RXR Expression Profiles in Yak Reproductive Tissues During Follicular, Luteal, and Pregnancy Phases
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Key Instruments and Reagents
2.3. Detection of RXRα, RXRβ, and RXRγ Expression Levels in Yak Ovaries, Uteri, and Fallopian Tubes Across Reproductive Phases
2.3.1. mRNA Expression Levels of RXRα, RXRβ, and RXRγ Across Reproductive Phases
2.3.2. Protein Expression Analysis of RXRα, RXRβ, and RXRγ in Yak Ovaries, Uteri, and Oviducts Across Reproductive Phases
2.4. Distribution Detection of RXRα, RXRβ, and RXRγ in Yak Ovaries, Uteri, and Oviducts Across Reproductive Phases
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. RXRα, RXRβ, and RXRγ Expression in Yak Ovaries, Uteri, and Oviducts Across Reproductive Phases
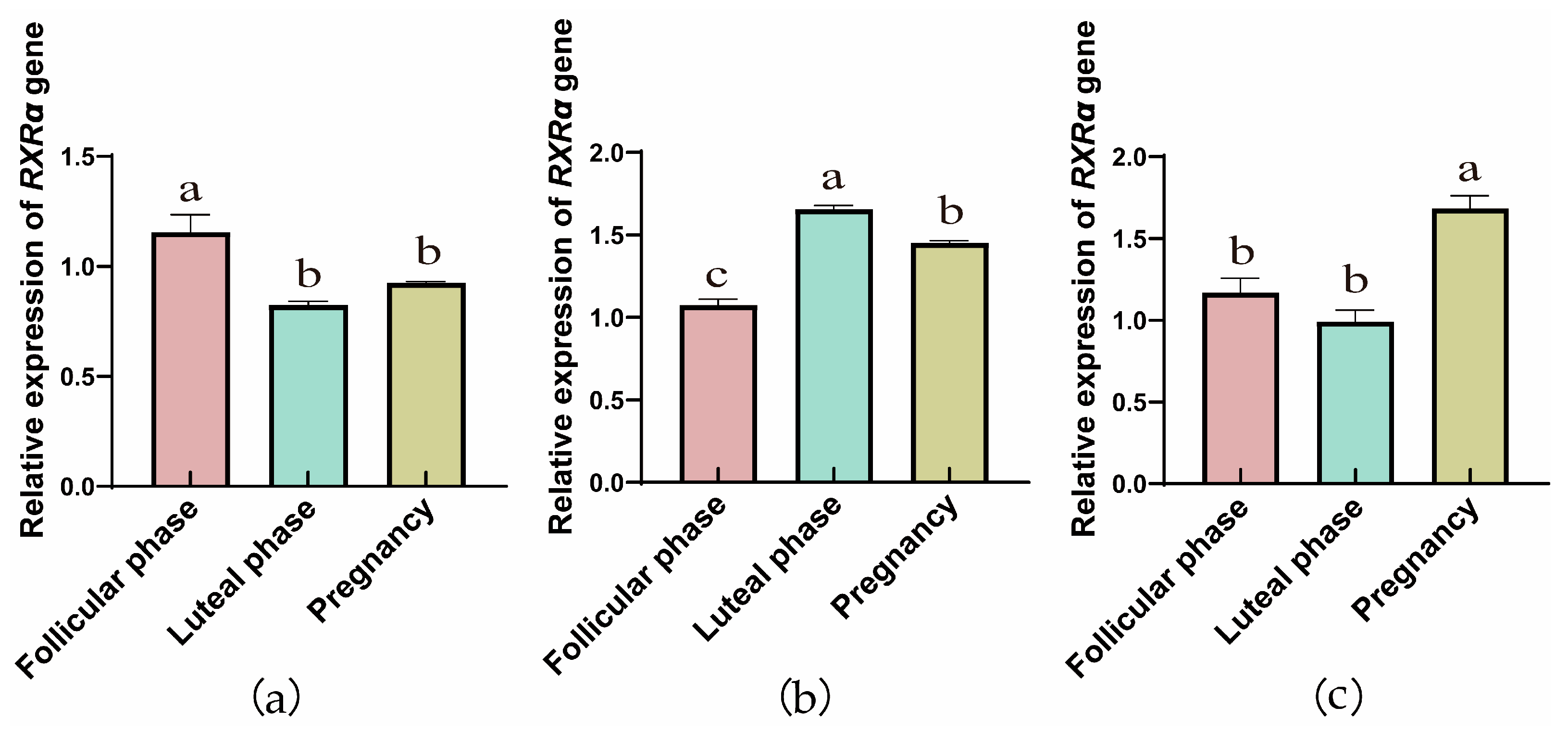
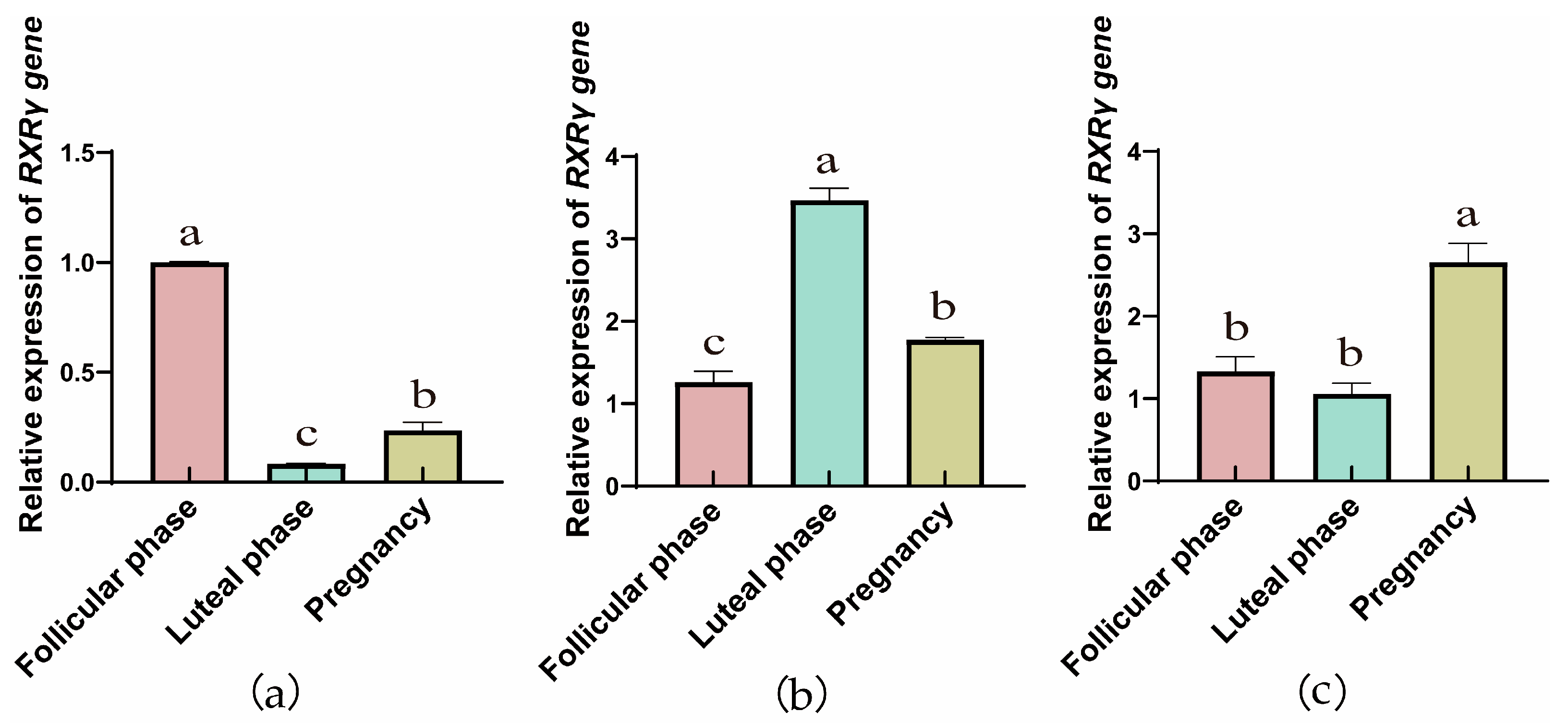
3.1.1. Comparison of RXRα, RXRβ, and RXRγ mRNA Relative Expression Across Reproductive Phases
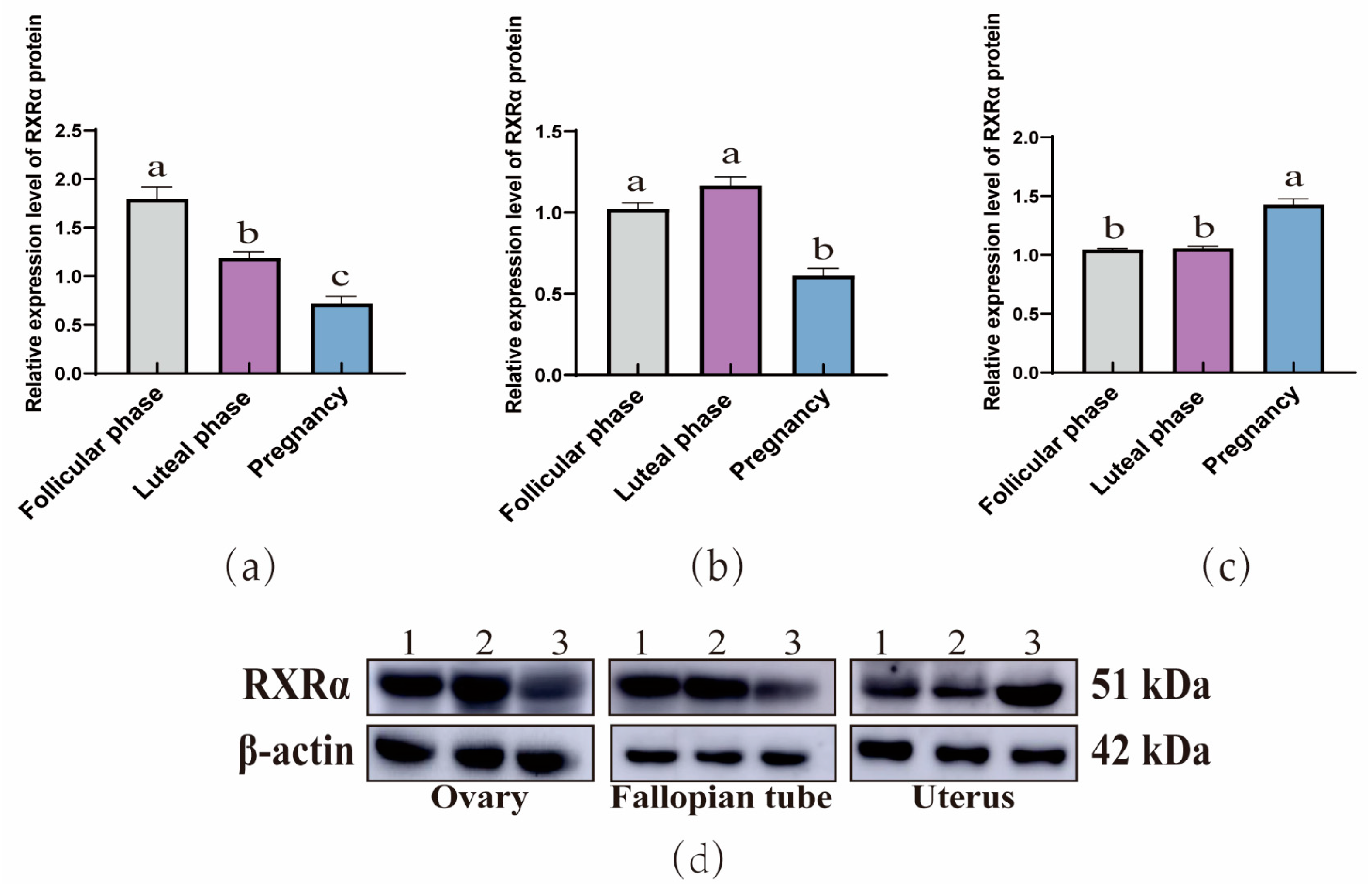
3.1.2. Comparing RXRα, RXRβ, and RXRγ Protein Levels Across Yak Reproductive Phases
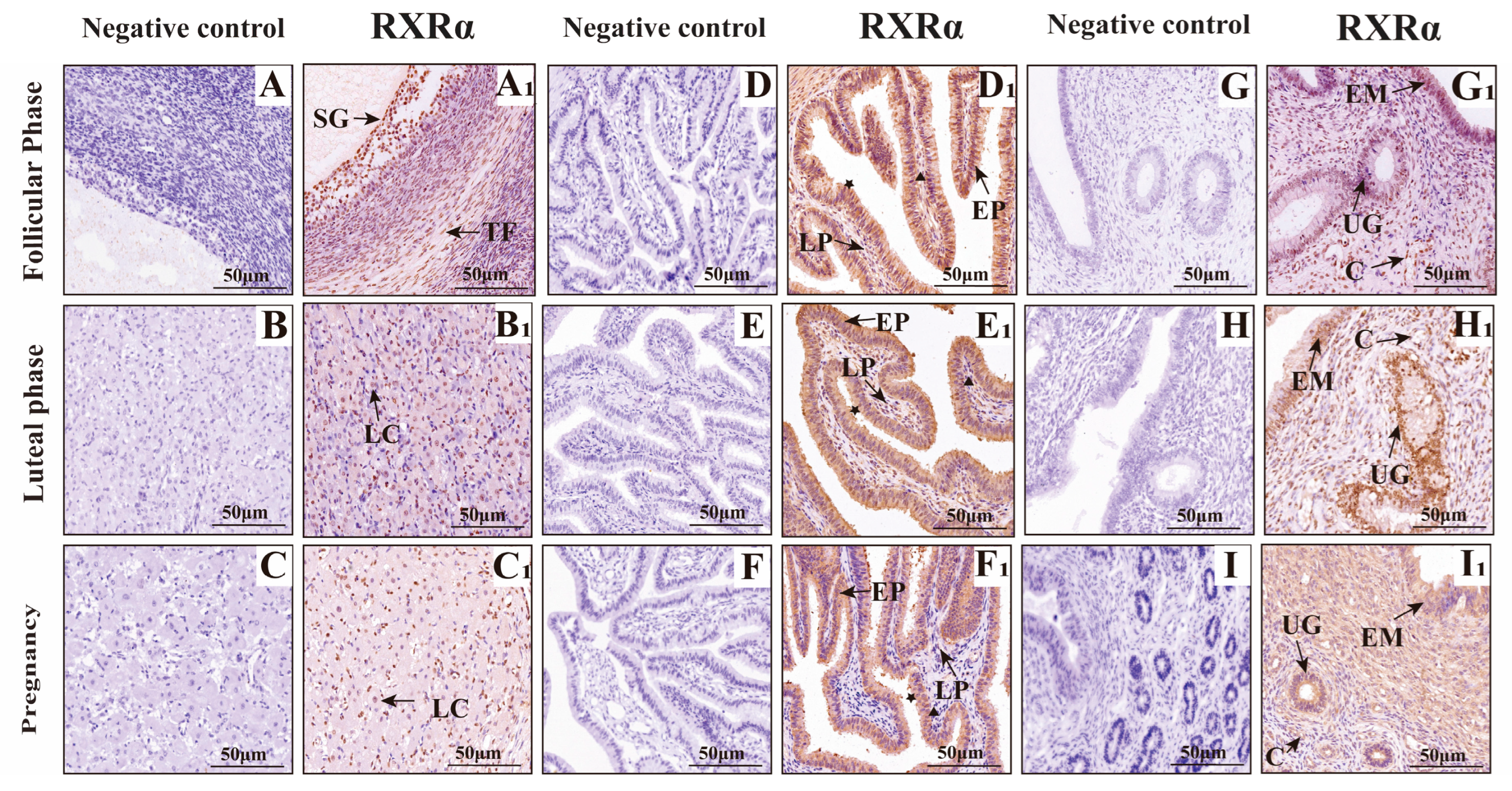
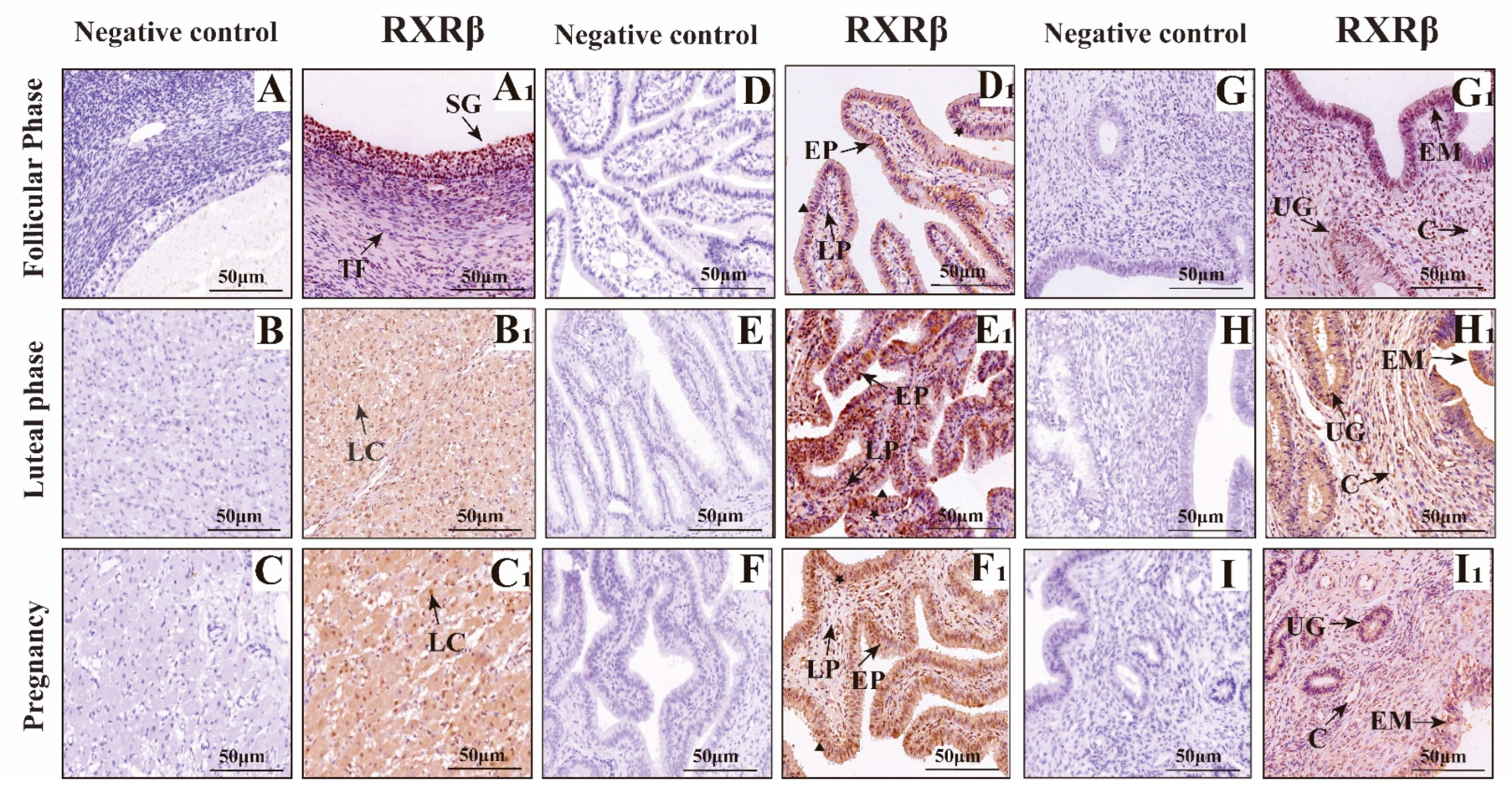
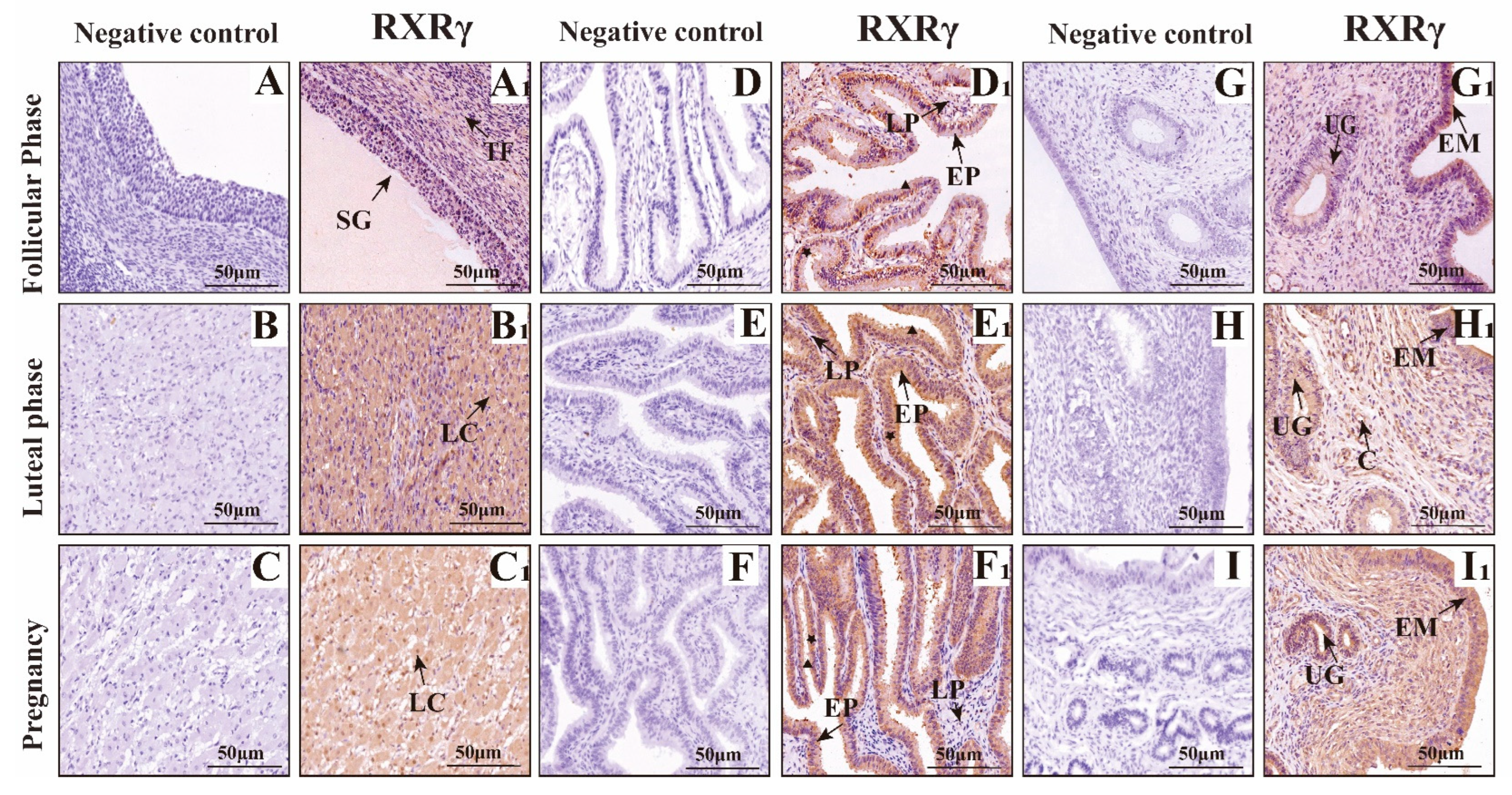
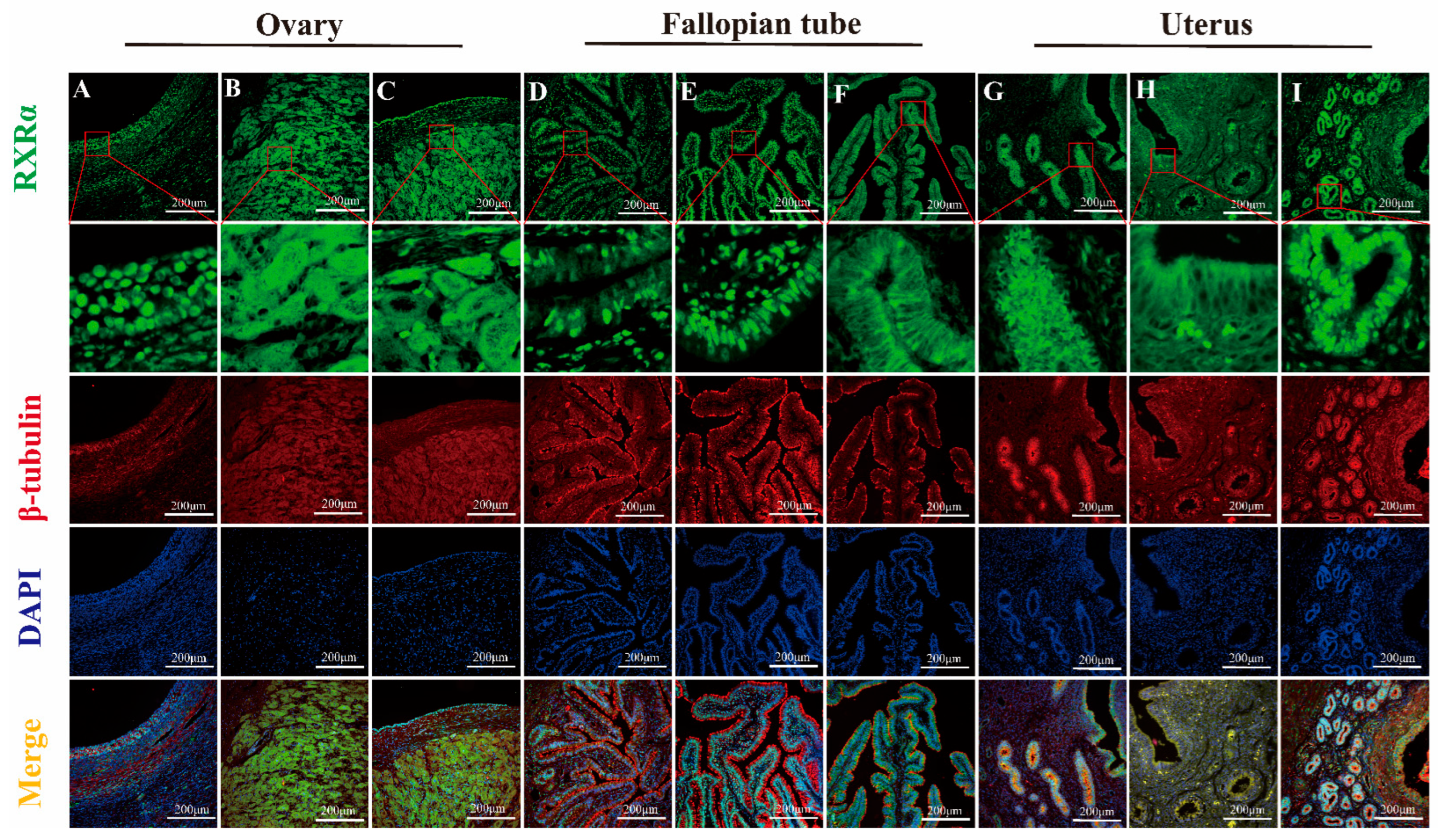
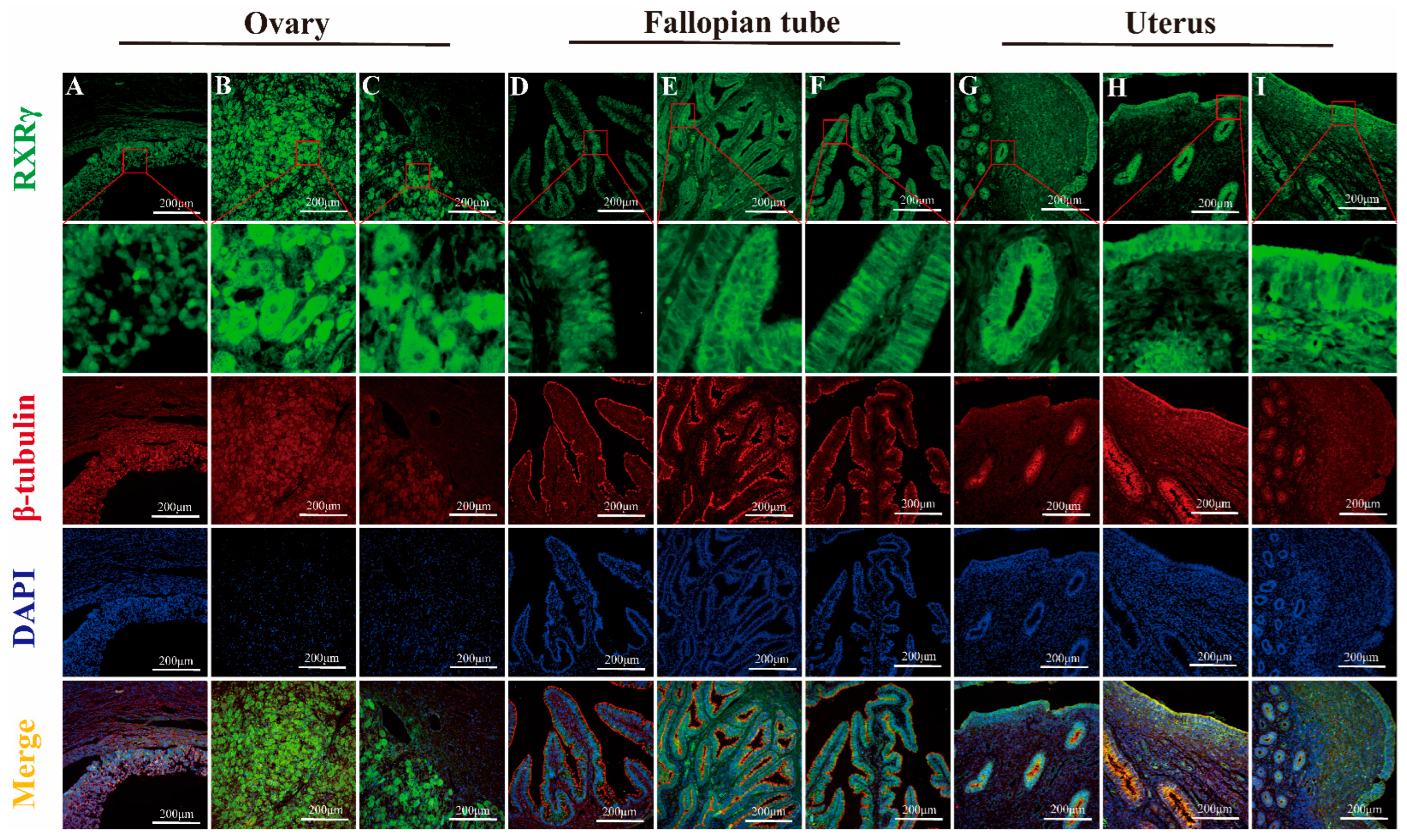
3.2. Mapping RXRα, RXRβ, and RXRγ Distribution in Yak Ovaries, Uteri, and Oviducts Across Reproductive Phases
IF Detection of RXRα, RXRβ, and RXRγ Distribution in Yak Ovaries, Oviducts, and Uteri Across Reproductive Phases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ayalew, W.; Chu, M.; Liang, C.; Wu, X.; Yan, P. Adaptation mechanisms of yak (Bos grunniens) to high-altitude environmental stress. Animals 2021, 11, 2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.F.; Zhang, H.; Pan, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.M.; Wang, B.F.; Dong, Y.J. Cloning of the yak BMP7 gene and its expression analysis in the ovary and uterus during the estrous cycle. Acta Ecol. Anim. Domest. 2023, 44, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal Yatoo, M.; Shabir, M.; Kubrevi, S.S.; Dar, R.A.; Angmo, K.; Kanwar, M.S.; Bhat, R.A.; Muheet; Parray, O.R. A study on biological rhythms of Himalayan yaks. Biol. Rhythm. Res. 2019, 51, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emily, R.W.; Xu, L.; Eric, A.O. The nuclear receptor superfamily: A structural perspective. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 1876–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcia, I.D.; Zebin, X. The retinoid X receptors and their ligands. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2012, 1821, 21–56. [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Borgmeyer, U.; Heyman, R.A.; Zhou, J.Y.; Ong, E.S.; Oro, A.E.; Kakizuka, A.; Evans, R.M. Characterization of three RXR genes that mediate the action of 9-cis retinoic acid. Genes Dev. 1992, 6, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gericke, J.; Ittensohn, J.; Mihály, J.; Alvarez, S.; Alvarez, R.; Töröcsik, D.; de Lera, A.R.; Rühl, R. Regulation of retinoid-mediated signaling involved in skin homeostasis by RAR and RXR agonists/antagonists in mouse skin. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- María Piedad, M.-G.; Mercedes, R. The multi-faceted role of retinoid X receptor in bone remodeling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 2135–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Chen, G. Transcriptional factors mediating retinoic acid signals in the control of energy metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 14210–14244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastner, P.; Grondona, J.M.; Mark, M.; Gansmuller, A.; LeMeur, M.; Decimo, D.; Vonesch, J.L.; Dollé, P.; Chambon, P. Genetic analysis of RXR alpha developmental function: Convergence of RXR and RAR signaling pathways in heart and eye morphogenesis. Cell 1994, 78, 987–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krezel, W.; Dupé, V.; Mark, M.; Dierich, A.; Kastner, P.; Chambon, P. RXR gamma null mice are apparently normal and compound RXR alpha +/-/RXR beta -/-/RXR gamma -/- mutant mice are viable. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 9010–9014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Di, R.; Guo, X.F.; Zhang, J.L.; Zhang, X.S.; Ma, L.; Chu, M.X.; Liu, W.J. Expression of RXRs genes in reproductive axis-related tissues of sheep and the relationship between RXRA gene polymorphism and seasonal estrus. J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 27, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar]
- Thiyagarajan, B.; Valivittan, K. Effect of all-trans retinol on in vitro development of preimplantation buffalo embryos. Animal 2009, 3, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamińska, A.; Pardyak, L.; Lustofin, S.; Gielata, K.; Arent, Z.; Pietsch-Fulbiszewska, A.; Hejmej, A. 9-cis-retinoic acid signaling in Sertoli cells regulates their immunomodulatory function to control lymphocyte physiology and Treg differentiation. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2024, 22, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.C.; Eichele, G.; Thaller, C. Ligand-bound RXR can mediate retinoid signal transduction during embryogenesis. Development 1997, 124, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froment, P. PPARs and RXRs in male and female fertility and reproduction. PPAR Res. 2008, 2008, 637490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE Guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammas, L.; Reinaud, P.; Bordas, N.; Dubois, O.; Germain, G.; Charpigny, G. Developmental regulation of prostacyclin synthase and prostacyclin receptors in the ovine uterus and conceptus during the peri-implantation period. Reproduction 2006, 131, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, F.; Inoue, N.; Manabe, N.; Ohkura, S. Follicular growth and atresia in mammalian ovaries: Regulation by survival and death of granulosa cells. J. Reprod. Dev. 2012, 58, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Lu, R.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shi, X.; Ma, W.; Wu, L.; Tian, X.; Liu, H.; Jiang, H.; et al. Molecular characterization and potential function of Rxrγ in gonadal differentiation of Chinese soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 233, 106360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Ticiani, E.; Pearl, S.; Martin, D.; Veiga-Lopez, A. The organotin triphenyltin disrupts cholesterol signaling in mammalian ovarian steroidogenic cells through a combination of LXR and RXR modulation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022, 453, 116209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, P.C.; Valerie, L.B. Corpus luteal contribution to maternal pregnancy physiology and outcomes in assisted reproductive technologies. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 304, R69–R72. [Google Scholar]
- Mattoso Miskulin Cardoso, A.P.; Tavares Pereira, M.; Dos Santos Silva, R.; Medeiros de Carvalho Sousa, L.M.; Giometti, I.C.; Kowalewski, M.P.; de Carvalho Papa, P. Global transcriptome analysis implicates cholesterol availability in the regulation of canine cyclic luteal function. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2021, 307, 113759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiromori, Y.; Yui, H.; Nishikawa, J.; Nagase, H.; Nakanishi, T. Organotin compounds cause structure-dependent induction of progesterone in human choriocarcinoma Jar cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 155 Pt B, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonouli, S.; Palmerini, M.G.; Bianchi, S.; Rossi, G.; Cecconi, S.; Belli, M.; Bernardi, S.; Khalili, M.A.; Familiari, G.; Nottola, S.A.; et al. Repeated hyperstimulation affects the ultrastructure of mouse fallopian tube epithelium. J. Reprod. Dev. 2020, 66, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.H.; He, H.H.; Wang, J.L.; Zhang, H.Z.; Ma, Y.; Ma, J.B.; Zhao, S.X.; Yu, S.J.; Cui, Y.; Fan, J.F. Expression of p38MAPK in the main reproductive organs of female yaks. Acta Vet. Zootech. Sinica 2019, 50, 1802–1812. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; You, X. Retinoid X receptor ligand regulates RXRγ/Nur77-dependent apoptosis via modulating its nuclear export and mitochondrial targeting. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2017, 10, 10770–10780. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Kolluri, S.K.; Lin, F.; Liu, W.; Han, Y.H.; Cao, X.; Dawson, M.I.; Reed, J.C.; Zhang, X.K. Conversion of Bcl-2 from protector to killer by interaction with nuclear orphan receptor Nur77/TR3. Cell 2004, 116, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudureyimu, A.; Ren, R.; Qiao, Z.L.; Li, Z.; Li, S.Y.; Deng, A.C.; Liu, Z.; Cai, Y. Expression changes of Bcl-2 and Bax in the fallopian tubes of yaks during the follicular and luteal phases. Chin. J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 48, 240–246. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.W.; Ma, L.; Yan, X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.K.; Cohen, P. Rapid apoptosis induction by IGFBP-3 involves an insulin-like growth factor-independent nucleomitochondrial translocation of RXRalpha/Nur77. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 16942–16948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweigert, F.J.; Siegling, C. Immunolocalization of retinol-binding protein, cellular retinoic acid-binding protein I and retinoid X receptor beta in the porcine reproductive tract during the oestrous cycle. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2001, 13, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.X.; Cui, Y.; Yu, S.J.; Yang, B. Observation of uterine tissue structure during the estrous cycle of yaks. Acta Vet. Zootech. Sin. 2010, 41, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Lechuga, T.J.; Qi, Q.R.; Magness, R.R.; Chen, D.B. Ovine uterine artery hydrogen sulfide biosynthesis in vivo: Effects of ovarian cycle and pregnancy. Biol. Reprod. 2019, 100, 1630–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aujla, T.; Darby, J.R.T.; Saini, B.S.; Lock, M.C.; Holman, S.L.; Bradshaw, E.L.; Perumal, S.R.; McInnes, S.J.P.; Voelcker, N.H.; Wiese, M.D.; et al. Impact of resveratrol-mediated increase in uterine artery blood flow on fetal haemodynamics, blood pressure and oxygenation in sheep. Exp. Physiol. 2021, 106, 1166–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweigert, F.J.; Bonitz, K.; Siegling, C.; Buchholz, I. Distribution of vitamin A, retinol-binding protein, cellular retinoic acid-binding protein I, and retinoid X receptor beta in the porcine uterus during early gestation. Biol. Reprod. 1999, 61, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Barbara, D.A. Review of the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha (PPARγ), beta (PPARβ), and gamma (PPARγ) in rodent and human development. Reprod. Toxicol. 2009, 27, 246–257. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Thomas, J.C.; Gregg, D. Mechanisms of retinoic acid signalling and its roles in organ and limb development. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, D.J.; Xu, C.S.; Ning, R.B.; Zhu, J.; Xie, H.; Lin, J.X. RXR agonists counteract high glucose-induced proliferation of rat vascular smooth muscle cells by inhibiting PKC activation. Chin. J. Pathophysiol. 2013, 29, 266–271. [Google Scholar]
- Szczepańska, A.A.; Łupicka, M.; Socha, B.M.; Korzekwa, A.J. The influence of arachidonic acid metabolites on PPAR and RXR expression in bovine uterine cells. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2018, 262, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Graham, K.; Glubrecht, D.D.; Lai, R.; Mackey, J.R.; Godbout, R. A fatty acid-binding protein 7/RXRβ pathway enhances survival and proliferation in triple-negative breast cancer. J. Pathol. 2012, 228, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Primer | GenBank Accession Number | Primer Sequence | PCR Product Lengths (bp) | Melting Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RXRα | NM_001304343.1 | F: GGTCATCCTGCTGCGAG R: GTTTGAGAGCCCCTTGG | 265 | 60 |
| RXRβ | NM_001083640.1 | F: CGGTGGGAAAGACAAAG R: GGCAAGGAGGAAAAGTG | 252 | 60 |
| RXRγ | XM_005890189 | F: CCTTTTCCCATCGCTC R: TGTTCTGGATACTTTTGCTT | 298 | 58 |
| β-actin | NM_173979.3 | F: CCGTGACATCAAGGAGAA R: AGGAAGGAAGGCTGGAAG | 172 | 60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Ma, W.; Ma, X.; Chang, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, Y. RXR Expression Profiles in Yak Reproductive Tissues During Follicular, Luteal, and Pregnancy Phases. Animals 2025, 15, 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192814
Zhang X, Ma W, Ma X, Chang J, Yang J, Wang M, Wang L, Zhang Q, Pan Y. RXR Expression Profiles in Yak Reproductive Tissues During Follicular, Luteal, and Pregnancy Phases. Animals. 2025; 15(19):2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192814
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaokun, Wenbin Ma, Xin Ma, Jianying Chang, Juan Yang, Meng Wang, Libin Wang, Qian Zhang, and Yangyang Pan. 2025. "RXR Expression Profiles in Yak Reproductive Tissues During Follicular, Luteal, and Pregnancy Phases" Animals 15, no. 19: 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192814
APA StyleZhang, X., Ma, W., Ma, X., Chang, J., Yang, J., Wang, M., Wang, L., Zhang, Q., & Pan, Y. (2025). RXR Expression Profiles in Yak Reproductive Tissues During Follicular, Luteal, and Pregnancy Phases. Animals, 15(19), 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192814





