Are We There Yet? A Review and Assessment of Archaeological Passive Airborne Optical Imaging Approaches in the Light of Landscape Archaeology
Abstract
1. Setting the Scene
1.1. The Vogue but Vague Concepts of Landscape (Archaeology)
1.2. Archaeological Remote Sensing
1.3. Sampling the Archaeological Record
1.4. Which Theory to Follow?
2. Capturing Multi-Dimensionality in Eight Key Characteristics
2.1. Bias Versus Cumulativety
2.2. The Usual Suspects
2.3. From Availability to Processing Complexity
3. How It All Started: Observer-Directed Aerial Photography
4. Removing the Camera-Angle Delusion: Total Coverage Aerial Photography
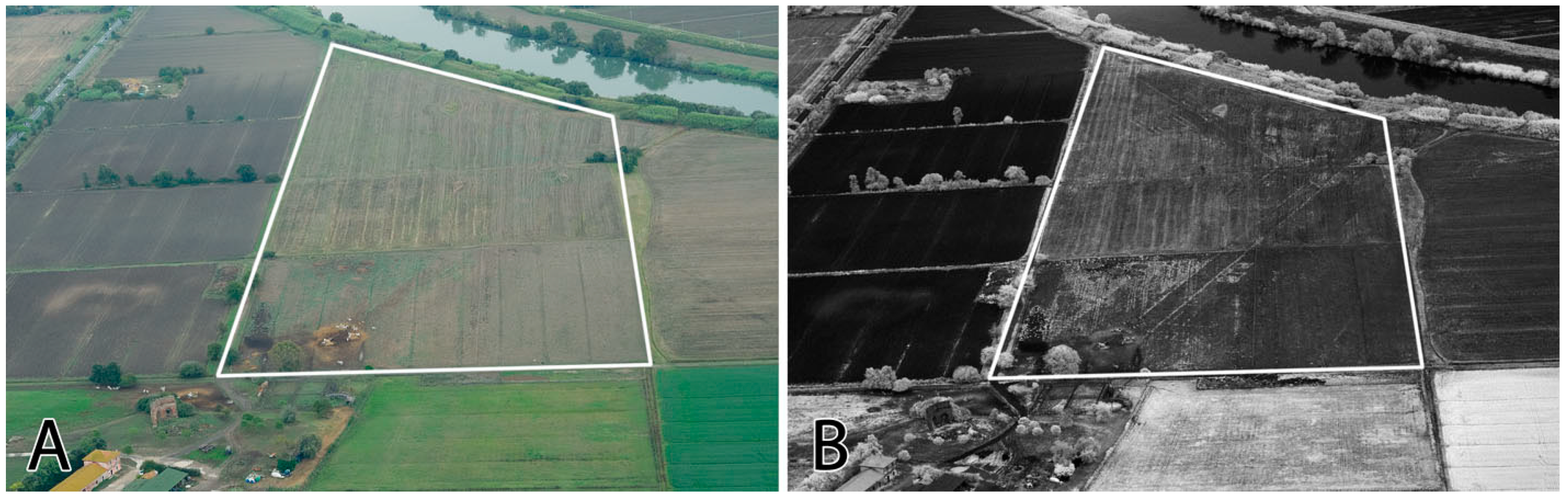
5. Increasing the Spectral Dimensions: VNIR Aerial Imaging
6. Overcoming the Spectral Delusion: Airborne Imaging Spectroscopy
7. Take the Best, Leave the Rest. A Discussion
- spaceborne data, consistently acquired over extended areas and often in invisible wavebands, might tackle the observer-directed and visible-radiation-limited biases. However, the data are less (or not at all) suited for the discovery and detailed recording of small archaeological features, as the spatial resolving power of the sensors exceeds one metre in all but a few panchromatic cases (a panchromatic image is a greyscale image created by one spectral band that is sensitive to more or less all (‘pan’) wavelengths (or colours, hence ‘chroma’) of visible electromagnetic energy). Moreover, the spectral bands of older spaceborne imagers (i.e., those whose products are freely available) are generally too broad or misplaced spectrally to truly detect the plant stress that governs vegetation marks [170];
- conventional airborne photographic imaging approaches are dominantly observer-directed, creating a strong geographical bias. They also lack the spectral resolving capabilities that are needed to digitise subtle reflectance features;
- existing multispectral solutions are often limited to four broad bands while the instrumentation is expensive and impossible to easily (de)mount into a light aircraft;
- hyperspectral imaging sensors do acquire data in narrow wavebands and are usually flown with a total coverage strategy in mind, but the combination of affordability, availability, data complexity, moderate temporal resolution and generally lower spatial resolving power also significantly restrict its frequent use (even of existing data) in archaeological research. Various biases and a lack of cumulative data are the result;
7.1. Geographically Unbiased and Vertical
7.2. Multispectral and Portable
7.3. The Processing and Interpretation Back-End
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gramsch, A. Theory in Central European Archaeology: Dead or alive? In The Death of Archaeological Theory; Bintliff, J.L., Pearce, M., Eds.; Oxbow: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 48–71. [Google Scholar]
- Rączkowski, W. Archeologia Lotnicza. Metoda Wobec Teorii; Wydawnictwo Naukowe Uniwersytetu im. Adama Mickiewicza: Poznań, Poland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Brophy, K.; Cowley, D.C. (Eds.) From the Air. Understanding Aerial Archaeology; Tempus: Stroud, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cowley, D.C. What kind of gaps? Some approaches to understanding bias in remote sensing data. Archeol. Aerea 2013, 7, 76–88. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, W.S. The Future of Aerial Archaeology (or Are Algorithms the Answer?). In Remote Sensing for Archaeology and Cultural Heritage Management, Proceedings of the 1st International EARSeL Workshop, CNR, Rome, 30 September–4 October 2008; Lasaponara, R., Masini, N., Eds.; Arracne: Rome, Italy, 2008; pp. 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Rączkowski, W. Beyond the technology: Do we need ‘meta-aerial archaeology’? In Aerial Archaeology: Developing Future Practice; Bewley, R.H., Rączkowski, W., Eds.; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 311–327. [Google Scholar]
- Rączkowski, W. Why interpretation?: Chairman’s Piece. AARGnews 2009, 39, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rączkowski, W. Towards integration: Two prospection methods and some thoughts. In From Space to Place, Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Remote Sensing in Archaeology, CNR, Rome, Italy, 4–7 December 2006; Campana, S., Forte, M., Eds.; Archaeopress: Oxford, UK, 2006; pp. 203–206. [Google Scholar]
- Campana, S. Sensing Ruralscapes. Third-Wave Archaeological Survey in the Mediterranean Area. In Digital Methods and Remote Sensing in Archaeology: Archaeology in the Age of Sensing; Forte, M., Campana, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 113–145. [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeven, G.J.J. BRDF and Its Impact on Aerial Archaeological Photography. Archaeol. Prospect. 2017, 24, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, G.J.J. Beyond Conventional Boundaries. New Technologies, Methodologies, and Procedures for the Benefit of Aerial Archaeological Data Acquisition and Analysis. Ph.D. Dissertation, Ghent University, Zelzate, Belgium, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeven, G.J.J.; Sevara, C. Trying to Break New Ground in Aerial Archaeology. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powlesland, D. Why bother? Large scale geomagnetic survey and the quest for “Real Archaeology”. In Seeing the Unseen: Geophysics and Landscape Archaeology; Campana, S., Piro, S., Eds.; CRC Press/Balkema: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Leiden, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 167–182. [Google Scholar]
- Campana, S. ‘Total Archaeology’ to reduce the need for Rescue Archaeology: The BREBEMI Project (Italy). In Remote Sensing for Archaeological Heritage Management, Proceedings of the 11th EAC Heritage Management Symposium, Reykjavík, Iceland, 25–27 March 2010; Cowley, D.C., Ed.; Europae Archaeologia Consilium (EAC), Association Internationale sans But Lucratif (AISBL): Brussels, Belgium, 2011; pp. 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, C.C. Total Archaeology or studies in the history of the landscape. In Landscapes and Documents; Rogers, A., Rowley, T., Eds.; Bedford Square Press of the National Council of Social Service: London, UK, 1974; pp. 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lock, G. Using Computers in Archaeology: Towards Virtual Pasts; Routledge: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cheetham, P.N. Noninvasive Subsurface Mapping Techniques, Satellite and Aerial Imagery in Landscape Archaeology. In Handbook of Landscape Archaeology, 1st ed.; David, B., Thomas, J., Eds.; Left Coast: Walnut Creek, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 562–582. [Google Scholar]
- Cowley, D.C. What Do the Patterns Mean? Archaeological Distributions and Bias in Survey Data. In Digital Methods and Remote Sensing in Archaeology: Archaeology in the Age of Sensing; Forte, M., Campana, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 147–170. [Google Scholar]
- Rodaway, P. Sensuous Geographies: Body, Sense and Place; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Wylie, J. Landscape; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bender, B. (Ed.) Landscape. Politics and Perspectives; Berg: Providence, RI, USA; Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Bruns, D.; Kühne, O.; Schönwald, A.; Theile, S. (Eds.) Landscape Culture—Culturing Landscapes. The Differentiated Construction of Landscapes; Springer: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Witcher, R.E. GIS and Landscapes of Perception. In Geographical Information Systems and Landscape Archaeology; Gillings, M., Mattingly, D.J., van Dalen, J., Eds.; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 1999; pp. 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Denham, T. Landscape Archaeology. In Encyclopedia of Geoarchaeology; Gilbert, A.S., Goldberg, P., Holliday, V.T., Mandel, R.D., Sternberg, R.S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 464–468. [Google Scholar]
- Mlekuž, D. Messy landscapes: Lidar and the practices of landscaping. In Interpreting Archaeological Topography: 3D Data, Visualisation and Observation; Opitz, R.S., Cowley, D.C., Eds.; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK; Oakville, ON, Canada, 2013; pp. 88–99. [Google Scholar]
- Mlekuž, D. Messy landscapes manifesto. AARGnews 2012, 44, 22–23. [Google Scholar]
- Darvill, T. Pathways to a Panoramic Past: A Brief History of Landscape Archaeology in Europe. In Handbook of Landscape Archaeology, 1st ed.; David, B., Thomas, J., Eds.; Left Coast: Walnut Creek, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 60–76. [Google Scholar]
- Aston, M.; Rowley, T. Landscape Archaeology. An Introduction to Fieldwork Techniques on Post-Roman Landscapes; David and Charles: Newton Abbot, UK, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Yamin, R.; Metheny, K.B. Landscape Archaeology. Reading and Interpreting the American Historical Landscape; University of Tennessee Press: Knoxville, TN, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ingold, T. The temporality of the landscape. World Archaeol. 1993, 25, 152–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M. Ideas of Landscape; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Knapp, A.B.; Ashmore, W. Archaeological Landscapes: Constructed, Conceptualized, Ideational. In Archaeologies of Landscape: Contemporary Perspectives; Ashmore, W., Knapp, A.B., Eds.; Blackwell: Malden, MA, USA, 1999; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, J.I. Distributional Archaeology, 1st ed.; University of New Mexico Press: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, D.H. Nonsite Sampling in Archaeology: Up the Creek Without a Site? In Sampling in Archaeology; Mueller, J.W., Ed.; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 1975; pp. 61–81. [Google Scholar]
- Dunnell, R.C. The Notion Site. In Space, Time, and Archaeological Landscapes; Rossignol, J., Wandsnider, L., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1992; pp. 21–41. [Google Scholar]
- Dunnell, R.C.; Dancey, W.S. The Siteless Survey: A regional Scale Data Collection Strategy. In Advances in Archaeological Method and Theory; Schiffer, M.B., Ed.; Academia Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; Volume 6, pp. 267–287. [Google Scholar]
- Foley, R. Off-site archaeology: An alternative approach for the short-sited. In Pattern of the Past: Studies in Honour of David Clarke; Hodder, I., Isaac, G., Hammond, N., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1981; pp. 157–183. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, R. An Archaeology of Natural Places; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Tilley, C.Y. A Phenomenology of Landscape. Places, Paths, and Monuments; Berg: Oxford, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Gramsch, A. Landscape Archaeology: Of Making and Seeing. J. Eur. Archaeol. 2013, 4, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, P. The past informs the future; Landscape archaeology and historic landscape characterisation in the UK. In Landscape Archaeology between Art and Science: From a Multi- to an Interdisciplinary Approach; Kluiving, S.J., Gutmann-Bond, E.B., Eds.; Amsterdam University Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 485–501. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, J. Archaeology, Landscape, and Dwelling. In Handbook of Landscape Archaeology, 1st ed.; David, B., Thomas, J., Eds.; Left Coast: Walnut Creek, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 300–306. [Google Scholar]
- Bender, B. Introduction: Landscape—Meaning and action. In Landscape: Politics and Perspectives; Bender, B., Ed.; Berg: Providence, RI, USA; Oxford, UK, 1993; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Boaz, J.S.; Uleberg, E. The potential of GIS-based studies of Iron Age cultural landscapes in eastern Norway. In Archaeology and Geographical Information Systems: A European Perspective; Lock, G.R., Stančič, Z., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1995; pp. 249–259. [Google Scholar]
- Mlekuž, D. Skin Deep: LiDAR and Good Practice of Landscape Archaeology. In Good Practice in Archaeological Diagnostics: Non-Invasive Survey of Complex Archaeological Sites; Corsi, C., Slapšak, B., Vermeulen, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- David, B.; Thomas, J. (Eds.) Handbook of Landscape Archaeology, 1st ed.; Left Coast: Walnut Creek, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Doneus, M. Die Hinterlassene Landschaft—Prospektion und Interpretation in der Landschaftsarchäologie; Verlag der Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften: Wien, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ashmore, W.; Knapp, A.B. (Eds.) Archaeologies of Landscape: Contemporary Perspectives; Blackwell: Malden, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Novaković, P. Osvajanje Prostora. Razvoj Prostorske in Krajinske Arheologije; Filozofska Fakulteta: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Denham, T. Environmental Archaeology: Interpreting Practices-in-the-Landscape through Geoarchaeology. In Handbook of Landscape Archaeology, 1st ed.; David, B., Thomas, J., Eds.; Left Coast: Walnut Creek, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 468–481. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, M. A History of Aerial Photography and Archaeology. Mata Hari’s Glass Eye and Other Stories; English Heritage: Swindon, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gojda, M. (Ed.) Ancient Landscape, Settlement Dynamics and Non-Destructive Archaeology. Czech Research Project 1997–2002 (Dávnověká Krajina a Sídla ve Světle Nedestruktivní Archeologie: Český Výzkumný Projekt 1997–2002); Academia: Prague, Czech Republic, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sever, T.L. Remote Sensing Methods. In Science and Technology in Historic Preservation; Williamson, R.A., Nickens, P.R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 21–51. [Google Scholar]
- Millican, K. The Outside Inside: Combining Aerial Photographs, Cropmarks and Landscape Experience. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2012, 19, 548–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D. Advancing Theory? Landscape Archaeology and Geographical Information Systems. Pap. Inst. Archaeol. 2011, 21, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquinucci, M.; Trément, F. (Eds.) Non-Destructive Techniques Applied to Landscape Archaeology; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Frachetti, M. Digital archaeology and the scalar structure of pastoral landscapes: Modeling mobile societies of prehistoric central Aasia. In Digital Archaeology: Bridging Method and Theory; Daly, P.T., Evans, T.L., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2006; pp. 128–147. [Google Scholar]
- Bowden, M. (Ed.) Unravelling the Landscape. An Inquisitive Approach to Archaeology; The History Press: Stroud, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Haupt, P. Landschaftsarchäologie. Eine Einführung; WBG (Wissenschaftliche Buchgesellschaf): Darmstadt, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Campana, S. Towards mapping the archaeological continuum. New perspectives and current limitationsin Planning-Led-Archaeology in Italy. In Looking to the Future, Caring for the Past: Preventive Archaeology in Theory and Practice; Boschi, F., Ed.; Bononia University Press: Bologna, Italy, 2016; pp. 27–40. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen, F. Aerial survey in an Italian landscape: From archaeological site-detection and monitoring to prevention and management. In Looking to the Future, Caring for the Past: Preventive Archaeology in Theory and Practice; Boschi, F., Ed.; Bononia University Press: Bologna, Italy, 2016; pp. 135–146. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.K. (Ed.) Remote Sensing in Archaeology. An Explicitly North American Perspective; University of Alabama Press: Tuscaloosa, AL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- David, A. Finding Sites. In Archaeology in Practice: A Student Guide to Archaeological Analyses; Balme, J., Paterson, A., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing: Malden, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Crutchley, S.; Crow, P. The Light Fantastic. Using Airborne Lidar in Archaeological Survey, 1st ed.; English Heritage: Swindon, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Doneus, M.; Briese, C.; Fera, M.; Janner, M. Archaeological prospection of forested areas using full-waveform airborne laser scanning. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2008, 35, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doneus, M.; Doneus, N.; Briese, C.; Pregesbauer, M.; Mandlburger, G.; Verhoeven, G.J.J. Airborne Laser Bathymetry—Detecting and recording submerged archaeological sites from the air. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 2136–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doneus, M.; Briese, C. Airborne Laser Scanning in forested areas—Potential and limitations of an archaeological prospection technique. In Remote Sensing for Archaeological Heritage Management, Proceedings of the 11th EAC Heritage Management Symposium, Reykjavík, Iceland, 25–27 March 2010; Cowley, D.C., Ed.; Europae Archaeologia Consilium (EAC), Association Internationale sans But Lucratif (AISBL): Brussels, Belgium, 2011; pp. 59–76. [Google Scholar]
- Opitz, R.S.; Cowley, D.C. (Eds.) Interpreting Archaeological Topography: 3D Data, Visualisation and Observation; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK; Oakville, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Briese, C.; Pfennigbauer, M.; Lehner, H.; Ullrich, A.; Wagner, W.; Pfeifer, N. Radiometric calibration of multi-wavelength airborne laser scanning data. In Proceedings of the XXII ISPRS Congress, Technical Commission VII. Imaging a Sustainable Future, Melbourne, Australia, 25 August–1 September 2012; Shortis, M.R., Wagner, W., Hyyppä, J., Eds.; International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (ISPRS): Melbourne, Australia, 2012; pp. 335–340. [Google Scholar]
- Briese, C.; Doneus, M.; Verhoeven, G.J.J. Radiometric calibration of ALS data for archaeological Interpretation. In Archaeological Prospection, Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Archaeological Prospection, Vienna, Austria, 29 May–2 June 2013; Neubauer, W., Trinks, I., Salisbury, R.B., Einwögerer, C., Eds.; Austrian Academy of Sciences: Vienna, Austria, 2013; pp. 427–429. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, D.R. Air Photo Interpretation for Archaeologists, 2nd ed.; Tempus: Stroud, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, J.M.; Grant, B.G. The Art of Radiometry; SPIE Press: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ohno, Y. Basic concepts in photometry, radiometry and colorimetry. In Handbook of Optoelectronics; Dakin, J.P., Brown, R.G.W., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 287–305. [Google Scholar]
- Schowengerdt, R.A. Remote Sensing. Models and Methods for Image Processing, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Burlington, ON, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N. (Eds.) Satellite Remote Sensing. A New Tool for Archaeology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Parcak, S.H. Satellite Remote Sensing for Archaeology; Routledge: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Comer, D.C.; Harrower, M.J. (Eds.) Mapping Archaeological Landscapes from Space; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, W.S.; Oltean, I.A. (Eds.) Archaeology from Historical Aerial and Satellite Archives; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Scardozzi, G. An introduction to satellite remote sensing in archaeology: State of the art, methods, and applications. In Looking to the Future, Caring for the Past: Preventive Archaeology in Theory and Practice; Boschi, F., Ed.; Bononia University Press: Bologna, Italy, 2016; pp. 217–239. [Google Scholar]
- Drennan, R.D. Statistics for Archaeologists. A Common Sense Approach, 2nd ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, D.L. Archaeology: The loss of innocence. Antiquity 1973, 47, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowgill, G.L. Some Sampling and Reliability Problems in Archaeology. In Archéologie et Calculateurs: Problèmes Sémiologiques et Mathématiques, Proceedings of the Colloques Internationaux du Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique: Sciences Humaines, Marseille, France, 7–12 April 1969; Gardin, J.-C., Ed.; Centre National de la Récherche Scientifique: Paris, France, 1970; pp. 161–175. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, M.B. Sources of bias in processual data: An appraisal. In Sampling in Archaeology; Mueller, J.W., Ed.; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 1975; pp. 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer, M.B. Formation Processes of the Archaeological Record; University of Utah Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Grabe, M. Measurement Uncertainties in Science and Technology; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nativ, A. No Compensation Needed: On Archaeology and the Archaeological. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2017, 24, 659–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, J.F.; Gamble, C.; Shennan, S. (Eds.) Sampling in Contemporary British Archaeology; British Archaeological Reports (B.A.R.): Oxford, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Orton, C.R. Sampling in Archaeology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, J.W. (Ed.) Sampling in Archaeology; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer, M.B. Toward the Identification of Formation Processes. Am. Antiq. 1983, 48, 675–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanPool, T.L.; Leonard, R.D. Quantitative Analysis in Archaeology; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lyman, R.L.; VanPool, T.L. Metric Data in Archaeology: A Study of Intra-analyst and Inter-analyst Variation. Am. Antiq. 2009, 74, 485–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, R.A.; Maschner, H.D.G.; Chippindale, C. (Eds.) Handbook of Archaeological Theories; AltaMira Press: Lanham, MD, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, S. Contradictions of Archaeological Theory. Engaging Critical Realism and Archaeological Theory; Routledge: Abingdon, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bintliff, J.L. The Death of Archaeological Theory? In The Death of Archaeological Theory; Bintliff, J.L., Pearce, M., Eds.; Oxbow: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 7–22. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.H. On the nature of theoretical archaeology and archaeological theory. Archaeol. Dialogues 2006, 13, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, M. Have Rumours of the ‘Death of Theory’ been Exaggerated? In The Death of Archaeological Theory; Bintliff, J.L., Pearce, M., Eds.; Oxbow: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 80–89. [Google Scholar]
- Rączkowski, W. Aerial Archaeology. In Encyclopedia of Global Archaeology; Smith, C., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Hodder, I. The Archaeological Process. An Introduction; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Banaszek, Ł. Przeszłe Krajobrazy w Chmurze Punktów; Wydawnictwo Naukowe Uniwersytetu im. Adama Mickiewicza: Poznań, Poland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, R.; Wylie, A. Evidential Reasoning in Archaeology; Bloomsbury Academic: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gojda, M. The Archaeology of Lowlands: A Few Remarks on the Methodology of Aerial Survey. In Landscape Ideologies; Meier, T., Ed.; Archaeolingua Alapítvány: Budapest, Hungary, 2006; pp. 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, R.A. Now. The Physics of Time, 1st ed.; W.W. Norton & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, I. One hundred and one dimensions. New Sci. 1995, 148, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Born, M.; Wolf, E. Principles of Optics. Electromagnetic Theory of Propagation, Interference and Diffraction of Light, 7th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeven, G.J.J. Basics of photography for cultural heritage imaging. In 3D Recording, Documentation and Management of Cultural Heritage; Stylianidis, E., Remondino, F., Eds.; Whittles Publishing: Caithness, UK, 2016; pp. 127–251. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, O.G.S. Air Survey and Archaeology; Ordnance Survey: Southampton, UK, 1924. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, O.G.S.; Keiller, A. Wessex from the Air; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1928. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, O.G.S. Air Photographs of the Middle East: A Paper Read at the Evening Meeting of the Society on 18 March 1929. Geogr. J. 1929, 73, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.R. Photographic Techniques in the Air. In Aerial Reconnaissance for Archaeology; Wilson, D.R., Ed.; Council for British Archaeology: London, UK, 1975; pp. 12–31. [Google Scholar]
- Crawshaw, A. Oblique Aerial Photography-Aircraft, Cameras and Films. In Proceedings of the Luftbildarchäologie in Ost- und Mitteleuropa/Aerial Archaeoloy in Eastern and Central Europe: Internationales Symposium, Kleinmachnow, Germany, 26–30 September 1994; Kunow, J., Ed.; Verlag Brandenburgisches Landesmuseum für Ur- und Frühgeschichte: Potsdam, Germany, 1995; pp. 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- Harman, W.E., Jr.; Miller, R.H.; Park, W.S.; Webb, J.P. Aerial photography. In Manual of Photogrammetry, 3rd ed.; Thompson, M.M., Eller, R.C., Radlinski, W.A., Speert, J.L., Eds.; American Society of Photogrammetry: Falls Church, VA, USA, 1966; Volume I, pp. 195–242. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, S. Luftbild und Luftbildinterpretation; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, R. If they used their own photographs they would not take them like that. In From the Air: Understanding Aerial Archaeology; Brophy, K., Cowley, D.C., Eds.; Tempus: Stroud, UK, 2005; pp. 94–116. [Google Scholar]
- Read, R.E.; Graham, R. Manual of Aerial Survey. Primary Data Acquisition; CRC Press/Whittles Publishing: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- The British Academy. Aerial Survey for Archaeology. Report of a British Academy Working Party 1999; The British Academy: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Musson, C.; Palmer, R.; Campana, S. Flights into the Past. Aerial Photography, Photo Interpretation and Mapping for Archaeology; AARG—ArcLand: Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, R. Aerial archaeology and sampling. In Sampling in Contemporary British Archaeology; Cherry, J.F., Gamble, C., Shennan, S., Eds.; British Archaeological Reports (B.A.R.): Oxford, UK, 1978; pp. 129–148. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, D.R. Bias in aerial reconnaissance. In From the Air: Understanding Aerial Archaeology; Brophy, K., Cowley, D.C., Eds.; Tempus: Stroud, UK, 2005; pp. 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- St Joseph, J.K.S. Air Reconnaissance of Roman Scotland, 1939-75. Glasg. Archaeol. J. 1976, 4, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.H. The advantages of bias in Roman studies. In From the Air: Understanding Aerial Archaeology; Brophy, K., Cowley, D.C., Eds.; Tempus: Stroud, UK, 2005; pp. 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Gould, R.A. Archaeological Survey by Air: A Case from the Australian Desert. J. Field Archaeol. 1987, 14, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, S. Taking Advantage: Vertical Aerial Photographs Commissioned for Local Authorities. In Populating Clay Landscapes; Mills, J., Palmer, R., Eds.; Tempus: Stroud, UK, 2007; pp. 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Doneus, M. Vertical and Oblique Photographs. AARGnews 2000, 20, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, J. Bias and the World of the Vertical Aerial Photograph. In From the Air: Understanding Aerial Archaeology; Brophy, K., Cowley, D.C., Eds.; Tempus: Stroud, UK, 2005; pp. 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, R. Seventy-Five Years v. Ninety Minutes: Implications of the 1996 Bedfordshire Vertical Aerial Survey on our Perceptions of Clayland Archaeology. In Populating Clay Landscapes; Mills, J., Palmer, R., Eds.; Tempus: Stroud, UK, 2007; pp. 88–103. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, R. Editorial. AARGnews 1996, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, D.C. A case study in the analysis of patterns of aerial reconnaissance in a lowland area of southwest Scotland. Archaeol. Prospect. 2002, 9, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doneus, M. On the archaeological use of vertical photographs. AARGnews 1997, 15, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Slater, P.N.; Doyle, F.J.; Fritz, N.L.; Welch, R. Photographic systems for remote sensing. In Manual of Remote Sensing: Volume 1: Theory, Instruments and Techniques, 2nd ed.; Colwell, R.N., Simonett, D.S., Ulaby, F.T., Eds.; American Society of Photogrammetry: Falls Church, VA, USA, 1983; pp. 231–291. [Google Scholar]
- Estes, J.E.; Hajic, E.J.; Tinney, L.R.; Carver, L.G.; Cosentino, M.J.; Mertz, F.C.; Pazner, M.I.; Ritter, L.R.; Sailer, C.T.; Stow, D.A.; et al. Fundamentals of Image Analyis: Analysis of Visible and Thermal Infrared Data. In Manual of Remote Sensing: Theory, Instruments and Techniques, 2nd ed.; Colwell, R.N., Simonett, D.S., Ulaby, F.T., Eds.; American Society of Photogrammetry: Falls Church, VA, USA, 1983; Volume 1, pp. 987–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Spurr, S.H. Photogrammetry and Photo-Interpretation. With a Section on Applications to Forestry, 2nd ed.; The Ronald Press Company: New York, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Lemmens, M. Digital Oblique Aerial Cameras (1): A Survey of Features and Systems. GIM Int. 2014, 28, 20–21, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Nurminen, K. Oblique aerial photographs—An “old-new” data source. Photogramm. J. Finl. 2015, 24, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remondino, F.; Gerke, M. Oblique Aerial Imagery—A Review. In Photogrammetric Week 2015; Fritsch, D., Ed.; Wichmann/VDE Verlag: Belin/Offenbach, Germany, 2015; pp. 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- IGI mbH. Penta DigiCAM. Available online: http://www.igi.eu/penta-digicam.html (accessed on 4 March 2016).
- Microsoft. UltraCam Osprey Prime II/Prime Lite. Available online: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/Ultracam/UltraCamOsprey.aspx (accessed on 4 March 2016).
- Rupnik, E.; Nex, F.; Toschi, I.; Remondino, F. Aerial multi-camera systems: Accuracy and block triangulation issues. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 101, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paine, D.P.; Kiser, J.D. Aerial Photography and Image Interpretation, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- General Staff. Notes on the Interpretation of Aeroplane Photographs; Revised March 1917; General Staff War Office: London, UK, 1917. [Google Scholar]
- Haala, N.; Rothermel, M.; Cavegn, S. Extracting 3D urban models from oblique aerial images. In Proceedings of the 2015 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Lausanne, Switzerland, 30 March–1 April 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Gerke, M.; Vosselman, G. Building extraction from oblique airborne imagery based on robust façade detection. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 68, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brophy, K.; Cowley, D.C. From the Air—An introduction. In From the Air: Understanding Aerial Archaeology; Brophy, K., Cowley, D.C., Eds.; Tempus: Stroud, UK, 2005; pp. 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeven, G.J.J. Near-Infrared Aerial Crop Mark Archaeology: From its Historical Use to Current Digital Implementations. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2012, 19, 132–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, G.J.J. Exploring the Edges of the Unseen: An Attempt to Digital Aerial UV Photography. In Remote Sensing for Archaeology and Cultural Heritage Management, Proceedings of the 1st International EARSeL Workshop, CNR, Rome, 30 September–4 October 2008; Lasaponara, R., Masini, N., Eds.; Arracne: Rome, Italy, 2008; pp. 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeven, G.J.J.; Schmitt, K.D. An attempt to push back frontiers—Digital near-ultraviolet aerial archaeology. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2010, 37, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, G.A.; Miller, R.L. Early detection of plant stress by digital imaging within narrow stress-sensitive wavebands. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 50, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoghue, D.N.M. Multispectral Remote Sensing for Archaeology. In Remote Sensing in Archaeology: XI Ciclo di Lezioni Sulla Ricerca Applicata in Archeologia, Certosa di Pontignano (Siena), 6–11 Dicembre 1999; Campana, S., Forte, M., Eds.; All’Insegna del Giglio: Firenze, Italy, 2001; pp. 181–192. [Google Scholar]
- Powlesland, D.; Lyall, J.; Hopkinson, G.; Donoghue, D.; Beck, M.; Harte, A.; Stott, D. Beneath the sand: Remote sensing, archaeology, aggregates and sustainability: A case study from Heslerton, the Vale of Pickering, North Yorkshire, UK. Archaeol. Prospect. 2006, 13, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challis, K.; Kincey, M.; Howard, A.J. Airborne remote sensing of valley floor geoarchaeology using Daedalus ATM and CASI. Archaeol. Prospect. 2009, 16, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqdus, S.A.; Drummond, J.; Hanson, W.S. Discovering Archaeological Cropmarks: A Hyperspectral Approach. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2008, 37, 361–365. [Google Scholar]
- Winterbottom, S.J.; Dawson, T. Airborne multi-spectral prospection for buried archaeology in mobile sand dominated systems. Archaeol. Prospect. 2005, 12, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meer, F.D.; de Jong, S.M. (Eds.) Imaging Spectrometry. Basic Principles and Prospective Applications; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, R.; Mansouri, A.; Hardeberg, J.Y. Multispectral imaging using a stereo camera: Concept, design and assessment. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2011, 57, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqdus, S.A.; Hanson, W.S.; Drummond, J. The potential of hyperspectral and multi-spectral imagery to enhance archaeological cropmark detection: A comparative study. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2012, 39, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, R.; Welham, K.; Hill, R.A.; Ford, A.L.J. The Application of Vegetation Indices for the Prospection of Archaeological Features in Grass-dominated Environments. Archaeol. Prospect. 2012, 19, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, R.M.; Licciardi, G.A.; Chanussot, J. Detection of Anomalies Produced by Buried Archaeological Structures Using Nonlinear Principal Component Analysis Applied to Airborne Hyperspectral Image. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, G.J.J.; Doneus, M.; Atzberger, C.; Wess, M.; Ruš, M.; Pregesbauer, M.; Briese, C. New approaches for archaeological feature extraction of airborne imaging spectroscopy data. In Archaeological Prospection, Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Archaeological Prospection, Vienna, Austria, 29 May–2 June 2013; Neubauer, W., Trinks, I., Salisbury, R.B., Einwögerer, C., Eds.; Austrian Academy of Sciences: Vienna, Austria, 2013; pp. 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, I. Aerial remote-sensing techniques used in the management of archaeological monuments on the British Army’s Salisbury Plain Training Area, Wiltshire, UK. Archaeol. Prospect. 2003, 10, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassani, C.; Cavalli, R.M.; Goffredo, R.; Palombo, A.; Pascucci, S.; Pignatti, S. Specific spectral bands for different land cover contexts to improve the efficiency of remote sensing archaeological prospection: The Arpi case study. J. Cult. Herit. 2009, 10, e41–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coren, F.; Visintini, D.; Prearo, G.; Sterzai, P. Integrating LiDAR Intensity Measures and Hyperspectral Data for Extracting of Cultural Heritage. In Proceedings of the Italy–Canada 2005 Workshop on 3D Digital imaging and Modeling: Applications of Heritage Industry, Medicine and Land, Padua, Italy, 17–18 March 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Emmolo, D.; Franco, V.; Lo Brutto, M.; Orlando, P.; Villa, B. Hyperspectral Techniques and GIS for Archaeological Investigation. In Proceedings of the ISPRS 2004 Commission IV—Geo-Imagery Bridging Continents. XXth ISPRS Congress, Istanbul, Turkey, 12–23 July 2004; Altan, O., Ed.; ISPRS: Istanbul, Turkey, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Forte, E.; Pipan, M.; Sugan, M. Integrated Geophysical Study of Archaeological Sites in the Aquileia Area. In Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on The New Technologies for Aquileia (NTA-2011), Aquileia, Italy, 2 May 2011; Roberto, V., Ed.; Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of Udine: Udine, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Merola, P.; Allegrini, A.; Bajocco, S. Hyperspectral MIVIS data to investigate the Lilybaeum (Marsala) Archaeological Park. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing for Environmental Monitoring, GIS Applications, and Geology V, Bruges, Belgium, 19 September 2005; Ehlers, M., Michel, U., Eds.; Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE): Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; pp. 212–222. [Google Scholar]
- Pietrapertosa, C.; Vellico, M.; Sterzai, P.; Coren, F. Remote Sensing Applied to the Detection of Archaeological Buried Structures in the Aquileia Site. In Proceedings of the 27° Convegno Nazionale GNGTS—2008, Trieste, Italy, 8 October 2008; pp. 368–372. [Google Scholar]
- Traviglia, A. Integration of MIVIS Hyperspectral Remotely Sensed Data and Geographical Information Systems to Study Ancient Landscapes: The Aquileia Case Study. Agri Centuriati 2005, 2, 139–170. [Google Scholar]
- White, D.A. AVIRIS and Archaeology in Southern Arizona. In AVIRIS Proceedings; NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Doneus, M.; Verhoeven, G.J.J.; Atzberger, C.; Wess, M.; Ruš, M. New ways to extract archaeological information from hyperspectral pixels. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 52, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzberger, C.; Wess, M.; Doneus, M.; Verhoeven, G.J.J. ARCTIS—A MATLAB® Toolbox for Archaeological Imaging Spectroscopy. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 8617–8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, G.A. Ratios of leaf reflectances in narrow wavebands as indicators of plant stress. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewley, R.; Rączkowski, W. Past achievements and prospects for the future development of aerial archaeology: An introduction. In Aerial Archaeology: Developing Future Practice; Bewley, R.H., Rączkowski, W., Eds.; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Brugioni, D.A. The Serendipity Effect of Aerial Reconnaissance. Interdiscip. Sci. Rev. 1989, 14, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawshaw, A. Letter. AARGnews 1997, 14, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Gates, T. Recording upland landscapes: A personal account from Northumberland. In From the Air: Understanding Aerial Archaeology; Brophy, K., Cowley, D.C., Eds.; Tempus: Stroud, UK, 2005; pp. 127–140. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, D.R. Vertical versus oblique photography. AARGnews 2005, 20 (Suppl. S1), 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Doody, M. Medium altitude aerial photographic survey in East Limerick and West Tipperary. J. Irish Archaeol. 2001, 10, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Doneus, M. Vom Luftbild zur Karte. In Aus der Luft-Bilder Unserer Geschichte: Luftbildarchäologie in Zentraleuropa: Katalog zur Ausstellung; Oexle, J., Ed.; Landesamt für Archäologie mit Landesmuseum für Vorgeschichte: Dresden, Germany, 1997; pp. 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Warner, W.S.; Graham, R.W.; Read, R.E. Small Format Aerial Photography; Whittles Publishing: Caithness, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, R.; Koh, A. Digital Aerial Survey. Theory and Practice; CRC Press/Whittles Publishing: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bäumker, M.; Brechtken, R.; Heimes, F.-J.; Richter, T. Practical Experiences with a High-Precision Stabilised Camera Platform Based on INS/(D)GPS. In Proceedings of the First North American Symposium on Small Format Aerial Photography, Cloquet, MN, USA, 14–17 October 1997; American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1997; pp. 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, J.P.; Newton, I.; Graham, R.W. Aerial Photography for Survey Purposes with a High Resolution, Small Format, Digital Camera. Photogramm. Rec. 1996, 15, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhof, R.K.; Doolittle, R.C. Mapping from oblique photographs. In Manual of Photogrammetry, 3rd ed.; Thompson, M.M., Eller, R.C., Radlinski, W.A., Speert, J.L., Eds.; American Society of Photogrammetry: Falls Church, VA, USA, 1966; Volume II, pp. 875–917. [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeven, G.J.J.; Doneus, M.; Briese, C.; Vermeulen, F. Mapping by matching: A computer vision-based approach to fast and accurate georeferencing of archaeological aerial photographs. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2012, 39, 2060–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, G.J.J.; Sevara, C.; Karel, W.; Ressl, C.; Doneus, M.; Briese, C. Undistorting the past: New techniques for orthorectification of archaeological aerial frame imagery. In Good Practice in Archaeological Diagnostics: Non-Invasive Survey of Complex Archaeological Sites; Corsi, C., Slapšak, B., Vermeulen, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 31–67. [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeven, G.J.J. Mesh Is More—Using All Geometric Dimensions for the Archaeological Analysis and Interpretative Mapping of 3D Surfaces. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2016, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, G.J.J.; Vermeulen, F. Engaging with the Canopy: Multi-Dimensional Vegetation Mark Visualisation Using Archived Aerial Images. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.L.; Bewley, R.H. Ancient Jordan from the Air; Council for British Research in the Levant: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Campana, S. Archaeological site detection and mapping: Some thoughts on differing scales of detail and archaeological ‘non-visibility’. In Seeing the Unseen: Geophysics and Landscape Archaeology; Campana, S., Piro, S., Eds.; CRC Press/Balkema: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Leiden, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 5–26. [Google Scholar]
- Deravignone, L.; Blankholm, H.P.; Pizziolo, G. Predictive Modeling and Artificial Neural Networks (ANN): From Model to Survey. In Mathematics and Archaeology; Barceló, J.A., Bogdanovic, I., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 335–351. [Google Scholar]
- Buschmann, C.; Nagel, E. In vivo spectroscopy and internal optics of leaves as basis for remote sensing of vegetation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datt, B. Visible/near infrared reflectance and chlorophyll content in Eucalyptus leaves. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 2741–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Merzlyak, M.N. Quantitative estimation of chlorophyll-a using reflectance spectra: Experiments with autumn chestnut and maple leaves. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 1994, 22, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, G.A.; Estep, L.; Muttiah, R.S. General spectral characteristics of leaf reflectance responses to plant stress and their manifestation at the landscape scale. In From Laboratory Spectroscopy to Remotely Sensed Spectra of Terrestrial Ecosystems; Muttiah, R.S., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 271–293. [Google Scholar]
- Agapiou, A.; Hadjimitsis, D.G.; Georgopoulos, A.; Sarris, A.; Alexakis, D.D. Towards an Archaeological Index: Identification of the Spectral Regions of Stress Vegetation due to Buried Archaeological Remains. In Progress in Cultural Heritage Preservation, Proceedings of the 4th International Conference, EuroMed 2012, Lemessos, Cyprus, 29 October–3 November 2012; Ioannides, M., Fritsch, D., Leissner, J., Davies, R., Remondino, F., Caffo, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeven, G.J.J.; Doneus, M. Balancing on the Borderline—A Low-cost Approach to Visualize the Red-edge Shift for the Benefit of Aerial Archaeology. Archaeol. Prospect. 2011, 18, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, J.A.; Petty, C.C. The Near-Infrared Absorption Spectrum of Liquid Water. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1951, 41, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, T.E.; Lyons, T.R. Remote Sensing. Aerial and Terrestrial Photography for Archeologists; Cultural Resources Management Division: Washington, DC, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.J.A.; Evans, R. Soil and Crop Marks in the Recognition of Archaeological Sites by Air Photography. In Aerial Reconnaissance for Archaeology; Wilson, D.R., Ed.; Council for British Archaeology: London, UK, 1975; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Sandmeier, S.R.; Itten, K.I. A Field Goniometer System (FIGOS) for Acquisition of Hyperspectral BRDF Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barceló, J.A. Computational Intelligence in Archaeology; Information Science Reference: Hershey, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- McCoy, M.D.; Ladefoged, T.N. New Developments in the Use of Spatial Technology in Archaeology. J. Archaeol. Res. 2009, 17, 263–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traviglia, A.; Cowley, D.C.; Lambers, K. Finding common ground: Human and computer vision in archaeological prospection. AARGnews 2016, 53, 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, R.; Cowley, D.C.; De Laet, V. The data explosion: Tackling the taboo of automatic feature recognition in airborne survey data. Antiquity 2014, 88, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, D.C. In with the new, out with the old? Auto-extraction for remote sensing archaeology. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing of the Ocean, Sea Ice, Coastal Waters, and Large Water Regions 2012 Conference, Edinburgh, UK, 26–27 September 2012; Bostater, C.R., Jr., Mertikas, S.P., Neyt, X., Nichol, C., Cowley, D.C., Bruyant, J.-P., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2012; p. 853206. [Google Scholar]
- Lambers, K.; Zingman, I. Towards Detection of Archaeological Objects in High-Resolution Remotely Sensed Images: The Silvretta Case Study. In Archaeology in the Digital Era. Volume II: E-Papers from the 40th Conference on Computer Applications and Quantitative Methods in Archaeology, Southampton, 26–30 March 2012; Earl, G.P., Sly, T., Chrysanthi, A., Murrieta-Flores, P., Papadopoulos, C., Romanowska, I., Wheatley, D., Eds.; Amsterdam University Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 781–791. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, W.S. The future of aerial archaeology in Europe. Photo Interprét. Eur. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2010, 46, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Sevara, C.; Pregesbauer, M.; Doneus, M.; Verhoeven, G.J.J.; Trinks, I. Pixel versus object—A comparison of strategies for the semi-automated mapping of archaeological features using airborne laser scanning data. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2016, 5, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llobera, M. Working the digital: Some thoughts from landscape archaeology. In Material Evidence: Learning from Archaeological Practice; Chapman, R., Wylie, A., Eds.; Routledge: Abingdon, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 173–188. [Google Scholar]
- Cowley, D.C. Creating the Cropmark Archaeological Record in East Lothian, South-East Scotland. In Prehistory without Borders: The Prehistoric Archaeology of the Tyne-Forth Region; Crellin, R., Fowler, C., Tipping, R., Eds.; Oxbox Books: Oxford, UK; Havertown, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Cowley, D.C. Remote sensing for archaeology and heritage management—Site discovery, interpretation and registration. In Remote Sensing for Archaeological Heritage Management, Proceedings of the 11th EAC Heritage Management Symposium, Reykjavík, Iceland, 25–27 March 2010; Cowley, D.C., Ed.; Europae Archaeologia Consilium (EAC), Association Internationale sans But Lucratif (AISBL): Brussels, Belgium, 2011; pp. 43–55. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, C.C. Aerial photography and the field archaeologist. In Aerial Reconnaissance for Archaeology; Wilson, D.R., Ed.; Council for British Archaeology: London, UK, 1975; pp. 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Löcker, K.; Kucera, M.; Trinks, I.; Neubauer, W. Successfully falsified… on epistomological problems of archaeological excavations and geophysical surveys. Archaeol. Pol. 2015, 53, 222–224. [Google Scholar]
- Seren, S.; Trinks, I.; Hinterleitner, A.; Neubauer, W. The anomaly that wasn’t there—On the visibility of archaeological prospection anomalies and their causative structures in the subsurface. In Archaeological Prospection, Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Archaeological Prospection, Vienna, Austria, 29 May–2 June 2013; Neubauer, W., Trinks, I., Salisbury, R.B., Einwögerer, C., Eds.; Austrian Academy of Sciences: Vienna, Austria, 2013; pp. 252–254. [Google Scholar]
- Fassbinder, J.W.E.; Irlinger, W.; Schleifer, N.; Stanjek, H. Methodische Untersuchungen zur Magnetometerprospektion: Das frühmittelalterliche Gräberfeld von Alburg, Stadt Straubing, Niederbayern. In Das archäologische Jahr in Bayern, 1998; Bayerisches Landesamt für Denkmalpflege, Ed.; Konrad Theiss Verlag: Darmstadt, Germany, 1999; pp. 112–114. [Google Scholar]
- Filzwieser, R.; Olesen, L.H.; Neubauer, W.; Trinks, I.; Mauritsen, E.S.; Schneidhofer, P.; Nau, E.; Gabler, M. Large-scale geophysical archaeological prospection pilot study at Viking Age and medieval sites in west Jutland, Denmark. Archaeol. Prospect. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filzwieser, R.; Olesen, L.H.; Verhoeven, G.J.J.; Mauritsen, E.S.; Neubauer, W.; Trinks, I.; Nowak, M.; Nowak, R.; Schneidhofer, P.; Nau, E.; et al. Integration of Complementary Archaeological Prospection Data from a Late Iron Age Settlement at Vesterager—Denmark. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2017, 24, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, A.; Linford, N.; Linford, P.; Martin, L.; Payne, A.; Jones, D.M. Geophysical Survey in Archaeological Field Evaluation; English Heritage: Swindon, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Roskams, S. Excavation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wallner, M.; Löcker, K.; Neubauer, W.; Doneus, M.; Jansa, V.; Verhoeven, G.J.J.; Trinks, I.; Seren, S.; Gugl, C.; Humer, F. ArchPro Carnuntum Project Large-scale non-invasive archaeological prospection of the Roman town of Carnuntum. Archaeol. Pol. 2015, 53, 400–403. [Google Scholar]
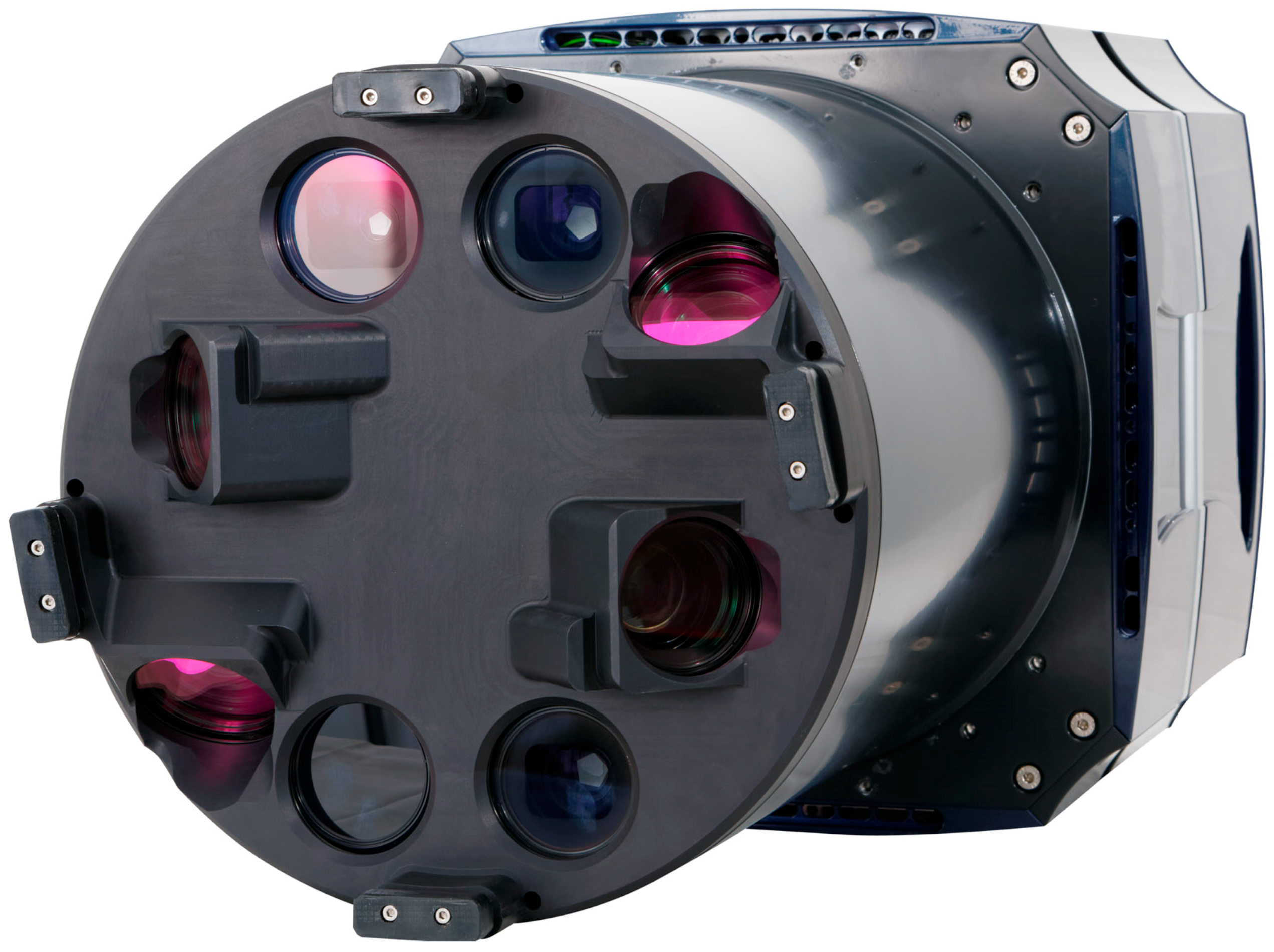
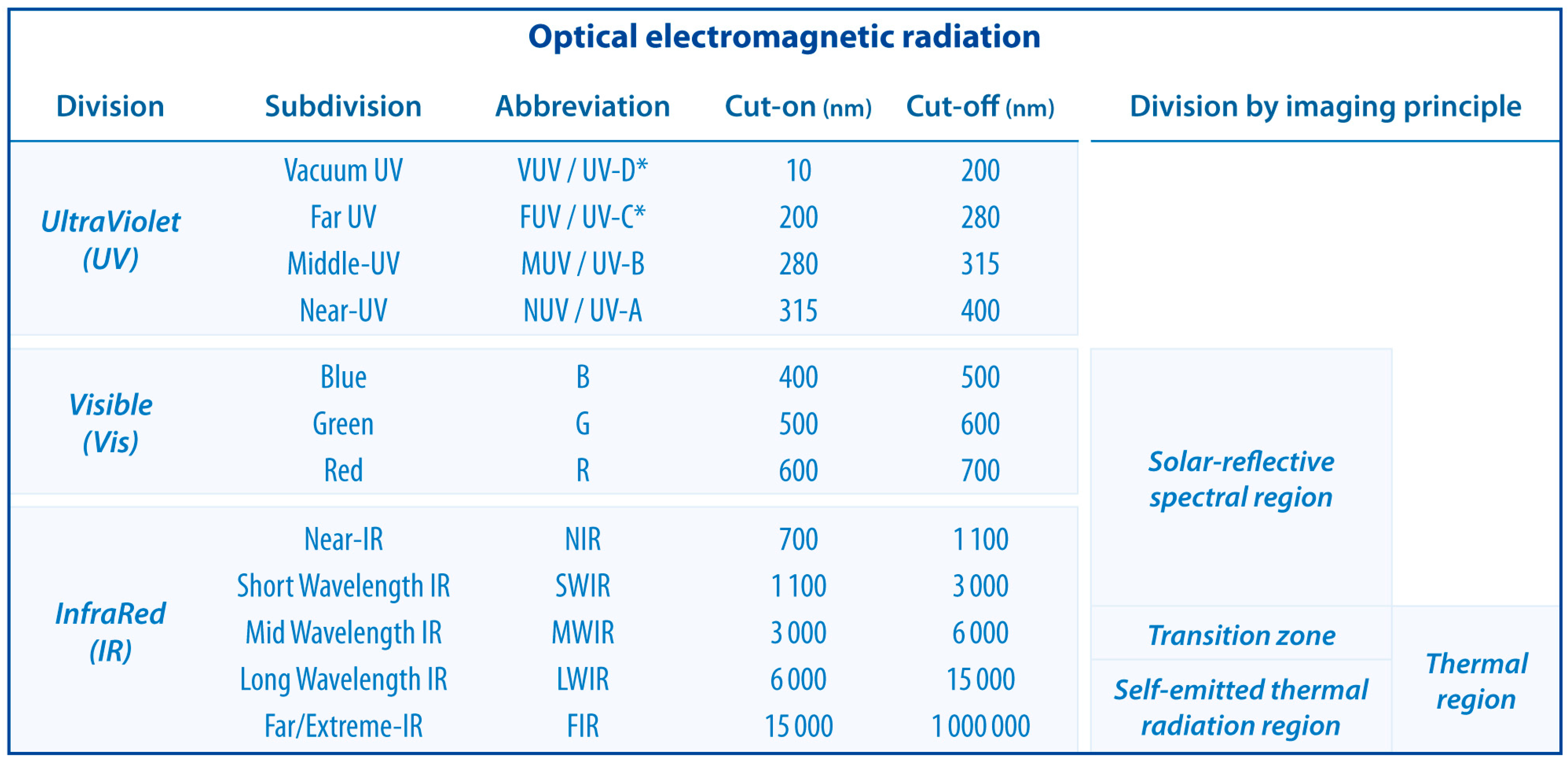
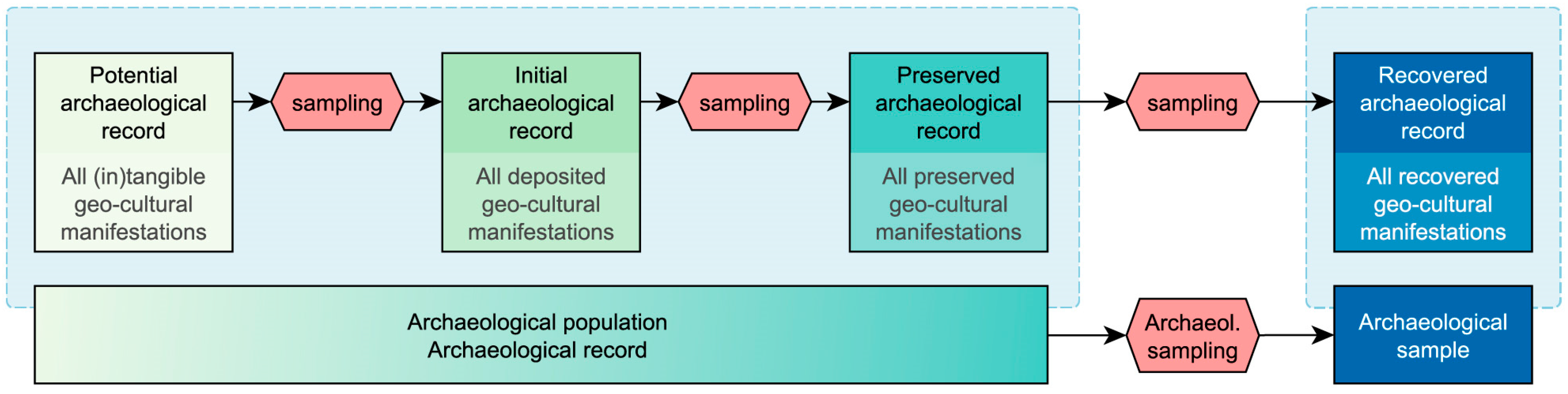
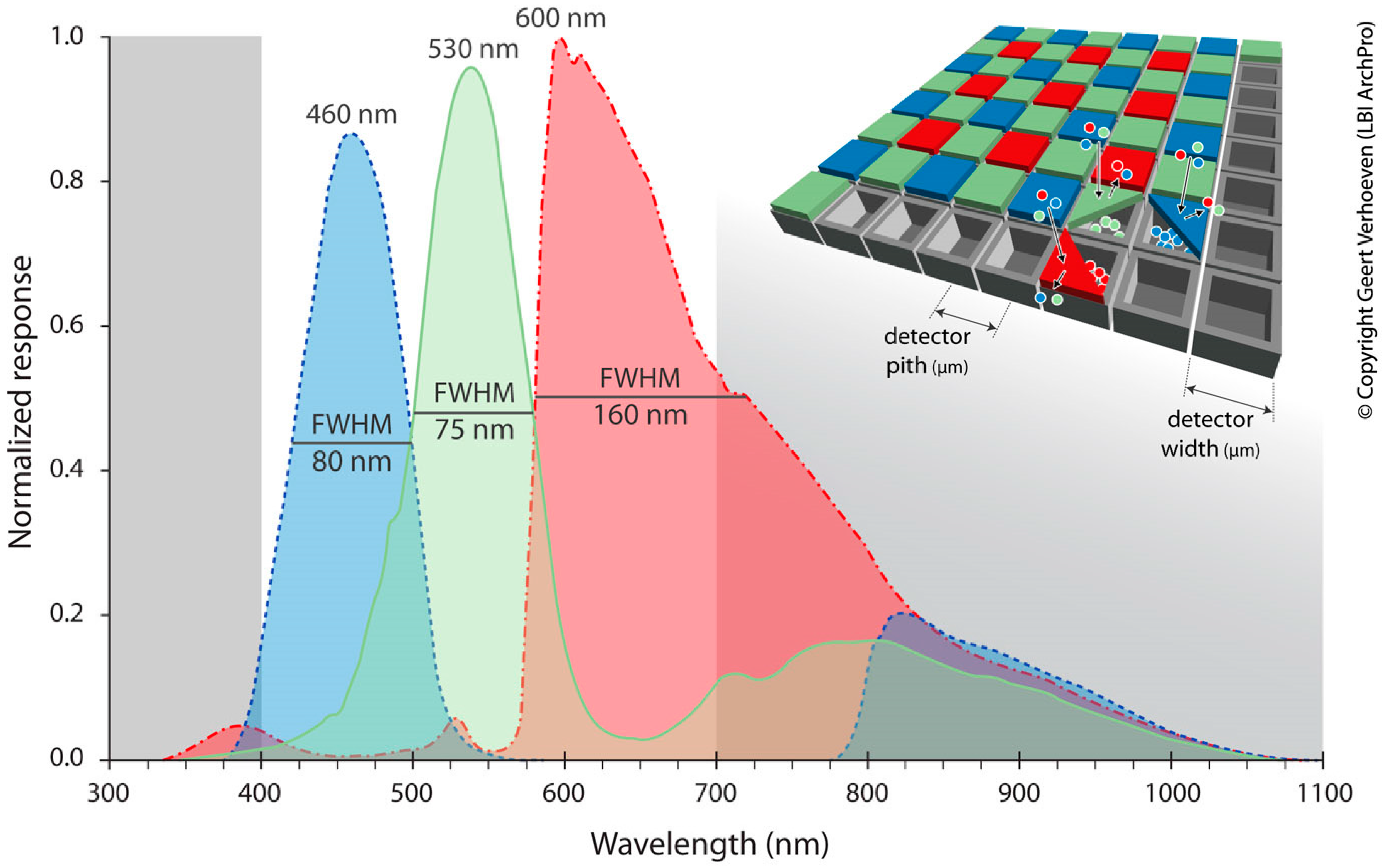
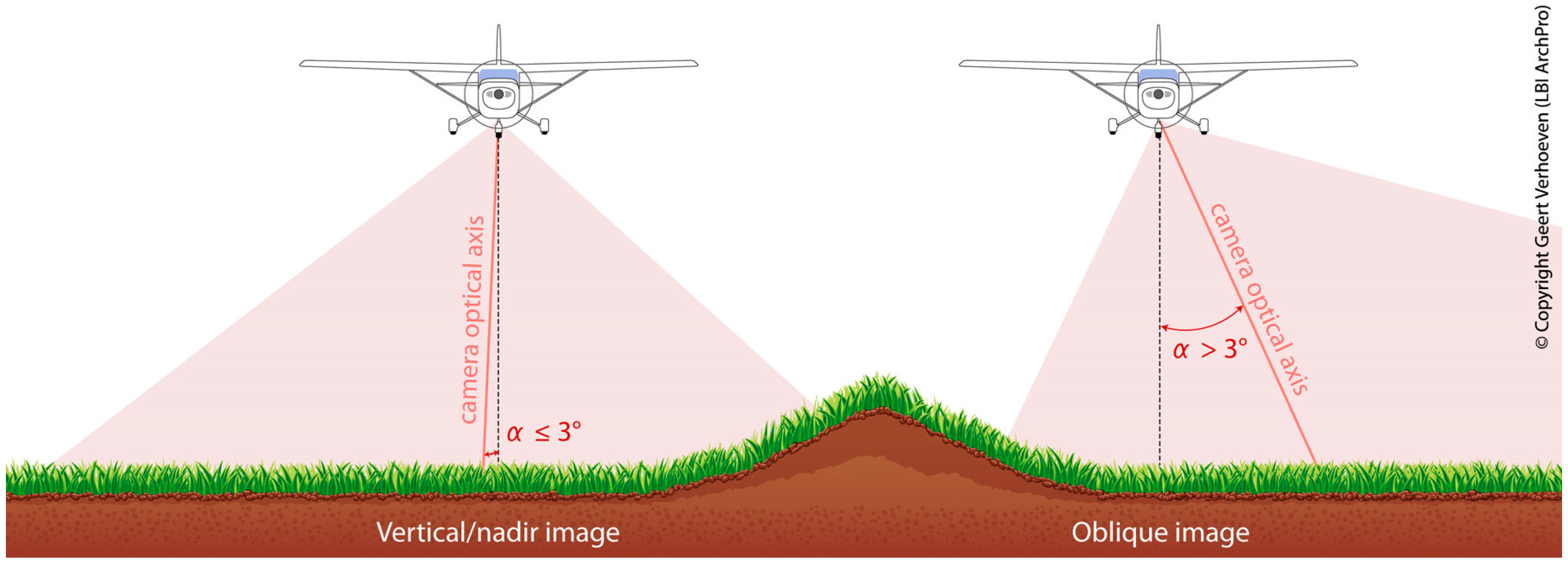


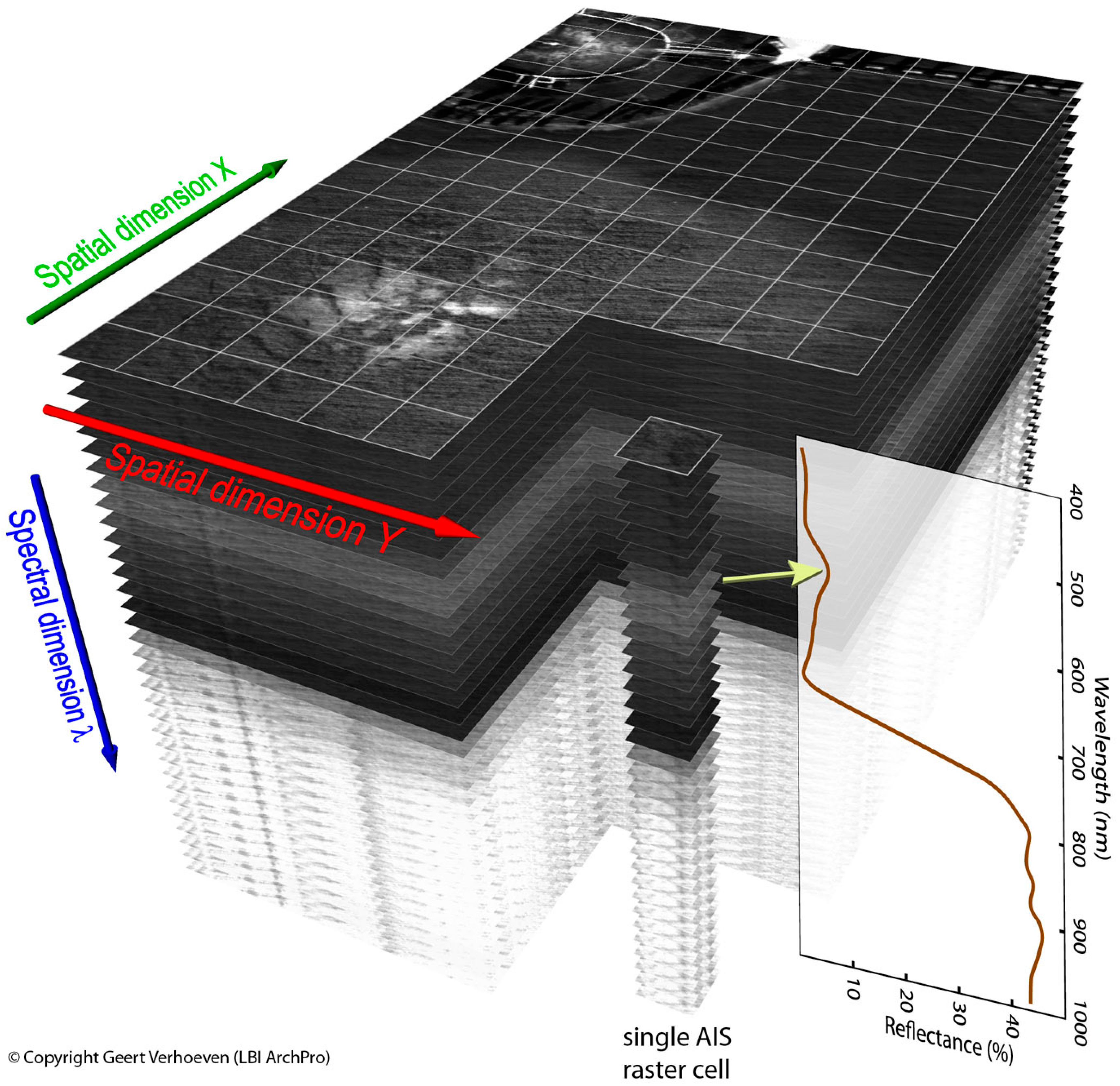
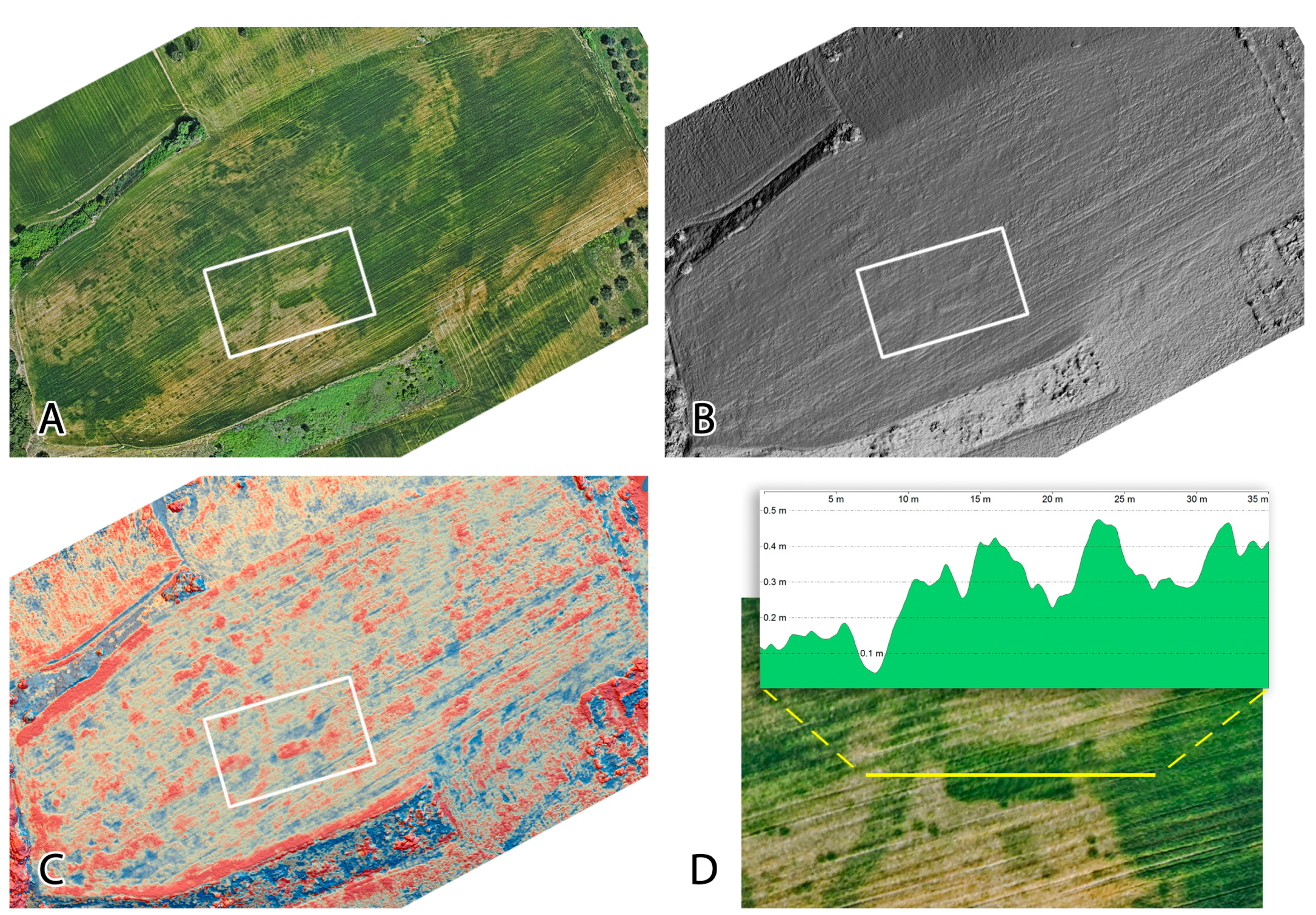
| Method | Spatial | Spectral | Temporal | Radiom. | Cost | Availability | Geo-bias | Processing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observer-directed aerial photography | + | − | + | + | + | + | − | 0 |
| Blanket aerial photography/multi-spectral imaging | +/0 | −/0 | 0 | + | 0 | 0 | + | + |
| Airborne imaging spectroscopy | 0 | + | 0 | + | − | − | + | − |
© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Verhoeven, G.J. Are We There Yet? A Review and Assessment of Archaeological Passive Airborne Optical Imaging Approaches in the Light of Landscape Archaeology. Geosciences 2017, 7, 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences7030086
Verhoeven GJ. Are We There Yet? A Review and Assessment of Archaeological Passive Airborne Optical Imaging Approaches in the Light of Landscape Archaeology. Geosciences. 2017; 7(3):86. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences7030086
Chicago/Turabian StyleVerhoeven, Geert J. 2017. "Are We There Yet? A Review and Assessment of Archaeological Passive Airborne Optical Imaging Approaches in the Light of Landscape Archaeology" Geosciences 7, no. 3: 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences7030086
APA StyleVerhoeven, G. J. (2017). Are We There Yet? A Review and Assessment of Archaeological Passive Airborne Optical Imaging Approaches in the Light of Landscape Archaeology. Geosciences, 7(3), 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences7030086





