The Discovery of the Theater of Akragas (Valley of Temples, Agrigento, Italy): An Archaeological Confirmation of the Supposed Buried Structures from a Geophysical Survey
Abstract
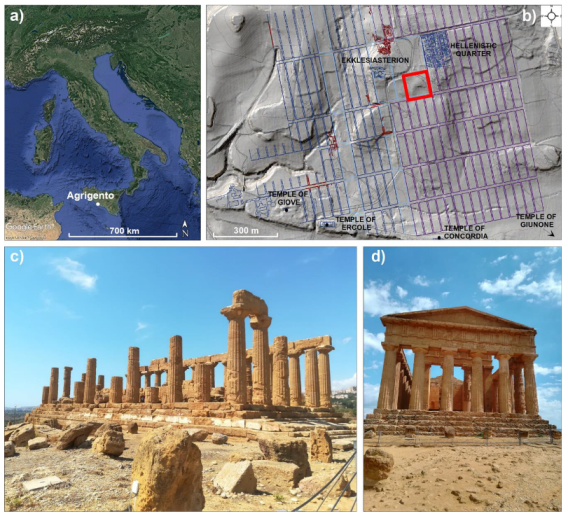
1. Introduction
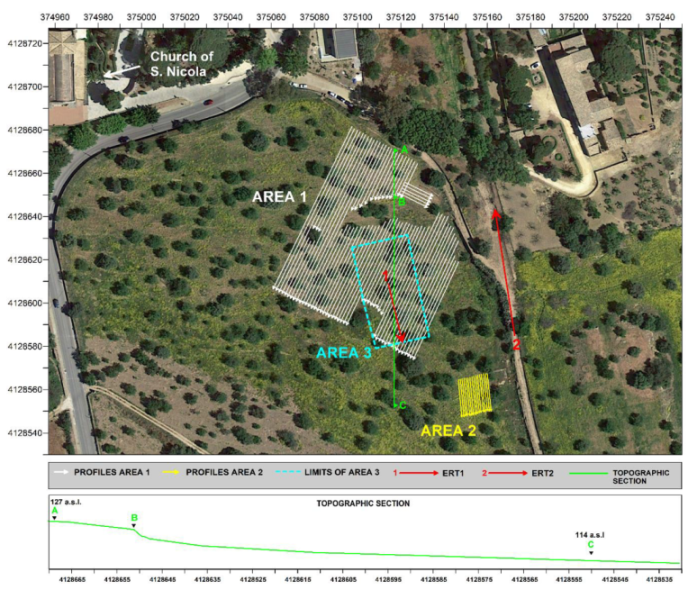
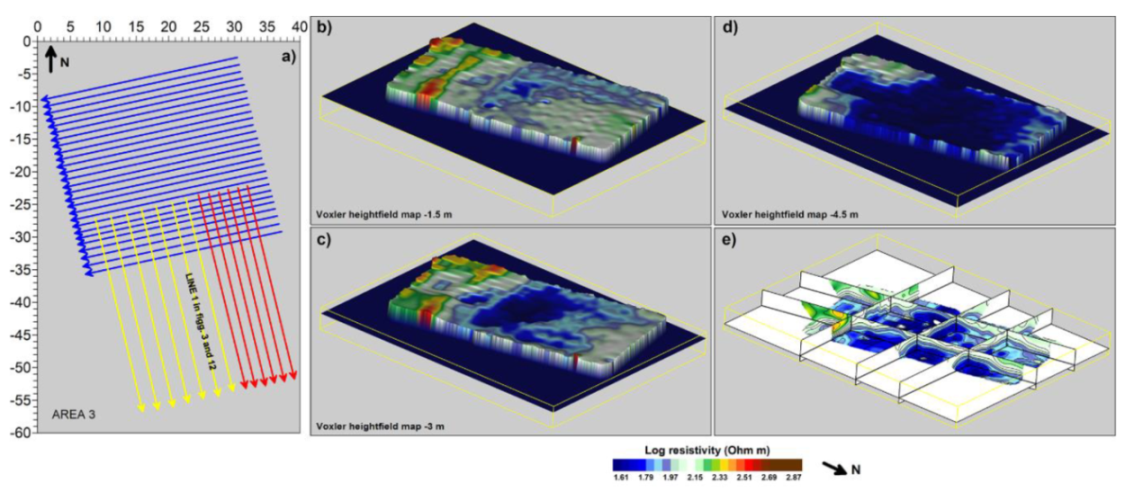
2. Materials and Methods
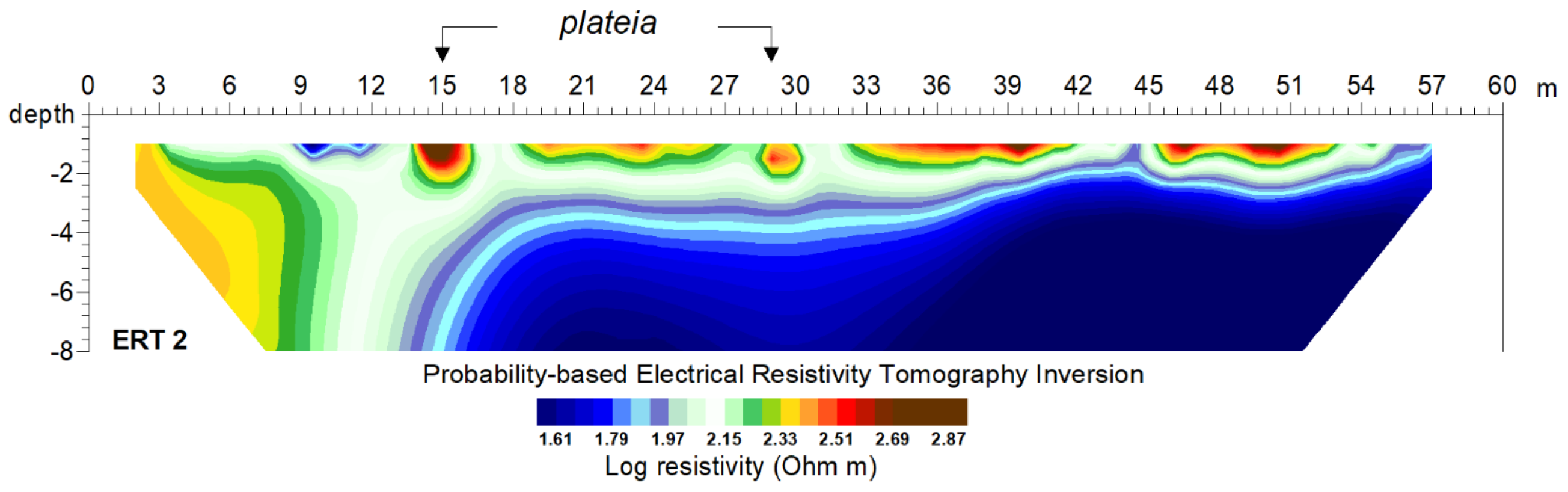
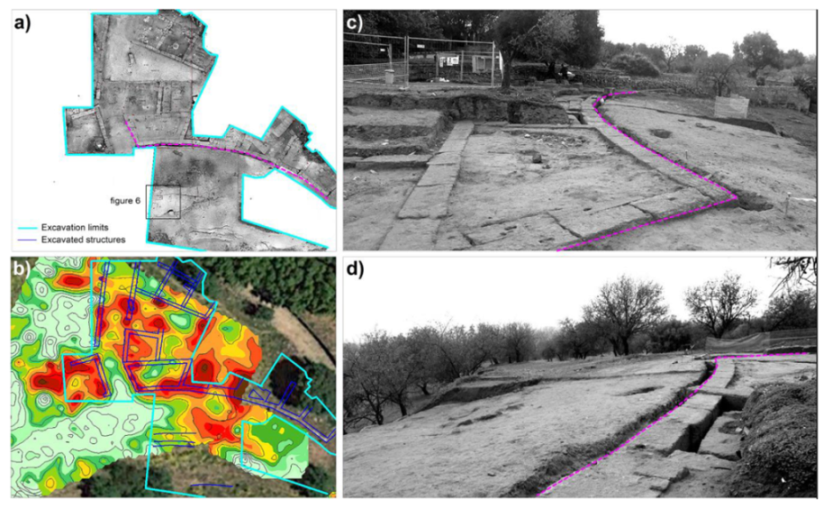
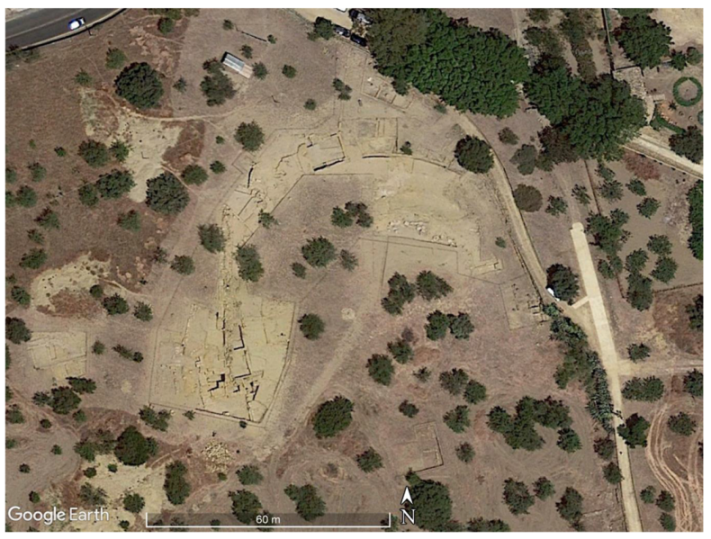
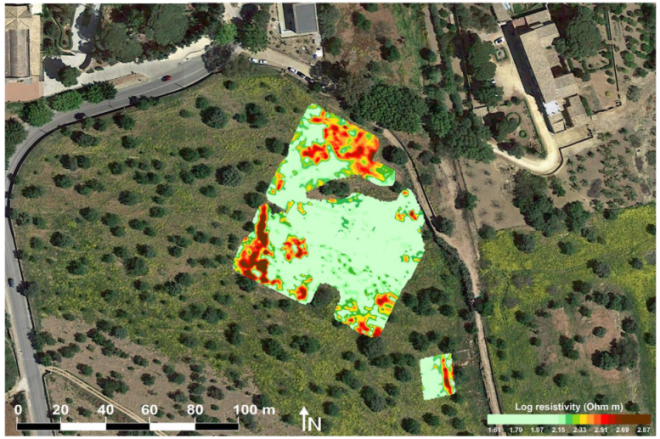
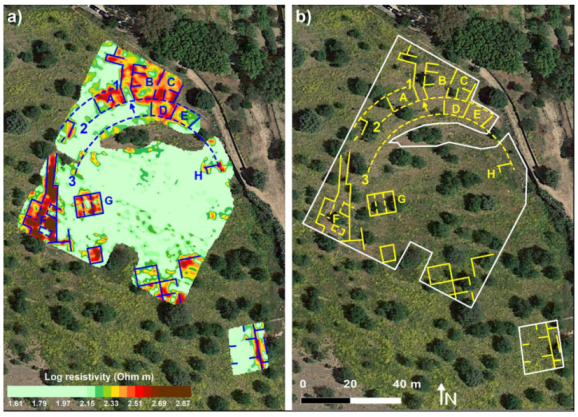
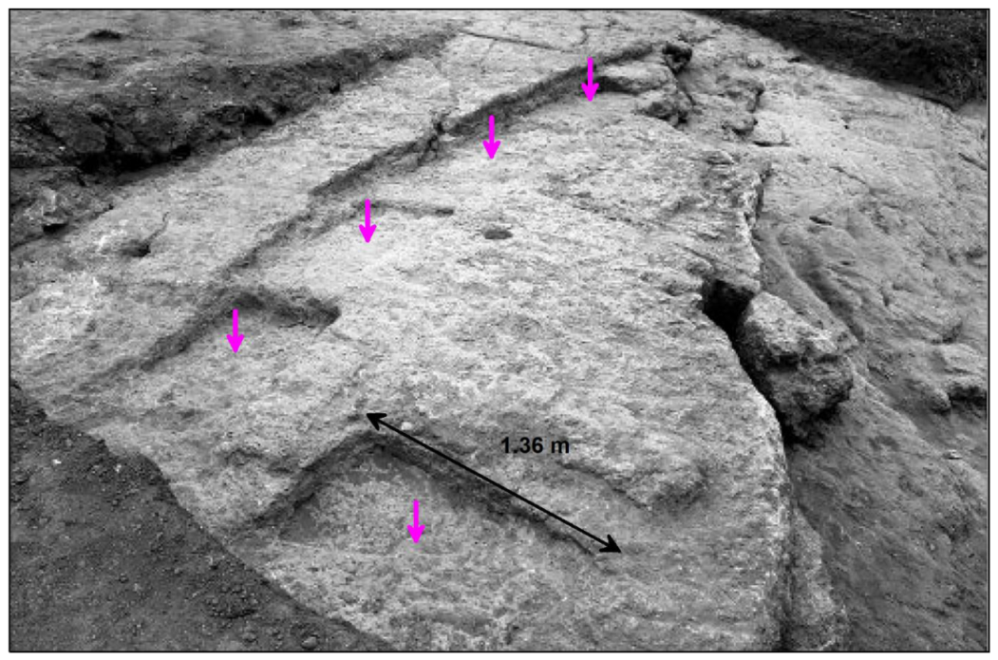
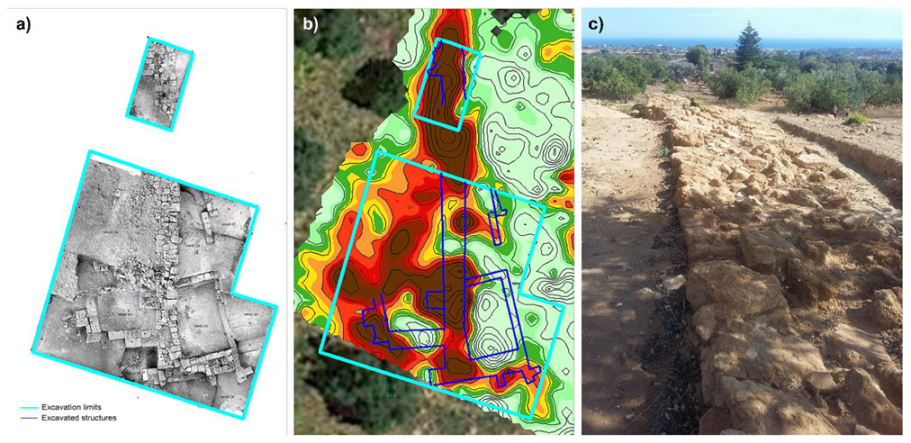
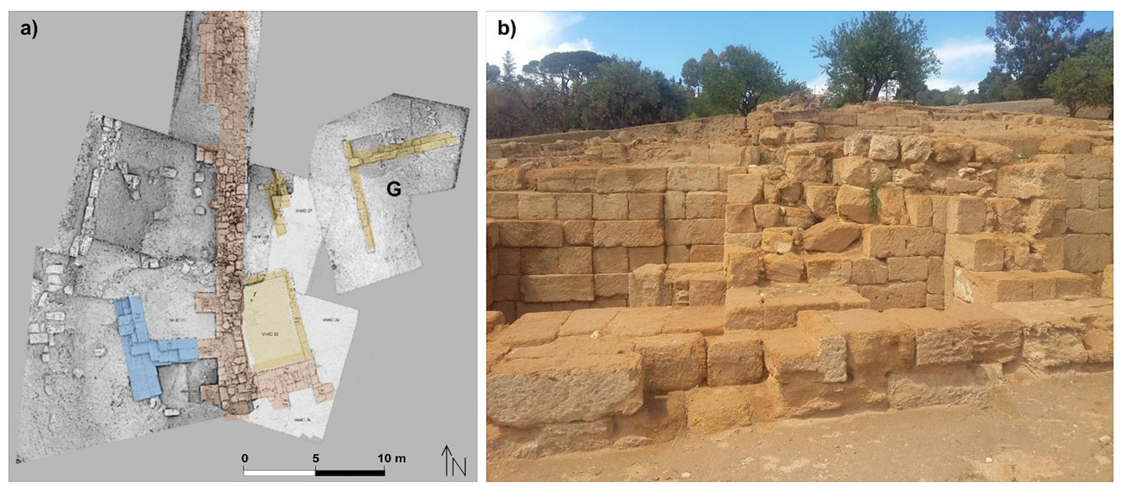
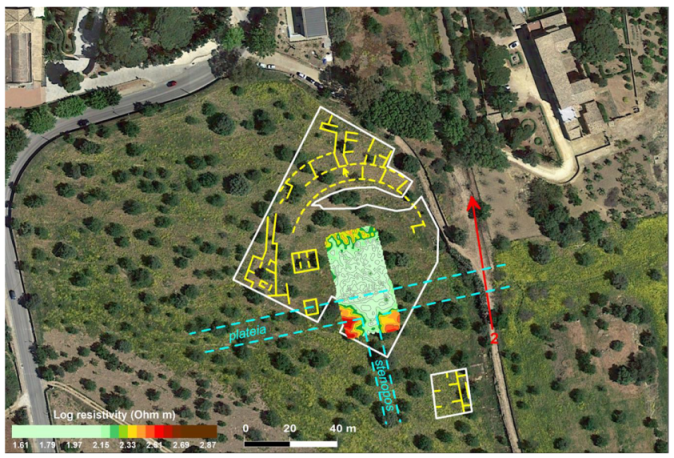
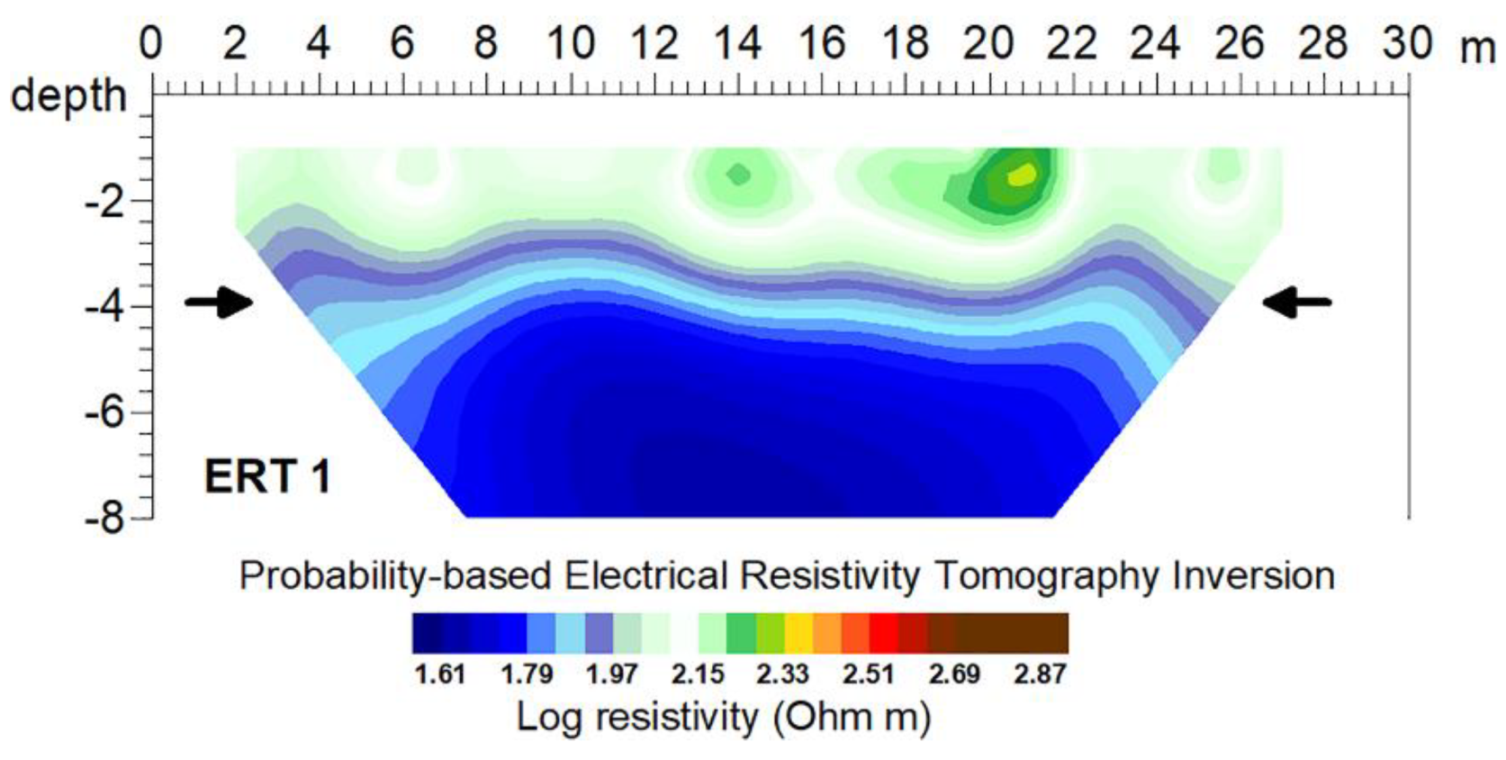
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colecchia, V.; Fiorillo, F.; Pagliarulo, R.; Reina, A. Caratteri geologici della Valle dei templi (Agrigento). Geol. Appl. Idrogeol. 1996, 31, 335–347. [Google Scholar]
- Caliò, L.M.; Caminneci, V.; Livadiotti, M.; Parello, M.C.; Rizzo, M.S. (Eds.) Agrigento. Nuove ricerche Sull’area Pubblica Centrale; Edizioni Quasar: Roma, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lepore, G.; Caliò, L.M. Agrigento: Archaeology of an ancient city. Urban form, sacred and civil spaces, productions, territory. In Proceedings of the 19th International Congress of Classical Archaeology, Archaeology and Economy in the Ancient World, Bonn, Germany, 22–26 May 2018; Bentz, M., Heinzelmann, M., Eds.; Propylaeum: Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 41. [Google Scholar]
- De Cesare, M.; Portale, E.C. Il Santuario di Zeus Olympios nel quadro urbano dell’antica Akragas. Archeol. Class. 2019, 70, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Camiceci, V. Una trepida attesa lunga cinque secoli: La scoperta del teatro di Agrigento. In Agrigento. Nuove Ricerche Sull’area Pubblica Centrale; Caliò, L.M., Caminneci, V., Livadiotti, M., Parello, M.C., Rizzo, M.S., Eds.; Edizioni Quasar: Roma, Italy, 2017; pp. 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Fazello, T. De Rebus Siculis Decades Duae; Panormi: Palermo, Italy, 1558. [Google Scholar]
- D’Orville, J.P. Sicula, Quibus Siciliae Veteris Rudera, Additis Antiquitatum Tabulis Illustrantur. Edidit, et Commentarium ad Numismata Sicula, XX Tabulis Aeneis Incisa, et ad Tres Inscriptiones Majores, Geloam, Tauromenitanam, et Rheginam; nec non Minorum Inscriptionum Syllogen, Orationem in Auctoris Obitum, et Praefationem Adjecit Petrus Burmannus Secundus; Apud Gerardum Tielenburg: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1724; pp. I–II. [Google Scholar]
- Muenter, F. Viaggio in Sicilia di Federico Muenter Tradotto dal Tedesco dal Tenente Colonnello D’artiglieria cav. D. Francesco Peranni con Note e Aggiunte del Medesimo; Tipografia Francesco Abbate: Palermo, Italy, 1823; p. I. [Google Scholar]
- Pancrazi, G.M. Le Antichità Siciliane Spiegate Colle Notizie Generali di Questo Regno. La Storia Particolare di Quelle Città Delle Quali Si Riportano ed Illustrano gli Antichi Monumenti; Stamperia Alessio Pellecchia: Naples, Italy, 1751; pp. I–II. [Google Scholar]
- de Saint Non, J.C.R. Voyage Pittoresque ou Description des Royaumes de Naples et de Sicile Ornée de Cartes, Plans, Vues, Figures; Vignettes et cul de Lampes; Clousier: Paris, France, 1781. [Google Scholar]
- della Torre di Rezzonico, C.G. Viaggio della Sicilia; Gli eredi Abbate Editori: Palermo, Italy, 1828. [Google Scholar]
- Griffo, P. Ebbe Agrigento un teatro nell’antichità? In Akragas. Bollettino di Studi, Scoperte ed Attività Varie; Soprintendenza alle Antichità di Agrigento: Agrigento, Italy, 1947; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Griffo, P. Bilancio di Cinque Anni di Scavi Nelle Province di Agrigento e Caltanissetta; Atti Accademia Scienze, Lettere e Arti di Agrigento; Dimora: Agrigento, Italy, 1953; Volume VIII, p. 142. [Google Scholar]
- Griffo, P. Del Teatro Greco di Agrigento; Dioniso: Agrigento, Italy, 1954; Volume VII, p. 141. [Google Scholar]
- Caliò, L.M. Il teatro di Agrigento e lo sviluppo della città monumentale. In THEAOMAI, Teatro e Società in Età Ellenistica, Proceedings of the Atti Delle XI Giornate Gregoriane, Agrigento, Italy, 2–3 December 2017; Caminneci, V., Parello, C., Rizzo, S., Eds.; All’Insegna del Giglio: Sesto Fiorentino, Italy, 2019; pp. 201–230. [Google Scholar]
- Cozzolino, M.; Di Meo, A.; Gentile, V. Il ruolo della diagnosi non invasiva nella scoperta del teatro ellenistico dell’antica Akragas, Agrigento. In Agrigento. Nuove Ricerche Sull’area Pubblica Centrale; Caliò, L.M., Caminneci, V., Livadiotti, M., Parello, M.C., Rizzo, M.S., Eds.; Edizioni Quasar: Roma, Italy, 2017; pp. 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Witten, A.J. Handbook of Geophysics and Archaeology; Equinox Pub: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, A.; Linford, P.; Lindford, N.; Gaffney, C.; David, A. (Eds.) EAC Guidelines for the Use of Geophysics in Archaeology; Archaeolingua Press: Budapest, Hungary, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, N.G.; Tsourlos, P.; Tsokas, G.N.; Sarris, A. Two-dimensional and three-dimensional resistivity imaging in archaeological site investigation. Archaeol. Prospect. 2006, 13, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Zeid, N.; Balducci, M.; Bartocci, F.; Regni, R.; Santarato, G. Indirect estimation of injected mortar volume in historical walls using the electrical resistivity tomography. J. Cult. Herit. 2009, 11, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavusi, M.; Giocoli, A.; Rizzo, E.; Lapenna, V. Geophysical characterisation of Carlo’s V Castle (Crotone, Italy). J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 67, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compare, V.; Cozzolino, M.; Mauriello, P.; Patella, D. Resistivity probability tomography at the Castle of Zena (Italy). EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2009, 2009, 693274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsokas, N.G.; Tsourlos, P.I.; Stampolidis, A.; Katsonopoulou, D.; Soter, S. Tracing a major Roman road in the area of ancient Helike by resistivity tomography. Archaeol. Prospect. 2009, 16, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mol, L.; Preston, P.R. The writing’s in the wall: A review of new preliminary applications of electrical resistivity tomography within archaeology. Archaeometry 2010, 52, 1079–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, M.; Di Giovanni, E.; Mauriello, P.; Vanni Desideri, A.; Patella, D. Resistivity tomography in the Park of Pratolino at Vaglia (Florence, Italy). Archaeol. Prospect. 2012, 19, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentini, M.C.; Pakkanen, J.; Sarris, A. Naxos of Sicily in the 5th Century BC: New Research. In Greek Colonization. New Data, Current Approaches, Proceedings of the Scientific Meeting, Thessaloniki, Greece, 6 February 2015; Veleni, P., Tsagari, D., Eds.; Alpha Bank: Athens, Greece, 2015; pp. 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Tsokas, G.N.; Tsourlos, P.I.; Kim, J.H.; Yi, M.J.; Vargemezis, G.; Lefantzis, M.; Fikos, E.; Peristeri, K. ERT imaging of the interior of the huge tumulus of Kastas in Amphipolis (northern Greece). Archaeol. Prospect. 2018, 25, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supriyadi, A.; Suprianto, A.; Priyantari, N.; Cahyono, B.E.; Sholeha, I. Assessment of validated geoelectrical resistivity methods to reconstruct buried archaeological site (case study: Beteng Site-Sidomekar, Jember Regency). J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1153, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabas, M. Theory and practice of the new fast electrical imaging system ARP©. In Seeing the Unseen. Geophysics and Landscape Archaeology; Campana, S., Piro, S., Eds.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2009; pp. 105–126. [Google Scholar]
- Piroddi, L.; Calcina, S.V.; Trogu, A.; Ranieri, G. Automated Resistivity Profiling (ARP) to explore wide archaeological areas: The prehistoric site of Mont’e Prama, Sardinia, Italy. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouteau, M.; Vallières, S.; Toe, E. A multi-dipole mobile array for the non-destructive evaluation of pavement and concrete infrastructures: A feasability study. In Proceedings of the International Symposium Non-Destructive Testing in Civil Engineering (NDT-CE 2003), Berlin, Germany, 16–19 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, A.J. Seeing Beneath the Soil. Prospecting Methods in Archeology; B.T. Batsford: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney, C.; Gater, J. Revealing the Buried Past: Geophysics for Archaeologists; Tempus Publishing: Stroud, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, Y. 3-D resistivity inversion using the finite element method. Geophysics 1994, 59, 1839–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.H.; Barker, R.D. Rapid least-squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudosections by a quasi-Newton method. Geophys. Prospect. 1996, 44, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsourlos, P.; Ogilvy, R. An algorithm for the 3-D inversion of tomographic resistivity and induced polarization data: Preliminary results. J. Balk. Geophys. Soc. 1999, 2, 30–45. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlin, T. The development of electrical imaging techniques. Comput. Geosci. 2001, 27, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidlisecky, A.; Haber, E.; Knight, R. RESINVM3D: A 3D resistivity inversion package. Geophysics 2007, 72, H1–H10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, N.G.; Tsourlos, P.; Tsokas, G.N.; Sarris, A. Efficient ERT measuring and inversion strategies for 3D imaging of buried antiquities. Near Surf. Geophys. 2007, 5, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marescot, L.; Lopes, S.P.; Rigobert, S.; Green, A.G. Nonlinear inversion of geoelectric data acquired across 3D objects using a finite-element approach. Geophysics 2008, 73, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, N.G.; Tsourlos, P.; Papazachos, C.; Tsokas, G.N.; Sarris, A.; Kim, J.H. An algorithm for fast 3D inversion of surface electrical resistivity tomography data: Application on imaging buried antiquities. Geophys. Prospect. 2011, 59, 557–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauriello, P.; Patella, D. A data-adaptive probability-based fast ERT inversion method. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2009, 97, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patella, D. Introduction to ground surface selfpotential tomography. Geophys. Prospect. 1997, 45, 653–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauriello, P.; Patella, D. Resistivity anomaly imaging by probability tomography. Geophys. Prospect. 1999, 47, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minelli, A.; Cozzolino, M.; Di Nucci, A.; Guglielmi, S.; Giannantonio, M.; D’Amore, D.; Pittoni, E.; Groot, A.M. The prehistory of the Colombian territory: The results of the Italian archaeological investigation on the Checua site (Municipality of Nemocòn, Cundinamarca Department). J. Biol. Res. 2012, 85, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, V.; Cozzolino, M.; De Benedittis, G.; Di Paola, G.; Gentile, V.; Giordano, C.; Marino, P.; Rosskopf, C.M.; Valente, E. An integrated quantitative approach to assess the archaeological heritage in highly anthropized areas: The case study of Aesernia (southern Italy). Acta IMECO 2016, 5, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, M.; Mauriello, P.; Patella, D. Resistivity Tomography Imaging of the substratum of the Bedestan Monumental Complex at Nicosia, Cyprus. Archaeometry 2014, 56, 331–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Valente, E.; Ascione, A.; Ciotoli, G.; Cozzolino, M.; Porfido, S.; Sciarra, A. Do moderate magnitude earthquakes generate seismically induced ground effects? The case study of the Mw = 5.16, 29th December 2013 Matese earthquake (southern Apennines, Italy). Int. J. Earth Sci. 2013, 107, 517–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, M.; Longo, F.; Pizzano, N.; Rizzo, M.L.; Voza, O.; Amato, V. Multidisciplinary Approach to the Study of the Temple of Athena in Poseidonia-Paestum (Southern Italy): New Geomorphological, Geophysical and Archaeological Data. Geosciences 2019, 9, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, M.; Mauriello, P.; Moisidi, M.; Vallianatos, F. A Probability Electrical Resistivity Tomography Imaging of complex tectonic features in the Kissamos and Paleohora urban areas, Western Crete (Greece). Ann. Geophys. Italy 2019, 62, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cozzolino, M.; Caliò, L.M.; Gentile, V.; Mauriello, P.; Di Meo, A. The Discovery of the Theater of Akragas (Valley of Temples, Agrigento, Italy): An Archaeological Confirmation of the Supposed Buried Structures from a Geophysical Survey. Geosciences 2020, 10, 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10050161
Cozzolino M, Caliò LM, Gentile V, Mauriello P, Di Meo A. The Discovery of the Theater of Akragas (Valley of Temples, Agrigento, Italy): An Archaeological Confirmation of the Supposed Buried Structures from a Geophysical Survey. Geosciences. 2020; 10(5):161. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10050161
Chicago/Turabian StyleCozzolino, Marilena, Luigi Maria Caliò, Vincenzo Gentile, Paolo Mauriello, and Andrea Di Meo. 2020. "The Discovery of the Theater of Akragas (Valley of Temples, Agrigento, Italy): An Archaeological Confirmation of the Supposed Buried Structures from a Geophysical Survey" Geosciences 10, no. 5: 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10050161
APA StyleCozzolino, M., Caliò, L. M., Gentile, V., Mauriello, P., & Di Meo, A. (2020). The Discovery of the Theater of Akragas (Valley of Temples, Agrigento, Italy): An Archaeological Confirmation of the Supposed Buried Structures from a Geophysical Survey. Geosciences, 10(5), 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10050161