Morphological and Molecular Identification of Sarcocystis arctica in Captive Cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus) in China Helps Clarify Phylogenetic Relationships with Sarcocystis caninum and Sarcocystis felis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Sampling and Morphological Examination of Sarcocysts from Cheetahs
2.2. DNA Isolation, PCR Amplification, Cloning, and Sequence Analysis
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Characteristics of Sarcocysts in Cheetahs
3.2. Intraspecific and Interspecific Sequence Similarities of the Sarcocystis sp. from Cheetahs
3.3. Phylogenetic Trees
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 18S rRNA | 18S ribosomal RNA |
| 28S rRNA | 28S ribosomal RNA |
| ITS-1 | Internal transcribed spacer 1 |
| cox1 | Cytochrome oxidase subunit 1 |
| LM | Light microscopy |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| Vp | Villous protrusions |
| Edl | Electron-dense layer |
| Gsl | Ground substance layer |
References
- Dubey, J.P.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Speer, C.A.; Fayer, R. Sarcocystosis of Animals and Humans, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 52–59+269–280+309–315. [Google Scholar]
- Broomhall, L.S.; Mills, M.G.L.; du Toit, J.T. Home range and habit use by cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus) in the Kruger National Park. J. Zool. Lond. 2003, 261, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, M.B.; Leathers, C.W.; Foreyt, W.J. Sarcocystis felis in captive cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus). J. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 1993, 60, 277–279. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, J.P.; Hamir, A.N.; Kirkpatrick, C.E.; Todd, K.S.; Rupprecht, C.E. Sarcocystis felis sp. n. (Protozoa: Sarcocystidae) from the bobcat (Felis rufus). J. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 1992, 59, 227–229. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, J.P.; Bwangamoi, O. Sarcocystis felis (Protozoa: Sarcocystidae) from the African lion (Panthera leo). J. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 1994, 61, 113–114. [Google Scholar]
- Gjerde, B.; Schulze, J. Muscular sarcocystosis in two arctic foxes (Vulpes lagopus) due to Sarcocystis arctica n. sp.: Sarcocyst morphology, molecular characteristics and phylogeny. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Thompson, P.C.; Verma, S.K.; Mowery, J.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Antunes Murata, F.H.; Sinnett, D.R.; Van Hemert, C.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Dubey, J.P. Morphological and molecular characterization of Sarcocystis arctica-like sarcocysts from the Arctic fox (Vulpes lagopus) from Alaska, USA. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Sykes, J.E.; Shelton, G.D.; Sharp, N.; Verma, S.K.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Viviano, J.; Sundar, N.; Khan, A.; Grigg, M.E. Sarcocystis caninum and Sarcocystis svanai n. spp. (Apicomplexa: Sarcocystidae) associated with severe myositis and hepatitis in the domestic dog (Canis familiaris). J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2015, 62, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjerde, B.; Josefsen, T.D. Molecular characterization of Sarcocystis lutrae n. sp. and Toxoplasma gondii from the musculature of two Eurasian otters (Lutra lutra) in Norway. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Liang, Y.; Hu, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y. First isolation of Sarcocystis caninum sarcocysts from two domestic dogs (Canis familiaris) from China. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3613–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duszynski, D.W.; Kvičerová, J.; Seville, R.S. The Biology and Identification of the Coccidia (Apicomplexa) of Carnivores of the World; Academic Press: London, UK, 2018; pp. 235–270. [Google Scholar]
- Gjerde, B. Phylogenetic relationships among Sarcocystis species in cervids, cattle and sheep inferred from the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I gene. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäkel, T.; Raisch, L.; Richter, S.; Wirth, M.; Birenbaum, D.; Ginting, S.; Khoprasert, Y.; Mackenstedt, U.; Wassermann, M. Morphological and molecular phylogenetic characterization of Sarcocystis kani sp. nov. and other novel, closely related Sarcocystis spp. infecting small mammals and colubrid snakes in Asia. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2023, 22, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañón-Franco, W.A.; López-Orozco, N.; Christoff, A.U.; de Castilho, C.S.; de Araújo, F.A.; Verma, S.K.; Dubey, J.P.; Soares, R.M.; Gennari, S.M. Molecular and morphologic characterization of Sarcocystis felis (Apicomplexa: Sarcocystidae) in South American wild felids from Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 217, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Pérez, P.; Wibbelt, G.; Brinkmann, A.; Puentes, J.A.G.; Tuh, F.Y.; Lakim, M.B.; Nitsche, A.; Wells, K.; Jäkel, T. Description of Sarcocystis scandentiborneensis sp. nov. from treeshrews (Tupaia minor, T. tana) in northern Borneo with annotations on the utility of COI and 18S rDNA sequences for species delineation. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2020, 12, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juozaitytė-Ngugu, E.; Švažas, S.; Šneideris, D.; Rudaitytė-Lukošienė, E.; Butkauskas, D.; Prakas, P. The role of birds of the family Corvidae in transmitting Sarcocystis protozoan parasites. Animals 2021, 11, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Máca, O.; González-Solís, D. Role of three bird species in the life cycle of two Sarcocystis spp. (Apicomplexa, Sarcocystidae) in the Czech Republic. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2022, 17, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, N.; Ren, H.; Yang, L.; Mao, G.; Li, J.; Su, C.; Yang, Y. Direct evidence of cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus) as intermediate host of Toxoplasma gondii through isolation of viable strains. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.L.; Ye, Y.L.; Wen, T.; Huang, Z.M.; Pan, J.; Hu, J.J.; Tao, J.P.; Song, J.L. Prevalence and morphological and molecular characteristics of Sarcocystis bertrami in horses in China. Parasite 2020, 27, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barta, J.R.; Martin, D.S.; Liberator, P.A.; Dashkevicz, M.; Anderson, J.W.; Feighner, S.D.; Elbrecht, A.; Perkins-Barrow, A.; Jenkins, M.C.; Danforth, H.D.; et al. Phylogenetic relationships among eight Eimeria species infecting domestic fowl inferred using complete small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. J. Parasitol. 1997, 83, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.; Odening, K. Characterization of bovine Sarcocystis species by analysis of their 18S ribosomal DNA sequences. J. Parasitol. 1998, 84, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenger, C.K.; Granstrom, D.E.; Langemeier, J.L.; Stamper, S.; Donahue, J.M.; Patterson, J.S.; Gajadhar, A.A.; Marteniuk, J.V.; Xiaomin, Z.; Dubey, J.P. Identification of opossums (Didelphis virginiana) as the putative definitive host of Sarcocystis neurona. J. Parasitol. 1995, 81, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugridge, N.B.; Morrison, D.A.; Johnson, A.M.; Luton, K.; Dubey, J.P.; Votýpka, J.; Tenter, A.M. Phylogenetic relationships of the genus Frenkelia: A review of its history and new knowledge gained from comparison of large subunit ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene sequences. Int. J. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 957–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanhauser, S.M.; Yowell, C.A.; Cutler, T.J.; Greiner, E.C.; MacKay, R.J.; Dame, J.B. Multiple DNA markers differentiate Sarcocystis neurona and Sarcocystis falcatula. J. Parasitol. 1999, 85, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjerde, B. Sarcocystis species in red deer revisited: With a re-description of two known species as Sarcocystis elongata n. sp. and Sarcocystis truncata n. sp. based on mitochondrial cox1 sequences. Parasitology 2014, 141, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Tommaso, P.; Moretti, S.; Xenarios, I.; Orobitg, M.; Montanyola, A.; Chang, J.M.; Taly, J.F.; Notredame, C. T-Coffee: A web server for the multiple sequence alignment of protein and RNA sequences using structural information and homology extension. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W13–W17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calero-Bernal, R.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Verma, S.K.; Mowery, J.; Carmena, D.; Beckmen, K.; Dubey, J.P. Sarcocystis arctica (Apicomplexa: Sarcocystidae): Ultrastructural description and its new host record, the Alaskan wolf (Canis lupus). Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 2893–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillis, K.D.; MacKay, R.J.; Yowell, C.A.; Levy, J.K.; Greiner, E.C.; Dame, J.B.; Cheadle, M.A.; Hernandez, J.; Massey, E.T. Naturally occurring Sarcocystis infection in domestic cats (Felis catus). Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsheikha, H.M.; Kennedy, F.A.; Murphy, A.J.; Soliman, M.; Mansfield, L.S. Sarcocystosis of Sarcocystis felis in cats. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2006, 36, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Greiner, E.C.; Roelke, M.E.; Atkinson, C.T.; Dubey, J.P.; Wright, S.D. Sarcocystis sp. in muscles of free-ranging Florida panthers and cougars (Felis concolor). J. Wildl. Dis. 1989, 25, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsel, M.J.; Briggs, M.B.; Venzke, K.; Forge, O.; Murnane, R.D. Gastric spiral bacteria and intramuscular sarcocysts in African lions from Namibia. J. Wildl. Dis. 1998, 34, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlásek, I.; Máca, O. Morphological and molecular identification of Sarcocystis arctica sarcocysts in three red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from the Czech Republic. Parasitol. Int. 2017, 66, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillova, V.; Prakas, P.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Gavarāne, I.; Fernández-García, J.L.; Martínez-González, M.; Rudaitytė-Lukošienė, E.; Martínez-Estéllez, M.Á.H.; Butkauskas, D.; Kirjušina, M. Identification and genetic characterization of Sarcocystis arctica and Sarcocystis lutrae in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from Baltic States and Spain. Parasit. Vectors. 2018, 11, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenter, A.M.; Baverstock, P.R.; Johnson, A.M. Phylogenetic relationships of Sarcocystis species from sheep, goats, cattle and mice based on ribosomal RNA sequences. Int. J. Parasitol. 1992, 22, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.J.; Liu, T.T.; Liu, Q.; Esch, G.W.; Chen, J.Q.; Huang, S.; Wen, T. Prevalence, morphology, and molecular characteristics of Sarcocystis spp. in domestic goats (Capra hircus) from Kunming, China. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 3973–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Ortega-Perez, P.; Wibbelt, G.; Lakim, M.B.; Ginting, S.; Khoprasert, Y.; Wells, K.; Hu, J.; Jäkel, T. A cyst-forming coccidian with large geographical range infecting forest and commensal rodents: Sarcocystis muricoelognathis sp. nov. Parasites Vectors 2024, 17, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakas, P.; Liaugaudaitė, S.; Kutkienė, L.; Sruoga, A.; Švažas, S. Molecular identification of Sarcocystis rileyi sporocysts in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) and raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in Lithuania. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 1671–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakas, P.; Bea, A.; Juozaitytė-Ngugu, E.; Olano, I.; Villanúa, D.; Švažas, S.; Butkauskas, D. Molecular identification of Sarcocystis halieti in the muscles of two species of birds of prey from Spain. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.F.; Wellehan, J.F., Jr.; Weisman, J.L.; Rush, M.; Childress, A.L.; Lindsay, D.S. Massive muscular infection by a Sarcocystis species in a South American rattlesnake (Crotalus durissus terrificus). J. Parasitol. 2015, 101, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roemer, G.W.; Donlan, C.J.; Courchamp, F. Golden eagles, feral pigs, and insular carnivores: How exotic species turn native predators into prey. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Gil, A.; Carral, J.M.; Barrientos, L.M.; García, L.; Benito, L.; de Gabriel Hernando, M. Observations of golden eagles attacking and consuming wolf pups. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2024, 70, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, R.S.; Davis, A.G.; Buij, R.; Cox, J.J.; Kapila, S.; Parmuntoro, L.; Thomsett, S.; Virani, M.Z.; Njoroge, P.; van Langevelde, F. Africa’s overlooked top predator: Towards a better understanding of martial eagle feeding ecology in the Maasai Mara, Kenya. Wildl. Biol. 2024, 2024, e01223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyly, M.S.; Villers, A.; Koivisto, E.; Helle, P.; Ollila, T.; Korpimäki, E. Avian top predator and the landscape of fear: Responses of mammalian mesopredators to risk imposed by the golden eagle. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Máca, O.; González-Solís, D. White-tailed eagle (Haliaeetus albicilla) as the definitive host of Sarcocystis lutrae in the Czech Republic. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 981829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard, B.; Carbyn, L.N.; Smith, D.W. Wolf interactions with non-prey. In Wolves: Behavior, Ecology, and Conservation; Mech, L.D., Boitani, L., Eds.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA; London, UK, 2003; pp. 259–271. [Google Scholar]
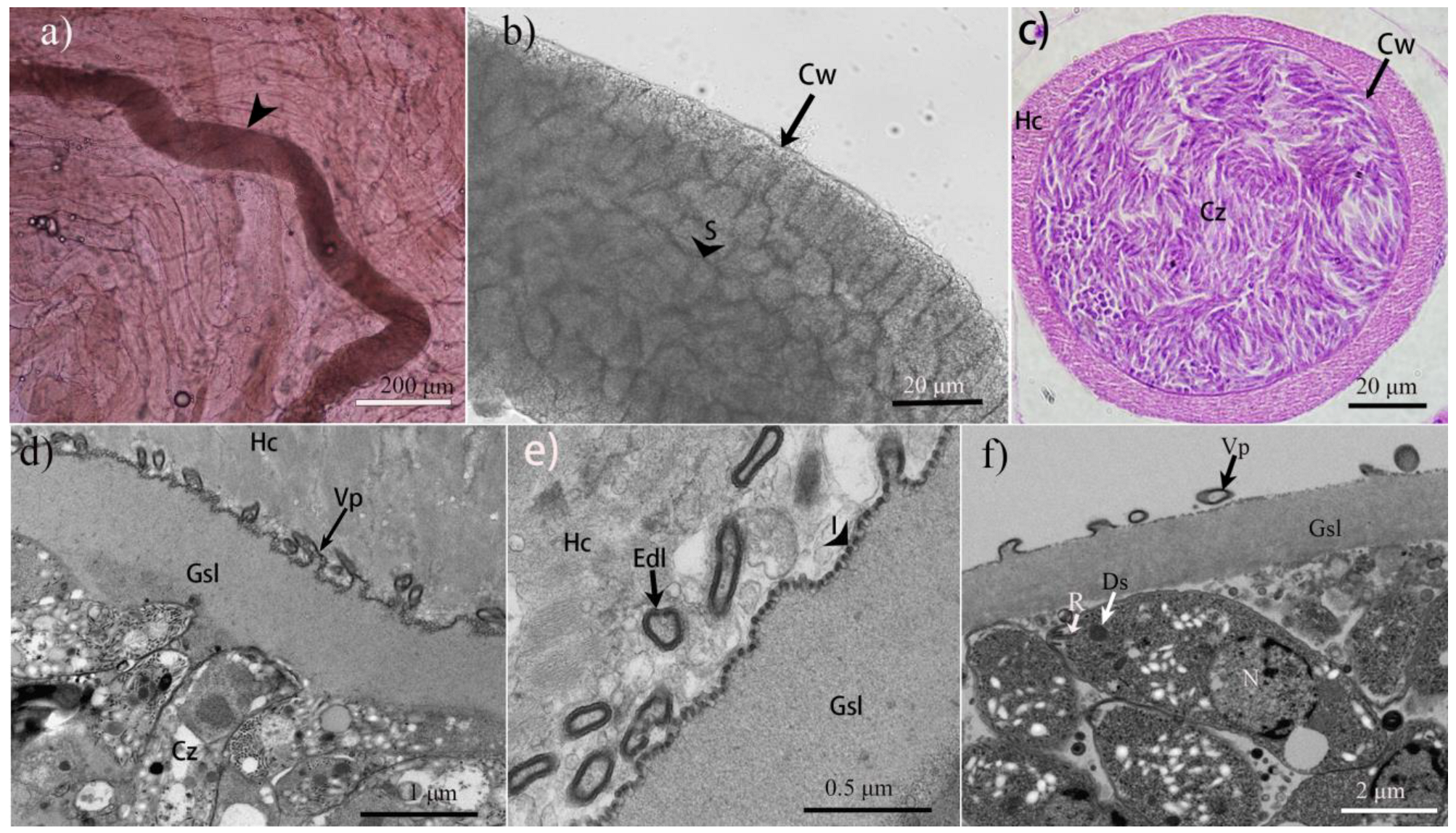
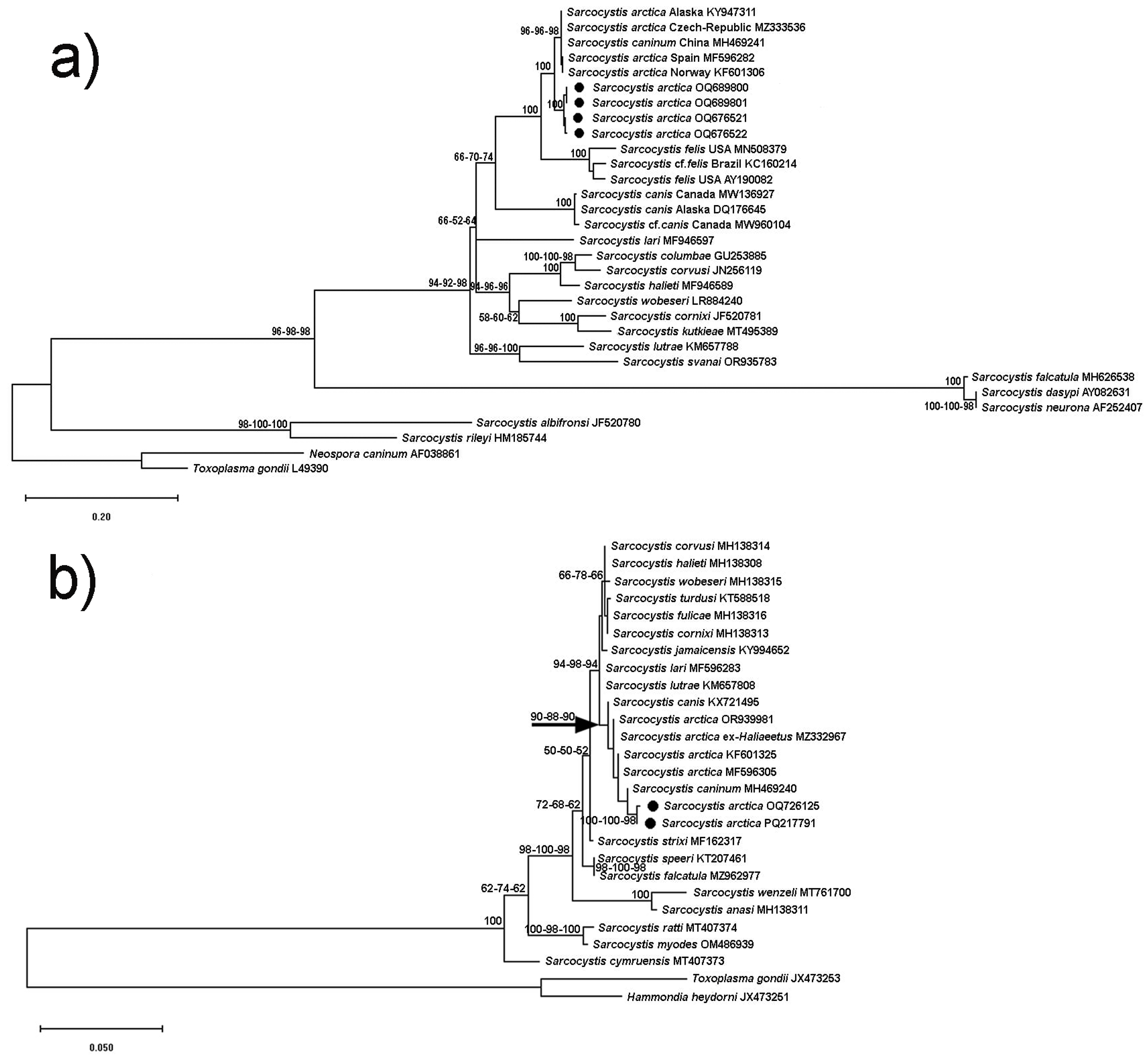
| Morphological Trait | Sarcocystis ex, Cheetah, China * | S. arctica * | S. caninum | S. felis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sarcocyst wall type | 9c | 9c | 9c | 9c |
| Appearance of Vp | Pleomorphic Vp, wavy wall, no microtubules | Pleomorphic Vp, no microtubules, some anastomosing | Elongated Vp, wavy wall, no microtubules | Hobnail-like bumps and Vp, no microtubules |
| Size of Vp in μm | 1.7 × 0.5 | 1.5 × 0.5 | 1.0 × 0.8 | 0.6–1.2 × 0.3–0.4 |
| Sarcocyst size | 0.5–2.7 mm long, 120–180 μm wide | Up to 12 mm long, 250 μm wide | Up to 1.2 mm long, 75 μm wide | 2.1 mm long, 150 μm wide |
| Sarcocyst wall, thickness in μm (Gsl + Vp) | 1.4–2.1 | Up to 3.5 | Up to 2.0 | 1.0–1.5 |
| Cystozoites *, size in μm (length × width) | 7.1–11.0 [av. 9.1] × 1.7–3.6 [av. 2.7] | Ex Canis lupus, 9.4–9.8 [av. 9.5] × 1.3–1.6 [av. 1.5]; ex Vulpes lagopus, 6.9–9.5 × 1.4–2.7 | 7.5–9.0 long | 7.0–10.0 × 1.5 |
| DNA Regions | Accession Numbers (Length, bp) | Identity with Sequences Previously Deposited in GenBank | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sarcocystis sp. (Accession Numbers) | % Query Coverage | % Identity (Average) | ||
| 18S rRNA | OQ689797–OQ689799 (1803–1804) | S. caninum (MH469238, MH469239, KM362427) | 92–100 | 99.9–100 (99.8) |
| S. arctica (MZ329343, KX022100–KX022102, MF59623717–MF596237, KF601301) | 92–100 | 99.8–100 (99.9) | ||
| S. svanai (KM362428) | 92 | 99.4–99.5 (99.5) | ||
| S. columbae (GU253883) | 90 | 99.4 | ||
| S. felis (AY190080, AY576489) | 20–39 | 99.2–99.4 (99.3) | ||
| S. canis from Ursus americanus and Zalophus californianus (OR654898, OR339987) | 88 | 99.1 | ||
| 28S rRNA | OR436907–OR436910 (3285–3287) | S. caninum (MH469239) | 100 | 99.5 |
| S. arctica (KY947309, MF596240–MF596260, KX22104–KX22107, KY609323, KY947308) | 44–45 | 99.3–99.5 (99.4) | ||
| S. (Frenkelia) glareoli (AF044251) | 100 | 98.3 | ||
| ITS-1 | OQ689800, OQ689801, OQ676521, OQ676522 (948–949) | S. caninum (MH469241, JX993923) | 100 | 95.9–97.5 (96.7) |
| S. arctica (MZ333536, KY947311, KF601306, KX022108–KX022111, KF601308, KY947310, OK481372–OK481376, KX156837, MF596262–MF596282) | 49–92 | 96.3–97.3 (96.3) | ||
| S. felis from domestic cats (AY190081, AY190082, MN508375–MN508379) | 35–79 | 87.8–88.9 (88.3) | ||
| S. felis from wild felids (KC160213, KC160214) | 48–72 | 87.5–88.5 (88.0) | ||
| S. canis from Ursus spp. (DQ176645, MW960104) | 83–86 | 89.6–89.8 (89.7) | ||
| S. svanai (OR935783) | 58 | 78.4 | ||
| S. lari (MF946597, MN450357) | 49–97 | 76.1–88.3 | ||
| S. lutrae (KM657788, KM657805) | 86 | 84.9 | ||
| cox1 | OQ726125, PQ217791 (1085) | S. caninum (MH469240) | 100 | 99.6 |
| S. arctica (KX022112–KX022115, KY947304, KY947305, KY609324, MF596286–MF596306, KF601318–KF601321, MZ332967) | 85–96 | 99.2–99.7 (99.5) | ||
| S. lari (MF596283, MF946584) | 96 | 99.1 | ||
| S. lutrae (KM657808) | 97 | 98.8 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, Z.; Zhu, N.; Yang, Y.; Deng, S.; Jäkel, T.; Hu, J. Morphological and Molecular Identification of Sarcocystis arctica in Captive Cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus) in China Helps Clarify Phylogenetic Relationships with Sarcocystis caninum and Sarcocystis felis. Animals 2025, 15, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15020180
Liao Z, Zhu N, Yang Y, Deng S, Jäkel T, Hu J. Morphological and Molecular Identification of Sarcocystis arctica in Captive Cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus) in China Helps Clarify Phylogenetic Relationships with Sarcocystis caninum and Sarcocystis felis. Animals. 2025; 15(2):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15020180
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Zhe, Niuping Zhu, Yurong Yang, Shuangsheng Deng, Thomas Jäkel, and Junjie Hu. 2025. "Morphological and Molecular Identification of Sarcocystis arctica in Captive Cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus) in China Helps Clarify Phylogenetic Relationships with Sarcocystis caninum and Sarcocystis felis" Animals 15, no. 2: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15020180
APA StyleLiao, Z., Zhu, N., Yang, Y., Deng, S., Jäkel, T., & Hu, J. (2025). Morphological and Molecular Identification of Sarcocystis arctica in Captive Cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus) in China Helps Clarify Phylogenetic Relationships with Sarcocystis caninum and Sarcocystis felis. Animals, 15(2), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15020180








