, U.; Tucker-Drob, E.M. Education and Cognitive Functioning Across the Life Span. Psychol. Sci. Public Interest 2020, 21, 6–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.T.; Bhaskar, B.; Hinerman, A.; Basak, C. Past Gaming Experience and Cognition as Selective Predictors of Novel Game Learning Across Different Gaming Genres. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernik, A.; Tomičić, I.; Hatlak, D. Influence of Video Games on Cognitive Abilities andIntelligence. Teh. Glas. 2023, 17, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boot, W.R.; Blakely, D.P.; Simons, D.J. Do Action Video Games Improve Perception and Cognition? Front. Psychol. 2011, 2, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.S.; Kattner, F.; Eichenbaum, A.; Bediou, B.; Adams, D.M.; Mayer, R.E.; Bavelier, D. Playing Some Video Games but Not Others Is Related to Cognitive Abilities: A Critique of Unsworth et al. (2015). Psychol. Sci. 2017, 28, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.; Shin, S.-H.; Ryu, J.-K.; Jung, K.-I.; Kim, S.-Y.; Park, M.-H. Commercial Video Games and Cognitive Functions: Video Game Genres and Modulating Factors of Cognitive Enhancement. Behav. Brain Funct. 2020, 16, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oei, A.C.; Patterson, M.D. Enhancing Perceptual and Attentional Skills Requires Common Demands between the Action Video Games and Transfer Tasks. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, V.; Young, M.; Fiocco, A.J. The Association Between Video Game Play and Cognitive Function: Does Gaming Platform Matter? Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2017, 20, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.A.; Shibuya, A.; Ihori, N.; Swing, E.L.; Bushman, B.J.; Sakamoto, A.; Rothstein, H.R.; Saleem, M. Violent Video Game Effects on Aggression, Empathy, and Prosocial Behavior in Eastern and Western Countries: A Meta-Analytic Review. Psychol. Bull. 2010, 136, 151–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, C.R.; Bartholow, B.D.; Kerr, G.T.; Bushman, B.J. This Is Your Brain on Violent Video Games: Neural Desensitization to Violence Predicts Increased Aggression Following Violent Video Game Exposure. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2011, 47, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greitemeyer, T. The Spreading Impact of Playing Violent Video Games on Aggression. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 80, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, S.M.; Warburton, W.; Swit, C.; Stockdale, L.; Dyer, W.J. Who Is Most at Risk for Developing Physical Aggression After Playing Violent Video Games? An Individual Differences Perspective From Early Adolescence to Emerging Adulthood. J. Youth Adolesc. 2023, 52, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushman, B.J.; Anderson, C.A. Comfortably Numb: Desensitizing Effects of Violent Media on Helping Others. Psychol. Sci. 2009, 20, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, S.M.; Stockdale, L.A.; Warburton, W.; Gentile, D.A.; Yang, C.; Merrill, B.M. Pathological Video Game Symptoms from Adolescence to Emerging Adulthood: A 6-Year Longitudinal Study of Trajectories, Predictors, and Outcomes. Dev. Psychol. 2020, 56, 1385–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgard, J.; Engelhardt, C.R.; Rouder, J.N. Overstated Evidence for Short-Term Effects of Violent Games on Affect and Behavior: A Reanalysis of Anderson et al. (2010). Psychol. Bull. 2017, 143, 757–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühn, S.; Kugler, D.T.; Schmalen, K.; Weichenberger, M.; Witt, C.; Gallinat, J. Does Playing Violent Video Games Cause Aggression? A Longitudinal Intervention Study. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 1220–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tear, M.J.; Nielsen, M. Video Games and Prosocial Behavior: A Study of the Effects of Non-Violent, Violent and Ultra-Violent Gameplay. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 41, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, C.J.; Wang, J.C.K. Aggressive Video Games Are Not a Risk Factor for Future Aggression in Youth: A Longitudinal Study. J. Youth Adolesc. 2019, 48, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elson, M.; Ferguson, C.J. Twenty-Five Years of Research on Violence in Digital Games and Aggression: Empirical Evidence, Perspectives, and a Debate Gone Astray. Eur. Psychol. 2014, 19, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, P.J.C.; Willoughby, T. The Effect of Violent Video Games on Aggression: Is It More than Just the Violence? Aggress. Violent Behav. 2011, 16, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachen, C.M.; Hernández-Ramos, P.F.; Raphael, C. Simulating REAL LIVES: Promoting Global Empathy and Interest in Learning Through Simulation Games. Simul. Gaming 2012, 43, 437–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulansari, O.D.E.; Pirker, J.; Kopf, J.; Guetl, C. Video Games and Their Correlation to Empathy: How to Teach and Experience Empathic Emotion. In The Impact of the 4th Industrial Revolution on Engineering Education; Auer, M.E., Hortsch, H., Sethakul, P., Eds.; Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 1134, pp. 151–163. ISBN 978-3-030-40273-0. [Google Scholar]
- Greitemeyer, T.; Osswald, S. Effects of Prosocial Video Games on Prosocial Behavior. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2010, 98, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greitemeyer, T.; Osswald, S.; Brauer, M. Playing Prosocial Video Games Increases Empathy and Decreases Schadenfreude. Emotion 2010, 10, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prot, S.; Gentile, D.A.; Anderson, C.A.; Suzuki, K.; Swing, E.; Lim, K.M.; Horiuchi, Y.; Jelic, M.; Krahé, B.; Liuqing, W.; et al. Long-Term Relations Among Prosocial-Media Use, Empathy, and Prosocial Behavior. Psychol. Sci. 2014, 25, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, B.; O’Connell, M. Video Games as Virtual Teachers: Prosocial Video Game Use by Children and Adolescents from Different Socioeconomic Groups Is Associated with Increased Empathy and Prosocial Behaviour. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 63, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happ, C.; Melzer, A.; Steffgen, G. Like the Good or Bad Guy—Empathy in Antisocial and Prosocial Games. Psychol. Pop. Media Cult. 2015, 4, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happ, C.; Melzer, A.; Steffgen, G. Bringing Empathy into Play: On the Effects of Empathy in Violent and Nonviolent Video Games. In Entertainment Computing—ICEC 2011; Anacleto, J.C., Fels, S., Graham, N., Kapralos, B., Saif El-Nasr, M., Stanley, K., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 6972, pp. 371–374. ISBN 978-3-642-24499-5. [Google Scholar]
- Devilly, G.J.; Brown, K.; Pickert, I.; O’Donohue, R. An Evolutionary Perspective on Cooperative Behavior in Gamers. Psychol. Pop. Media Cult. 2017, 6, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducheneaut, N.; Moore, R.J.; Nickell, E. Virtual “Third Places”: A Case Study of Sociability in Massively Multiplayer Games. Comput. Support. Coop. Work CSCW 2007, 16, 129–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, S.; Ferguson, C.J.; John Wang, C.K. Prosocial Video Game Content, Empathy and Cognitive Ability in a Large Sample of Youth. J. Youth Adolesc. 2022, 51, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greitemeyer, T.; Cox, C. There’s No “I” in Team: Effects of Cooperative Video Games on Cooperative Behavior. Eur. J. Soc. Psychol. 2013, 43, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greitemeyer, T. Playing Video Games Cooperatively Increases Empathic Concern. Soc. Psychol. 2013, 44, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerabeck, J.M.; Ferguson, C.J. The Influence of Solitary and Cooperative Violent Video Game Play on Aggressive and Prosocial Behavior. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2013, 29, 2573–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.-H.; Ahn, D. Associations Between Game Use and Cognitive Empathy: A Cross-Generational Study. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2013, 16, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartanto, A.; Toh, W.X.; Yang, H. Age Matters: The Effect of Onset Age of Video Game Play on Task-Switching Abilities. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2016, 78, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kral, T.R.A.; Stodola, D.E.; Birn, R.M.; Mumford, J.A.; Solis, E.; Flook, L.; Patsenko, E.G.; Anderson, C.G.; Steinkuehler, C.; Davidson, R.J. Neural Correlates of Video Game Empathy Training in Adolescents: A Randomized Trial. Npj Sci. Learn. 2018, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Cheng, C. The Benefits of Video Games on Brain Cognitive Function: A Systematic Review of Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, S.E.; Woldorff, M.G.; Mitroff, S.R. Video Game Players Show More Precise Multisensory Temporal Processing Abilities. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2010, 72, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castel, A.D.; Pratt, J.; Drummond, E. The Effects of Action Video Game Experience on the Time Course of Inhibition of Return and the Efficiency of Visual Search. Acta Psychol. 2005, 119, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oei, A.C.; Patterson, M.D. Enhancing Cognition with Video Games: A Multiple Game Training Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waris, O.; Jaeggi, S.M.; Seitz, A.R.; Lehtonen, M.; Soveri, A.; Lukasik, K.M.; Söderström, U.; Hoffing, R.A.C.; Laine, M. Video Gaming and Working Memory: A Large-Scale Cross-Sectional Correlative Study. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2019, 97, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Marquez, E.; Prieto, A.; Mayas, J.; Toril, P.; Reales, J.M.; Ballesteros, S. Effects of Nonaction Videogames on Attention and Memory in Young Adults. Games Health J. 2019, 8, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbet, D.J.; Sergio, L.E. Move Faster, Think Later: Women Who Play Action Video Games Have Quicker Visually-Guided Responses with Later Onset Visuomotor-Related Brain Activity. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0189110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baniqued, P.L.; Kranz, M.B.; Voss, M.W.; Lee, H.; Cosman, J.D.; Severson, J.; Kramer, A.F. Cognitive Training with Casual Video Games: Points to Consider. Front. Psychol. 2014, 4, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso-Leite, P.; Bavelier, D. Video Game Play, Attention, and Learning: How to Shape the Development of Attention and Influence Learning? Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2014, 27, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, J.; Bavelier, D.; Gazzaley, A. How to Assess Gaming-Induced Benefits on Attention and Working Memory. Games Health J. 2012, 1, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.S.; Bavelier, D. Learning, Attentional Control, and Action Video Games. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, R197–R206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert-Wallander, B.; Green, C.S.; Bavelier, D. Stretching the Limits of Visual Attention: The Case of Action Video Games. WIREs Cogn. Sci. 2011, 2, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bediou, B.; Adams, D.M.; Mayer, R.E.; Tipton, E.; Green, C.S.; Bavelier, D. Meta-Analysis of Action Video Game Impact on Perceptual, Attentional, and Cognitive Skills. Psychol. Bull. 2018, 144, 77–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bediou, B.; Rodgers, M.A.; Tipton, E.; Mayer, R.E.; Green, C.S.; Bavelier, D. Effects of Action Video Game Play on Cognitive Skills: A Meta-Analysis. Technol. Mind Behav. 2023, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alho, K.; Moisala, M.; Salmela-Aro, K. Effects of Media Multitasking and Video Gaming on Cognitive Functions and Their Neural Bases in Adolescents and Young Adults. Eur. Psychol. 2022, 27, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavelier, D.; Green, C.S. Enhancing Attentional Control: Lessons from Action Video Games. Neuron 2019, 104, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampalo, M.; Lázaro, E.; Luna, P.-M. Action Video Gaming and Attention in Young Adults: A Systematic Review. J. Atten. Disord. 2023, 27, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Spence, I.; Pratt, J. Playing an Action Video Game Reduces Gender Differences in Spatial Cognition. Psychol. Sci. 2007, 18, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, G.; Kattner, F.; Bavelier, D.; Green, C.S. Cognitive Abilities of Action Video Game and Role-Playing Video Game Players: Data from a Massive Open Online Course. Psychol. Pop. Media 2020, 9, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glueck, A.C.; Han, D.Y. Improvement Potentials in Balance and Visuo-Motor Reaction Time after Mixed Reality Action Game Play: A Pilot Study. Virtual Real. 2020, 24, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irons, J.L.; Remington, R.W.; Mclean, J.P. Not so Fast: Rethinking the Effects of Action Video Games on Attentional Capacity. Aust. J. Psychol. 2011, 63, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, D.A.; Swing, E.L.; Lim, C.G.; Khoo, A. Video Game Playing, Attention Problems, and Impulsiveness: Evidence of Bidirectional Causality. Psychol. Pop. Media Cult. 2012, 1, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boot, W.R.; Kramer, A.F.; Simons, D.J.; Fabiani, M.; Gratton, G. The Effects of Video Game Playing on Attention, Memory, and Executive Control. Acta Psychol. 2008, 129, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaarani, B.; Ortigara, J.; Yuan, D.; Loso, H.; Potter, A.; Garavan, H.P. Association of Video Gaming With Cognitive Performance Among Children. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2235721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horoszkiewicz, K.; Horoszkiewicz, B.; Załęski, G. Psychomotor Performance in Video Games. J. Educ. Health Sport 2022, 12, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Won, J. The Effects of Adolescents’ Participation in Video Games on Cognitive Function and Motor Control Skills. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Y.; McGlone, E.R.; Camm, C.F.; Khan, O.A. Does Playing Video Games Improve Laparoscopic Skills? Int. J. Surg. 2013, 11, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynaldo, C.; Christian, R.; Hosea, H.; Gunawan, A.A.S. Using Video Games to Improve Capabilities in Decision Making and Cognitive Skill: A Literature Review. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 179, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleuze, J.; Christiaens, M.; Nuyens, F.; Billieux, J. Shoot at First Sight! First Person Shooter Players Display Reduced Reaction Time and Compromised Inhibitory Control in Comparison to Other Video Game Players. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 72, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.; Andrews, G.; Williams, K. Does video game playing impact on short-term memory task performance? In Beyond the Lab: Applications of Cognitive Research in Memory and Learning; Andrews, G., Neumann, D., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Özçetin, M.; Gümüştaş, F.; Çağ, Y.; Gökbay, İ.Z.; Özmel, A. The Relationships between Video Game Experience and Cognitive Abilities in Adolescents. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2019, 15, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattar, S.; Khan, D.S.; Yousaf, R. Impact of playing video games on cognitive functioning and learning styles. Sukkur IBA J. Comput. Math. Sci. 2021, 5, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucatelli, A.; Goulart, A.A.; Silveira, P.S.P.; Siqueira, J.D.O.; Carmona, M.J.C.; Pereira, V.F.A.; Valentin, L.S.S.; Vieira, J.E. Assessment of a Digital Game as a Neuropsychological Test for Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction. Braz. J. Anesthesiol. Engl. Ed. 2022, 72, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitbourne, S.K.; Ellenberg, S.; Akimoto, K. Reasons for Playing Casual Video Games and Perceived Benefits Among Adults 18 to 80 Years Old. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2013, 16, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boot, W.R.; Champion, M.; Blakely, D.P.; Wright, T.; Souders, D.J.; Charness, N. Video Games as a Means to Reduce Age-Related Cognitive Decline: Attitudes, Compliance, and Effectiveness. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laganà, L. Cognitive Gains from Video Game Use in Older Age: A Review of the Literature Corroborating Them. Int. J. Fam. Community Med. 2018, 2, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguera, J.A.; Gazzaley, A. Video Games, Cognitive Exercises, and the Enhancement of Cognitive Abilities. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2015, 4, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charchat-Fichman, H.; Uehara, E.; Santos, C.F. New Technologies in Assessment and Neuropsychological Rehabilitation. Temas Em Psicol. 2014, 22, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toril, P.; Reales, J.M.; Mayas, J.; Ballesteros, S. Video Game Training Enhances Visuospatial Working Memory and Episodic Memory in Older Adults. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toril, P.; Reales, J.M.; Ballesteros, S. Video Game Training Enhances Cognition of Older Adults: A Meta-Analytic Study. Psychol. Aging 2014, 29, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anguera, J.A.; Boccanfuso, J.; Rintoul, J.L.; Al-Hashimi, O.; Faraji, F.; Janowich, J.; Kong, E.; Larraburo, Y.; Rolle, C.; Johnston, E.; et al. Video Game Training Enhances Cognitive Control in Older Adults. Nature 2013, 501, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschini, S.; Bertoni, S.; Lulli, M.; Pievani, T.; Facoetti, A. Short-Term Effects of Video-Games on Cognitive Enhancement: The Role of Positive Emotions. J. Cogn. Enhanc. 2022, 6, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, C.; Boot, W.R.; Voss, M.W.; Kramer, A.F. Can Training in a Real-Time Strategy Video Game Attenuate Cognitive Decline in Older Adults? Psychol. Aging 2008, 23, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutting, J.; Copeland, B.; McNab, F. Higher Working Memory Capacity and Distraction-Resistance Associated with Strategy (Not Action) Game Playing in Younger Adults, but Puzzle Game Playing in Older Adults. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Koo, M.; Nam, K. Game Experience Leads to Improvement in Cognitive Functioning of the Early Middle-Aged Adults in Contrast with the Young-Aged Adults. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2022, 129, 107153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, F.C.; Fisch, S.M. Introduction: Digital Games as a Context for Cognitive Development, Learning, and Developmental Research. New Dir. Child Adolesc. Dev. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latham, A.J.; Patston, L.L.M.; Tippett, L.J. The Virtual Brain: 30 Years of Video-Game Play and Cognitive Abilities. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unsworth, N.; Redick, T.S.; McMillan, B.D.; Hambrick, D.Z.; Kane, M.J.; Engle, R.W. Is Playing Video Games Related to Cognitive Abilities? Psychol. Sci. 2015, 26, 759–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, G.; Tatlidil, K.S.; Gobet, F. Video Game Training Does Not Enhance Cognitive Ability: A Comprehensive Meta-Analytic Investigation. Psychol. Bull. 2018, 144, 111–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redick, T.S.; Unsworth, N.; Kane, M.J.; Hambrick, D.Z. Don’t Shoot the Messenger: Still No Evidence That Video-Game Experience Is Related to Cognitive Abilities—A Reply to Green et al. (2017). Psychol. Sci. 2017, 28, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zioga, T.; Nega, C.; Roussos, P.; Kourtesis, P. Validation of the Gaming Skills Questionnaire in Adolescence: Effects of Gaming Skills on Cognitive and Affective Functioning. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2024, 14, 722–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Macken, B. Questioning Short-Term Memory and Its Measurement: Why Digit Span Measures Long-Term Associative Learning. Cognition 2015, 144, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, D.L.; Kishiyama, M.M.; Yund, E.W.; Herron, T.J.; Edwards, B.; Poliva, O.; Hink, R.F.; Reed, B. Improving Digit Span Assessment of Short-Term Verbal Memory. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2011, 33, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsi, P.M. Human Memory and the Medial Temporal Region of the Brain; ProQuest Information & Learning: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1973; Volume 34, p. 891. [Google Scholar]
- Kessels, R.P.C.; Van Zandvoort, M.J.E.; Postma, A.; Kappelle, L.J.; De Haan, E.H.F. The Corsi Block-Tapping Task: Standardization and Normative Data. Appl. Neuropsychol. 2000, 7, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessels, R.P.C.; Van Den Berg, E.; Ruis, C.; Brands, A.M.A. The Backward Span of the Corsi Block-Tapping Task and Its Association With the WAIS-III Digit Span. Assessment 2008, 15, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaacs, E.B.; Vargha-Khadem, F. Differential Course of Development of Spatial and Verbal Memory Span: A Normative Study. Br. J. Dev. Psychol. 1989, 7, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandierendonck, A.; Kemps, E.; Fastame, M.C.; Szmalec, A. Working Memory Components of the Corsi Blocks Task. Br. J. Psychol. 2004, 95, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deary, I.J.; Liewald, D.; Nissan, J. A Free, Easy-to-Use, Computer-Based Simple and Four-Choice Reaction Time Programme: The Deary-Liewald Reaction Time Task. Behav. Res. Methods 2011, 43, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, E.J.; Shaw, P.; Baker, D.; Baron-Cohen, S.; David, A.S. Measuring Empathy: Reliability and Validity of the Empathy Quotient. Psychol. Med. 2004, 34, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron-Cohen, S.; Wheelwright, S. The Empathy Quotient: An Investigation of Adults with Asperger Syndrome or High Functioning Autism, and Normal Sex Differences. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2004, 34, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pehlivanidis, A.; Tasios, K.; Papanikolaou, K.; Douzenis, A.; Michopoulos, I. Validation of the Empathy Quotient (EQ)—Greek Version. Psychiatriki 2021, 32, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; RStudio, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Revelle, W. Psych: Procedures for Psychological, Psychometric, and Personality Research; Northwestern University: Evanston, IL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kazdin, A.E. Research Design in Clinical Psychology, 5th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022; ISBN 978-1-108-99521-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wilms, I.L.; Petersen, A.; Vangkilde, S. Intensive Video Gaming Improves Encoding Speed to Visual Short-Term Memory in Young Male Adults. Acta Psychol. 2013, 142, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacker, K.J.; Curby, K.M. Enhanced Visual Short-Term Memory in Action Video Game Players. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2013, 75, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.; Bavelier, D. Enumeration versus Multiple Object Tracking: The Case of Action Video Game Players. Cognition 2006, 101, 217–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, E.G.; Green, C.S. Cognitive Skills Acquired from Video Games. In Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Communication; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2023; ISBN 978-0-19-022861-3. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J.J.; Blair, M.R.; Henrey, A.J. Over the Hill at 24: Persistent Age-Related Cognitive-Motor Decline in Reaction Times in an Ecologically Valid Video Game Task Begins in Early Adulthood. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shute, V.J.; Ventura, M.; Ke, F. The Power of Play: The Effects of Portal 2 and Lumosity on Cognitive and Noncognitive Skills. Comput. Educ. 2015, 80, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungur, H.; Boduroglu, A. Action Video Game Players Form More Detailed Representation of Objects. Acta Psychol. 2012, 139, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, R.; Swing, E.L.; Anderson, C.A.; Prot, S. The Contrasting Effects of an Action Video Game on Visuo-Spatial Processing and Proactive Cognitive Control. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kefalis, C.; Kontostavlou, E.Z.; Drigas, A. The Effects of Video Games in Memory and Attention. Int. J. Eng. Pedagogy IJEP 2020, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tsai, M.-J. Eye-Hand Coordination Strategies during Active Video Game Playing: An Eye-Tracking Study. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 51, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dye, M.W.G.; Green, C.S.; Bavelier, D. Increasing Speed of Processing With Action Video Games. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2009, 18, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dye, M.W.G.; Green, C.S.; Bavelier, D. The Development of Attention Skills in Action Video Game Players. Neuropsychologia 2009, 47, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, J.; Zinni, M.; Bavelier, D.; Hillyard, S.A. Neural Basis of Superior Performance of Action Videogame Players in an Attention-Demanding Task. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Molloy, K. The Changes of Cognition in Teenagers after Playing Video Games. J. Stud. Res. 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaus, M.; Marron, E.M.; Viejo-Sobera, R.; Redolar-Ripoll, D. Neural Basis of Video Gaming: A Systematic Review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisholm, J.D.; Hickey, C.; Theeuwes, J.; Kingstone, A. Reduced Attentional Capture in Action Video Game Players. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2010, 72, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, M.J.; Cregan, S.C.; Joyce, J.M.; Kowal, M.; Toth, A.J. Comparing the Cognitive Performance of Action Video Game Players and Age-matched Controls Following a Cognitively Fatiguing Task: A Stage 2 Registered Report. Br. J. Psychol. 2024, 115, 363–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal, M.; Toth, A.J.; Exton, C.; Campbell, M.J. Different Cognitive Abilities Displayed by Action Video Gamers and Non-Gamers. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 88, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Lu, A.S. Narrative and Active Video Game in Separate and Additive Effects of Physical Activity and Cognitive Function among Young Adults. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockmyer, J.F. Playing Violent Video Games and Desensitization to Violence. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 24, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvert, S.L.; Appelbaum, M.; Dodge, K.A.; Graham, S.; Nagayama Hall, G.C.; Hamby, S.; Fasig-Caldwell, L.G.; Citkowicz, M.; Galloway, D.P.; Hedges, L.V. The American Psychological Association Task Force Assessment of Violent Video Games: Science in the Service of Public Interest. Am. Psychol. 2017, 72, 126–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.A.; Bushman, B.J. Effects of Violent Video Games on Aggressive Behavior, Aggressive Cognition, Aggressive Affect, Physiological Arousal, and Prosocial Behavior: A Meta-Analytic Review of the Scientific Literature. Psychol. Sci. 2001, 12, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.A.; Dill, K.E. Video Games and Aggressive Thoughts, Feelings, and Behavior in the Laboratory and in Life. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2000, 78, 772–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.; Warburton, W. The Impact of Violent Video Games: An Overview. In Growing Up Fast and Furious: Reviewing the Impacts of Violent and Sexualised Media on Children; Federation Press: Alexandria, Australia, 2012; pp. 56–84. [Google Scholar]
- Mahood, C.; Hanus, M. Role-Playing Video Games and Emotion: How Transportation into the Narrative Mediates the Relationship between Immoral Actions and Feelings of Guilt. Psychol. Pop. Media Cult. 2017, 6, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.S.; Bavelier, D. Effect of Action Video Games on the Spatial Distribution of Visuospatial Attention. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2006, 32, 1465–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colzato, L.S.; Van Den Wildenberg, W.P.M.; Zmigrod, S.; Hommel, B. Action Video Gaming and Cognitive Control: Playing First Person Shooter Games Is Associated with Improvement in Working Memory but Not Action Inhibition. Psychol. Res. 2013, 77, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.; Jiwal, S.; Jain, A. Impact of Playing Action and Puzzle Video-Games on Attention and Executive Function: A Comparative Study. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 63, 122–129. [Google Scholar]
- Oei, A.C.; Patterson, M.D. Playing a Puzzle Video Game with Changing Requirements Improves Executive Functions. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 37, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gaming Skill | Mean | SD | Range | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Low | 26.93 | 4.274 | 20–38 |
| Medium | 29.00 | 5.359 | 21–40 | |
| High | 29.28 | 4.122 | 21–38 | |
| Total | 28.39 | 4.680 | 20–40 | |
| Education | Low | 16.40 | 2.343 | 12–21 |
| Medium | 17.24 | 3.055 | 12–25 | |
| High | 15.93 | 2.298 | 12–20 | |
| Total | 16.52 | 2.610 | 12–25 | |
| Sport Games Skill | Low | 2.27 | 0.450 | 2–3 |
| Medium | 3.17 | 0.928 | 2–6 | |
| High | 3.69 | 1.228 | 2–6 | |
| Total | 3.03 | 1.090 | 2–6 | |
| FPS Games Skill | Low | 2.13 | 0.346 | 2–3 |
| Medium | 2.72 | 0.797 | 2–5 | |
| High | 4.41 | 1.615 | 2–9 | |
| Total | 3.08 | 1.420 | 2–9 | |
| RPG Games Skill | Low | 2.10 | 0.305 | 2–3 |
| Medium | 3.03 | 1.239 | 2–7 | |
| High | 6.86 | 2.656 | 2–11 | |
| Total | 3.98 | 2.660 | 2–11 | |
| Action Games Skill | Low | 2.27 | 0.640 | 2–4 |
| Medium | 3.62 | 1.898 | 2–10 | |
| High | 6.31 | 2.140 | 2–11 | |
| Total | 4.05 | 2.370 | 2–11 | |
| Strategy Games Skill | Low | 2.07 | 0.365 | 2–4 |
| Medium | 2.76 | 0.988 | 2–5 | |
| High | 4.86 | 2.532 | 2–12 | |
| Total | 3.22 | 1.960 | 2–12 | |
| Puzzle Games Skill | Low | 2.43 | 0.626 | 2–4 |
| Medium | 3.52 | 1.326 | 2–6 | |
| High | 5.52 | 2.309 | 2–11 | |
| Total | 3.81 | 2.02 | 2–11 | |
| Total Gaming Skill | Low | 13.27 | 1.143 | 12–15 |
| Medium | 18.83 | 2.633 | 16–24 | |
| High | 31.66 | 5.627 | 25–43 | |
| Total | 21.16 | 8.540 | 12–43 | |
| Digit Span Forward Recall | Low | 16.13 | 2.849 | 8–20 |
| Medium | 16.07 | 2.685 | 9–20 | |
| High | 16.79 | 2.411 | 11–20 | |
| Total | 16.33 | 2.650 | 8–20 | |
| Digit Span Backward Recall | Low | 13.97 | 3.429 | 9–19 |
| Medium | 15.00 | 3.082 | 8–20 | |
| High | 15.69 | 3.486 | 3–20 | |
| Total | 14.88 | 3.380 | 3–20 | |
| Corsi Block Forward Recall | Low | 7.23 | 2.687 | 3–13 |
| Medium | 7.86 | 3.020 | 2–14 | |
| High | 9.90 | 3.745 | 2–17 | |
| Total | 8.32 | 3.340 | 2–17 | |
| Corsi Block Backward Recall | Low | 6.97 | 2.632 | 3–11 |
| Medium | 7.90 | 3.457 | 3–13 | |
| High | 9.55 | 3.709 | 2–16 | |
| Total | 8.13 | 3.430 | 2–16 | |
| Deary-Liewald Single Reaction Time | Low | 282.60 | 46.154 | 231–462 |
| Medium | 286.07 | 57.681 | 207–462 | |
| High | 255.59 | 27.800 | 195–303 | |
| Total | 274.84 | 47.070 | 195–462 | |
| Deary-Liewald Choice Reaction Time | Low | 470.03 | 119.097 | 331–804 |
| Medium | 433.55 | 69.300 | 296–641 | |
| High | 395.21 | 48.565 | 310–521 | |
| Total | 433.35 | 89.340 | 296–804 | |
| Empathy Quotient | Low | 44.57 | 9.134 | 18–62 |
| Medium | 42.86 | 12.397 | 18–66 | |
| High | 40.55 | 12.126 | 22–63 | |
| Total | 42.68 | 11.280 | 18–66 |
| DST-FR | DST-BR | CBT-FR | CBT-BR | DLSRT | DLCRT | EQ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.08 | 0.20 | 0.30 ** | −0.27 * | 0.14 | 0.13 | −0.24 * |
| Education | −0.06 | −0.03 | −0.18 | −0.14 | 0.09 | 0.16 | −0.07 |
| SpGS | 0.04 | 0.25 * | 0.13 | 0.18 | −0.17 | −0.18 | −0.08 |
| FPSGS | −0.02 | 0.11 | 0.25 * | 0.23 * | −0.27 * | −0.23 * | −0.21 |
| RPGS | 0.17 | 0.35 * | 0.35 * | 0.27 * | −0.10 | −0.16 | −0.26 * |
| AGS | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.12 | −0.39 *** | −0.32 ** | −0.12 |
| StGS | 0.03 | −0.01 | 0.34 * | 0.18 | −0.12 | −0.03 | −0.21 |
| PGS | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.25 * | 0.28 ** | −0.18 | −0.21 | −0.08 |
| TGS | 0.13 | 0.22 * | 0.29 ** | 0.27 * | −0.26 * | −0.24 * | −0.20 |
| Predicted | Predictors | β Coefficient | p-Value (β) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digit Span Forward Recall | Null Model | - | - | - |
| Digit Span Backward Recall | Role-Playing Games Skills | 0.35 | 0.004 * | 0.12 |
| Corsi Blocks Forward Recall | Age | 0.24 | 0.022 * | 0.20 |
| Role-Playing Games Skills | 0.32 | 0.003 ** | ||
| Corsi Blocks Backward Recall | Age | 0.23 | 0.028 * | 0.19 |
| Puzzle Games Skills | 0.25 | 0.018 * | ||
| Deary–Liewald Single Reaction Time | Action Games Skills | −0.39 | 0.001 *** | 0.16 |
| Deary–Liewald Choice Reaction Time | Action Games Skills | −0.32 | 0.008 ** | 0.10 |
| Empathy Quotient | Role-Playing Games Skills | −0.26 | 0.014 * | 0.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zioga, T.; Ferentinos, A.; Konsolaki, E.; Nega, C.; Kourtesis, P. Video Game Skills across Diverse Genres and Cognitive Functioning in Early Adulthood: Verbal and Visuospatial Short-Term and Working Memory, Hand–Eye Coordination, and Empathy. Behav. Sci. 2024, 14, 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14100874
Zioga T, Ferentinos A, Konsolaki E, Nega C, Kourtesis P. Video Game Skills across Diverse Genres and Cognitive Functioning in Early Adulthood: Verbal and Visuospatial Short-Term and Working Memory, Hand–Eye Coordination, and Empathy. Behavioral Sciences. 2024; 14(10):874. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14100874
Chicago/Turabian StyleZioga, Triantafyllia, Aristotelis Ferentinos, Eleni Konsolaki, Chrysanthi Nega, and Panagiotis Kourtesis. 2024. "Video Game Skills across Diverse Genres and Cognitive Functioning in Early Adulthood: Verbal and Visuospatial Short-Term and Working Memory, Hand–Eye Coordination, and Empathy" Behavioral Sciences 14, no. 10: 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14100874
APA StyleZioga, T., Ferentinos, A., Konsolaki, E., Nega, C., & Kourtesis, P. (2024). Video Game Skills across Diverse Genres and Cognitive Functioning in Early Adulthood: Verbal and Visuospatial Short-Term and Working Memory, Hand–Eye Coordination, and Empathy. Behavioral Sciences, 14(10), 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14100874








