Spatial Analysis of Infections by Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum (Protozoa: Apicomplexa) in Small Ruminants in Northern Italy
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
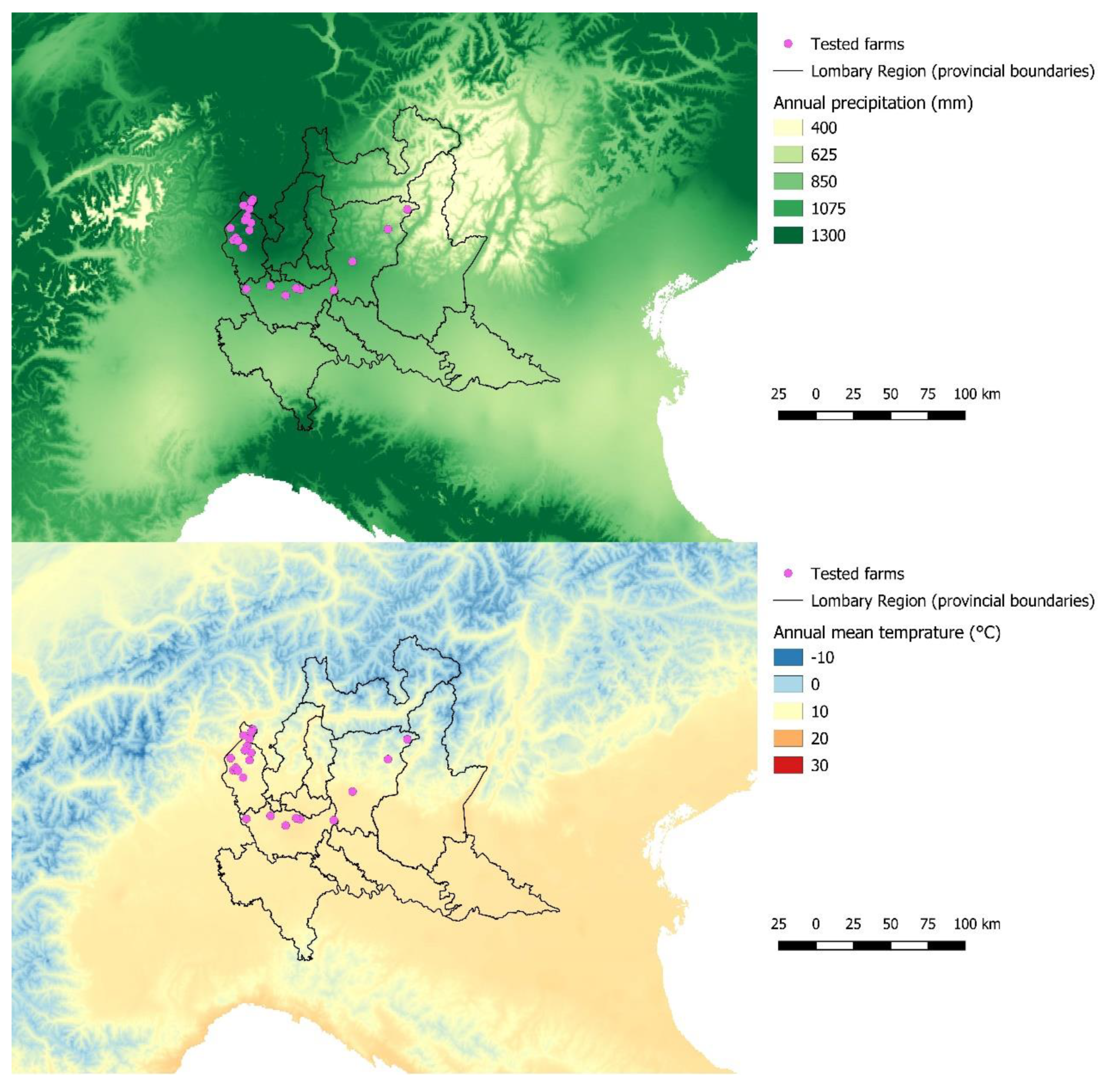
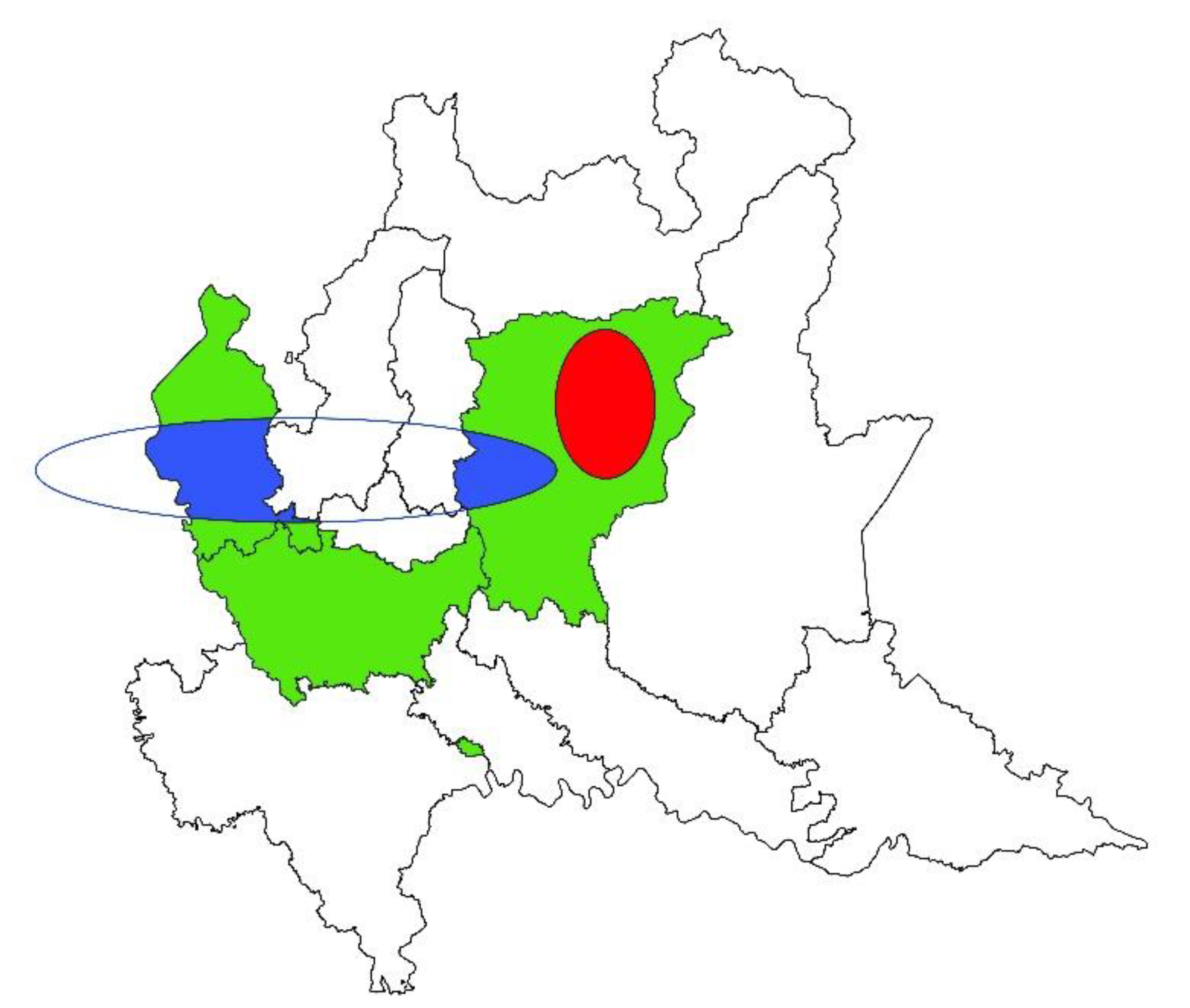
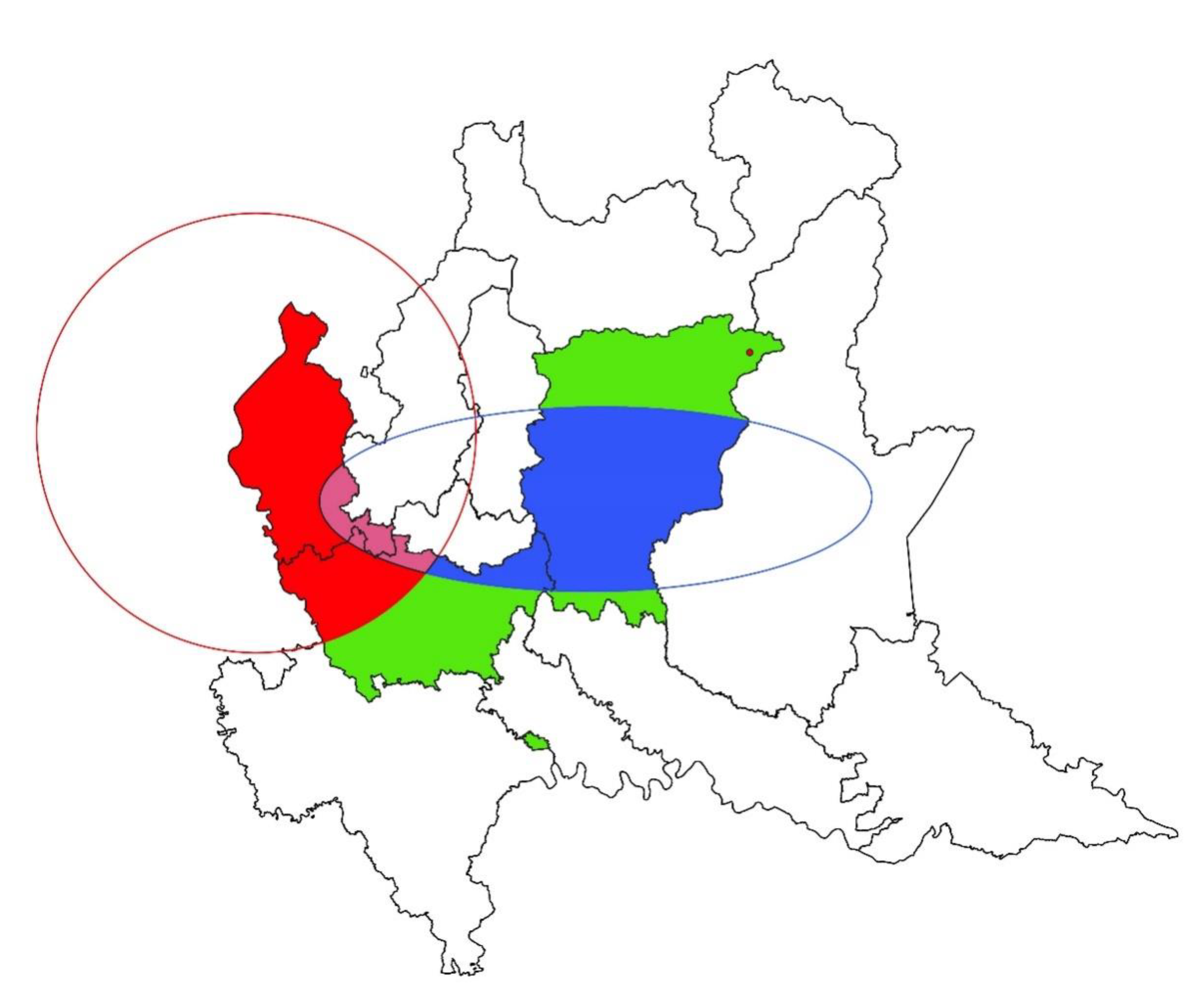
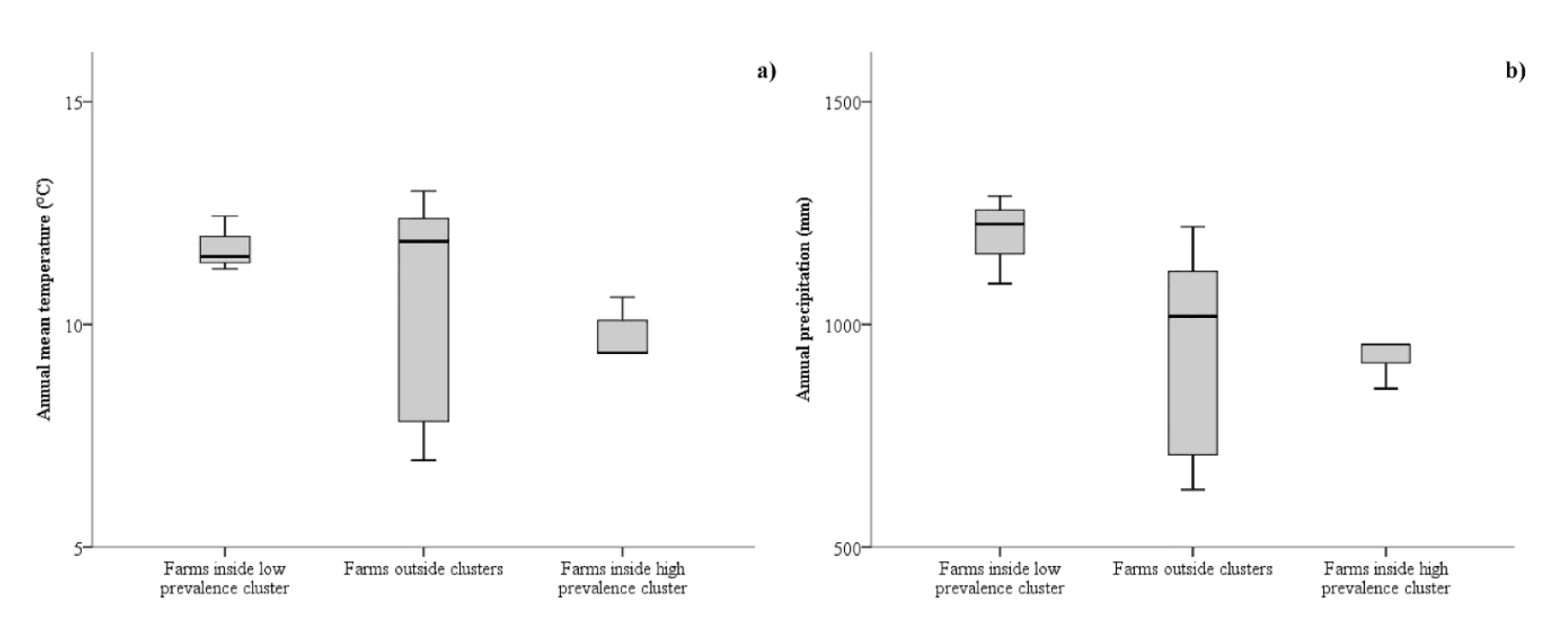
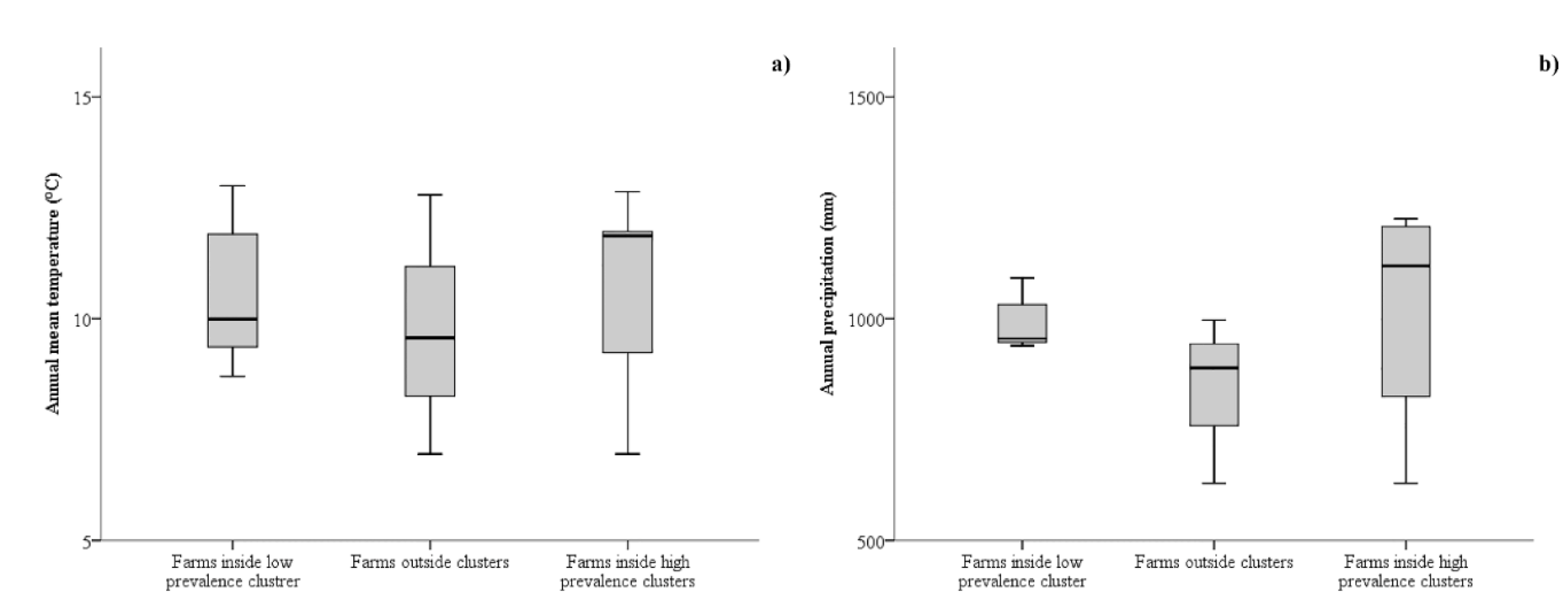
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Analysis
3.2. Risk Factors Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EFSA-ECDC. The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2017. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05500. [Google Scholar]
- Pappas, G.; Roussos, N.; Falagas, M.E. Toxoplasmosis snapshots: Global status of Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence and implications for pregnancy and congenital toxoplasmosis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.; Khan, W. Congenital toxoplasmosis: An overview of the neurological and ocular manifestations. Parasitol. Int. 2018, 67, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, L.M.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis: A history of clinical observations. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djurković-Djaković, O.; Dupouy-Camet, J.; Van der Giessen, J.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis: Overview from a One Health perspective. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijlstra, A.; Jongert, E. Control of the risk of human toxoplasmosis transmitted by meat. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Mora, L.M.; Gottstein, B.; Conraths, F.J.; Buxton, D. Protozoal Abortion in Farm Ruminants: Guidelines for Diagnosis and Control, 2nd ed.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Berger-Schoch, A.E.; Bernet, D.; Doherr, M.G.; Gottstein, B.; Frey, C.F. Toxoplasma gondii in Switzerland: A Serosurvey Based on Meat Juice Analysis of Slaughtered Pigs, Wild Boar, Sheep and Cattle. Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovu, A.; Györke, A.; Mircean, V.; Gavrea, R.; Cozma, V. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in dairy goats from Romania. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 186, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanidakis, N.; Maksimov, P.; Conraths, F.J.; Kiossis, E.; Brozos, C.; Sotiraki, S.; Schares, G. Toxoplasma gondii in sheep and goats: Seroprevalence and potential risk factors under dairy husbandry practices. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 190, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Bocanegra, I.; Cabezón, O.; Hernández, E.; Martínez-Cruz, M.S.; Martínez-Moreno, Á.; Martínez-Moreno, J. Toxoplasma gondii in Ruminant Species (Cattle, Sheep, and Goats) from Southern Spain. J. Parasitol. 2013, 99, 438–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.P.; Dubey, J.P.; Neto, F.; Rodrigues, A.; Martins, T.; Rodrigues, M.; Cardoso, L. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in cattle, sheep, goats and pigs from the North of Portugal for human consumption. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 193, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenci-Goga, B.T.; Ciampelli, A.; Sechi, P.; Veronesi, F.; Moretta, I.; Cambiotti, V.; Thompson, P.N. Seroprevalence and risk factors for Toxoplasma gondii in sheep in Grosseto district, Tuscany, Italy. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazzonis, A.L.; Veronesi, F.; Di Cerbo, A.R.; Zanzani, S.A.; Molineri, G.; Moretta, I.; Moretti, A.; Fioretti, D.P.; Invernizzi, A.; Manfredi, M.T. Toxoplasma gondii in small ruminants in Northern Italy-prevalence and risk factors. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2015, 22, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazzonis, A.L.; Alvarez Garcia, G.; Zanzani, S.A.; Ortega Mora, L.M.; Invernizzi, A.; Manfredi, M.T. Neospora caninum infection in sheep and goats from north-eastern Italy and associated risk factors. Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 140, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djokić, V.; Klun, I.; Musella, V.; Rinaldi, L.; Cringoli, G.; Sotiraki, S.; Djurković-Djaković, O. Spatial epidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii infection in goats in Serbia. Geospat. Health 2014, 8, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, M.C.; Connor, S.J. Environmental information systems for the control of arthropod vectors of disease. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2000, 14, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.N.; Lv, S.; Yang, G.J.; Kristensen, T.K.; Bergquist, N.R.; Utzinger, J.; Malone, J.B. Spatial epidemiology in zoonotic parasitic diseases: Insights gained at the international symposium on geospatial health in Lijiang, China, 2007. Parasit. Vectors 2009, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, M.T.; Di Cerbo, A.R.; Zanzani, S.; Moriggia, A.; Fattori, D.; Siboni, A.; Bonazza, V.; Filice, C.; Brunetti, E. Prevalence of echinococcosis in humans, livestock and dogs in northern Italy. Helminthologia 2011, 48, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meurs, L.; Mbow, M.; Boon, N.; van den Broeck, F.; Vereecken, K.; Dièye, T.N.; Abatih, E.; Huyse, T.; Mboup, S.; Polman, K. Micro-Geographical Heterogeneity in Schistosoma mansoni and S. haematobium Infection and Morbidity in a Co-Endemic Community in Northern Senegal. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassini, R.; Mulatti, P.; Zanardello, C.; Simonato, G.; Signorini, M.; Cazzin, S.; Tambalo, P.G.; Cobianchi, M.; Pietrobelli, M.; Capelli, G. Retrospective and spatial analysis tools for integrated surveillance of cystic echinococcosis and bovine cysticercosis in hypo-endemic areas. Geospat. Health. 2014, 8, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, E.; Gazzonis, A.L.; Zanzani, S.A.; Veronesi, F.; Manfredi, M.T. Seasonal dynamics of adult Dermacentor reticulatus in a peri-urban park in southern Europe. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2017, 8, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanzani, S.; Rimoldi, S.; Manfredi, M.; Grande, R.; Gazzonis, A.L.; Merli, S.; Olivieri, E.; Giacomet, V.; Antonori, S.; Cislaghi, G.; et al. Lyme borreliosis incidence in Lombardy, Italy (2000–2015): Spatiotemporal analysis and environmental risk factors. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 101257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frössling, J.; Nødtvedt, A.; Lindberg, A.; Björkman, C. Spatial analysis of Neospora caninum distribution in dairy cattle from Sweden. Geospat. Health 2008, 3, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klevar, S.; Norström, M.; Tharaldsen, J.; Clausen, T.; Björkman, C. The prevalence and spatial clustering of Neospora caninum in dairy herds in Norway. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 170, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogareda, C.; Jubert, A.; Kantzoura, V.; Kouam, M.K.; Feidas, H.; Theodoropoulos, G. Geographical distribution modelling for Neospora caninum and Coxiella burnetii infections in dairy cattle farms in northeastern Spain. Epidemiol. Infect. 2013, 141, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condoleo, R.; Musella, V.; Maurelli, M.P.; Bosco, A.; Cringoli, G.; Rinaldi, L. Mapping, cluster detection and evaluation of risk factors of ovine toxoplasmosis in Southern Italy. Geospat. Health 2016, 11, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzonis, A.L.; Villa, L.; Riehn, K.; Hamedy, A.; Minazzi, S.; Olivieri, E.; Zanzani, S.A.; Manfredi, M.T. Occurrence of selected zoonotic food-borne parasites and first molecular identification of Alaria alata in wild boars (Sus scrofa) in Italy. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 2207–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzonis, A.L.; Zanzani, S.A.; Santoro, A.; Veronesi, F.; Olivieri, E.; Villa, L.; Lubian, E.; Lovati, S.; Bottura, F.; Epis, S.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii infection in raptors from Italy: Seroepidemiology and risk factors analysis. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 60, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzonis, A.L.A.L.; Marangi, M.; Villa, L.; Ragona, M.E.M.E.; Olivieri, E.; Zanzani, S.A.S.A.; Giangaspero, A.; Manfredi, M.T.M.T. Toxoplasma gondii infection and biosecurity levels in fattening pigs and sows: Serological and molecular epidemiology in the intensive pig industry (Lombardy, Northern Italy). Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, L.; Gazzonis, A.L.; Álvarez-García, G.; Diezma-Díaz, C.; Zanzani, S.A.; Manfredi, M.T. First detection of anti-Besnoitia spp. specific antibodies in horses and donkeys in Italy. Parasitol. Int. 2018, 67, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanzani, S.A.; Cerbo, A.D.; Gazzonis, A.L.; Epis, S.; Invernizzi, A.; Tagliabue, S.; Manfredi, M.T. Parasitic and Bacterial Infections of Myocastor coypus in a Metropolitan Area of Northwestern Italy. J. Wildl. Dis. 2016, 52, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulldorff, M. A spatial scan statistic. Commun. Stat.-Theory Methods 1997, 26, 1481–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Tiwari, R.C.; Zou, Z.; Kulldorff, M.; Feuer, E.J. Weighted Normal spatial scan statistic for heterogeneous population data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2009, 104, 886–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schares, G.; Bärwald, A.; Staubach, C.; Ziller, M.; Klöss, D.; Wurm, R.; Rauser, M.; Labohm, R.; Dräger, K.; Fasen, W.; et al. Regional distribution of bovine Neospora caninum infection in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate modelled by Logistic regression. Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yániz, J.L.; López-Gatius, F.; García-Ispierto, I.; Bech-Sàbat, G.; Serrano, B.; Nogareda, C.; Sanchez-Nadal, J.A.; Almeria, S.; Santolaria, P. Some factors affecting the abortion rate in dairy herds with high incidence of neospora-associated abortions are different in cows and heifers. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2010, 45, 699–705. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, D.S.; Dubey, J.P.; Duncan, R.B. Confirmation that the dog is a definitive host for Neospora caninum. Vet. Parasitol. 1999, 82, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumètre, A.; Dardé, M.L. How to detect Toxoplasma gondii oocysts in environmental samples? FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, L.; Fusco, G.; Musella, V.; Veneziano, V.; Guarino, A.; Taddei, R.; Cringoli, G. Neospora caninum in pastured cattle: Determination of climatic, environmental, farm management and individual animal risk factors using remote sensing and geographical information systems. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 128, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wapenaar, W.; Jenkins, M.C.; O’Handley, R.M.; Barkema, H.W. Neospora caninum-like oocysts observed in feces of free-ranging red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) and coyotes (Canis latrans). J. Parasitol. 2006, 92, 1270–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barling, K.S.; Sherman, M.; Peterson, M.J.; Thompson, J.A.; McNeill, J.W.; Craig, T.M.; Adams, L.G. Spatial associations among density of cattle, abundance of wild canids, and seroprevalence to N. caninum in a population of beef calves. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2000, 217, 1361–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloney, B.J.; Heuer, C.; Kirkland, P.D. Neospora caninum in beef herds in New South Wales, Australia. 2: Analysis of risk factors. Aust. Vet. J. 2017, 95, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelzer, S.; Basso, W.; Benavides Silván, J.; Ortega-Mora, L.M.; Maksimov, P.; Gethmann, J.; Conraths, F.J.; Schares, G. Toxoplasma gondii infection and toxoplasmosis in farm animals: Risk factors and economic impact. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, B.C.; Conrad, P.A.; Breitmeyer, R.; Sverlow, K.; Anderson, M.L.; Reynolds, J.; Chauvet, A.E.; Dubey, J.P.; Ardans, A.A. Congenital Neospora infection in calves born from cows that had previously aborted Neospora-infected fetuses: Four cases (1990–1992). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1993, 202, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hietala, S.K.; Thurmond, M.C. Postnatal Neospora caninum transmission and transient serologic responses in two dairies. Int. J. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 1669–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schares, G.; Peters, M.; Wurm, R.; Bärwald, A.; Conraths, F.J. The efficiency of vertical transmission of Neospora caninum in dairy cattle analysed by serological techniques. Vet. Parasitol. 1998, 80, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasia, D.; Elias, P.; Nikolaos, P.; Charilaos, K.; Nektarios, G. Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum seroprevalence in dairy sheep and goats mixed stock farming. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 198, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoste, H.; Sotiraki, S.; Landau, S.Y.; Jackson, F.; Beveridge, I. Goat-Nematode interactions: Think differently. Trends Parasitol. 2010, 26, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opsteegh, M.; Kortbeek, T.M.; Havelaar, A.H.; Van Der Giessen, J.W.B. Intervention strategies to reduce human Toxoplasma gondii disease burden. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% Confidence Interval (CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual mean temperature (continuous variable) | 0.080 | 0.001–5.959 | 0.130 |
| Annual rainfall (continuous variable) | 0.997 | 0.992–1.001 | 0.140 |
| Variables | Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% Confidence Interval (CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual mean temperature (continuous variable) | 2.271 | 1.219–4.232 | 0.010 |
| Annual rainfall (continuous variable) | 1.093 | 1.022–1.169 | 0.009 |
| Annual mean temperature/ annual rainfall interaction | 0.9991 | 0.9984–0.9997 | 0.007 |
| Variables | Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% Confidence Interval (CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual mean temperature (continuous variable) | 1.004 | 0.964–1.046 | 0.835 |
| Annual rainfall (continuous variable) | 1.001 | 0.997–1.006 | 0.584 |
| Variable | Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% Confidence Interval (CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual mean temperature (continuous variable) | 0.567 | 0.381–0.844 | 0.005 |
| Annual rainfall (continuous variable) | 0.947 | 0.908–0.987 | 0.010 |
| Annual mean temperature/ annual rainfall interaction | 1.0006 | 1.0002–1.001 | 0.005 |
| Variables | Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% Confidence Interval (CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual mean temperature (continuous variable) | 0.945 | 0.880–1.014 | 0.116 |
| Annual rainfall (continuous variable) | 1.105 | 0.971–1.257 | 0.130 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gazzonis, A.; Villa, L.; Manfredi, M.; Zanzani, S. Spatial Analysis of Infections by Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum (Protozoa: Apicomplexa) in Small Ruminants in Northern Italy. Animals 2019, 9, 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9110916
Gazzonis A, Villa L, Manfredi M, Zanzani S. Spatial Analysis of Infections by Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum (Protozoa: Apicomplexa) in Small Ruminants in Northern Italy. Animals. 2019; 9(11):916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9110916
Chicago/Turabian StyleGazzonis, Alessia, Luca Villa, MariaTeresa Manfredi, and Sergio Zanzani. 2019. "Spatial Analysis of Infections by Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum (Protozoa: Apicomplexa) in Small Ruminants in Northern Italy" Animals 9, no. 11: 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9110916
APA StyleGazzonis, A., Villa, L., Manfredi, M., & Zanzani, S. (2019). Spatial Analysis of Infections by Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum (Protozoa: Apicomplexa) in Small Ruminants in Northern Italy. Animals, 9(11), 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9110916






