Molecular Characterization and Antibiotic Resistance of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) Isolates from Broiler Chickens in Algeria
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling, E. coli Isolation, and Identification
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Serotyping
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. PCR-Based Screening of Virulence Genes
2.6. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Assessment
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Confirmation of E. coli
3.2. Serotype Determination
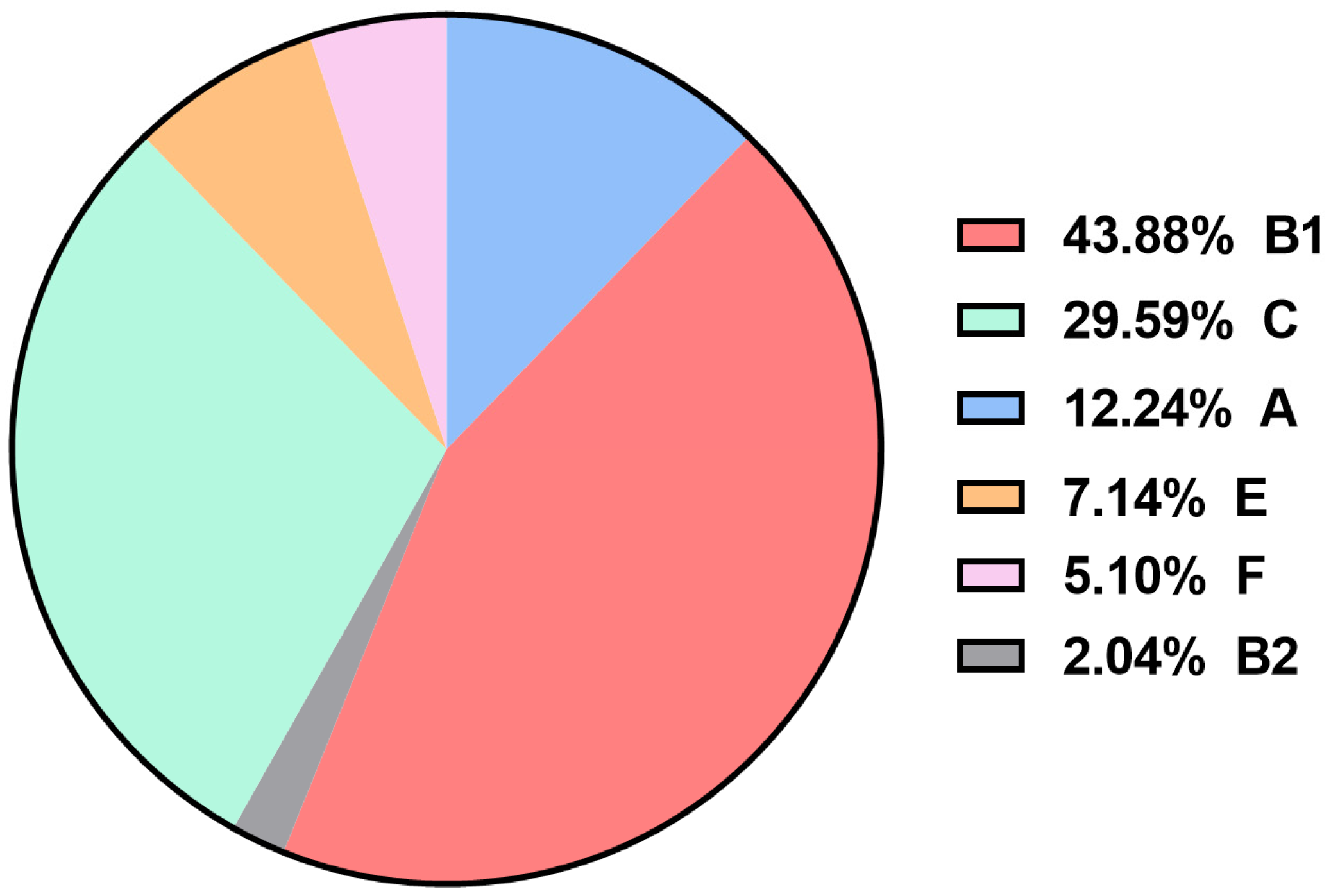
3.3. Identification of APEC Phylogenetic Groups
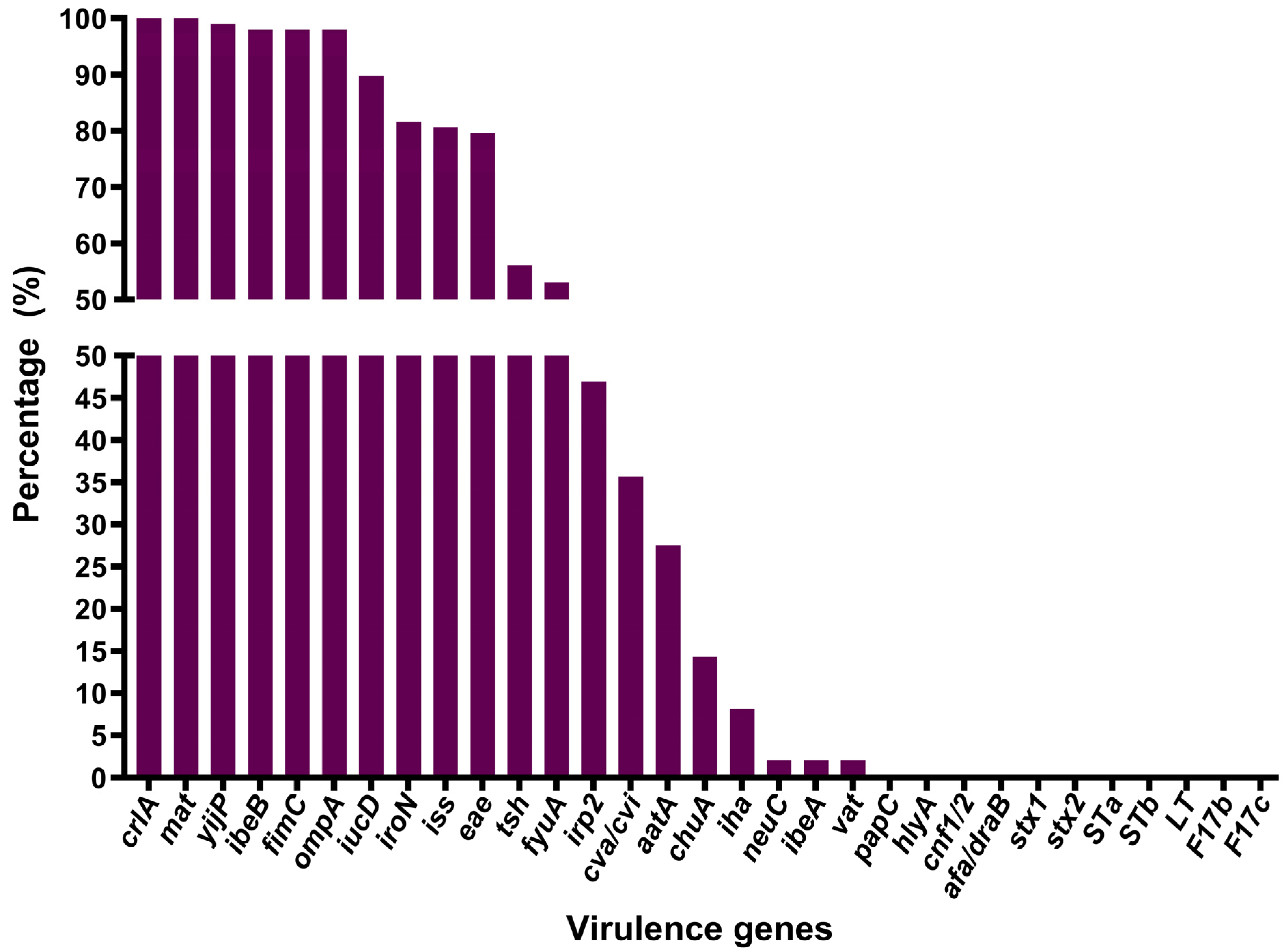
3.4. Virulence Gene Detection and Distribution
3.5. Distribution of Virulence Genes Across Serotypes and Phylogenetic Groups
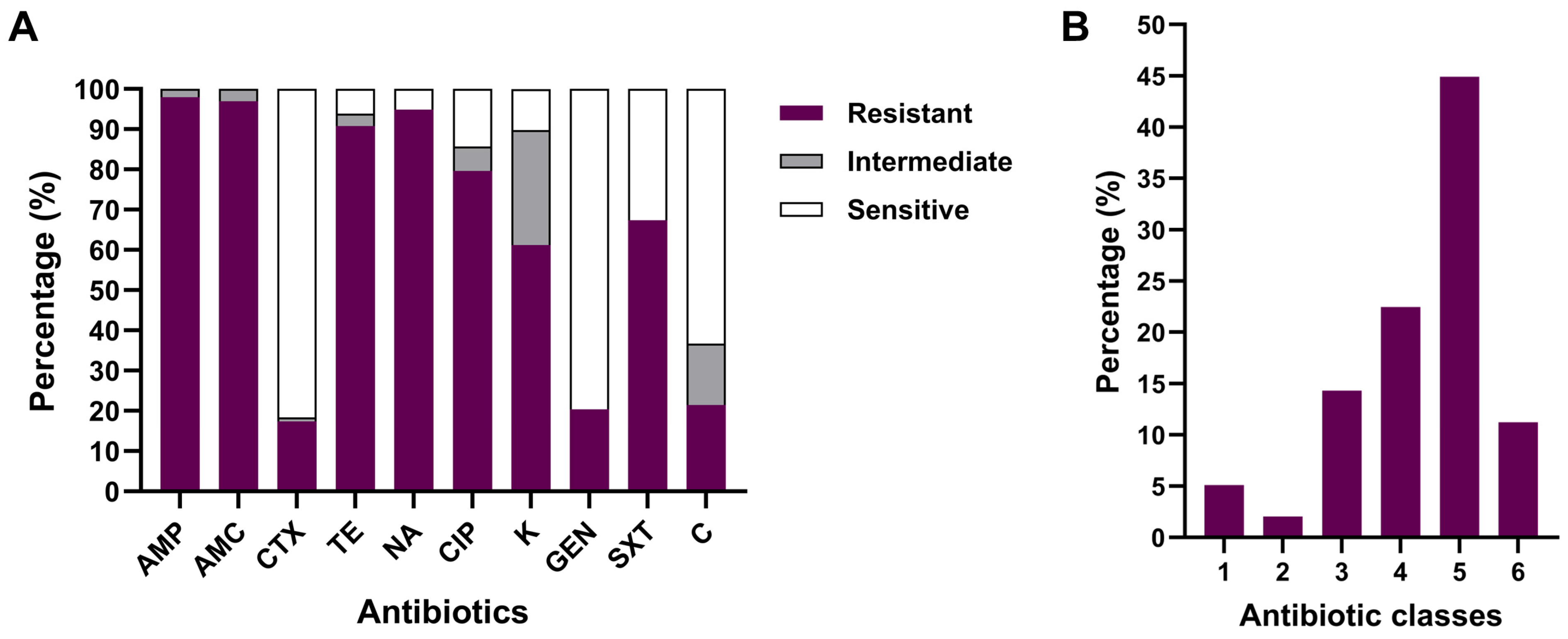
3.6. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing of APEC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kathayat, D.; Lokesh, D.; Ranjit, S.; Rajashekara, G. Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC): An Overview of Virulence and Pathogenesis Factors, Zoonotic Potential, and Control Strategies. Pathogens 2021, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, L.K.; Vaillancourt, J.-P.; Barbieri, N.L.; Logue, C.M. Colibacillosis. In Diseases of Poultry; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 770–830. ISBN 978-1-119-37119-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guabiraba, R.; Schouler, C. Avian Colibacillosis: Still Many Black Holes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, fnv118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Jennings, M.; Barbieri, N.; Zhang, L.; Adhikari, P.; Ramachandran, R. Characterization of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Isolated from Broiler Breeders with Colibacillosis in Mississippi. Poultry 2023, 2, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Wannemuehler, Y.; Doetkott, C.; Johnson, S.J.; Rosenberger, S.C.; Nolan, L.K. Identification of Minimal Predictors of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Virulence for Use as a Rapid Diagnostic Tool. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3987–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmett, K.; Humphrey, T.; Rushton, S.; Close, A.; Wigley, P.; Williams, N.J. A Longitudinal Study Simultaneously Exploring the Carriage of APEC Virulence Associated Genes and the Molecular Epidemiology of Faecal and Systemic E. coli in Commercial Broiler Chickens. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schouler, C.; Schaeffer, B.; Brée, A.; Mora, A.; Dahbi, G.; Biet, F.; Oswald, E.; Mainil, J.; Blanco, J.; Moulin-Schouleur, M. Diagnostic Strategy for Identifying Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Based on Four Patterns of Virulence Genes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1673–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Siek, K.E.; Giddings, C.W.; Doetkott, C.; Johnson, T.J.; Nolan, L.K. Characterizing the APEC Pathotype. Vet. Res. 2005, 36, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, A.; Wigley, P. Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli: An Overview of Infection Biology, Antimicrobial Resistance and Vaccination. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clermont, O.; Christenson, J.K.; Denamur, E.; Gordon, D.M. The Clermont Escherichia coli Phylo-Typing Method Revisited: Improvement of Specificity and Detection of New Phylo-Groups. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logue, C.M.; Wannemuehler, Y.; Nicholson, B.A.; Doetkott, C.; Barbieri, N.L.; Nolan, L.K. Comparative Analysis of Phylogenetic Assignment of Human and Avian ExPEC and Fecal Commensal Escherichia coli Using the (Previous and Revised) Clermont Phylogenetic Typing Methods and Its Impact on Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) Classification. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Afayibo, D.J.A.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, H.; Yao, L.; Guo, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Peng, H. Characteristics, Pathogenic Mechanism, Zoonotic Potential, Drug Resistance, and Prevention of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC). Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1049391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.; Arafat, N.; Elhadidy, M. Genetic Elements Associated with Antimicrobial Resistance among Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2016, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velhner, M.; Todorović, D.; Grego, E.; Kišek, T.C.; Ljubojević, D.; Špik, V.C.; Pajić, M.; Kozoderović, G. Characterisation of Multidrug Resistant Escherichia coli from Poultry Litter and Poultry Carrying Virulence Genes for Evaluation of Poultry Farm Management. Eur. Poult. Sci. 2020, 84, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranabhat, G.; Subedi, D.; Karki, J.; Paudel, R.; Luitel, H.; Bhattarai, R.K. Molecular Detection of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) in Broiler Meat from Retail Meat Shop. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.S.; Hashad, M.E.; Atef, Y.; Badr, H.; Elhariri, M.; Kadry, M. Public Health Threat of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Genes in Escherichia coli from Human-Chicken Transmission in Egypt. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, F.; Hacène, I.; Mohamed, B. Structuring and Development of Poultry Sectors in Algeria: Limits of Modernization Policies: The Case of the” Turkey” Sector (2000–2020). Agric. Sci. Dig. 2024, 44, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloui, N.; Ayachi, A. Biosecurity Practices in Algerian Poultry Farms. Online J. Anim. Feed Res. 2012, 2, 80–83. [Google Scholar]
- Kamel, K.; Merghad, A.; Barour, D.; Eddine Gherissi, D.; Khenenou, T. High Antimicrobial Resistance Rates and Multidrug Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae Isolates from Poultry in Souk Ahras Region, Algeria. Vet. World 2024, 17, 2709–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenouf, N.S.; Messaï, C.R.; Carvalho, I.; Álvarez-Gómez, T.; Silva, V.; Zitouni, A.; Hakem, A.; Poeta, P.; Torres, C. Serogrouping and Molecular Characterization of ESBL-Producing Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli from Broilers and Turkeys with Colibacillosis in Algeria. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, L.; Ge, Z.; Yuehua, L.; Yubin, G.; Rachid, K.; Mustapha, O.; Junwei, W.; Karine, O. Virulence Traits of Avian Pathogenic (APEC) and Fecal (AFEC) E. coli Isolated from Broiler Chickens in Algeria. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2018, 50, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Tu, J.; Han, X.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, C.; Yu, S. Development of Multiplex PCR Assay for Rapid Detection of Riemerella Anatipestifer, Escherichia coli, and Salmonella Enterica Simultaneously from Ducks. J. Microbiol. Methods 2011, 87, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, A.; Iyoda, S.; Seto, K.; Morita-Ishihara, T.; Scheutz, F.; Ohnishi, M. Escherichia coli O-Genotyping PCR: A Comprehensive and Practical Platform for Molecular O Serogrouping. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2427–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Meng, Q.; Dai, J.; Han, X.; Han, Y.; Ding, C.; Liu, H.; Yu, S. Development of an Allele-Specific PCR Assay for Simultaneous Sero-Typing of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Predominant O1, O2, O18 and O78 Strains. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Afayibo, D.J.A.; Qi, J.; Tian, M.; Ding, C.; et al. Establishment and Application of Multiplex PCR Method for Escherichia coli O8/O9/O149 and O157 Serotypes. Chin. J. Vet. Sci. 2022, 52, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Wang, S.; Han, X.; Han, Y.; Ding, C.; Dai, J.; Yu, S. Multiplex PCR Assay for Detection of Virulence Genes in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao = Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2014, 54, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, J.J.; Brown, T.P.; Steffens, W.L.; Thayer, S.G. The Occurrence of Ambient Temperature-Regulated Adhesins, Curli, and the Temperature-Sensitive Hemagglutinin Tsh among Avian Escherichia coli. Avian Dis. 1998, 42, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewers, C.; Li, G.; Wilking, H.; Kieβling, S.; Alt, K.; Antáo, E.-M.; Laturnus, C.; Diehl, I.; Glodde, S.; Homeier, T. Avian Pathogenic, Uropathogenic, and Newborn Meningitis-Causing Escherichia coli: How Closely Related Are They? Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 297, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xia, Y.; Dai, J.; Shi, Z.; Kou, Y.; Li, H.; Bao, Y.; Lu, C. Novel Roles for Autotransporter Adhesin AatA of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli: Colonization during Infection and Cell Aggregation. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 63, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, P.; Shi, Z.; Wei, J.; Shao, D.; Li, B.; Ma, Z. Molecular Characterization of Enterohemorrhagic E. coli O157 Isolated from Animal Fecal and Food Samples in Eastern China. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 946394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihannic, M.; Ghanbarpour, R.; Auvray, F.; Cavalié, L.; Châtre, P.; Boury, M.; Brugère, H.; Madec, J.-Y.; Oswald, E. Identification and Detection of Three New F17 Fimbrial Variants in Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Cattle. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowaczek, A.; Dec, M.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Urban-Chmiel, R.; Marek, A.; Różański, P. Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Profiles of Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Wild Birds in Poland. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Dai, J.; Meng, Q.; Han, X.; Han, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, D.; Ding, C.; Yu, S. DotU Expression Is Highly Induced during in Vivo Infection and Responsible for Virulence and Hcp1 Secretion in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 29th ed.; CLSI Supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- El-Shaer, S.; Abdel-Rhman, S.H.; Barwa, R.; Hassan, R. Virulence Characteristics, Serotyping and Phylogenetic Typing of Clinical and Environmental Escherichia coli Isolates. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2018, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M.T.; Lubbers, B.V.; Schwarz, S.; Watts, J.L. Applying Definitions for Multidrug Resistance, Extensive Drug Resistance and Pandrug Resistance to Clinically Significant Livestock and Companion Animal Bacterial Pathogens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1460–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halfaoui, Z.; Menoueri, N.M.; Bendali, L.M. Serogrouping and Antibiotic Resistance of Escherichia coli Isolated from Broiler Chicken with Colibacillosis in Center of Algeria. Vet. World 2017, 10, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsianos, D.; Athanasiou, L.V.; Mossialos, D.; Franzo, G.; Cecchinato, M.; Koutoulis, K.C. Investigation of Serotype Prevalence of Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Layer Poultry in Greece and Interactions with Other Infectious Agents. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtylla, T.; Circella, E.; Madio, A.; Boci, J.; Çabeli, P.; Kumbe, I.; Camarda, A. Biological characteristics and pathogenicity of avian Escherichia coli strains from Albanian poultry flocks. Sci. Pap. Ser. D Anim. Sci. 2012, 55, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Enany, M.E.; Ramadan, B.A.; Eid, S.; Abo Hashem, M.E.S. Prevalence and Serotyping of E. coli Isolated from Broiler Chickens at Ismailia Governorate. Suez Canal Vet. Med. J. SCVMJ 2024, 29, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azza, A.; Dahshan, A.H.M.; El-Nahass, E.-S.; Abd El-Mawgoud, A.I. Pathogenicity of Escherichia coli O157 in Commercial Broiler Chickens. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameer, M.A.; Wasey, A.; Salen, P. Escherichia coli (E. coli 0157 H7). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025; Available online: https://europepmc.org/article/nbk/nbk507845 (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Dipineto, L.; Santaniello, A.; Fontanella, M.; Lagos, K.; Fioretti, A.; Menna, L.F. Presence of Shiga Toxin—Producing Escherichia coli O157:H7 in Living Layer Hens. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.M.; El-Shall, N.A.; Khalil, D.S.; El-Hack, M.E.A.; Swelum, A.A.; Mahmoud, A.H.; Ebaid, H.; Komany, A.; Sammour, R.H.; Sedeik, M.E. Incidence, Pathotyping, and Antibiotic Susceptibility of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Among Diseased Broiler Chicks. Pathogens 2020, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczyński, J.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Wystalska, D.; Wernicki, A. Molecular and Serological Characteristics of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Isolated from Various Clinical Cases of Poultry Colibacillosis in Poland. Animals 2022, 12, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runcharoon, K.; Favro, M.E.; Logue, C.M. Longitudinal Analysis of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) Serogroups and Pathotypes from Avian Colibacillosis in Georgia: A Continued Investigation–Year 2 Analysis. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 104722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.A.; Cryer, T.L.; Lafi, S.Q.; Basha, E.-A.; Good, L.; Tarazi, Y.H. Identification of Escherichia coli from Broiler Chickens in Jordan, Their Antimicrobial Resistance, Gene Characterization and the Associated Risk Factors. BMC Vet Res 2019, 15, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afayibo, D.J.A.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, B.; Yao, L.; Abdelgawad, H.A.; Tian, M.; Qi, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S. Isolation, Molecular Characterization, and Antibiotic Resistance of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli in Eastern China. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Guo, G.; Hu, Z.; Miao, J.; Dong, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, X.; Han, X.; et al. O145 May Be Emerging as a Predominant Serogroup of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 266, 109358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kang, M.-S.; Lee, H.-J.; Kang, S.-I.; Lee, O.-M.; Kwon, Y.-K.; Kim, J.-H. Comparative Characteristics and Zoonotic Potential of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) Isolates from Chicken and Duck in South Korea. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, K.A.; Furian, T.Q.; De Brito, B.G.; De Brito, K.C.T.; Da Rocha, D.T.; Salle, C.T.P.; Moraes, H.L.D.S.; Do Nascimento, V.P. Characterization of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Isolates Based on Biofilm Formation, ESBL Production, Virulence-Associated Genes, and Phylogenetic Groups. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 54, 2413–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohmaz, M.; Askari Badouei, M.; Kalateh Rahmani, H.; Hashemi Tabar, G. Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Associated Genes and Phylogenetic Background Versus Plasmid Replicon Types: The Possible Associations in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC). BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovi, F.; Zhang, L.; Nabors, H.; Jia, L.; Adhikari, P. A Compilation of Virulence-Associated Genes That Are Frequently Reported in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) Compared to Other E. coli. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxad014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Jiang, W.; Chen, Z.; Yin, H.; Huang, C.; Han, X. Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC): Current Insights and Future Challenges. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixao, A.C.; Ferreira, A.C.; Fontes, M.; Themudo, P.; Albuquerque, T.; Soares, M.C.; Fevereiro, M.; Martins, L.; De Sá, M.C. Detection of Virulence-Associated Genes in Pathogenic and Commensal Avian Escherichia coli Isolates. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 1646–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Hu, B.; Fan, H.; Zhang, H.; Lian, S.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Yan, X.; Wang, S.; Bai, X. Molecular Epidemiology of Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli Causing Hemorrhagic Pneumonia in Mink in Northern China. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 781068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kandari, F.; Woodward, M.J. Genotypic and Phenotypic Diversity Differences of Presumptive Commensal and Avian Pathogenic E. coli. Br. Poult. Sci. 2019, 60, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awawdeh, L.; Forrest, R.; Turni, C.; Cobbold, R.; Henning, J.; Gibson, J. Virulence—Associated Genes in Faecal and Clinical Escherichia coli Isolates Cultured from Broiler Chickens in Australia. Aust. Vet. J. 2024, 102, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhunia, A.K. Escherichia Coli. In Foodborne Microbial Pathogens: Mechanisms and Pathogenesis; Springer New York: New York, NY, 2018; pp. 249–269. ISBN 978-1-4939-7349-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Su, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Sun, J.; Yan, Y. Clustered, Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat (CRISPR) Diversity and Virulence Factor Distribution in Avian Escherichia coli. Res. Microbiol. 2017, 168, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, S.-H.; Wass, C.A.; Stins, M.F.; Kim, K.S. The Gene Locus yijP Contributes to Escherichia coli K1 Invasion of Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 4751–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Siek, K.E.; Johnson, S.J.; Nolan, L.K. DNA Sequence of a ColV Plasmid and Prevalence of Selected Plasmid-Encoded Virulence Genes among Avian Escherichia coli Strains. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Johnson, S.J.; Nolan, L.K. Complete DNA Sequence of a ColBM Plasmid from Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Suggests That It Evolved from Closely Related ColV Virulence Plasmids. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 5975–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.R.; Jelacic, S.; Schoening, L.M.; Clabots, C.; Shaikh, N.; Mobley, H.L.T.; Tarr, P.I. The IrgA Homologue Adhesin Iha Is an Escherichia Coli Virulence Factor in Murine Urinary Tract Infection. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léveillé, S.; Caza, M.; Johnson, J.R.; Clabots, C.; Sabri, M.; Dozois, C.M. Iha from an Escherichia coli Urinary Tract Infection Outbreak Clonal Group A Strain Is Expressed In Vivo in the Mouse Urinary Tract and Functions as a Catecholate Siderophore Receptor. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 3427–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Niu, C.; Shi, Z.; Xia, Y.; Yaqoob, M.; Dai, J.; Lu, C. Effects of ibeA Deletion on Virulence and Biofilm Formation of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Wannemuehler, Y.; Johnson, S.J.; Stell, A.L.; Doetkott, C.; Johnson, J.R.; Kim, K.S.; Spanjaard, L.; Nolan, L.K. Comparison of Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli Strains from Human and Avian Sources Reveals a Mixed Subset Representing Potential Zoonotic Pathogens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 7043–7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Xue, T.; Qi, K.; Shao, Y.; Huang, B.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X. The irp2 and fyuA Genes in High Pathogenicity Islands Are Involved in the Pathogenesis of Infections Caused by Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC). Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2016, 19, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parreira, V.R.; Gyles, C.L. A Novel Pathogenicity Island Integrated Adjacent to the thrW tRNA Gene of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Encodes a Vacuolating Autotransporter Toxin. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 5087–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spurbeck, R.R.; Dinh, P.C.; Walk, S.T.; Stapleton, A.E.; Hooton, T.M.; Nolan, L.K.; Kim, K.S.; Johnson, J.R.; Mobley, H.L.T. Escherichia coli Isolates That Carry vat, fyuA, chuA, and yfcV Efficiently Colonize the Urinary Tract. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 4115–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murase, T.; Ozaki, H. Relationship between Phylogenetic Groups of Escherichia coli and Pathogenicity among Isolates from Chickens with Colibacillosis and Healthy Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 102007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuge, X.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Tang, F.; Xue, F.; Ren, J.; Dai, J. Chicken—Source Escherichia coli Within Phylogroup F Shares Virulence Genotypes and Is Closely Related to Extraintestinal Pathogenic E. coli Causing Human Infections. Transbounding Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 880–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberkane, C.; Messaï, A.; Messaï, C.R.; Boussaada, T. Antimicrobial Resistance Pattern of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli with Detection of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Isolates in Broilers in East Algeria. Vet. World 2023, 16, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpov, D.S.; Kazakova, E.M.; Kovalev, M.A.; Shumkov, M.S.; Kusainova, T.; Tarasova, I.A.; Osipova, P.J.; Poddubko, S.V.; Mitkevich, V.A.; Kuznetsova, M.V. Determinants of Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Factors in the Genome of Escherichia coli APEC 36 Strain Isolated from a Broiler Chicken with Generalized Colibacillosis. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johar, A.; Al-Thani, N.; Al-Hadidi, S.H.; Dlissi, E.; Mahmoud, M.H.; Eltai, N.O. Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Gene Patterns Associated with Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) from Broiler Chickens in Qatar. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Hu, J.; Zhang, B.; Qi, J.; Tian, M.; Bao, Y.; et al. Identification and Characterization of a Plasmid Co-Harboring blaCTX-M-55 and blaTEM-141 in Escherichia Albertii from Broiler in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2025, 24, 3212–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khalaifah, H.; Rahman, M.H.; Al-Surrayai, T.; Al-Dhumair, A.; Al-Hasan, M. A One-Health Perspective of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): Human, Animals and Environmental Health. Life 2025, 15, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocak, F.; Çöven, F.; Ertunç, E.; Eğilmez, T.; Türkyilmaz, S. Determination of the Most Significant Serotypes and Antimicrobial Susceptibilities of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Isolates in Turkey. Eur. Poult. Sci. 2018, 82, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barour, D.; Berghiche, A.; Boulebda, N. Antimicrobial Resistance of Escherichia coli Isolates from Cattle in Eastern Algeria. Vet. World 2019, 12, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, K.M.; White, D.G.; Hume, M.E.; Poole, T.L.; Nisbet, D.J. The Chloramphenicol Resistance Gene cmlA Is Disseminated on Transferable Plasmids That Confer Multiple-Drug Resistance in Swine Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 243, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, K.; Asai, T.; Kojima, A.; Ishihara, K.; Takahashi, T. Role of Coresistance in the Development of Resistance to Chloramphenicol in Escherichia coli Isolated from Sick Cattle and Pigs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2006, 67, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halfaoui, Z.; Rahab, H.; Achek, R.; Menoueri, M.N. First Report of Detection of Mcr-1 and Virulence Genes in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli in the Center of Algeria. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2024, 25, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaouadi, S.; Soufi, L.; Hamza, A.; Fedida, D.; Zied, C.; Awadhi, E.; Mtibaa, M.; Hassen, B.; Cherif, A.; Torres, C. Co-Occurrence of Mcr-1 Mediated Colistin Resistance and β-Lactamase-Encoding Genes in Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli from Broiler Chickens with Colibacillosis in Tunisia. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

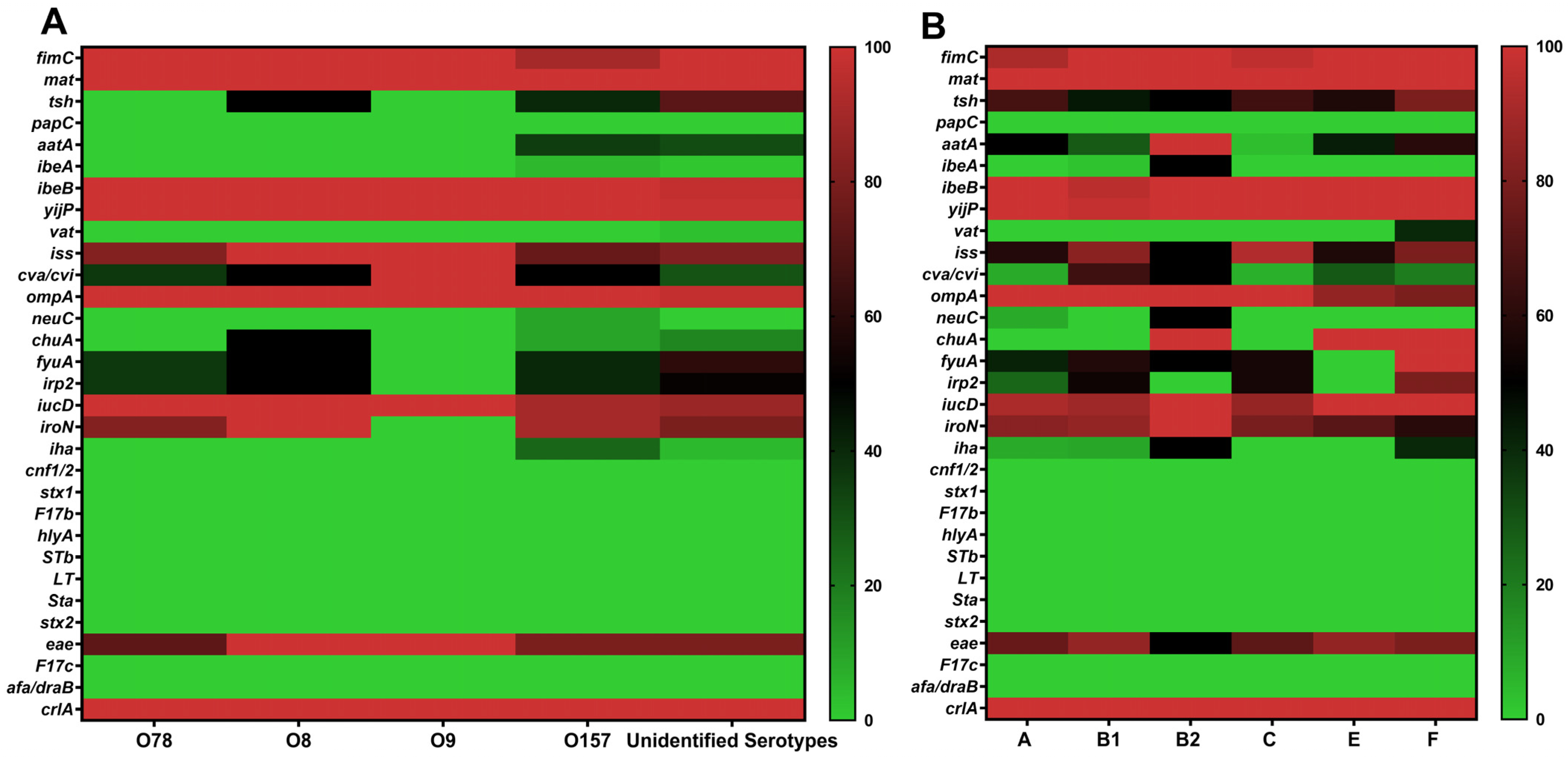
| Virulence Genes | O157 | O78 | O8 | O9 | Unidentified Serotypes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |
| crlA | 20 (100) | 11 (100) | 2 (100) | 1 (100) | 64 (100) |
| mat | 20 (100) | 11 (100) | 2 (100) | 0 (0) | 64 (100) |
| yijP | 20 (100) | 11 (100) | 2 (100) | 1 (100) | 63 (98.44) |
| ibeB | 20 (100) | 11 (100) | 2 (100) | 1 (100) | 62 (96.88) |
| fimC | 18 (90) | 11 (100) | 2 (100) | 1 (100) | 64 (100) |
| ompA | 20 (100) | 11 (100) | 2 (100) | 1 (100) | 62 (96.88) |
| iucD | 18 (90) | 11 (100) | 2 (100) | 1 (100) | 56 (87.50) |
| iroN | 18 (90) | 9 (81.82) | 2 (100) | 0 (0) | 51 (79.69) |
| iss | 15 (75) | 9 (81.82) | 2 (100) | 1 (100) | 52 (81.25) |
| eae | 16 (80) | 8 (72.73) | 2 (100) | 1 (100) | 51 (79.69) |
| tsh | 8 (40) | 0 (0) | 1 (50) | 0 (0) | 46 (71.88) |
| fyuA | 8 (40) | 4 (36.36) | 1 (50) | 0 (0) | 39 (60.94) |
| irp2 | 8 (40) | 4 (36.36) | 1 (50) | 0 (0) | 33 (51.56) |
| cva/cvi | 10 (50) | 4 (36.36) | 1 (50) | 1 (100) | 19 (29.69) |
| aatA | 7 (35) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 20 (31.25) |
| chuA | 2 (10) | 0 (0) | 1 (50) | 0 (0) | 11 (17.19) |
| iha | 5 (25) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (4.69) |
| neuC | 2 (10) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| ibeA | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.56) |
| vat | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (3.13) |
| Virulence Genes | No. (%) of APEC Isolates by Phylogenetic Group | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (n = 12) | B1 (n = 43) | B2 (n = 2) | C (n = 29) | E (n = 7) | F (n = 5) | |
| crlA | 12 (100) | 43 (100) | 2 (100) | 29 (100) | 7 (100) | 5 (100) |
| mat | 12 (100) | 43 (100) | 2 (100) | 29 (100) | 7 (100) | 5 (100) |
| yijP | 12 (100) | 42(97.67) | 2 (100) | 29 (100) | 7 (100) | 5 (100) |
| ibeB | 12 (100) | 41(95.35) | 2 (100) | 29 (100) | 7 (100) | 5 (100) |
| fimC | 11 (91.67) | 43 (100) | 2 (100) | 28 (96.55) | 7 (100) | 5 (100) |
| ompA | 12 (100) | 43 (100) | 2 (100) | 29 (100) | 6 (85.71) | 4 (80) |
| iucD | 11 (91.67) | 38 (88.37) | 2 (100) | 25 (86.21) | 7 (100) | 5 (100) |
| iroN | 10 (83.33) | 37 (86.05) | 2 (100) | 23 (79.31) | 5 (71.43) | 3 (60) |
| iss | 7 (58.33) | 36 (83.72) | 1 (50) | 27 (93.10) | 4 (57.14) | 4 (80) |
| eae | 9 (75) | 37 (86.05) | 1 (50) | 21 (72.41) | 6 (85.71) | 4 (80) |
| tsh | 8 (66.67) | 19 (44.19) | 1 (50) | 19 (65.52) | 4 (57.14) | 4 (80) |
| fyuA | 5 (41.67) | 25 (58.14) | 1 (50) | 16 (55.17) | 0 (0) | 5 (100) b |
| irp2 | 3 (25) | 23 (53.49) | 0 (0) | 16 (55.17) | 0 (0) | 4 (80) b |
| cva/cvi | 1 (8.33) | 28 (65.12) | 1 (50) | 2(6.90) | 2 (28.57) | 1 (20) |
| aatA | 6 (50) | 12 (27.91) | 2 (100) | 1(3.45) | 3 (42.86) | 3 (60) |
| chuA | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (100) | 0 (0) | 7 (100) | 5 (100) b |
| iha | 1 (8.33) | 4 (9.30) | 1 (50) | 0(0) | 0 (0) | 2 (40) |
| neuC | 1 (8.33) | 0 (0) | 1 (50) a | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| ibeA | 0 (0) | 1 (2.33) | 1 (50) a | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| vat | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (40) b |
| MVS c | 11.08 | 11.97 | 13.50 | 11.13 | 11.28 | 14.20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boulbair, I.; Hu, J.; Hammoudi, A.; Zhang, B.; Aissat, S.; Wang, X.; Foudil, M.; Wang, S. Molecular Characterization and Antibiotic Resistance of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) Isolates from Broiler Chickens in Algeria. Animals 2025, 15, 3324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223324
Boulbair I, Hu J, Hammoudi A, Zhang B, Aissat S, Wang X, Foudil M, Wang S. Molecular Characterization and Antibiotic Resistance of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) Isolates from Broiler Chickens in Algeria. Animals. 2025; 15(22):3324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223324
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoulbair, Ismail, Jiangang Hu, Abdelhamid Hammoudi, Beibei Zhang, Saad Aissat, Xinyu Wang, Mohammed Foudil, and Shaohui Wang. 2025. "Molecular Characterization and Antibiotic Resistance of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) Isolates from Broiler Chickens in Algeria" Animals 15, no. 22: 3324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223324
APA StyleBoulbair, I., Hu, J., Hammoudi, A., Zhang, B., Aissat, S., Wang, X., Foudil, M., & Wang, S. (2025). Molecular Characterization and Antibiotic Resistance of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) Isolates from Broiler Chickens in Algeria. Animals, 15(22), 3324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223324






