Valorization of Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus) By-Products into Antioxidant Protein Hydrolysates for Nutraceutical Applications
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Material
2.2. Evaluation of Proximate Composition of Blue Crab By-Products
2.3. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Blue Crab By-Products
2.4. Protein Hydrolysates Characterization and Assessment of Antioxidant Activity
2.4.1. Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.4.2. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
2.4.3. ABTS Radical Scavenging Activity
2.4.4. Ferric-Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP) Assay
2.4.5. Reducing Power
2.4.6. Cell Culture
2.4.7. Protective Effects of BCBP Hydrolysates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Yield and Proximate Composition
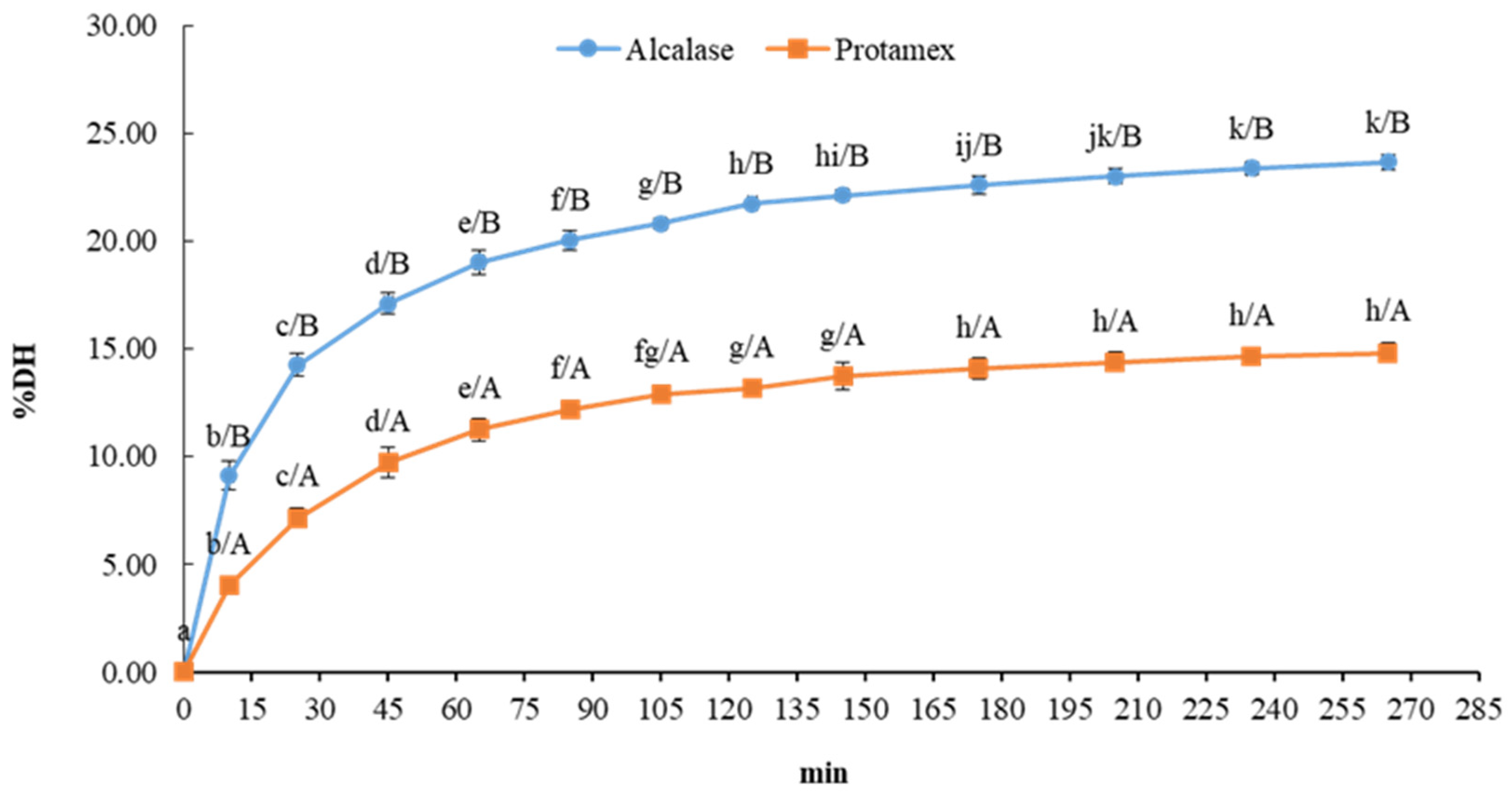
3.2. Degree of Hydrolysis
3.3. Characterization and Bioactivity Evaluation of Protein Hydrolysate
3.3.1. SDS-PAGE
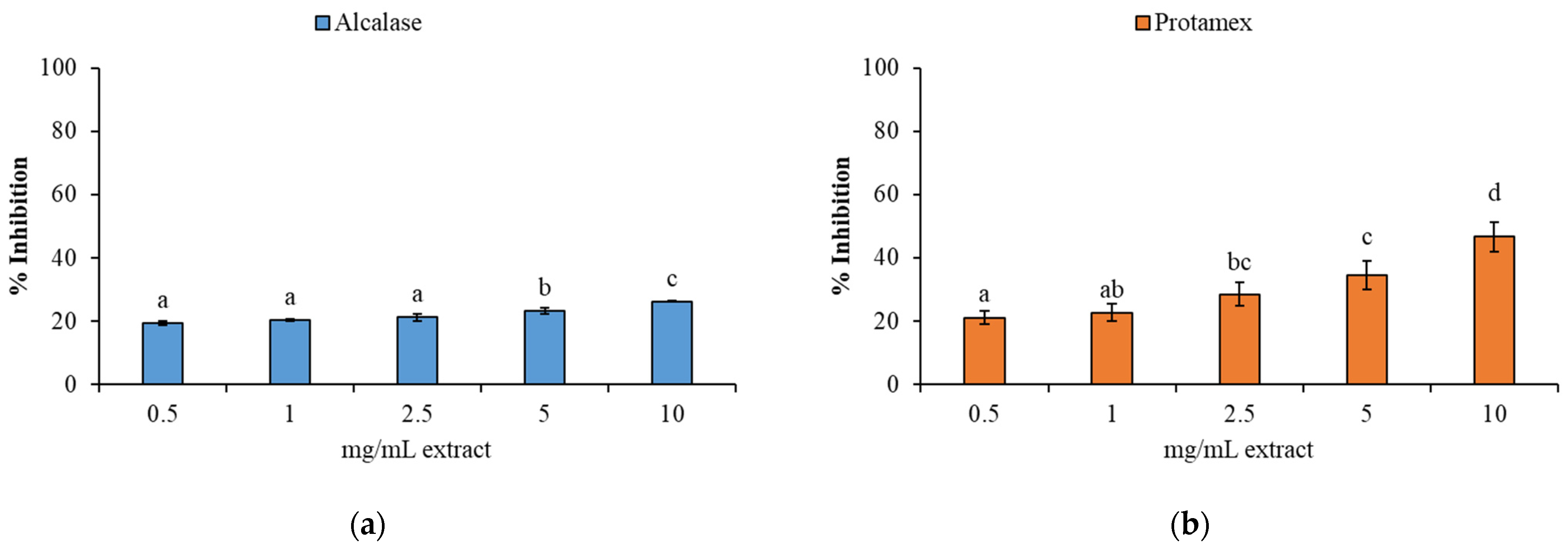
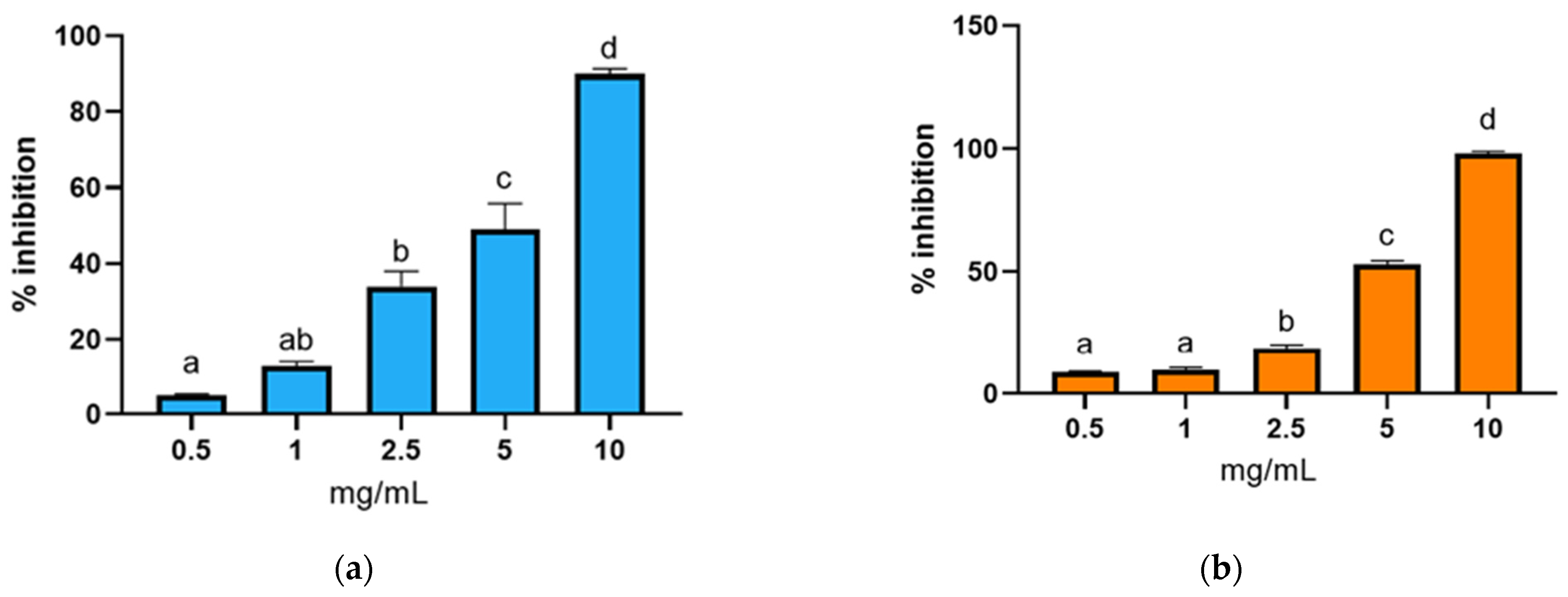
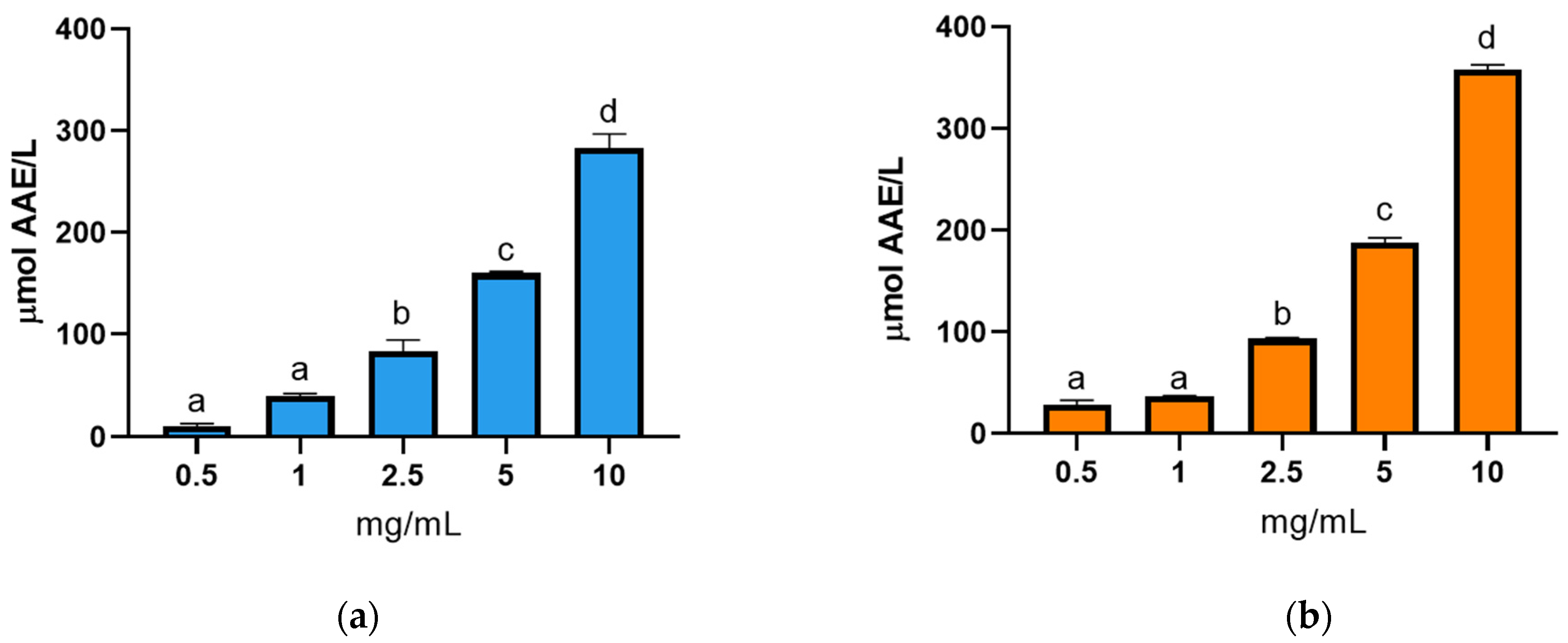
3.3.2. Antioxidant Activity
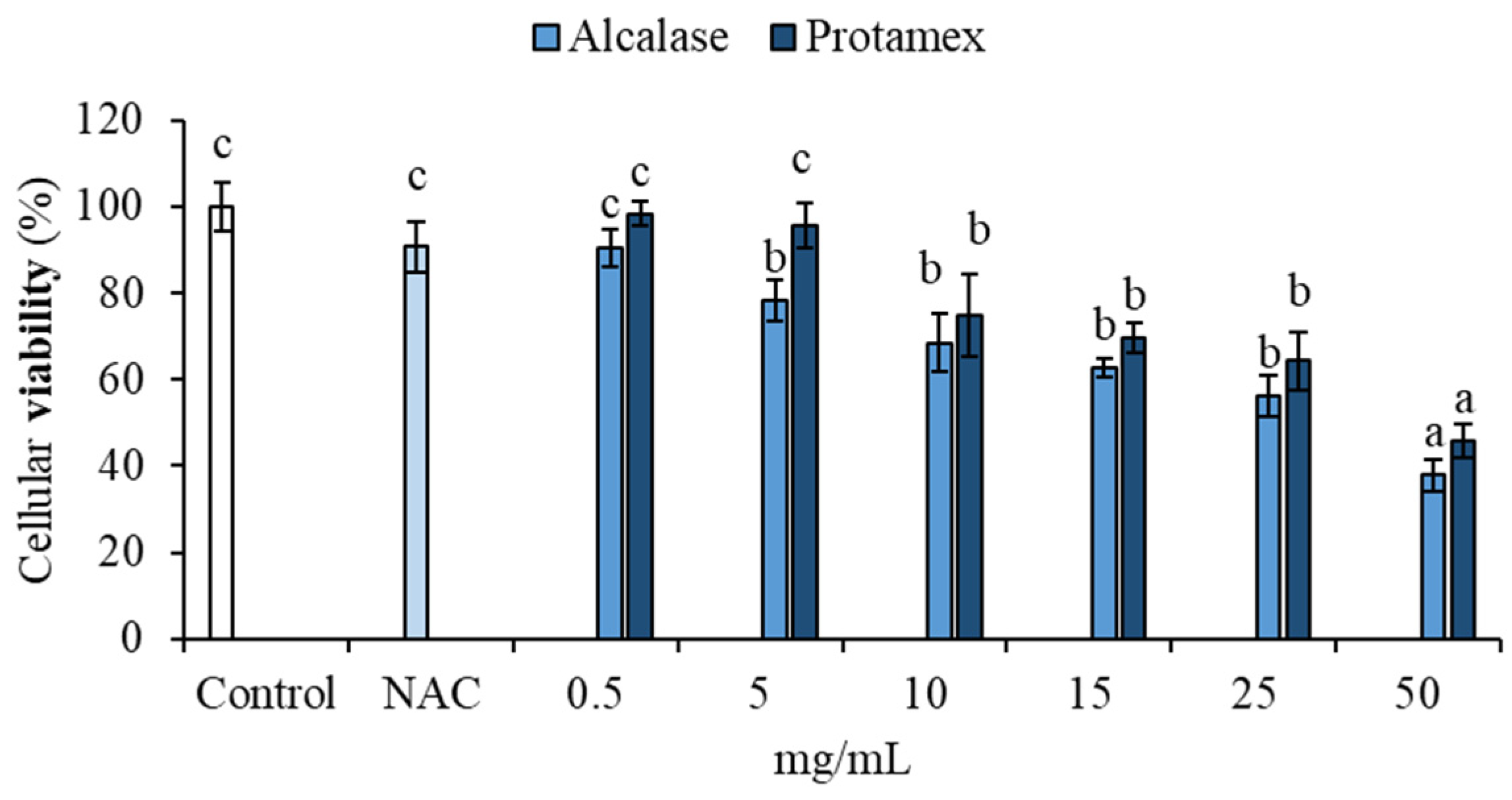
3.3.3. Antioxidant Capacity of Hydrolyzed Fractions In Vitro, at the Cellular Level
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCBP | Blue crab by-products |
| SDS PAGE | Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis |
| BSA | Bovine Serum Albumin |
| DPPH | 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| ABTS | 2′-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) |
| FRAP | Ferric-Reducing Antioxidant Power |
| HS68 | Human skin fibroblasts |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
References
- Kevrekidis, K.; Kevrekidis, T.; Mogias, A.; Boubonari, T.; Kantaridou, F.; Kaisari, N.; Malea, P.; Dounas, C.; Thessalou-Legaki, M. Fisheries Biology and Basic Life-Cycle Characteristics of the Invasive Blue Crab Callinectes sapidus Rathbun in the Estuarine Area of the Evros River (Northeast Aegean Sea, Eastern Mediterranean). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehring, S. Invasion History and Success of the American Blue Crab Callinectes sapidus in European and Adjacent Waters. In In the Wrong Place—Alien Marine Crustaceans: Distribution, Biology and Impacts; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 607–624. ISBN 978-94-007-0591-3. [Google Scholar]
- Mancinelli, G.; Bardelli, R.; Zenetos, A. A global occurrence database of the Atlantic blue crab Callinectes sapidus. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamassi, F.; Bahri, W.R.; Bhouri, A.M.; Chaffai, A.; Soufikechaou, E.; Ghanem, R.; Souissi, J. Ben Biochemical composition, nutritional value, and socio-economic impacts of the invasive crab Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896 in central Mediterranean Sea. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2022, 23, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taybi, A.F.; Mabrouki, Y. The American Blue Crab Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896 (Crustacea: Decapoda: Portunidae) is Rapidly Expanding Through the Mediterranean Coast of Morocco. Thalassas 2020, 36, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchessaux, G.; Mangano, M.C.; Bizzarri, S.; M’Rabet, C.; Principato, E.; Lago, N.; Veyssiere, D.; Garrido, M.; Scyphers, S.B.; Sarà, G. Invasive blue crabs and small-scale fisheries in the Mediterranean sea: Local ecological knowledge, impacts and future management. Mar. Policy 2023, 148, 105461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, R.; Renda, G.; Ottaviani Aalmo, G.; Debeaufort, F.; Maria Messina, C.; Santulli, A. Valorization of the Invasive Blue Crabs (Callinectes sapidus) in the Mediterranean: Nutritional Value, Bioactive Compounds and Sustainable By-Products Utilization. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Yu, S.; Wu, D.; Xia, M.; Wen, Z.; Yao, Z.; Tang, J.; Wu, W. A critical review of cast-off crab shell recycling from the perspective of functional and versatile biomaterials. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 31581–31591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekvapil, F.; Ganea, I.V.; Ciorîță, A.; Hirian, R.; Ogresta, L.; Glamuzina, B.; Roba, C.; Pinzaru, S.C. Wasted biomaterials from crustaceans as a compliant natural product regarding microbiological, antibacterial properties and heavy metal content for reuse in blue bioeconomy: A preliminary study. Materials 2021, 14, 4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelló, E.; Pinya, S.; Box, A.; Sureda, A.; Compa, M. Assessing heavy metal accumulation in the invasive blue crab (Callinectes sapidus): Environmental and human health implications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 32, 12579–12593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinales, C.; Romero-Peña, M.; Calderón, G.; Vergara, K.; Cáceres, P.J.; Castillo, P. Collagen, protein hydrolysates and chitin from by-products of fish and shellfish: An overview. Heliyon 2023, 9, e1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes-Valcareggi, S.A.; Ferreira, S.R.S.; Hense, H. Enzymatic hydrolysis of blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) waste processing to obtain chitin, protein, and astaxanthin-enriched extract. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Res. 2017, 3, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Félix-Valenzuela, L.; Higuera-Ciapara, I.; Goycoolea-Valencia, F.; Argüelles-Monal, W. Supercritical CO2/ethanol extraction of astaxanthin from blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) shell waste. J. Food Process Eng. 2001, 24, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnedy, P.A.; Fitzgerald, R.J. Bioactive proteins, peptides, and amino acids from macroalgae. J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, C.M.; Manuguerra, S.; Arena, R.; Renda, G.; Ficano, G.; Randazzo, M.; Fricano, S.; Sadok, S.; Santulli, A. In Vitro Bioactivity of Astaxanthin and Peptides from Hydrolisates of Shrimp (Parapenaeus longirostris) By-Products: From the Extraction Process to Biological Effect Evaluation, as Pilot Actions for the Strategy “From Waste to Profit”. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, G.; Floris, R.; Serangeli, C.; Di Paola, L. Fishery Wastes as a Yet Undiscovered Treasure from the Sea: Biomolecules Sources, Extraction Methods and Valorization. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, D.; Lauritano, C.; Esposito, F.P.; Riccio, G.; Rizzo, C.; De Pascale, D.; Santulli, A. Fish Waste: From Problem to Valuable Resource. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, V. Green processing of seafood waste biomass towards blue economy. Curr. Res. Environ. Sustain. 2022, 4, 100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirukumaran, R.; Anu Priya, V.K.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Ramakrishnan, P.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Resource recovery from fish waste: Prospects and the usage of intensified extraction technologies. Chemosphere 2022, 299, 134361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, S.; Kchaou, H.; Bkhairia, I.; Ben Slama-Ben Salem, R.; Boufi, S.; Debeaufort, F.; Nasri, M. Conception of active food packaging films based on crab chitosan and gelatin enriched with crustacean protein hydrolysates with improved functional and biological properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 116, 106639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debeaufort, F. Active biopackaging produced from by-products and waste from food and marine industries. FEBS Open Bio 2021, 11, 984–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Champi, D.; Romero-Orejon, F.L.; Muñoz, A.M.; Ramos-Escudero, F. The Revalorization of Fishery By-Products: Types, Bioactive Compounds, and Food Applications. Int. J. Food Sci. 2024, 2024, 6624083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yomar-Hattori, G.; Sampaio-Sant’Anna, B.; Amaro-Pinheiro, M.A. Meat yield of Callinectes bocourti A. Milne Edwards, 1879 (Crustacea, Portunidae) in Iguape, São Paulo, Brazil. Investig. Mar. 2006, 34, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis: Changes in Official Methods of Analysis Made at the Annual Meeting; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 1990; Volume 15, ISBN 9780935584752. [Google Scholar]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Stanley, G.H.S. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Official Method, 981.10 Crude protein in meat block digestion method. J. AOAC Int. 1992, 65, 1339. [Google Scholar]
- Khiari, Z.; Kelloway, S.; Mason, B. Turning Invasive Green Crab (Carcinus maenas) into Opportunity: Recovery of Chitin and Protein Isolate Through Isoelectric Solubilization/Precipitation. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajomsang, W.; Gonil, P. Preparation and characterization of α-chitin from cicada sloughs. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, J.E. Decalcification of Crustacean Meals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1971, 19, 236–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolat, Y.; Bilgin, Ş.; Günlü, A.; Izci, L.; Koca, S.B.; Çetinkaya, S.; Koca, H.U. Chitin-chitosan yield of freshwater crab (Potamon potamios, Olivier 1804) shell. Pak. Vet. J. 2010, 30, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Messina, C.; Renda, G.; Randazzo, M.; Laudicella, A.; Gharbi, S.; Pizzo, F.; Morghese, M.; Santulli, A. Extraction of bioactive compounds from shrimp waste. Bull. Inst. Natl. Sci. Technol. Mer 2015, 42, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Dumay, J.; Donnay-Moreno, C.; Barnathan, G.; Jaouen, P.; Bergé, J.P. Improvement of lipid and phospholipid recoveries from sardine (Sardina pilchardus) viscera using industrial proteases. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 2327–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Holanda, H.D.; Netto, F.M. Recovery of components from shrimp (Xiphopenaeus kroyeri) processing waste by enzymatic hydrolysis. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, C298–C303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzoni, D.; Skřivanová, E.; Rebucci, R.; Crotti, A.; Baldi, A.; Marchetti, L.; Giromini, C. Total Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity of In Vitro Digested Hemp-Based Products. Foods 2023, 12, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelaleem, M.A.; Elbassiony, K.R.A. Evaluation of phytochemicals and antioxidant activity of gamma irradiated quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa). Braz. J. Biol. 2021, 81, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, C.M.; Troia, A.; Arena, R.; Manuguerra, S.; Ioannou, T.; Curcuraci, E.; Renda, G.; Hellio, C.; Santulli, A. Species-specific antioxidant power and bioactive properties of the extracts obtained from wild mediterranean Calendula spp. (Asteraceae). Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuguerra, S.; Caccamo, L.; Mancuso, M.; Arena, R.; Rappazzo, A.C.; Genovese, L.; Santulli, A.; Messina, C.M.; Maricchiolo, G. The antioxidant power of horseradish, Armoracia rusticana, underlies antimicrobial and antiradical effects, exerted in vitro. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 11, 1567–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, C.M.; Manuguerra, S.; Renda, G.; Santulli, A. Biotechnological Applications for the Sustainable Use of Marine By-products: In Vitro Antioxidant and Pro-apoptotic Effects of Astaxanthin Extracted with Supercritical CO2 from Parapeneus longirostris. Mar. Biotechnol. 2019, 21, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, C.M.; Pizzo, F.; Santulli, A.; Bušelić, I.; Boban, M.; Orhanović, S.; Mladineo, I. Anisakis pegreffii (Nematoda: Anisakidae) products modulate oxidative stress and apoptosis-related biomarkers in human cell lines. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbes, M.; Baati, H.; Guermazi, S.; Messina, C.; Santulli, A.; Gharsallah, N.; Ammar, E. Biological properties of carotenoids extracted from Halobacterium halobium isolated from a Tunisian solar saltern. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Robbens, J.; Heyndrickx, M.; Debode, J.; Raes, K. Bioprocessing of marine crustacean side-streams into bioactives: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.A.; Velazquez, G.; Cando, D.; Núñez-Flores, R.; Borderías, A.J.; Moreno, H.M. Effects of high pressure processing on protein fractions of blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) meat. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 41, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cretton, M.; Malanga, G.; Mazzuca Sobczuk, T.; Mazzuca, M. Lipid Fraction from Industrial Crustacean Waste and Its Potential as a Supplement for the Feed Industry: A Case Study in Argentine Patagonia. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 2311–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naczk, M.; Williams, J.; Brennan, K.; Liyanapathirana, C.; Shahidi, F. Compositional characteristics of green crab (Carcinus maenas). Food Chem. 2004, 88, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakar, M.; Manivannan, K.; Soundrapandian, P. Nutritive Value of Hard and Soft Shell Crabs of Portunus sanguinolentus (Herbst). Int. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2009, 1, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, A.C.D.A.S.; Martí-Quijal, F.J.; Barba, F.J.; Tappi, S.; Rocculi, P. Innovative non-thermal technologies for recovery and valorization of value-added products from crustacean processing by-products—An opportunity for a circular economy approach. Foods 2021, 10, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadkelayeh, S.; Hawboldt, K. Extraction of lipids and astaxanthin from crustacean by-products: A review on supercritical CO2 extraction. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthiban, F.; Balasundari, S.; Gopalakannan, A.; Rathnakumar, K.; Felix, S. Comparison of the Quality of Chitin and Chitosan from Shrimp, Crab and Squilla Waste. Curr. World Environ. 2017, 12, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilasoa-Martínez, M.; López-Hernández, J.; Lage-Yusty, M.A. Protein and amino acid contents in the crab, Chionoecetes opilio. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 1330–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeur, F.; Mechri, S.; Mensi, F.; Gharbi, I.; Naser, Y.B.; Kriaa, M.; Bejaoui, N.; Bachouche, S.; Badis, A.; Annane, R.; et al. Extraction and characterization of chitin, chitosan, and protein hydrolysate from the invasive Pacific blue crab, Portunus segnis (Forskål, 1775) having potential biological activities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 36023–36039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, D.; Costantini, M.; Coppola, D.; Lauritano, C.; Núñez Pons, L.; Ruocco, N.; di Prisco, G.; Ianora, A.; Verde, C. Biotechnological Applications of Bioactive Peptides From Marine Sources. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2018, 73, 171–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Singh, A.; Xavier, M.; Ravishankar, C.N.; Benjakul, S. Chitin, Chitosan, and their Derivatives from Seafood Waste and Processing Byproducts. In Fish Waste to Valuable Products; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 253–278. ISBN 978-981-99-8593-7. [Google Scholar]
- Jabeen, F.; Younis, T.; Sidra, S.; Muneer, B.; Nasreen, Z.; Saleh, F.; Mumtaz, S.; Saeed, R.F.; Abbas, A.S. Extraction of chitin from edible crab shells of Callinectes sapidus and comparison with market purchased chitin. Braz. J. Biol. 2021, 83, e246520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metin, C.; Alparslan, Y.; Baygar, T.; Baygar, T. Physicochemical, Microstructural and Thermal Characterization of Chitosan from Blue Crab Shell Waste and Its Bioactivity Characteristics. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 2552–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.; Dudakli, F.; Asan-Ozusaglam, M.; Cakmak, Y.S.; Baran, T.; Mentes, A.; Erdogan, S. Porous and nanofiber α-chitosan obtained from blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) tested for antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. LWT 2016, 65, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, C.; Marques, A.; Carvalho, M.L.; Batista, I.B. Chemical Characterization of Cancer pagurus, Maja squinado, Necora puber and Carcinus maenas shells. Poult. Fish. Wildl. Sci. 2017, 5, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahú, T.B.; Santos, S.D.; Mendes, A.; Córdula, C.R.; Chavante, S.F.; Carvalho, L.B.; Nader, H.B.; Bezerra, R.S. Recovery of protein, chitin, carotenoids and glycosaminoglycans from Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) processing waste. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, C.M.; Arena, R.; Manuguerra, S.; Pericot, Y.; Curcuraci, E.; Kerninon, F.; Renda, G.; Hellio, C.; Santulli, A. Antioxidant Bioactivity of Extracts from Beach Cast Leaves of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, T.R.; Mantoan, P.; Ramos, P.; Monserrat, J.M.; Prentice, C.; Fernandes, C.C.; Zambuzzi, W.F.; Valenti, W.C. Bioactivity of the Protein Hydrolysates Obtained from the Most Abundant Crustacean Bycatch. Mar. Biotechnol. 2021, 23, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.S.; Dora, K.C. Optimization of the production of shrimp waste protein hydrolysate using microbial proteases adopting response surface methodology. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, J.; Kannuchamy, N.; Kannaiyan, S.; Chakraborti, R.; Gudipati, V. Protein Hydrolysates from Shrimp (Metapenaeus dobsoni) Head Waste: Optimization of Extraction Conditions by Response Surface Methodology. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2015, 24, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaibani, M.E.; Heidari, B.; Khodabandeh, S.; Shahangian, S.; Mirdamadi, S.; Mirzaei, M. Antioxidant and antibacterial properties of protein hydrolysate from rocky shore crab, Grapsus albolineathus, as affected by progress of hydrolysis. Int. J. Aquat. Biol. 2020, 8, 184–193. [Google Scholar]
- Ovissipour, M.; Abedian, A.; Motamedzadegan, A.; Rasco, B.; Safari, R.; Shahiri, H. The effect of enzymatic hydrolysis time and temperature on the properties of protein hydrolysates from Persian sturgeon (Acipenser persicus) viscera. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Sillero, J.; Ramos, P.; Monserrat, J.M.; Prentice, C. Evaluation of the Antioxidant Activity In Vitro and in Hippocampal HT-22 Cells System of Protein Hydrolysates of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) By-Product. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2017, 27, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Nayak, Y.; Dash, S. Fish protein hydrolysate production, treatment methods and current potential uses: A review. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2021, 9, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorres, J.M.; Rios, D.G.; Saggiomo, G.; Wasielesky, W.; Prentice-Hernandez, C. Functional and antioxidant properties of protein hydrolysates obtained from white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordbar, S.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Zarei, M.; Hamid, A.A.; Saari, N. Alcalase-generated proteolysates of stone fish (Actinopyga lecanora) flesh as a new source of antioxidant peptides. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 1541–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Hu, S.; Li, S.; Liu, Y. Biochemical and antioxidant properties of peptidic fraction generated from crab (Portunus trituberculatus) shells by enzymatic hydrolysis. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 2479–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Yoon, N.Y.; Shim, K.B.; Lim, C.W. Antioxidant and angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activities of northern shrimp (Pandalus borealis) by-products hydrolysate by enzymatic hydrolysis. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 19, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aklakur, M. Natural antioxidants from sea: A potential industrial perspective in aquafeed formulation. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bernardini, R.; Harnedy, P.; Bolton, D.; Kerry, J.; O’Neill, E.; Mullen, A.M.; Hayes, M. Antioxidant and antimicrobial peptidic hydrolysates from muscle protein sources and by-products. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoo, M.; Regenstein, J.M.; Yasemi, M. Protein Hydrolysates from Fishery Processing By-Products: Production, Characteristics, Food Applications, and Challenges. Foods 2023, 12, 4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoo, M.; Benjakul, S.; Yasemi, M.; Ahmadi Gavlighi, H.; Xu, X. Hydrolysates from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) processing by-product with different pretreatments: Antioxidant activity and their effect on lipid and protein oxidation of raw fish emulsion. LWT 2019, 108, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaich, K.M.; Tian, X.; Xie, J. Reprint of “Hurdles and pitfalls in measuring antioxidant efficacy: A critical evaluation of ABTS, DPPH, and ORAC assays”. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 782–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Montaño, E.; Sarmiento-Machado, R.M.; Osuna-Ruíz, I.; Benítez-García, I.; Pacheco-Aguilar, R.; Navarro-Peraza, R.S.; Sánchez, M.E.L.; Ortiz, A.V.; Báez, L.J.G.; Bañuelos-Vargas, I.; et al. Effect of Degree of Hydrolysis on Biochemical Properties and Biological Activities (Antioxidant and Antihypertensive) of Protein Hydrolysates from Pacific Thread Herring (Ophistonema libertate) Stickwater. Waste Biomass Valorization 2022, 13, 1015–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Sillero, J.; Gharsallaoui, A.; Prentice, C. Peptides from Fish By-product Protein Hydrolysates and Its Functional Properties: An Overview. Mar. Biotechnol. 2018, 20, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerard, F.; Sumaya-Martinez, M.T.; Laroque, D.; Chabeaud, A.; Dufossé, L. Optimization of free radical scavenging activity by response surface methodology in the hydrolysis of shrimp processing discards. Process Biochem. 2007, 42, 1486–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnedy, P.A.; FitzGerald, R.J. Bioactive peptides from marine processing waste and shellfish: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, N.Y.; Shim, K.B.; Lim, C.W.; Kim, S.B. Antioxidant and angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory activities of red snow crab Chionoecetes japonicas shell hydrolysate by enzymatic hydrolysis. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 16, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, F.; Ng, W.; Ooi, A.; Lem, F.; Chai, T. Carp-Derived Antioxidant Peptides and Hydrolysates: Biological Effects and Potential Applications in Health and Food. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.L.; Gao, M.; Wang, Y.Z.; Li, X.R.; Wang, P.; Wang, B. Antioxidant Peptides From Protein Hydrolysate of Marine Red Algae Eucheuma cottonii: Preparation, Identification, and Cytoprotective Mechanisms on H2O2 Oxidative Damaged HUVECs. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 791248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Chi, C.F. Marine Bioactive Peptides—Structure, Function, and Application 2.0. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Yang, F.; Liu, G.; Dong, X.; Chen, G.; Cao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S.; et al. Three novel antioxidant peptides isolated from C-phycocyanin against H2O2-induced oxidative stress in zebrafish via Nrf2 signaling pathway. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1098091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, Z.; Yang, G.; Zhang, D.; Qin, H.; Xia, B.; Liu, S.; Chen, J. Supplementation of Enzymatic Hydrolysate in Low-Fishmeal and Low-Crop Diet Improves Growth, Antioxidant Capacity, and Immunity of Juvenile Sea Cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka). Fishes 2025, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| % | |
|---|---|
| Yield meat | 21.87 ± 2.38 |
| Waste | 72.45 ± 4.08 |
| Components | % |
|---|---|
| Ash | 35.38 ± 0.30 |
| Total Lipid | 2.57 ± 0.09 |
| Protein | 31.21 ± 1.12 |
| Chitin | 10.57 ± 0.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arena, R.; Manuguerra, S.; Gonzalez, M.M.; Petrosillo, E.; Lanzoni, D.; Poulain, C.; Debeaufort, F.; Giromini, C.; Francesca, N.; Messina, C.M.; et al. Valorization of Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus) By-Products into Antioxidant Protein Hydrolysates for Nutraceutical Applications. Animals 2025, 15, 2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202952
Arena R, Manuguerra S, Gonzalez MM, Petrosillo E, Lanzoni D, Poulain C, Debeaufort F, Giromini C, Francesca N, Messina CM, et al. Valorization of Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus) By-Products into Antioxidant Protein Hydrolysates for Nutraceutical Applications. Animals. 2025; 15(20):2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202952
Chicago/Turabian StyleArena, Rosaria, Simona Manuguerra, Michelle Marchan Gonzalez, Elena Petrosillo, Davide Lanzoni, Clément Poulain, Frédéric Debeaufort, Carlotta Giromini, Nicola Francesca, Concetta Maria Messina, and et al. 2025. "Valorization of Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus) By-Products into Antioxidant Protein Hydrolysates for Nutraceutical Applications" Animals 15, no. 20: 2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202952
APA StyleArena, R., Manuguerra, S., Gonzalez, M. M., Petrosillo, E., Lanzoni, D., Poulain, C., Debeaufort, F., Giromini, C., Francesca, N., Messina, C. M., & Santulli, A. (2025). Valorization of Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus) By-Products into Antioxidant Protein Hydrolysates for Nutraceutical Applications. Animals, 15(20), 2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202952







