Development and Validation of an LC–MS/MS Method for Quantifying Gabapentin in Plasma: Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study in Cats
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Chemical and Standards
2.3. Calibration Standards and Quality Control
2.4. Sample Preparation
2.5. LC-MS/MS Instrumentation and Setting
2.6. Method Validation
2.6.1. Selectivity and Specificity
2.6.2. Linearity
2.6.3. Accuracy and Precision
2.6.4. Matrix Effect
2.6.5. Stability
2.6.6. Carryover
2.6.7. Dilution Integrity
2.7. Pharmacokinetics
3. Results
3.1. LC-MS/MS Method Development
3.2. Method Validation
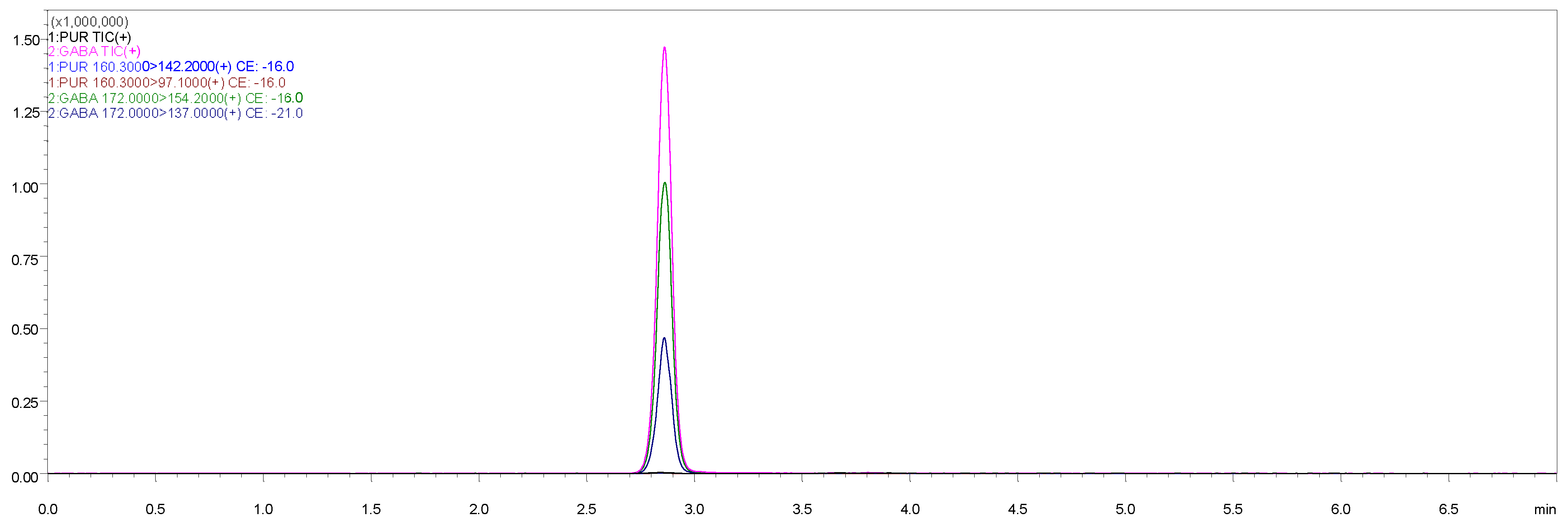
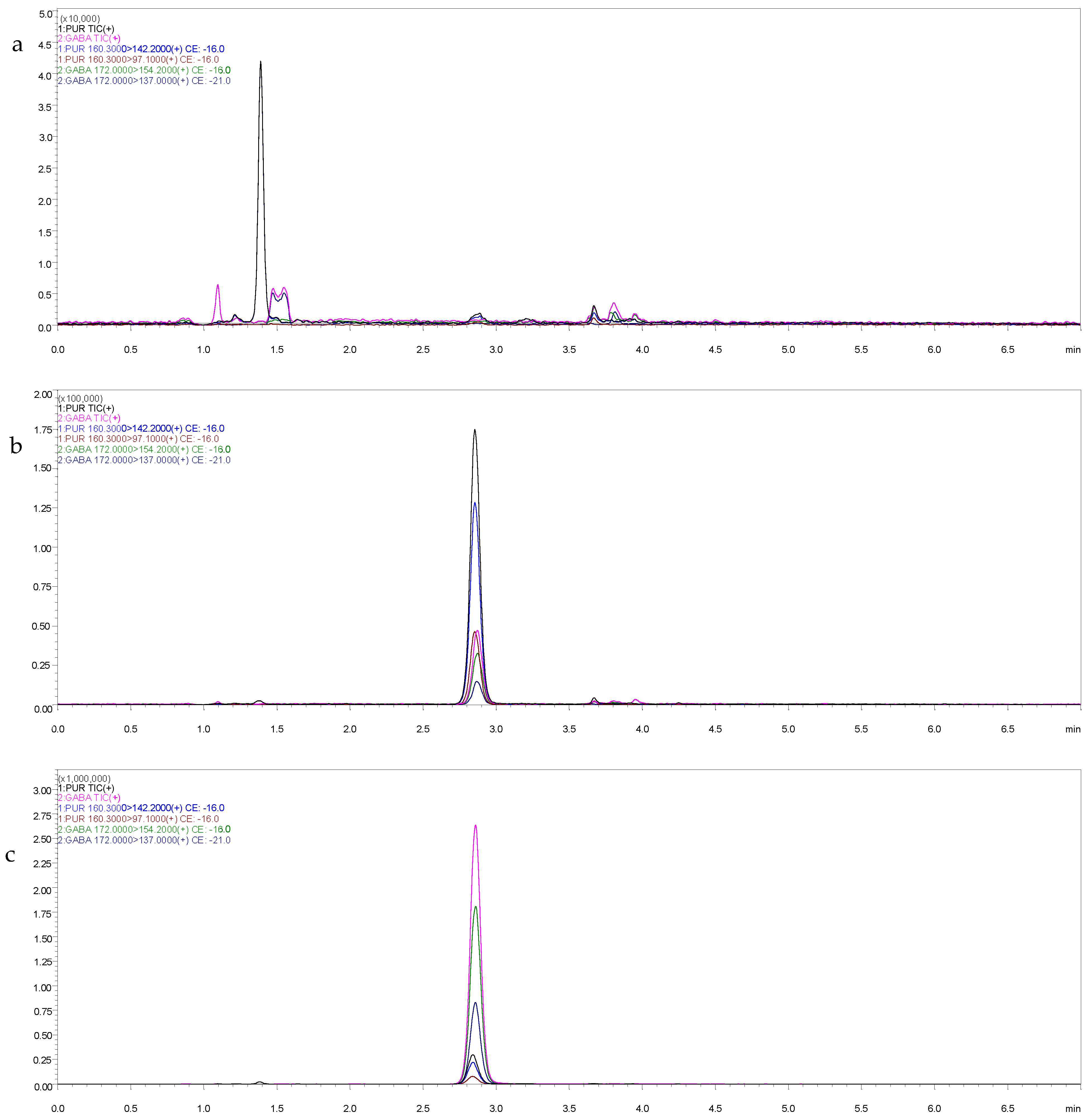
3.2.1. Selectivity and Specificity
3.2.2. Linearity
3.2.3. Accuracy and Precision
3.2.4. Matrix Effect
3.2.5. Stability
3.2.6. Carryover
3.2.7. Dilution Integrity
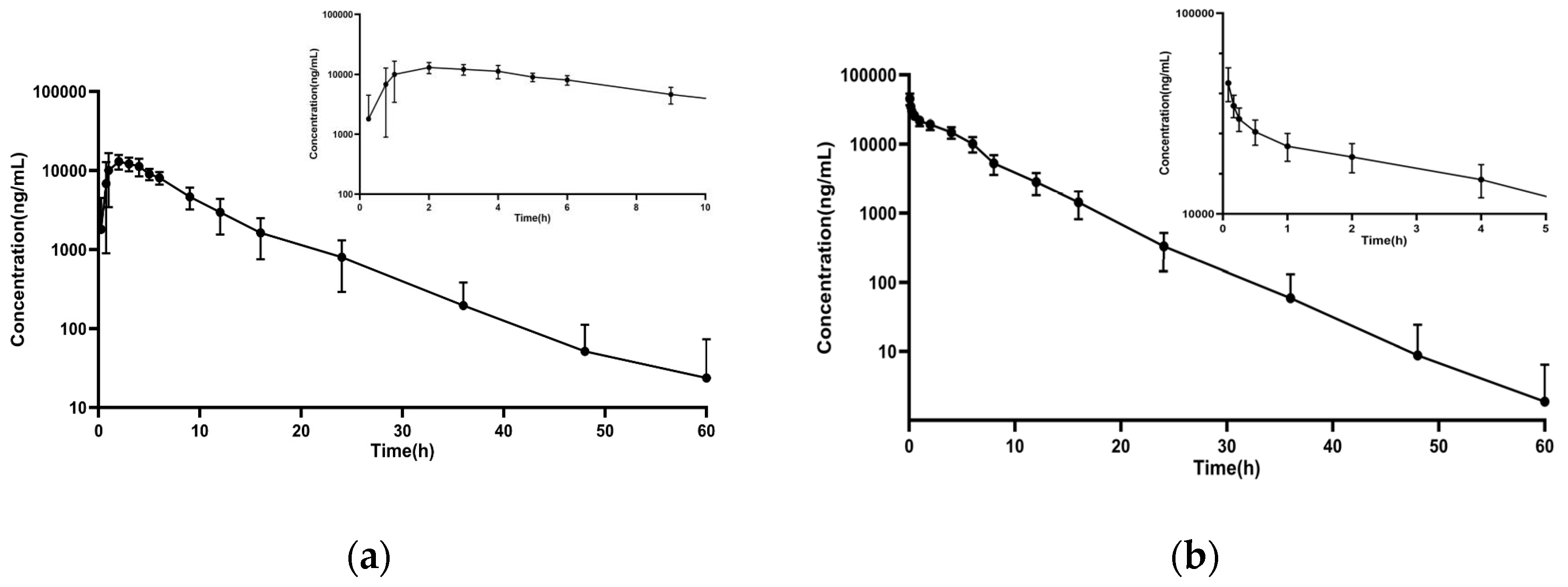
3.3. Pharmacokinetics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tucker, L.E.; Sanchez, A.; Valverde, A.; Blois, S.; Uccello, O.; Rutherford, A.; Monteith, G.; Reinhart, J.M.; Keating, S.; Gu, Y.; et al. Pharmacokinetic, sedative, and physiological effects of oral compounded formulations of trazodone alone or in combination with gabapentin in male cats. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 46, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, V.; Ververidis, C.; Mylonakis, M.E.; Savvas, I.; Kazakos, G. Orally administered gabapentin and alprazolam induce comparable levels of anxiolysis and sedation in cats. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2024, 262, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, Y.; Kanda, T. Effects of Pre-Anesthesia Anxiety on Propofol Induction Dose in Cats. Animals 2021, 11, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodan, I.; Sundahl, E.; Carney, H.; Gagnon, A.-C.; Heath, S.; Landsberg, G.; Seksel, K.; Yin, S. AAFP and ISFM feline-friendly handling guidelines. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2011, 13, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemer, S.; Heritier, C.; Windschnurer, I.; Pratsch, L.; Arhant, C.; Affenzeller, N. A Review on Mitigating Fear and Aggression in Dogs and Cats in a Veterinary Setting. Animals 2021, 11, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, A.; Harbin, K.; MacPherson, J.; Rundle, K.; Overall, K.L. A review of pre-appointment medications to reduce fear and anxiety in dogs and cats at veterinary visits. Can. Vet. J. 2021, 62, 952–960. [Google Scholar]
- van Haaften, K.A.; Forsythe, L.R.E.; Stelow, E.A.; Bain, M.J. Effects of a single preappointment dose of gabapentin on signs of stress in cats during transportation and veterinary examination. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2017, 251, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankratz, K.E.; Ferris, K.K.; Griffith, E.H.; Sherman, B.L. Use of single-dose oral gabapentin to attenuate fear responses in cage-trap confined community cats: A double-blind, placebo-controlled field trial. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2018, 20, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruszka, M.; Graff, E.; Medam, T.; Masson, S. Clinical evaluation of the effects of a single oral dose of gabapentin on fear-based aggressive behaviors in cats during veterinary examinations. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2021, 259, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, C.; Allen, N.J.; Susman, M.W.; O’Rourke, N.A.; Park, C.Y.; Ozkan, E.; Chakraborty, C.; Mulinyawe, S.B.; Annis, D.S.; Huberman, A.D.; et al. Gabapentin receptor α2δ-1 is a neuronal thrombospondin receptor responsible for excitatory CNS synaptogenesis. Cell 2009, 139, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siao, K.T.; Pypendop, B.H.; Ilkiw, J.E. Pharmacokinetics of gabapentin in cats. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2010, 71, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintero, G.C. Review about gabapentin misuse, interactions, contraindications and side effects. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017, 9, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrian, D.; Papich, M.G.; Baynes, R.; Stafford, E.; Lascelles, B.D.X. The pharmacokinetics of gabapentin in cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 1996–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coetzee, J.F.; Mosher, R.A.; Anderson, D.E.; Robert, B.; Kohake, L.E.; Gehring, R.; White, B.J.; Kukanich, B.; Wang, C. Impact of oral meloxicam administered alone or in combination with gabapentin on experimentally induced lameness in beef calves. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 816–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, R.W.; Chatterjea, D.; Feng, M.R.; Taylor, C.P.; Hammond, D.L. Gabapentin and pregabalin can interact synergistically with naproxen to produce antihyperalgesia. Anesthesiology 2002, 97, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, B. Gabapentin use in neuropathic pain syndromes. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2000, 101, 359–371. [Google Scholar]
- Ouellet, D.; Bockbrader, H.N.; Wesche, D.L.; Shapiro, D.Y.; Garofalo, E. Population pharmacokinetics of gabapentin in infants and children. Epilepsy Res. 2001, 47, 229–241. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, D.; Millington, C. Analysis of pregabalin at therapeutic concentrations in human plasma/serum by reversed-phase HPLC. Ther. Drug Monit. 2005, 27, 451–456. [Google Scholar]
- Sagirli, O.; Cetin, S.M.; Onal, A. Determination of gabapentin in human plasma and urine by high-performance liquid chromatography with UV-vis detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 42, 618–624. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, M.A.; Dewey, C.W.; Schwark, W.S.; Rishniw, M.; Boothe, D.M. Pharmacokinetics of Single-Dose Oral Pregabalin Administration in Normal Cats. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalizadeh, H.; Souri, E.; Tehrani, M.B.; Jahangiri, A. Validated HPLC method for the determination of gabapentin in human plasma using pre-column derivatization with 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2007, 854, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Kleinhenz, M.D.; Davis, D.; Weeder, M.M.; Leslie, A.; Reppert, E.J.; Kompalage, K.; Tucker, R.; Coetzee, J.F. Pharmacokinetic report: Pharmacokinetics of a single oral dose of gabapentin in goats (Capra hircus). J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 47, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, J.R.; Grubb, T.L.; Cox, S.; Malavasi, L.; Villarino, N.L. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of repeat dosing of gabapentin in adult horses. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2022, 36, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercolini, L.; Mandrioli, R.; Amore, M.; Raggi, M.A. Simultaneous HPLC-F analysis of three recent antiepileptic drugs in human plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 53, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomann, J.; Vogt, S.B.; Guessoum, A.; Meyer, M.; Vogel, M.; Liechti, M.E.; Luethi, D.; Duthaler, U. Development and validation of an LC-MS/MS method for quantifying diamorphine and its major metabolites 6-monoacetylmorphine, morphine, morphine-3-glucuronide, and morphine-6-glucuronide in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2024, 1237, 124104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, X.-T.; Bi, J.-B.; Qiu, X.; Bian, Y.; Wang, K.-F.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, X.-S. Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Alnustone in Rats after Intravenous Administration by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2019, 24, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukanich, B.; Cohen, R.L. Pharmacokinetics of oral gabapentin in greyhound dogs. Vet. J. 2011, 187, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirikolu, L.; Dafalla, A.; Ely, K.J.; Connerly, A.L.; Jones, C.N.; ElkHoly, H.; Lehner, A.F.; Thompson, K.; Tobin, T. Pharmacokinetics of gabapentin in horses. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 31, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R.; Ellenbogen, A.; Gidal, B. Interindividual Variability in the Bioavailability of Gabapentin Enacarbil Extended Release in Healthy Adults: An Analysis of Data from 6 Phase I Studies. Ther. Drug Monit. 2022, 44, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulovic, L.L.; Türck, D.; von Hodenberg, A.; Vollmer, K.O.; McNally, W.P.; DeHart, P.D.; Hanson, B.J.; Bockbrader, H.N.; Chang, T. Disposition of gabapentin (neurontin) in mice, rats, dogs, and monkeys. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1995, 23, 441–448. [Google Scholar]
- Terry, R.L.; McDonnell, S.M.; Van Eps, A.W.; Soma, L.R.; Liu, Y.; Uboh, C.E.; Moate, P.J.; Driessen, B. Pharmacokinetic profile and behavioral effects of gabapentin in the horse. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 33, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.T.; Sedykh, A.; Chakravarti, S.K.; Saiakhov, R.D.; Zhu, H. Critical evaluation of human oral bioavailability for pharmaceutical drugs by using various cheminformatics approaches. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, S.A. Managing Neuropathic Pain in Dogs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goich, M.; Bascuñán, A.; Faúndez, P.; Valdés, A. Multimodal analgesia for treatment of allodynia and hyperalgesia after major trauma in a cat. J. Feline Med. Surg. Open Rep. 2019, 5, 2055116919855809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashmore, R.G.; Harcourt-Brown, T.R.; Freeman, P.M.; Jeffery, N.D.; Granger, N. Clinical diagnosis and treatment of suspected neuropathic pain in three dogs. Aust. Vet. J. 2009, 87, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.S.; Moore, V.W.; Drozdzynska, M.J. Successful treatment of suspected sciatic neuritis following canine total hip arthroplasty. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruel, H.L.M.; Watanabe, R.; Evangelista, M.C.; Beauchamp, G.; Auger, J.-P.; Segura, M.; Steagall, P.V. Pain burden, sensory profile and inflammatory cytokines of dogs with naturally-occurring neuropathic pain treated with gabapentin alone or with meloxicam. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santifort, K.M.; Carrera, I.; Platt, S. Case report: Traumatic hemorrhagic cervical myelopathy in a dog. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1260719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Analyte | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Product Ion (m/z) | Collision Energy (V) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gabapentin | 172.0 | 154.2 1/137.0 | 16/21 |
| Pregabalin | 160.3 | 142.2 1/97.1 | 16/16 |
| Analyte | Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | Intra-Day (n = 6) | Inter-Day (n = 18) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured Concentration (mean ± SD, ng/mL) | Precision (CV%) | Accuracy (%) | Measured Concentration (mean ± SD, ng/mL) | Precision (CV%) | Accuracy (%) | ||
| Gabapentin | 50 | 46.57 ± 1.76 | 3.45 | 93.15 | 50.67 ± 5.78 | 3.13 | 101.34 |
| 100 | 94.85 ± 9.35 | 9.00 | 94.85 | 100.62 ± 9.61 | 5.99 | 100.62 | |
| 500 | 515.77 ± 30.84 | 5.46 | 103.15 | 521.11 ± 31.50 | 5.76 | 104.22 | |
| 4000 | 3660.63 ± 116.84 | 2.91 | 91.52 | 3620.75 ± 106.73 | 1.96 | 90.52 | |
| Analyte | Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | Short-Term (24 h, 25 °C) | Long-Term (−20 °C, 30 d) | Freeze–Thaw Stability 3 cycles) | Autosampler (30 h, 4 °C) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured Concentration (ng/mL) | Accuracy (%) | Measured Concentration (ng/mL) | Accuracy (%) | Measured Concentration (ng/mL) | Accuracy (%) | Measured Concentration (ng/mL) | Accuracy (%) | ||
| Gabapentin | 100 | 110.16 | 2.05 | 109.40 | 6.40 | 112.61 | 2.08 | 114.06 | 2.57 |
| 4000 | 4405.26 | 4.95 | 4133.93 | 5.87 | 4466.99 | 2.82 | 4309.72 | 4.19 | |
| Parameters | Unit | Oral | IV |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1/2 | h | 5.60 ± 1.79 | 3.87 ± 0.64 |
| Tmax | h | 1.83 ± 0.75 | * |
| Cmax | μg/mL | 13.94 ± 3.75 | 44.88 ± 7.82 |
| CL/F | L/h | 0.89 ± 0.17 | * |
| Vd/F | L | 7.03 ± 2.21 | * |
| AUC0–t | (μg/mL) h | 115.54 ± 27.56 | 160.44 ± 32.65 |
| AUC0–∞ | (μg/mL) h | 116.48 ± 27.46 | 161.70 ± 32.95 |
| C0 | μg/mL | * | 58.82 ± 15.34 |
| CL | L/h | * | 0.65 ± 0.15 |
| Vd | L | * | 3.50 ± 0.37 |
| Vss | L | * | 3.26 ± 0.39 |
| F | % | 78.71 ± 18.55 | * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, F.; Lin, C.; Wu, Y.; Luo, X.; Han, N.; Xiong, W.; Zeng, Z. Development and Validation of an LC–MS/MS Method for Quantifying Gabapentin in Plasma: Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study in Cats. Animals 2025, 15, 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15070950
Zhao F, Lin C, Wu Y, Luo X, Han N, Xiong W, Zeng Z. Development and Validation of an LC–MS/MS Method for Quantifying Gabapentin in Plasma: Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study in Cats. Animals. 2025; 15(7):950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15070950
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Feifei, Changcheng Lin, Yunying Wu, Xinyue Luo, Ning Han, Wenguang Xiong, and Zhenling Zeng. 2025. "Development and Validation of an LC–MS/MS Method for Quantifying Gabapentin in Plasma: Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study in Cats" Animals 15, no. 7: 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15070950
APA StyleZhao, F., Lin, C., Wu, Y., Luo, X., Han, N., Xiong, W., & Zeng, Z. (2025). Development and Validation of an LC–MS/MS Method for Quantifying Gabapentin in Plasma: Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study in Cats. Animals, 15(7), 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15070950




