Unusual Epidemic of Tyzzer’s Disease in Commercial Rabbit Breeders: Clinical, Pathological, and Therapeutic Observations
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case History and Clinical Findings
2.2. Post Mortem Examination
2.3. Microbiological and Parasitological Examinations
2.4. Histopathology and Histochemistry
2.5. Therapy
3. Results
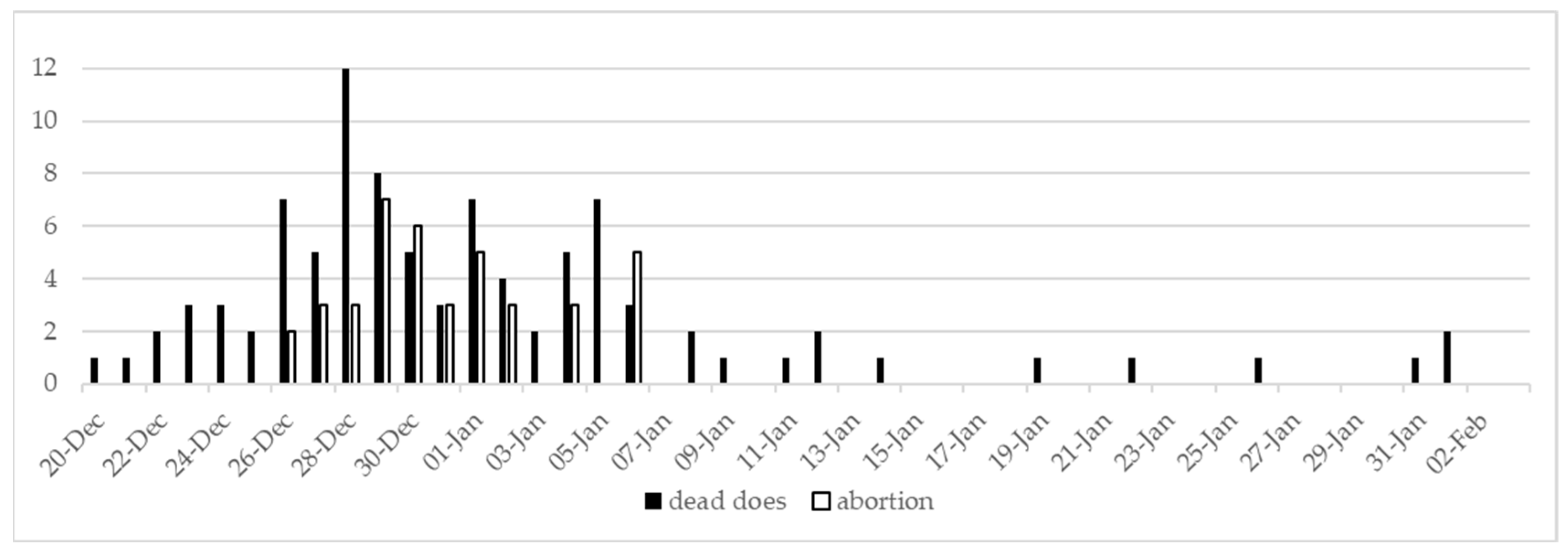
3.1. Case History and Clinical Findings
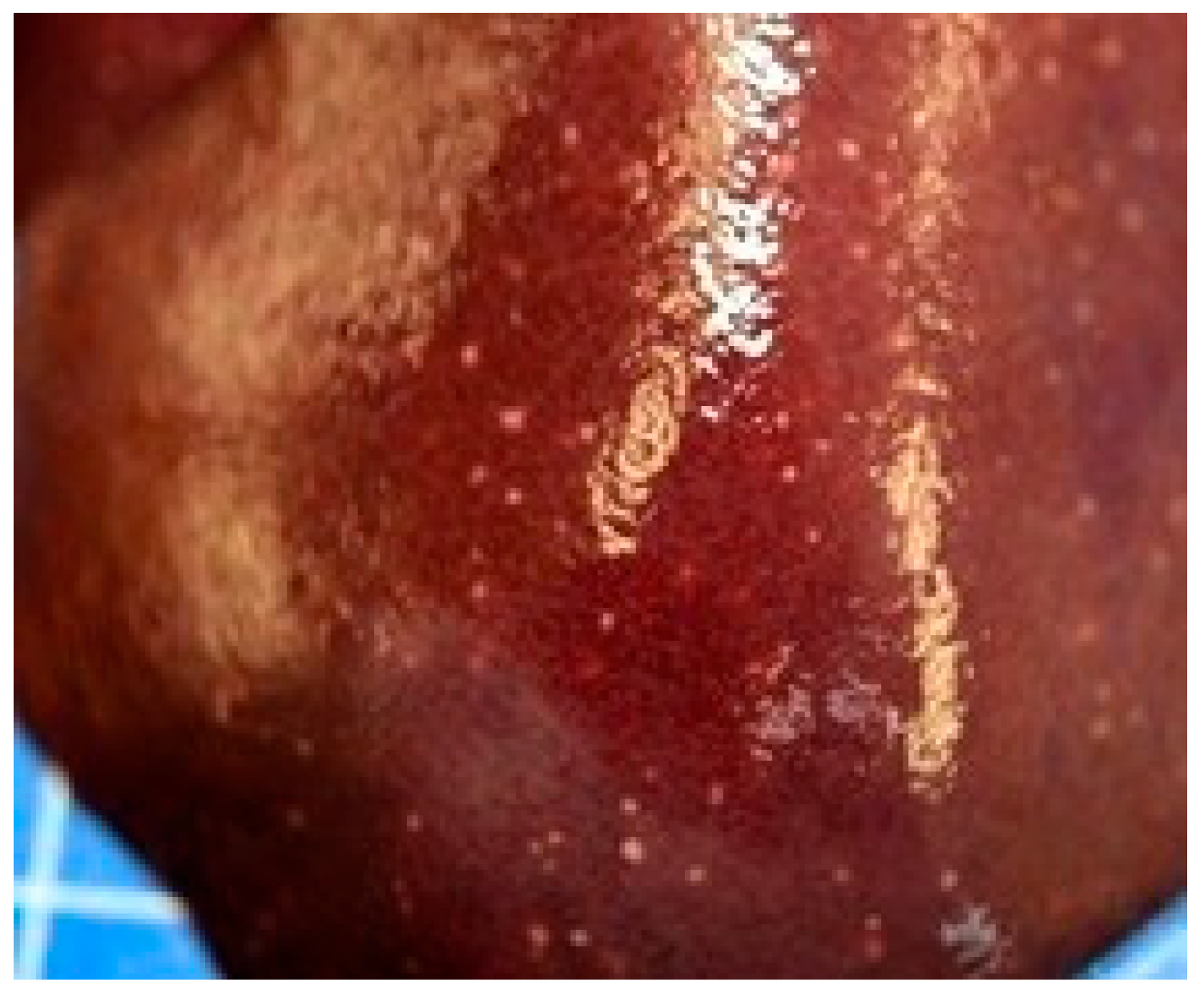
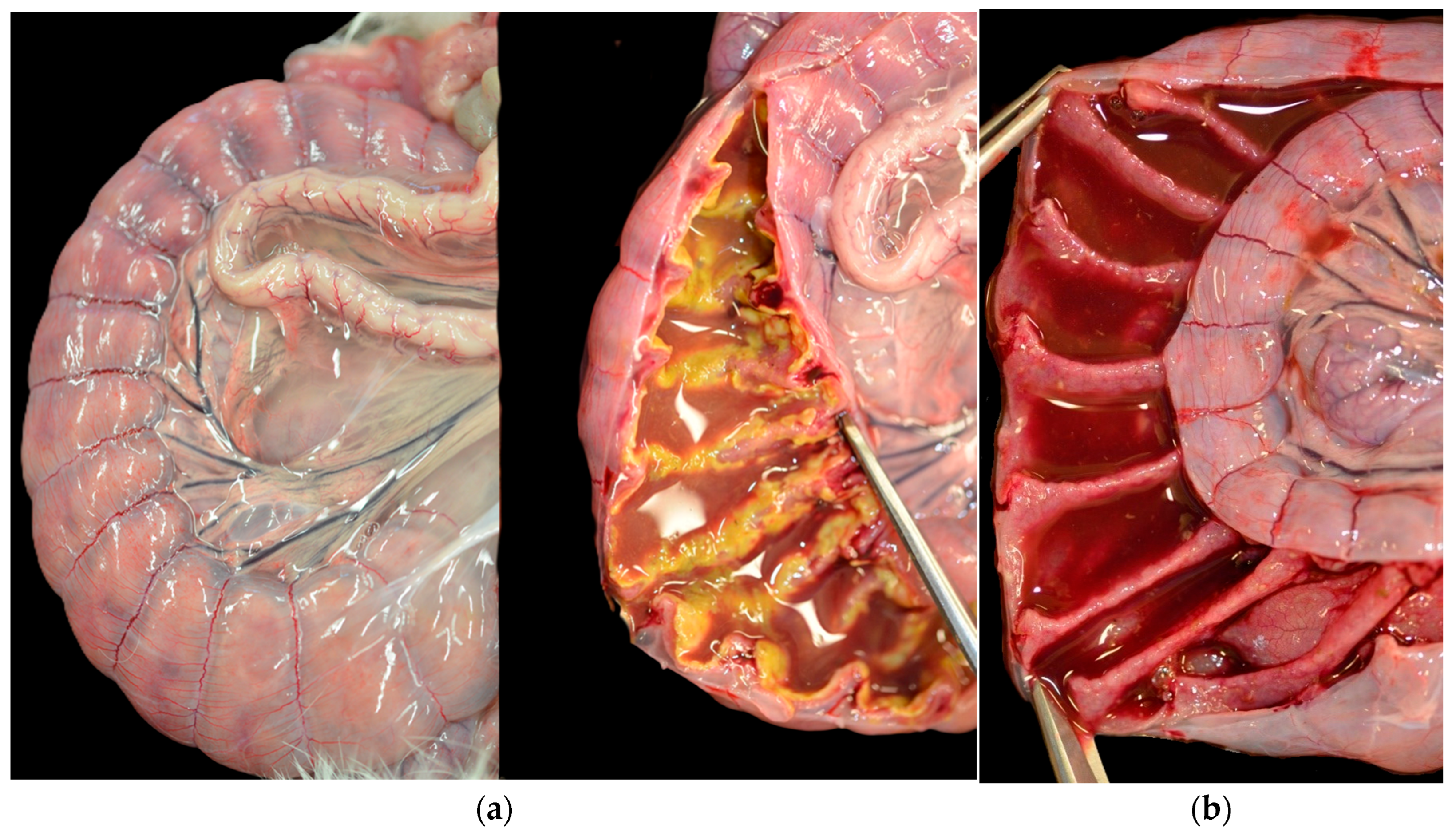
3.2. Post-Mortem Examination
3.3. Microbiological and Parasitological Examination
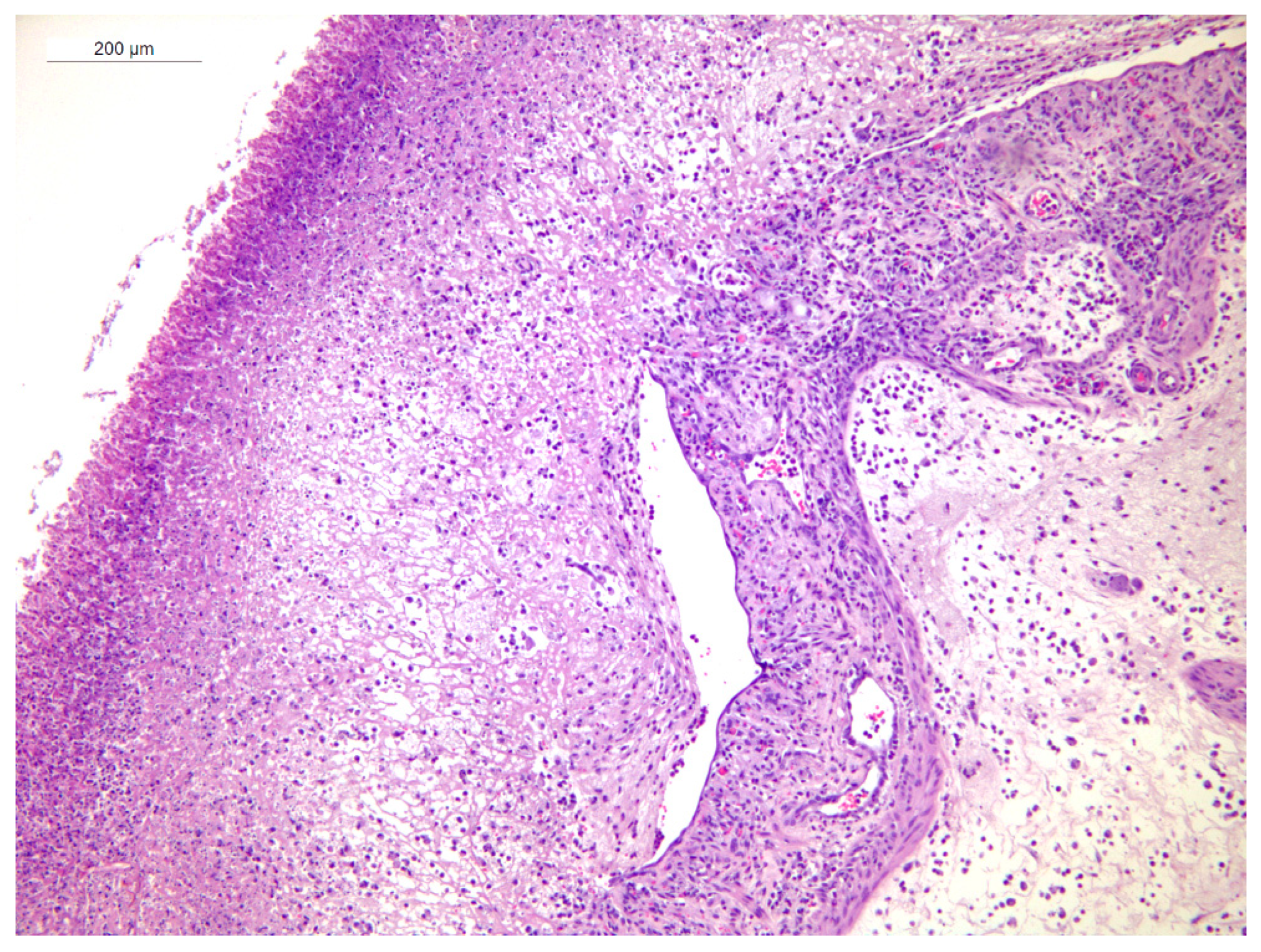
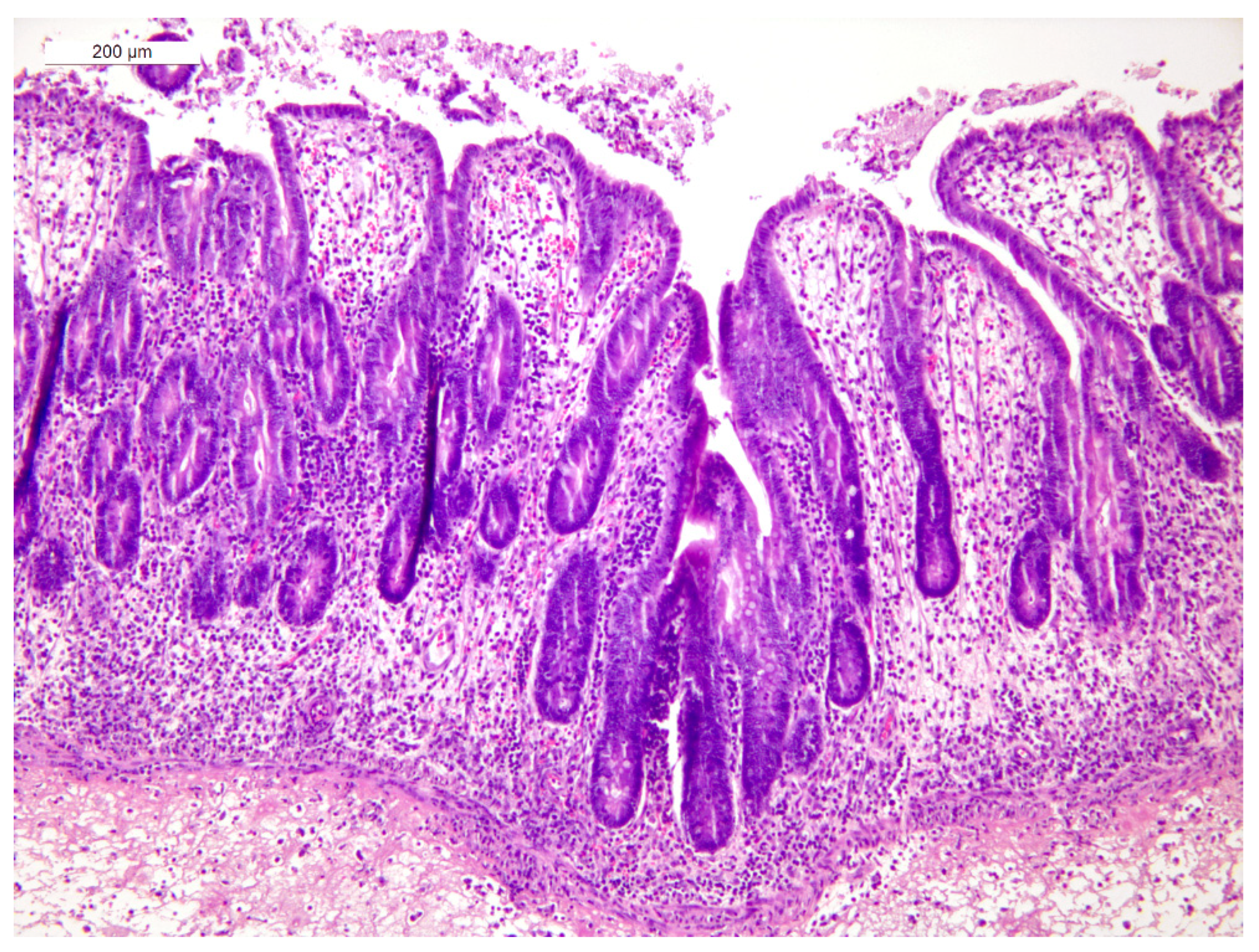
3.4. Histopathology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tyzzer, E.E. A fatal disease of the Japanese Waltzing Mouse caused by a spore-bearing Bacillus (Bacillus piliformis, N. SP.). J. Med. Res. 1917, 37, 307–338.5. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duncan, A.J.; Carman, R.J.; Olsen, G.J.; Wilson, K.H. Assignment of the Agent of Tyzzer’s Disease to Clostridium piliforme comb. nov. on the Basis of 16S rRNA Sequence Analysis. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1993, 43, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percy, D.H.; Barthold, S.W. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits, 3rd ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Ames, IA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Swerczek, T.W. Multi-focal hepatic necrosis and hepatitis in foals caused by Bacillus piliformis (Tyzzer’s disease). Vet. Annu. 1976, 17, 130–132. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, A.M.; Ganaway, J.R.; Moore, T.D.; Kinard, R.F. Tyzzer’s Disease Syndrome in Laboratory Rabbits. Am. J. Pathol. 1965, 46, 859–882. [Google Scholar]
- Ganaway, J.R.; Allen, A.M.; Moore, T.D. Tyzzer’s disease. Am. J. Pathol. 1971, 64, 717–730. [Google Scholar]
- Peeters, J.E.; Charlier, G.; Halen, P.; Geeroms, R.; Raeymaekers, R. Naturally-occurring Tyzzer’s disease (Bacillus piliformis infection) in commercial rabbit: A clinical and pathological study. Ann. De Rech. Vétérinaires 1985, 16, 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, M. Textbook of Rabbit Medicine, 2nd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann/Elsevier: Edinburgh, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Camguilhem, R.; Milon, A. Biotypes and O serogroups of Escherichia coli involved in intestinal infections of weaned rabbits: Clues to diagnosis of pathogenic strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, S.H.; Kiavand, A.; Seidelin, M.; Reiske, H.R. Ribosomal RNA Sequences of Clostridium piliforme Isolated from Rodent and Rabbit: Re-examining the Phylogeny of the Tyzzer’s Disease Agent and Development of a Diagnostic Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2006, 45, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ho, M.S.; Barr, B.C.; Marsh, A.E.; Anderson, M.L.; Rowe, J.D.; Tarantal, A.F.; Hendrickx, A.G.; Sverlow, K.; Dubey, J.P.; Conrad, P.A. Identification of bovine Neospora parasites by PCR amplification and specific small-subunit rRNA sequence probe hybridization. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehricht, R.; Slickers, P.; Goellner, S.; Hotzel, H.; Sachse, K. Optimized DNA microarray assay allows detection and genotyping of single PCR-amplifiable target copies. Mol. Cell. Probes 2006, 20, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, L.S.; Brewer, T.C.; Bruckner, D.A. Fluorescence detection of Cryptosporidium oocysts in human fecal specimens by using monoclonal antibodies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1987, 25, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, V.R.; Adney, D.R.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Gordy, P.W.; Felix, T.A.; Olea-Popelka, F.J.; Bowen, R.A. Pathogenesis and immune responses of Francisella tularensis strians in wild-caught cottontail rabbits (Sylvilagus spp.). J. Wildl. Dis. 2015, 51, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, D.W. Generalized lymphosarcoma in a juvenile rabbit. A case report. Cornell Vet. 1970, 60, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Cutlip, R.C.; Amtower, W.C.; Beall, C.W.; Matthews, P.J. An epizootic of Tyzzer’s disease in rabbits. Comp. Med. 1971, 21, 356–361. [Google Scholar]
- Carman, R.J.; Borriello, S.P. Infectious nature of Clostridium spiroforme-mediated rabbit enterotoxaemia. Vet. Microbiol. 1984, 9, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehg, J.E.; Lu, Y. Clostridium difficile Colitis in a Rabbit Following Antibiotic Therapy for Pasteurellosis. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1981, 179, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keel, M.K.; Songer, J.G. The Comparative Pathology of Clostridium difficile-associated Disease. Vet. Pathol. 2006, 43, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drigo, I.; Mazzolini, E.; Bacchin, C.; Tonon, E.; Puiatti, C.; Bano, L.; Spigaglia, P.; Barbanti, F.; Agnoletti, F. Molecular characterization and antimicrobial susceptibility of Clostridium difficile isolated from rabbits raised for meat production. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 181, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantey, J.R.; Blake, R.K. Diarrhea Due to Escherichia coli in the Rabbit: A Novel Mechanism. J. Infect. Dis. 1977, 135, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, J.E.; Geeroms, R.; Glorieux, B. Experimental Escherichia coli enteropathy in weanling rabbits: Clinical manifestations and pathological findings. J. Comp. Pathol. 1984, 94, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, I.C.; Ribeiro-Almeida, M.; Silveira, L.; Prata, J.C.; de Carvalho, A.P.; Roque, C.; Gomes, J.P.; Borges, V.; Pista, Â.; Martins da Costa, P. Unveiling a Listeria monocytogenes Outbreak in a Rabbit Farm: Clinical Manifestation, Antimicrobial Resistance, Genomic Insights and Environmental Investigation. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Laboratory Examination | Sample | Method | Doe 1 | Doe 2 | Doe 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteriological examination | Intestinal content | Standard culture | E. coli B19 C. perfringens | Citrobacter sediakii C. perfringens | E. coli B31 C. perfringens |
| Liver | Negative | Negative | Negative | ||
| Parasitological examination | Intestinal content | Direct microscopy | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| C. spiroforme | Intestinal content | Gram stain | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| C. piliforme | Cecal wall | PCR | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| Liver | Negative | Positive | Negative | ||
| Cryptosporidium sp. and Giardia sp. | Pooled cecal content | Immunofluorescent essay | Negative | ||
| Toxoplasma gondii | Spleen (doe 3) and uterus (does 1 and 3) | PCR | Negative | NT * | Negative |
| Chlamydophila sp. | Negative | NT * | Negative | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cordioli, B.; Garbuio, M.; Palazzolo, L.; Dorigo, F.; Zandonà, L.; Viel, L.; Zanardello, C.; Bano, L. Unusual Epidemic of Tyzzer’s Disease in Commercial Rabbit Breeders: Clinical, Pathological, and Therapeutic Observations. Animals 2025, 15, 2920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192920
Cordioli B, Garbuio M, Palazzolo L, Dorigo F, Zandonà L, Viel L, Zanardello C, Bano L. Unusual Epidemic of Tyzzer’s Disease in Commercial Rabbit Breeders: Clinical, Pathological, and Therapeutic Observations. Animals. 2025; 15(19):2920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192920
Chicago/Turabian StyleCordioli, Benedetta, Manuel Garbuio, Luca Palazzolo, Francesco Dorigo, Luca Zandonà, Laura Viel, Claudia Zanardello, and Luca Bano. 2025. "Unusual Epidemic of Tyzzer’s Disease in Commercial Rabbit Breeders: Clinical, Pathological, and Therapeutic Observations" Animals 15, no. 19: 2920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192920
APA StyleCordioli, B., Garbuio, M., Palazzolo, L., Dorigo, F., Zandonà, L., Viel, L., Zanardello, C., & Bano, L. (2025). Unusual Epidemic of Tyzzer’s Disease in Commercial Rabbit Breeders: Clinical, Pathological, and Therapeutic Observations. Animals, 15(19), 2920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192920






