Integrating Desert Sand Utilization in Saltwater Aqua-Vegeculture Production: Performance Evaluation of Yield and Biochemical Composition
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
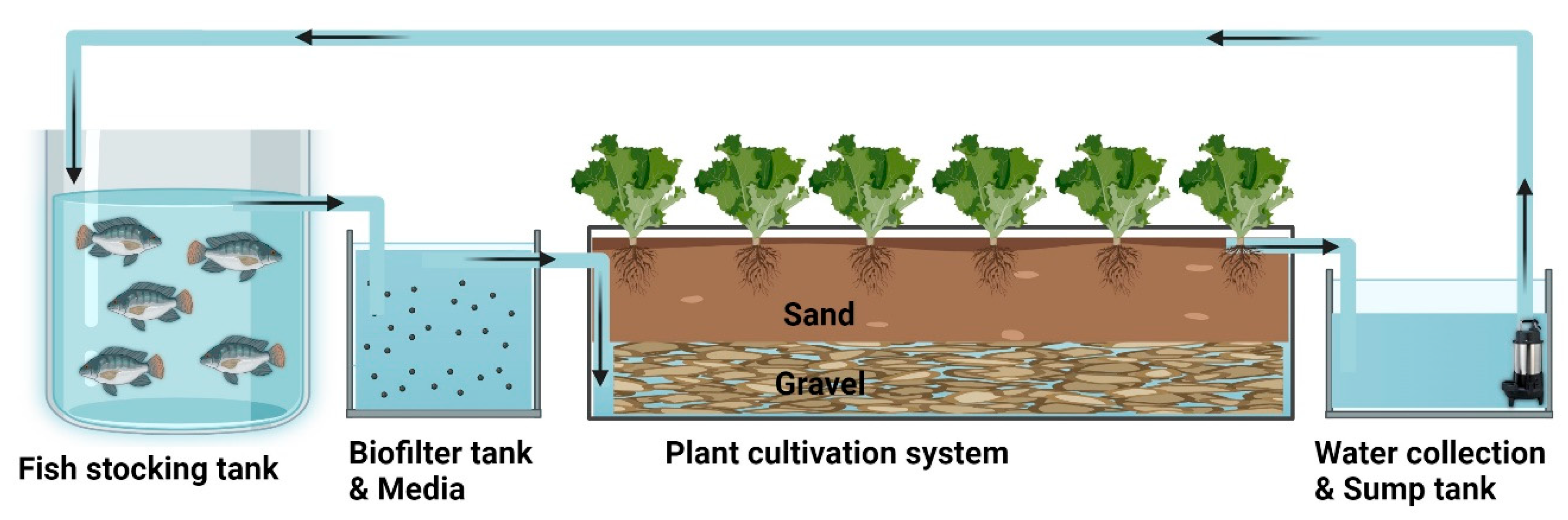
2.1. System Description
2.2. Procurement and Acclimatization of the Experimental Fish
2.3. Experimental Water Preparation
2.4. Plant Growth Setup
2.5. Fish Growth Parameters
2.6. Plant Growth Parameters
2.7. Water Quality Parameters
2.8. Proximate Composition Analysis
2.9. Experimental Sampling and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Water Quality Parameters
3.2. Fish Growth Parameters
3.3. Proximate Composition of the Fish Carcass and Blood Chemistry
3.4. Lettuce Plant Growth Parameters and Yield
3.5. Proximate Composition Analysis
Macro and Micro Elements Concentration of Lettuce
4. Discussion
4.1. Water Quality Parameters
4.2. Fish Growth Parameters, Proximate Composition, and Blood Chemistry
4.3. Growth Performance and Biochemical Quality of the Lettuce
4.4. Proximate Composition Analysis
4.5. Macro and Micro Elements Concentration of Lettuce
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thorarinsdottir, R.I. Aquaponics Guidelines; Eco-innovation Initiative of the European Union; Haskolaprent: Reykjavik, Iceland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gunning, D.; Maguire, J.; Burnell, G. The Development of Sustainable Saltwater-Based Food Production Systems: A Review of Established and Novel Concepts. Water 2016, 8, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, P.M.; Azaizeh, H.; Leon, D. Hardening of Root Cell Walls: A Growth Inhibitory Response to Salinity Stress. Plant Cell Environ. 1994, 17, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joesting, H.M.; Blaylock, R.; Biber, P.; Ray, A. The Use of Marine Aquaculture Solid Waste for Nursery Production of the Salt Marsh Plants Spartina Alterniflora and Juncus Roemerianus. Aquac. Rep. 2016, 3, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS (U.S. Geological Survey). Where Is Earth’s Water? Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/special-topics/water-science-school/science/where-earths-water (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Makokha, P.; Ssali, R.T.; Rajendran, S.; Wanjala, B.W.; Matasyoh, L.G.; Kiplagat, O.K.; McEwan, M.A.; Low, J.W. Comparative Analysis for Producing Sweetpotato Pre-Basic Seed Using Sandponics and Conventional Systems. J. Crop Improv. 2020, 34, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masato, B.; Naoki, I. Industrial Cultivation Using the Latest Sandponics System. SEI Tech. Rev. 2015, 80, 98. [Google Scholar]
- Siegner, A.; Sowerwine, J.; Acey, C. Does Urban Agriculture Improve Food Security? Examining the Nexus of Food Access and Distribution of Urban Produced Foods in the United States: A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurtry, M.R.; Sanders, D.C.; Cure, J.D.; Hodson, R.G. Effects of Biofilter/Culture Tank Volume Ratios on Productivity of a Recirculating Fish/Vegetable Co-Culture System. J. Appl. Aquac. 1997, 7, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewilam, H.; Kimera, F.; Nasr, P.; Dawood, M. A Sandponics Comparative Study Investigating Different Sand Media Based Integrated Aqua Vegeculture Systems Using Desalinated Water. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimera, F.; Mugwanya, M.; Dawood, M.; Sewilam, H. Growth Response of Kale (Brassica oleracea) and Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus) under Saline Aqua-Sandponics-Vegeculture System. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurtry, M.R. Performance of an Integrated Aquaculture-Olericulture System as Influenced by Component Ratio. Ph.D. Thesis, NC University, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 1988. Available online: https://www.lib.ncsu.edu/resolver/1840.20/41550 (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- McMurtry, M.R. Sand Culture of Vegetables Using Recirculated Aquacultural Effluents. Appl. Agric. Res. 1990, 5, 280–284. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, A.; Rakocy, J.E.; Hargreaves, J.A. (Eds.) Water quality characteristics of a closed recirculating system for tilapia culture and tomato hydroponics. In Proceedings of the Water Quality Characteristic Second International Conference on Warmwater Aquaculture Finfish, Laie, HI, USA, 5–8 February 1985; Division of Continuing Education, Brigham Young University: Laie, HI, USA, 1985; pp. 223–254. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture—Opportunities and Challenges (SOFIA); Graziano da Silva, J., Ed.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2014; 223p, ISBN 978-92-5-108275-1. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/b673bef5-f7a3-43eb-baf9-05221a9c34ef/content (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- El-Sayed, A.F.M. Tilapia Culture in Salt Water: Environmental Requirements, Nutritional Implications and Economic Potentials. In Avances En Nutrición Acuícola VIII.VIII Simposium Internacional de Nutrición Acuícola; Suárez, L.E.C., Marie, D.R., Salazar, M.T., López, M.G.N., Cavazos, D.A.V., Ortega, A.C.P.C.A.G., Eds.; Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León: Monterrey, México, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Amoudi, M.M. Acclimation of Commercially Cultured Oreochromis Species to Sea Water—An Experimental Study. Aquaculture 1987, 65, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, R. Stickney Tilapia Tolerance of Saline Waters: A Review. Progress. Fish-Cult. 1986, 48, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Spradlin, A.; Saha, S. Saline Aquaponics: A Review of Challenges, Opportunities, Components, and System Design. Aquaculture 2022, 555, 738173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, C.P. Pluchea. In Indian Herbal Remedies Rational Western Therapy, Ayurvedic and Other Traditional Usage, Botany; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 375–376. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, Q.C.; Teo, S.S. Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) Growth Performance in Saltwater, Soil and Aquaponic System. Agric. Food Sci. Res. 2019, 6, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pascale, S.; Barbieri, G. Effects of Soil Salinity from Long-Term Irrigation with Saline-Sodic Water on Yield and Quality of Winter Vegetable Crops. Sci. Hortic. 1995, 64, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turhan, A.; Kuscu, H.; Ozmen, N.; Serbeci, M.S.; Demir, A.O. Effect of Different Concentrations of Diluted Seawater on Yield and Quality of Lettuce. Chilian J. Agric. Res. 2014, 74, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahgoub Azooz, M.; Hamed, A.A.; Latef, A. The Accumulation and Compartmentation of Proline in Relation to Salt Tolerance of Three Sorghum Cultivars. Artic. Indian. J. Plant Physiol. 2004, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Orsini, F.; Kahane, R.; Nono-Womdim, R.; Gianquinto, G. Urban Agriculture in the Developing World: A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 695–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, E.R. Aquaponics: Community and Economic Development. Master’s Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Radhakrishnan, S.; Belal, I.E.H.; Seenivasan, C.; Muralisankar, T.; Bhavan, P.S. Impact of Fishmeal Replacement with Arthrospira Platensis on Growth Performance, Body Composition and Digestive Enzyme Activities of the Freshwater Prawn, Macrobrachium Rosenbergii. Aquac. Rep. 2016, 3, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percie Du Sert, N.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The ARRIVE Guidelines 2.0: Updated Guidelines for Reporting Animal Research. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overton, J.L.; Bayley, M.; Paulsen, H.; Wang, T. Salinity Tolerance of Cultured Eurasian Perch, Perca Fluviatilis L.: Effects on Growth and on Survival as a Function of Temperature. Aquaculture 2008, 277, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, R.K.; Martinez-Alvarez, R.M.; DePedro, N.; Delgado, M.J. Growth, food intake regulation and metabolic adaptations in goldfish (Carassius auratus) exposed to different salinities. Aquaculture 2008, 276, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 15th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemist: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Method for the Examination of Water and Wastewaters, 21st ed.; American Water Works Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Fatema, U.K.; Hossain, M.A. Assessment of Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) Growth and Yield in Two Different Aquaponics System. Ann. Bangladesh Agric. 2018, 22, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Resh, H.M. Hydroponic Food Production: A Definitive Guidebook for the Advanced Home Gardener and the Commercial Hydroponic Grower; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, R.D.; Shamim, A.A.; Labrique, A.B.; Ali, H.; Schulze, K.; Rashid, M.; Christian, P.; West, K.P. Validation of Two Portable Instruments to Measure Iron Concentration in Groundwater in Rural Bangladesh. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2009, 27, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattan, S.R.; Grieve, C.M. Salinity ± mineral Nutrient Relations in Horticultural Crops. Sci. Hortic. 1999, 78, 127–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.C.; Patten, K.D.; Drew, M.C. Mineral Composition of Young Rabbiteye and Southern Highbush Blueberry Exposed to Salinity and Supplemental Calcium. J. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 1994, 119, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, Y.P. Bioremediation of Salt Affected Soils: An Indian Perspective; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 1–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafkafi, U.; Valoras, N.; Letey, J. Chloride Interaction with Nitrate and Phosphate Nutrition in Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.). J. Plant Nutr. 1982, 5, 1369–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli, A.; Moncada, A.; D’Anna, F. Effect of Salt Stress in Lettuce Cultivation. Acta Hortic. 2003, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bañuelos, G.S.; Arroyo, I.; Pickering, I.J.; Yang, S.I.; Freeman, J.L. Selenium Biofortification of Broccoli and Carrots Grown in Soil Amended with Se-Enriched Hyperaccumulator Stanleya Pinnata. Food Chem. 2015, 166, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvy, J.E.; Symonds, J.E.; Hilton, Z.; Walker, S.P.; Tremblay, L.A.; Casanovas, P.; Herbert, N.A. The Relationship of Feed Intake, Growth, Nutrient Retention, and Oxygen Consumption to Feed Conversion Ratio of Farmed Saltwater Chinook Salmon (Oncorhynchus Tshawytscha). Aquaculture 2022, 554, 738184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, A.H.M.M.; Mair, G.C. Salinity Tolerance in Superior Genotypes of Tilapia, Oreochromis Niloticus, Oreochromis Mossambicus and Their Hybrids. Aquaculture 2005, 247, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira De Azevedo, R.; Figueiredo De Oliveira, K.; Flores-Lopes, F.; Arruda Teixeira-Lanna, E.; Sanae Takishita, S.; Luís, G.; Tavares-Braga, G. Responses of Nile tilapia to different levels of water salinity. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2015, 43, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bœuf, G.; Payan, P. How Should Salinity Influence Fish Growth? Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2001, 130, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauel, M.J.; Miller, D.L.; Merrill, A. Hematologic and plasma biochemical values of healthy hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis aureus × Oreochromis nilotica) maintained in a recirculating system. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2007, 38, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasonga, A.G.; Daniel, W.A.; Brian, O. Interspecific Hybridization of Tilapiines in Lake Victoria, Kenya. J. Fish. Livest. Prod. 2017, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, N.A.; Saad, M.F.; Shukry, M.; El-Keredy, A.M.S.; Nasif, O.; Doan, H.V.; Dawood, M.A.O. Physiological and ion changes of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) under the effect of salinity stress. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 19, 100567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, S.; Bron, J.E.; Rana, K.J. Ontogenic Changes in the Osmoregulatory Capacity of the Nile Tilapia Oreochromis Niloticus and Implications for Aquaculture. Aquaculture 2012, 356–357, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, K.; Kaneko, T.; Miyazaki, H.; Hasegawa, S.; Hirano, T. Excellent Salinity Tolerance of Mozambique Tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus): Elevated Chloride Cell Activity in the Branchial and Opercular Epithelia of the Fish Adapted to Concentrated Seawater. Zool. Sci. 2000, 17, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.C.; Lin, C.R.; Chen, S.M. Acclimation of Mozambique Tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) to Salinity Changes Alters Protein Content of the Larvae and Their Liver and Kidney. Aquac. Res. 2005, 36, 936–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.; Vargas-Chacoff, L.; Hachero-Cruzado, I.; Ruíz-Jarabo, I.; Rodiles, A.; Navas, J.I.; Mancera, J.M. Osmoregulatory changes in wedge sole (Dicologoglossa cuneata Moreau, 1881) after acclimation to different environmental salinities. Aquac. Res. 2009, 40, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withyachumnarnkul, B.; Foroutan, B.; Chotwiwatthanakun, C.; Kanjanasopa, D.; Kongplong, S.; Krishna, S.; Pongtippatee, P.; Saedan, S.; Santimanawong, W.; Withyachumnarnkul, B.; et al. Increased Lipogenesis in the Liver of Seawater-Acclimated Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis Niloticus. Trends Sci. 2025, 22, 9257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriolo, J.L.; da Luz, G.L.; Witter, M.H.; Godoi, R.d.S.; Barros, G.T.; Bortolotto, O.C. Growth and Yield of Lettuce Plants under Salinity. Hortic. Bras. 2005, 23, 931–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriolo, J.L.; da Luz, G.L.; Giraldi, C.; Godoi, R.d.S.; Barros, G.T. Cultivo Hidropônico Da Alface Empregando Substratos: Uma Alternativa a NFT? Hortic. Bras. 2004, 22, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buriol, G.A.; Estefanel, V.; Andriolo, J.L.; Matzenauer, R.; Tazzo, I.F. Disponibilidade de Radiação Solar Para o Cultivo Do Tomateiro Durante o Inverno No Estado Do Rio Grande Do Sul. Pesqui. Agropecuária Gaúcha 2000, 6, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Alamgir, A.; Ali, M.Y. Effect of Salinity on Leaf Pigments, Sugar and Protein Concentrations and Chloroplast ATPase Activity of Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Bangladesh J. Bot. 1999, 28, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Gadallah, M.A.A. Effects of Proline and Glycinebetaine on Vicia Faba Responses to Salt Stress. Biol. Plant 1999, 42, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumarasamy, M.; Gupta, S.D.; Panneerselvam, R. Enhancement of Peroxidase, Polyphenol Oxidase and Superoxide Dismutase Activities by Triadimefon in NaCl Stressed Raphanus Sativus L. Biol. Plant. 2000, 43, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, A.; Das, A.B.; Das, P. NaCl stress causes changes in photosynthetic pigments, proteins, and other metabolic components in the leaves of a true mangrove, Bruguiera parviflora, in hydroponic cultures. J. Plant Biol. 2002, 45, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nii, N. Changes in Chlorophyll, Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase-Oxygenase, Glycine Betaine Content, Photosynthesis and Transpiration in Amaranthus Tricolor Leaves during Salt Stress. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2000, 75, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali-Dinar, H.M.; Ebert, G.; Lüdders, P. Growth, Chlorophyll Content, Photosynthesis and Water Relations in Guava (Psidium guajava L.) Under Salinity and Different Nitrogen Supply. Gartenbauwissenschaften 1999, 64, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartzoulakis, K.; Klapaki, G. Response of Two Greenhouse Pepper Hybrids to NaCl Salinity during Different Growth Stages. Sci. Hortic. 2000, 86, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.A.; Olmos, E.; Corpas, F.J.; Sevilla, F.; del Río, L.A. Salt-Induced Oxidative Stress in Chloroplasts of Pea Plants. Plant Sci. 1995, 105, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerepesi, I.; Galiba, G. Osmotic and Salt Stress-Induced Alteration in Soluble Carbohydrate Content in Wheat Seedlings. Crop Sci. 2000, 40, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatkar, D.; Kuhad, M.S. Short-Term Salinity Induced Changes in Two Wheat Cultivars at Different Growth Stages. Biol. Plant 2000, 43, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Sharma, H.C.; Goswami, A.M.; Datta, S.P.; Singh, S.P. In Vitro Growth and Leaf Composition of Grapevine Cultivars as Affected by Sodium Chloride. Biol. Plant 2000, 43, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, A.K.; Das, A.B. Salt tolerance and salinity effects on plants: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 60, 324–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias de Aragao, M.E.; Jolivet, Y.; Guia Silva Lima, M.; Fernandes de Melo, D.; Dizengremel, P. NaCl-induced changes of NAD(P) malic enzyme activities in Eucalyptus citriodora leaves. Trees Struct. Funct. 1997, 12, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, J.C.; Meyer, G.; Michalowski, C.B.; Schmitt, J.M.; Bohnert, H.J. Salt Stress Leads to Differential Expression of Two Isogenes of Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxylase during Crassulacean Acid Metabolism Induction in the Common Ice Plant. Plant Cell 1989, 1, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Meinzer, F.C. Efficiency of C4 Photosynthesis in Atriplex lentiformis under Salinity Stress. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 1999, 26, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allakhverdiev, S.I.; Nishiyama, Y.; Miyairi, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Inagaki, N.; Kanesaki, Y.; Murata, N. Salt Stress Inhibits the Repair of Photodamaged Photosystem II by Suppressing the Transcription and Translation of PsbA Genes in Synechocystis. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 1443–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, W.Y.; Tsai, H.C.; Tsai, T.T. Effect of NaCl and Nitrogen Availability on Growth and Photosynthesis of Seedlings of a Mangrove Species, Kandelia candel (L.) Druce. J. Plant Physiol. 2001, 158, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Aranda, R.; Soria, T.; Cuartero, J. Tomato Plant-Water Uptake and Plant-Water Relationships under Saline Growth Conditions. Plant Sci. 2001, 160, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soussi, M.; Ocaña, A.; Lluch, C. Effects of Salt Stress on Growth, Photosynthesis and Nitrogen Fixation in Chick-Pea (Cicer arietinum L.). J. Exp. Bot. 1998, 49, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, A.K.; Das, A.B.; Mittra, B. Effects of Salt on Growth, Ion Accumulation, Photosynthesis and Leaf Anatomy of the Mangrove, Bruguiera Parviflora. Trees—Struct. Funct. 2004, 18, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbanl, H.; Saneoka, H.; Nehira, K.; Adilla, R.; Premachandra, G.S.; Fujita, K. Effect of salinity on growth, photosynthesis and mineral composition in leguminous plant alhagi pseudoalhagi (bieb.). Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1999, 45, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, I.; Khan, M.A. Experimental Assessment of Salinity Tolerance of Ceriops Tagal Seedlings and Saplings from the Indus Delta, Pakistan. Aquat. Bot. 2001, 70, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ungar, I.A.; Showalter, A.M. Effects of salinity on growth, ion content, and osmotic relations in Halopyrum mucronatum (L.) Stapf. J. Plant Nutr. 1999, 22, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ungar, I.A.; Showalter, A.M. Effects of sodium chloride treatments on growth and ion accumulation of the halophyte Haloxylon recurvum. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2000, 31, 2763–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Part of the System | Height (m) | Length/Width (m) | Filling Depth (m) | Water Volume (m3) | No of the Tanks | Total Water Volume (m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fish stocking tank | 0.900 | 0.548 | 0.838 | 0.198 | 2 | 0.396 |
| Biofilter tank | 0.900 | 0.548 | 0.838 | 0.198 | 2 | 0.396 |
| Plant culture raceway | 0.277 | 0.900 | 0.237 | 0.050 | 3 | 0.150 |
| Collect and pumping tank | 0.577 | 0.900 | 0.347 | 0.143 | 1 | 0.143 |
| Total | 1.085 | |||||
| Experiment | Total Water Volume (m3) | Average Salinity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| (T1) Control | 1.085 | 0 |
| (T2) | 1.085 | 2.5 |
| (T3) | 1.085 | 5 |
| (T4) | 1.085 | 7.5 |
| Experiment | Months | Temperature (°C) | Dissolved Oxygen (mg/L) | pH | Total Dissolved Solids (ppm) | Electrical Conductivity (S/m) | Ammonia (mg/L) | Nitrate (mg/L) | Nitrite (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 1 | 22.16 ± 1.02 a | 7.08 ± 0.77 a | 6.81 ± 0.19 ab | 377.38 ± 45.08 de | 0.15 ± 0.07 c | 0.25 ± 0.18 e | 6.96 ± 1.79 a | 0.23 ± 0.11 ab |
| 2 | 22.79 ± 1.14 a | 5.96 ± 0.34 b | 6.26 ± 0.05 b | 665.08 ± 55.27 bc | 0.33 ± 0.08 b | 0.61 ± 0.08 abc | 13.45 ± 0.71 b | 0.18 ± 0.01 ab | |
| 3 | 22.65 ± 1.05 a | 5.76 ± 0.35 b | 6.86 ± 0.56 ab | 848.40 ± 85.42 ab | 0.45 ± 0.06 a | 0.81 ± 0.07 a | 15.67 ± 0.64 b | 0.29 ± 0.02 ab | |
| T2 | 1 | 21.56 ± 1.46 a | 6.70 ± 1.19 a | 6.89 ± 0.53 ab | 382.67 ± 83.91 de | 0.26 ± 0.11 c | 0.23 ± 0.17 e | 5.55 ± 2.02 a | 0.13 ± 0.06 b |
| 2 | 22.26 ± 1.35 a | 6.21 ± 0.35 b | 6.20 ± 0.03 b | 679.15 ± 198.1 bc | 0.49 ± 0.07 ab | 0.49 ± 0.04 cd | 14.94 ± 2.01 b | 0.26 ± 0.04 ab | |
| 3 | 21.94 ± 1.56 a | 6.22 ± 0.53 b | 6.60 ± 0.11 ab | 991.63 ± 6.79 a | 0.53 ± 0.07 a | 0.73 ± 0.05 ab | 15.30 ± 0.29 b | 0.46 ± 0.27 a | |
| T3 | 1 | 21.69 ± 1.33 a | 7.48 ± 0.62 a | 6.68 ± 0.12 ab | 350.05 ± 20.34 de | 0.29 ± 0.03 c | 0.30 ± 0.11 de | 6.40 ± 0.95 a | 0.19 ± 0.15 ab |
| 2 | 22.17 ± 1.15 a | 5.85 ± 0.52 bc | 6.24 ± 0.01 b | 575.56 ± 65.44 cd | 0.51 ± 0.04 b | 0.58 ± 0.02 bc | 14.36 ± 4.12 b | 0.23 ± 0.08 ab | |
| 3 | 22.25 ± 1.39 a | 5.55 ± 0.71 bc | 7.06 ± 0.18 a | 671.33 ± 7.78 bc | 0.65 ± 0.10 a | 0.83 ± 0.08 a | 15.42 ± 1.07 b | 0.29 ± 0.01 ab | |
| T4 | 1 | 22.11 ± 1.21 a | 7.35 ± 0.59 a | 7.10 ± 0.22 a | 334.42 ± 15.68 de | 0.30 ± 0.03 c | 0.15 ± 0.04 e | 4.91 ± 1.12 a | 0.12 ± 0.05 b |
| 2 | 21.46 ± 0.29 a | 6.38 ± 0.79 b | 6.63 ± 0.06 ab | 386.84 ± 31.69 de | 0.57 ± 0.11 b | 0.53 ± 0.08 bc | 7.65 ± 0.82 b | 0.30 ± 0.01 ab | |
| 3 | 22.15 ± 1.21 a | 4.77 ± 0.89 c | 6.85 ± 0.47 ab | 836.63 ± 225.99 ab | 0.76 ± 0.09 a | 0.73 ± 0.06 ab | 14.88 ± 0.30 b | 0.47 ± 0.25 a |
| Growth Parameters | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Fish (Initial) | 20.00 ± 0.00 | 20.00 ± 0.00 | 20.00 ± 0.00 | 20.00 ± 0.00 |
| Length Initial | 4.13 ± 0.32 | 4.47 ± 0.55 | 3.87 ± 0.35 | 4.50 ± 0.50 |
| Weight Initial | 13.67 ± 0.29 | 14.13 ± 0.60 | 13.83 ± 0.29 | 14.07 ± 0.51 |
| No of Fish Final | 18.00 ± 1.00 a | 18.00 ± 1.00 a | 18.33 ± 0.58 a | 18.00 ± 1.00 a |
| Length Final | 11.97 ± 0.58 a | 12.67 ± 1.00 a | 12.33 ± 0.58 a | 12.27 ± 0.58 a |
| Weight Final | 183.33 ± 7.64 a | 186.00 ± 8.54 a | 178.33 ± 7.64 a | 166.67 ± 7.64 b |
| Weight gain (g) | 169.67 ± 7.42 a | 171.87 ± 8.26 a | 164.50 ± 7.70 a | 152.60 ± 7.38 b |
| Feed intake (g) | 147.33 ± 2.52 a | 149.67 ± 4.51 a | 143.67 ± 2.08 a | 145.67 ± 3.06 a |
| Feed conversion ratio (%) | 0.80 ± 0.05 a | 0.81 ± 0.05 a | 0.81 ± 0.03 a | 0.82 ± 0.05 a |
| Survival (%) | 90.00 ± 5.00 a | 90.00 ± 5.00 a | 91.67 ± 2.89 a | 90.00 ± 5.00 a |
| Hepatosomatic index (%) | 1.09 ± 0.04 a | 1.00 ± 0.05 a | 1.00 ± 0.03 a | 1.05 ± 0.07 a |
| Specific growth rate (%) | 4.04 ± 0.35 a | 4.09 ± 0.38 a | 3.99 ± 0.26 a | 3.63 ± 0.37 a |
| Carcass Proximate Composition (%) | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | 80.00 ± 0.64 a | 79.71 ± 1.77 a | 79.78 ± 1.77 a | 80.05 ± 0.28 a |
| Ash | 1.60 ± 0.35 a | 1.53 ± 0.15 a | 1.47 ± 0.07 a | 1.26 ± 0.15 a |
| Crude protein | 14.75 ± 0.78 a | 15.47 ± 0.35 a | 15.32 ± 0.66 a | 15.09 ± 1.10 a |
| Fat | 2.40 ± 0.49 a | 2.43 ± 0.15 a | 2.37 ± 0.15 a | 2.67 ± 0.32 a |
| Fiber | 1.50 ± 0.09 a | 1.49 ± 0.08 a | 1.50 ± 0.05 a | 1.49 ± 0.22 a |
| Carbohydrate | 3.74 ± 0.34 a | 3.09 ± 0.11 bc | 3.68 ± 0.20 ab | 2.98 ± 0.18 c |
| Serum biochemical (mM) | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
| Sodium | 26.75 ± 2.19 c | 37.90 ± 1.73 b | 50.09 ± 1.73 a | 49.50 ± 6.01 a |
| Chloride | 23.60 ± 1.06 d | 30.53 ± 1.27 c | 34.47 ± 1.48 b | 41.26 ± 1.27 a |
| Potassium | 3.90 ± 0.95 a | 4.32 ± 0.12 a | 3.48 ± 0.12 a | 4.04 ± 0.25 a |
| Glucose | 5.40 ± 0.49 a | 5.43 ± 0.15 a | 4.87 ± 0.56 a | 4.67 ± 0.32 a |
| Experiment | Harvest | TL | GL | RL | TW | GW | RW | LW | LL | LWI | LN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 1 | 84.80 ± 1.20 a | 33.35 ± 2.12 a | 51.45 ± 0.92 ab | 548.39 ± 35.42 a | 473.18 ± 39.66 a | 75.21 ± 4.24 a | 34.51 ± 1.32 a | 31.19 ± 0.83 a | 27.88 ± 0.81 a | 20.00 ± 1.41 a |
| 2 | 75.70 ± 1.41 b | 27.15 ± 1.27 b | 48.55 ± 0.14 ab | 550.48 ± 7.07 a | 479.91 ± 5.34 a | 70.57 ± 1.73 b | 26.83 ± 1.32 b | 26.87 ± 0.83 b | 24.38 ± 0.81 b | 18.00 ± 1.41 bc | |
| 3 | 66.30 ± 3.54 c | 26.30 ± 0.71 bc | 40.00 ± 2.83 cd | 402.57 ± 14.68 c | 342.78 ± 15.38 d | 59.79 ± 0.71 c | 21.96 ± 1.32 bc | 25.64 ± 0.83 bc | 22.98 ± 0.81 b | 16.00 ± 1.41 bc | |
| T2 | 1 | 86.30 ± 1.41 a | 31.30 ± 0.71 a | 55.00 ± 2.2 a | 489.84 ± 8.29 b | 437.33 ± 11.12 b | 52.51 ± 2.83 b | 34.67 ± 1.32 a | 30.99 ± 0.83 a | 27.68 ± 0.81 a | 21.00 ± 2.83 a |
| 2 | 74.10 ± 1.41 b | 27.20 ± 0.71 b | 46.90 ± 2.12 bc | 461.10 ± 19.09 b | 401.73 ± 20.51 c | 59.37 ± 1.41 d | 25.74 ± 1.32 bc | 25.74 ± 0.83 bc | 23.38 ± 0.81 b | 18.00 ± 1.41 ab | |
| 3 | 65.60 ± 1.41 c | 26.60 ± 0.71 bc | 39.00 ± 0.71 d | 392.05 ± 4.95 c | 337.25 ± 6.36 d | 54.80 ± 1.41 d | 22.65 ± 1.32 bc | 26.09 ± 0.83 b | 23.28 ± 0.81 b | 14.50 ± 0.71 cd | |
| T3 | 1 | 42.70 ± 3.54 d | 22.90 ± 2.12 cd | 19.80 ± 5.66 e | 255.80 ± 13.44 d | 231.10 ± 12.73 e | 24.70 ± 0.71 e | 22.65 ± 1.32 cd | 24.99 ± 0.83 bc | 19.98 ± 0.81 c | 11.00 ± 1.41 ef |
| 2 | 40.40 ± 1.41 de | 21.30 ± 2.83 d | 19.10 ± 4.24 e | 233.60 ± 12.73 de | 210.43 ± 10.61 ef | 23.17 ± 2.12 e | 25.74 ± 1.32 d | 23.89 ± 0.83 cd | 22.68 ± 0.81 b | 12.50 ± 0.71 de | |
| 3 | 36.20 ± 0.71 e | 20.20 ± 3.54 d | 16.00 ± 2.83 ef | 206.97 ± 7.07 e | 184.23 ± 5.66 f | 22.74 ± 1.41 e | 16.89 ± 1.32 d | 23.29 ± 0.83 d | 18.28 ± 0.81 c | 13.50 ± 0.71 bc | |
| T4 | 1 | 22.70 ± 0.71 f | 14.90 ± 0.71 e | 7.80 ± 1.41 g | 91.30 ± 7.07 f | 76.60 ± 6.36 g | 14.70 ± 0.71 f | 12.65 ± 1.32 e | 14.99 ± 0.83 e | 9.98 ± 0.81 d | 9.00 ± 1.41 f |
| 2 | 23.90 ± 4.95 f | 12.80 ± 0.71 e | 11.10 ± 5.66 fg | 79.60 ± 7.07 f | 67.42 ± 6.34 g | 12.19 ± 0.73 f | 15.74 ± 1.32 e | 13.89 ± 0.83 e | 12.68 ± 0.81 d | 8.00 ± 1.41 f | |
| 3 | 24.20 ± 2.12 f | 11.70 ± 1.41 e | 12.50 ± 3.54 fg | 77.47 ± 2.12 f | 64.40 ± 1.17 g | 13.07 ± 0.95 f | 16.89 ± 1.32 e | 13.29 ± 0.83 e | 14.28 ± 0.81 e | 8.50 ± 0.71 f |
| Experiment | Moisture (%) | Ash (%) | Protein (mg/kg) | Fiber (mg/kg) | Fat (mg/kg) | NFE (%) | Chlorophyll (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 96.23 ± 0.16 a | 20.53 ± 0.90 a | 28.70 ± 1.78 a | 12.13 ± 0.15 a | 2.83 ± 0.45 a | 33.33 ± 2.40 a | 1.40 ± 0.24 a |
| T2 | 96.39 ± 0.05 a | 20.77 ± 1.14 a | 24.23 ± 0.91 b | 12.53 ± 0.80 a | 2.93 ± 0.81 a | 31.40 ± 2.31 a | 0.95 ± 0.02 ab |
| T3 | 95.68 ± 0.24 a | 18.37 ± 1.63 b | 20.90 ± 0.70 c | 10.00 ± 0.78 b | 2.53 ± 0.35 a | 32.57 ± 1.48 a | 0.94 ± 0.45 ab |
| T4 | 90.65 ± 1.56 b | 9.63 ± 0.59 c | 14.63 ± 0.81 d | 8.27 ± 1.05 c | 1.37 ± 0.12 b | 22.70 ± 1.39 b | 0.82 ± 0.14 b |
| Ca | Na | K | Mg | P | S | Co | Fe | Mn | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 1.57 ± 0.06 a | 0.87 ± 0.08 d | 0.56 ± 0.05 a | 0.66 ± 0.04 a | 0.81 ± 0.05 a | 0.36 ± 0.02 a | 1.49 ± 0.60 a | 144.03 ± 25.25 a | 158.50 ± 37.69 a | 116.63 ± 5.56 a |
| T2 | 1.52 ± 0.05 b | 1.58 ± 0.20 c | 0.42 ± 0.03 b | 0.59 ± 0.04 b | 0.78 ± 0.00 a | 0.35 ± 0.01 a | 1.10 ± 0.36 ab | 148.40 ± 31.21 a | 136.87 ± 18.39 a | 72.10 ± 9.03 b |
| T3 | 1.34 ± 0.10 c | 2.59 ± 0.22 b | 0.36 ± 0.02 c | 0.41 ± 0.02 c | 0.68 ± 0.01 b | 0.29 ± 0.01 b | 0.69 ± 0.11 c | 83.43 ± 6.33 b | 91.50 ± 5.29 b | 42.93 ± 2.46 c |
| T4 | 0.90 ± 0.13 d | 4.10 ± 0.08 a | 0.25 ± 0.03 d | 0.33 ± 0.02 d | 0.41 ± 0.04 c | 0.26 ± 0.01 c | 0.63 ± 0.02 c | 75.53 ± 22.64 b | 78.77 ± 3.48 b | 35.20 ± 1.56 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Subramanian, R.; Nair, C.S.; Manoharan, R.; Nishanth, D.; Jaleel, A. Integrating Desert Sand Utilization in Saltwater Aqua-Vegeculture Production: Performance Evaluation of Yield and Biochemical Composition. Animals 2025, 15, 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091246
Subramanian R, Nair CS, Manoharan R, Nishanth D, Jaleel A. Integrating Desert Sand Utilization in Saltwater Aqua-Vegeculture Production: Performance Evaluation of Yield and Biochemical Composition. Animals. 2025; 15(9):1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091246
Chicago/Turabian StyleSubramanian, Radhakrishnan, Chythra Somanathan Nair, Ramya Manoharan, Drishya Nishanth, and Abdul Jaleel. 2025. "Integrating Desert Sand Utilization in Saltwater Aqua-Vegeculture Production: Performance Evaluation of Yield and Biochemical Composition" Animals 15, no. 9: 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091246
APA StyleSubramanian, R., Nair, C. S., Manoharan, R., Nishanth, D., & Jaleel, A. (2025). Integrating Desert Sand Utilization in Saltwater Aqua-Vegeculture Production: Performance Evaluation of Yield and Biochemical Composition. Animals, 15(9), 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091246





