Abstract
The stable carbon isotope ratios of coalbed methane (CBM) demonstrate diagnostic changes that systematically vary with production and desorption times. These shifts can provide decisive, predictive information on the behaviour and potential performance of CBM operations. Samples from producing CBM wells show a general depletion in 13C-methane with increasing production times and corresponding shifts in δ13C-CH4 up to 35.8‰. Samples from canister desorption experiments show mostly enrichment in 13C for methane with increasing desorption time and isotope shifts of up to 43.4‰. Also, 13C-depletion was observed in some samples with isotope shifts of up to 32.1‰. Overall, the magnitudes of the observed isotope shifts vary considerably between different sample sets, but also within samples from the same source. The δ13C-CH4 values do not have the anticipated signature of methane generated from coal. This indicates that secondary processes, including desorption and diffusion, can influence the values. It is also challenging to deconvolute these various secondary processes because their molecular and isotope effects can have similar directions and/or magnitudes. In some instances, significant alteration of CBM gases has to be considered as a combination of secondary alteration effects.
1. Introduction
The production of natural gas from unconventional sources, such as coalbed methane (CBM), also referred to as coal seam gas (CSG) or coal seam methane (CSM), and from shale gas, continues to be a major source of fossil fuels, with an estimated resource potential of ~200 to ~270 TCM (Kawata and Fujita [1]; Al-Jubori et al. [2]; IEA [3]). This is in response to the dwindling supply of conventional reserves of natural gas (186–197 TCM, e.g., Xu et al. [4]; Abas et al. [5]) and to the growing consumer market. The increase in natural gas consumption also reflects the recognition of the partial benefits that natural gas has as a somewhat “cleaner” fossil fuel. For example, natural gas produces 53 kg CO2/1.06 GJ compared with 79 for oil and 98 for coal (EPA [6]). In concert with these factors, exploration and production economics and reserve potential of CBM compare favourably with offshore oil and gas production. There is also centuries-old knowledge that the presence of natural gas in coal seams can be a hazard and has previously resulted in devastating coal-mining accidents by methane gas explosions and asphyxiation. At the end of the 1800s and the start of the 1900s, coal gas became the focus of scientific research on the identification of the sources, amounts and compositions of these gases. Emphasis was also on how to anticipate and handle these gases as prevention for future mine explosions (e.g., Chamberlain [7]). The increasing demand for natural gas as an energy source lead to a re-intensification of coal and coal gas research in the late 20th century. This included the physical, chemical and geological parameters influencing the ability of coal to store gases [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29]. The application of stable isotopes to CBM was initiated by Colombo et al. [30] with a study of δ13C-CH4 values from German coals. Even in this early paper, the importance of secondary processes, such as adsorption, desorption and diffusion was emphasized by the authors. Subsequent papers, such as [31,32,33,34,35], addressed the variations in molecular and stable isotope composition for humic and coal derived gases.
Support for the interpretation of empirical field measurements of coal-based natural gases of different ranks has been provided by pyrolysis experiments (e.g., [36,37,38]). However, much of these pyrolysis-based papers did not fully address the effects due to secondary processes operating on gases in natural coal settings. Work by Colombo et al. [30], Friedrich and Jüntgen [39,40], Smith et al. [41], Gould et al. [42] and Hosgörmez [43] considered CBM samples collected directly from the coal during desorption experiments. However, these studies are limited in sample number, or they only cover a short total desorption duration. In some cases, discrete samples were not taken, rather, the desorption experiments are mixtures, or composites of gases desorbing from the coal over time. More detailed CBM work, with a strong focus on the Illinois Basin, was carried out by Strąpoć et al. [33,44,45,46].
This study aims to measure the changes on the molecular and isotope composition of gases, both from canister desorption and produced gas. We designed experiments to understand the systematics of gas composition from producing wells, similar to the work by Strąpoć et al. [33], covering a wide range of different ranks and other coal petrological parameters, such as maceral content. In concert with this, we conducted analogous, longer-term gas desorption experiments of coal cores obtained during drilling and coal samples collected in an active underground mine. We also seek to find approaches and parameters that differentiate commingling processes between thermogenic CBM and (a) microbial gas; (b) different kerogen types and (c) gas generated from different coals.
Although changes in CBM composition due to secondary processes can make the genetic classification of the original coal gases difficult, consistent molecular and isotope fractionations due to secondary processes may be useful to understand mechanisms and response of an active CBM system.
2. Samples and Methods
Three CBM production well sample sets (P1, P2, P3) and seven desorption experiment sample sets (D1 to D7) were collected from seven coal bearing basins. In total, over 1000 gas samples from 10 sampling campaigns were obtained. An overview of the samples is given in Table 1.

Table 1.
Coal characteristics and information about type and duration of used sample methods.
Production samples were taken from CBM wells that had already been producing prior to first sampling. Sampling took place once a week, directly at the wellhead, and samples were transferred into pre-evacuated 25 mL Wheaton glass sample bottles for storage until measured. Wheaton bottles were sealed with thick silicone septa to avoid any gas loss during storage. The samples were analysed in due time to avoid extended storage times (less than a month).
Coal cores only were used for the desorption experiments, with the exceptions of sample sets D4 and D5, which were sampled from coal fragments collected underground. Cores were collected during the drilling of exploration wells and were flushed with N2 and sealed into desorption canisters as quickly as possible after reaching surface to avoid unnecessary gas loss or change. Sample sets D4 and D5 were collected from a fresh surface created within the mine. The coal’s overburden was very low and it was expected that the coal already suffered gas loss due to the reduced pressure conditions. The samples range in coal maturities from sub-bituminous coal to anthracite. Desorption experiment samples were collected over different desorption time spans, ranging from 1.5 to 2733 h whereas the production samples were collected at intervals up to a total of 6312 h. Desorption experiment samples were collected from desorption canisters following the recovery of coal cores from the exploration well according to the method described in Bertard et al. [8], Yee et al. [18], McLennan et al. [22] and Diamond and Schatzel [23]. Following the volumetric measurement of desorbed gas, a sample was removed from the system and transferred into pre-evacuated Wheaton sample bottles for storage until measured. The sampling time intervals were chosen to account for the fact that most gas desorbs from the coal early during the desorption experiments and that the volume decreases significantly over time. Based on the schedule by Ryan and Dawson [19], our desorption samples were collected immediately after sealing the coal into the canister, then every 30 min for the first two hours, every five hours up to a desorption time of 22 h, and once a day for the remaining experiment and immediately before terminating the experiment.
The relative hydrocarbon (HC) abundance and 13C/12C ratios (δ13C) were determined for methane (CH4), ethane, propane, i- and n-butane (C2+) and carbon dioxide (CO2). Other possible gases, such as nitrogen and carbon monoxide were not measured. The 2H/1H ratios (δ2H) were measured on methane only. All compositional and isotope analyses were made using Continuous Flow-Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry (CF-IRMS, Meier-Augenstein [47]; Niemann [48]).
The gases were partitioned on a GSQ PLOT column with Varian 3400 GC, then combusted and transferred online in a Cu/Pt wire micro-combustion oven at 870 °C to a Finnigan MAT Delta XL IRMS. Carbon and hydrogen isotope ratios are reported in the usual delta notation (δ13C, δ2H) relative to Vienna-Pee Dee Belemnite (VPDB) and Vienna-Standard Mean Ocean Water (VSMOW) respectively according to Equation (1), e.g., Coplen [49].
The relative abundance of the HC gases was calculated from the m/z 44 peak area for the sample relative to a standard gas sample, and is expressed in relative %.
The CH4 abundance was generally >10 times the amounts of C2+ gases in CBM samples (e.g., for CH4/C2+ > 10, Table 2). The restricted dynamic range of the IRMS (~10) and potential problems related to methane peak tailing required a modified procedure with separate analytical runs for CH4 and C2+. Although the CH4 measurements were routine, the δ13C-C2+ measurements utilized a larger injection sample loop volume (1–2 mL) to attain the minimum analytical limit for the IRMS (similar to the procedures described by Henning et al. [50]). In order to have sufficient gas for δ13C-C2+ measurements, excess amounts of CH4 are co-injected. This combusted CH4 would tail, and thus isobarically interfere with the following CO2 and combusted ethane peak. To solve this, we used a liquid nitrogen pre-concentration trap (−196 °C) between the injection loop and the GC. The C2+ is retained on the trap, whereas most of the CH4 is separated and thus removed. This allowed sufficient reduction of the confounding CH4 to permit uncontaminated δ13CO2 and δ13C2 measurements.

Table 2.
Gas composition of samples collected from all 10 sample sets. Samples from different wells and canisters per sample set are averaged and presented per sample set. Volume percentages are normalized on the basis of methane, ethane, propane, n-butane, i-butane and carbon dioxide.
3. Results
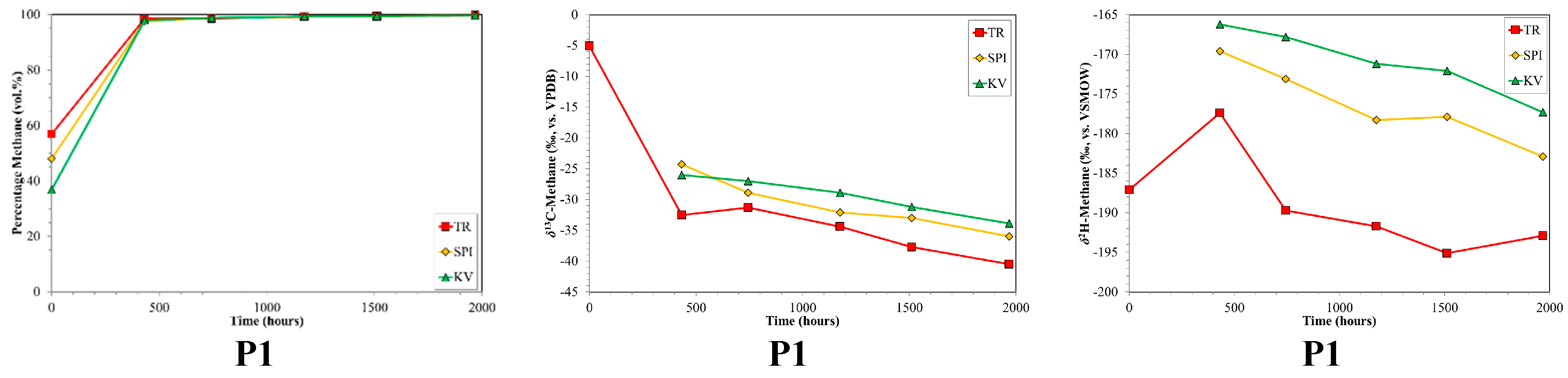
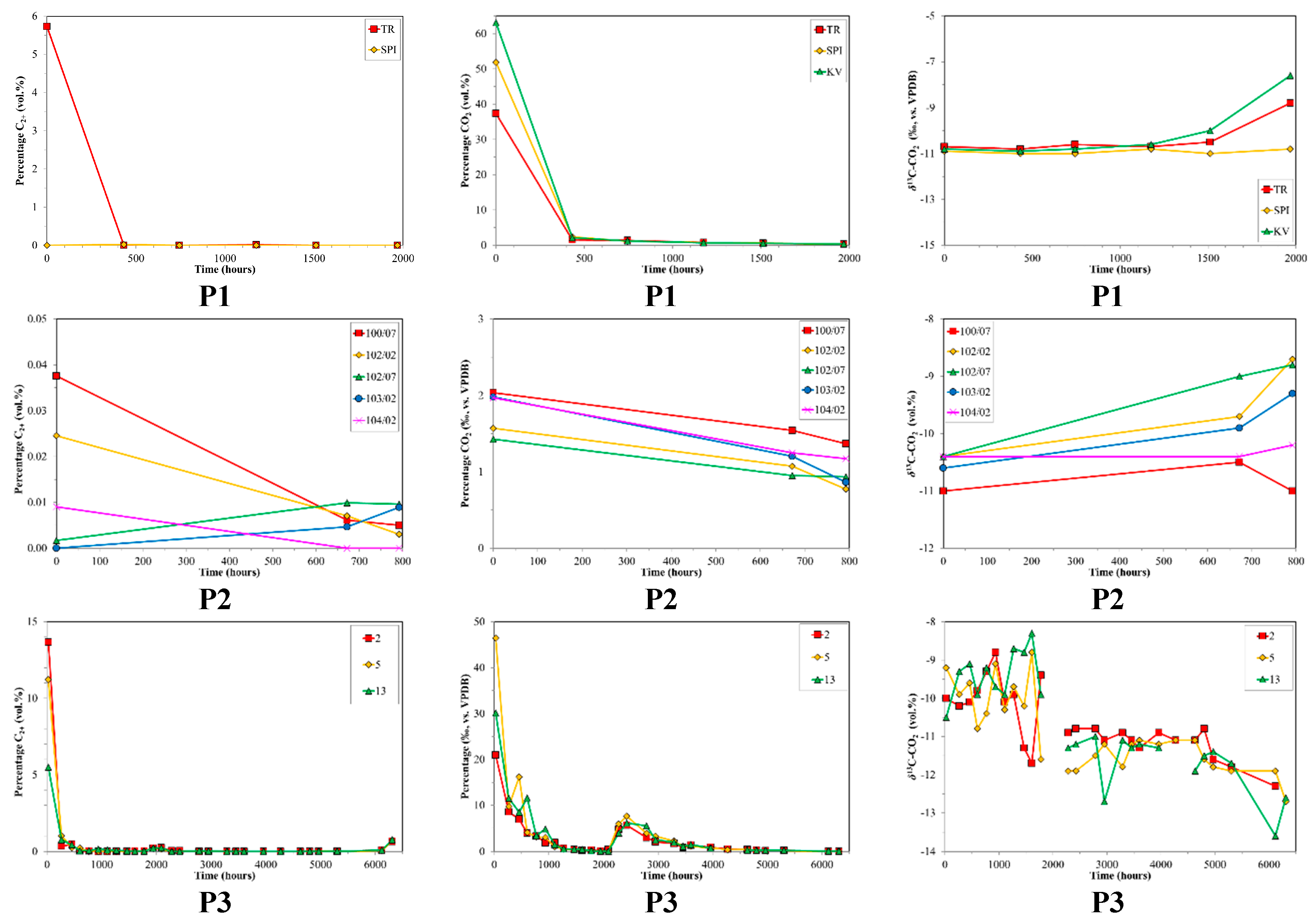
Within the text, figures and tables, all compositional information are given in volume % (vol. %), normalized to the range methane to butane and CO2. Average, relative gas compositions for each per sample set are given for orientation in Table 2. In the production well samples, methane was the dominant gas with average relative abundances of 90.4 to 98.7 vol. %. However, there were clear trends with the relative amount of methane consistently increasing with time, sometimes to a great extent (i.e., from 40 to 100 vol. %) as shown in Figure 1. Consequently, both the fractions of higher hydrocarbons (HCs; C2+) and CO2 decreased in relative abundance with production time (Figure 2). C2+ comprised a variable fraction of the gas in the production wells, with initial relative abundances ranging from ~0 vol. % (Well 103/02) to 13.7 vol. % (Well 2–24). Carbon dioxide was more abundant than C2+, with initial relative abundances decreasing from maxima of up to 63.1 vol. % (KV) (Figure 2).
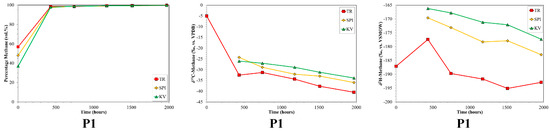
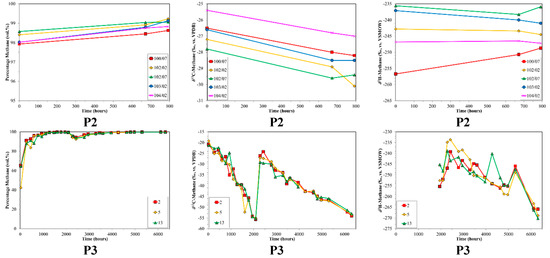
Figure 1.
Time series of volume % methane, δ13C-CH4 and δ2H-CH4 for production sample sets P1, P2 and P3 versus production time. The 0 h value corresponds to the first samples collected. Note the different scales between production sample sets.
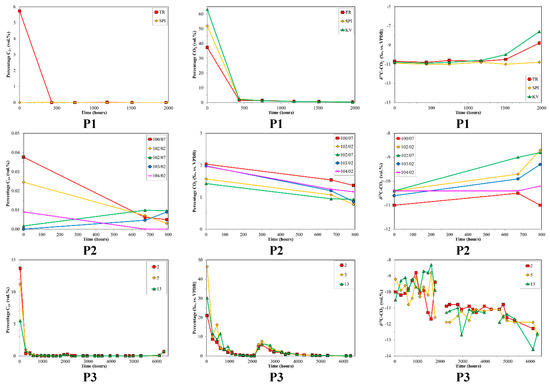
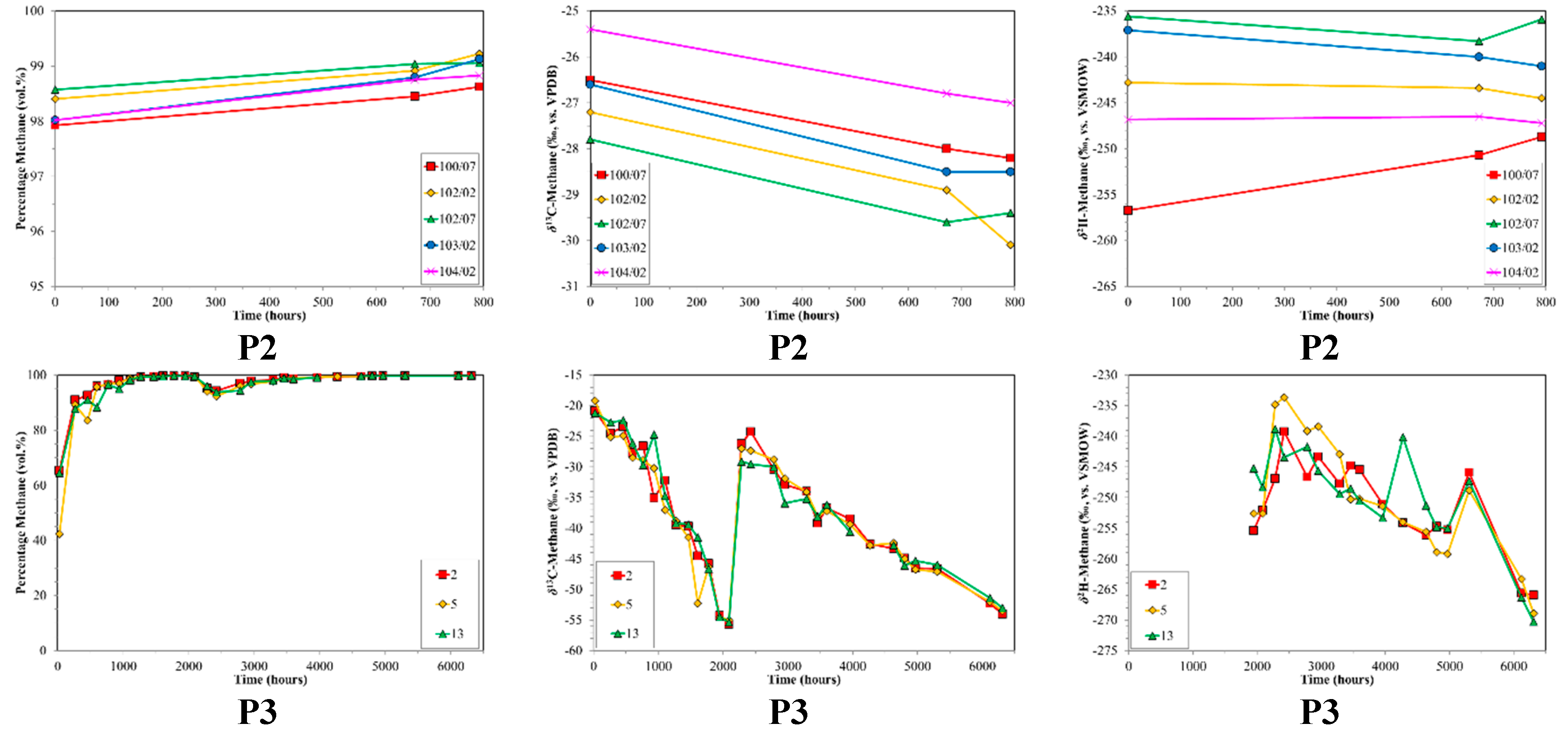
Figure 2.
Time series of volume % C2+, volume % CO2 and δ13C-CO2 for production sample sets P1, P2 and P3 versus production time. The 0 h value corresponds to the first samples collected. Note the different scales between production sample sets.
The carbon isotope ratios of the production samples exhibited wide, yet systematic ranges in values (Figure 1). In general, the production wells showed progressive 12C-enrichments for δ13C-CH4 as a function of increasing production time. Initial production samples had δ13C-CH4 ratios that were variable with those in P1 unusually enriched in 13C (δ13C-CH4~−5‰, Figure 1). The direction of the 13C-depletion trend was the same for all three sample sets, but the magnitude varies. Initial δ13C-CH4 ratios were as heavy as −5‰ (P1) and isotope shifts of up to 35.8‰ were observed. Sample set P3 revealed a particular interesting isotope trend. Initially, analogous with the other production sample sets, a 13C-depletion with increasing production time was observed with the δ13C-CH4 shifting from ~−20‰ to ~−55‰ (P3, Figure 1). Between samples 14 and 15 (~one week time difference) a dramatic shift in δ13C-CH4 occurred and δ13C-CH4 increased to ~−25‰. These changes occurred contemporaneously in all three P3 sample sets. Following these sharp δ13C-CH4 changes, the previously observed 13C-depletion trend in P3 continued (Figure 1). It is important to note that the clear isotope shift was only weakly observed as a shift in the % methane time series of P3 (Figure 1). The δ13C-CO2 in the production wells were not constant, but did not have a consistent shift direction or pattern (Figure 2). The initial δ13C-CO2 was around −10 to −11‰ and shifted only 1–3‰.
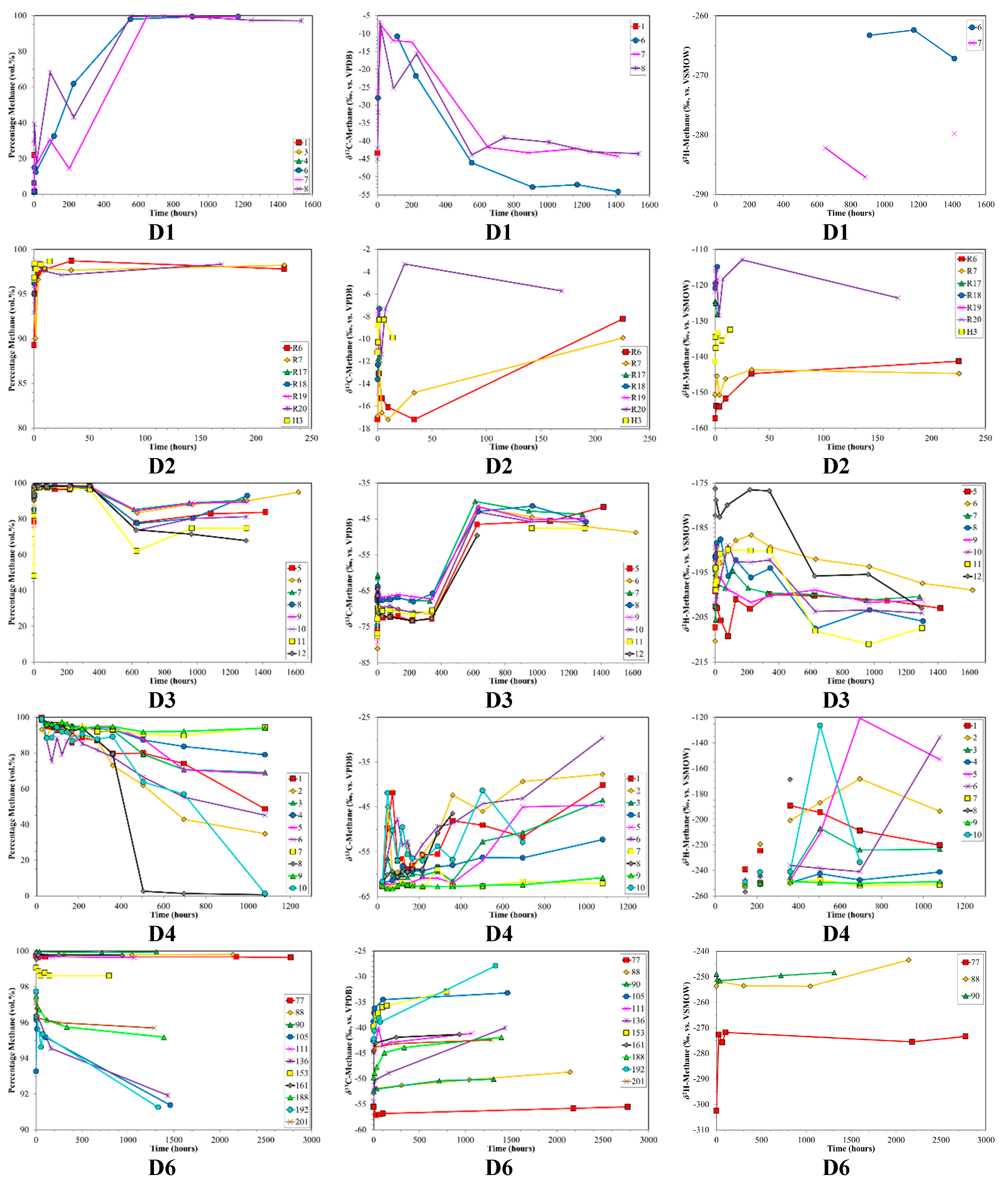
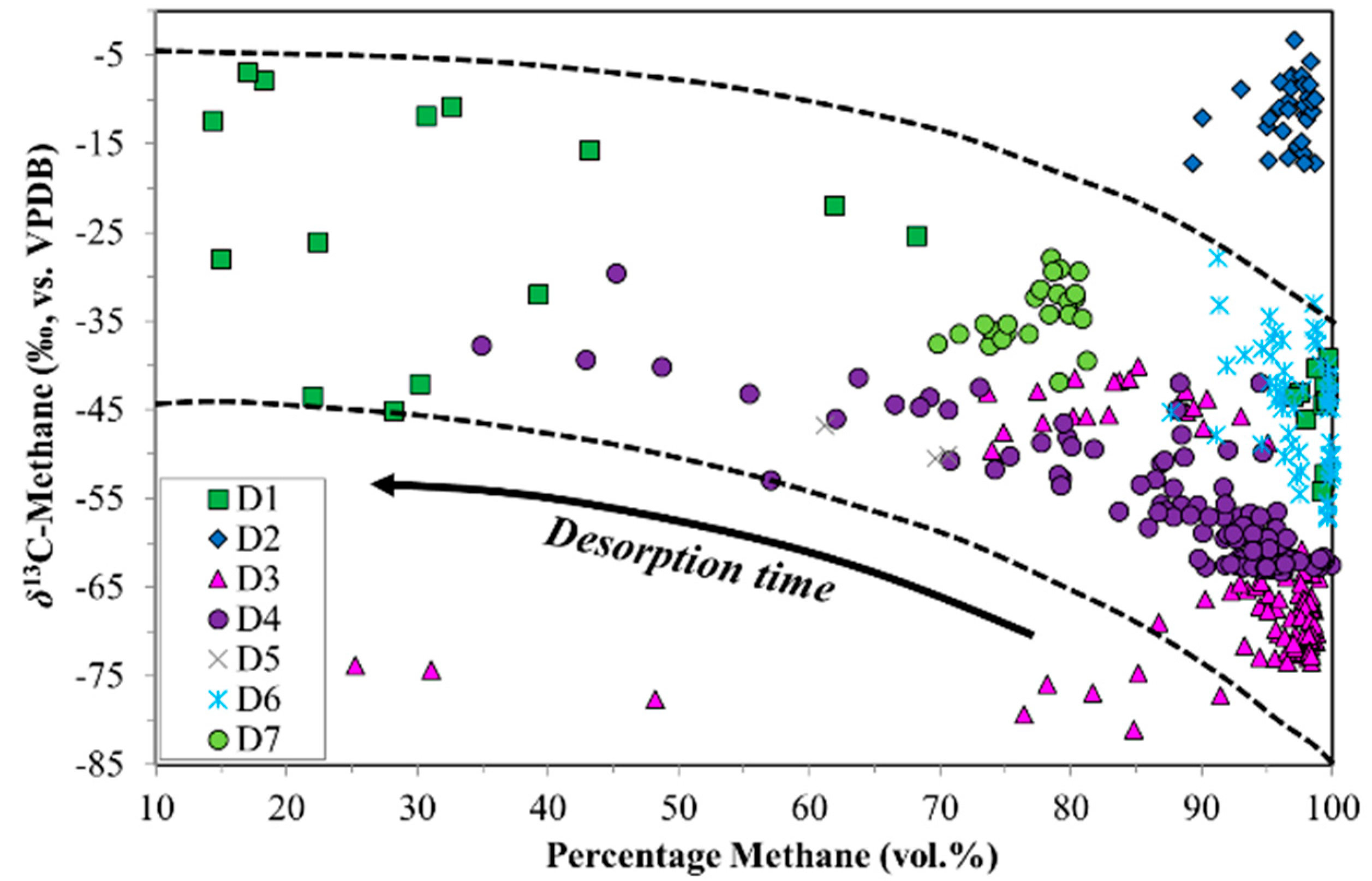
The desorption samples also had interesting variations in molecular and isotope composition with time, which were different from those observed in the production samples. Typically, the initial gas sampled was wet (higher C2+ content up to 15 vol. %). However, in several cases the relative % methane increased rapidly at the outset. As desorption continues, in some cases the relative % methane rose to ~100 vol. %, while in others it decreased (Figure 3). In general, the average C2+ content was low (<0.5 vol. % to 2.5 vol. %), with the exception of D7 (C2+ ~ 8.2 vol. %, Niemann et al., 2005 [51]). In contrast, CO2 was a major constituent in the desorbed gas, and sometimes exceeded the relative % methane (Figure 4). These variations in composition are instructive.
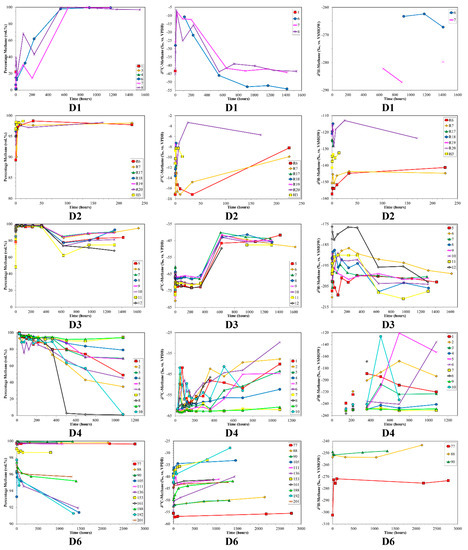
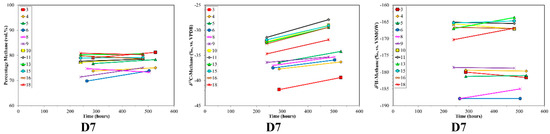
Figure 3.
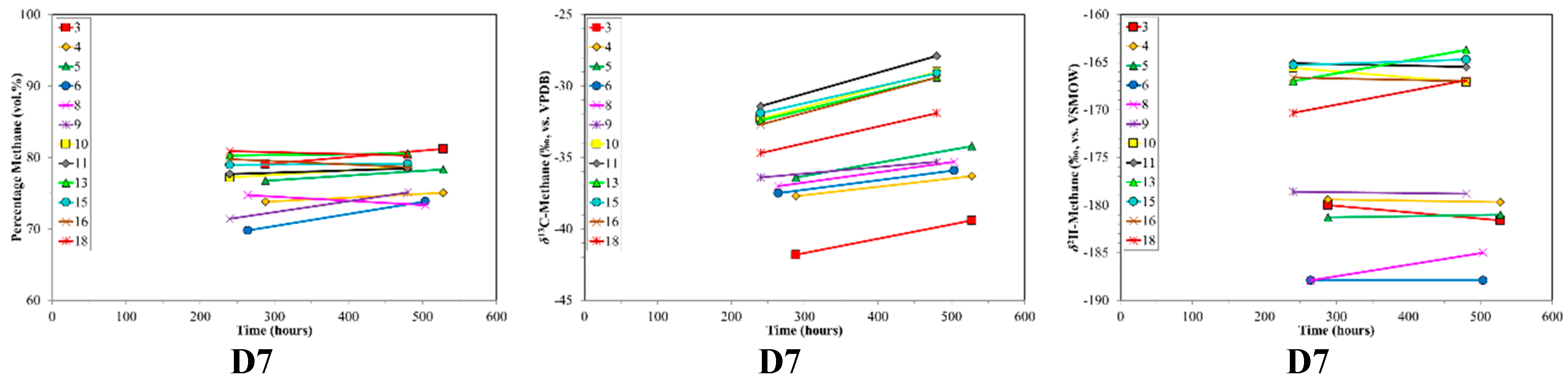
Time series of volume % methane, δ13C-CH4 and δ2H-CH4 for desorption samples sets (top to bottom) versus production time. Sample set D5 was not plotted due to insufficient data. Note the different scales between sample sets.
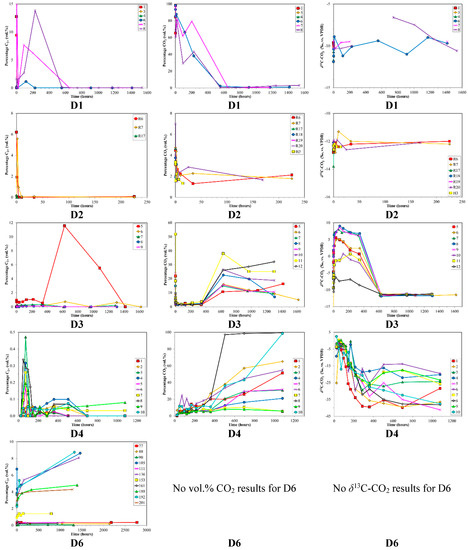
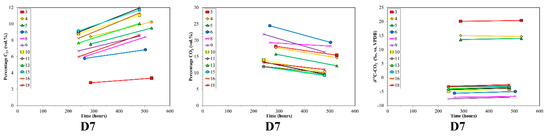
Figure 4.
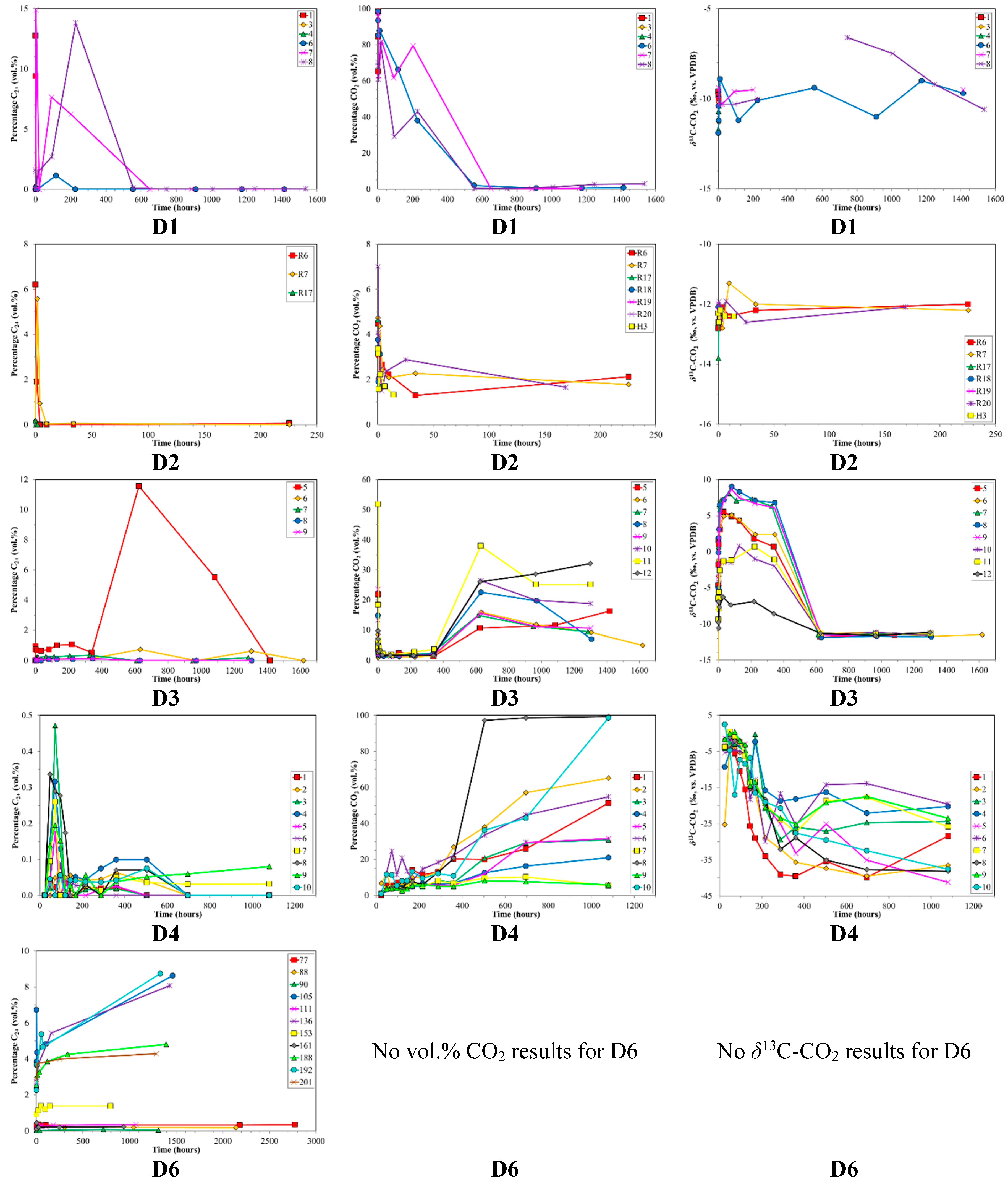
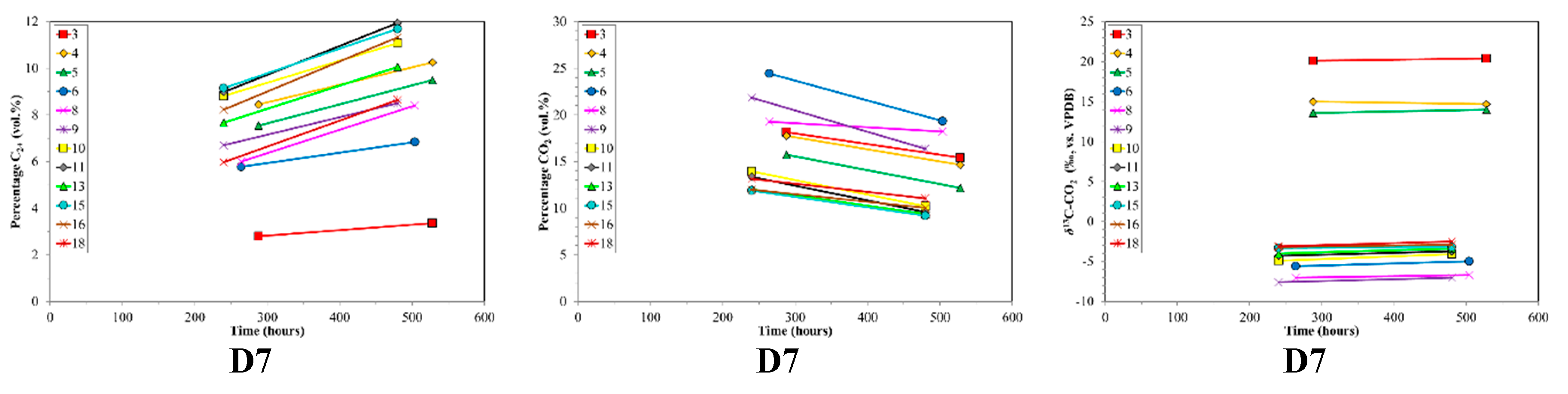
Time series of volume % C2+, volume % CO2 and δ13C-CO2 for desorption samples sets (top to bottom) versus production time. Sample set D5 was not plotted due to insufficient data. Note the different scales between sample sets.
The δ13C-CH4 ratios of desorption samples showed large variability (Figure 3). For most of the sample sets there was an overall progressive 13C-enrichment with increasing desorption time (Figure 3). D2 initially showed a different trend, with 13C-depletion followed by 13C-enrichment. D3 followed a two-stage trend, with relatively stable δ13C-CH4 ratios around −70‰ and −45‰ separated by abrupt 13C-depletion. D1 and D7 showed overall 13C-depletion with increasing desorption time. Initial δ13C-CH4 ratios for the different sample sets covered a wide range from −12‰ (D2) to −77‰ (D3). Isotope shifts of up to 35‰ were observed with increasing desorption time.
4. Discussion
It is often assumed that CBM was generated from the coal itself, i.e., source and reservoir (Levine [16]; Hunt [52]). Often the primary gas is interpreted to be only of thermogenic origin (Jüntgen and Karweil [53]; Jüntgen and Klein [54]; Das et al. [55]; Rice [17]; Flores [56]). Thermogenic HCs generated from non-humic sources, such as Type II kerogen sources, can migrate into a coal seam and influence the gas character (Niemann et al. [51]; Niemann [48]). Admixtures of early and late stage generation microbial methane in coals sometimes comprise a considerable fraction of CBM, as noted by several authors, e.g., Rice [17], Smith and Pallasser [57], Aravena et al. [58], Faiz et al. [59]; Kotarba and Lewan [38], Pashin [60], Strąpoć et al. [44,61], Flores et al. [62]. In addition, there is in situ microbial methane production by the conversion of coal to methane by the introduction of microbial nutrients and/or microbial consortia (e.g., Scott [63]; Budwill et al. [64]; Gao et al. [65]; Ashby et al. [66]; Zhang et al. [67]; Mastalerz et al. [68]).
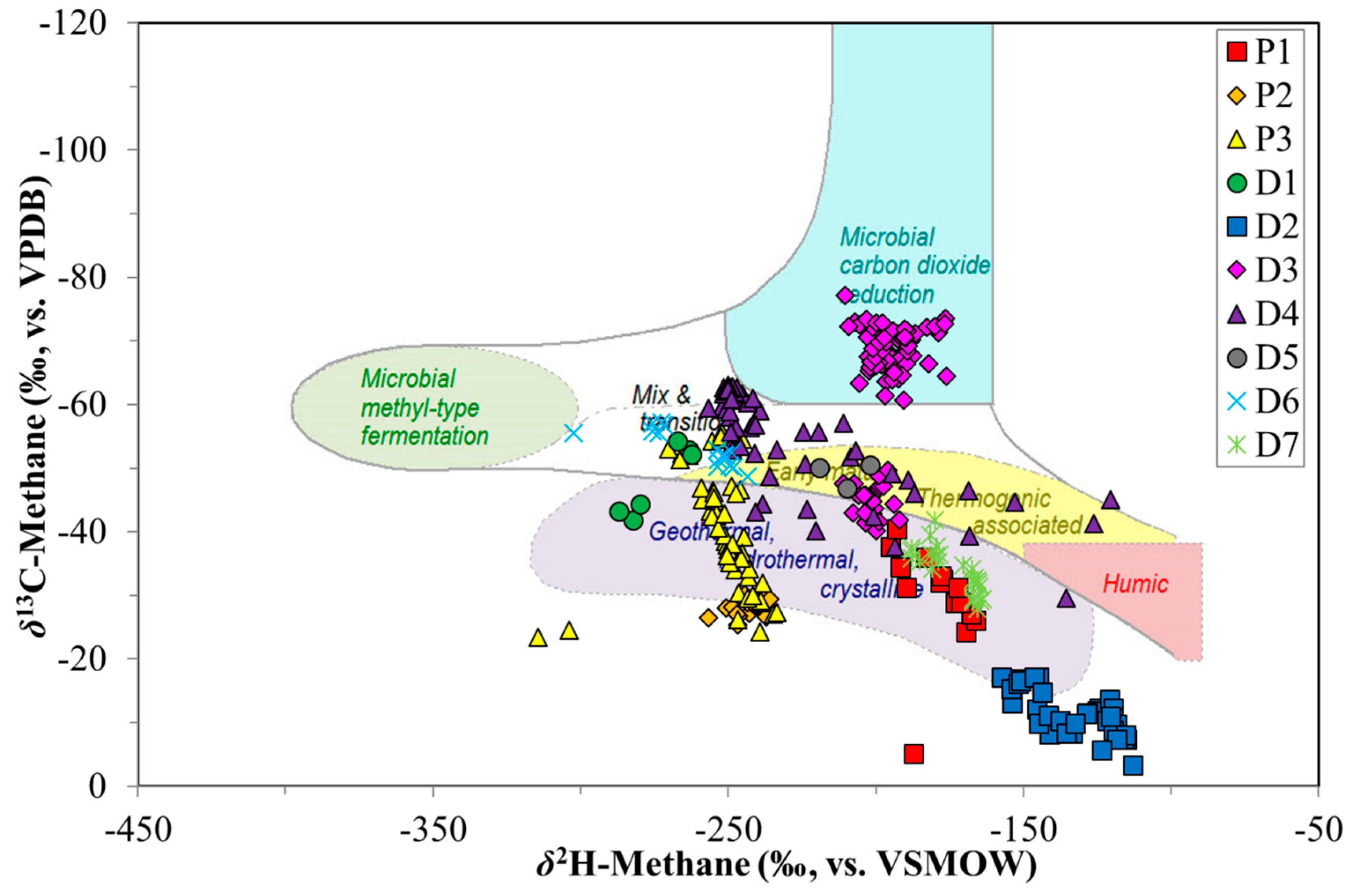
The basis for the source distinctions of CBM gas types has relied largely on the molecular gas composition and on their carbon and hydrogen isotope signatures. The thermogenic and microbial origins of CBM gases can be visually delineated with cross plots of δ13C-CH4 vs. δ2H-CH4 (CD-diagram; Figure 5, e.g., Whiticar [31]; Golding et al. [35]). However, secondary effects, such as alteration, oxidation and mixing can confound a simple source assignment. In this paper, we show that the processes of desorption and production can also alter the original signature of the CBM, and need to be considered in any interpretation. The data from the production and desorption experiment sample sets, plotted in a CD diagram (Figure 5), are examples of this issue. As observed in Figure 1 and Figure 3, the isotope shifts in δ13C-CH4 and δ2H-CH4 show extensive trends, rather than unique tight data clusters expected for primary generated gas isotope compositions. Therefore, due to secondary effects, it is difficult to ascribe a robust source classification to these CBM gases. Therefore, the use of the CD diagram for the differentiation of gas generation pathways for coal gases, as suggested by several authors, (e.g., Smith et al. [41]; Kotarba and Lewan [38]) is challenging. The evolution of the δ13C and δ2H ratios with both production and desorption time indicates processes, including desorption and diffusion, that can alter CBM compositions. New approaches for the genetic classification of coal gases, including CBM, will be necessary, incorporating the effect of secondary processes and attendant molecular and isotopic fractionation.
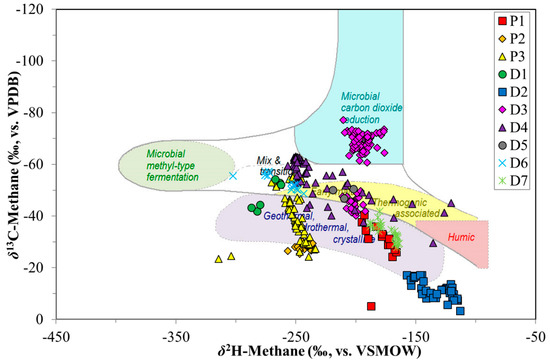
Figure 5.
Cross-plot of methane δ2H and δ13C ratios. Based on the methane isotope composition, potentially different origins can be determined and are shown in the diagram with distinct areas. Data points indicate example wells or canisters for the different sample sets. See text for details. Modified from Whiticar [31].
It is anticipated that desorption and diffusion processes should affect the gases from producing wells and from coal cores. The gas first desorbs from the coal, then diffuses into the fractures and cleats. Then diffusion or advection mechanisms transport the gases to the production wellbores, or to the canister headspaces (desorption experiments). The actual physical locations where these secondary processes operate are different for the two sample types. As a consequence, there may be differences between production and canister samples in the direction of isotope fractionation due to these secondary processes. In addition, the magnitude of isotope fractionation between production and canister samples may also show differences.
Coal cores placed into the canister for desorption experiments show a pressure drop, i.e., from formation pressure to atmospheric pressure. This pressure reduction results in a proportion of the sorbed gas to desorb from the coal into the canister headspace, with the remaining gas retained in the coal. In addition, the pressure reduction is homogeneously distributed across the open pore network of the entire coal core; closed pores will maintain an elevated pressure. The small size and volume of coal cores greatly reduces the migration pathlength compared with natural coal seams. In contrast, the diffusion pathlength is determined by the spacing of the cleat network, and whether these cleats are open or closed. Short diffusion lengths are expected between sorption sites and cleats. This constraint is equally applicable to both natural coals (production wells) and coal cores (canister). Laubach et al. [25] reported that cleat spacing is in the order of centimetres, which means that several cleats can be present in the canister coal cores. In coal cores, gas migration distances within the fracture and cleat network are short, and there is no significant isotope fractionation related to Darcy flow gas mass movement within such networks (Fuex [69]; McLennan et al. [22]).
Production of CBM from coal seams in the sub-surface is achieved by lowering the hydrostatic pressure, which in turn depends on the degree of water removal from the coal seam. The total pressure reduction in coal seams is substantially smaller compared with the pressure decrease experienced by the coal cores at the surface. The small pressure reduction differential in CBM production, relative to canister experiments, results in a smaller fraction of gas desorbed from the coal, with a greater residual fraction remaining in the coal. In addition, the pressure reduction decreases as it propagates into the coal seam, resulting in a pressure gradient, with relatively low pressure at and around the wellbore and higher pressure further into the formation. This pressure gradient causes differences in proportions of gas desorbed from the coal. All the wells considered in this study were subjected to hydraulic fracturing, creating artificial fractures accessing coal that was further away from the wellbore, which could have disrupted the natural pressure regime.
Both desorption and diffusion have attendant mass dependent fractionation effects that lead to both molecular and isotope partitioning. Typically, methane desorbs initially and preferentially from the pore surfaces in coal, followed by slower diffusion through the pores (Smith and Williams [70]). Several studies have shown that methane is less strongly sorbed onto minerals and organic matter than CO2 and or C2+ HCs, e.g., Colombo et al. [30], Lebedev and Syngayevskiy [71], Friedrich and Jüntgen [39], Faber [72], Hunt [52], Yee et al. [18]. Ettinger et al. [73] demonstrated that sorption strength of HC gases is proportional to their boiling points. This corresponds to methane being preferentially desorbed, with increasing CO2 and or C2+ HCs released with desorption time, as is observed for the canister desorption experiments (Figure 3). The preferential loss of 12C-enriched molecules, especially CH4, during desorption and diffusion is also reported by Strąpoć et al. [44].
Sevenster [74] and Thimons and Kissell [75] identified that the diffusion of gases through coal pore spaces is predominantly by Knudsen flow if the capillary diameter is less than the mean free path of the gas molecule. In such cases, the diffusion is inversely proportional to the square root of the gas molecular mass and proportional to the gas pressure. However, the structural heterogeneity of coal complicates this relationship, as pore and fracture/crack sizes can vary significantly within coal, e.g., Airey [76]. For diffusion within the coal matrix, then molecular diffusion dominates, allowing the application of the ‘unipore’ diffusion model, governed by Fick’s law, e.g., Clarkson and Bustin [77], He and Dickerson [78]. The actual differential partitioning is not always clear. For example, Cui and Bustin [79] showed that the diffusivity of CO2 in dry coal is higher than CH4, whereas Leythäuser et al. [80] and Kroos [81] showed that methane moves discriminately faster compared to CO2 and C2+ HCs. Again, there are dependencies on factors such as coal maceral content, rank and moisture content, e.g., Ettinger et al. [73], Levine et al. [82], Bustin et al. [21], Laxminarayana and Crosdale [83], Clarkson and Bustin [84], Busch et al. [85]. Ultimately, the combination of desorption and diffusion leads to the observed molecular compositional changes in the production and canister desorption time series.
Similarly, mass differences between the isotopologues of gases, e.g., carbon isotopologues of CH4, CO2 and the C2+ HCs, are subject to isotope effects that lead to isotope fractionations. In general, the heavier isotopologue, e.g., 13CH4, is more strongly sorbed than 12CH4, resulting in more of the former retained on the surfaces and more of the latter in the transport phase. Also, the diffusive mobility of isotopologues is mass dependent (mass transport), whereby the lighter isotopologue has a higher velocity than the heavier isotopologue. Such explanations have been suggested by others, including Gould et al. [42], Faiz et al. [86] and Chanton [87]. This simplistic version, however, is frequently inadequate to describe true transport in low permeability porous rocks, such as coal and shale, where diffusion and adsorption/desorption are coupled (Xia and Tang [88]). The situation has remained controversial since the early paper of Columbo et al. [89] with some authors supporting isotope fractionation in mass transport (Lebedev and Syngayevskij [71]; Pernaton et al. [90]; Prinzhofer and Pernaton [91]), while other works discounted isotope fractionation in mass transport (Fuex [69]; Zhang and Krooss [92]; Schloemer and Krooss [93]). A separate treatment of sorption/desorption and diffusion isotope effects is generally not possible in coals, therefore the observed effects on CBM should be considered as the result of various processes operating in concert.
4.1. Canister Desorption Experiments
The initial samples of the desorption experiments had an extreme range in δ13C-CH4 (−75‰ to −6‰, Figure 3). Thus, the starting point was dramatically different between samples. Generally, the δ13C-CH4 had a progressive shift towards a final value around −40‰ (Figure 3) as would be consistent with thermogenic coal gases. The 13C-enrichment with increasing desorption time observed for some of the samples was similar to the pattern observed by Strąpoć et al. [33], albeit theirs had a smaller δ13C-CH4 shift. The wide range in initial δ13C-CH4 is difficult to definitively explain, but is determined by the gas desorption and migration history of the coal and sample. The interesting point is that regardless of the δ13C-CH4 starting value, as desorption proceeds, the later δ13C-CH4 tends toward a typical coal gas value (ca. −40‰) after ca. 600 h of desorption (Figure 3). Hamilton et al. [94], based on the method described by Strąpoć et al. [33], employed this finding to guide their sampling to the desorption time midpoint (50% of desorbed gas). The sample set D2, which was anthracite, behaved very differently from the sub-bituminous and bituminous coals. The δ13C-CH4 for these gases is extremely 13C-enriched (−3‰ to −17‰), which is likely due to the high maturity of the coal and/or intense degassing.
There are also wide ranges and shifts in δ2H-CH4 between the various desorption experiment coals (−120‰ to −300‰, Figure 3). As is the case for carbon, the different hydrogen isotope isotopologues for methane should lead to analogous mass discrimination related to sorption/desorption and diffusion, albeit smaller in scale due to the low 2H natural abundance. However, in some coals the δ2H-CH4 data show a less systematic behaviour. A remarkable feature with δ2H-CH4 comes from the CD diagram (Figure 5). Despite large excursions in both δ13C-CH4 and δ2H-CH4, for each coal (D1–D7) there were pronounced trends in the combined data. Samples relatively depleted in 13C were also 2H-depleted, and as the 13C/12C increases this was tracked by a corresponding increase in 2H/1H. This indicated that the C, H-isotope signatures of the desorbing gases were determined by mass dependent processes.
The shifts in δ13C-CH4 and δ2H-CH4 corresponded to shifts in the % methane in the desorbed gas. Generally, the initial gas had less methane (higher CO2 and C2+) followed by methane-rich, dry gas. Unfortunately for interpretation, this pattern was not consistent. For example, sample sets D1 and D4 repeatedly displayed the opposite trend. What was remarkable though, was the strong correspondence between the % methane and δ13C-CH4 as observed clearly in Figure 6. A high % methane correlated with relatively 13C-depleted methane, whereas relatively low % methane correlated with relatively 13C-enriched methane. The arrow in Figure 6 depicts only an approximate trajectory of desorption time. This % methane–δ13C-CH4 relationship appeared to be independent of the actual time in the desorption time series. This points to desorption mechanisms, which predict the relative dominance of 12CH4 over 13CH4 where the relative amounts of methane dominate over CO2 and C2+ HCs. In a classic interpretation, dry, 13C-depleted gas would suggest microbial input. Any microbial gas (primary or secondary) not sorbed onto the coal, but present in the cleat network, would be released into the canister headspace before any sorbed gas. Any microbial gas present in the pore space as free gas however, would be in equilibrium with the sorbed phase. Given the presence of thermogenic gases in the pore spaces, no distinct microbial gas signature should be expected. Therefore, it is more likely that the observed change over the time series indicates that these gases were an ‘artefact’ of desorption and diffusion, not a change in gas type.
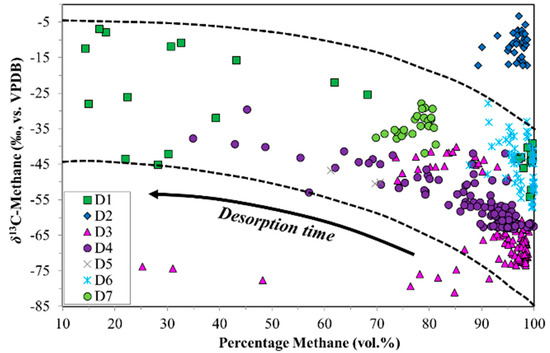
Figure 6.
δ13C-CH4 ratios from coalbed methane (CBM) desorption experiments versus % methane.
The anthracite sample set (D2) behaved very differently from the sub-bituminous and bituminous coals. The δ13C-CH4 was extremely 13C-enriched (−3‰ to −17‰) and the gas was dry (~>95 vol. %). Due to the high rank, it appears that the C2+ HCs was cracked and the 12C-enriched methane was lost.
4.2. CBM Production Experiments
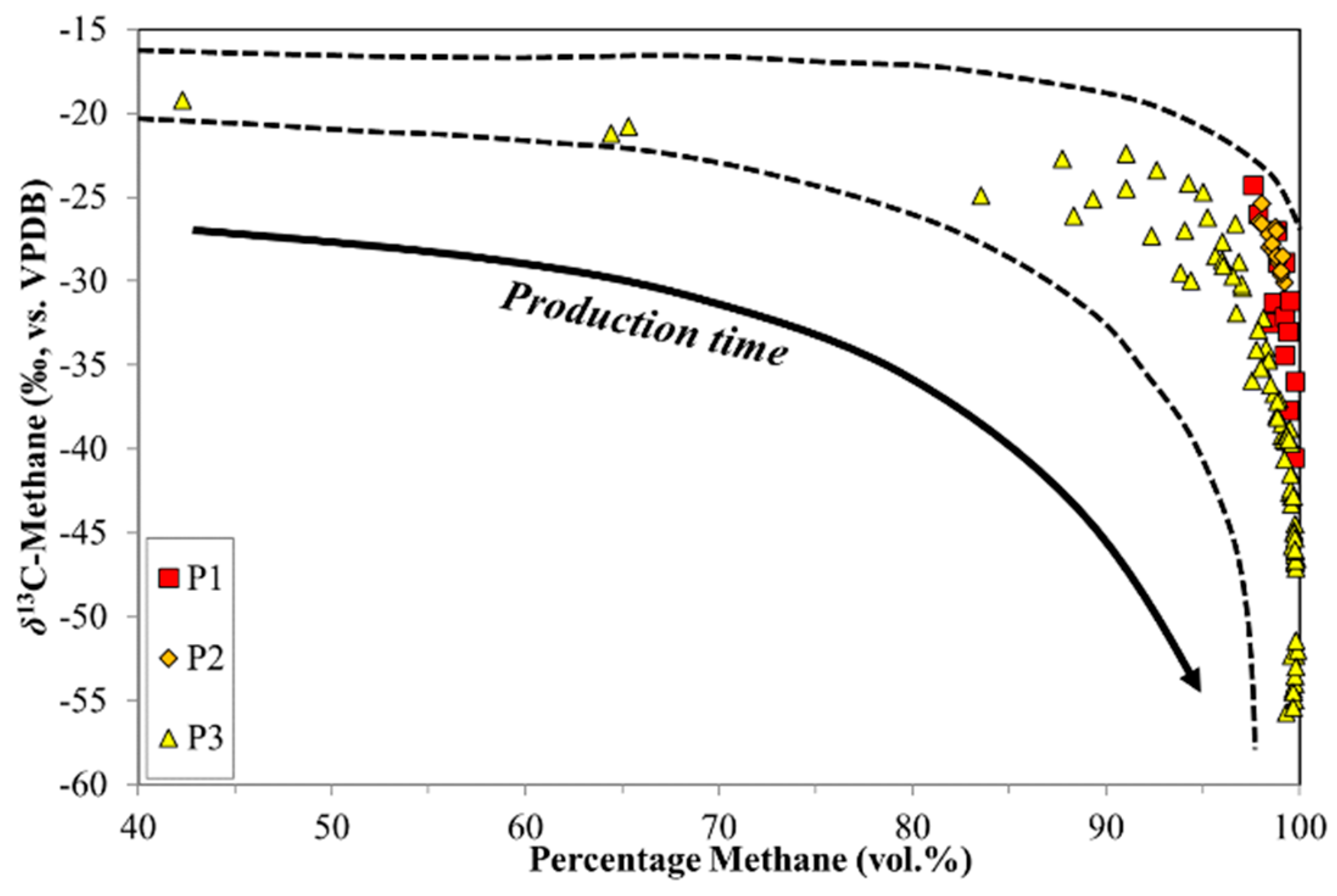
The molecular composition of the production experiments were similar to the desorption experiments, in that the initial gases recovered were wetter in C2+ HCs (Figure 1), and then become dryer (up to 100% methane) with production time. In addition, the % CO2 dropped rapidly with production time (Figure 2), contributing to the dry gas nature. However, in contrast to the desorption experiment, the δ13C-CH4 of the production experiments showed 12C-enrichment with increasing production time. This was the opposite trend of the desorption experiments. Similarly, the δ2H-CH4 generally became 1H-enriched with increasing production (Figure 1). Certainly, these shifts in the molecular and isotope ratios were the result of desorption and diffusion mechanisms. In contrast to the canister desorption, the pathlength, permeability, but also the sorption-desorption phenomena, determined the composition of the production gases. Figure 7 illustrates the relationship between the δ13C-CH4 and the % methane of the production samples. Overall the trend of the relationship for the production gases was similar to the canister desorption gases (Figure 6), but a key difference was the approximate time trajectories, which had the opposite direction. Although it could be anticipated that 12C-methane would migrate faster than 13C-methane, i.e., the early desorbed and diffused gas should be relatively enriched in methane and 12C, but the coupled diffusion and adsorption/desorption mechanisms discussed above complicate the interpretation.
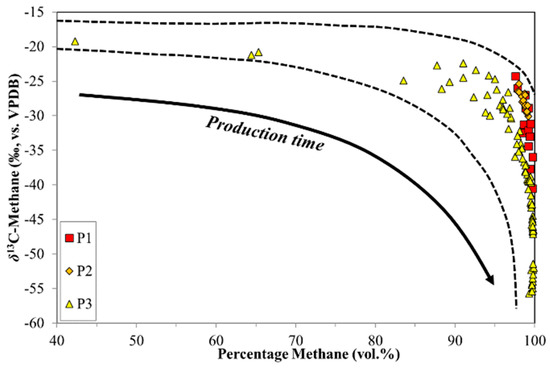
Figure 7.
δ13C-CH4 ratios from CBM production wells versus volume percentage of methane.
Percent methane and δ13C-CH4 from production samples did not show the classically expected trends for desorption and diffusion, but these processes must have been active during the liberation of the gases and their propagation from the sorption sites to the wellbore. As the three production sites have undergone hydraulic fracturing, this process was potentially responsible for the compositional changes. Hydraulic fracturing produces artificial fractures in coal seams radiating away from the wellbore that create pathways for enhanced gas flow. The size of the pathways would preclude substantial fractionation of the migrating gas, and likely enhance desorption. Additionally, water removal and thus pressure reduction can extend into coals further removed from the wellbore. This pressure gradient has implications for gas desorption. The influences of hydraulic fracturing on the coal seam and consequently on the ability to produce CBM gases are greatest proximal to the wellbore and decrease with increasing distance.
The aperture of the created fractures will be widest close to the wellbore and decreases towards zero with increasing distance. Besides major fractures, smaller and micro-fractures are generated during hydraulic fracturing and these smaller fractures are concentrated in coal close to the wellbore. These small fracture systems might reduce the natural spacing of the cleat and fracture network in these coals, resulting in smaller diffusion lengths. These dependencies on distance from the wellbore have several implications for CBM production. The physical characteristics of the coal and the success of hydraulic fracturing determine the propagation distance from the wellbore, and hence the coal volume accessed from the wellbore. As a result of the geometries and pressures, gases produced near the wellbore represent a large fraction of the overall adsorbed CBM gases in this volume, even if the overall gas quantity from this volume is small. Distal from the wellbore, the overall desorbed and produced quantities of CBM gases are higher because of the larger volume of coal accessed. However, these gases represent only a relatively small fraction of the overall adsorbed CBM gases in these volumes. Additionally, due to the lower pressure close to the wellbore, large quantities of the total adsorbed gas may rapidly desorb. In coal experiencing minimal pressure reduction, there is only minimal desorption. The overall effect is that molecular and isotope fractionation due to desorption and diffusion will increase with increasing distance away from the wellbore.
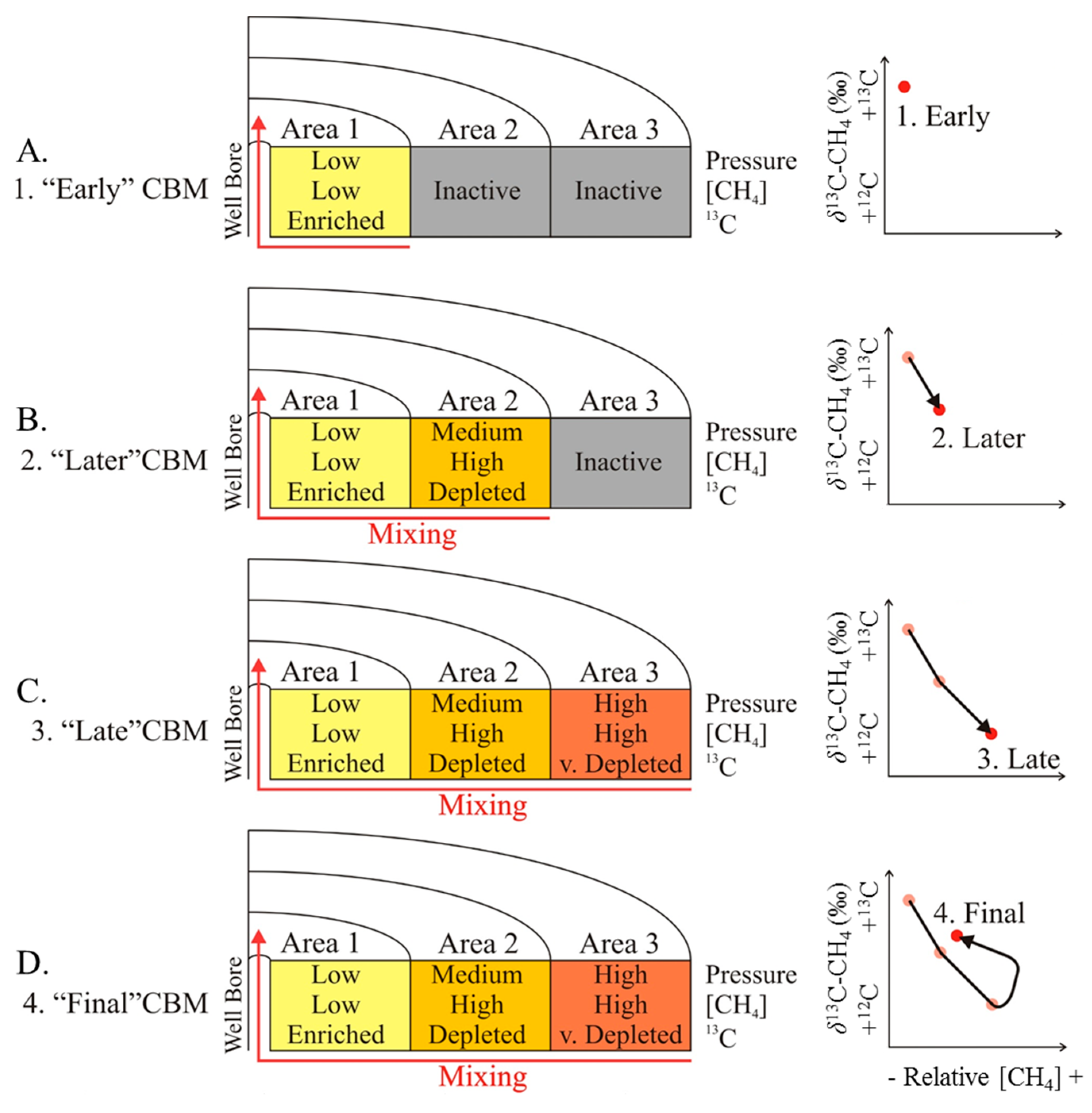
A conceptual model to explain the molecular and isotope trends observed for our CBM production samples is presented in Figure 8. The validity of the model is restricted to several limitations and constraints, including:
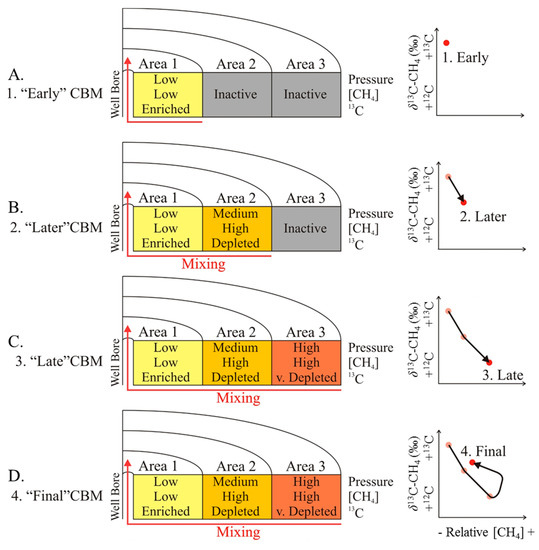
- Magnitudes of the molecular and isotope fractionation factors for desorption and diffusion,
- Influence of pressure and temperature on the magnitude of isotope fractionation associated with desorption and diffusion,
- Actual pressure reduction in the coal seam and the pressure gradient throughout the seam,
- Extent (spacing, aperture, length) of natural and artificial fractures,
- Molecular and isotope composition of the original (unaltered) gas, sorbed onto the coal.
In the first ‘early’ stage (Figure 8A), the gas produced desorbs from the coal in Area 1 directly adjacent to the wellbore. This gas originates from a relatively small coal volume around the wellbore. At this point in time, the deeper Areas 2 and 3 are not contributing to the recovered gas point. Relatively small proportions of methane and elevated proportions of C2+, HCs, and CO2, as well as methane relatively enriched in 13C are observed at this stage. Because of the strong impact of hydraulic fracturing, reduced hydrostatic pressures and short pathlengths, gas velocities and differential sorption create the compositions observed (low % methane and 13C-enriched methane). Due to the artificially created fractures and micro-fractures and the consequently closer cleat spacing, isotope fractionation due to diffusion is minimal.
The gas from the later, mid-stage production (Figure 8B), is a mixture of gases desorbing from coal close to the wellbore (Area 1) and from coal further away from the wellbore. Area 3 is still not contributing at this point. Area 2, relative to coal from Area 1, has a lesser pressure drop, but Area 2 represents a greater coal volume than Area 1. Therefore, the overall gas produced increases, but due to the still elevated pressure, these gases represent only relatively small fractions of the total adsorbed gas in Area 2. The desorbing gas is enriched in methane with smaller proportions of C2+, HCs, and CO2. The δ13C-CH4 compared to Area 1, is depleted in 13C, due to the fact that 13C is more strongly adsorbed than 12C and further pressure reductions within the area are required for desorption of more 12C-enriched methane. Overall, the isotope fractionation due to desorption and diffusion, relative to the total adsorbed gas, is expected to be greater for gases from Area 2, due to the reduced influence of hydraulic fracturing and the associated effects. Gases from Area 2 commingle during their migration with gases from Area 1. Relative to gases entirely originated from Area 1, this mixed gas is enriched in methane and depleted in 13C. This is enhanced by the access of larger volumes of gas from Area 2, due to the larger coal volume.
During Stage 3 (Figure 8C), the produced gases include late gases from Areas 1 and 2 and gas desorbing from the coal of Area 3. The coal in Area 3 experiences only a relatively minimal pressure reduction, resulting in desorption of almost exclusively methane, which is strongly depleted in 13C. The affected volume of coal in Area 3 is greater than the volume for Section 2, resulting in desorption and production of huge proportions of methane, but which represents only a small fraction of the total adsorbed gas volume in this section. The proportions of C2+, HCs, and CO2 are predicted to be low, because the pressure reduction is insufficient for desorption of elevated quantities of these gas species. The admixture of this gas from Area 3 to the gases from Area 1 and 2 should lead to an overall enrichment of methane in the late produced gas, and this methane should be even more 12C-enriched than the previously produced methane. This trend is enhanced by the access of large volumes of gas from Area 3, due to the relatively large volume of coal, and the depletion of gas in Areas 1 and 2.
In the final Stage 4 (Figure 8D) the continuous production of gas and extended water removal from Areas 1 to 3, lead to gas more depleted in methane, enriched in CO2 and C2+ HCs and methane enriched in 13C. This assumes that no “early” gas from sections further away from the wellbore than Area 3 is admixed to the pool of late gas.
Carbon dioxide in coalbed gas can provide additional insight into the depositional environment and processes (Smith and Pallasser [57]). The relative amount of carbon dioxide in the production samples was elevated at the outset, but rapidly dropped to low levels (Figure 2). The may be related to an initial higher amount of CO2 in the fractures or perhaps the higher diffusivity of CO2 in dry coal discussed by Cui and Bustin [79]. The average δ13C-CO2 is around −10‰ to −11‰ and shows only minor change (1–3‰) with time as the CO2 decreases, suggesting an organic source for the CO2.
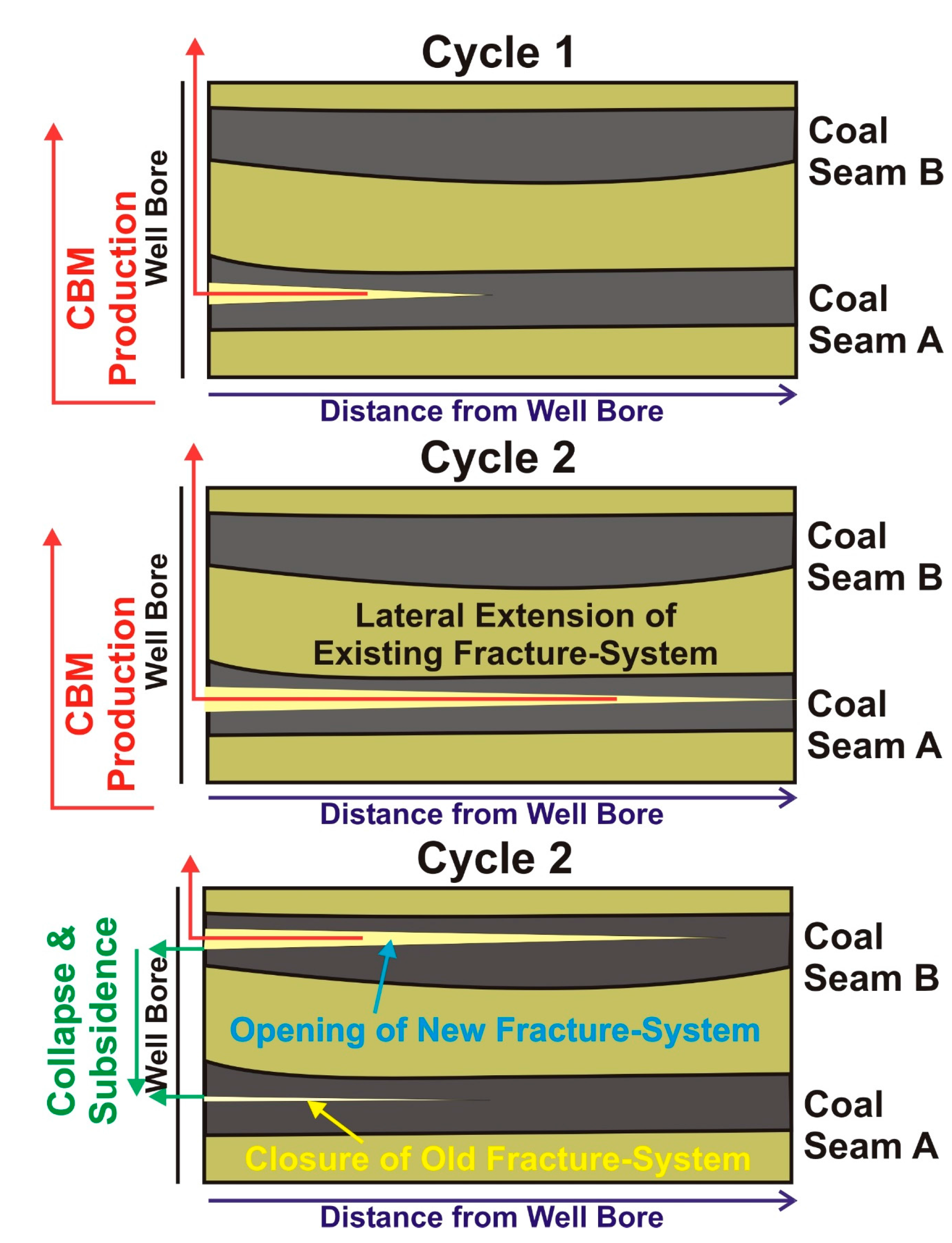
4.3. Indications for Opening of New Fracture Systems
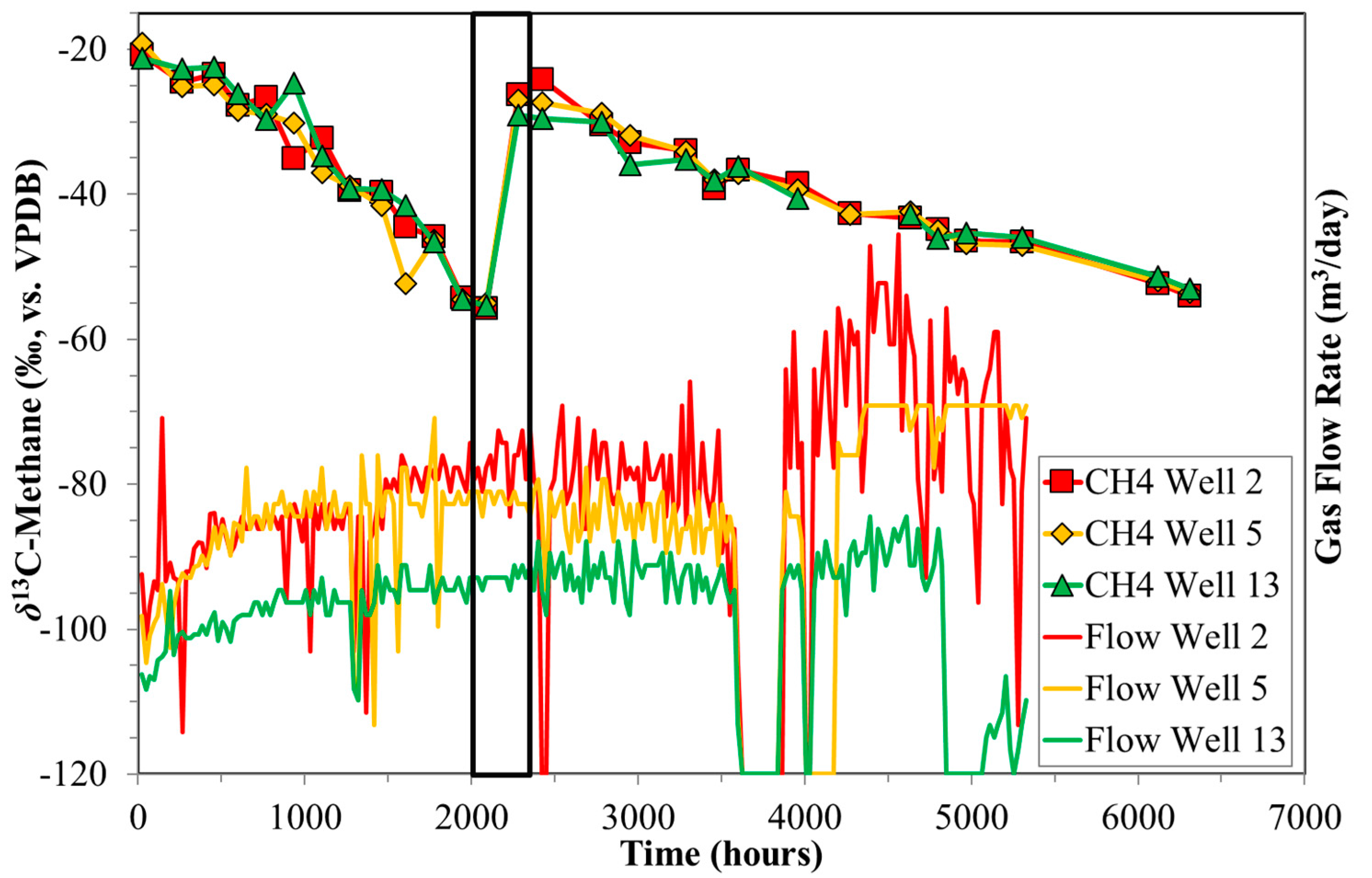
Production samples from all three wells of P3 revealed an interesting time series feature that is particularly evident from the isotope data. Over up to 2088 h of production, the wells showed relatively initial low % methane that then increased steadily with increasing production time up to ~100 vol. %. After 2088 h, the % methane suddenly decreased to ~94 vol. %, then slowly increased again to ~100 vol. % (Figure 1). At this time point, CO2 and to a lesser degree C2+ and HCs, also showed a brief increase. This change in molecular composition at 2088 h would likely have not been noticed were it not for the dramatic shift in δ13C-CH4 (Figure 1). During this time, production continued as normal, and daily production data did not reveal any drop in produced volumes (Figure 9). Therefore, a possible explanation for the observed molecular and isotope trends in sample set P3 at ca. 2088 h is due to the closing and opening of fracture systems due to production, as presented in the schematic model (Figure 10).
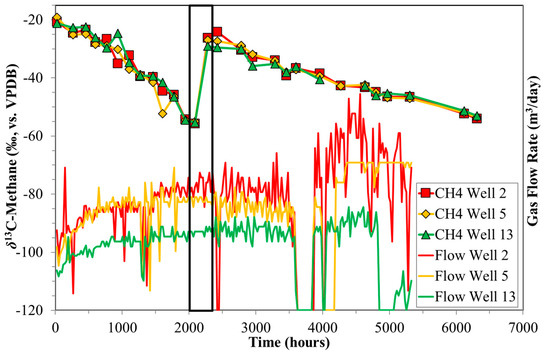
Figure 9.
Time series of δ13C-CH4 versus production time for sample set P3. Also shown are the production profiles for the three wells comprising P3. The 0 h value corresponds to the first samples collected. No change in production values correlating with the change in δ13C-CH4 between 2088 and 2280 h (black box) can be observed.
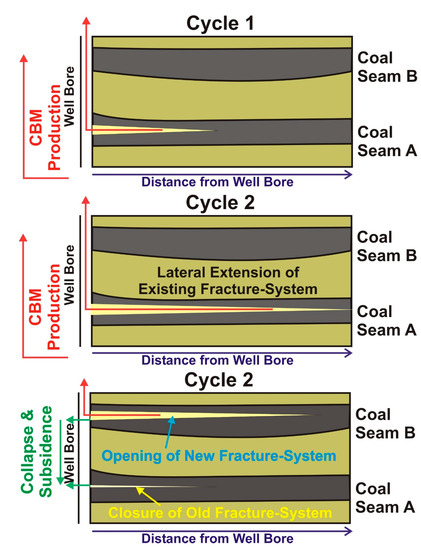
Figure 10.
Idealized model showing closing and opening of fracture systems in coal seams and lateral extension of fracture system as a result of the production of CBM from wells of production sample set P3.
The initial production (Phase 1, 0–2088 h) displayed an expected shift with production to methane-rich gas, with the methane becoming more 12C-enriched. This was consistent with the trends resulting from the mixing of gas from different regions/depth into the fracture system of the coal seam, as described in Figure 7 and Figure 8. At 2088 h, (Phase 2) there was an abrupt and apparent ‘reset’ of the time series, followed with further time by a resumption of the trends analogous to Phase 1. The opening of a new fracture system at 2088 h that up to that time had not, or had only minimally contributed to the gas production, dominated the gas production. Harpalani and Schraufnagel [95] and St. George and Barakat [96] reported shrinkage processes in coal as an effect of gas desorption and release. These shrinkage processes in coal might initiate the collapse of an existing fracture system and the subsequent opening of a new one. This new fracture system might occur in the same coal seam, e.g., lateral or angular extensions relative to the existing system, or it may involve a different coal seam that is intersected by the well and screened for production (Figure 10).
The process of opening a new fracture system or the extension of an existing one has to occur quickly and be substantial, because the measured gas flow for all three P3 wells expressed similar behaviour at 2088 h. The three wells were drilled in a triangular geometry with a distance of several hundred metres between the wells, but all three wells produced CBM from the same coal seam. Therefore, opening new fracture systems or extending existing ones must operate on a relatively large scale. The important point here is that the isotope trends are potentially a sensitive indicator of fracture system performance, and hence recovery estimations.
5. Conclusions
Interpretative challenges are due to the retentive capacity of coals, mixtures between gases of different origins (thermogenic, microbial), and mixtures of gases generated at different stages of the coalification process. Secondary processes, i.e., adsorption, desorption, mixing, and diffusion can significantly alter the molecular and isotope composition of CBM gases. CBM is most likely a mixture of gases generated from the coal at different times of the coalification process. This includes possible admixtures of primary and secondary microbial gas and, sometimes, gases generated from other coals and/or gases generated from different source rocks. The δ13C-CH4 from desorption experiment and production samples showed opposite trends with increasing desorption/production time. The methane from the former showed 13C-enrichment with increasing desorption time, while those from production showed 13C-depletion with increasing production time.
A schematic model was proposed to explain the observed isotope trend for CBM production samples of relative and rather quick 13C-enrichment for methane with increasing production time, indicating mixing of CBM gases desorbing from different regions of an active coal seam during CBM production. Indications are found for a potential sudden closure and correlating opening of fractures and fracture–systems in coal seams leading to desorption and consequently production of CBM from different sections of the coal or even from different intersected coal seams.
With additional knowledge about the impact of secondary processes on the molecular and isotopical composition of CBM, the analyses of stable carbon isotopes in CBM may provide further information about the total gas content of a given coal seam, including a more sophisticated estimation of lost and residual gas, and may be therefore competitive to the currently used desorption canister approach.
Acknowledgments
The samples provided by several energy companies for the research are gratefully acknowledged. Funding of this work was provided by research grants from NSERC (MJW) and the British Columbia Ministry for Energy and Mines. Special thanks to Paul Eby for analytical support and Barry Ryan for his time, support and help throughout the work. We would also like to thank the reviewers for their helpful comments, which made the manuscript clearer and more precise.
Author Contributions
Martin Niemann and Michael J. Whiticar conceived and designed the experiments; Martin Niemann performed the experiments; Martin Niemann and Michael J. Whiticar analyzed the data; and Martin Niemann and Michael J. Whiticar wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kawata, Y.; Kazuo, F. Some predictions of possible unconventional hydrocarbons availability until 2100. In Proceedings of the SPE Asia Pacific Oil and Gas Conference and Exhibition, Jakarta, Indonesia, 17–19 April 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Jubori, A.; Johnston, S.; Boyer, C.; Lambert, S.W.; Bustos, O.A.; Pashin, J.C.; Wray, A. Coal bed methane: Clean energy for the world. Oilfield Rev. 2009, 21, 4–13. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Energy Information Administration. Annual Energy Outlook 2013 with Projections to 2040; EIA: Washington, DC, USA, 2013.
- Xu, C.; Dunnahoe, T.; Slocum, M.T.; Bell, L. Reserves grow modestly as crude oil production climbs. Oil Gas J. 2015, 113, 20–35. [Google Scholar]
- Abas, N.; Kalair, A.; Khan, N. Review of fossil fuels and future energy technologies. Futures 2015, 69, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency. Compilation of Air Pollutant Emission Factors; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1998.
- Chamberlin, R.T. Notes on explosive mine gases and dusts, with special reference to the explosions in the Monongah, Darr and Naomi coal mines. U.S. Geol. Surv. Bull. 1909, 383. Available online: https://digital.library.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metadc38812/ (accessed on 6 January 2017).
- Bertard, C.; Bruyet, B.; Gunther, J. Determination of desorbable gas concentration of coal (direct method). Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 1970, 7, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, J.L.; Grein, C.T.; Bienstock, D. Effect of moisture on the methane capacity of American coals. Fuel 1974, 53, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, C.M.; Diamond, W.P. Inexpensive method helps predict methane content of coalbeds. Coal Age 1976, 81, 102–106. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, A.G. Estimating methane content of bituminous coalbeds from adsorption data. U.S. Bur. Mines Rep. Investig. 1977, 8245, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Diamond, W.P.; Levine, J.R. Direct method determination of the gas content of coal: Procedures and results. U.S. Bur. Mines Rep. Investig. 1981, 8515, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Rigby, D.; Smith, J.W. An isotopic study of gases and hydrocarbons in the Cooper basin. Aust. Pet. Explor. Assoc. J. 1981, 21, 222–229. [Google Scholar]
- Meissner, F.F. Cretaceous and Lower Tertiary coals as sources for gas accumulations in the Rocky Mountain area. In Hydrocarbon Source Rocks of the Greater Rocky Mountain Region; Woodward, J., Meissner, F.F., Clayton, J.L., Eds.; Rocky Mountain Association of Geologists: Denver, CO, USA, 1984; pp. 401–431. ISBN 9780933979062. [Google Scholar]
- Creedy, D.P. Geological controls on the formation and distribution of gas in British coal measure strata. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1988, 10, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, J.R. Coalification: The evolution of coal as a source rock and reservoir rock for oil and gas. In Hydrocarbons from Coal; Law, B.E., Rice, D.D., Eds.; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1993; Volume 38, pp. 39–77. ISBN 9781629811048. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, D.D. Compositions and origins of coalbed gas. In Hydrocarbons from Coal; Law, B.E., Rice, D.D., Eds.; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1993; Volume 34, pp. 159–184. ISBN 9780891810469. [Google Scholar]
- Yee, D.; Seidle, J.P.; Hanson, W.B. Gas sorption on coal and measurement of gas content. In Hydrocarbons from Coal; Law, B.E., Rice, D.D., Eds.; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1993; Volume 38, pp. 203–218. ISBN 9780891810469. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, B.D.; Dawson, F.M. Coalbed methane canister desorption techniques. In Geological Fieldwork 1993; A Summary of Field Activities and Current Research; Grant, B., Newell, J.M., Eds.; British Columbia Geological Survey: Victoria, BC, Canada, 1994; pp. 245–256. [Google Scholar]
- Beamish, B.B.; Crosdale, P.J. The influence of maceral content on the sorption of gases by coal and the association with outbursting. In Management and Control of High Gas Outbursts in Underground Coal Mines; Lama, R.D., Ed.; Westonprint: Kiama, NSW, Australia, 1995; pp. 353–362. [Google Scholar]
- Bustin, R.M.; Clarkson, C.; Levy, J. Coalbed methane adsorption of coals of the Bulli and Wongawilli seams, southern Sydney basin: Effect of maceral composition. In Proceedings of the 29th Newcastle Symposium on Advances in the Study of the Sydney Basin, Newcastle, NSW, Australia, 6–9 April 1995; pp. 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- McLennan, J.D.; Schafer, P.S.; Pratt, T.J. A Guide to Determining Coalbed Gas Content; Gas Research Institute: Des Plaines, IL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Diamond, W.P.; Schatzel, S.J. Measuring the gas content of coal: A review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1998, 35, 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosdale, P.J.; Beamish, B.B.; Valix, M. Coalbed methane sorption related to coal composition. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1998, 35, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laubach, S.E.; Marrett, R.A.; Olson, J.E.; Scott, A.R. Characteristics and origins of coal cleat: A review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1998, 35, 175–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, O.C.; Bennett, M.E.; Clark, C.E. Volatiles lost during coalification. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2000, 44, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radlinski, A.P.; Mastalerz, M.; Hinde, A.L.; Hainbuchner, M.; Rauch, H.; Maron, M.; Lin, J.-S.; Fan, L.; Thiyagarajan, P. Application of SAXS and SANS in evaluation of porosity, pore size distribution and surface area of coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2004, 59, 245–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastalerz, M.; Drobniak, A.; Strąpoć, D.; Solana Acosta, W.; Rupp, J. Variations in pore characteristics in high-volatile bituminous coals: Implications for coal bed gas content. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2008, 76, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnichenko, Y.B.; Radlinski, A.P.; Mastalerz, M.; Cheng, G.; Rupp, J. Characterization of the CO2 fluid adsorption in coal as a function of pressure using neutron scattering techniques (SANS and USANS). Int. J. Coal Geol. 2009, 77, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, U.; Gazzarrini, F.; Gonfiantini, R.; Kneuper, G.; Teichmüller, M.; Teichmüller, R. Carbon isotope study on methane from German coal deposits. In Advances in Organic Geochemistry 1966, Proceedings of the 3rd International Congress on Organic Geochemistry, London, UK, 26–28 September 1966; Hobson, G.D., Speers, G.C., Eds.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1970; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Whiticar, M.J. Stable isotope geochemistry of coals, humic kerogens and related natural gases. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1996, 32, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, J.L. Geochemistry of coalbed gas—A review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1998, 35, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strąpoć, D.; Schimmelmann, A.; Mastalerz, M. Carbon isotopic fractionation of CH4 and CO2 during canister desorption of coal. Org. Geochem. 2006, 37, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Ni, Y.; Zou, C.; Tao, S.; Hu, G.; Hu, A.; Yang, C.; Tao, X. Stable carbon isotopes of alkane gases from the Xujiahe coal measures and implication for gas-source correlation in the Sichuan Basin, SW China. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golding, S.D.; Boreham, C.J.; Esterle, J.S. Stable isotope geochemistry of coal bed and shale gas and related production waters: A review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2013, 120, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaschnitz, R.; Kroos, B.M.; Gerling, P.; Faber, E.; Littke, R. On-line pyrolysis-GC-IRMS: Isotope fractionation of thermally generated gases from coal. Fuel 2001, 80, 2139–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, B. Methane generation from coal during open system pyrolysis investigated by isotope specific, Gaussian distributed reaction kinetics. Org. Geochem. 2004, 35, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotarba, M.J.; Lewan, M.D. Characterizing thermogenic coalbed gas from Polish coals of different ranks by hydrous pyrolysis. Org. Geochem. 2004, 35, 615–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, H.U.; Jüntgen, H. Some measurements of the 12C/13C ratio in methane or ethane desorbed from hard coal or released by pyrolysis. In Advances in Organic Geochemistry 1971, Proceedings of the 5th International Congress on Organic Geochemistry, Hannover, Germany, 7–10 September 1971; Gärtner, H.R., Wehner, H., Eds.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1972; pp. 639–646. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich, H.U.; Jüntgen, H. Aussagen zum 13C/12C-Verhältnis des bei der Inkohlung gebildeten Methans aufgrund von Pyrolyse-Versuchen. Erdöl Kohle-Erdgas Petrochem. 1973, 26, 636–639. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.W.; Rigby, D.; Gould, K.W.; Hart, G.; Hargraves, A.J. An isotopic study of hydrocarbon generation processes. Org. Geochem. 1985, 8, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, K.W.; Hargraves, A.J.; Smith, J.W. Variation in the composition of seam gases issuing from coal. Bull. Aust. Inst. Min. Metall. 1987, 292, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Hosgörmez, H.; Yalcin, M.N.; Cramer, B.; Gerling, P.; Faber, E.; Schäfer, R.G.; Mann, U. Isotopic and molecular composition of coal-bed gas in the Amasre region (Zonguldak basin–Western Black Sea). Org. Geochem. 2002, 33, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strąpoć, D.; Mastalerz, M.; Eble, C.; Schimmelmann, A. Characterization of the origin of coalbed gases in southeastern Illinois Basin by compound-specific carbon and hydrogen stable isotope ratios. Org. Geochem. 2007, 38, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strąpoć, D.; Mastalerz, M.; Schimmelmann, A.; Drobniak, A.; Hedges, S. Variability of geochemical properties in a microbially dominated coalbed gas system from the eastern margin of the Illinois Basin, USA. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2008, 76, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strąpoć, D.; Picardal, F.W.; Turich, C.; Schaperdoth, I.; Macalady, J.L.; Lipp, J.S.; Lin, Y.; Ertefai, T.F.; Schubotz, F.; Hinrichs, K.; et al. Methane-producing microbial community in a coal bed of the Illinois Basin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2424–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Augenstein, W. Applied gas chromatography coupled to isotope ratio mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. 1999, 842, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, M. Stable Isotope Systematics of Coalbed Methane. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Victoria, Victoria, BC, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Coplen, T.B. Guidelines and recommended terms for expression of stable-isotope-ratio and gas-ratio measurement results. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectorm. 2011, 25, 2538–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, M.; Strąpoć, D.; Lis, G.P.; Sauer, P.; Fong, J.; Schimmelmann, A.; Pratt, L.M. Versatile inlet system for on-line compound-specific δD and δ13C gas chromatography–oxidation/reduction–isotope ratio mass spectrometry analysis of gaseous mixtures. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectorm. 2007, 21, 2269–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemann, M.; Clarke, P.R.; Cornelius, C.T.; Ryan, B.; Whiticar, M.J. Gas origin of the Blackhawk formation, Castlegate coalbed methane field, Utah. In Proceedings of the Rocky Mountain Section AAPG Annual Meeting, Jackson, WY, USA, 24–26 September 2005; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, J.M. Generation of gas and oil from coal and other terrestrial organic matter. Org. Geochem. 1991, 17, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jüntgen, H.; Karweil, J. Gasbildung und gasspeicherung in steinkohlenflözen. Part 1. gasbildung. Erdöl Kohle-Erdgas Petrochem. 1966, 19, 251–258. [Google Scholar]
- Jüntgen, H.; Klein, J. Entstehung von Erdgas aus kohligen Sedimenten: Erdol and Kohle. Erdgas Petrochem. Erganz. 1975, 1, 52–68. [Google Scholar]
- Das, B.M.; Nikols, D.J.; Das, Z.U.; Hucka, V.J. Factors affecting rate and total volume of methane desorbed from coalbeds. In Coalbed Methane of Western North America-Guidebook for the Rocky Mountain Association of Geologists Fall Conference and Field Trip; Schwochow, S.D., Murray, D.K., Fahy, M.F., Eds.; Rocky Mountain Association of Geologists: Denver, CO, USA, 1991; pp. 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, R.M. Coalbed methane: From hazard to resource. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1998, 35, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.W.; Pallasser, R.J. Microbial origin of Australian coalbed methane. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 1996, 80, 891–897. [Google Scholar]
- Aravena, R.; Harrison, S.M.; Barker, J.F.; Abercombie, H.; Rudolph, D. Origin of methane in the Elk Valley coalfield, southeastern British Columbia, Canada. Chem. Geol. 2003, 195, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, M.M.; Stalker, L.; Sherwood, N.; Saghafi, A.; Wold, M.; Barclay, S.; Choudhury, J.; Barker, W.; Wang, I. Bio-enhancement of coalbed methane resources in the southern Sydney Basin. APPEA J. 2003, 43, 595–610. [Google Scholar]
- Pashin, J.C. Hydrodynamics of coalbed methane reservoirs in the Black Warrior Basin: Key to understanding reservoir performance and environmental issues. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 2257–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strąpoć, D.; Mastalerz, M.; Dawson, K.; Macalady, J.; Callaghan, A.V.; Wawrik, B.; Turich, C.; Ashby, M. Biogeochemistry of microbial coal-bed methane. Annu. Earth Planet. Rev. 2011, 39, 617–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, R.M.; Rice, C.A.; Stricker, G.D.; Warden, A.; Ellis, M.S. Methanogenic pathways of coal-bed gas in the Powder River Basin, United States: The geologic factor. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2008, 76, 52–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.R. Improving coal gas recovery with microbially enhanced coalbed methane. In Coalbed Methane: Scientific, Environmental and Economic Evaluation; Mastalerz, M., Glikson, M., Golding, S.D., Eds.; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 89–110. ISBN 9780792356981. [Google Scholar]
- Budwill, K.; Beaton, A.; Bustin, M.; Muehlenbachs, K.; Gunter, W.D. Methanogenic activity on coal and sequestered CO2 for enhanced coalbed methane recovery. In Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies, Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies, Kyoto, Japan, 1–4 October 2002; Gale, J., Kaya, Y., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 697–702. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Mastalerz, M.; Schimmelmann, A. The origin of coalbed methane. In Coal Bed Methane-from Prospect to Pipeline; Thakur, P., Schatzel, S., Aminian, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 7–29. ISBN 9780128008805. [Google Scholar]
- Ashby, M.; Wood, L.; Lidstrom, U.; Clarke, C.; Gould, A.; Strąpoć, D.; Lambo, A.J.; Huizinga, B.J. Compositions and Methods for Identifying and Modifying Carbonaceous Compositions. U.S. Patent 9,206,682 B2, 9 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liang, Y.; Harpalani, S. Optimization of methane production from bituminous coal through biogasification. Appl. Energy 2016, 183, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastalerz, M.; Drobniak, A.; Schimmelmann, A. Characteristics of microbial coalbed gas during production; example from Pennsylvanian coals in Indiana, USA. Geosciences 2017, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuex, A.N. Experimental evidence against an appreciable isotopic fractionation of methane during migration. In Advances in Organic Geochemistry 1979, Proceedings of the 9th International Meeting on Organic Geochemistry, Newcastle-Upon-Tyne, UK, September 1979; Douglas, A.G., Maxwell, J.R., Eds.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1980; pp. 725–732. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.M.; Williams, F.L. Diffusion models for gas production from coals: Application to methane content determination. Fuel 1984, 63, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, V.S.; Syngayevskiy, Ye. D. The isotopic effect during sorption processes. Geokhimiya 1971, 5, 615–619. [Google Scholar]
- Faber, E. Zur Isotopengeochemie gasförmiger Kohlenwasserstoffe. Erdöl Erdgas und Kohle 1987, 103, 210–218. [Google Scholar]
- Ettinger, I.; Eremin, I.; Zimakov, B.; Yanovska, M. Natural factors influencing coal sorption properties. I. Petrography and sorption properties of coals. Fuel 1966, 45, 267. [Google Scholar]
- Sevenster, P.G. Diffusion of gases through coal. Fuel 1959, 38, 403–418. [Google Scholar]
- Thimons, E.D.; Kissell, F.N. Diffusion of methane through coal. Fuel 1973, 52, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airey, E.M. Gas emission from broken coal. An experimental and theoretical investigation. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 1968, 5, 475–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, C.R.; Bustin, R.M. The effect of pore structure and gas pressure upon the transport properties of coal: A laboratory and modeling study. 2. Adsorption rate modeling. Fuel 1999, 78, 1345–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Lv, W.; Dickerson, J.H. Gas diffusion mechanisms and models. In Gas Transport in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Bustin, M. Controls of coal fabric and coalbed gas production and compositional shift in both field production and canister desorption tests. SPE J. 2006, 11, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leythäuser, D.; Schäfer, R.G.; Yükler, A. Diffusion of light hydrocarbons through near-surface rocks. Nature 1980, 284, 522–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroos, B.M. Diffusion of C1 to C5 hydrocarbons in water-saturated sedimentary rocks. Erdöl Kohle-Erdgas Petrochem. 1986, 39, 399–402. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, J.R.; Johnson, P.; Beamish, B.B. High pressure microbalance sorption studies. In Proceedings of the International Coalbed Methane Symposium, Tuscaloosa, AL, USA, 17–21 May 1993; pp. 187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Laxminarayana, C.; Crosdale, P.J. Role of coal type and rank on methane sorption characteristics of Bowen Basin, Australia coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1999, 40, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, C.R.; Bustin, R.M. Binary gas adsorption/desorption isotherms: Effect of moisture and coal composition upon carbon dioxide selectivity over methane. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2000, 42, 241–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, A.; Gensterblum, Y.; Krooss, B.M. Methane and CO2 sorption and desorption measurements on dry Argonne premium coals: Pure components and mixtures. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2003, 55, 205–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, M.M.; Barclay, S.; Saghafi, A.; Stalker, L.; Wold, M.; Esterle, J.; Sherwood, N. Coal Bed Methane Reservoir Characterization–KP-1 and WG-1, PEL-2, Southern Sydney Basin; CSIRO Petroleum Confidential Report 7; CSIRO: Clayton South, Victoria, Australia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chanton, J.P. The effect of gas transport on the isotope signature of methane in wetlands. Org. Geochem. 2005, 36, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Tang, Y. Isotope fractionation of methane during natural gas flow with coupled diffusion and adsorption/desorption. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 77, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, U.; Gazzarrini, F.; Sironi, G. Carbon isotope composition of individual hydrocarbons from Italian natural gases. Nature 1965, 205, 1303–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernaton, E.; Prinzhofer, A.; Schneider, F. Reconsideration of methane isotope signature as a criterion for the genesis of natural gas: Influence of migration on isotopic signatures. Rev. Inst. Fr. Pét. 1996, 51, 635–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinzhofer, A.; Pernaton, É. Isotopically light methane in natural gas: Bacterial imprint or diffusive fractionation? Chem. Geol. 1997, 142, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Krooss, B.M. Experimental investigation on the carbon isotope fractionation of methane during gas migration by diffusion through sedimentary rocks at elevated temperature and pressure. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 2723–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloemer, S.; Krooss, B.M. Molecular transport of methane, ethane and nitrogen and the influence of diffusion on the chemical and isotopic composition of natural gas accumulations. Geofluids 2004, 4, 81–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S.K.; Golding, S.D.; Baublys, K.A.; Esterle, J.S. Stable isotopic and molecular composition of desorbed coal seam gases from the Walloon Subgroup, eastern Surat Basin, Australia. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 122, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpalani, S.; Schraufnagel, R.A. Measurement of parameters impacting methane recovery from coal seams. Int. J. Min. Geol. Eng. 1990, 8, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. George, J.D.; Barakat, M.A. The change in effective stress associated with shrinkage from gas desorption in coal. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2001, 45, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).