Molecular Characterization and Pathogenicity Analysis of Novel Goose Parvovirus Isolated in Shandong Province Provide Insights into Viral Epidemic Tendency and Genetic Basis for Cross-Species Transmission and Pathogenicity Attenuation
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Treatment
2.2. Virus Detection
2.3. NPGV Isolation and Purification
2.4. Genome Amplification and Sequencing
2.5. Genetic Evolution and Mutation Analysis
2.6. NGPV Pathogenicity and Serology in Ducklings
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
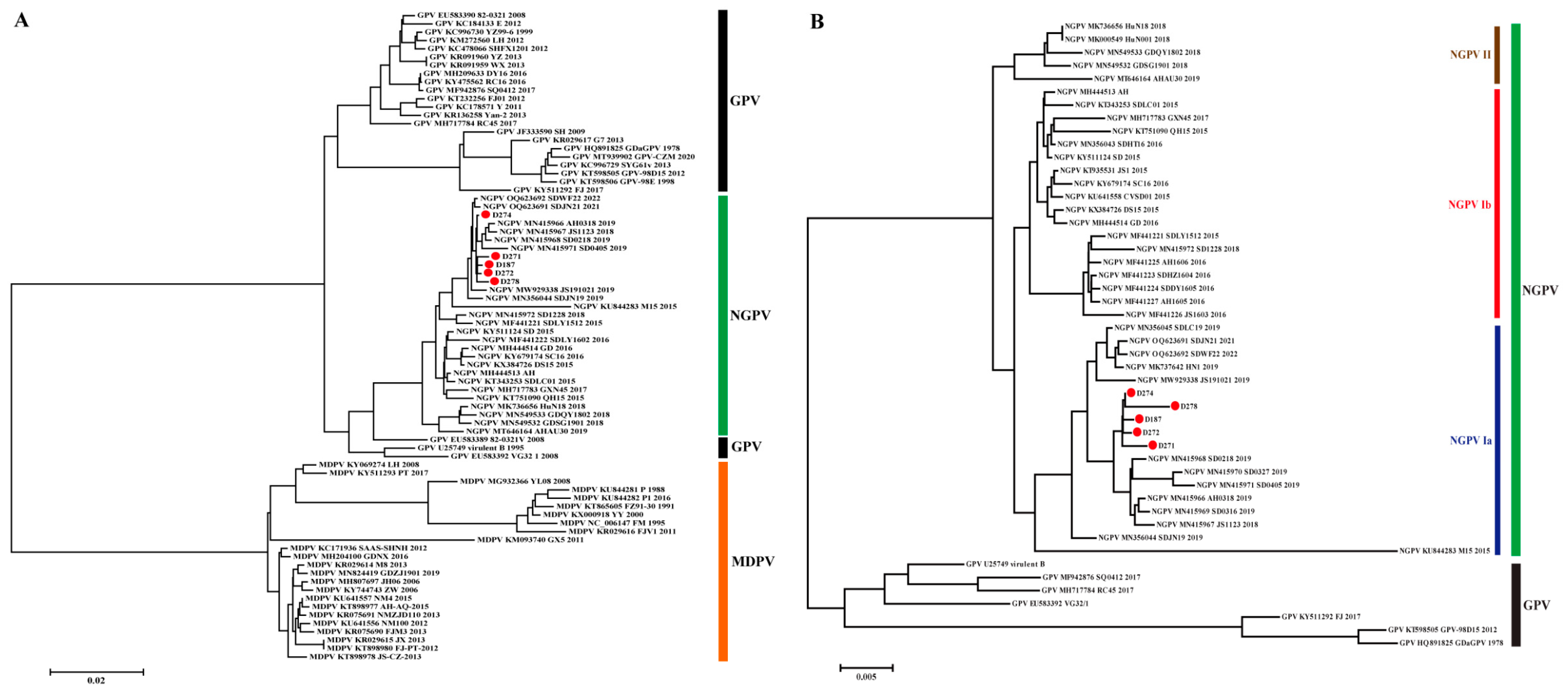
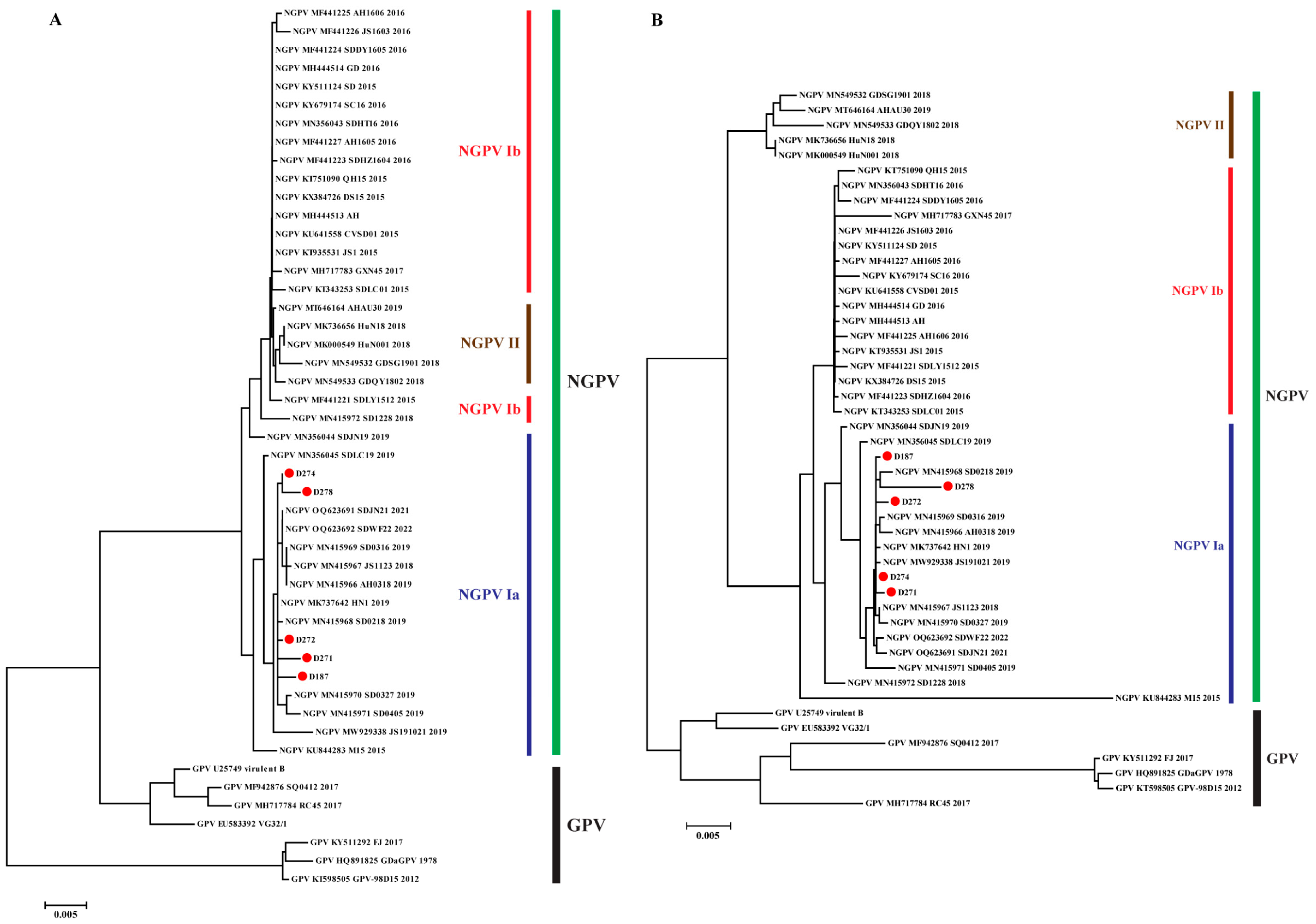
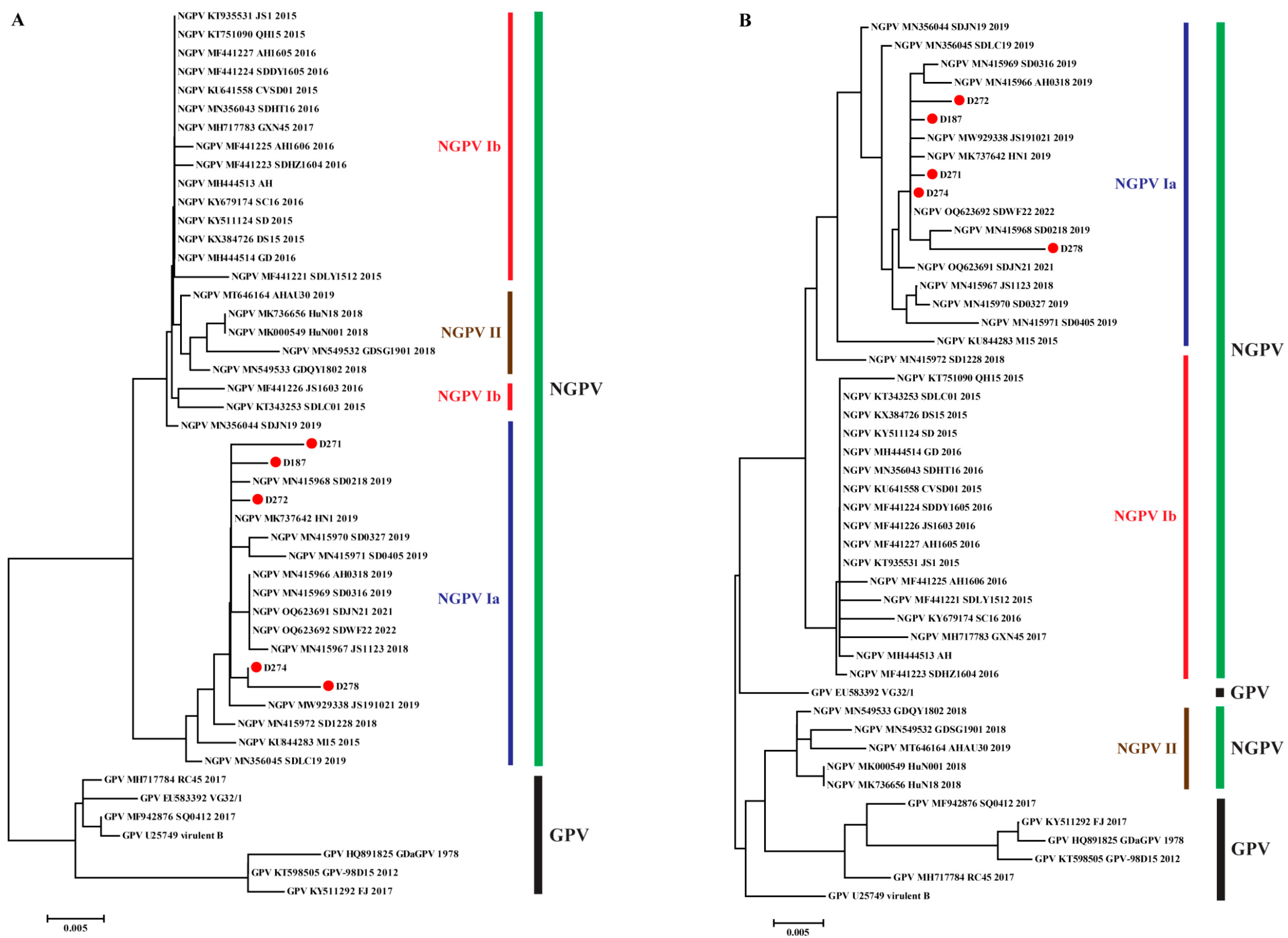
3.1. Isolation and Sequencing of NGPV
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of NGPV Genes
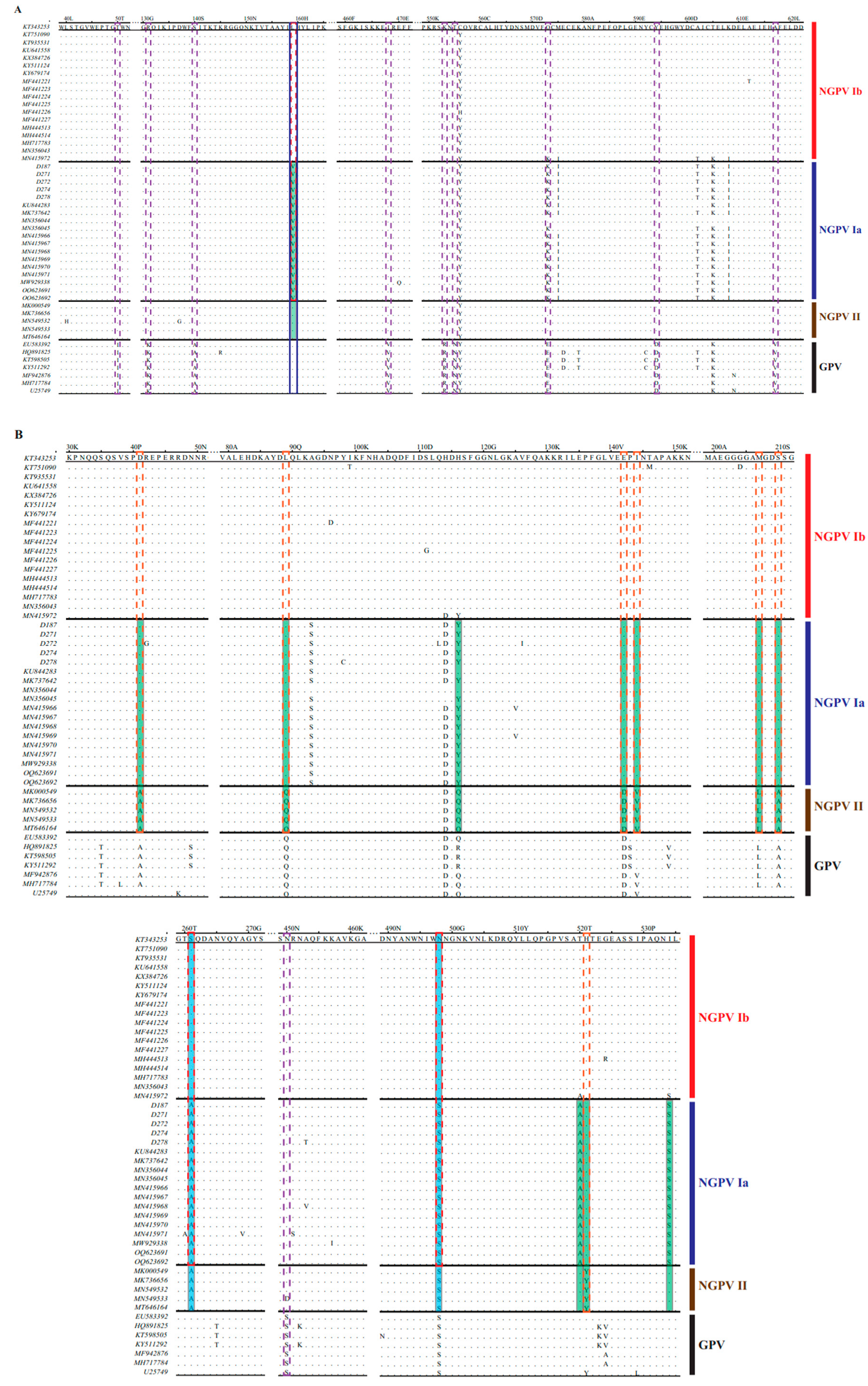
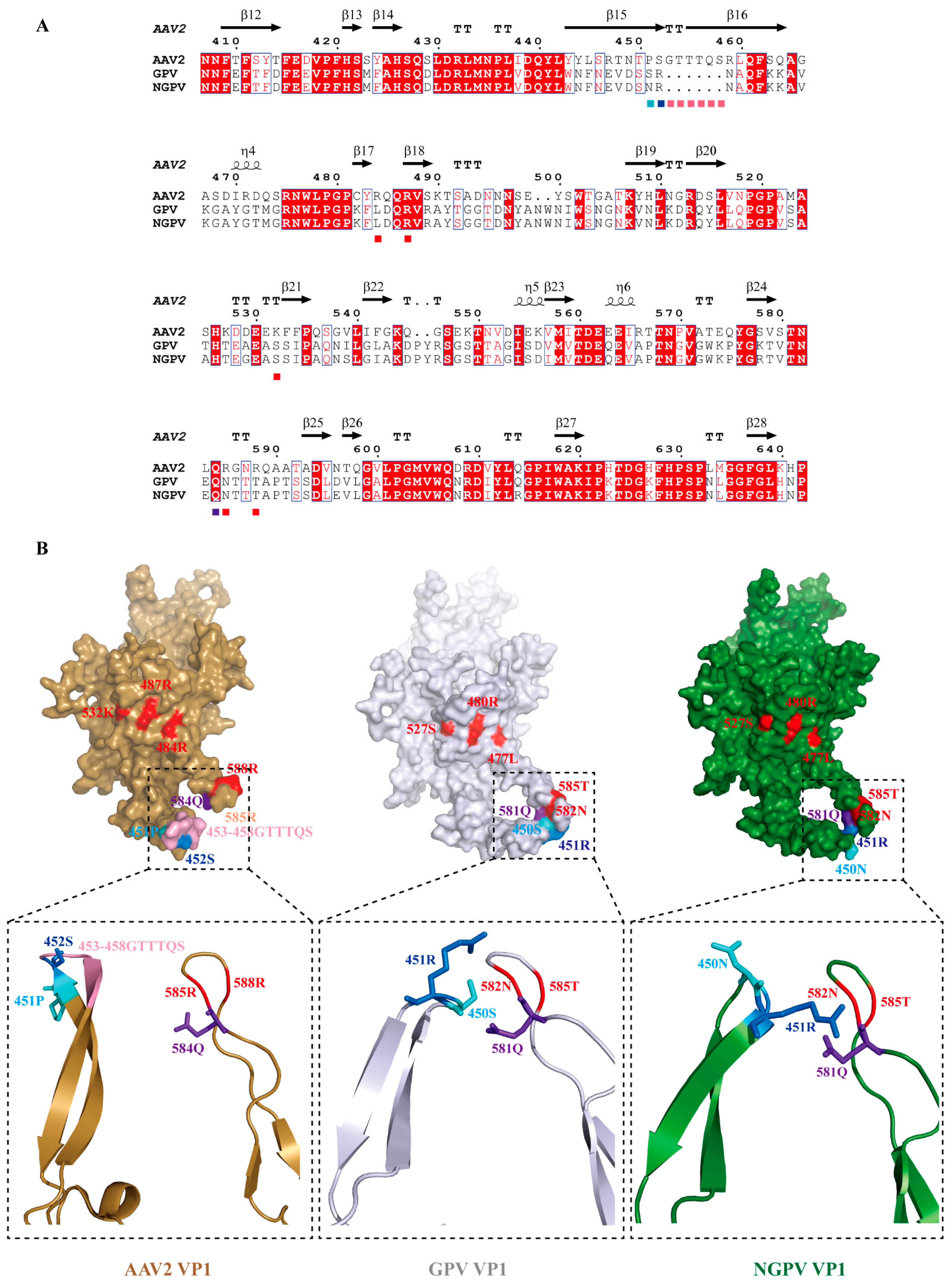
3.3. Mutation Analysis of NGPV Proteins
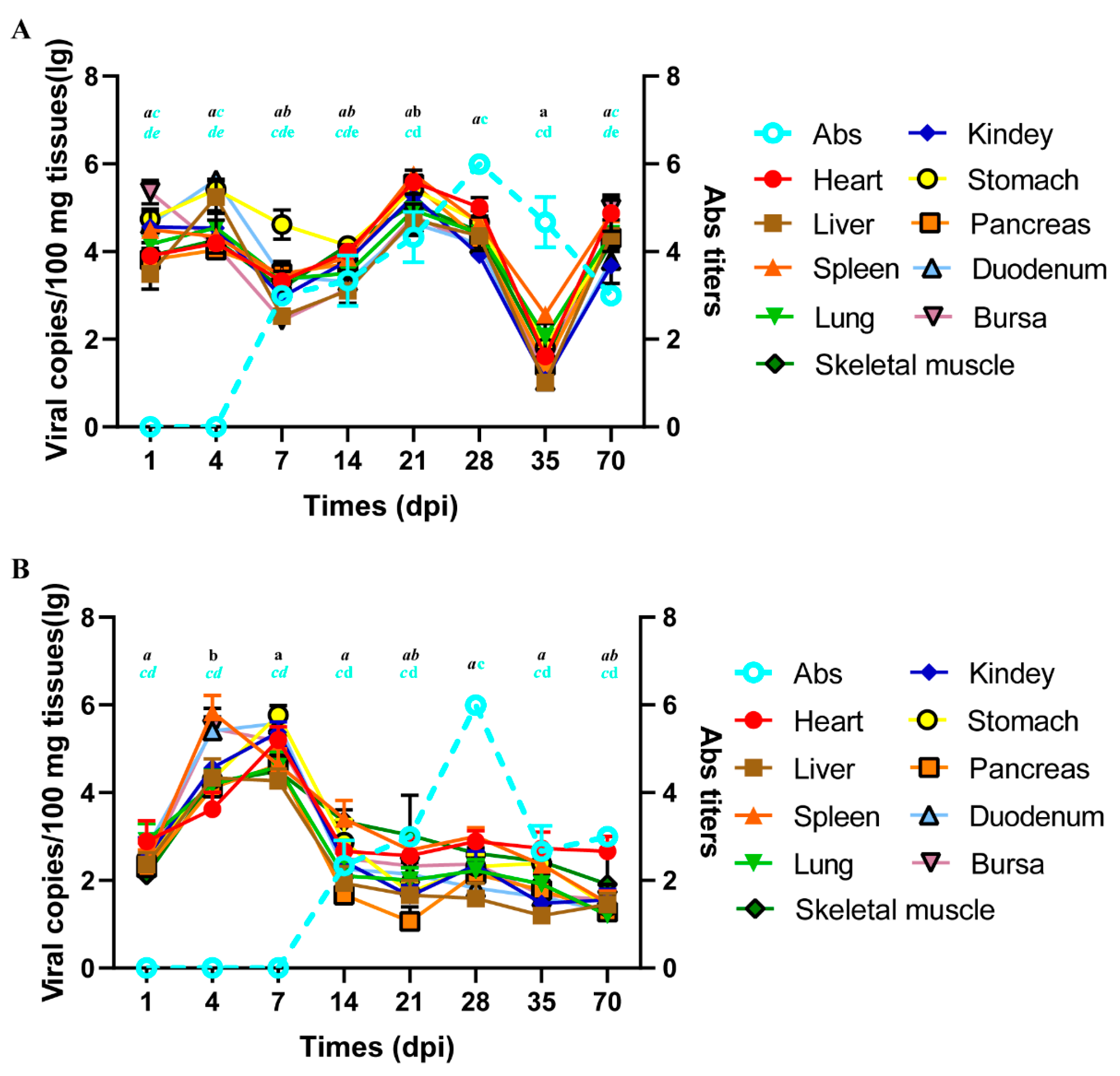
3.4. Pathogenicity of NGPV Isolates to Ducklings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NGPV | Novel goose parvovirus |
| SBDS | Short beak and dwarfism syndrome |
| GPV | Goose parvovirus |
| MDPV | Muscovy duck parvovirus |
| ORF | Open reading frames |
| UTR | Untranslated regions |
| ITR | Inverted terminal repeats |
| MLTF | Major late transcription factor |
| RBS | Rep protein binding site |
| ATF/CREB | Activating transcription factor/cAMP response element binding protein |
| bp | Base pair |
| aa | Amino acid |
| SF3 | Helicase superfamily 3 |
| PLA2 | Phospholipase A2 |
| NLS | Nuclear localization signal |
| Ab | Antibody |
| AGP | Agar gel precipitation |
References
- Lópezbueno, A.; Villarreal, L.P.; Almendral, J.M. Parvovirus Variations in Diseases: A Difference from RNA Viruses? In Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 299, pp. 349–370. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.Y.; Li, W.M.; Gong, X.Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Wang, Y.; Ling, J.Y.; Jiang, Z.W.; Zhu, G.Q.; Li, Y.F. Recombination and Amino Acid Point Mutations in VP3 Exhibited a Synergistic Effect on Increased Virulence of rMDPV. Virulence 2024, 15, 2366874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.L.; Huang, Y.; Wan, C.H.; Fu, G.H.; Qi, B.M.; Cheng, L.F.; Shi, S.H.; Chen, H.M.; Liu, R.C.; Chen, Z.H. Genomic and Pathogenic Analyses of a Muscovy Duck Parvovirus Strain Causing Short Beak and Dwarfism Syndrome without Tongue Protrusion. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 115, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shien, J.H.; Wang, Y.S.; Chen, C.H.; Shieh, H.K.; Hu, C.C.; Chang, P.C. Identification of Sequence Changes in Live Attenuated Goose Parvovirus Vaccine Strains Developed in Asia and Europe. Avian Pathol. 2008, 37, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.S.; Lin, D.F.; Lee, Y.L.; Liao, Y.K.; Tsai, H.J. Infectious Bill Atrophy Syndrome Caused by Parvovirus in a Co-Outbreak with Duck Viral Hepatitis in Ducklings in Taiwan. Avian Dis. 1993, 37, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palya, V.; Zolnai, A.; Benyeda, Z.; Kovács, E.; Kardi, V.; Mató, T. Short Beak and Dwarfism Syndrome in Mule Ducks is Caused by a Distinct Lineage of Goose Parvovirus. Avian Pathol. 2009, 38, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Dou, Y.G.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zheng, X.Q.; Niu, X.Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, X.L.; Diao, Y.X. Isolation and Genomic Characterization of a Duck-Origin GPV-Related Parvovirus from Cherry Valley Ducklings in China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.X.; Ma, X.L.; Sheng, Z.Z.; Qi, L.H.; Liu, C.X.; Wang, D.; Huang, B.; Li, F.; Song, M.X. Identification of Goose-Origin Parvovirus as a Cause of Newly Emerging Beak Atrophy and Dwarfism Syndrome in Ducklings. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1999–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lin, S.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Sun, D.; Lan, J.; Song, S.; Xie, Z.; Jiang, S. The Isolation and Characterization of Novel Goose Parvovirus-Related Virus Reveal the Evolution of Waterfowl Parvovirus. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, e284–e295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.C.; Huang, C.C.; Huang, T.S.; Chang, C.Y.; Lin, Y.J.; Chien, M.S.; Jong, M.H. Phylogenetic Analysis of Classical Swine Fever Viruses Isolated from Taiwan. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 106, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Z.G.; Jiao, A.Q.; Xu, M.L.; Wu, J.Q.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Lu, L.; Jiang, W.C.; Zhu, G.W.; Sun, W.B.; et al. Genetic Diversity and Evolution of Goose Astrovirus in the East of China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e2059–e2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Wang, S.; Cheng, X.X.; Xiao, S.F.; Zhu, X.L.; Lin, F.Q.; Wu, N.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Huang, M.Q.; Zheng, M.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of a Distinct Duck-Origin Goose Parvovirus Causing an Outbreak of Ducking Short Beak and Dwarfism Syndrome in China. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 2407–2416. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matczuk, A.K.; Chmielewska-Władyka, M.; Siedlecka, M.; Bednarek, K.J.; Wieliczko, A. Short Beak and Dwarfism Syndrome in Ducks in Poland Caused by Novel Goose Parvovirus. Animals 2020, 10, 2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.S.; Ahmed, M.E.; Mohamed, S.; Osama, M.; Soad, A.N. Detection of Novel Goose Parvovirus Disease Associated with Short Beak and Dwarfism Syndrome in Commercial Ducks. Animals 2020, 10, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, J.; Liang, J.H.; Luo, Y.H.; Liu, L.; Peng, H.; Li, J.J.; Li, A.Q.; Wei, R.; et al. Isolation, Identification, and Pathogenicity of Two Novel Goose Astrovirus from Goslings with Severe Gout in China. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 194, 106829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Xin, X.G.; Yu, K.Z.; Yang, H.L.; Li, Y.B.; Zhao, P.; Bi, Y.Z. Cloning, Purification, and Biological Characteristics of the Isolated Swine Influenza H3N2 Subtype Virus Isolated from China. Chin. J. Vet. Sci. 2003, 23, 560–563. [Google Scholar]
- Murrell, B.; Wertheim, J.O.; Moola, S.; Weighill, T.; Scheffler, K.; Kosakovsky, P.S.L. Detection of Individual Sites Subject to Episodic Selection Diversification. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002764. [Google Scholar]
- Kosakovsky, P.S.L.; Frost, S.D.W. Not so Different After All: A Comparison of Methods for Detecting Amino Acid Sites Under Selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1208–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrell, B.; Moola, S.; Mabona, A.; Weighill, T.; Sheward, D.; Kosakovsky, P.S.L.; Scheffler, K. FUBAR: A Fast, Unconstrained Bayesian Approximation for Inferring Selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.A.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2-A Multiple Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.L.; Gao, Y.H.; Li, Y.F.; Jiang, Z.W.; Zhu, G.Q.; Wang, X.B. Reproduction and Pathogenesis of Short Beak and Dwarfish Syndrome in Cherry Valley Pekin Ducks Infected with the Rescued Novel Goose Parvovirus. Virulence 2022, 13, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadori, Z.; Stefancsik, R.; Rauch, T.; Kisary, J. Analysis of the Complete Nucleotide Sequences of Goose and Muscovy Duck Parvoviruses Indicates Common Ancestral Origin with Adeno-Associated Virus 2. Virology 1995, 212, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, J.A.; Escalante, C.R.; Yoon-Robarts, M.; Edwards, T.A.; Linden, R.M.; Aggarwal, A.K. Crystal Structure of the SF3 Helicase from Adeno-Associated Virus Type 2. Structure 2003, 11, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astell, C.R.; Mol, C.D.; Anderson, W.F. Structural and Functional Homology of Parvovirus and Papovavirus Polypeptides. J. Gen. Virol. 1987, 68, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niskanen, E.A.; Kalliolinna, O.; Ihalainen, T.O.; Häkkinen, M.; Vihinen-Ranta, M. Mutations in DNA Binding and Transactivation Domains Affect the Dynamics of Parvoviral NS1 Protein. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 11762–11774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, M.Y.; Liu, F.; Chen, S.; Wang, M.S.; Cheng, A.C. The Role of Capsid Proteins in Parvoviral Infections. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Ni, W.J.; Liang, S.M.; Dong, L.H.; Xiang, M.; Cai, Z.; Niu, D.P.; Zhang, Q.H.; Wang, D.H.; Zheng, Y.C.; et al. Vaccination with Span, an Antigen Guided by SARS-CoV-2 S Protein Evolution, Protects Against Challenge with Viral Variants in Mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eabo3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Z.L.; Tang, Z.C.; Han, L.X.; Wei, X.H.; Xie, X.L.; Ren, S.M.; Meng, K.; Liu, Y.Y.; Xu, M.L.; et al. Efficient Identification of Tembusu Virus CTL Epitopes in Inbred HBW/B4 Ducks Using a Novel MHC Class I-Restricted Epitope Screening Scheme. J. Immunol. 2022, 209, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.D.; Liu, T.J.; Chen, Q.G.; Li, D.B.; Zhou, J.; Dong, S.H.; Hu, A.K. Whole Genome Amplification and Genetic Evolution Analysis of a Novel Goose Parvovirus Isolated from Shandong and Guangxi. China Poult. 2024, 46, 44–55. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Sehaar, H.M.; Rust, M.J.; Waarts, B.L.; van der Ende-Metselaar, H.; Kuhn, R.J.; Wilschut, J.; Zhuang, X.W.; Smit, J.M. Characterization of the Early Events in Dengue Virus Cell Entry by Biochemical Assays and Single-Virus Tracking. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12019–12028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Bu, W.S.; Bhatia, S.; Hare, J.; Somasundaram, T.; Azzi, A.; Chapman, M.S. The Atomic Structure of Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV-2), a Vector for Human Gene Therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 96, 10405–10410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.E.; Helenius, A. How Viruses Enter Animal Cells. Science 2004, 304, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, C.; Thompson, G. Canine Parvovirus: The Worldwide Occurrence of Antigenic Variants. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 2043–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Yu, T.F. Immunologic Cross-Reactivity Between Muscovy Duck Parvovirus and Goose Parvovirus on the Basis of Epitope Prediction. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2013, 44, 519–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fan, W.T.; Sun, Z.Y.; Shen, T.T.; Xu, D.N.; Huang, K.H.; Zhou, J.Y.; Song, S.Q.; Yan, L.P. Analysis of Evolutionary Processes of Species Jumping in Waterfowl Parvoviruses. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 14, 421. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.F.; Ma, B.; Wang, J.W. Identification of Linear B Cell Epitopes in Goose Parvovirus Nonstructural Proteins. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2016, 179, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, G.Z.; Ma, H.B.; Luo, M.P.; Gong, F.P.; Li, B.; Wang, G.P.; Mohiuddin, M.; Liao, M.; Yuan, J.F. Identification and Genomic Analysis of Two Novel Duck-Origin GPV-Related Parvoviruses in China. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opie, S.R.; Warrington, K.H.; Agbandje-McKenna, M.; Zolotukhin, S.; Muzyczka, N. Identification of Amino Acid Residues in the Capsid Proteins of Adeno-Associated Virus Type 2 that Contribute to Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan Binding. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 6995–7006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.F.; Sgro, J.Y.; Parrish, C.R. Multiple Amino Acids in the Capsid Structure of Canine Parvovirus Coordinately Determine the Canine Host Range and Specific Antigenic and Hemagglutination Properties. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 6858–6867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindasamy, L.; Hueffer, K.; Parrish, C.R.; Agbandje-McKenna, M. Structures of Host Range-Controlling Regions of the Capsids of Canine and Feline Parvoviruses and Mutants. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 12211–12221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.L.; Jia, J.Y.; Mi, Q.L.; Li, Y.F.; Gao, Y.H.; Zhu, G.Q.; Wang, J.Y. Molecular Characteristics and Phylogenetic Analysis of Novel Goose Parvovirus Strains Associated with Short Beak and Dwarfism Syndrome. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.J.; Yu, Y.L.; Jian, F.C.; Song, W.L.; Yisimayi, A.; Chen, X.S.; Xu, Y.L.; Wang, P.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.L.; et al. Antigenicity and Infectivity Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, e457–e459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, M.S.; Rossmann, M.G. Comparison of Surface Properties of Picornaviruses: Strategies for Hiding the Receptor Site from Immune Surveillance. Virology 1993, 195, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.J.; Crank, M.C.; Shiver, J.; Graham, B.S.; Mascola, J.R.; Nabel, G.J. Next-Generation Influenza Vaccines: Opportunities and Challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulder, P.J.R.; Sewell, A.K.; Lalloo, D.G.; Price, D.A.; Whelan, J.A.; Evans, J.; Taylor, G.P.; Luzzi, G.; Giangrande, P.; Phillips, R.E.; et al. Patterns of Immunodominance in HIV-1-Specific Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Responses in Two Human Histocompatibility Leukocyte Antigen (HLA)-Identical Siblings with HLA-A*0201 Are Influenced by Epitope Mutation. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altenburg, A.F.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; de Vries, R.D. Virus-Specific T Cells as Correlation (Cross-Protective Immunity Against Influenza). Vaccine 2015, 33, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Sequence (5′–3′) | Position | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1F 1): CTYATTGGAGGGTTCGTT | 1–191 | 191 |
| 1R 2): GCATGCGCGTGGTCAACCTAACA | |||
| 2 | 2F: GCATGCCGCGCGGTCAGCCCAAT | 186–1575 | 1390 |
| 2R: AGGGTACAGCATGGRCAATAG | |||
| 3 | 3F: CACCACCGGGAAGACCAACAT | 1526–2487 | 962 |
| 3R: CAGCTTTCAGATTCCGCCACG | |||
| 4 | 4F: GASTGGTATGAGACTGCAGCCG | 2442–3112 | 671 |
| 4R: TYTCCCATCCATTGGGAATCG | |||
| 5 | 5F: GGGGGTGCCGATGGAGTGGGTA | 3048–4228 | 1181 |
| 5R: TTCTGCCACACCATKCCWGGTA | |||
| 6 | 6F: KWTAGCTAAAGATCCATACAGA | 4022–5052 | 1031 |
| 6R: CTTATTGGAGGGTTCGTTCGTTC |
| Name | Collection Time | Collection Location | Duck Variety | Age (d) | Death Time of Embryo | ELD50/ 0.2 mL | Accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D187 | 13 November 2022 | Jinan | Cherry Valley | 10 | 96 h (3th generation) | 10−2.318 | PQ807633 |
| D271 | 11 March 2023 | Heze | Cherry Valley | 18 | 48 h (3th generation) | 10−6.32 | PQ807634 |
| D272 | 11 March 2023 | Yantai | Cherry Valley | 36 | 96 h (4th generation) | 10−3.50 | PQ807635 |
| D274 | 18 March 2023 | Linyi | Cherry Valley | 10 | 72 h (4th generation) | 10−4.42 | PQ807636 |
| D278 | 18 March 2023 | Binzhou | Cherry Valley | 14 | 144 h (3th generation) | 10−6.16 | PQ807637 |
| Protein | Residue | MEME 1) p Value | SLAC 2) p Value | FUBAR 3) Positively Probability | Major | Characteristic | Mutation | Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NS1 | 293 | 0.07 | 0.752 | L | non-polar | Q | polar | |
| 498 | 0 | 0.119 | 0.992 | R | polar | E/K/T | pola | |
| 602 | 0.198 | 0.977 | A | non-polar | T | polar | ||
| VP1 | 93 | 0.07 | 0.702 | A | non-polar | S | polar | |
| 180 | 0.06 | 0.769 | V | non-polar | A | non-polar | ||
| 261 | 0.03 | 0.854 | S | polar | A | non-polar | ||
| 453 | 0.02 | 0.714 | A | non-polar | T/V | polar/non-polar | ||
| 468 | 0 | 0.733 | R | polar | C/H | polar |
| Strain | SDLC19 (Ia) | QH15 (Ib) | AHAU30 (II) | Virulent B (GPV) | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleotide | Amino Acid | Nucleotide | Amino Acid | Nucleotide | Amino Acid | Nucleotide | Amino Acid | |||||||||||||
| G 1) | NS1 | VP1 | NS1 | VP1 | G | NS1 | VP1 | NS1 | VP1 | G | NS1 | VP1 | NS1 | VP1 | G | NS1 | VP1 | NS1 | VP1 | |
| D187 | 99.5 | 99.6 | 99.8 | 99.4 | 99.6 | 97.9 | 98.9 | 98.7 | 98.4 | 97.8 | 97.7 | 98.9 | 97.3 | 98.4 | 97.0 | 94.8 | 96.7 | 96.1 | 96.8 | 97.7 |
| D271 | 99.4 | 99.6 | 99.8 | 99.0 | 99.6 | 97.8 | 98.9 | 98.7 | 98.1 | 97.8 | 97.6 | 98.9 | 97.4 | 98.1 | 97.0 | 94.8 | 96.6 | 96.1 | 96.5 | 97.7 |
| D272 | 99.5 | 99.8 | 99.7 | 99.5 | 99.3 | 97.9 | 99.1 | 98.6 | 98.6 | 97.5 | 97.7 | 99.1 | 97.2 | 98.6 | 96.7 | 94.8 | 96.8 | 96.0 | 97.0 | 97.4 |
| D274 | 99.0 | 99.8 | 99.9 | 99.5 | 99.7 | 97.5 | 99.1 | 98.8 | 98.6 | 98.0 | 97.2 | 99.1 | 97.4 | 98.6 | 97.1 | 94.5 | 96.9 | 96.2 | 97.3 | 97.8 |
| D278 | 99.2 | 99.6 | 99.1 | 98.9 | 98.4 | 97.6 | 98.9 | 98.1 | 97.9 | 96.9 | 97.3 | 98.9 | 96.6 | 97.9 | 95.8 | 94.6 | 96.7 | 95.5 | 96.7 | 96.5 |
| Virus/Genotype/Subtype | NS1 | VP1 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 131 | 140 | 159 | 468 | 553 | 555 | 573 | 594 | 617 | 41 | 89 | 142 | 144 | 207 | 210 | 261 | 450 | 498 | 521 | |
| NPGV 1) | T | R | S | I | K | T | Q/K | Y | A | N/D | ||||||||||
| GPV 2) | I | K | A | V | R | N | E | D | V | S | ||||||||||
| NPGV I | D | L | E | I | M | S | H | |||||||||||||
| NGPV II | A | Q | D | V | L | A | Y | |||||||||||||
| NPGV Ia | V | A | S | |||||||||||||||||
| NGPV Ib | L | S | N | |||||||||||||||||
| NPGV Ia | V | |||||||||||||||||||
| NPGV Ib/II and GPV | L | |||||||||||||||||||
| Items | NS1 | VP1 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 159 | 41 | 89 | 116 | 142 | 144 | 207 | 210 | 261 | 498 | 520 | 521 | 534 | |
| NGPV 1) after 2017 (NPGV Ia/II) | A | S | |||||||||||
| NGPV during 2015–2017 (NPGV Ib) | S | N | |||||||||||
| NPGV Ia | V | D | L | Y/H | E | I | M | S | A | H | S | ||
| NPGV II | L | A | Q | Q | D | V | L | A | T | Y | I | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, L. Molecular Characterization and Pathogenicity Analysis of Novel Goose Parvovirus Isolated in Shandong Province Provide Insights into Viral Epidemic Tendency and Genetic Basis for Cross-Species Transmission and Pathogenicity Attenuation. Animals 2025, 15, 2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182696
Huang Y, Wang Y, Ding Y, Wang J, Gao X, Zhang L. Molecular Characterization and Pathogenicity Analysis of Novel Goose Parvovirus Isolated in Shandong Province Provide Insights into Viral Epidemic Tendency and Genetic Basis for Cross-Species Transmission and Pathogenicity Attenuation. Animals. 2025; 15(18):2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182696
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yueyan, Yuzhou Wang, Yaling Ding, Junkun Wang, Xiaojie Gao, and Lin Zhang. 2025. "Molecular Characterization and Pathogenicity Analysis of Novel Goose Parvovirus Isolated in Shandong Province Provide Insights into Viral Epidemic Tendency and Genetic Basis for Cross-Species Transmission and Pathogenicity Attenuation" Animals 15, no. 18: 2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182696
APA StyleHuang, Y., Wang, Y., Ding, Y., Wang, J., Gao, X., & Zhang, L. (2025). Molecular Characterization and Pathogenicity Analysis of Novel Goose Parvovirus Isolated in Shandong Province Provide Insights into Viral Epidemic Tendency and Genetic Basis for Cross-Species Transmission and Pathogenicity Attenuation. Animals, 15(18), 2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182696





