Multi-Omics Insights into Postnatal Skeletal Muscle Development in Duroc Pigs
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals and Cells
2.2. Total RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.3. Western Blot Detection of Protein Expression
2.4. Hematoxylin–Eosin (HE) Staining
2.5. Immunofluorescence Assay
2.6. RNA-Seq and LC-MS Analyses
2.7. Statistical Analysis of the Data
3. Results
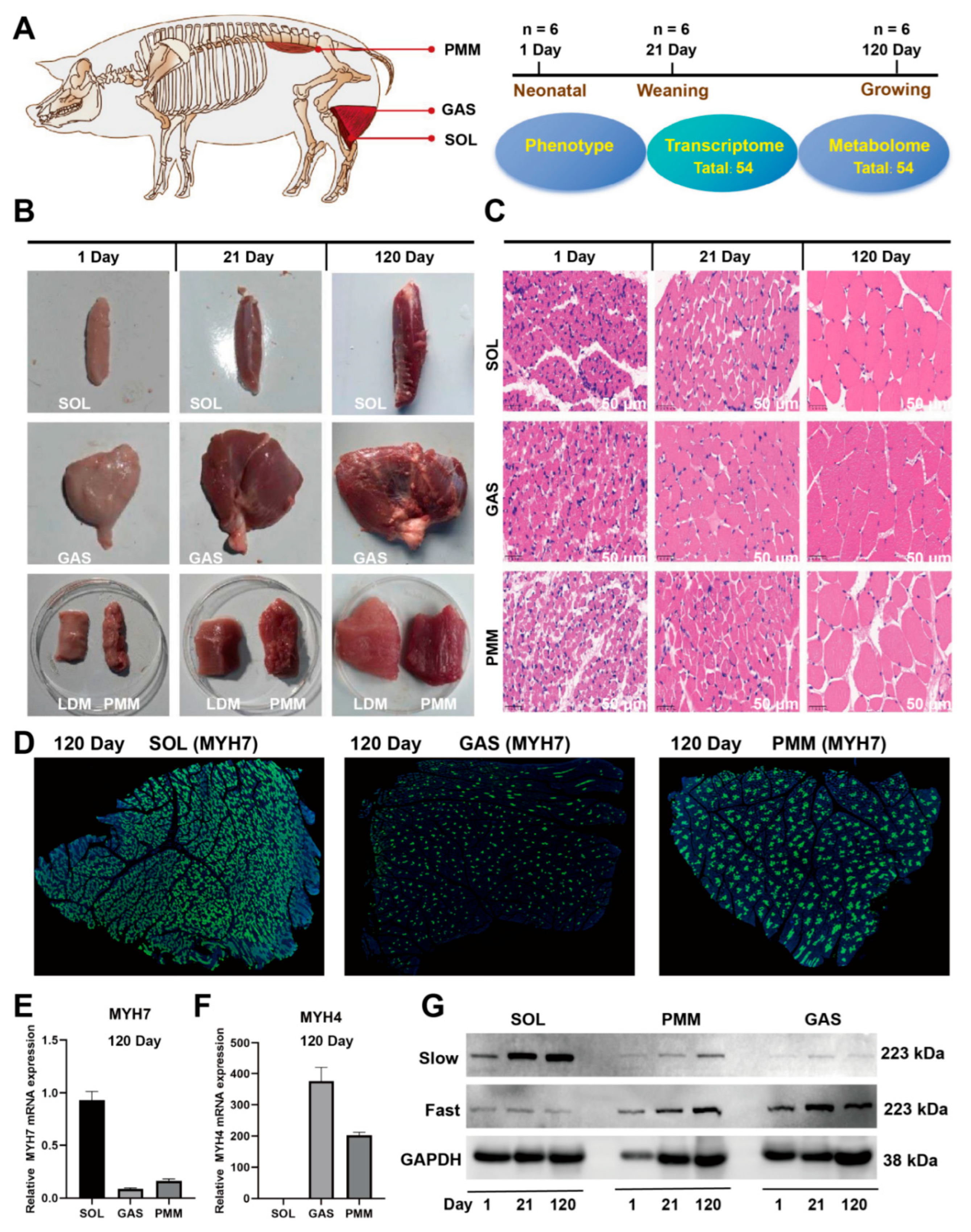
3.1. Phenotypic Assessment of SOL, GAS, and PMM in Duroc Pigs
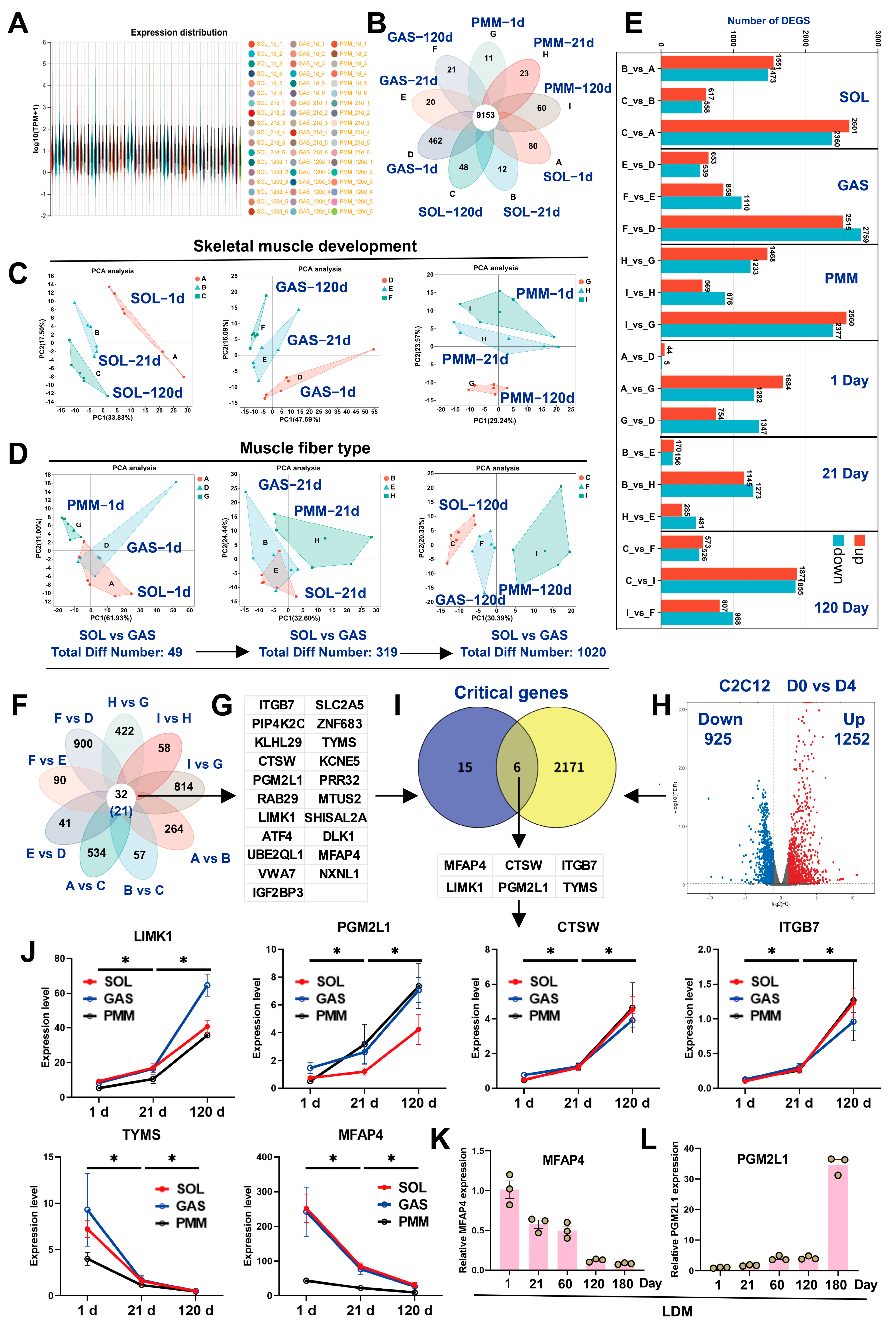
3.2. Identification of DEGs by Bulk RNA-Seq During Multiple Skeletal Muscle Development
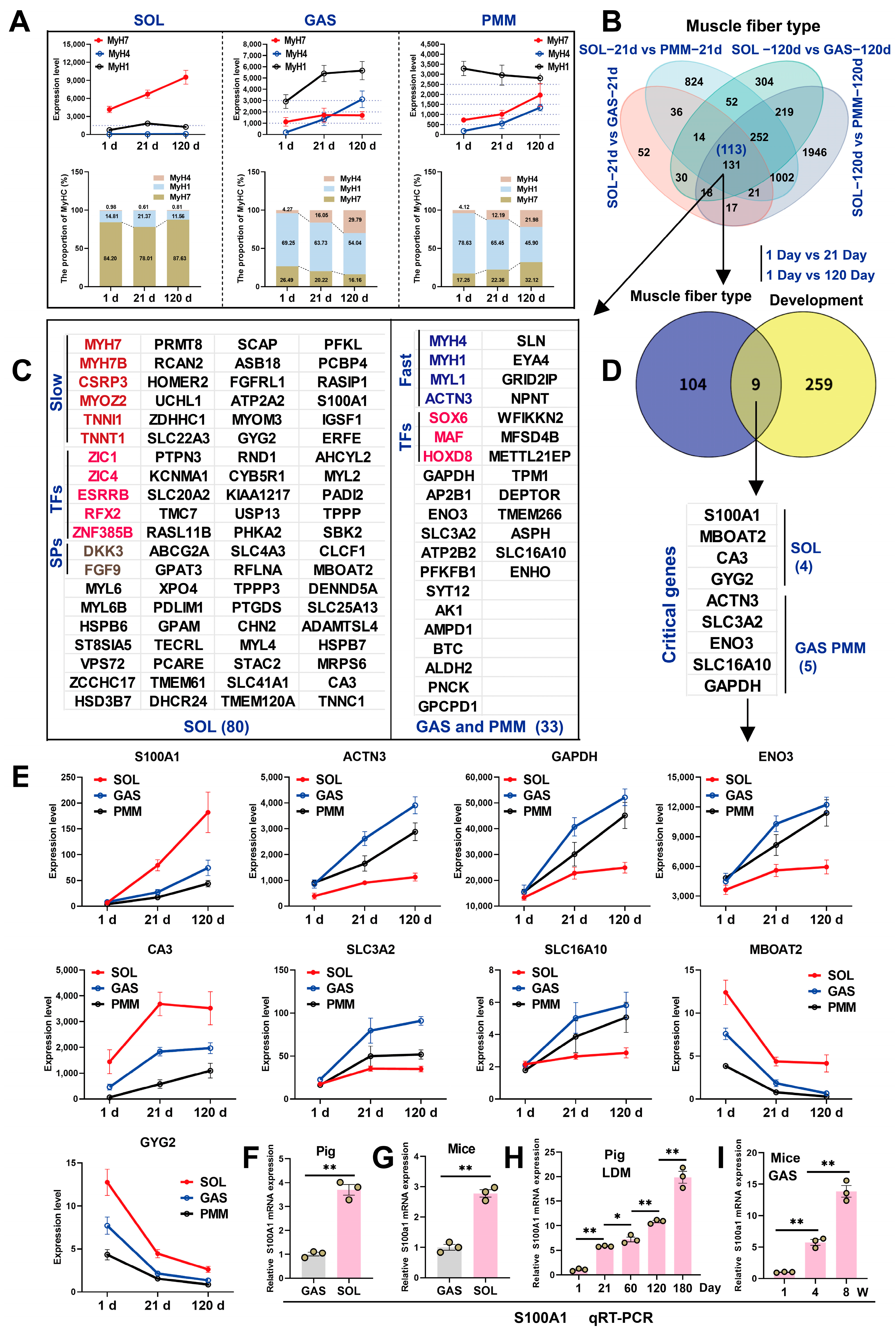
3.3. Identification of DEGs by Bulk RNA-Seq in Fast-Twitch and Slow-Twitch Muscles
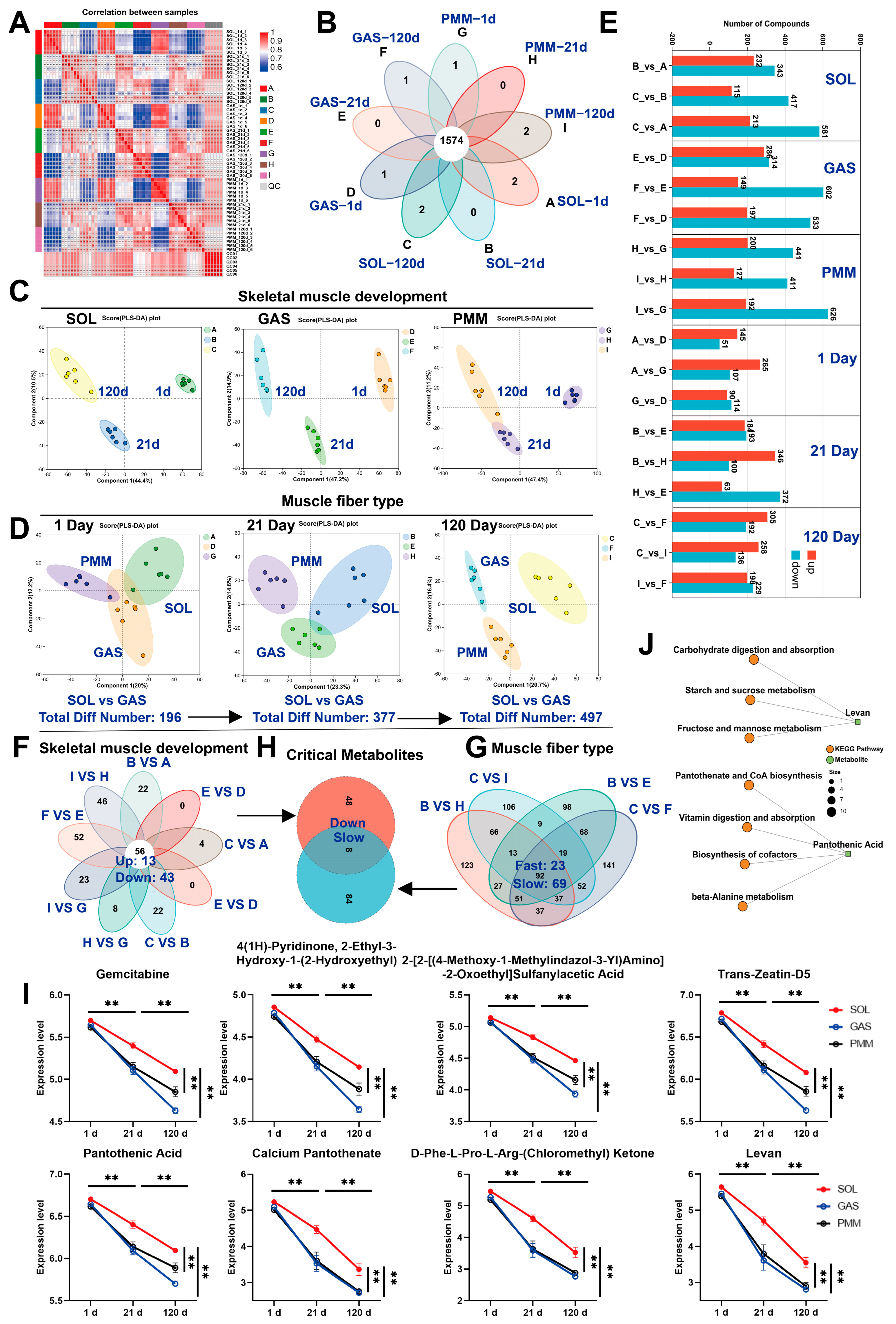
3.4. LC-MS Reveals Critical Metabolites for Skeletal Muscle Development and Myofiber Transformation
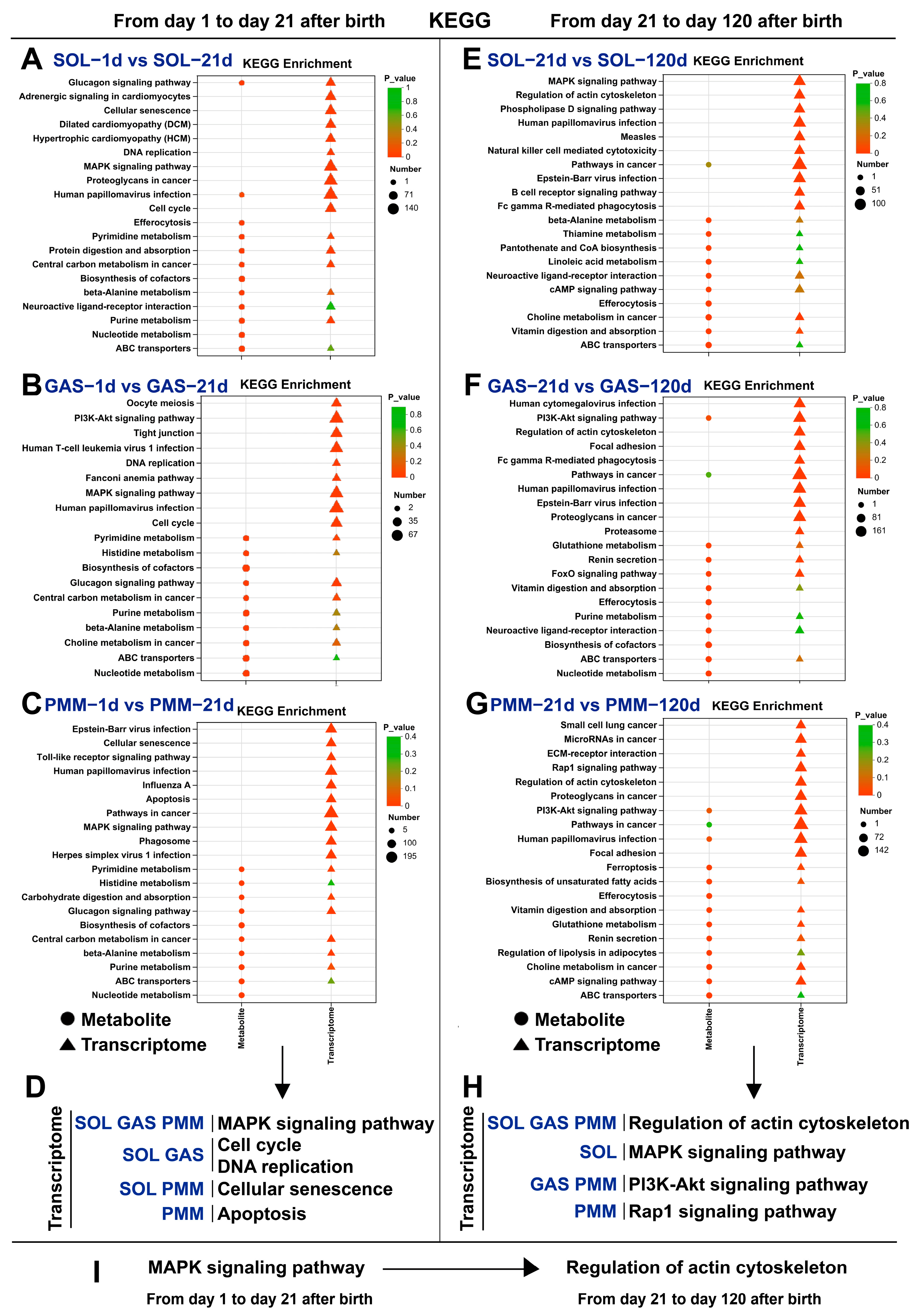
3.5. Analysis of KEGG Pathway Enrichment in Different Stages of Muscle Development
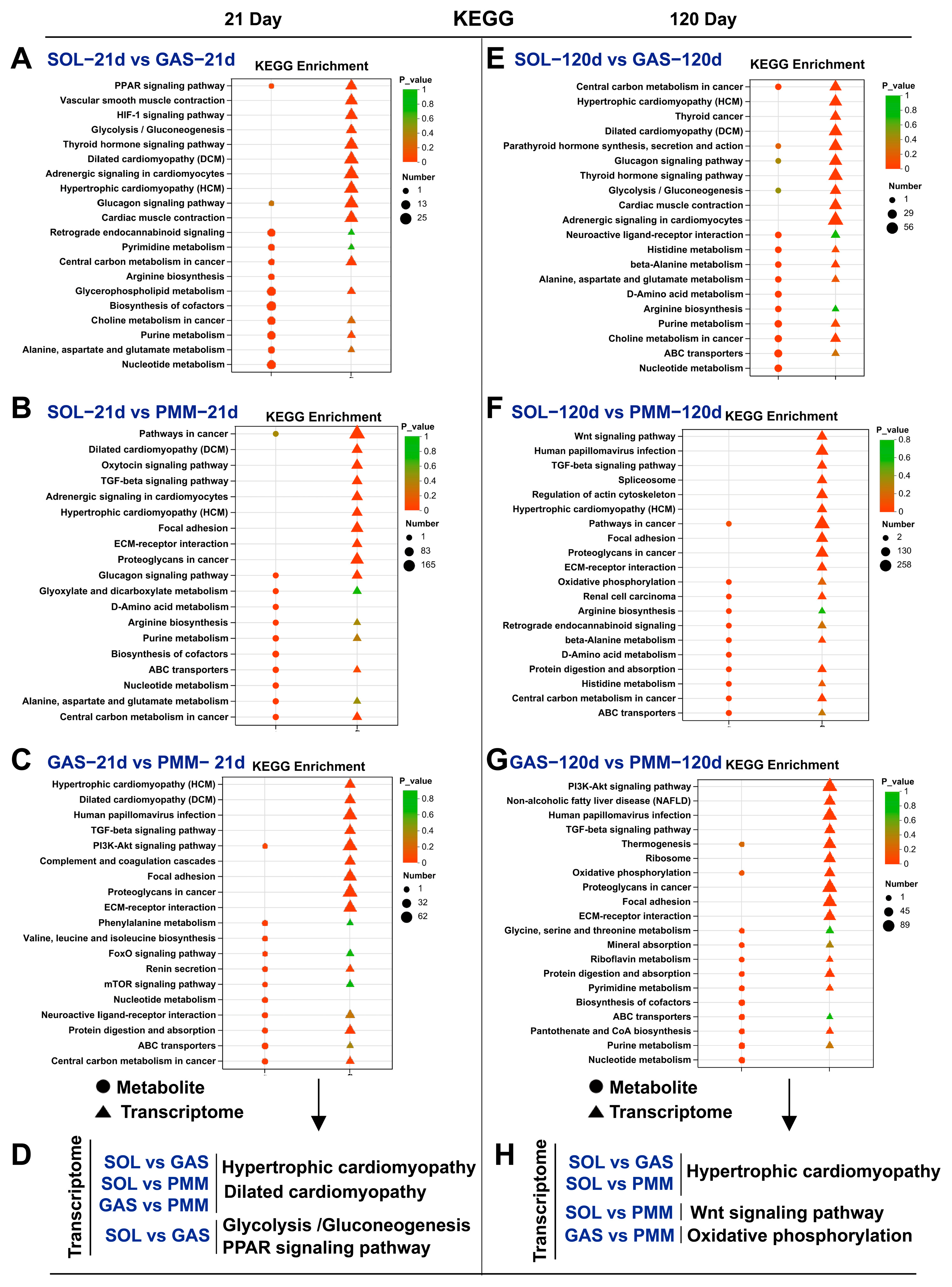
3.6. Analysis of KEGG Pathway Enrichment in Different Muscles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frontera, W.R.; Ochala, J. Skeletal muscle: A brief review of structure and function. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2015, 96, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Koishi, K.; McLennan, I.S. Skeletal muscle fibre types: Detection methods and embryonic determinants. Histol. Histopathol. 1998, 13, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grefte, S.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M.; Torensma, R.; Hoff, J.W.V.D. Skeletal muscle development and regeneration. Stem Cells Dev. 2007, 16, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, C.; Yi, L.; Liufu, S.; Chen, W.; Liu, X.; Chen, B.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; et al. LMOD2 interaction with ACTC1 regulates myogenic differentiation. BMC Genom. 2025, 26, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.; Hong, L.; Xiao, L.; Wu, J.; Lu, G.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Zheng, E.; Cai, G.; Li, Z.; et al. Rewiring of 3D chromatin topology orchestrates transcriptional reprogramming in muscle fiber-type specification and transformation. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry, E.E.; Zhang, X.; Hoffmann, C.; Hughes, L.D.; Lewis, S.A.; Li, J.; Wallace, M.J.; Riley, L.; Douglas, C.M.; Gutierrez-Montreal, M.A.; et al. Transcriptional profiling reveals extraordinary diversity among skeletal muscle tissues. eLife 2018, 7, e34613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Tang, Q.; Hu, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zeng, B.; Wang, Y.; He, M.; Li, Y.; Gui, L.; et al. A pig BodyMap transcriptome reveals diverse tissue physiologies and evolutionary dynamics of transcription. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yan, J.; Fan, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Yi, G.; Liu, Y.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. The genome variation and developmental transcriptome maps reveal genetic differentiation of skeletal muscle in pigs. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, R.; Li, H.; Tong, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Ren, Z.; et al. Transcriptional Diversity in Response to Aging Across Skeletal Muscles. Aging Cell 2025, 9, e70164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, F.A.; Baechler, B.L.; Quadrilatero, J. Key considerations for investigating and interpreting autophagy in skeletal muscle. Autophagy 2024, 20, 2121–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Yang, J.; Ren, Y.; Jia, J.; Yang, G.; Liao, M.; Jin, J.; Shi, X. Identification of different myofiber types in pigs muscles and construction of regulatory networks. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, B.; Lefaucheur, L.; Berri, C.; Duclos, M.J. Muscle fibre ontogenesis in farm animal species. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2003, 42, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, T.; Du, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Gao, X.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Gao, H. Transcriptomic analysis reveals diverse expression patterns underlying the fiber diameter of oxidative and glycolytic skeletal muscles in steers. Meat Sci. 2023, 207, 109350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hettige, P.; Tahir, U.; Nishikawa, K.C.; Gage, M.J. Comparative analysis of the transcriptomes of EDL, psoas, and soleus muscles from mice. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Tian, T.; Yu, H.; Cao, C.; Zhang, Z.; He, Z.; Ma, Z.; Cai, R.; Li, F.; Pang, W. Identification of porcine fast/slow myogenic exosomes and their regulatory effects on lipid accumulation in intramuscular adipocytes. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 15, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachman, J.F.; Chakkalakal, J.V. Satellite cells in the growth and maintenance of muscle. In Current Topics in Developmental Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; Volume 158, pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liufu, S.; Lan, Q.; Liu, X.; Chen, B.; Xu, X.; Ai, N.; Li, X.; Yu, Z.; Ma, H. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Age-Related Developmental Dynamics Pattern of the Longissimus Dorsi Muscle in Ningxiang Pigs. Genes 2023, 14, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Liu, C.; Liu, J.; Wen, S.; Chen, Y.; Ren, R.; Gao, N.; Ding, X.; He, J.; Zhang, Y. Integrative Analysis of ATAC-Seq and RNA-Seq Identifies Key Genes Affecting Muscle Development in Ningxiang Pigs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Luo, W.; Ren, T.; Huang, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, X. Sox6 Differentially Regulates Inherited Myogenic Abilities and Muscle Fiber Types of Satellite Cells Derived from Fast- and Slow-Type Muscles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaki, S.; Tsuji, R.; Hayashi, T.; Watanabe, M.; Iwai, R.; Wenchao, G.; Semenova, E.A.; Sultanov, R.I.; Zhelankin, A.V.; Generozov, E.V.; et al. Large MAF transcription factors reawaken evolutionarily dormant fast-glycolytic type IIb myofibers in human skeletal muscle. Skelet. Muscle 2025, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wilde, J.; Hulshof, M.F.; Boekschoten, M.V.; de Groot, P.; Smit, E.; Mariman, E.C. The embryonic genes Dkk3, Hoxd8, Hoxd9 and Tbx1 identify muscle types in a diet-independent and fiber-type unrelated way. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, D.; Deng, C.; Xiong, Y.; Lei, M.; Li, F.; Jiang, S.; Zuo, B.; Zheng, R. Expression pattern and polymorphism of three microsatellite markers in the porcine CA3 gene. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2008, 40, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maco, B.; Uhrík, B.; Heizmann, C.W. Distribution of the Ca2+-binding S100A1 protein at different sarcomere lengths of slow and fast rat skeletal muscles. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2001, 19, 237–244. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Xu, J.; Zhou, W.; Chen, S.; Shi, H.; Han, M.; Yang, Z.; Duan, Y.; Pang, W.; Yin, Y.; et al. Metabolome and RNA-seq reveal discrepant metabolism and secretory metabolism profile in skeletal muscle between obese and lean pigs at different ages. Sci. China Life Sci. 2025, 68, 1102–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield, J.; Harris, R.C.; Broad, E.M.; Patterson, A.K.; Ross, M.L.; Shaw, G.; Spriet, L.L.; Burke, L.M. Chronic pantothenic acid supplementation does not affect muscle coenzyme A content or cycling performance. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 46, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikanth, R.; Siddartha, G.; Reddy, C.H.S.; Harish, B.S.; Ramaiah, M.J.; Uppuluri, K.B. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory levan produced from Acetobacter xylinum NCIM2526 and its statistical optimization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 123, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, T. Postnatal skeletal muscle myogenesis governed by signal transduction networks: MAPKs and PI3K-Akt control multiple steps. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 682, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millward, D.J. Post-natal muscle growth and protein turnover: A narrative review of current understanding. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2023, 37, 143–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.-J.; Li, J.-H.; Chen, H.-F.; Tan, Y.-Y.; Liu, S.-R.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Yang, J.-H.; Liu, S.; Zheng, L.-L.; et al. Inhibition of the JNK/MAPK signaling pathway by myogenesis-associated miRNAs is required for skeletal muscle development. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1581–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Ou, Y.-W.; Xie, S.-J.; Chen, P.-P.; Mei, S.-Q.; Huang, Q.-J.; Zheng, L.-L.; Qu, L.-H. PERK Signaling Controls Myoblast Differentiation by Regulating MicroRNA Networks. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 670435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memme, J.M.; Sanfrancesco, V.C.; Hood, D.A. Activating transcription factor 4 regulates mitochondrial content, morphology, and function in differentiating skeletal muscle myotubes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2023, 325, C224–C242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocsak, E.; Szabo, V.; Kalman, N.; Antus, C.; Cseh, A.; Sumegi, K.; Eros, K.; Hegedus, Z.; Gallyas, F.; Sumegi, B.; et al. PARP inhibition protects mitochondria and reduces ROS production via PARP-1-ATF4-MKP-1-MAPK retrograde pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 108, 770–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, N.A.; Wang, Y.X.; Rudnicki, M.A. Intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms regulating satellite cell function. Development 2015, 142, 1572–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunello, E.; Fusi, L. Regulating Striated Muscle Contraction: Through Thick and Thin. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2023, 86, 255–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, R.J.; Le, A.M.; Zhang, L.; Kahn, M.; Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I.; Bennett, A.M. MAPK phosphatase-1 facilitates the loss of oxidative myofibers associated with obesity in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 3817–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Du, J.; Xia, Y.; Tan, Z.; Fu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Li, X.; Tang, G.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Genome-wide landscape of DNA methylomes and their relationship with mRNA and miRNA transcriptomes in oxidative and glycolytic skeletal muscles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Genes | F: Sequence (5′ to 3′) | R: Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pig | MYH1 | GAAGTTGCATCCCTAAAGGCAG | CGATGACTTGGCGTCAAAAGG |
| Pig | MYH2 | GGAGGCTGAGGAACAATCCA | GCATCGGGACAGCCTTACTC |
| Pig | MYH4 | AGTTCCGTAAGATCCAGCACG | CCTGTCACCTCTCAACAGAAAGA |
| Pig | MYH7 | AGTCCCAGGTCAACAAGCTG | TTCCACCTAAAGGGCTGTTG |
| Pig | MFAP4 | CGGCGTGTACCTCATCTACC | GCCGTTGAACCTCTTCTGGA |
| Pig | PGM2L1 | CGTCTTTTCACGGAGTCGGA | TGAAGTTCTGCCACTGCCAA |
| Pig | S100A1 | GAACTGGAGACAGCGATGGA | TTGTTACAGGCCACTGTGAGG |
| Mouse | S100A1 | AGAGTGCCATGGAGACCCTC | GCTCAACTGGTCTCCCAGAA |
| Pig, Mouse | GAPDH | AGGGCATCCTGGGCTACACT | TCCACCACCCTGTTGCTGTAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Liufu, S.; Xiao, L.; Chen, B.; Chen, W.; Jiang, J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, H. Multi-Omics Insights into Postnatal Skeletal Muscle Development in Duroc Pigs. Animals 2025, 15, 2715. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182715
Wang K, Li X, Liu X, Liufu S, Xiao L, Chen B, Chen W, Jiang J, Liu Y, Ma H. Multi-Omics Insights into Postnatal Skeletal Muscle Development in Duroc Pigs. Animals. 2025; 15(18):2715. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182715
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kaiming, Xin Li, Xibing Liu, Sui Liufu, Lanlin Xiao, Bohe Chen, Wenwu Chen, Jun Jiang, Yan Liu, and Haiming Ma. 2025. "Multi-Omics Insights into Postnatal Skeletal Muscle Development in Duroc Pigs" Animals 15, no. 18: 2715. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182715
APA StyleWang, K., Li, X., Liu, X., Liufu, S., Xiao, L., Chen, B., Chen, W., Jiang, J., Liu, Y., & Ma, H. (2025). Multi-Omics Insights into Postnatal Skeletal Muscle Development in Duroc Pigs. Animals, 15(18), 2715. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182715




