Effects of Dietary Rumen-Protected Glucose and Rumen-Protected Taurine Levels on Growth Performance, Serum Biochemical Indicators, and Liver Health in Yaks
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
2.2. Determination of Growth Performance
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Collection and Determination of Organ Samples
2.5. Determination of Serum Biochemical and Immune Indexes
2.6. Determination of Liver Antioxidant Index
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance
3.2. Organ Index
3.3. Serum Biochemical Indexes
3.4. Serum Immune Indices
3.5. Hepatic Antioxidation Capacity
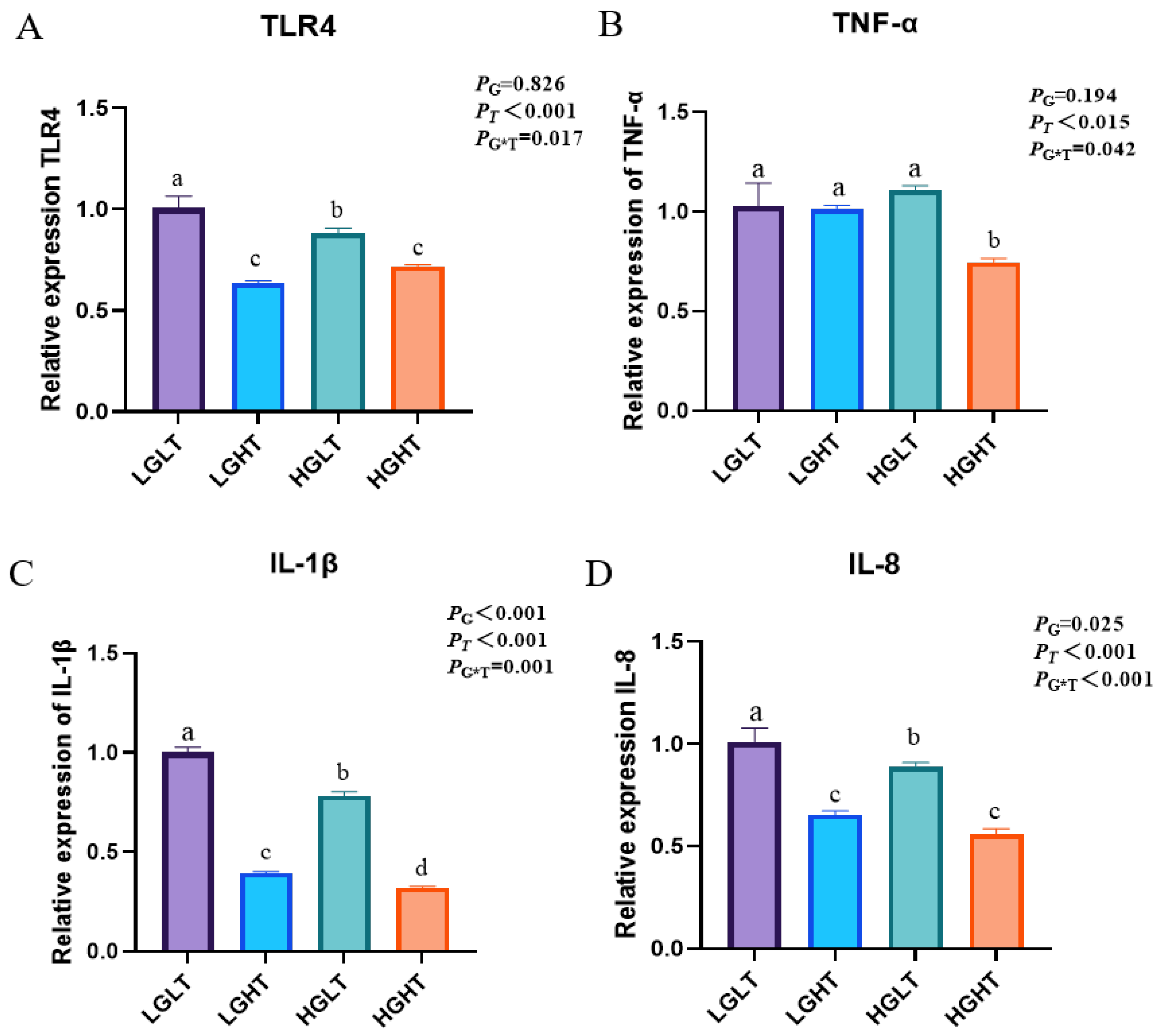
3.6. Hepatic Inflammatory
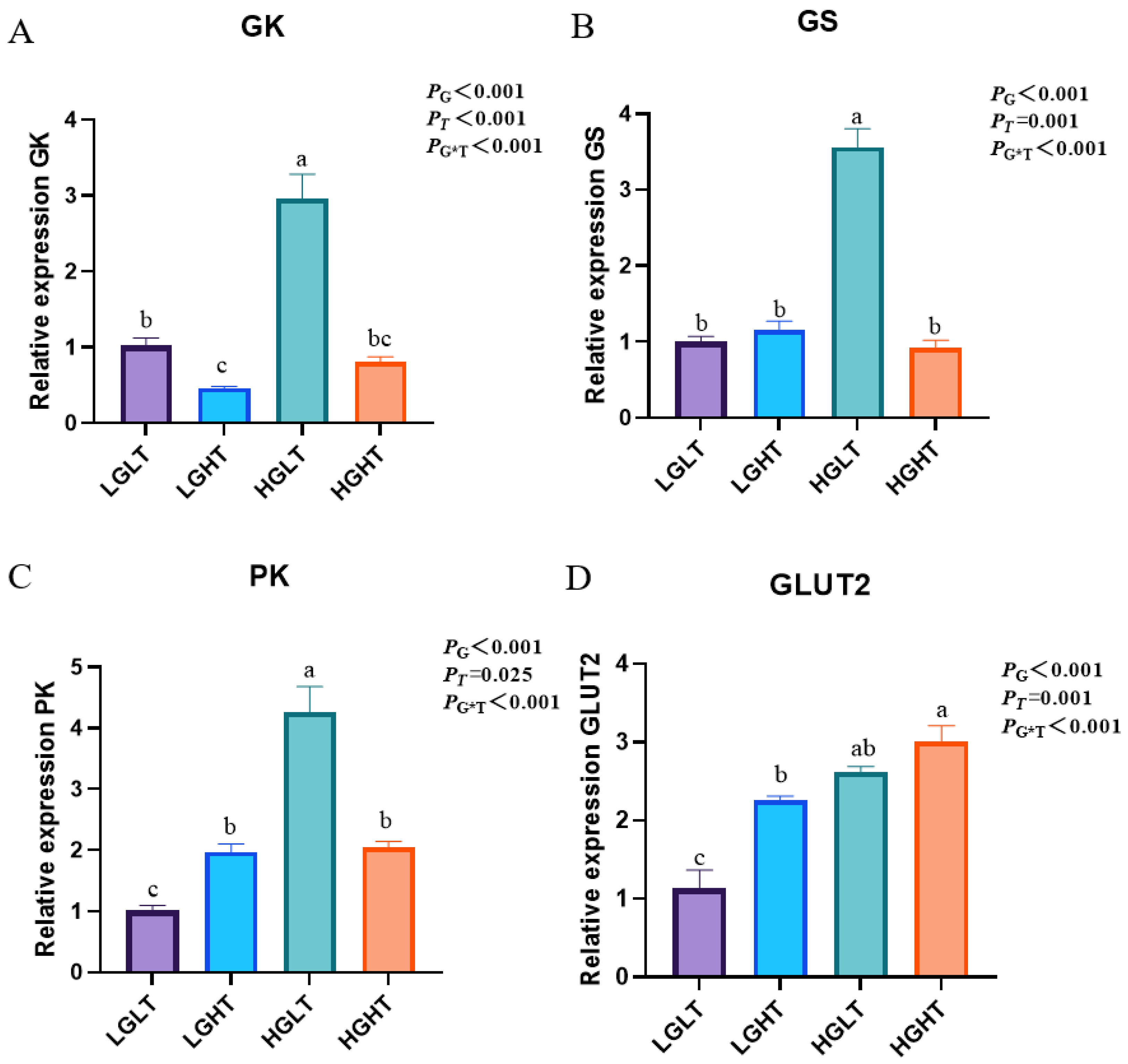
3.7. Hepatic Glucose Metabolism
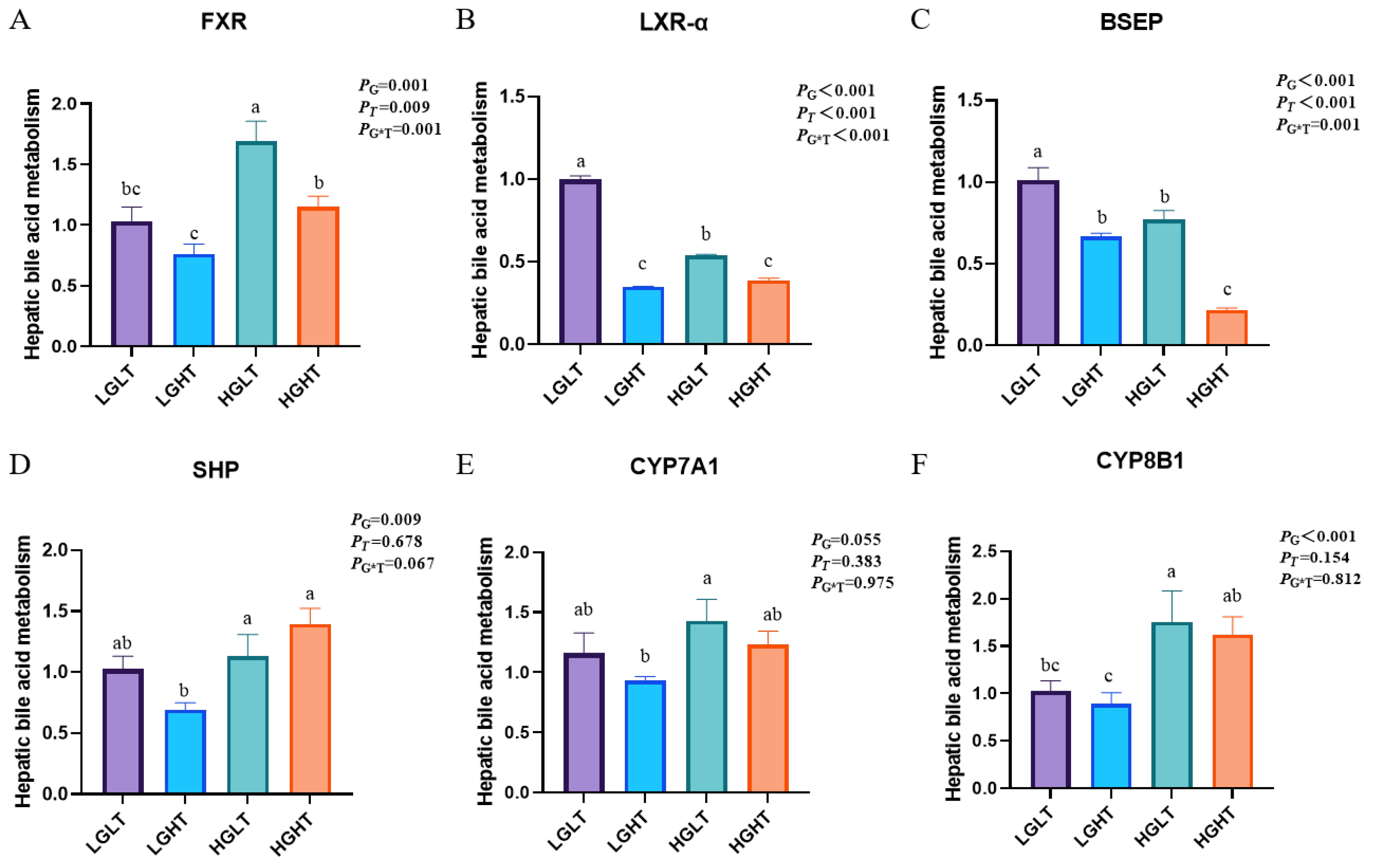
3.8. Hepatic Bile Acid Metabolism
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Zong, W.; Zhao, S.; Qie, M.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y. Nutrition and edible characteristics, origin traceability and authenticity identification of yak meat and milk: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 139, 104133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Ma, T.; Qian, W.; Wang, J.; Ye, Z.; Cao, C.; Hu, Q.; Kim, J.; Larkin, D.M.; et al. The yak genome and adaptation to life at high altitude. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 946–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, B.; Zhao, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.S. Seasonal changes in weight and body composition of yak grazing on alpine-meadow grassland in the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau of China. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 83, 1908–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Gu, Z.; Liu, P.; Lan, Q. Physiological and metabolic adaptation to heat stress at different altitudes in yaks. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, J.; Cao, M.; Lu, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, B.; Shao, C.; et al. Effects of dietary rumen-protected glucose level and taurine supplementation on weight change and oxidative stress state of yaks after transport. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1492747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Cai, M.; Hua, D.K.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, L.S.; Zhao, Y.G.; Wang, H.; Nan, X.M.; Xiong, B.H. Metabolomics reveals effects of rumen-protected glucose on metabolism of dairy cows in early lactation. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2020, 269, 114620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.P.; Tan, Z.L.; Jiao, J.Z.; Long, D.L.; Zhou, C.S.; Yi, K.L.; Liu, C.H.; Kang, J.H.; Wang, M.; Duan, F.H.; et al. Supplementation with fat-coated rumen-protected glucose during the transition period enhances milk production and influences blood biochemical parameters of liver function and inflammation in dairy cows. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2019, 252, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, C.S.; Dooley, B.C.; Branstad, E.H.; Kramer, A.J.; Horst, E.A.; Mayorga, E.J.; Al-Qaisi, M.; Abeyta, M.A.; Perez-Hernandez, G.; Goetz, B.M.; et al. Energetic metabolism, milk production, and inflammatory response of transition dairy cows fed rumen-protected glucose. J. Dairy. Sci. 2020, 103, 7451–7461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.W.; Minotto, J.B.; de Oliveira, M.R.; Zanotto-Filho, A.; Behr, G.A.; Rocha, R.F.; Moreira, J.C.; Klamt, F. Scavenging and antioxidant potential of physiological taurine concentrations against different reactive oxygen/nitrogen species. Pharmacol. Rep. 2010, 62, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Shen, M.; Yan, E.; Wei, C.; Yu, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T. Dietary taurine supplementation attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses and oxidative stress of broiler chickens at an early age. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghfouri, A.H.; Shoura, S.M.S.; Fathollahi, P.; Shadbad, M.A.; Papi, S.; Ostadrahimi, A.; Faghfuri, E. Profiling inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers following taurine supplementation: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of controlled trials. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 76, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inam-u-Ilah; Piao, F.Y.; Aadil, R.M.; Suleman, R.; Li, K.X.; Zhang, M.R.; Wu, P.A.; Shahbaz, M.; Ahmed, Z. Ameliorative effects of taurine against diabetes: A review. Amino Acids. 2018, 50, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Zhong, L.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, J.; Che, C.; Fu, G.; Hu, Y.; Mai, K. Taurine supplements in high-fat diets improve survival of juvenile Monopterus albus by reducing lipid deposition and intestinal damage. Aquaculture 2022, 547, 737431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRC. Nutrient Requirements of Small Ruminants: Sheep, Goats, Cervids and New World Camelids; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tilley, J.M.A.; Terry, R.A. A two-stage technique for the in vitro digestion of forage crops. Grass Forage Sci. 1963, 18, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Shen, X.; Liu, C.; Cheng, L.; Li, M.; Zhao, G. Taurine drives body protein renewal and accretion in beef steers. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumkhong, S.; Marandel, L.; Plagnes-Juan, E.; Veron, V.; Boonanuntanasarn, S.; Panserat, S. Glucose Injection into Yolk Positively Modulates Intermediary Metabolism and Growth Performance in Juvenile Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Han, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Du, H. Taurine enhances growth performance by improving intestinal integrity and antioxidant capacity of weaned piglets. J. Anim. Sci. 2024, 102, skae311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Ye, Y.; Zhou, S.; Qiu, Y.; Ruan, D.; Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Wu, Z.; et al. Integrated single-trait and multi-trait GWASs reveal the genetic architecture of internal organ weight in pigs. Animals 2023, 13, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, K.; Mousa, C.; Cavalier, E. Alkaline Phosphatases: Biochemistry, Functions, and Measurement. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2023, 112, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, J.; Ratner, M.; Shaw, M.; Bailey, W.; Schomaker, S. The current state of serum biomarkers of hepatotoxicity. Toxicology 2008, 245, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Grandi, A.; Franzini, M.; Rosipal, S.; Rosipal, R.; Debreova, M.; Corti, A.; Ruetzler-Dichtl, E.; Scholl-Buergi, S.; Paolicchi, A.; Pompella, A.; et al. Highly elevated plasma γ-Glutamyltransferase elevations: A trait caused by γ-Glutamyltransferase 1 transmembrane mutations. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1124–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagar, H.H. The protective effect of taurine against cyclosporine A-induced oxidative stress and hepatotoxicity in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 151, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.C.; Hoe, B.C.; Li, X.; Lian, D.; Zeng, X. Glucose metabolism-modifying natural materials for potential feed additive development. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Nan, X.; Wang, Y.; Cai, M.; Jiang, L.; Luo, Q.; Xiong, B. Rumen-protected glucose supplementation alters fecal microbiota and its metabolic profiles in early lactation dairy cows. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1034675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Tan, H.Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.J.; Lao, L.; Wong, C.W.; Feng, Y. The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Liver Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 26087–26124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wu, X.; Zheng, L.; Dai, Z.; Wu, L. Effect of acute exposure to ammonia and BFT alterations on Rhynchocypris lagowski: Digestive enzyme, inflammation response, oxidative stress and immunological parameters. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 78, 103380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagawa, M. Protein carbonylation: Molecular mechanisms, biological implications, and analytical approaches. Free Radic. Res. 2021, 55, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosemberg, D.B.; Da, R.R.; Rico, E.P.; Zanotto-Filho, A.; Dias, R.D.; Bogo, M.R.; Bonan, C.D.; Moreira, J.C.; Klamt, F.; Souza, D.O. Taurine prevents enhancement of acetylcholinesterase activity induced by acute ethanol exposure and decreases the level of markers of oxidative stress in zebrafish brain. Neuroscience 2010, 171, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Yang, M.; Liu, D.; Pan, M.; Wu, C.; Zhang, W.; Mai, K. Dietary taurine modulates hepatic oxidative status, ER stress and inflammation in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) fed high carbohydrate diets. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2021, 109, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroz, L.A.; Talako, T.M.; Potapnev, M.P.; Soroka, N.F. Dichotomy of local Th1-and systemic Th2/Th3-dependent types of Immune response in rheumatoid arthritis. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2019, 167, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantuaria, A.; Figueiredo, T.M.; Freire, M.S.; Lima, S.; Almeida, J.A.; Franco, O.L.; Rezende, T. The effects of glucose concentrations associated with lipopolysaccharide and interferon-gamma stimulus on mediators’ production of RAW 264.7 cells. Cytokine 2018, 107, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like Receptors and Their Crosstalk with Other Innate Receptors in Infection and Immunity. Immunity 2011, 34, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, H.; Pluta, H.J.; Braunbeck, T. Sublethal effects of prolonged exposure to disulfoton in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Cytological alterations in the liver by a potent acetylcholine esterase inhibitor. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1996, 34, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Das, A.K.; Sil, P.C. Taurine ameliorates oxidative stress induced inflammation and ER stress mediated testicular damage in STZ-induced diabetic Wistar rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 124, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Chiu, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, M.; Hsu, T.; Tzang, B. Taurine Attenuates Hepatic Inflammation in Chronic Alcohol-Fed Rats Through Inhibition of TLR4/MyD88 Signaling. J. Med. Food. 2015, 18, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Deng, S.; Qin, Q.; Ran, C.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L. Mechanism of taurine reducing inflammation and organ injury in sepsis mice. Cell Immunol. 2022, 375, 104503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Xiong, B.; Qin, G.; Sooranna, S.R.; Pinhu, L. Investigation of association between IL-8 serum levels and IL8 polymorphisms in Chinese patients with sepsis. Gene 2016, 594, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fang, H.; Xie, J.; Wu, Y.; Tang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Lv, J.; Yu, J. Physiological responses of cucumber seedlings to different supplemental light duration of red and blue LED. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 709313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierans, S.J.; Taylor, C.T. Glycolysis: A multifaceted metabolic pathway and signaling hub. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 107906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Shi, M.; Luk, A.O.Y.; Kong, A.P.S.; Ma, R.C.W.; Li, C.; Chen, L.; Chow, E.; Chan, J.C.N. Impaired GK—GKRP interaction rather than direct GK activation worsens lipid profiles and contributes to long-term complications: A Mendelian randomization study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Wilamowitz-Moellendorff, A.; Hunter, R.W.; Garcia-Rocha, M.; Kang, L.; Lopez-Soldado, I.; Lantier, L.; Patel, K.; Peggie, M.W.; Martinez-Pons, C.; Voss, M.; et al. Glucose-6-Phosphate-Mediated activation of liver glycogen synthase plays a key role in hepatic glycogen synthesis. Diabetes 2013, 62, 4070–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, T.; Inoue, H.; Tanaka, T. The M1- and M2-type isozymes of rat pyruvate kinase are produced from the same gene by alternative RNA splicing. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 13807–13812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, S.; Guo, T.; Liu, Z.; Fang, H.; Zheng, L.; Xie, J.; Tian, L.; Liu, Y.; Jin, N. High dietary starch inclusion impairs growth and antioxidant status, and alters liver organization and intestinal microbiota in largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 1806–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Pan, M.; Huang, D.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Yu, X.; Mai, K.; Zhang, W. The Molecular Mechanism of Farnesoid X Receptor Alleviating Glucose Intolerance in Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Cells 2024, 13, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschiazzo, H.; Exton, J.H.; Park, C.R. Effects of glucose on glycogen synthetase, phosphorylase, and glycogen deposition in the perfused rat liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1970, 65, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perino, A.; Demagny, H.; Velazquez-Villegas, L.; Schoonjans, K. Molecular physiology of bile acid signaling in health, disease, and aging. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 683–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, J.L. Bile formation and secretion. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 1035–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrabah, W.; Aumercier, P.; Gheeraert, C.; Dehondt, H.; Bouchaert, E.; Alexandre, J.; Ploton, M.; Mazuy, C.; Caron, S.; Tailleux, A.; et al. Glucose sensing O-GlcNAcylation pathway regulates the nuclear bile acid receptor farnesoid X receptor (FXR). Hepatology 2014, 59, 2022–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Item | LG | HG | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LT (5 g/d) | HT (20 g/d) | LT (5 g/d) | HT (20 g/d) | |
| Ingredients % DM | ||||
| Corn | 15.5 | 15.5 | 14.7 | 14.7 |
| Wheat bran | 5.6 | 5.6 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| Soybean meal | 9.0 | 9.0 | 9.4 | 9.4 |
| Rapeseed meal | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| Palm oil | 2.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Straw | 35.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 |
| Leymus chinensis | 27.0 | 27.0 | 27.0 | 27.0 |
| Calcium hydrogen phosphate | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Calcium carbonate | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Sodium chloride | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Premix 1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Rumen-protected glucose | 1.0 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| Nutrient level 2 % DM | ||||
| Neg, MJ/kg | 5.97 | 5.97 | 5.97 | 5.97 |
| CP | 9.88 | 9.88 | 9.82 | 9.82 |
| NDF | 46.2 | 46.2 | 45.9 | 45.9 |
| ADF | 30.7 | 30.7 | 30.6 | 30.6 |
| Ca | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| P | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.34 | 0.34 |
| Gene | Primer Sequences (5′–3′) | Accession Number | Amplification Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TLR4 | F: GGATGAAGACTGGGTGCGGAATG | XM_005891938.1 | 102 |
| R: CTGGATGATATTGGCGGCGATGG | |||
| IL-8 | F: GCTGGCTGTTGCTCTCTTGGC | XM_005891246.2 | 108 |
| R: GGGGTGGAAAGGTGTGGAATGTG | |||
| TNF-α | F: CTGGCGGAGGAGGTGCTCTC | XM_005904178.1 | 105 |
| R: GGAGGAAGGAGAAGAGGCTGAGG | |||
| IL-1β | F: ATGAAGAGCTGCATCCAACACCTG | NM_174093.1 | 101 |
| R: ACCGACACCACCTGCCTGAAG | |||
| GS | F: CTGGCTGAGGGTGTGTTGCTG | XM_005900427.2 | 106 |
| R: CGGTGAAGGGAAGAGTGTGAATGG | |||
| GLUT2 | F: GCGGACTTCTGTGGACCTTATGTG | XM_005905570.2 | 108 |
| R: CCCTCTTCTTTCGGAACTCTGCTG | |||
| PK | F: GCCATAATCGTCCTCACCAAGTCTG | XM_005905593.1 | 99 |
| R: CTTACACACCACAGGGAAGATGCC | |||
| GK | F: TCGTTGGCTCCTTGACAATGTGAG | XM_005899746.1 | 107 |
| R: TCGTTGGCTCCTTGACAATGTGAG | |||
| FXR | F: GCTGTTCTGATGGATGGGATGACTG | XM_005892526.2 | 102 |
| R: GGGAGGTTTCTTTGTCTGCTCTGAG | |||
| CYP7A1 | F: AGCTGACGGAGGGCTTGAGAC | NM_001205677.2 | 108 |
| R: AGGACTGCGAGGAGTGACTTGG | |||
| CYP8B1 | F: GCAGAGGAAGCTAGACTTTGTGGAG | XM_005222522.5 | 109 |
| R: GCTTGGTGCTGGCTGAGTGTATC | |||
| BSEP | F: GGCACTGGACAATGAGAGCGAAG | XM_005887600.2 | 105 |
| R: GATAGGCGATGAGCGACAGAGATG | |||
| SHP | F: GACGGAGGCTCAGTACAAGTTCATC | XM_005907490.2 | 104 |
| R: GTTCTTCATTGCTGGCGGGTAGG | |||
| LXR-α | F: GTTTGCCTTGCTCATTGCCATCAG | XM_005898931.2 | 108 |
| R: CGGAGGCTCACCAGTTTCATCAG | |||
| β-actin | F: GGTTGGATCGAGCATTCCCA R: AAAAGCGATCACCTCCCCTG | XM_005887322.2 | 104 |
| Items | LG | HG | SEM | p-Values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LT | HT | LT | HT | G | T | G*T | ||
| Initial weight, kg | 192.75 | 187.92 | 195.75 | 197.83 | 4.52 | 0.50 | 0.88 | 0.72 |
| Final weight, kg | 218.25 | 210.52 | 219.75 | 220.33 | 4.03 | 0.51 | 0.67 | 0.62 |
| ADG, kg/d | 0.40 | 0.36 | 0.38 | 0.36 | 0.02 | 0.77 | 0.42 | 0.79 |
| DMI, kg/d | 4.28 | 4.26 | 4.36 | 4.28 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.10 |
| F/G, % | 11.91 | 12.13 | 11.86 | 12.32 | 0.51 | 0.95 | 0.75 | 0.91 |
| Items | LG | HG | SEM | p-Values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LT | HT | LT | HT | G | T | G*T | ||
| Organ weight | ||||||||
| Heart, kg | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.88 | 0.93 | 0.02 | 0.2 | 0.86 | 0.20 |
| Liver, kg | 2.47 | 2.31 | 2.40 | 2.52 | 0.05 | 0.46 | 0.87 | 0.15 |
| Spleen, kg | 0.46 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.41 | 0.01 | 0.47 | 0.44 | 0.82 |
| Kidney, kg | 0.40 | 0.36 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.01 | 0.56 | 0.22 | 0.14 |
| Final weight, kg | 218.25 | 210.52 | 219.75 | 220.33 | 4.03 | 0.51 | 0.67 | 0.62 |
| Organ Index | ||||||||
| Heart, % | 0.41 | 0.39 | 0.41 | 0.43 | 0.01 | 0.19 | 1.00 | 0.16 |
| Liver, % | 1.15 | 1.11 | 1.12 | 1.17 | 0.01 | 0.63 | 0.94 | 0.14 |
| Spleen, % | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.01 | 0.42 | 0.60 | 0.89 |
| Kidney, % | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.16 | 0.12 |
| Items | LG | HG | SEM | p-Values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LT | HT | LT | HT | G | T | G*T | ||
| ALP/(U/L) | 68.2 | 69.75 | 62.00 | 69.00 | 4.24 | 0.74 | 0.67 | 0.58 |
| AST/(U/L) | 84.46 | 82.10 | 77.25 | 64.70 | 3.68 | 0.07 | 0.25 | 0.42 |
| GGT/(U/L) | 10.63 | 10.70 | 10.12 | 8.46 | 0.48 | 0.04 | 0.23 | 0.19 |
| HDL-C/(mmol/L) | 1.94 | 2.21 | 2.19 | 2.07 | 0.07 | 0.65 | 0.56 | 0.13 |
| LDL-C/(mmol/L) | 0.83 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.90 | 0.04 | 0.68 | 0.58 | 0.12 |
| TC/(mmol/L) | 2.47 | 2.95 | 2.97 | 2.67 | 0.12 | 0.61 | 0.67 | 0.08 |
| Glu/(mmol/L) | 2.86 | 2.66 | 3.29 | 3.17 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.27 | 0.79 |
| TP/(g/L) | 64.85 | 64.19 | 63.16 | 64.45 | 1.48 | 0.83 | 0.93 | 0.77 |
| ALB/(g/L) | 27.16 | 27.53 | 28.42 | 27.27 | 0.49 | 0.67 | 0.74 | 0.52 |
| LDH/(U/L) | 997.05 ab | 1119.25 a | 951.18 ab | 857.20 b | 39.83 | 0.01 | 0.59 | 0.03 |
| TBA/(umol/L) | 26.34 | 26.71 | 27.87 | 28.03 | 0.14 | 0.83 | 0.97 | 1.00 |
| Items | LG | HG | SEM | p-Values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LT | HT | LT | HT | G | T | G*T | ||
| IL-1β, ng/L | 52.04 | 53.69 | 54.07 | 52.29 | 0.08 | 0.88 | 0.97 | 0.36 |
| TNF-α, ng/L | 257.72 | 263.52 | 266.26 | 244.26 | 5.44 | 0.54 | 0.51 | 0.58 |
| IL-6, ng/L | 71.23 | 16.69 | 16.64 | 17.20 | 0.27 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.35 |
| IL-4, ng/L | 96.55 | 92.33 | 92.78 | 94.82 | 1.49 | 0.84 | 0.73 | 0.33 |
| IL-10, ng/L | 42.46 | 41.42 | 45.57 | 44.46 | 0.71 | 0.03 | 0.72 | 0.97 |
| Items | LG | HG | SEM | p-Values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LT | HT | LT | HT | G | T | G*T | ||
| AST, U/g | 592.08 | 574.02 | 581.97 | 581.59 | 11.742 | 0.960 | 0.713 | 0.724 |
| ALT, U/g | 310.16 | 291.32 | 270.84 | 284.52 | 14.952 | 0.461 | 0.942 | 0.601 |
| PCO, nmol/mgprot | 5.68 | 3.64 | 4.70 | 2.67 | 0.374 | 0.144 | 0.005 | 0.979 |
| SOD, U/mgprot | 6.27 | 6.90 | 7.16 | 6.65 | 0.38 | 0.482 | 0.895 | 0.223 |
| MDA, nmol/mgprot | 2.73 | 2.29 | 3.19 | 2.66 | 0.114 | 0.052 | 0.027 | 0.839 |
| CAT, U/mgprot | 447.07 | 410.18 | 392.98 | 424.80 | 11.855 | 0.110 | 0.592 | 0.425 |
| GSH-PX, U/mgprot | 73.99 | 67.47 | 77.49 | 67.40 | 2.498 | 0.734 | 0.109 | 0.724 |
| T-AOC, mmol/mL | 0.85 | 0.89 | 0.70 | 0.87 | 0.03 | 0.168 | 0.091 | 0.271 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, L.; Zhang, B.; Yang, H.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Peng, Q.; Xue, B. Effects of Dietary Rumen-Protected Glucose and Rumen-Protected Taurine Levels on Growth Performance, Serum Biochemical Indicators, and Liver Health in Yaks. Animals 2025, 15, 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15081152
Chen Y, Wang X, Lu L, Zhang B, Yang H, Zhao S, Wang Z, Wang L, Peng Q, Xue B. Effects of Dietary Rumen-Protected Glucose and Rumen-Protected Taurine Levels on Growth Performance, Serum Biochemical Indicators, and Liver Health in Yaks. Animals. 2025; 15(8):1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15081152
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yuanyuan, Xiaolin Wang, Lianghao Lu, Bao Zhang, Huaming Yang, Shoupei Zhao, Zhisheng Wang, Lizhi Wang, Quanhui Peng, and Bai Xue. 2025. "Effects of Dietary Rumen-Protected Glucose and Rumen-Protected Taurine Levels on Growth Performance, Serum Biochemical Indicators, and Liver Health in Yaks" Animals 15, no. 8: 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15081152
APA StyleChen, Y., Wang, X., Lu, L., Zhang, B., Yang, H., Zhao, S., Wang, Z., Wang, L., Peng, Q., & Xue, B. (2025). Effects of Dietary Rumen-Protected Glucose and Rumen-Protected Taurine Levels on Growth Performance, Serum Biochemical Indicators, and Liver Health in Yaks. Animals, 15(8), 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15081152






