Comparison of PlanetScope and Sentinel-2 Spectral Channels and Their Alignment via Linear Regression for Enhanced Index Derivation
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Questions
1.2. PlanetScope and Sentinel-2: Key Factors
1.3. Research Development
1.4. Literature Review on Prominent Soil and Vegetation Indices Which Benefit Alignment
1.5. Examples of Indirect Relationships Between Indices and Their Use for Revealing Information
1.6. Evaluation of Band Calibration Through RMSE and MAE
2. Materials and Methods
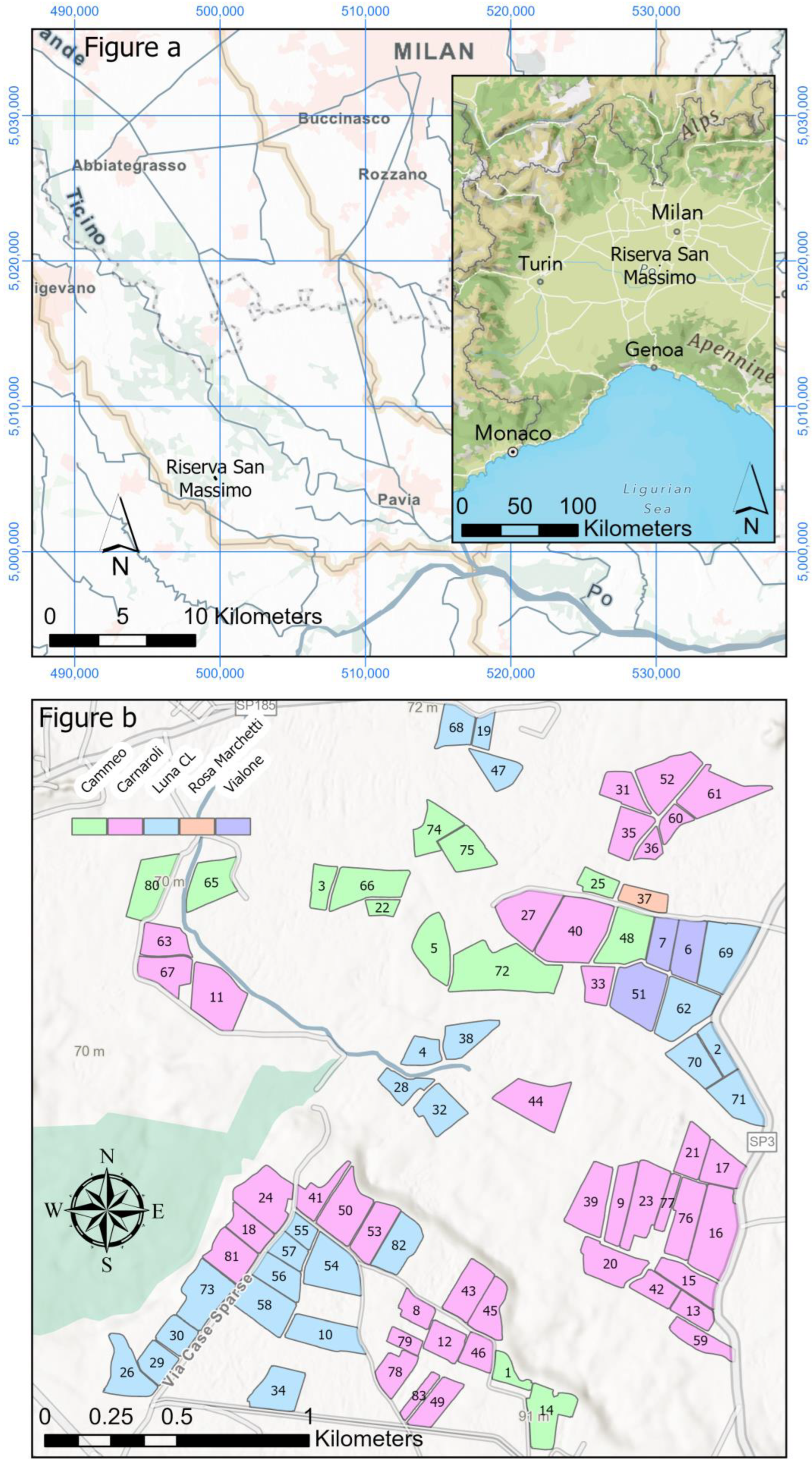
2.1. Riserva San Massimo Test Site
2.2. Variable Rate Application to Precision Farming at “Riserva San Massimo”
2.3. Sentinel-2
2.4. PlanetScope
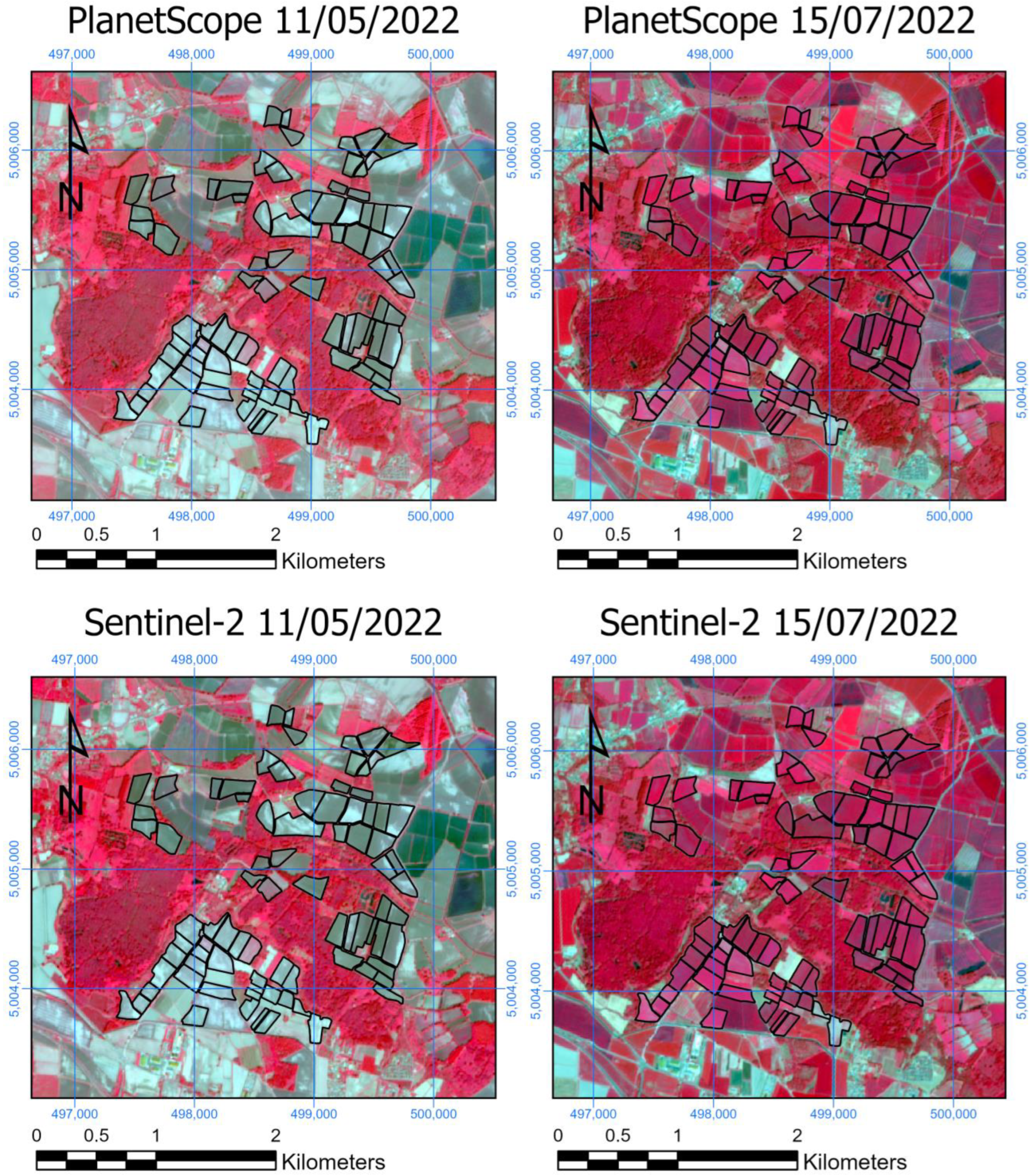
2.5. Choice of Images
- Sentinel-2: B2 (Blue): 492.7 (65) nm; B3 (Green): 559.8 (35) nm; B4 (Red): 664.6 (30) nm. All these bands have 10 m of spatial resolution.
- PlanetScope: Band 2 (Blue): 490 (50) nm; Band 4 (Green): 565 (36) nm; Band 6 (Red): 665 (31) nm. All these bands have 3 m of spatial resolution.
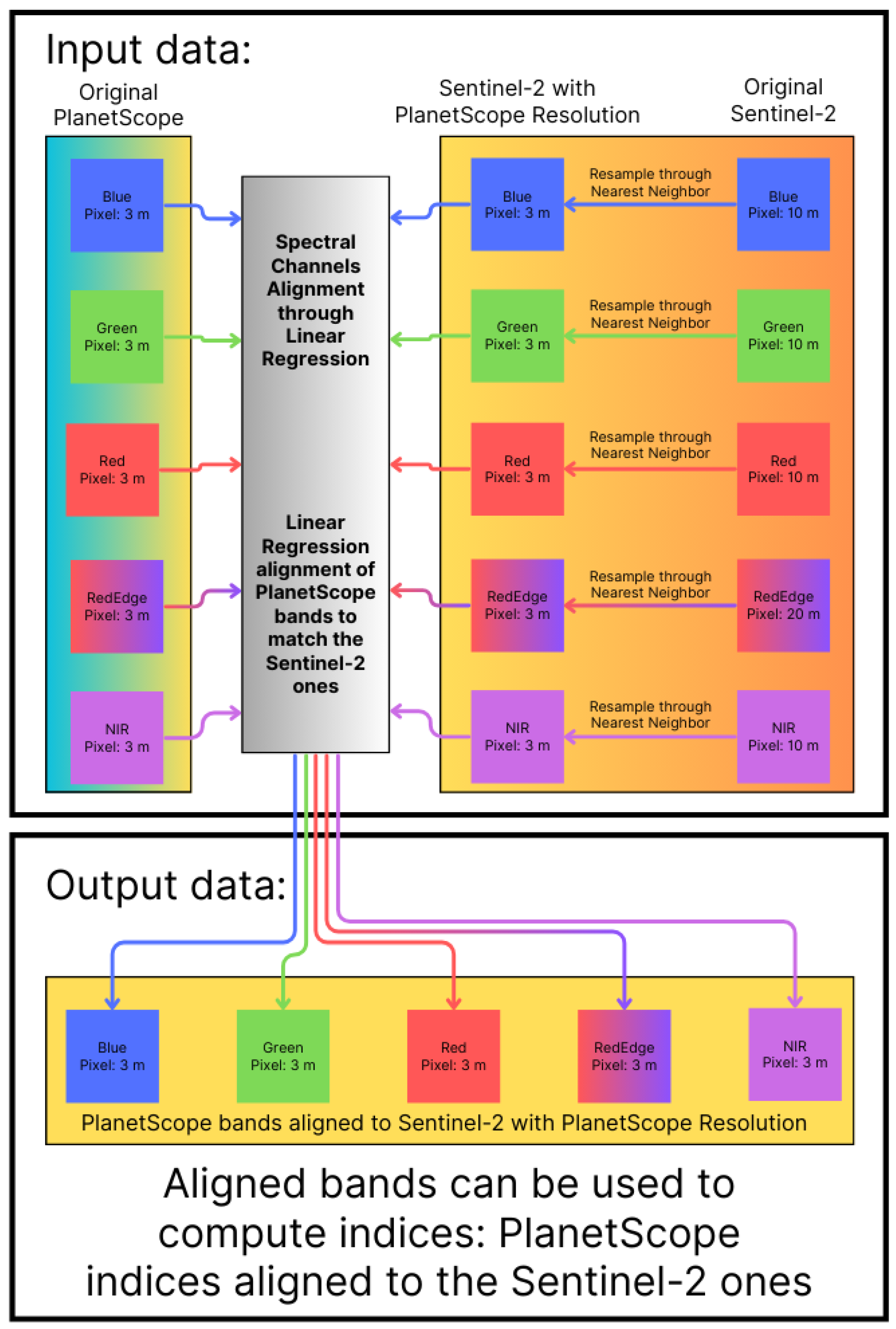
2.6. Band Alignment Through Linear Regression and Nearest Neighbor Sentinel-2 Oversampling
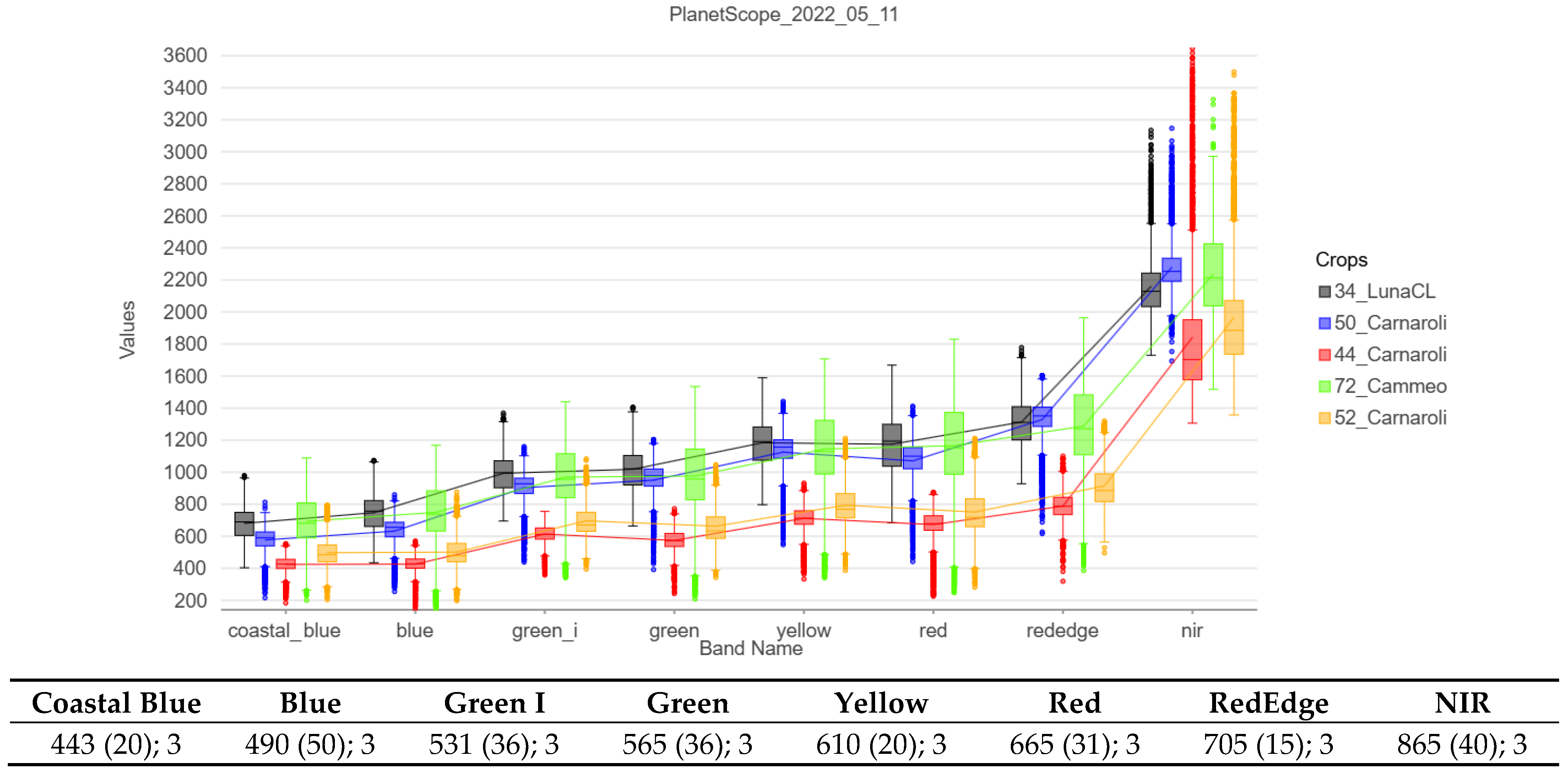
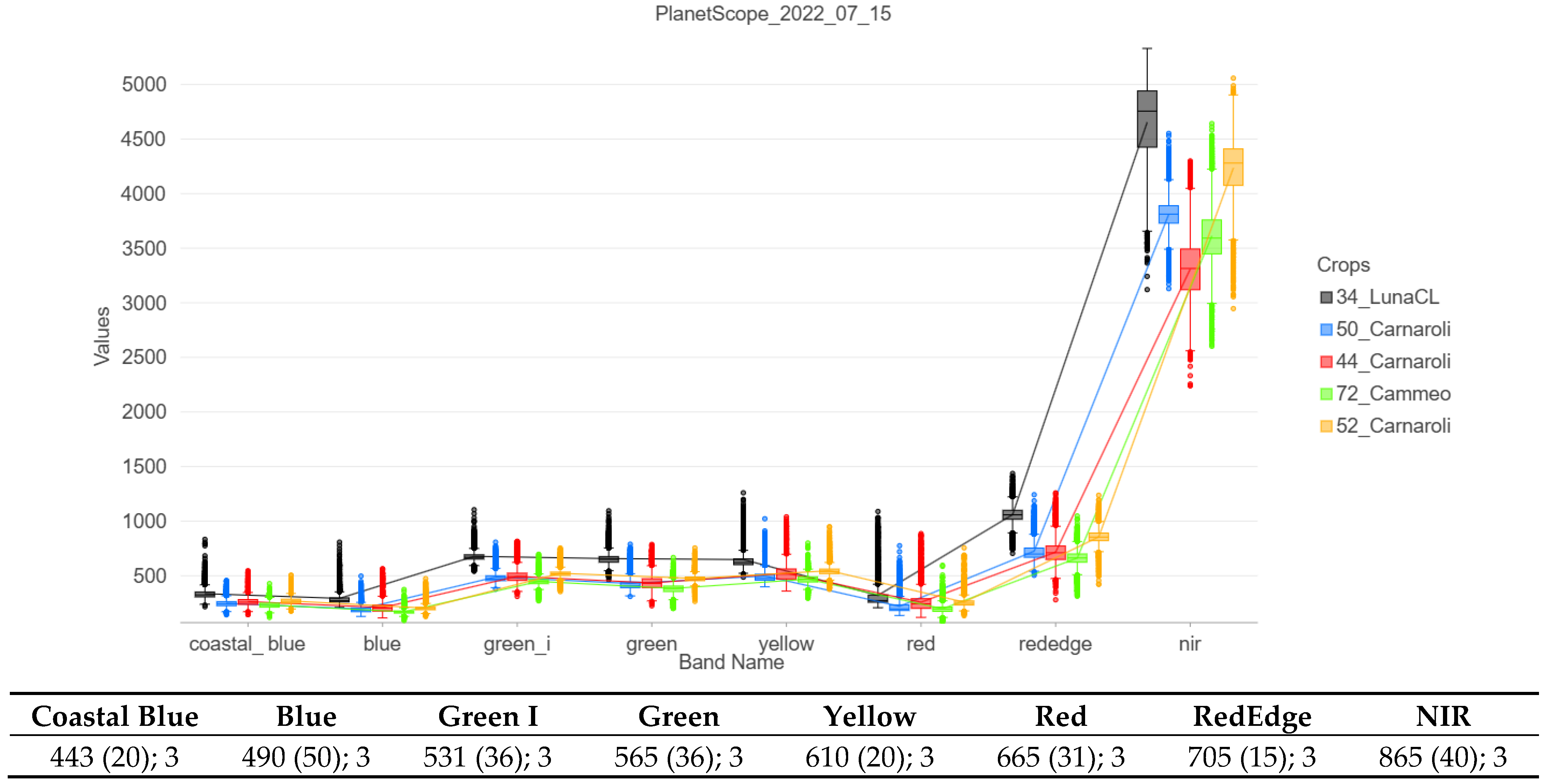
2.7. Spectral Profiles of Original Bands (Before Resampling)
3. Results
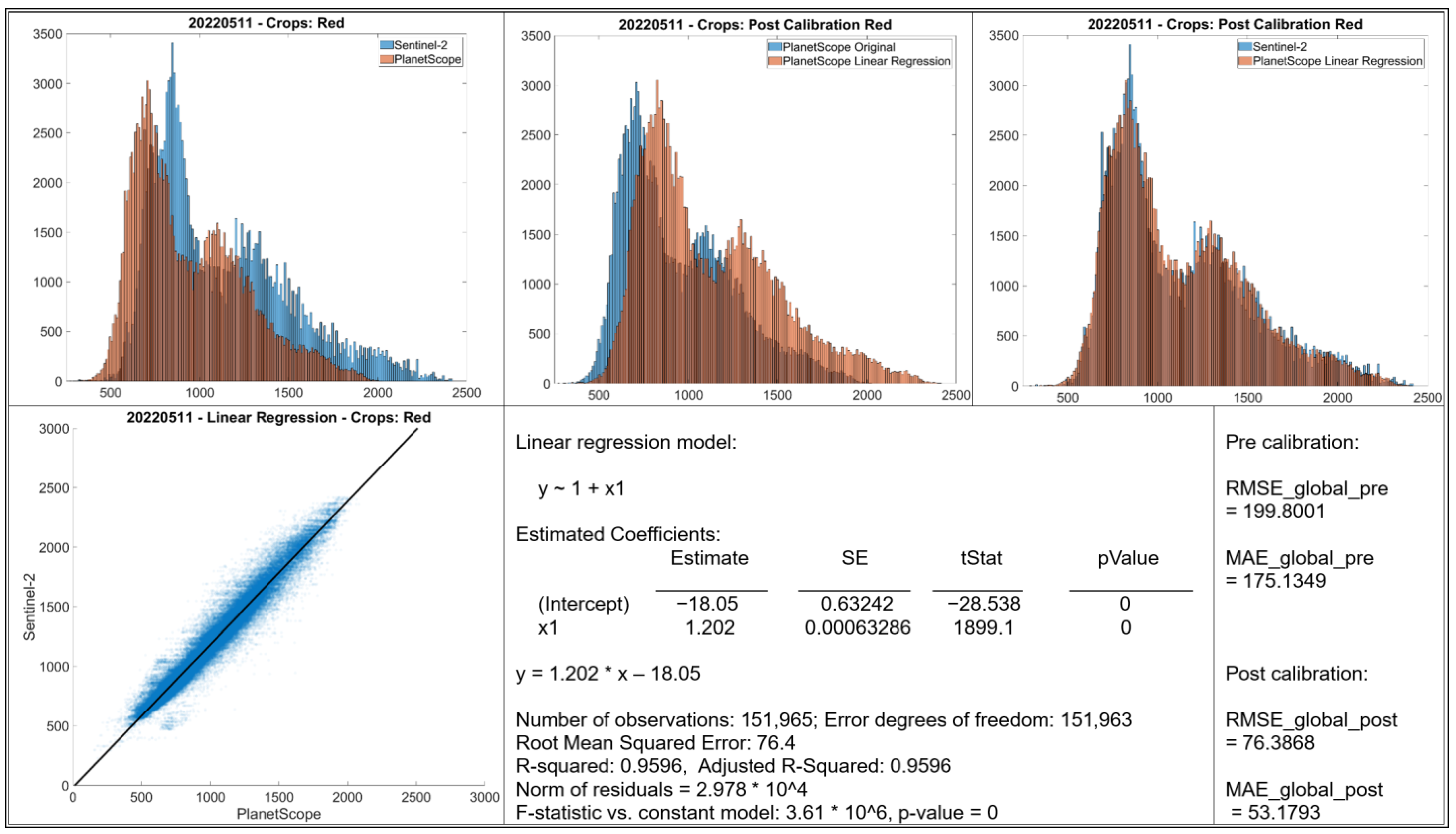
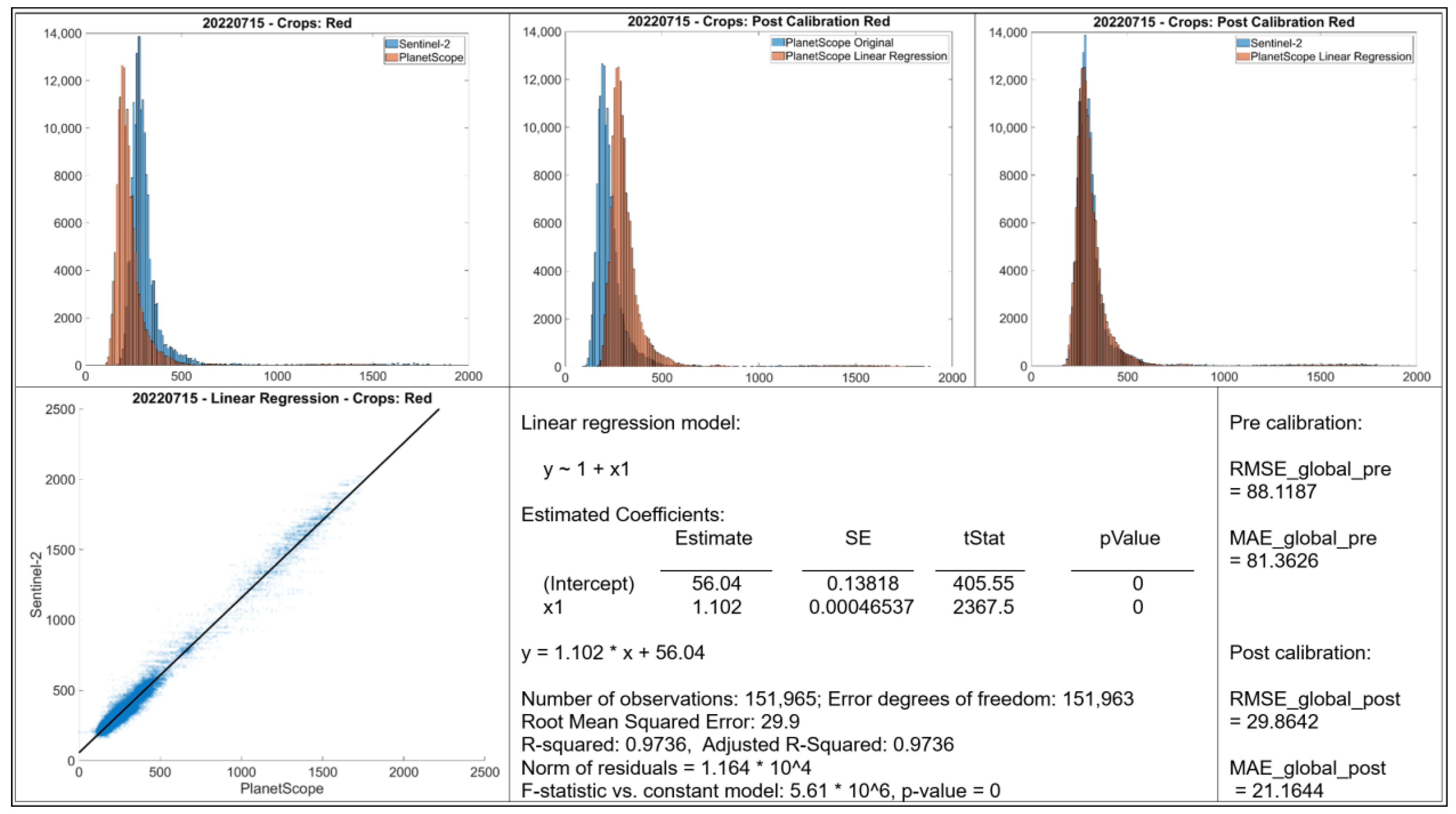
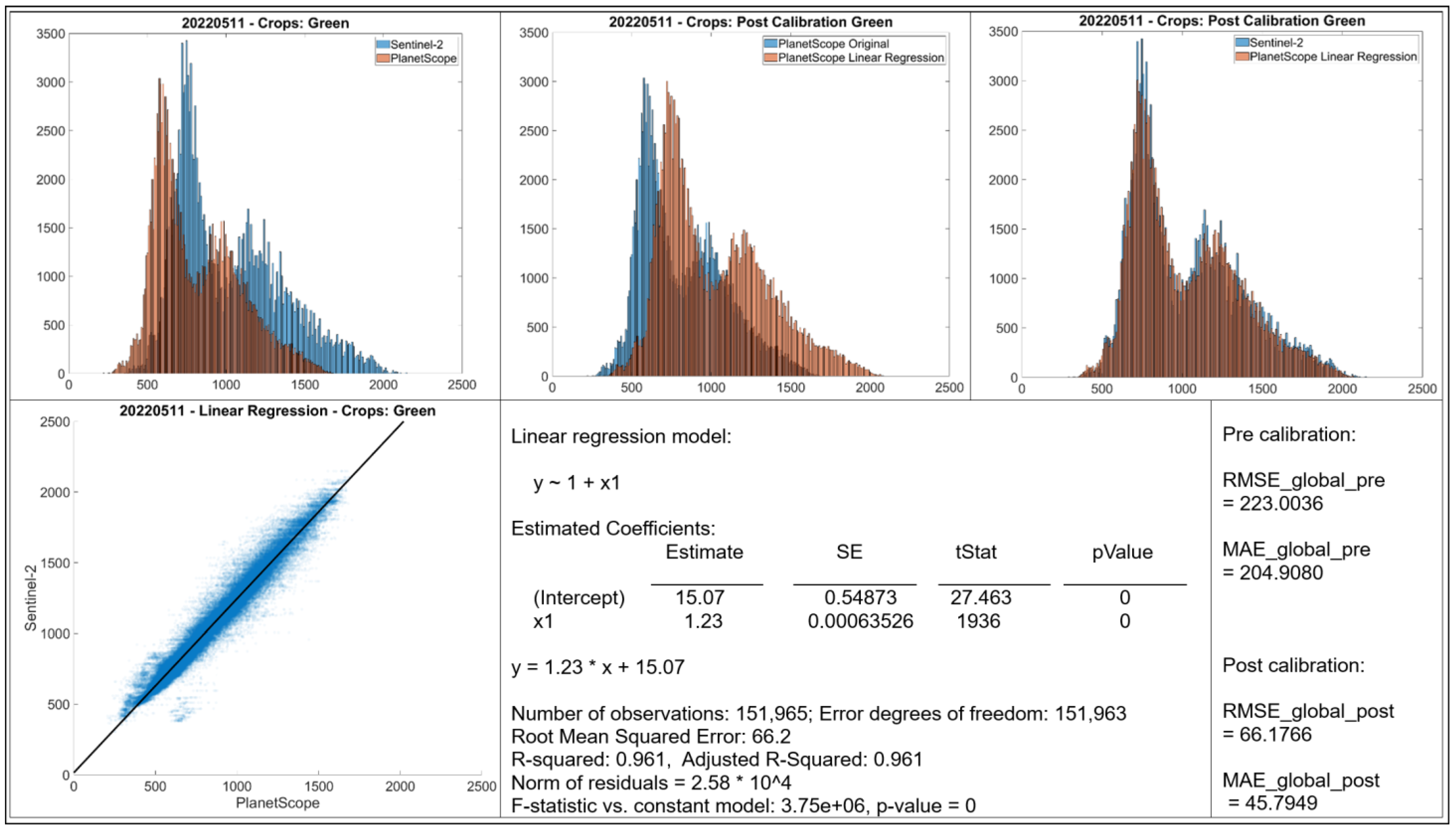
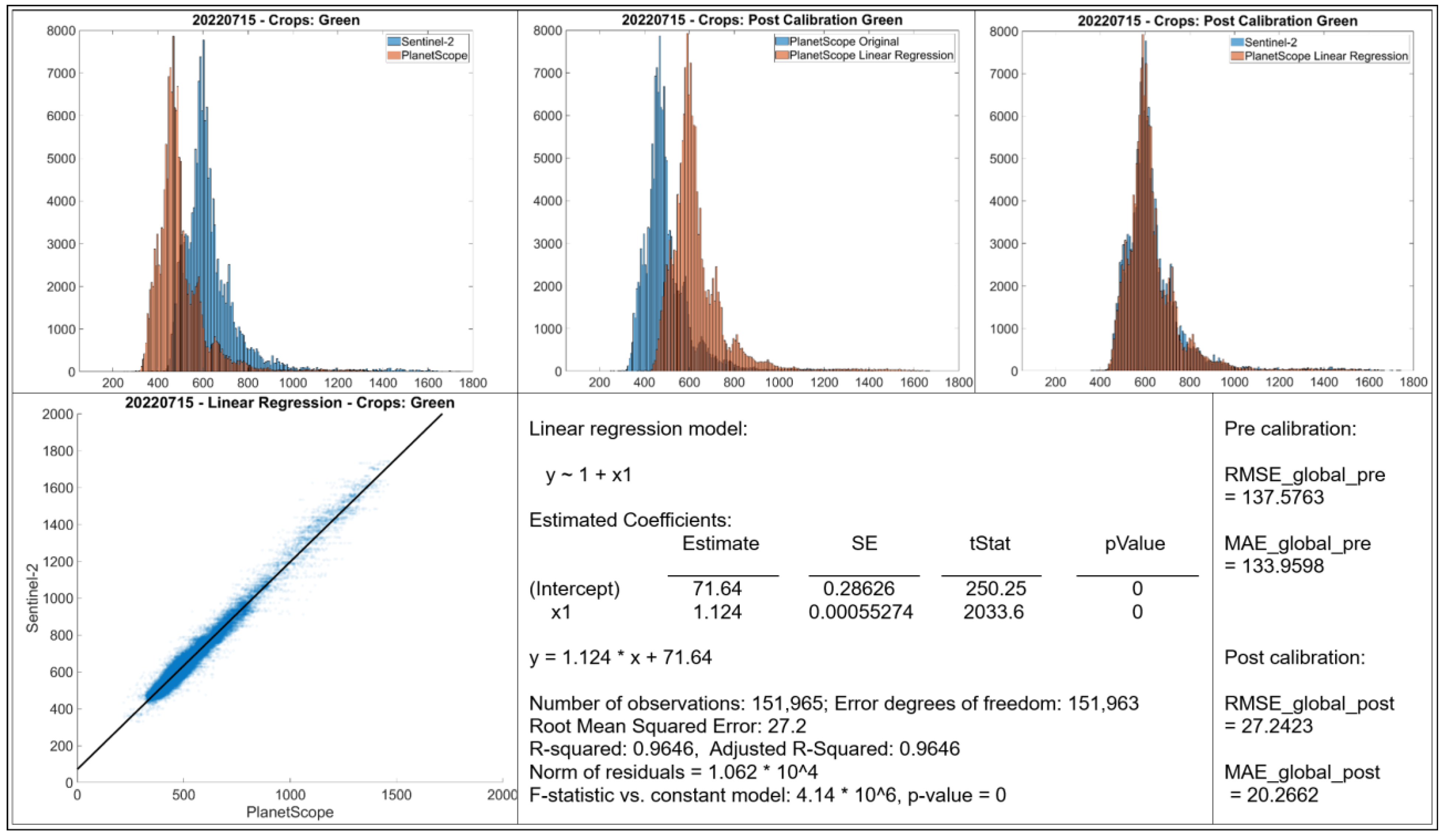
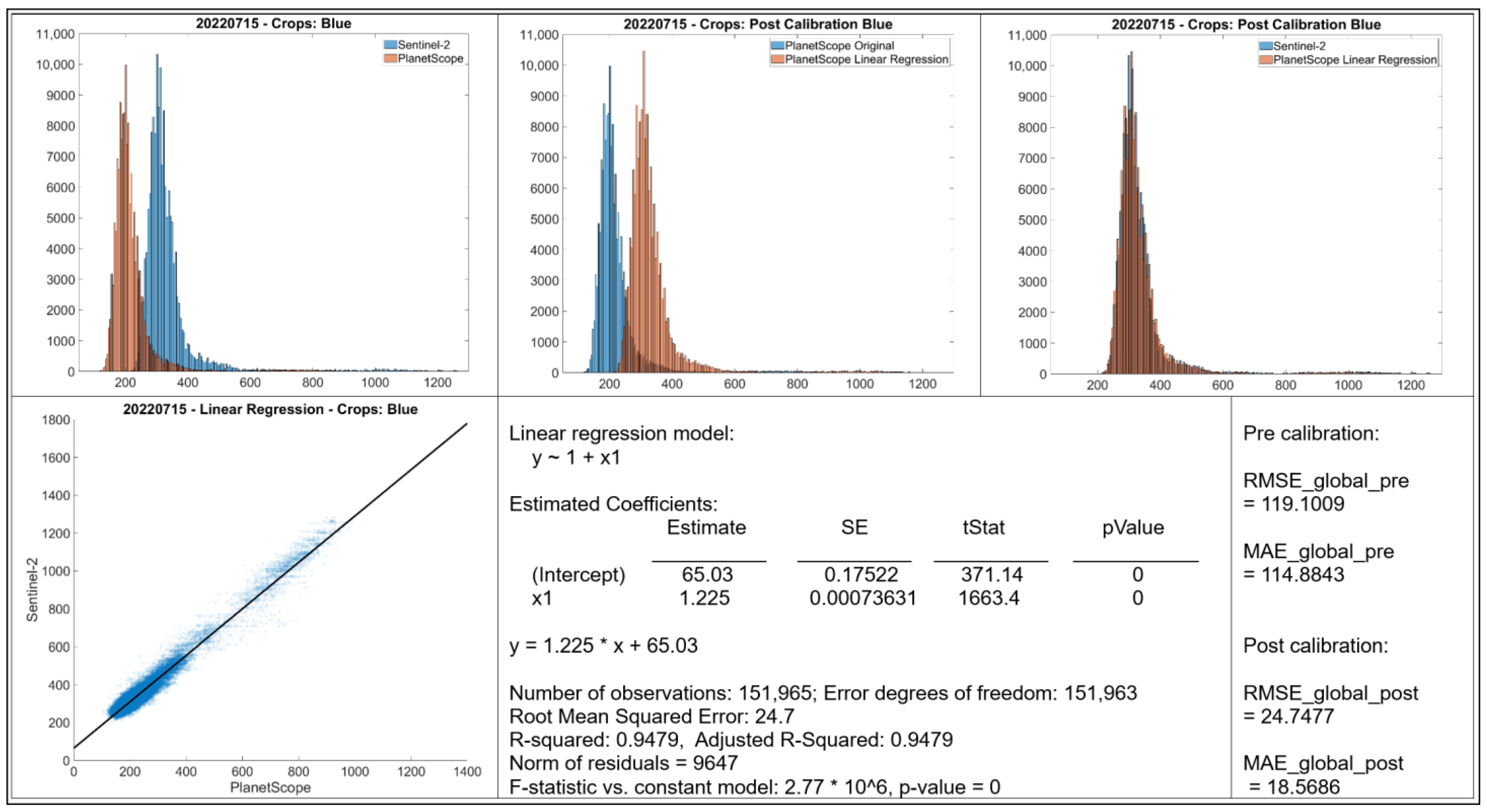
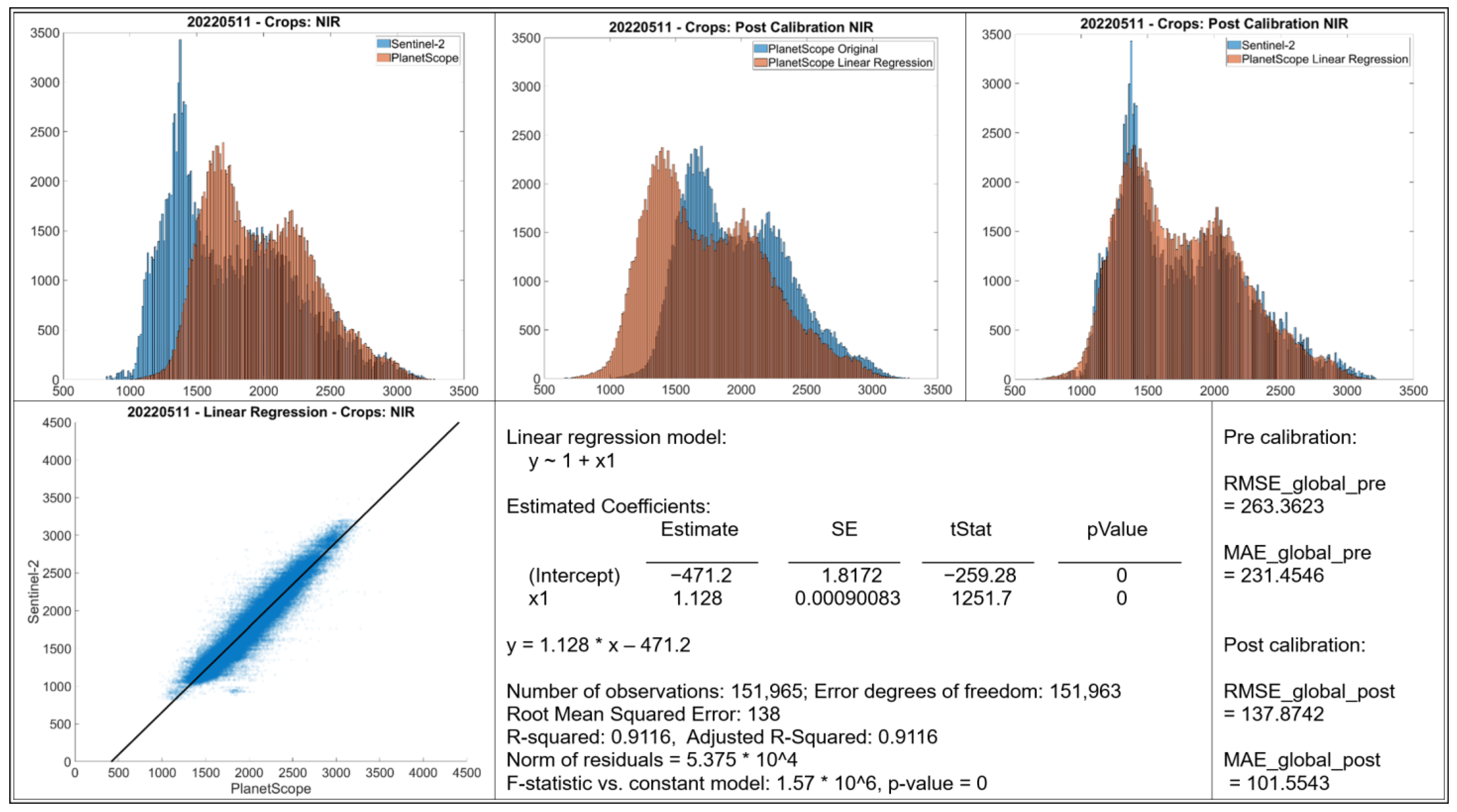
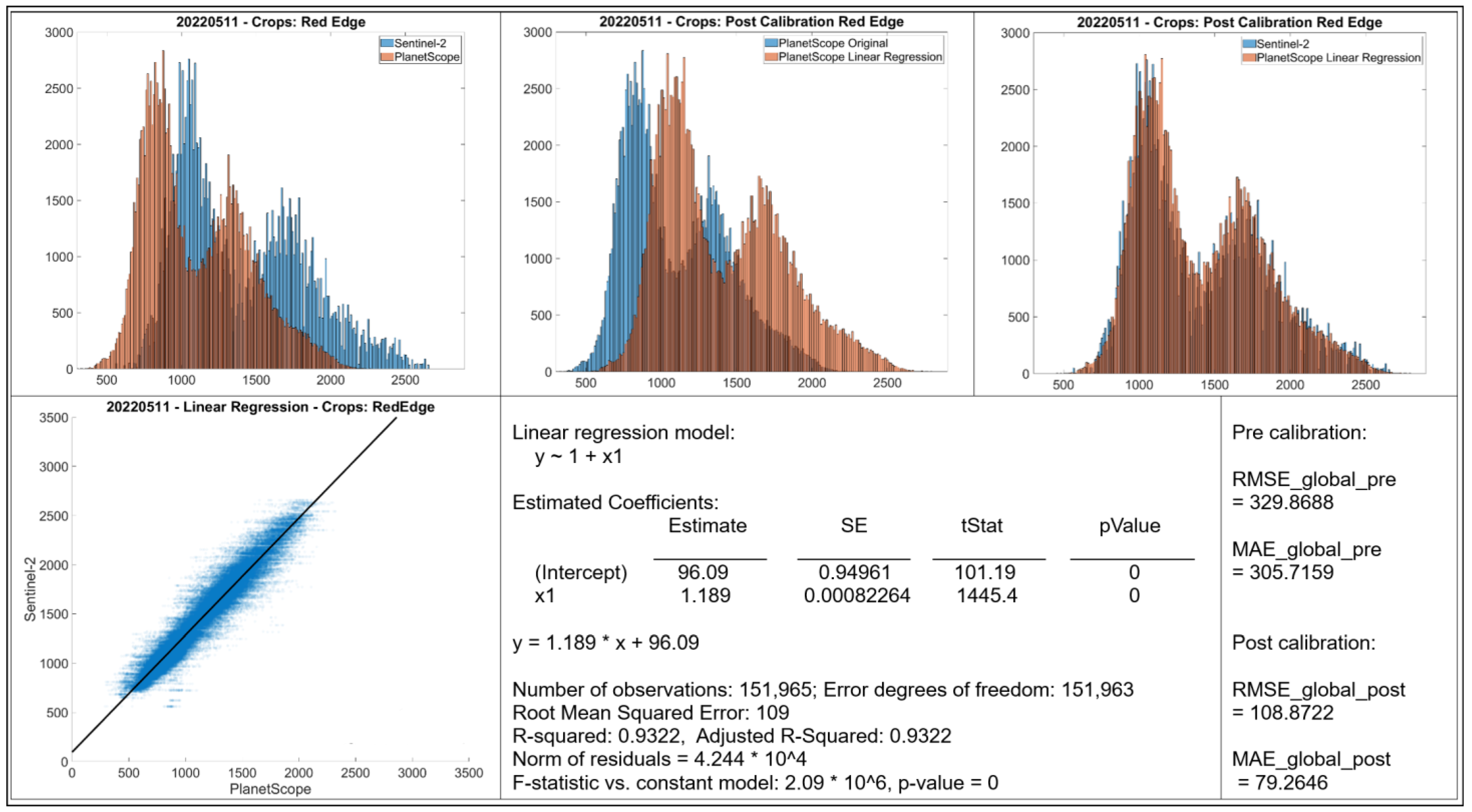
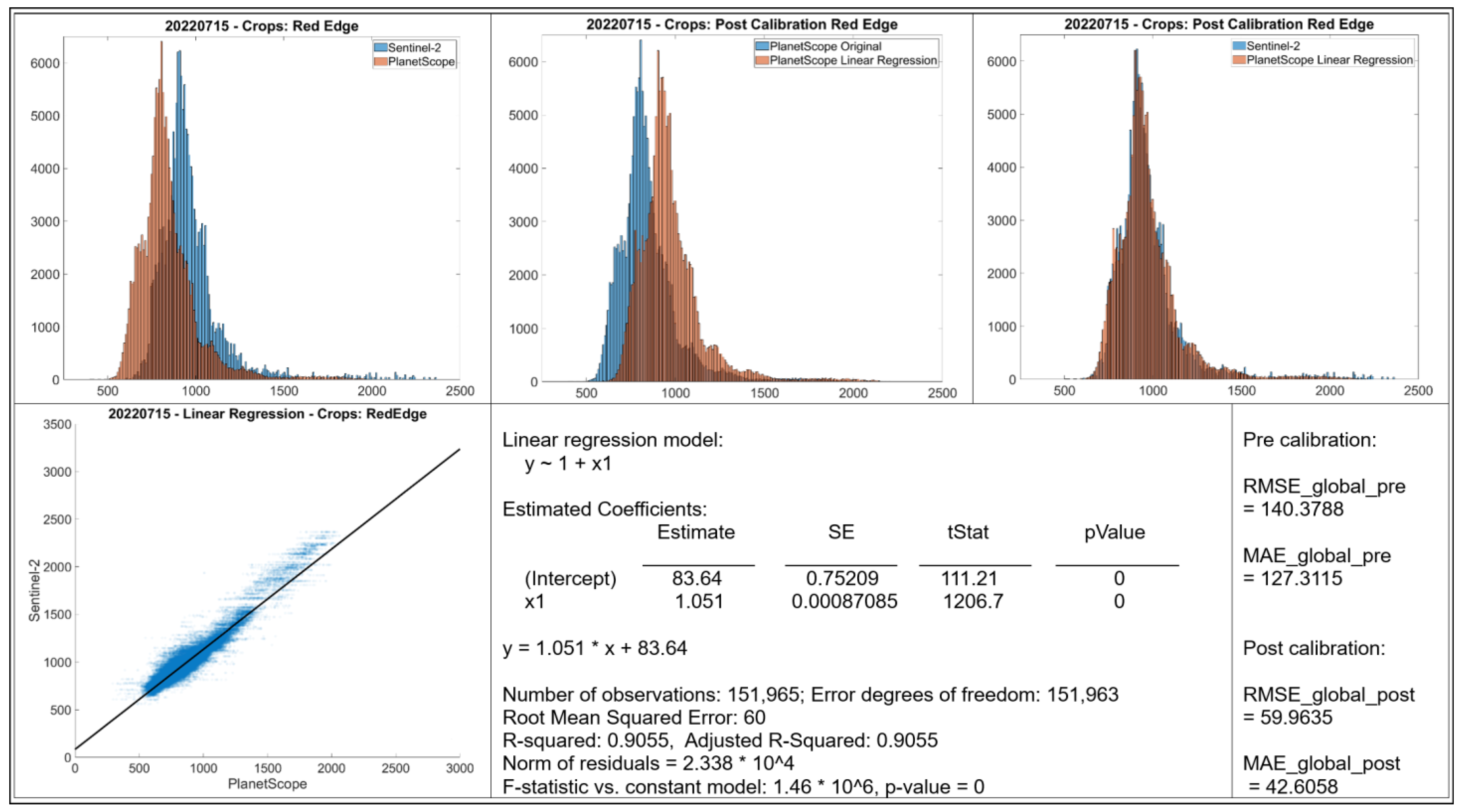
- Histograms: The top row displays histograms of the band values. The leftmost plot displays the original distributions for Sentinel-2 and PlanetScope, showing differences in the range and frequency distribution of values between the two sensors. The middle and rightmost plots present the distributions after applying linear regression-based calibration to the PlanetScope data. In each case, the calibrated PlanetScope distribution is more closely aligned with the Sentinel distribution compared to the original data.
- Scatter Plot: The bottom left plot presents a scatter plot illustrating individual data points of Sentinel-2 band values against original PlanetScope band values. Each case demonstrates a strong linear relationship, with data points clustering along a diagonal trajectory, indicating that a linear model is an appropriate choice for calibration.
- Linear Regression Model: Information about the fitted linear regression model is given, where Y represents the predicted Sentinel-2 value and X represents the original PlanetScope value.
- The RMSE and MAE values before and after linear regression are shown.
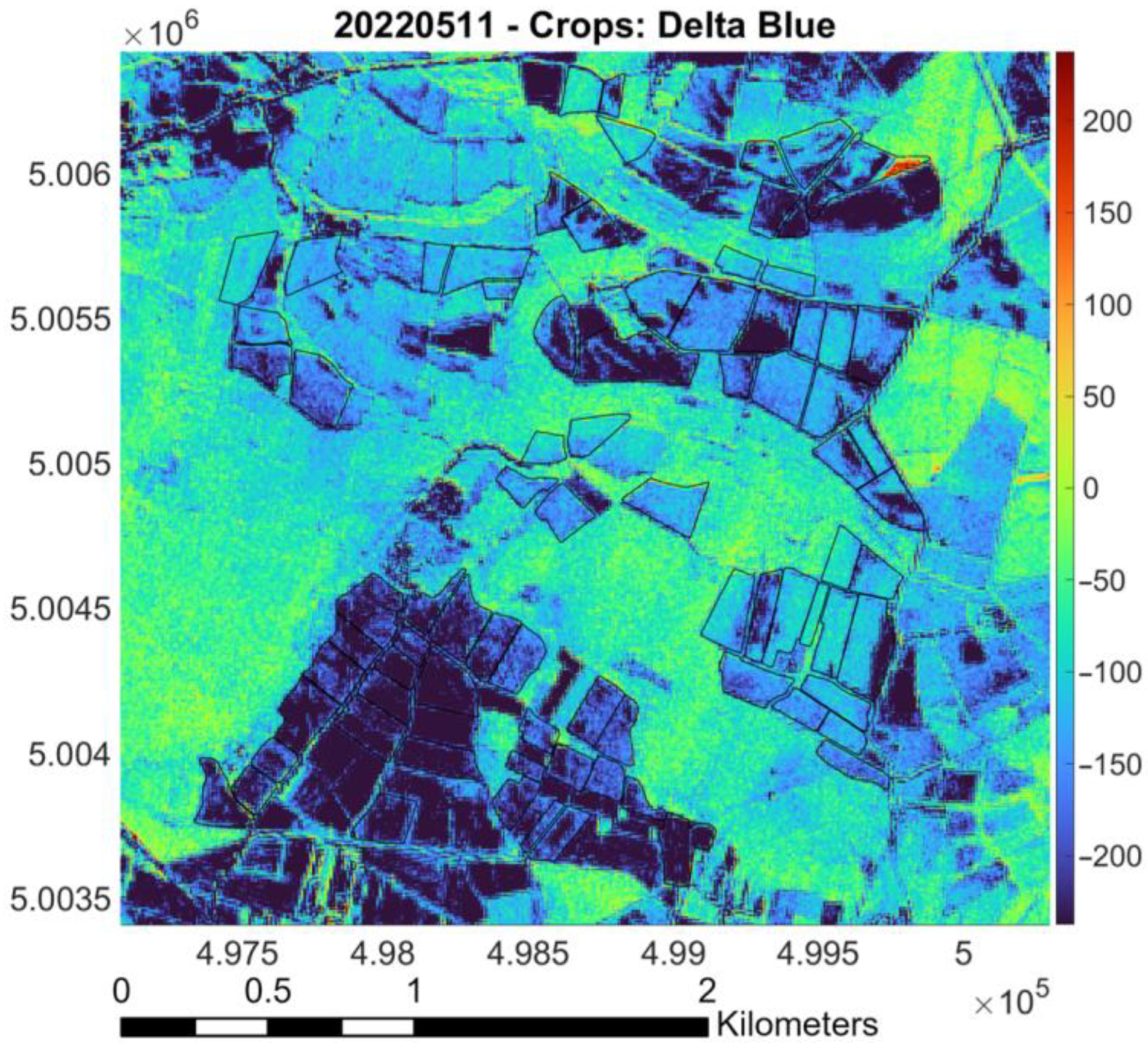
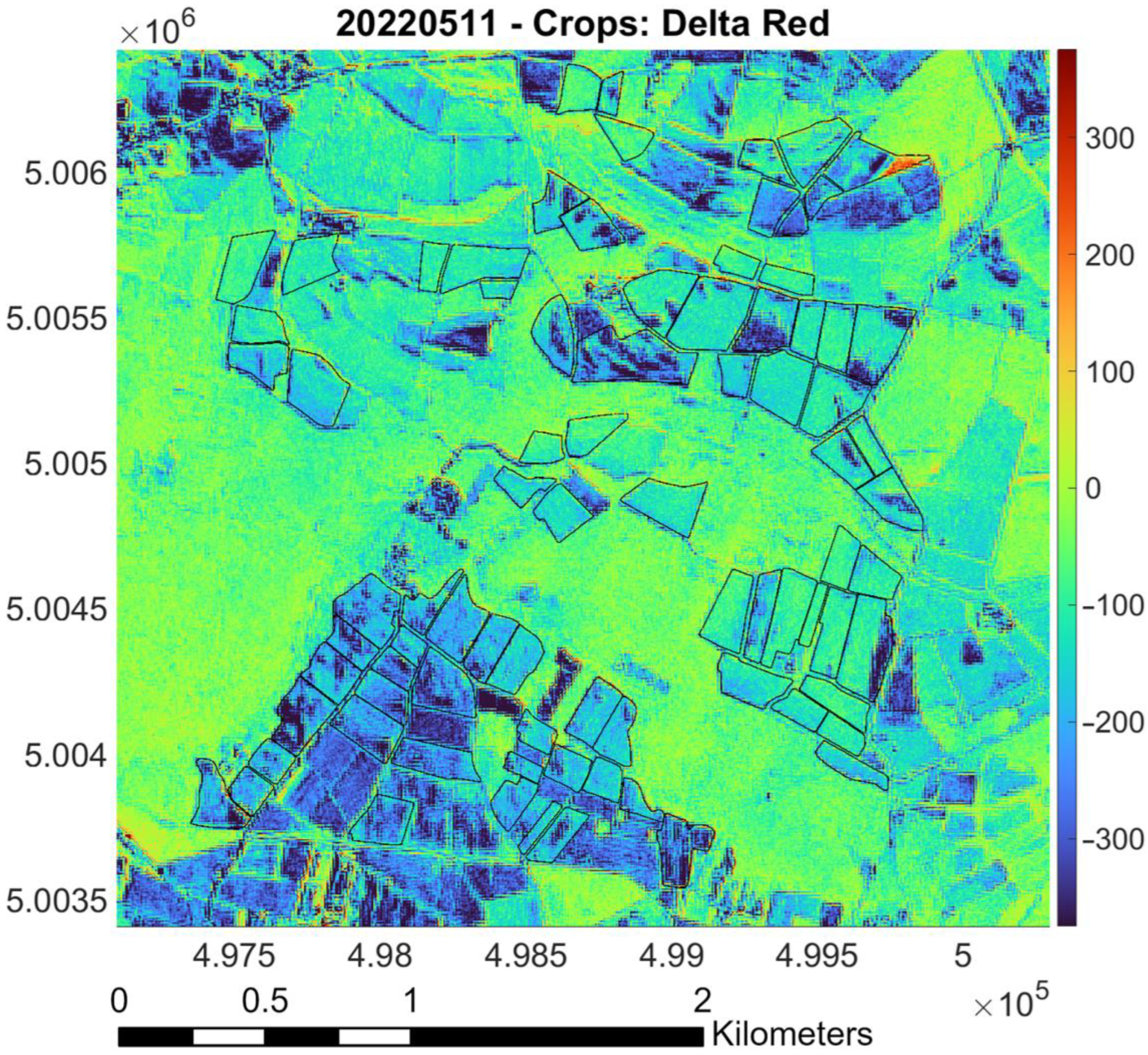
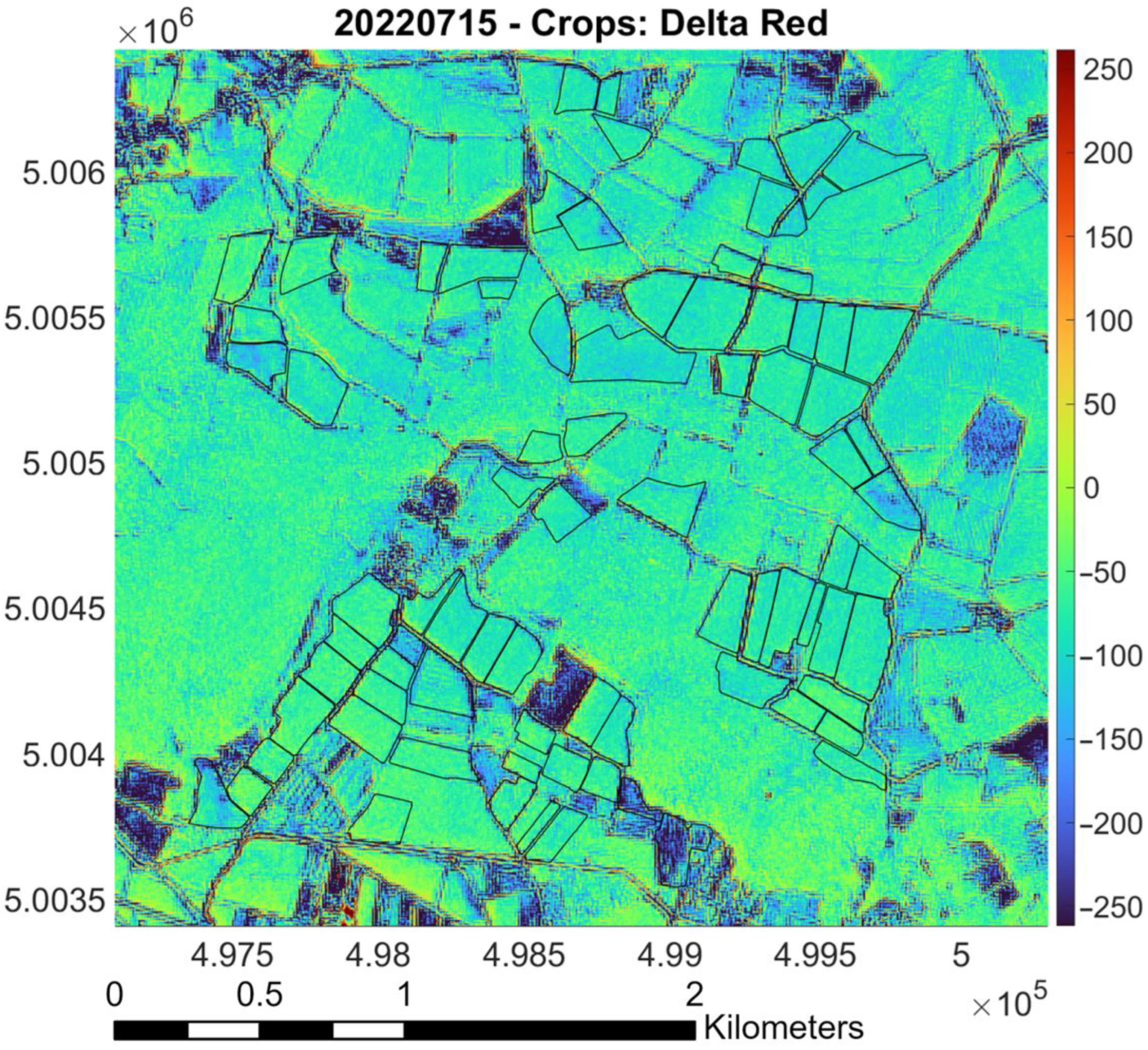
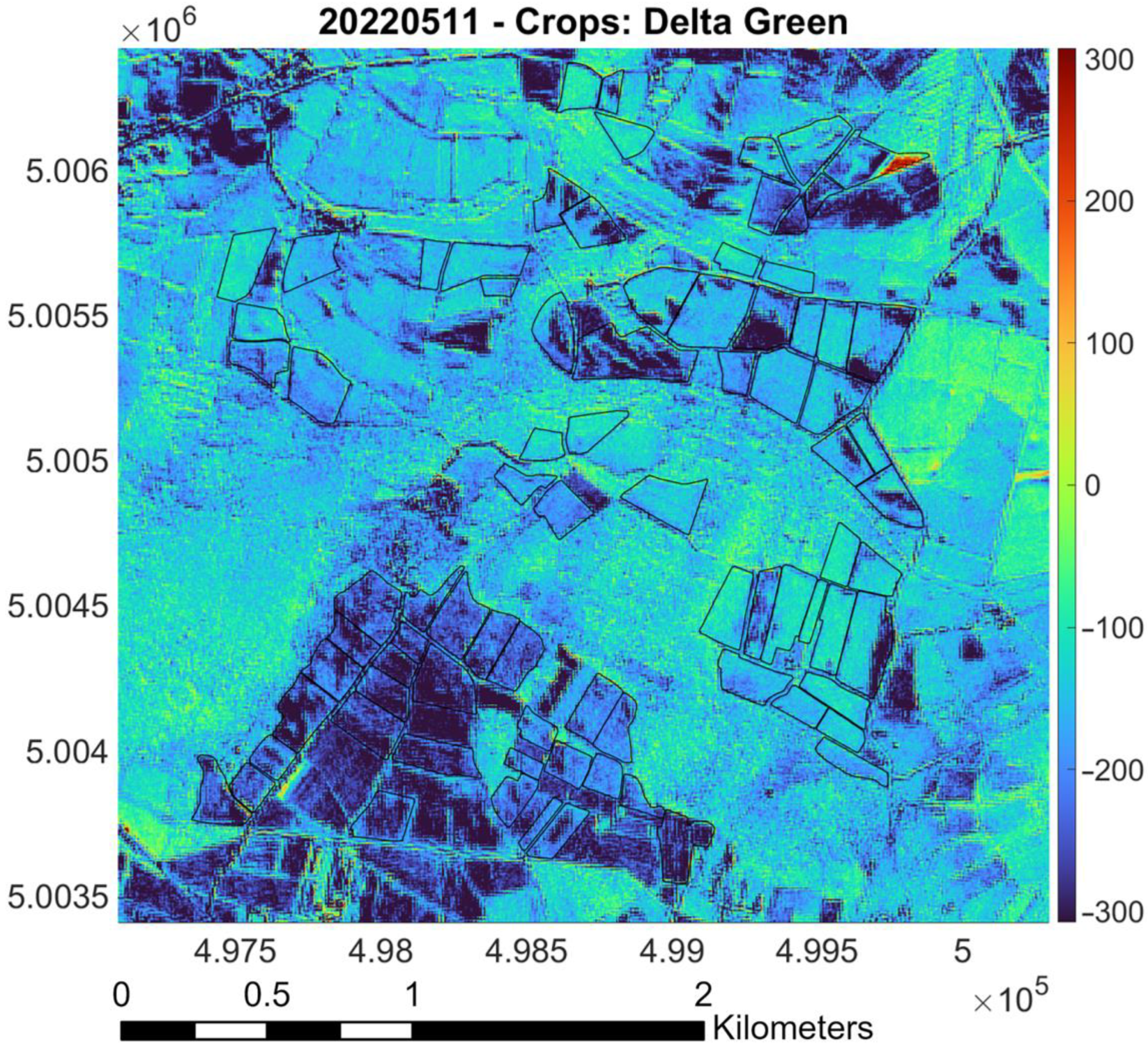
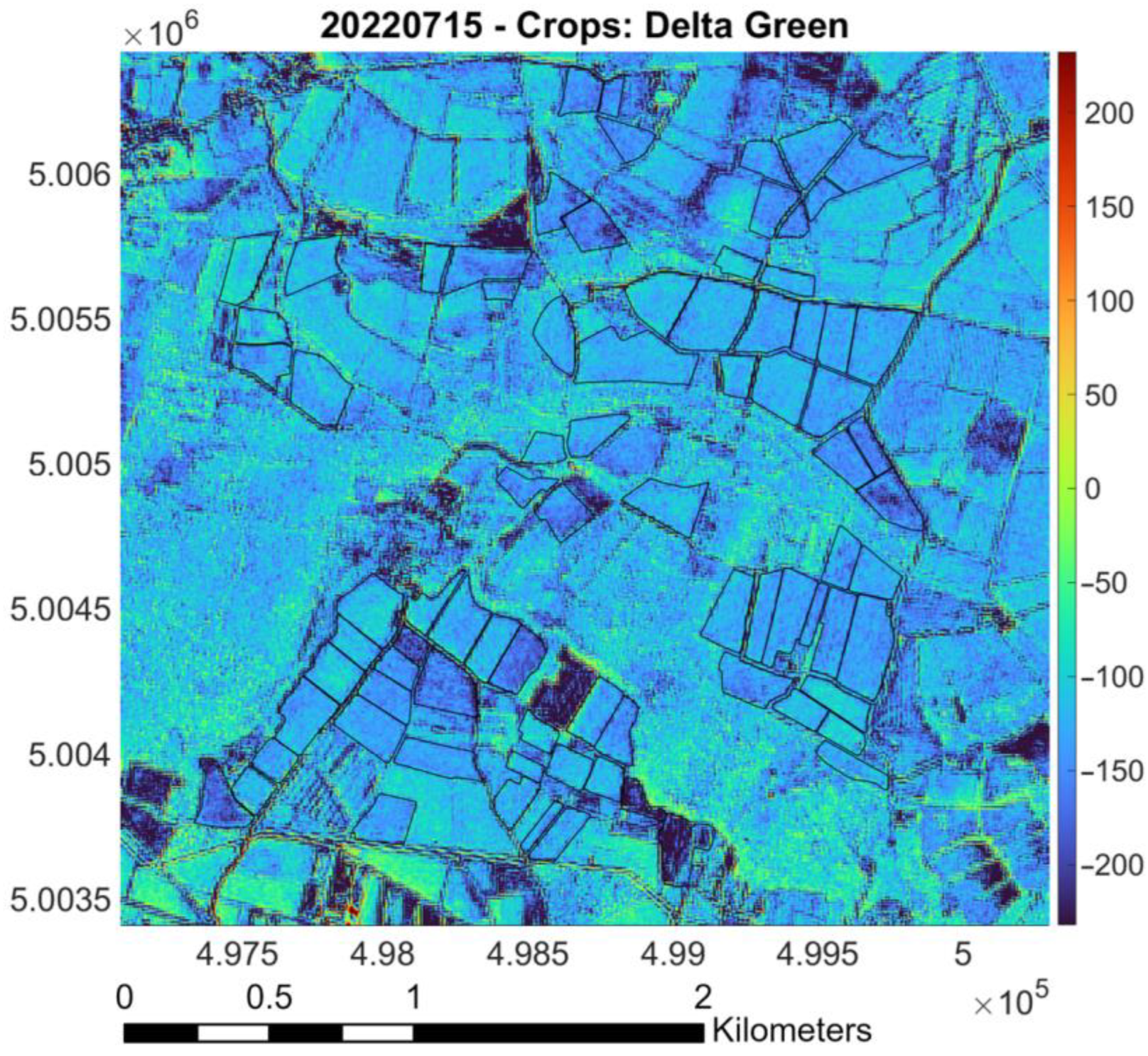
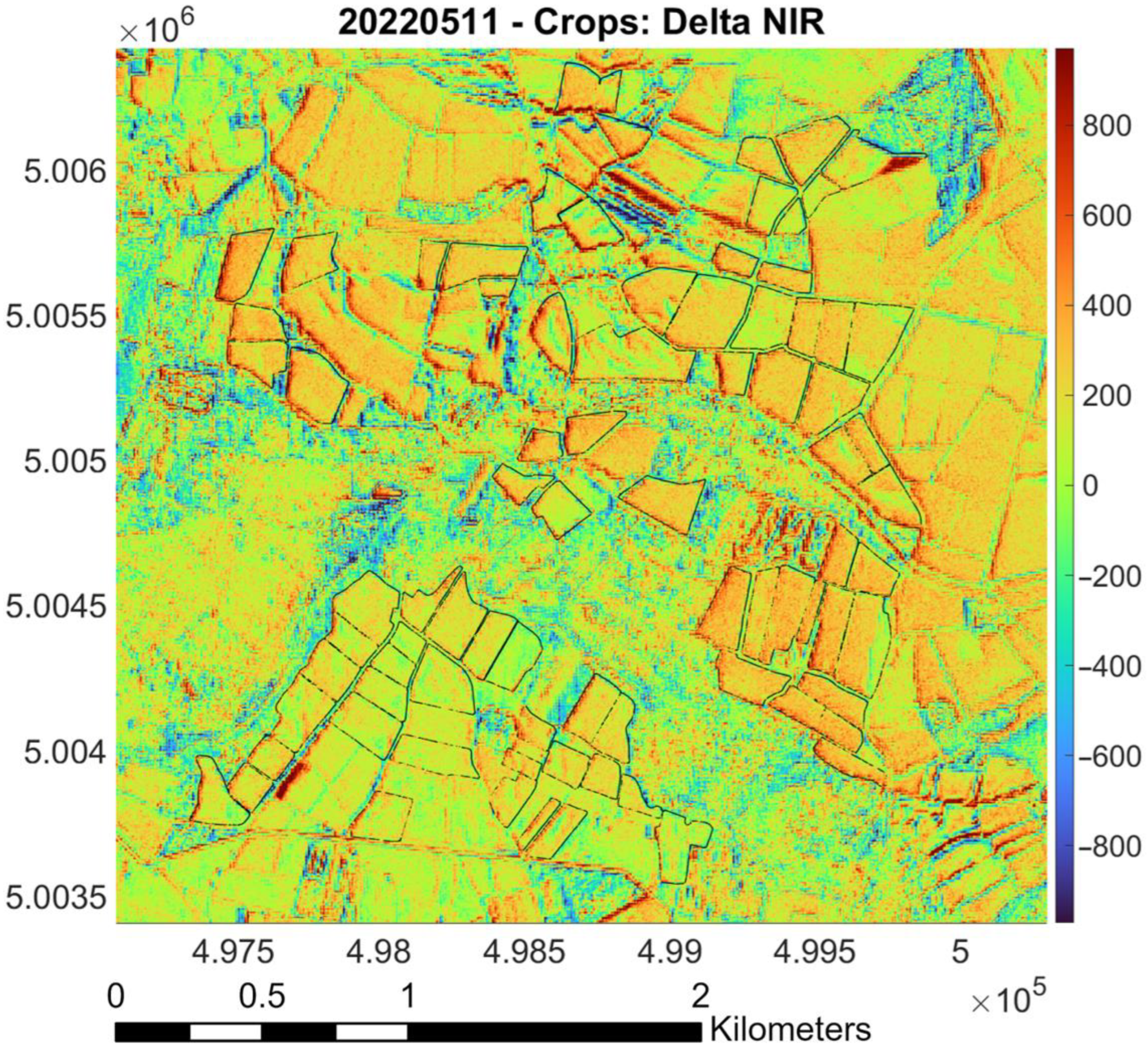
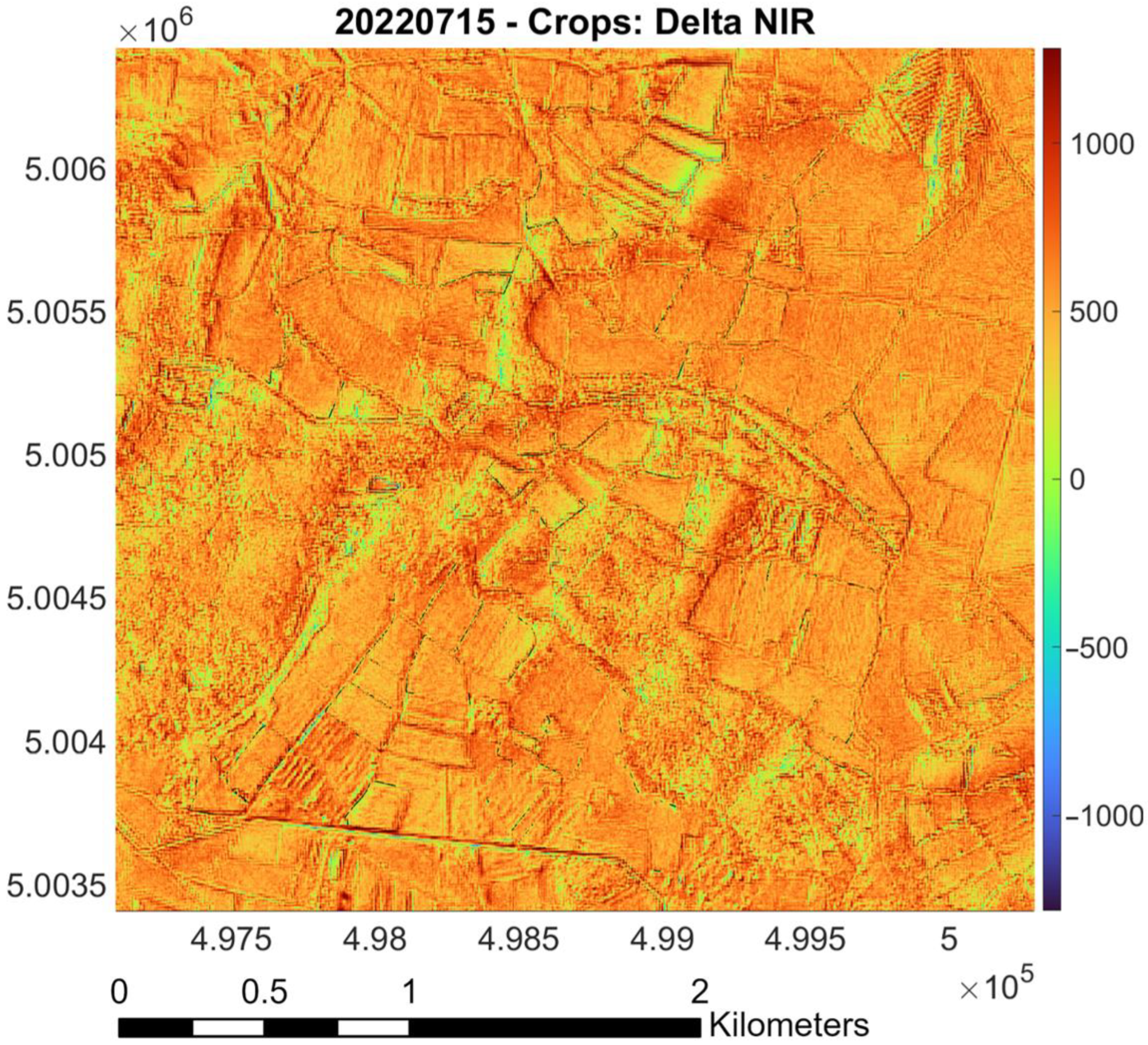
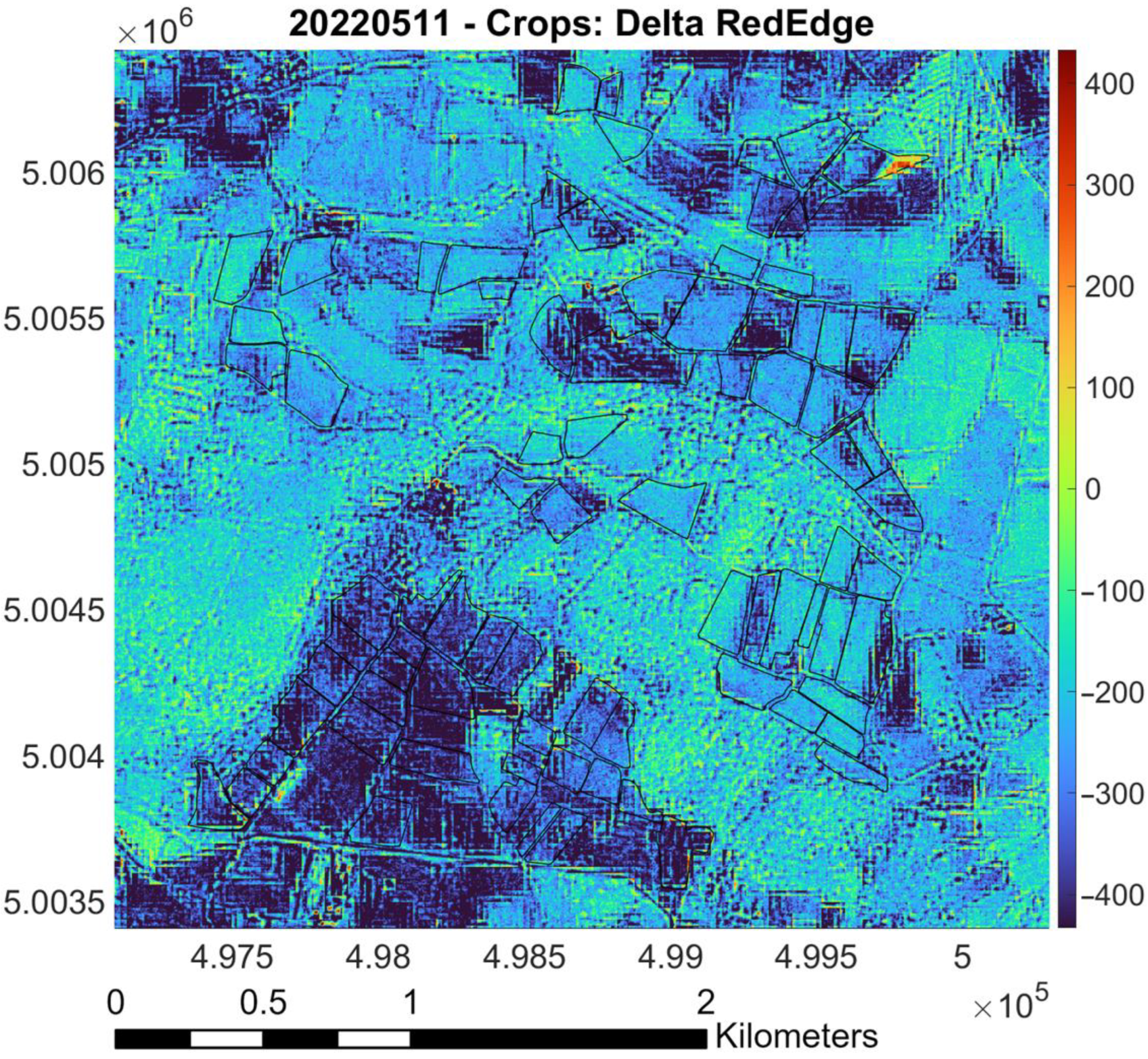
- Raster difference between PlanetScope and Sentinel-2 (as reference): Red pixels indicate areas where PlanetScope values are significantly higher than Sentinel-2 values; blue pixels represent regions where Sentinel-2 values surpass those of PlanetScope. Green and yellow markers denote areas with similar values, based on the magnitude of the difference. The color bar indicates the values of the difference between the surface reflectances measured by the two sensors. Black lines outline “Riserva San Massimo” rice crop boundaries.
3.1. Calibration for Red Band (May and July)
3.2. Calibration for Green Band (May and July)
3.3. Calibration for Blue Band (May and July)
3.4. Calibration for NIR Band (May and July)
3.5. Calibration for RedEdge Band (May and July)
3.6. Differences Between Histograms
4. Discussion
- Analyzing the specific contributions of individual bands: Examining how each spectral band contributes to the indices.
- Investigating seasonal and interannual variations: Tracking how the relationship between single band values and histogram indices changes throughout the year and across multiple years to capture the effects of seasonal cycles.
- Identifying driving factors: Determining the key environmental factors (e.g., temperature, precipitation, soil moisture) that influence the observed variations in single band values and histogram indices.
- Evaluation of DTM impact on previous factors: Figure 32 shows that the southern crops are at a higher elevation than others, indicating a need for further assessment of water supply and management differences.
5. Conclusions
5.1. Main Findings
5.2. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United States Department of Agriculture Remote Sensing. Information Sheet. Available online: https://www.fsa.usda.gov/Internet/FSA_File/remote_sensing_info_sheet_15.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Baldin, C.M.; Casella, V.M. Comparison Between the Vegetation Indices Obtained from Sentinel-2 and Planet: A Case Study over a Rice Farm in Northern Italy. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2024, 2088, 257–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldin, C.M.; Rocca, M.T.; Franzini, M.; Casella, V.M. L’uso Di Immagini Planet Nell’agricoltura Di Precisione: Una Prima Sperimentazione Relativa al Riso. In Proceedings of the Intersezioni Disciplinare—Convegno Sifet 2023, Arezzo, Italy, 27 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Baldin, C.M.; Casella, V.M. Vegetative Index Intercalibration Between PlanetScope and Sentinel-2 Through a SkySat Classification in the Context of “Riserva San Massimo” Rice Farm in Northern Italy. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PlanetScope. Available online: https://developers.planet.com/docs/data/planetscope/ (accessed on 31 July 2024).
- Vizzari, M. PlanetScope, Sentinel-2, and Sentinel-1 Data Integration for Object-Based Land Cover Classification in Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Understanding PlanetScope Instruments. Available online: https://developers.planet.com/docs/apis/data/sensors/ (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- PlanetScope Overview—Earth Online. Available online: https://earth.esa.int/eogateway/missions/planetscope/description (accessed on 31 July 2024).
- Collison, A.; Jumpasut, A.; Bourne, H. On-Orbit Radiometric Calibration of the Planet Satellite Fleet Doves and Skysats. Available online: https://assets.planet.com/docs/radiometric_calibration_white_paper.pdf (accessed on 31 July 2024).
- Dmitry, V.; Luke, R.; Stephanie, H.; Manuela, R.; James, V.; Frank, A.; Paul, B.; Luis, H. Assessment of the Radiometric Calibration of PlanetScope 2 Dove Imagery. Available online: https://earth.esa.int/eogateway/documents/20142/1305226/JACIE-2017-DVarlyguin-GDA-NGA-ASMTofRadCal-PlanetScope2.pdf (accessed on 13 September 2024).
- Baldin, C.M.; Casella, V.M. Assessment of Planetscope Imagery for the “Riserva San Massimo” Rice Farm: Evaluating Benefits and Calibration in Relation to Sentinel-2 Data (Poster). Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/11571/1523277 (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Sentinel-2 MSI User Guide. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/user-guides/sentinel-2-msi (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Sentinel-2 MSI Technical Guide. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/technical-guides/sentinel-2-msi (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Szantoi, Z.; Strobl, P. Copernicus Sentinel-2 Calibration and Validation. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 52, 253–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Zhou, W.; Paliwal, A. Mapping Smallholder Yields Using Planet and Sentinel-2 Satellite Data. In Remote Sensing of Agriculture and Land Cover/Land Use Changes in South and Southeast Asian Countries; Vadrevu, K.P., Le Toan, T., Ray, S.S., Justice, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 187–199. ISBN 978-3-030-92365-5. [Google Scholar]
- Annovazzi-Lodi, L.; Casella, V.; Baldin, C.M.; Bernini, A.; Adeniyi, O.D.; Maerker, M. Per Un Uso Del Suolo Dinamico: Classificazione Di Serie Storiche Di Immagini Sentinel-2. In Proceedings of the ASITA, Genova, Italy, 1–2, 9, 16, and 23 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- do Amaral, L.R.; Oldoni, H.; Baptista, G.M.M.; Ferreira, G.H.S.; Freitas, R.G. Vegetation Indices from Sentinel-2 and PlanetScope Imagery and Their Relationship with Soybean Yield. In Precision Agriculture ’23; Wageningen Academic: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 879–886. [Google Scholar]
- Copernicus Sentinel-2 Leads Precision Farming into New Era—Sentinel Success Stories—Sentinel Online. Available online: https://sentinels.copernicus.eu/web/success-stories/-/copernicus-sentinel-2-leads-precision-farming-into-new-era (accessed on 31 July 2024).
- The Riserva San Massimo. Available online: https://riservasanmassimo.net/?lang=en (accessed on 31 July 2024).
- I Dati Dai Satelliti per Una Risaia Sostenibile. Available online: https://www.risoitaliano.eu/i-dati-dai-satelliti-per-una-risaia-sostenibile/ (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- Borgogno Mondino, E.; Zamperlin, P. Geomatics for Environmental Monitoring: From Data to Services; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Borgogno Mondino, E.; Zamperlin, P. ASITA—Geomatics for Green and Digital Transition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; Volume 2, ISBN 978-3-031-91144-6. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, R.L.S.; Amorim, R.S.S.; da Silva, D.D.; Fernandes-Filho, E.I.; Veloso, G.V.; Macedo, R.H.F. Relative Radiometric Normalization for the PlanetScope Nanosatellite Constellation Based on Sentinel-2 Images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, K.C.; Singha, C.; Pradhan, B. Estimating Total Rice Biomass and Crop Yield at Field Scale Using PlanetScope Imagery Through Hybrid Machine Learning Models. Earth Syst. Environ. 2024, 8, 1713–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.-E.; Grafton, M.; Bretherton, M.; Irwin, M.; Sandoval, E. Evaluation of the Use of Two-Stage Calibrated PlanetScope Images and Environmental Variables for the Development of the Grapevine Water Status Prediction Model. Technol. Agron. 2023, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, P. Assessment of the Suitability of PlanetScope SuperDove Imagery for Aquatic Remote Sensing at Lake Junin in Central Peru. Available online: https://elib.dlr.de/206635/ (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Malczewska, A.; Malczewski, J.; Hejmanowska, B. Challenges in Preparing Datasets for Super-Resolution on the Example of Sentinel-2 And Planet Scope Images. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, XLVIII-1-W3-2023, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latte, N.; Lejeune, P. PlanetScope Radiometric Normalization and Sentinel-2 Super-Resolution (2.5 m): A Straightforward Spectral-Spatial Fusion of Multi-Satellite Multi-Sensor Images Using Residual Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayer, T.C.; Douglas, M.M.; Cordeiro, M.C.R.; Tayer, A.D.N.; Callow, J.N.; Beesley, L.; McFarlane, D. Improving the Accuracy of the Water Detect Algorithm Using Sentinel-2, Planetscope and Sharpened Imagery: A Case Study in an Intermittent River. GIsci. Remote Sens. 2023, 60, 2168676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segarra, J.; Buchaillot, M.L.; Araus, J.L.; Kefauver, S.C. Remote Sensing for Precision Agriculture: Sentinel-2 Improved Features and Applications. Agronomy 2020, 10, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagajewski, B.; Kluczek, M.; Zdunek, K.B.; Holland, D. Sentinel-2 versus PlanetScope Images for Goldenrod Invasive Plant Species Mapping. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašparović, M.; Medak, D.; Pilaš, I.; Jurjević, L.; Balenović, I. Fusion of Sentinel-2 And Planetscope Imagery for Vegetation Detection and Monitoring. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, XLII-1, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franch, B.; San Bautista, A.; Fita, D.; Rubio, C.; Tarrazó-Serrano, D.; Sánchez, A.; Skakun, S.; Vermote, E.; Becker-Reshef, I.; Uris, A. Within-Field Rice Yield Estimation Based on Sentinel-2 Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fita, D.; Rubio, C.; Uris, A.; Castiñeira-Ibáñez, S.; Franch, B.; Tarrazó-Serrano, D.; San Bautista, A. Remote Sensor Images and Vegetation Indices to Optimize Rice Yield Analysis for Specific Growth Stages Within Extensive Data. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebbers, R.; Adamchuk, V.I. Precision Agriculture and Food Security. Science 2010, 327, 828–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, T.O. Root-Mean-Square Error (RMSE) or Mean Absolute Error (MAE): When to Use Them or Not. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2022, 15, 5481–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NDVI. the Foundation for Remote Sensing Phenology|U.S. Geological Survey. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/special-topics/remote-sensing-phenology/science/ndvi-foundation-remote-sensing-phenology (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Voitik, A.; Kravchenko, V.; Pushka, O.; Kutkovetska, T.; Shchur, T.; Kocira, S. Comparison of NDVI, NDRE, MSAVI and NDSI Indices for Early Diagnosis of Crop Problems. Agric. Eng. 2023, 27, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiarskii, B.; Hasegawa, H. Comparison of NDVI and NDRE Indices to Detect Differences in Vegetation and Chlorophyll Content. J. Mech. Contin. Math. Sci. 2019, 4, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, L.; Serdiuk, S.; Dovhanenko, D.; Okhotnyk, K.; Ishchenko, K. Application of Remote Sensing Techniques for Estimation and Mapping of Iron Oxides and Iron-Containing Minerals in Open Pits of the Kryvyi Rih Iron Ore Basin. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1348, 012055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Kumar Tripathy, J.; Behera, S.S. Remote Sensing Studies for Mapping of Iron Oxide Regions in Keonjhor District, Odisha, India. Ecol. Environ. Conserv. 2022, 28, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Hung, T. Application of remote sensing technique to detect and map iron oxide, clay minerals, and ferrous minerals in Thai Nguyen Province (Vietnam). Min. Sci. Technol. 2016, 1, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sirisathitkul, Y.; Sirisathitkul, C. Decoding Soil Color: Origins, Influences, and Methods of Analysis. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birth, G.S.; McVey, G.R. Measuring the Color of Growing Turf with a Reflectance Spectrophotometer. Agron. J. 1968, 60, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathworks Interpret Linear Regression Results: Fit Linear Regression and ANOVA. Available online: https://it.mathworks.com/help/stats/understanding-linear-regression-outputs.html (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Linear Regression. Available online: https://it.mathworks.com/help/matlab/data_analysis/linear-regression.html (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Fit Linear Regression Model—MATLAB Fitlm. Available online: https://it.mathworks.com/help/stats/fitlm.html (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Farbo, A.; Meloni, R.; Blandino, M.; Sarvia, F.; Reyneri, A.; Borgogno-Mondino, E. Spectral Measures from Sentinel-2 Imagery vs Ground-Based Data from Rapidscan© Sensor: Performances on Winter Wheat. In Proceedings of the Geomatics for Green and Digital Transition, ASITA 2022, Genova, Italy, 20–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, C.; Zai, X.; Song, Y.; Zhang, X. Optimizing Fertilizer Use for Sustainable Food Systems: An Evaluation of Integrated Water-Fertilizer System Adoption among Cotton Farmers in China. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1310426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International, J.; Leone, S. Technical Package on Rice Production, Revised ed.; Sustainable Rice Development Project in Sierra Leone (JICA-SRDP); Prepared by Sustainable Rice Development Project; Min-istry of Agriculture, Forestry and Food Security (MAFFS): Freetown, Sierra Leone; Republic of Sierra Leone Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA): Tokyo, Japan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bonfil, D.J.; Michael, Y.; Shiff, S.; Lensky, I.M. Optimizing Top Dresseing Nitrogen Fertilization Using Venμs and Sentinel-2 L1 Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Cheng, X.; Xi, X.; Weng, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R. Effects of a Novel Weeding and Fertilization Scheme on Yield and Quality of Rice. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzari, M.; Santaga, F.; Benincasa, P. Sentinel 2-Based Nitrogen VRT Fertilization in Wheat: Comparison between Traditional and Simple Precision Practices. Agronomy 2019, 9, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Bai, J.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Z.; Chen, C. Research on Precise Fertilization Method of Rice Tillering Stage Based on UAV Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Prescription Map. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaga, F.; Benincasa, P.; Vizzari, M. Using Sentinel 2 Data to Guide Nitrogen Fertilization in Central Italy: Comparison Between Flat, Low VRT and High VRT Rates Application in Wheat. In Proceedings of the Computational Science and Its Applications—ICCSA 2020, Cagliari, Italy, 1–4 July 2020; Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bio-in-formatics). Volume 12253, pp. 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żuk, L.; Królewicz, S. Uses of Sentinel-1 and -2 Images in Heritage Management: A Case Study from Lednica Landscape Park (Poland). Geosciences 2022, 12, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellón, B.; Bégué, A.; Lo Seen, D.; De Almeida, C.A.; Simões, M. A Remote Sensing Approach for Regional-Scale Mapping of Agricultural Land-Use Systems Based on NDVI Time Series. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenney, M.P.; Woodcock, C.E.; Collins, J.B.; Hamdi, H. The Status of Agricultural Lands in Egypt: The Use of Multitemporal NDVI Features Derived from Landsat TM. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 56, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, U.K. Spectral Color Indices Based Geospatial Modeling of Soil Organic Matter in Chitwan District, Nepal. Available online: https://isprs-archives.copernicus.org/articles/XLI-B2/43/2016/ (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Woebbecke, D.M.; Meyer, G.E.; Von Bargen, K.; Mortensen, D.A. Color Indices for Weed Identification Under Various Soil, Residue, and Lighting Conditions. Trans. ASAE 1995, 38, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sruthi, S.; Aslam, M.A.M. Agricultural Drought Analysis Using the NDVI and Land Surface Temperature Data; a Case Study of Raichur District. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 4, 1258–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farbo, A.; Sarvia, F.; De Petris, S.; Borgogno-Mondino, E. Preliminary Concerns About Agronomic Interpretation of NDVI Time Series from Sentinel-2 Data: Phenology and Thermal Efficiency of Winter Wheat In Piemonte (New Italy). Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, XLIII-B3-2022, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, R.; Rossini, P. On the Use of NDVI Profiles as a Tool for Agricultural Statistics: The Case Study of Wheat Yield Estimate and Forecast in Emilia Romagna. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 45, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indices Gallery—ESRI ArcGIS. Available online: https://pro.arcgis.com/en/pro-app/latest/help/data/imagery/indices-gallery.htm (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Bannari, A.; Morin, D.; Bonn, F.; Huete, A.R. A Review of Vegetation Indices. Remote Sens. Rev. 1995, 13, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Hao, D.; Huete, A.; Dechant, B.; Berry, J.; Chen, J.M.; Joiner, J.; Frankenberg, C.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Ryu, Y.; et al. Optical Vegetation Indices for Monitoring Terrestrial Ecosystems Globally. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidotto, F.; Ferrero, A. Interactions Between Weedy Rice and Cultivated Rice in Italy. Ital. J. Agron. 2009, 4, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, A.; Bàrberi, P.; Vidotto, F.; Ferrero, A.; Zanin, G. Water Management as a Key Component of Integrated Weed Management. Ital. J. Agron. 2006, 1, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tediosi, A.; Ferrari, F.; Voccia, D.; Gharsallah, O.; Lamastra, L.; Botteri, L.; Rossi, R.; Ferrari, T.; Ballerini, N.; Gilardi, G.L.C.; et al. Herbicide and Nutrient Monitoring in Surface Waters and Groundwater of a Paddy District in Northern Italy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 52963–52979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voccia, D.; Lamastra, L.; Fragkoulis, G.; Facchi, A.; Gharsallah, O.; Ferrari, F.; Tediosi, A.; Trevisan, M. Improving a Herbicide Risk Assessment Model in Paddy Rice Cultivation. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Van de Voorde, T.; Roberts, D.; Zhao, H.; Chen, J. Detection of Ground Materials Using Normalized Difference Indices with a Threshold: Risk and Ways to Improve. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orynbassarova, E.; Ahmadi, H.; Adebiyet, B.; Bekbotayeva, A.; Abdullayeva, T.; Beiranvand Pour, A.; Ilyassova, A.; Serikbayeva, E.; Talgarbayeva, D.; Bermukhanova, A. Mapping Alteration Minerals Associated with Aktogay Porphyry Copper Mineralization in Eastern Kazakhstan Using Landsat-8 and ASTER Satellite Sensors. Minerals 2025, 15, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.; Olsen, S.D.; Pedersen, B.C.; Thorning, L. ASTER Data Analysis Applied to Mineral and Geological Mapping in North East Greenland. Available online: https://data.geus.dk/pure-pdf/32607_GEUS_R_2019_7_opt.pdf (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Jędrejek, A.; Jadczyszyn, J.; Pudełko, R. Increasing Accuracy of the Soil-Agricultural Map by Sentinel-2 Images Analysis—Case Study of Maize Cultivation under Drought Conditions. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovynska, V.; Bayat, B.; Bol, R.; Moradi, S.; Rahmati, M.; Raj, R.; Sytnyk, S.; Wiche, O.; Wu, B.; Montzka, C. Monitoring Heavy Metals and Metalloids in Soils and Vegetation by Remote Sensing: A Review. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Macias, K.J.; Martínez-Sifuentes, A.R.; Márquez-Guerrero, S.Y.; Reyes-González, A.; Preciado-Rangel, P.; Yescas-Coronado, P.; Trucíos-Caciano, R. Machine-Learning Approaches in N Estimations of Fig Cultivations Based on Satellite-Born Vegetation Indices. Nitrogen 2024, 5, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, T.H.; Lundy, M.E.; Linquist, B.A. Comparative Sensitivity of Vegetation Indices Measured via Proximal and Aerial Sensors for Assessing N Status and Predicting Grain Yield in Rice Cropping Systems. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, R.F. How Lithology Impacts Global Topography, Vegetation, and Animal Biodiversity: A Global-Scale Analysis of Mountainous Regions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL088649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardelli, V.; Cocco, S.; Agnelli, A.; Nardi, S.; Pizzeghello, D.; Fernández-Sanjurjo, M.J.; Corti, G. Chemical and Biochemical Properties of Soils Developed from Different Lithologies in Northwestern Spain (Galicia). Forests 2017, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupla, X.; Claustre, R.; Bonvin, E.; Graf, I.; Le Bayon, R.-C.; Grand, S. Let the Dust Settle: Impact of Enhanced Rock Weathering on Soil Biological, Physical, and Geochemical Fertility. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElGalladi, A.; Araffa, S.; Mekkawi, M.; Abd-AlHai, M. Exploring Mineralization Zones Using Remote Sensing and Aeromagnetic Data, West Allaqi Area, Eastern-Desert, Egypt. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2022, 25, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirico, R.; Mondillo, N.; Laukamp, C.; Mormone, A.; Di Martire, D.; Novellino, A.; Balassone, G. Mapping Hydrothermal and Supergene Alteration Zones Associated with Carbonate-Hosted Zn-Pb Deposits by Using PRISMA Satellite Imagery Supported by Field-Based Hyperspectral Data, Mineralogical and Geochemical Analysis. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 152, 105244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raihana, H.; Sinaga, J.E.E.; Cahyani, A.G.; Halauddin, H.; Suhendra, S.; Hutauruk, A.; Sugianto, N. Identification of Alteration Zones Based on Resistivity and Induced Polarization Geoelectric Survey. Jambura Geosci. Rev. 2023, 5, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osinowo, O.O.; Gomy, A.; Isseini, M. Mapping Hydrothermal Alteration Mineral Deposits from Landsat 8 Satellite Data in Pala, Mayo Kebbi Region, Southwestern Chad. Sci. Afr. 2021, 11, e00687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivarajan, S.; Maharlooei, M.; Kandel, H.; Buetow, R.R.; Nowatzki, J.; Bajwa, S.G. Evaluation of OptRxTM Active Optical Sensor to Monitor Soybean Response to Nitrogen Inputs. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Jin, Y.; Alsina, M.M.; McElrone, A.J.; Bambach, N.; Kustas, W.P. Vine Water Status Mapping with Multispectral UAV Imagery and Machine Learning. Irrig. Sci. 2022, 40, 715–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina Di Iorio Il Riso Migliore D’italia Cresce in una Riserva Naturale a Due Passi da Milano. Available online: https://www.milanotoday.it/cibo/riserva-san-massimo-storia-del-riso-migliore-d-italia.html (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- Ezio Zigliani Gambero Rosso: Il Miglior Riso Carnaroli è Riserva San Massimo. Available online: https://corrieredelvino.it/news/gambero-rosso-il-miglior-riso-carnaroli-e-riserva-san-massimo/ (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- Riso Carnaroli Riserva San Massimo Protagonista Della Sfida in Esterna. Available online: https://masterchef.sky.it/foto/riso-carnaroli-riserva-san-massimo-protagonista-della-sfida-in-esterna#00 (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- Giovanni Chiodini Riserva San Massimo, Dal Ticino un Riso per Sceicchi. Available online: https://www.ilgiorno.it/cronaca/ticino-riso-carnaroli-d48bd91f (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- SIC IT2080015 San Massimo. Available online: https://www.regione.lombardia.it/wps/wcm/connect/f52af3cb-1469-4628-95bc-a9bbde4529c8/IT2080015+San+Massimo.pdf?MOD=AJPERES&CACHEID=ROOTWORKSPACE-f52af3cb-1469-4628-95bc-a9bbde4529c8-obJUljP (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Site: IT2080015—San Massimo—For Special Protection Areas (SPA). Available online: https://download.mase.gov.it/Natura2000/Trasmissione%20CE_dicembre2024/schede_mappe/Lombardia/ZSC_schede/Site_IT2080015.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Miniotti, E.; Tenni, D.; Beltarre, G.; Sacco, D.; Rognoni, G.; Finzi, A.; Sgrelli, S.; Bergonzi, C.; Romani, M. Riso Sensori Ottici e Droni per Ottimizzare La Concimazione. Terra Vita 2015, 15, 62–64. [Google Scholar]
- Tenni, D.; Rognoni, G.; Finzi, A.; Bergonzi, C.; Sgrelli, S.; Sacco, D.; Miniotti, E.; Beltarre, G.; Romani, M. Concimazione Azotata Di Precisione in Risaia. In Proceedings of the Conferenza ESRI Italia 2019, Rome, Italy, 10–11 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ente Nazionale Risi. Available online: https://www.enterisi.it/servizi/notizie/notizie_homepage.aspx (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Copernicus. Available online: https://www.esa.int/Applications/Observing_the_Earth/Copernicus (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Gascon, F.; Bouzinac, C.; Thépaut, O.; Jung, M.; Francesconi, B.; Louis, J.; Lonjou, V.; Lafrance, B.; Massera, S.; Gaudel-Vacaresse, A.; et al. Copernicus Sentinel-2A Calibration and Products Validation Status. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentinel-2C Joins the Copernicus Family in Orbit. Available online: https://www.esa.int/Applications/Observing_the_Earth/Copernicus/Sentinel-2/Sentinel-2C_joins_the_Copernicus_family_in_orbit (accessed on 13 September 2024).
- Sentinel-2 Mission Guide. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/missions/sentinel-2 (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Sentinel-2 MSI Instrument. Available online: https://sentinels.copernicus.eu/web/sentinel/technical-guides/sentinel-2-msi/msi-instrument (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Li, S.; Ganguly, S.; Dungan, J.L.; Wang, W.; Nemani, R.R.; Li, S.; Ganguly, S.; Dungan, J.L.; Wang, W.; Nemani, R.R. Sentinel-2 MSI Radiometric Characterization and Cross-Calibration with Landsat-8 OLI. Adv. Remote Sens. 2017, 6, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentinel-2 License. Available online: https://open.esa.int/copernicus-sentinel-satellite-imagery-under-open-licence/ (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Greenberg, J. On-Orbit Radiometric Calibration and Validation of Planet’s Constellations. Available online: https://calval.cr.usgs.gov/apps/sites/default/files/jacie/OnOrbitRadiometricCalibrationandValidationofPlanetsConstellations.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2024).
- Mascaro, J. Estimating Soil Moisture with PlanetScope for Agricultural Resilience in Indonesia. Available online: https://www.planet.com/pulse/publications/measuring-soil-moisture-with-planetscope-for-agricultural-resilience-in-indonesia/ (accessed on 26 April 2025).
- Roy, D.P.; Huang, H.; Houborg, R.; Martins, V.S. A Global Analysis of the Temporal Availability of PlanetScope High Spatial Resolution Multi-Spectral Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Ghosh, S.K. Evaluating the Potential Of 8 Band Planetscope Dataset for Crop Classification Using Random Forest and Gradient Tree Boosting by Google Earth Engine. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, XLVIII-M-1–2023, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planet Labs. Licensing Information. Available online: https://www.planet.com/licensing-information/ (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Sentinel-2A (10 m) Satellite Sensor—Satellite Imaging Corporation. Available online: https://www.satimagingcorp.com/satellite-sensors/other-satellite-sensors/sentinel-2a/ (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Payne, A.; Thompson, G.; Johnson, C.; Johnston, K.; Morgan, H.; Harrell, J.; Morgan, T. Using Color Infrared (CIR) Imagery A Guide for Understanding, Interpreting and Benefiting from CIR Imagery; N.C. Department of Information Technology: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- USGS. What Do the Different Colors in a Color-Infrared Aerial Photograph Represent? Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/faqs/what-do-different-colors-color-infrared-aerial-photograph-represent (accessed on 28 April 2025).
- Sripada, R.P.; Heiniger, R.W.; White, J.G.; Meijer, A.D. Aerial Color Infrared Photography for Determining Early In-Season Nitrogen Requirements in Corn. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PlanetScope PlanetScope—Surface Reflectance—Technical Specification. Available online: https://docs.planet.com/data/imagery/arps/techspec/ (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- MapPostingsReference—Matlab Help. Available online: https://it.mathworks.com/help/map/ref/map.rasterref.mappostingsreference.html (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- MapCellsReference—Matlab Help. Available online: https://it.mathworks.com/help/map/ref/map.rasterref.mapcellsreference.html (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Matlab—Change Image Size. Available online: https://it.mathworks.com/help/visionhdl/ug/image-downsize.html (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Nearest-Neighbor Interpolation Algorithm in MATLAB. Available online: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/nearest-neighbor-interpolation-algorithm-in-matlab/ (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Classification Using Nearest Neighbors. Available online: https://it.mathworks.com/help/stats/classification-using-nearest-neighbors.html (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Zhang, T.; Su, J.; Liu, C.; Chen, W.H.; Liu, H.; Liu, G. Band Selection in Sentinel-2 Satellite for Agriculture Applications. In Proceedings of the ICAC 2017—2017 23rd IEEE International Conference on Automation and Computing: Addressing Global Challenges Through Automation and Computing, Huddersfield, UK, 7–8 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallinis, G.; Mitsopoulos, I.; Chrysafi, I. Evaluating and Comparing Sentinel 2A and Landsat-8 Operational Land Imager (OLI) Spectral Indices for Estimating Fire Severity in a Mediterranean Pine Ecosystem of Greece. GIsci. Remote Sens. 2018, 55, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.H.; Heurich, M.; Beudert, B.; Premier, J.; Pflugmacher, D. Comparison of Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 Data for Estimation of Leaf Area Index in Temperate Forests. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarau, A.; Richter, R.; Schlapfer, D.; Reinartz, P. APDA Water Vapor Retrieval Validation for Sentinel-2 Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segl, K.; Richter, R.; Küster, T.; Kaufmann, H. End-to-End Sensor Simulation for Spectral Band Selection and Optimization with Application to the Sentinel-2 Mission. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Cheng, Q.; Jing, L.; Wang, F.; Zhao, M.; Ding, H. Assessment of the Capability of Sentinel-2 Imagery for Iron-Bearing Minerals Mapping: A Case Study in the Cuprite Area, Nevada. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, D.; Haß, E.; Uhl, A.; Stoffels, J.; Hill, J. Improvement of the Fmask Algorithm for Sentinel-2 Images: Separating Clouds from Bright Surfaces Based on Parallax Effects. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.C.; Maingi, J.K. Evaluating Landsat- and Sentinel-2-Derived Burn Indices to Map Burn Scars in Chyulu Hills, Kenya. Fire 2024, 7, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandanici, E.; Bitelli, G. Preliminary Comparison of Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 Imagery for a Combined Use. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiyani, K.; Gonçalves, T.; Rato, L.; Salgueiro, P.; Marques da Silva, J.R. Sentinel-2 Image Scene Classification: A Comparison between Sen2Cor and a Machine Learning Approach. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, M.A.; Simis, S.G.H.; Martinez-Vicente, V.; Poser, K.; Bresciani, M.; Alikas, K.; Spyrakos, E.; Giardino, C.; Ansper, A. Assessment of Atmospheric Correction Algorithms for the Sentinel-2A MultiSpectral Imager over Coastal and Inland Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 267–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main-Knorn, M.; Pflug, B.; Louis, J.; Debaecker, V.; Müller-Wilm, U.; Gascon, F. Sen2Cor for Sentinel-2. In Proceedings of the Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XXIII, Warsaw, Poland, 11–14 September 2017; Bruzzone, L., Bovolo, F., Benediktsson, J.A., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Laake, A. Electromagnetic Spectral Bands Used for Remote Sensing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-I. Correlation and Spatial Autocorrelation. Encyclopedia of GIS; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 360–368. [Google Scholar]
- Permai, S.D.; Jauri, R.; Chowanda, A. Spatial Autoregressive (SAR) Model for Average Expenditure of Papua Province. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 157, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horst, F Electromagnetic Spectrum. Available online: https://www.e-education.psu.edu/geog160/node/1958 (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- ESRI Spectral Profile. Available online: https://pro.arcgis.com/en/pro-app/latest/help/data/imagery/spectral-profile-chart.htm (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Streit, M.; Gehlenborg, N. Bar Charts and Box Plots. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxplot—Mathworks. Available online: https://it.mathworks.com/help/stats/boxplot.html (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Visualizing the Box and Whisker Plot. Available online: https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/edu/power-pouvoir/ch12/5214889-eng.htm (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- ROI-Based Processing—MATLAB & Simulink—MathWorks Italia. Available online: https://it.mathworks.com/help/images/roi-based-processing.html (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Resample (Data Management)—ArcGIS Pro|Documentation. Available online: https://pro.arcgis.com/en/pro-app/latest/tool-reference/data-management/resample.htm (accessed on 31 July 2024).
- Mapresize. Available online: https://it.mathworks.com/help/map/ref/mapresize.html (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Resample Image with Gridded Interpolation. Available online: https://it.mathworks.com/help/matlab/math/resample-image-with-gridded-interpolation.html (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Makima. Available online: https://it.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/makima.html (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Geoportale Lombardia. Available online: https://www.geoportale.regione.lombardia.it/ (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Lombardia Cartografia Geologica e Progetto CARG. Available online: https://www.regione.lombardia.it/wps/portal/istituzionale/HP/DettaglioServizio/servizi-e-informazioni/Enti-e-Operatori/Territorio/sistema-informativo-territoriale-sit/cartografia-geologica-progetto-carg/cartografia-geologica-progetto-carg (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- REACT-EU—Dottorati Ricerca Innovazione e Green. Available online: https://ecs-nodes.eu/en/project (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Dorian Project—UNIPV. Available online: https://dicar.dip.unipv.it/it/node/187 (accessed on 26 March 2025).











| Index | Applications | Band | Detection Capability |
|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI | Assessing vegetation presence, density, vigor, and overall health. Widely used in agriculture, forestry, and ecological monitoring. | Red, NIR | Quantifies the “greenness” of vegetation. Strongly correlated with chlorophyll content, leaf area index (LAI), and photosynthetic activity. Can saturate in dense vegetation. |
| NDRE | Assessing vegetation health, chlorophyll content, and nitrogen status, particularly useful in mid-to-late growth stages or dense canopies. | Red Edge, NIR | Sensitive to chlorophyll concentration deeper within the canopy. Less prone to saturation than NDVI in dense vegetation. Often used as an indicator of plant stress or nitrogen levels. |
| Iron Oxide Ratio | Highlighting areas with surface iron oxide (Fe3+) staining (e.g., hematite, goethite). Used in geological mapping and mineral exploration. | Red, Blue | Identifies surfaces exhibiting strong red reflectance relative to blue reflectance, characteristic of reddish iron oxide minerals or weathered lateritic soils. |
| Coloration Index | Identifying areas dominated by reddish/yellowish coloration, often associated with ferric iron (Fe3+) minerals like limonite, jarosite, goethite. Used in hydrothermal alteration mapping. | Red, Green | Detects surfaces where red reflectance significantly exceeds green reflectance, indicating the presence of various ferric iron minerals common in altered or weathered zones. |
| Bands | Sentinel-2 | PlanetScope |
|---|---|---|
| Blue | Band 2—Blue | Band 2—Blue |
| Green | Band 3—Green | Band 4—Green |
| Red | Band 4—Red | Band 6—Red |
| Red Edge | Band 5—RedEdge 705 | Band 7—RedEdge |
| NIR | Band 8—NIR | Band 8—NIR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baldin, C.M.; Casella, V.M. Comparison of PlanetScope and Sentinel-2 Spectral Channels and Their Alignment via Linear Regression for Enhanced Index Derivation. Geosciences 2025, 15, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15050184
Baldin CM, Casella VM. Comparison of PlanetScope and Sentinel-2 Spectral Channels and Their Alignment via Linear Regression for Enhanced Index Derivation. Geosciences. 2025; 15(5):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15050184
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaldin, Christian Massimiliano, and Vittorio Marco Casella. 2025. "Comparison of PlanetScope and Sentinel-2 Spectral Channels and Their Alignment via Linear Regression for Enhanced Index Derivation" Geosciences 15, no. 5: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15050184
APA StyleBaldin, C. M., & Casella, V. M. (2025). Comparison of PlanetScope and Sentinel-2 Spectral Channels and Their Alignment via Linear Regression for Enhanced Index Derivation. Geosciences, 15(5), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15050184






