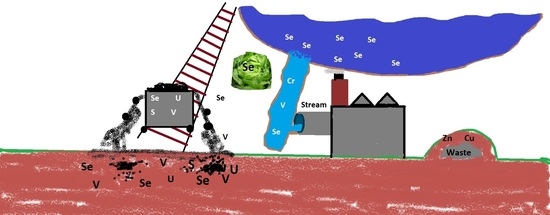
Selenium, Sulphur, Trace Metal, and BTEX Levels in Soil, Water, and Lettuce from the Croatian Raša Bay Contaminated by Superhigh-Organic-Sulphur Coal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
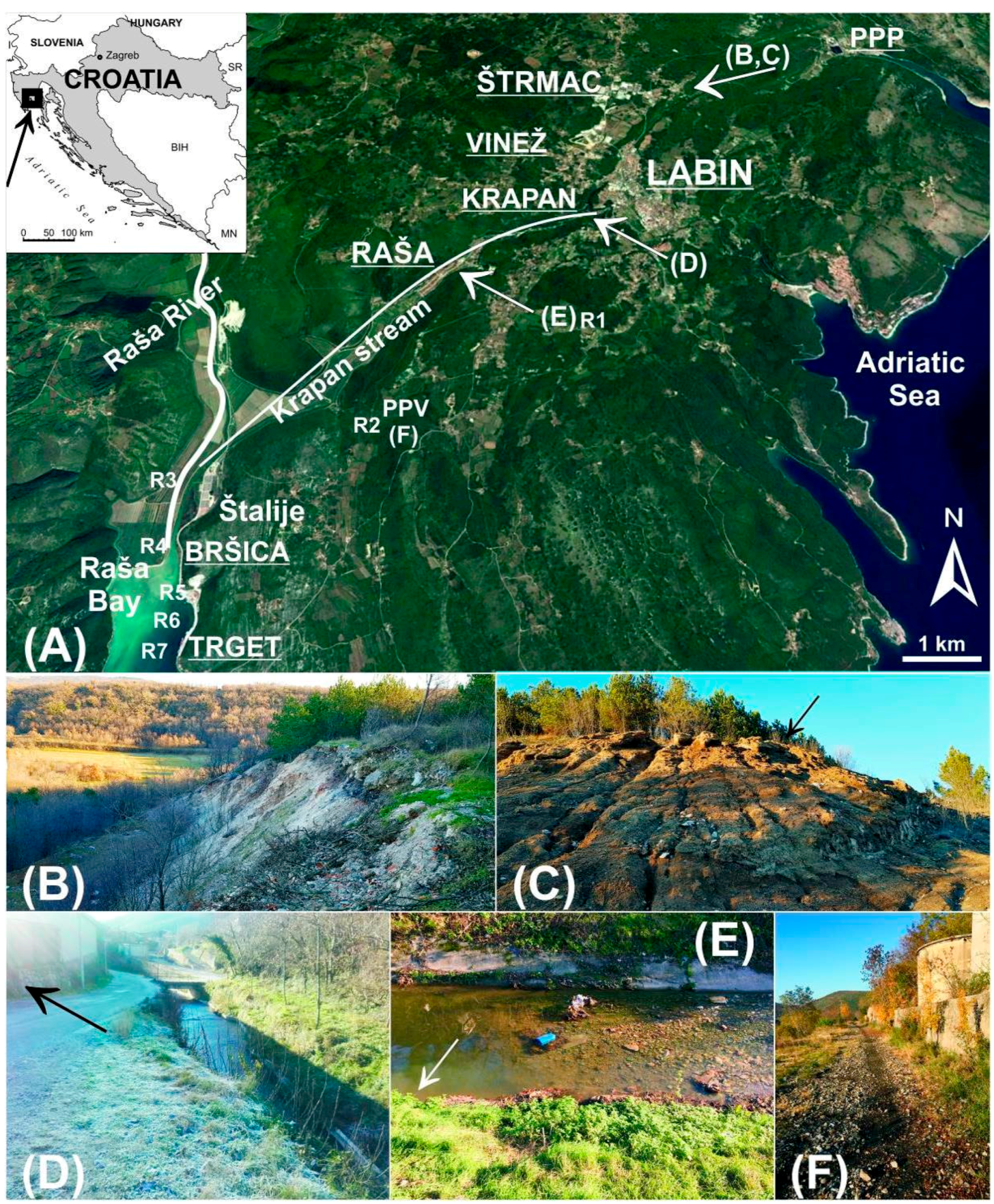
2.1. Site Description and Sampling Strategy
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.3. Ecological Risk Assessment
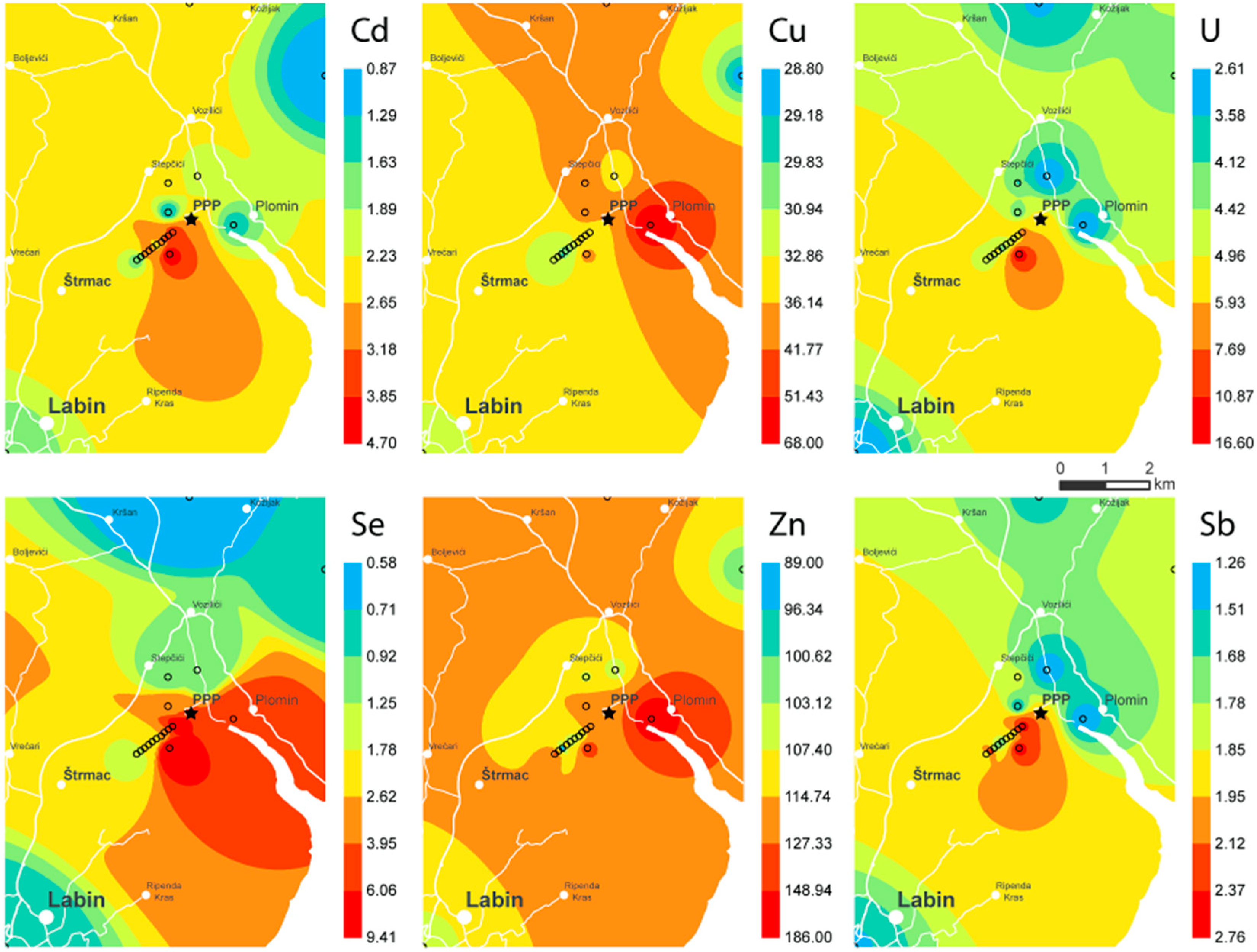
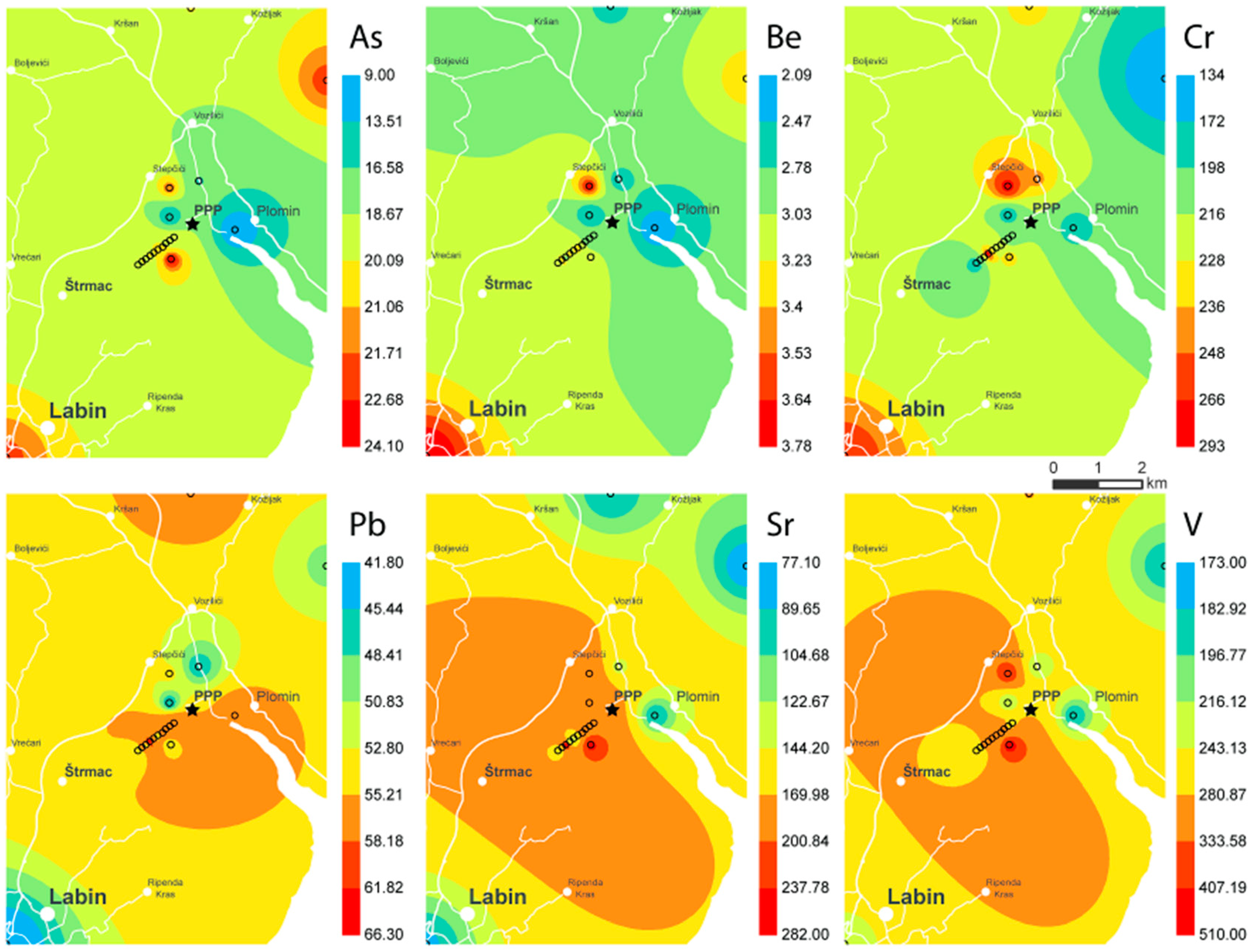
2.4. Contour Maps
3. Results and Discussion
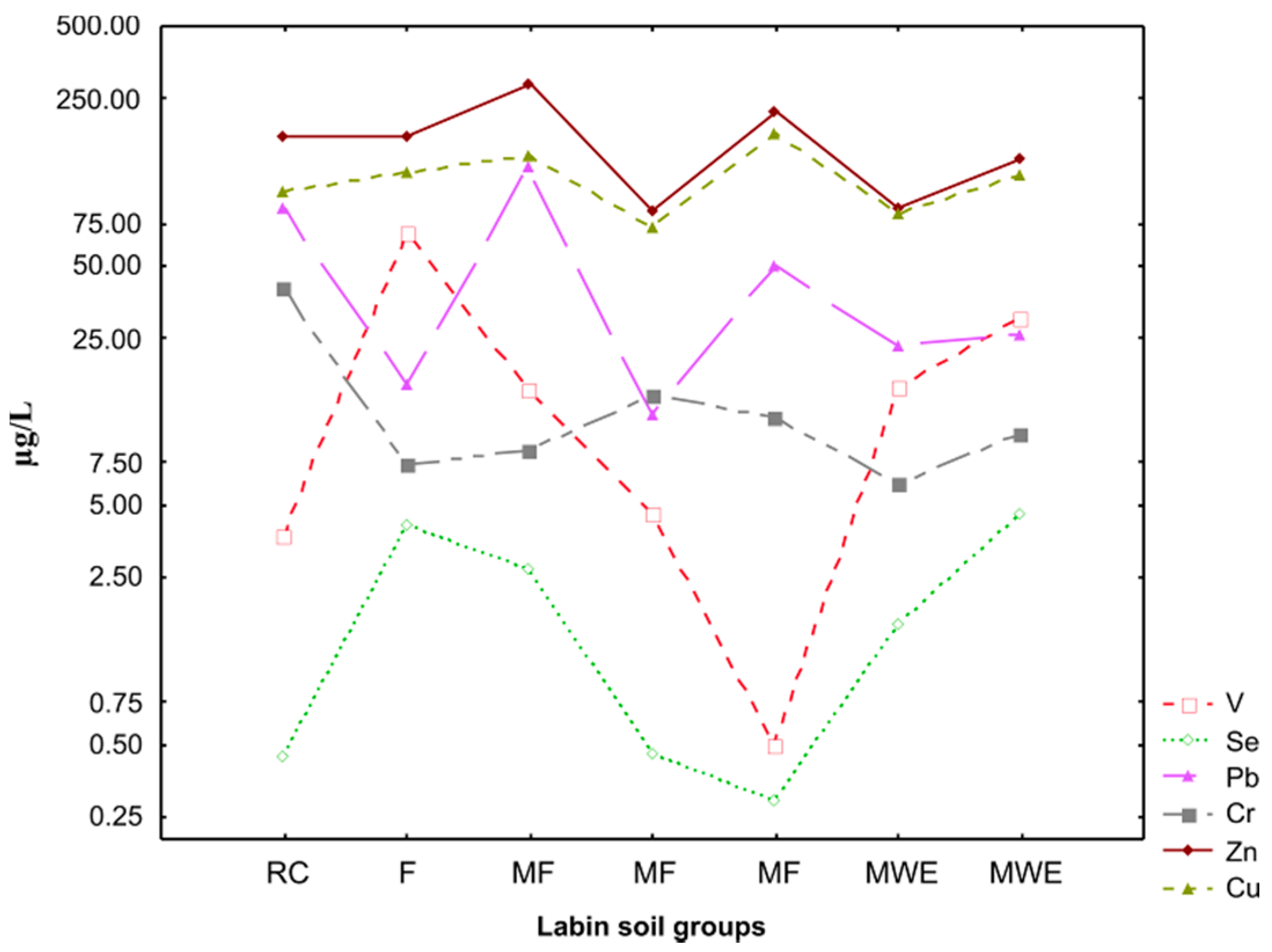
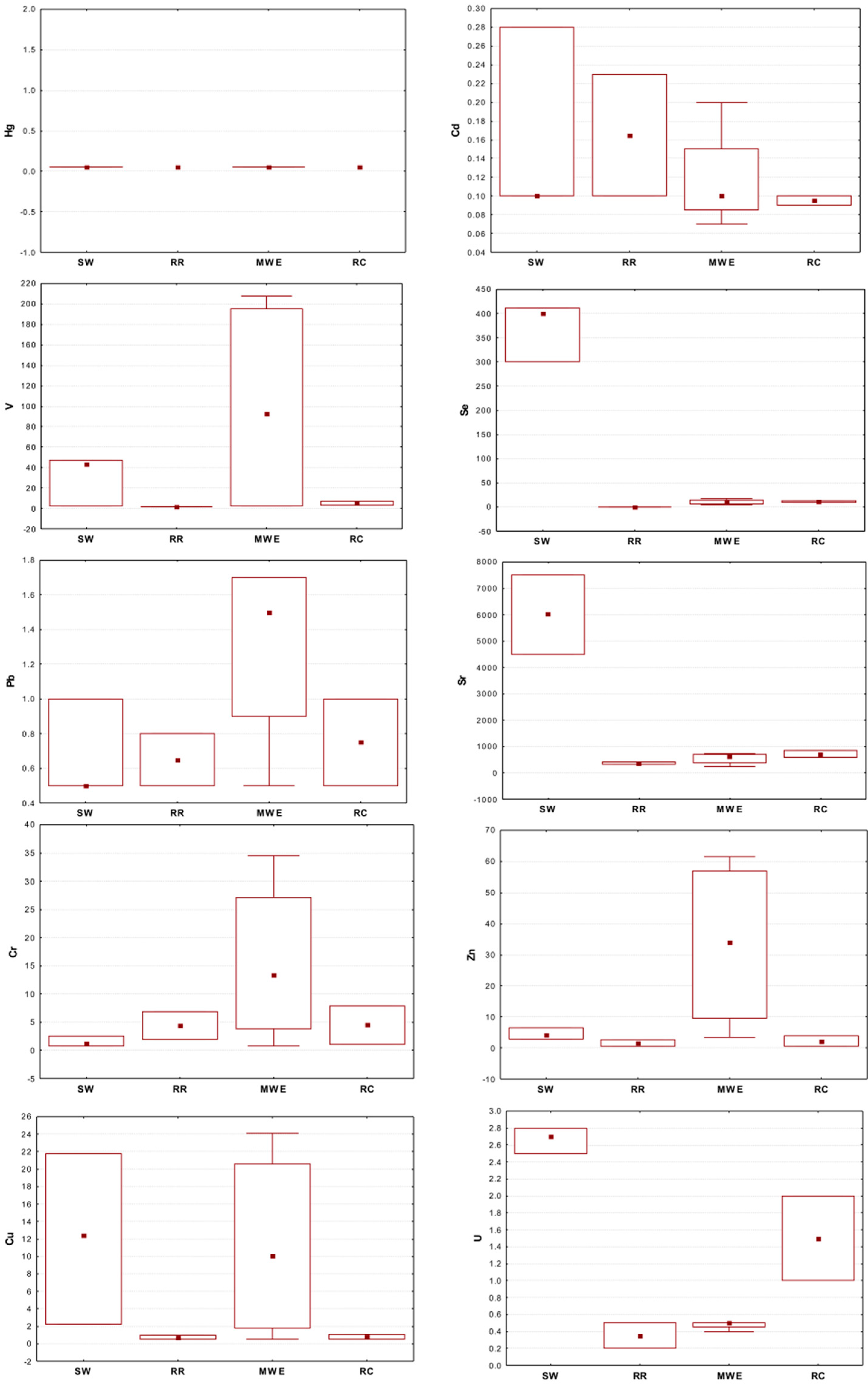
3.1. Levels of Se and Trace Metals in Soil and Sediment
3.2. Levels of Se, Trace Metals, and BTEX in Water and Lettuce Samples
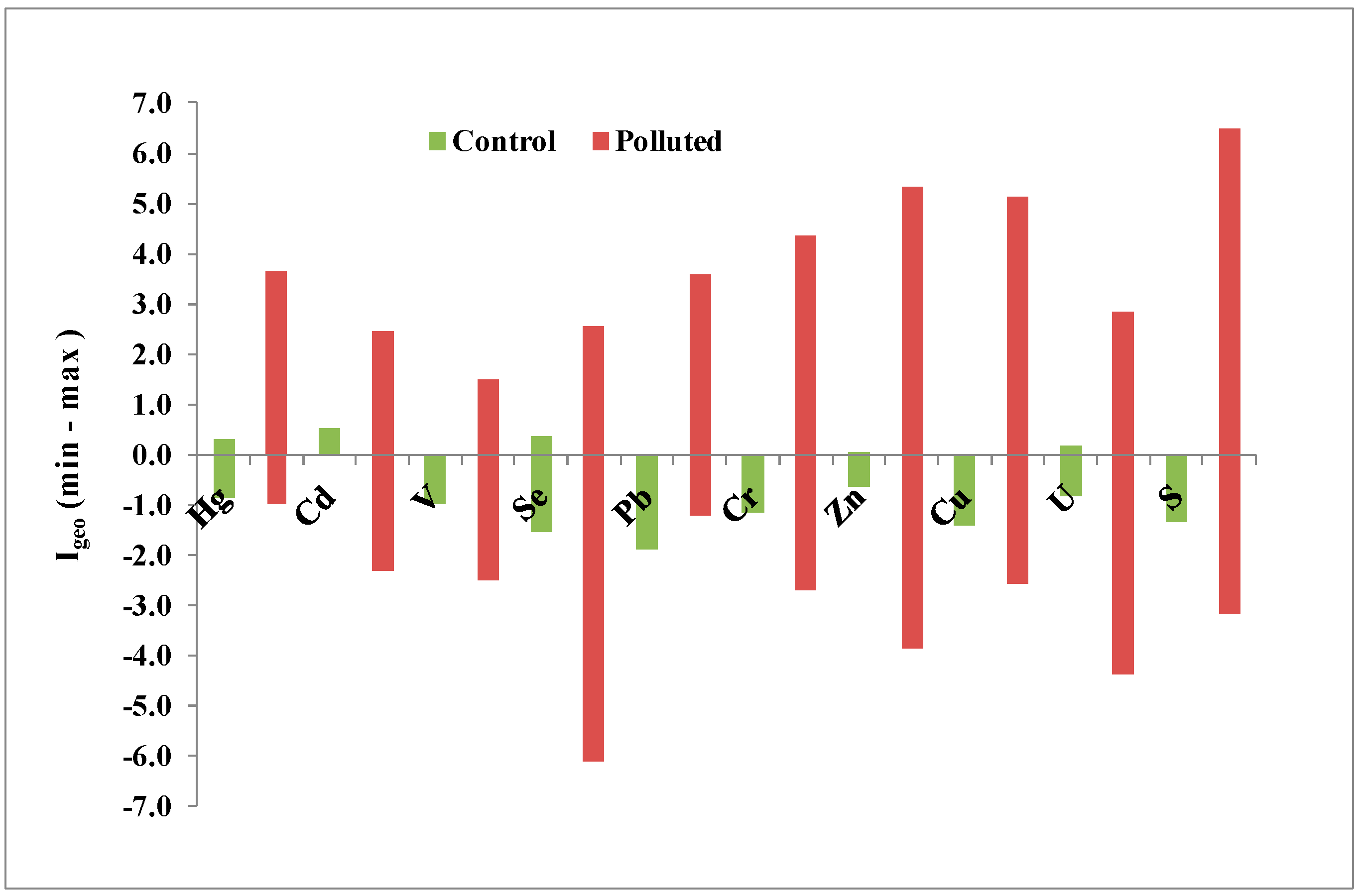
3.3. Ecological Risk Assessment Indices
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Awoyemi, O.M.; Dzantor, E.K. Toxicity of coal fly ash (CFA) and toxicological response of switchgrass in mycorrhiza-mediated CFA-soil admixtures. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 144, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofilić, T.; Brnardić, I.; Šimunić-Mežnarić, V.; Šorša, A. Soil pollution caused by landfilling of nonhazardous waste from steel production processes. Chem. Ind. 2013, 62, 381–388. [Google Scholar]
- Saikia, J.; Saikia, P.; Boruah, R.; Saikia, B.K. Ambient air quality and emission characteristics in and around a non-recovery type coke oven using high sulphur coal. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 530, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medunić, G.; Mondol, D.; Rađenović, A.; Nazir, S. Review of the latest research on coal, environment, and clean technologies. Min. Geol. Pet. Eng. Bull. 2018, 33, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, L.B.; Sloss, L.L. Trace Elements—Emissions from Coal Combustion and Gasification; IEA Coal Research: London, UK, 1992; p. 111. [Google Scholar]
- Medunić, G.; Šmit, Z. Organic micropollutants in the Sava and Bosna river overbank and floodplain sediments during the May through June 2014 catastrophic flood. Min. Geol. Pet. Eng. Bull. 2015, 31, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medunić, G.; Rađenović, A.; Bajramović, M.; Švec, M.; Tomac, M. Once grand, now forgotten: What do we know about the superhigh-organic-sulphur Raša coal? Min. Geol. Pet. Eng. Bull. 2016, 34, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medunić, G.; Kuharić, Ž.; Krivohlavek, A.; Fiket, Ž.; Rađenović, A.; Gödel, K.; Kampić, Š.; Kniewald, G. Geochemistry of Croatian superhigh-organic-sulphur Raša coal, imported low-S coal, and bottom ash: Their Se and trace metal fingerprints in seawater, clover, foliage, and mushroom specimens. Int. J. Oil Gas Coal Technol. 2018, 18, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medunić, G.; Ahel, M.; Božičević Mihalić, I.; Gaurina Srček, V.; Kopjar, N.; Fiket, Ž. Toxic airborne S, PAH, and trace element legacy of the superhigh-organic-sulphur Raša coal combustion: Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity assessment of soil and ash. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radić, S.; Medunić, G.; Kuharić, Ž.; Roje, V.; Maldini, K.; Vujčić, V.; Krivohlavek, A. The effect of hazardous pollutants from coal combustion activity: Phytotoxicity assessment of aqueous soil extracts. Chemosphere 2018, 199, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiket, Ž.; Medunić, G.; Kniewald, G. Rare earth elements distribution in soil nearby thermal power plant. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Bhatnagar, P.; Chatterjee, S.; John, P.J.; Soni, I.P. Bio Nanotechnological Intervention: A Sustainable Alternative to Treat Dye Bearing Waste Waters. Indian J. Pharm. Biol. Res. 2017, 5, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halamić, J.; Peh, Z.; Miko, S.; Galović, L.; Šorša, A. Geochemical atlas of Croatia: environmental implications and geodynamical thread. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 115, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miko, S.; Prohić, E.; Durn, G.; Šparica, M. Selenium distribution and mobility in Mediterranean karst soils from a coal mining region in Istria, Croatia. In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Environmental Geochemistry, Edinburgh, Scotland, 7–11 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Durn, G.; Ottner, F.; Slovenec, D. Mineralogical and geochemical indicators of the polygenetic nature of terra rossa in Istria, Croatia. Geoderma 1999, 91, 125–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. Standard Test Methods for Total Sulfur in the Analysis Sample of Refuse-Derived Fuel. Available online: https://www.astm.org/Standards/E775.htm (accessed on 7 September 2018).
- Fiket, Ž.; Roje, V.; Mikac, N.; Kniewald, G. Determination of arsenic and other trace elements in bottled waters by high resolution inductively coupled plasmamass spectrometry. Croat. Chem. Acta 2007, 80, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Halamić, J.; Miko, S. Geochemical Atlas of the Republic of Croatia; Croatian Geological Survey: Zagreb, Croatia, 2009; p. 87. [Google Scholar]
- Loska, K.; Wiechula, D.; Korus, I. Metal contamination of farming soils affected by industry. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Yang, L. A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem. J. 2010, 94, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; p. 548. ISBN I978-1-4200-9368-1. [Google Scholar]
- Prohić, E.; Hausberger, G.; Davis, J.C. Geochemical patterns in soils of the karst region, Croatia. J. Geochem. Explor. 1997, 60, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; de Caritat, P. Chemical Elements in the Environment: Factsheets for the Geochemist and Environmental Scientist; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; p. 398. ISBN 978-3-642-72016-1. [Google Scholar]
- Adriano, D.C. Trace Elements in Terrestrial Environments: Biogeochemistry, Bioavailability, and Risks of Metal; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001; p. 867. ISBN 978-0-387-21510-5. [Google Scholar]
- Official Gazette. Regulations on the Protection of the Agricultural Land from Pollution. Available online: https://narodne-novine.nn.hr/clanci/sluzbeni/2010_03_32_745.html (accessed on 8 November 2018).
- Frančišković-Bilinski, S.; Scholger, R.; Bilinski, H.; Tibljaš, D. Magnetic, geochemical and mineralogical properties of sediments from karstic and flysch rivers of Croatia and Slovenia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 3939–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croatian Environment Agency. Croatian Soil Monitoring Programme. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/life/project/Projects/index.cfm?fuseaction=home.showFile&rep=file&fil=Soilmonitoring_Croatian.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2018).
- SMSP and FALCONBRIDGE NC SAS. Koniambo Project, Environmental Baseline Study—Summary. Available online: http://www.koniambonickel.nc/media/pdf/doc_pdf/resum_english.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2018).
- Baruah, B.P.; Khare, P. Mobility of trace and potentially harmful elements in the environment from high sulfur Indian coal mines. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.L.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, M.P.; Kumar, A. Environmentally sensitive major and trace elements in Indonesian coal and their geochemical significance. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2015, 37, 1836–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Seredin, V.V.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, W.; Song, W.; Wang, P. Enrichment of U–Se–Mo–Re–V in coals preserved within marine carbonate successions: Geochemical and mineralogical data from the Late Permian Guiding Coalfield, Guizhou, China. Miner. Depos. 2015, 50, 159–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hower, J.C.; Greb, S.F.; Cobb, J.C.; Williams, D.A. Discussion on origin of vanadium in coals: Parts of the Western Kentucky (USA) No. 9 coal rich in vanadium. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 2000, 157, 1257–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, N.; Li, S.; Li, L.; Su, H.; Liu, C. Distribution and transport of selenium in Yutangba, China: Impact of human activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 392, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yudovich, Y.E.; Ketris, M.P. Selenium in coal: A review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2006, 67, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naftz, D.L.; Rice, J.A. Geochemical processes controlling selenium in ground water after mining, Powder River Basin, Wyoming, U.S.A. Appl. Geochem. 1989, 4, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkness, J.S.; Sulkin, B.; Vengosh, A. Evidence for coal ash ponds leaking in the Southeastern United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6583–6592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valković, V.; Makjanić, J.; Jakšić, M.; Popović, S.; Bos, A.J.J.; Vis, R.D.; Wiederspahn, K.; Verheul, H. Analysis of fly ash by X-ray emission spectroscopy and proton microbeam analysis. Fuel 1984, 63, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helios Rybicka, E. Impact of mining and metallurgical industries on the environment in Poland. Appl. Geochem. 1996, 11, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verner, J.F.; Ramsey, M.H.; Helios Rybicka, E.; Jedrzejczyk, B. Heavy metal contamination of soils around a PbZn smelter in Bukowno, Poland. Appl. Geochem. 1996, 11, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svete, P.; Milačić, R.; Pihlar, B. Optimisation of an extraction procedure for determination of total water-soluble Zn, Pb and Cd and their species in soils from a mining area. Ann. Chim. 2000, 90, 323–334. [Google Scholar]
- Medunić, G.; Tomašić, N.; Balen, D.; Oreščanin, V.; Prohić, E.; Kampić, Š.; Ivanišević, D. Distribution of copper and zinc in the soil of an industrial zone in the city of Garešnica, Croatia. Geol. Croat. 2009, 62, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.Q.; Wang, S.Z.; Zhou, R.H.; Sun, S.Z. Endemic selenium intoxication of humans in China. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1983, 37, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.D. Use of sewage sludge on land in the United Kingdom. Water Sci. Technol. 1987, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksander-Kwaterczak, U.; Helios Rybicka, E. Contaminated sediments as a potential source of Zn, Pb, and Cd for a river system in the historical metalliferous ore mining and smelting industry area of South Poland. J. Soils Sediments 2009, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, L.J. Contamination of sediments by lead, zinc and cadmium: A review. Environ. Pollut. Ser. B Chem. Phys. 1981, 2, 401–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Gazette. Regulations on Classification of Waters. Available online: https://narodne-novine.nn.hr/clanci/sluzbeni/full/1998_06_77_1037.html (accessed on 7 November 2018).
- Ternjej, I.; Gaurina Srček, V.; Mihaljević, Z.; Kopjar, N. Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of water and sediment samples from gypsum mining area in channel catfish ovary (CCO) cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 98, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Official Gazette. Regulations on Water from Karst and Table Waters. Available online: https://narodne-novine.nn.hr/clanci/sluzbeni/2013_06_81_1723.html (accessed on 7 November 2018).
- Swartjes, F.A. Risk-based assessment of soil and groundwater quality in the Netherlands: Standards and remediation urgency. Risk Anal. 1999, 19, 1235–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentine, J.L.; Kang, H.K.; Spivey, G.H. Selenium levels in human blood, urine, and hair in response to exposure via drinking water. Environ. Res. 1978, 17, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemly, A.D. Environmental implications of excessive selenium: A review. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 1997, 10, 415–435. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dreher, G.B.; Finkelman, R.B. Selenium mobilization in a surface coal mine, Powder River Basin, Wyoming, U.S.A. Environ. Geol. Water Sci. 1992, 19, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemly, A.D. Guidelines for evaluating selenium data from aquatic monitoring and assessment studies. Environ. Monit. Assess. 1993, 28, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stančić, Z.; Vujević, D.; Gomaz, A.; Bogdan, S.; Vincek, D. Detection of heavy metals in common vegetables at Varaždin City Market, Croatia. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Occup. Med. 2016, 67, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry, N.; Zayed, A.M.; de Souza, M.P.; Tarun, A.S. Selenium in higher plants. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 2000, 51, 401–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klapec, T.; Mandić, M.L.; Grgić, J.; Primorac, L.; Perl, A.; Krstanović, V. Selenium in selected foods grown or purchased in eastern Croatia. Food Chem. 2004, 85, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappa, E.C.; Pappas, A.C.; Surai, P.F. Selenium content in selected foods from the Greek market and estimation of the daily intake. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 372, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, A.; Sengupta, D. An assessment of soil contamination due to heavy metals around a coal-fired thermal power plant in India. Environ. Geol. 2006, 51, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernàndez-Martínez, J.; Zacchini, M.; Fernández-Marín, B.; García-Plazaola, J.I.; Fleck, I. Gas-exchange, photo-and antioxidant protection, and metal accumulation in I-214 and Eridano Populus sp. clones subjected to elevated zinc concentrations. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 107, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mean | SD | Min | Max | Range a | Median b | Mean c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hg | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.06–0.50 | 0.06 | 0.07 |
| Cd | 0.72 | 0.08 | 0.64 | 0.81 | 0.40–0.90 | 0.40 | 0.41 |
| V | 163 | 27.2 | 132 | 189 | 141–243 | 148 | 129 |
| Se | 1.32 | 0.77 | 0.60 | 2.24 | - | 1.15 * | 0.44 |
| Pb | 37.1 | 3.13 | 33.8 | 41.8 | 33.0–46.0 | 48.0 | 27.0 |
| Sr | 99.2 | 28.2 | 55.9 | 122 | 99.0–258 | 117 | 175 |
| Cr | 61.6 | 3.89 | 56.1 | 65.4 | 115–142 | 60.0 | 59.5 |
| Zn | 126 | 25.5 | 103.7 | 167 | 88.0–116 | 108 | 70.0 |
| Cu | 31.9 | 3.91 | 27.9 | 37.4 | 17.0–35.0 | 31.0 | 38.9 |
| U | 2.62 | 0.81 | 1.97 | 3.97 | - | 2.32 * | 3.00 |
| S | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.08 | - | 0.06 * | - |
| pH | 7.05 | 0.13 | 6.90 | 7.20 | |||
| CaCO3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| LOI | 12.5 | 1.73 | 10.3 | 14.6 | |||
| CEC | 21.1 | 3.76 | 16.1 | 25.2 |
| Variable | Present Study | Published Data | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Min | Max | Sediment | a | b | c | d | e | |
| Hg | 0.55 | 0.34 | 0.05 | 1.14 | 0.38 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.50–1.00 | 50 | |
| 0.09 | 0.01–0.1 | 2.49 | 0.20 (2 *) | |||||||
| Cd | 0.7 | 0.97 | 0.12 | 3.29 | 0.21 | 0.3 | 0.50–1.00 | 50 | ||
| 1.8 | 0.53 | 0.26 | 0.60 (10 *) | |||||||
| V | 194 | 216 | 38.9 | 624 | 33.7 | 90 | ||||
| 98 | 32.8 | |||||||||
| Se | 2.78 | 2.91 | 0.03 | 10.3 | 0.84 | 0.3 | ||||
| 2.3 | <5.00 | 0.63 | ||||||||
| Pb | 136 | 190 | 30.8 | 872 | 193 | 17 | 50.0–100 | 1000 | ||
| 26 | 80.0–100 | 21.2 | 31.0 (250 *) | |||||||
| Sr | 250 | 165 | 25.7 | 655 | 374 | 240 | ||||
| 187 | 224.7 | |||||||||
| Cr | 160 | 411 | 14 | 1860 | 31.4 | 80 | 40.0–80.0 | 750 | ||
| 64 | 44.9 | 26.0 (110 *) | ||||||||
| Zn | 990 | 1850 | 11.2 | 6580 | 350 | 70 | 60.0–150 | 1200 | ||
| 80 | 70.4 | 90.0 (200 *) | ||||||||
| Cu | 367 | 621 | 8.91 | 1850 | 116 | 25 | 60.0–90.0 | 500 | ||
| 19 | 28.9 | 28.0 (110 *) | ||||||||
| U | 5.93 | 6.78 | 0.17 | 25.2 | 0.51 | 2.7 | ||||
| 5 | 0.49 | |||||||||
| S | 2.77 | 2.81 | 0.01 | 8.1 | - | 0.08 | ||||
| pH | 7.29 | 0.39 | 6.5 | 7.92 | - | |||||
| CaCO3 | 30.3 | 17.1 | 1.27 | 55.9 | - | |||||
| LOI | 29 | 18.5 | 11 | 83.1 | - | |||||
| CEC | 12.5 | 7.77 | 1.6 | 25.5 | - | |||||
| a | b | c | d | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LW 1, 2 | LW 3–5 | SW 1 | SW 2 | ||||
| Cd | 0.01 | 5.00 | 0.10–0.50 | 0.50–5.00 | 0.10–0.50 | 0.50–2.50 | 0.11 |
| Cr | <0.01 | 50.0 | 1.00–6.00 | 6.00–20.0 | 1.00–6.00 | 6.00–20.0 | 0.30 |
| Cu | 0.26 | 2000 | 2.00–10.0 | 10.0–20.0 | 2.00–10.0 | 10.0–20.0 | 0.25 |
| Hg | 1.00 | 0.005–0.02 | 0.02–1.00 | 0.005–0.02 | 0.02–0.30 | 0.03 | |
| Pb | 0.01 | 10.0 | 0.10–2.00 | 2.00–80.0 | 0.10–2.00 | 2.00–80.0 | 0.03 |
| Se | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 0.20 | |
| Sr | 601 | 7900 | |||||
| U | 3.20 | ||||||
| V | 0.18 | 5.00 | 100 | 200 | 100 | 200 | 2.50 |
| Zn | 0.60 | 3,000 | 50.0–80.0 | 80.0–200 | 50.0–80.0 | 80.0–200 | 0.03 |
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 9.82 | 4.83 | 13.1 | 18.0 | 13.8 | 18.6 | 13.5 |
| As | 0.54 | 0.35 | 0.69 | 0.58 | 0.78 | 0.64 | 0.98 |
| Cd | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.002 | 0.02 |
| Co | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| Cr | 0.94 | 1.07 | 1.08 | 0.68 | 2.02 | 0.68 | 0.53 |
| Cu | 2.51 | 0.92 | 2.02 | 56.6 | 1.50 | 2.91 | 2.25 |
| Fe | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.35 | 0.04 |
| Hg | 0 | 0.04 | 0 | 0.03 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0 |
| Mn | 0.78 | 0 | 8.48 | 0.97 | 0.83 | 1.28 | 0.47 |
| Pb | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.20 | 0.39 |
| Se | 6.32 | 8.57 | 0.57 | 0.04 | 0 | 0.41 | 0.41 |
| Zn | 3.45 | 0 | 7.34 | 0.68 | 1.60 | 6.47 | 4.39 |
| Benzene | 0 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.83 | 0 | 0.73 | 0 |
| Toluene | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.07 |
| Ethylbenzene | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| m, p-xylene | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| o-xylene | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Control | Polluted | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EF | Cf | Cdeg | EF | Cf | Cdeg | |
| Hg | 1.67 | 1.33 | 6.67 | 6.55 | 9.15 | 182 |
| Cd | 2.25 | 1.79 | 8.94 | 1.46 | 1.76 | 35.1 |
| V | 1.36 | 1.10 | 5.52 | 0.97 | 1.31 | 26.2 |
| Se | 1.29 | 1.15 | 5.75 | 1.41 | 2.42 | 48.4 |
| Pb | 0.99 | 0.77 | 3.86 | 1.82 | 2.83 | 56.7 |
| Cr | 1.33 | 1.03 | 5.13 | 4.35 | 2.67 | 53.4 |
| Zn | 1.51 | 1.17 | 5.84 | 5.19 | 9.17 | 183 |
| Cu | 1.20 | 0.91 | 4.55 | 8.55 | 10.5 | 210 |
| U | 1.37 | 1.13 | 5.64 | 1.37 | 2.56 | 51.1 |
| S | 1.16 | 0.97 | 4.83 | 27.9 | 46.2 | 924 |
| IPI | Mean | SD | Min | Max | ||
| C | 1.13 | 0.38 | 0.52 | 2.03 | ||
| P | 8.86 | 21.1 | 0.02 | 135 | ||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medunić, G.; Kuharić, Ž.; Krivohlavek, A.; Đuroković, M.; Dropučić, K.; Rađenović, A.; Lužar Oberiter, B.; Krizmanić, A.; Bajramović, M. Selenium, Sulphur, Trace Metal, and BTEX Levels in Soil, Water, and Lettuce from the Croatian Raša Bay Contaminated by Superhigh-Organic-Sulphur Coal. Geosciences 2018, 8, 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8110408
Medunić G, Kuharić Ž, Krivohlavek A, Đuroković M, Dropučić K, Rađenović A, Lužar Oberiter B, Krizmanić A, Bajramović M. Selenium, Sulphur, Trace Metal, and BTEX Levels in Soil, Water, and Lettuce from the Croatian Raša Bay Contaminated by Superhigh-Organic-Sulphur Coal. Geosciences. 2018; 8(11):408. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8110408
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedunić, Gordana, Željka Kuharić, Adela Krivohlavek, Marija Đuroković, Kristina Dropučić, Ankica Rađenović, Borna Lužar Oberiter, Aleksandra Krizmanić, and Mladen Bajramović. 2018. "Selenium, Sulphur, Trace Metal, and BTEX Levels in Soil, Water, and Lettuce from the Croatian Raša Bay Contaminated by Superhigh-Organic-Sulphur Coal" Geosciences 8, no. 11: 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8110408
APA StyleMedunić, G., Kuharić, Ž., Krivohlavek, A., Đuroković, M., Dropučić, K., Rađenović, A., Lužar Oberiter, B., Krizmanić, A., & Bajramović, M. (2018). Selenium, Sulphur, Trace Metal, and BTEX Levels in Soil, Water, and Lettuce from the Croatian Raša Bay Contaminated by Superhigh-Organic-Sulphur Coal. Geosciences, 8(11), 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8110408