The Results After One Year of an Experimental Protocol Aimed at Reducing Paratuberculosis in an Intensive Dairy Herd
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Farm
2.2. Samples and Data Collection
2.3. Serology
2.4. IS900 qPCR
2.5. Digital PCR (dPCR)
2.6. Bacteriology
2.7. Whole Genome Sequencing
2.8. Statistical Analysis of Apparent Seroprevalences
3. Results
3.1. First Inspection of the Herd for the Evaluation of the Risk of Transmission of Paratuberculosis
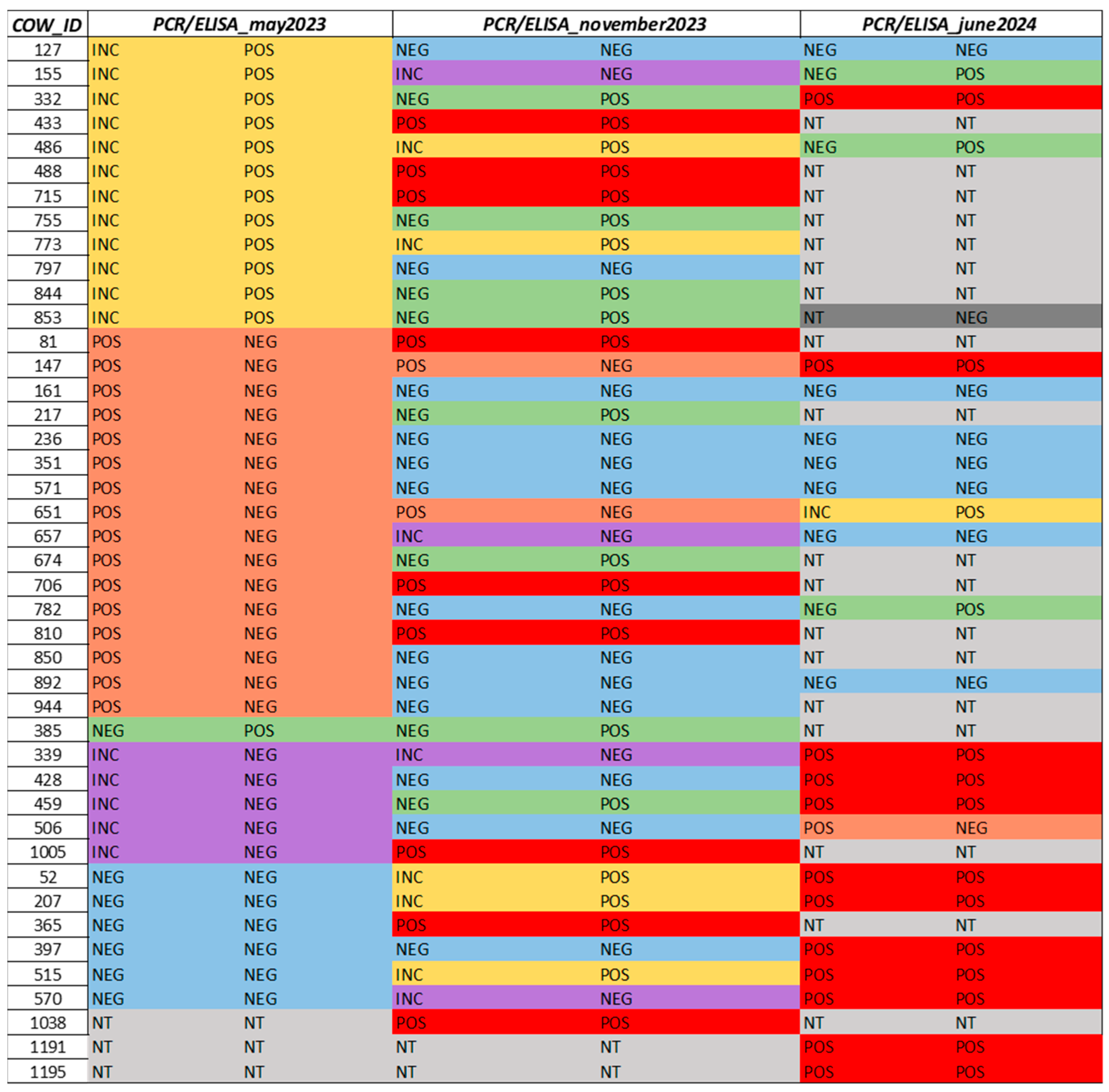
3.2. First Sampling
3.3. Second Sampling
3.4. Second Inspection of the Herd for the Evaluation of the Risk of Transmission of Paratuberculosis
3.5. Third Sampling
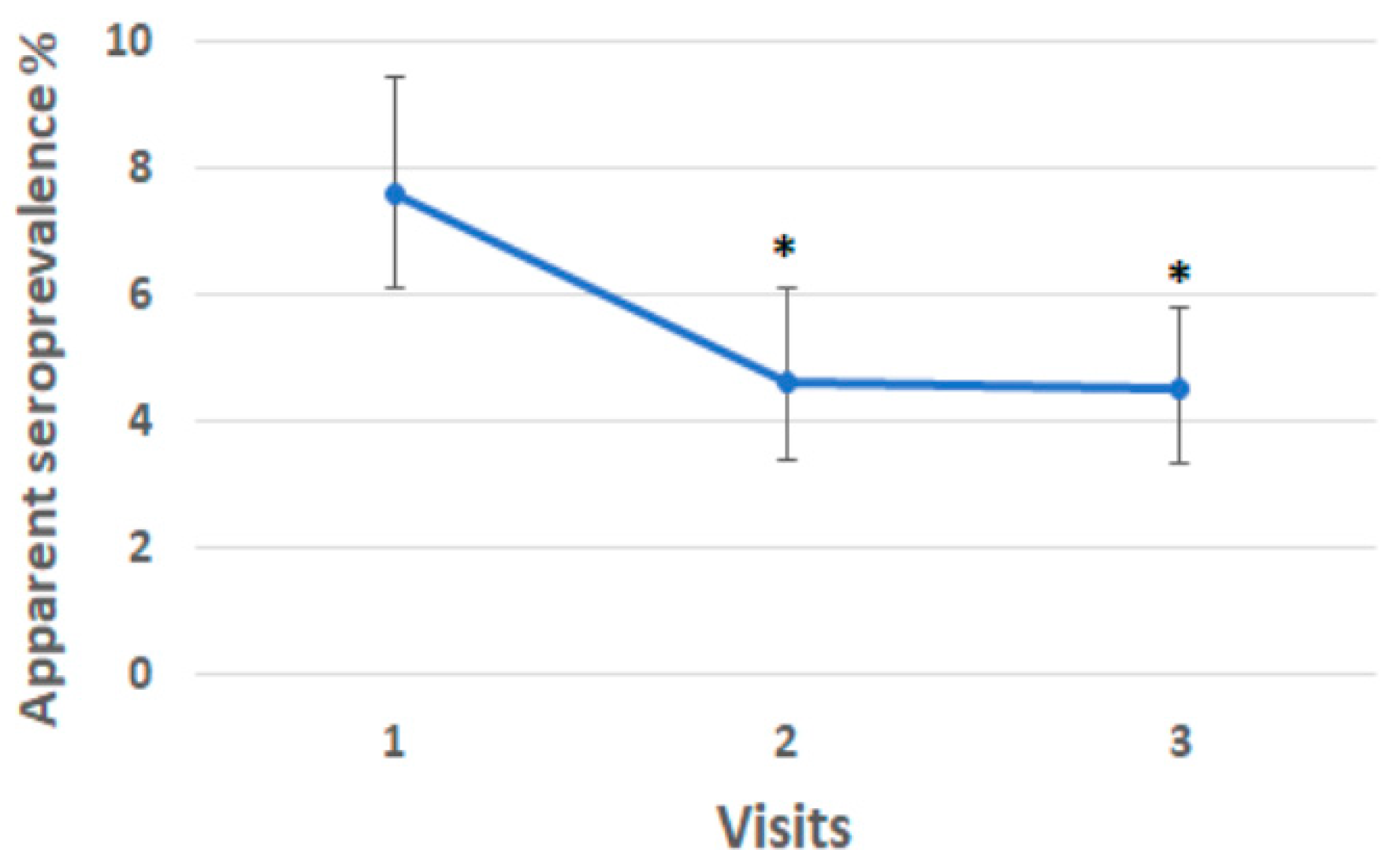
3.6. Paratuberculosis Apparent Seroprevalence During the Study
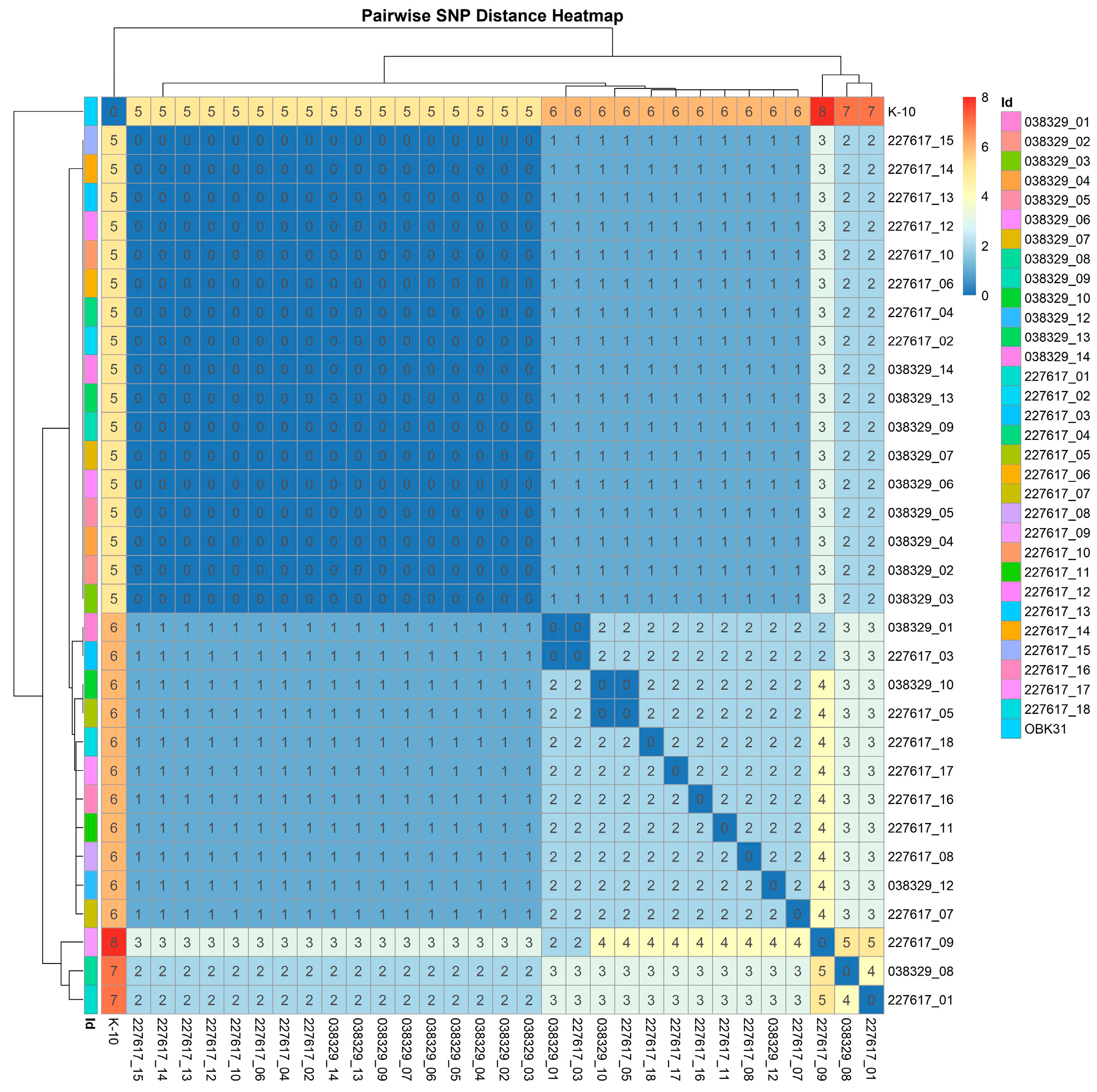
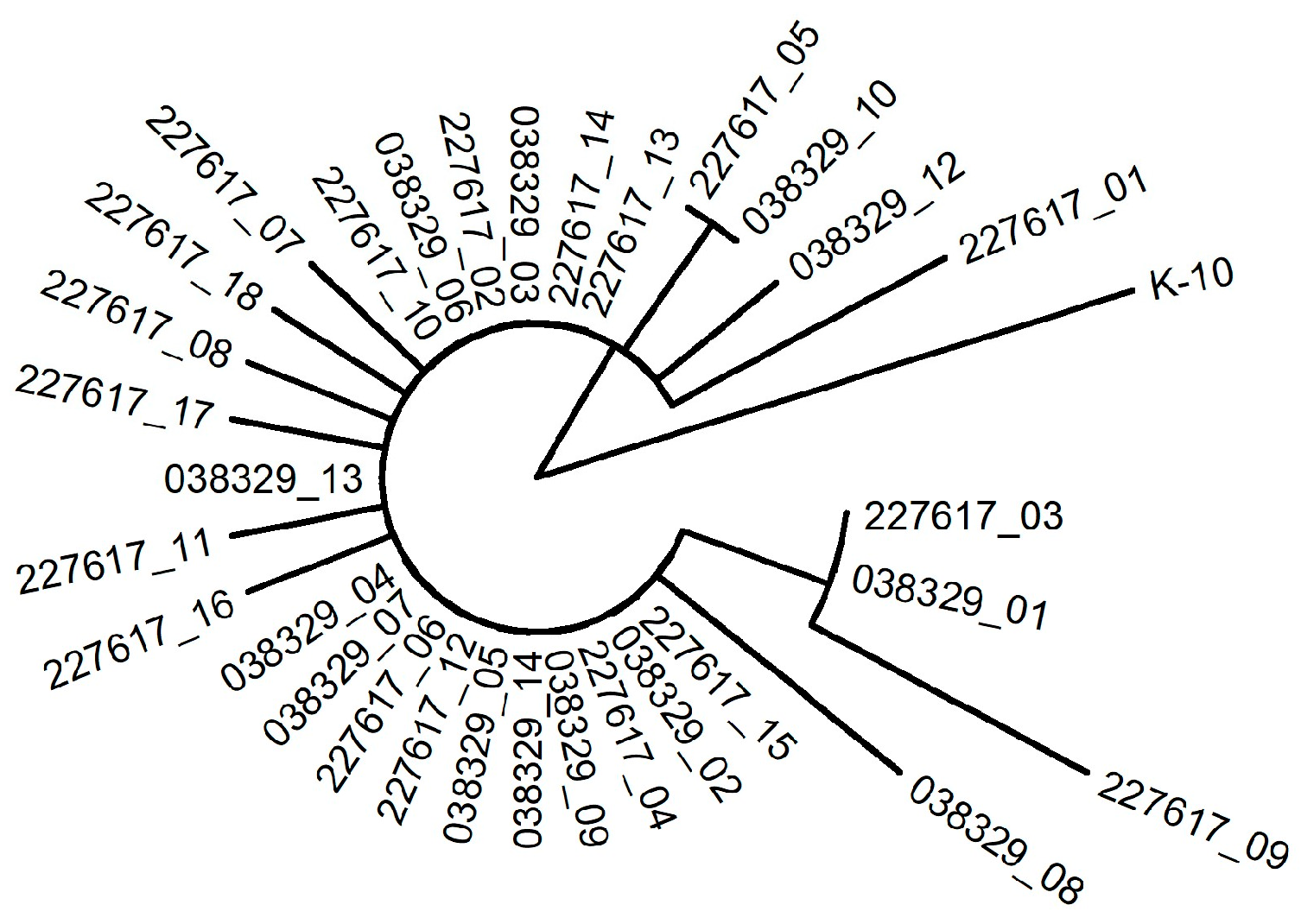
3.7. Whole Genome Sequencing Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| MAP | Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| dPCR | Digital polymerase chain reaction |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| WGS | Whole genome sequencing |
| Cq | Cycle of quantification |
References
- Rasmussen, P.; Barkema, H.W.; Osei, P.P.; Taylor, J.; Shaw, A.P.; Conrady, B.; Chaters, G.; Muñoz, V.; Hall, D.C.; Apenteng, O.O.; et al. Global losses due to dairy cattle diseases: A comorbidity-adjusted economic analysis. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 6945–6970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Animal Health and Welfare (AHAW); More, S.; Bicout, D.; Bøtner, A.; Butterworth, A.; Calistri, P.; Depner, K.; Edwards, S.; Garin-Bastuji, B.; Good, M.; et al. Assessment of listing categorisation of animal diseases within the framework of the Animal Health Law (Regulation (EU) No 2016/429): Paratuberculosis. Efsa J. 2017, 15, e04957. [Google Scholar]
- Idris, S.M.; Eltom, K.H.; Okuni, J.B.; Ojok, L.; Elmagzoub, W.A.; Wahed, A.A.E.; Eltayeb, E.; Gameel, A.A. Paratuberculosis: The hidden killer of small ruminants. Animals 2022, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, M. Mycobacterium avium paratuberculosis: A disease burden on the dairy industry. Animals 2020, 10, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savi, R.; Ricchi, M.; Cammi, G.; Garbarino, C.; Leo, S.; Pongolini, S.; Arrigoni, N. Survey on the presence of Mycobacterium avium subsp paratuberculosis in ground beef from an industrial meat plant. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 177, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecteau, M.E. Paratuberculosis in Cattle. Vet. Clin. Food Anim. Pract. 2018, 34, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittington, R.; Donat, K.; Weber, M.F.; Kelton, D.; Nielsen, S.S.; Eisenberg, S.; Arrigoni, N.; Juste, R.; Sáez, J.L.; Dhand, N.; et al. Control of paratuberculosis: Who, why and how. A review of 48 countries. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meles, D.K.; Mustofa, I.; Khairullah, A.R.; Wurlina, W.; Mustofa, R.I.; Suwasanti, N.; Akintunde, A.O.; Putra, S.W.; Kusala, M.K.J.; Moses, I.B.; et al. A comprehensive review of paratuberculosis in animals and its implications for public health. Open Vet. J. 2024, 14, 2731–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH). Manual of Standard Diagnostic Test and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals; World Organisation for Animal Health: Paris, France, 2024; Chapter 3. [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney, R.W. Pathogenesis of Paratuberculosis. Vet. Clin. Food Anim. Pract. 2011, 27, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, R.J.; Marshall, D.J.; Nicholls, P.J.; Marsh, I.B.; Reddacliff, L.A. Survival and Dormancy of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in theEnvironment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 2989–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britton, L.E.; Cassidy, J.P.; O’Donovan, J.; Gordon, S.V.; Markey, B. Potential application of emerging diagnostic techniques to the diagnosis of bovine Johne’s disease (paratuberculosis). Vet. J. 2016, 209, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slater, N.; Mitchell, R.M.; Whitlock, R.H.; Fyock, T.; Pradhan, A.K.; Knupfer, E.; Schukken, Y.H.; Louzoun, Y. Impact of the shedding level on transmission of persistent infections in Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis (MAP). Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow, C.T.; Alvarez, B.L. Mycobacterium paratuberculosis zoonosis is a One Health emergency. Ecohealth 2022, 19, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitlock, R.H.; Sweeney, R.W.; Fyock, T.L.; Smith, J. MAP Super-Shedders: Another factor in the control of Johne’s disease. In Proceedings of the 8th International Colloquium on Paratuberculosis, Copenhagen, Denmark, 14–17 August 2005; Volume 8, p. 42. [Google Scholar]
- Kralik, P.; Pribylova-Dziedzinska, R.; Kralova, A.; Kovarcik, K.; Slana, I. Evidence of passive fecal shedding of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in a Limousin cattle herd. Vet. J. 2014, 201, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitlock, R.H.; Gardner, I.A.; Mangold, B.L.; Smith, J.; Sweeney, R.W. Johne’s Disease: Mycobacterium paratuberculosis Super-shedders: Detection and Contribution to Passive Shedding (False-posive Fecal Cultures). Am. Assoc. Bov. Pract. 2006, 39, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, A.K.; Mitchell, R.M.; Kramer, A.J.; Zurakowski, M.J.; Fyock, T.L.; Whitlock, R.H.; Smith, J.M.; Hovingh, E.; Van Kessel, J.A.; Karns, J.S.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in a longitudinal study of three dairy herds. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donat, K.; Einax, E.; Rath, D.; Klassen, A. Successful Control of Mycobacterium avium Subspecies paratuberculosis Infection in a Dairy Herd within a Decade—A Case Study. Animals 2024, 14, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, W.G.; Porter, C.A.; Hawkins, N.; Schofield, M.J.; Pollock, J.M. Johne’s disease: A successful eradication programme in a dairy goat herd. Vet. Rec. 2018, 182, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, S.; Giorgio, G.; Leo, S.; Arrigoni, N.; Garbarino, C.; Ricchi, M. Validation of IS900- qPCR assay to assess the presence of Mycobacterium avium subs. paratuberculosis in fecal samples according to the OIE procedure. Prev. Vet. Med. 2022, 208, 105732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, S.; Cortimiglia, C.; Filippi, A.; Palladini, G.; Garbarino, C.; Massella, E.; Ricchi, M. Validation of digital PCR assay for the quantification of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in bovine feces according to the ISO 20395:2019. J. Microbiol. Methods 2023, 213, 106825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricchi, M.; Bertasio, C.; Boniotti, M.B.; Vicari, N.; Russo, S.; Tilola, M.; Bellotti, M.A.; Bertasi, B. Comparison among the quantification of bacterial pathogens by qPCR, dPCR, and cultural methods. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricchi, M.; Barbieri, G.; Taddei, R.; Belletti, G.L.; Carra, E.; Cammi, G.; Garbarino, C.A.; Arrigoni, N. Effectiveness of combination of Mini-and Microsatellite loci to sub-type Mycobacterium avium subsp paratuberculosis Italian type C isolates. Bmc Vet. Res. 2011, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzoni, L.; Scaltriti, E.; Russo, S.; Pongolini, S.; Garbarino, C.; Leo, S.; Arrigoni, N.; Ricchi, M. Transmission patterns of a Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis clone within a single heard investigated by Whole Genome Sequencing. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 263, 109272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allam, A.; Kalnis, P.; Solovyev, V. Karect: Accurate correction of substitution, insertion and deletion errors for next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3421–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; Von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R.; Teeling, E. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G. Using ggtree to visualize data on tree-like structures. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 69, e96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, K. Genetic diversity of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis and the influence of strain type on infection and pathogenesis: A review. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conferenza Permanente per i Rapporti tra lo Stato, le Regioni e le Province Autonome di Trento e Bolzano. 2013, pp. 1–22. Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/atto/serie_generale/caricaDettaglioAtto/originario?atto.dataPubblicazioneGazzetta=2013-11-19&atto.codiceRedazionale=13A09123&elenco30giorni=false (accessed on 3 September 2025).
- Conferenza Permanente Per i Rapporti tra lo Stato, le Regioni e le Province Autonome di Trento e Bolzano. 2023, pp. 1–22. Available online: https://www.statoregioni.it/it/conferenza-stato-regioni/sedute-2023/seduta-del-19042023/verbale-della-seduta-del-19042023/ (accessed on 3 September 2025).
- Liening-Ewert, T.; Tichy, A.; Mader, C.; Spergser, J.; Sodoma, E.; Ortner, P.; Kössler, J.; Khol, J.L. Management and housing factors associated with paratuberculosis-positive herds in small structured alpine cattle husbandry. Prev. Vet. Med. 2023, 218, 105999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpellini, R.; Giacometti, F.; Savini, F.; Arrigoni, N.; Garbarino, C.A.; Carnevale, G.; Mondo, E.; Piva, S. Bovine paratuberculosis: Results of a control plan in 64 dairy farms in a 4-year period. Prev. Vet. Med. 2023, 215, 105923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; De Leo, G.A.; Pongolini, S.; Natalini, S.; Zarenghi, L.; Ricchi, M.; Bolzoni, L. The Potential Role of Direct and Indirect Contacts on Infection Spread in Dairy Farm Networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, N.L.; McAloon, C.G.; Gavey, L.; Mee, J.F. Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis infection in cattle–a review in the context of seasonal pasture-based dairy herds. Ir. Vet. J. 2022, 75, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.A.; Plain, K.M.; Toribio, J.-A.L.M.L.; Whittington, R.J. Evaluation of a test-and-cull strategy to control bovine paratuberculosis based on the detection of Mycobacterium avium ssp. paratuberculosis DNA using the HT-J fecal PCR test. J. Dairy Sci. 2025, 108, 8767–8786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Gonzalez, N.; Fourichon, C.; Blanquefort, P.; Delafosse, A.; Joly, A.; Ngwa-Mbot, D.; Biet, F.; Boichard, D.; Schibler, L.; Journaux, L.; et al. Longitudinal study of Mycobacterium avium ssp. paratuberculosis fecal shedding patterns and concurrent serological patterns in naturally infected dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 9117–9137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dane, H.; Stewart, L.D.; Grant, I.R. Culture of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis: Challenges, limitations and future prospects. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxac017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schukken, Y.H.; Whitlock, R.H.; Wolfgang, D.; Grohn, Y.; Beaver, A.; VanKessel, J.; Zurakowski, M.; Mitchell, R. Longitudinal data collection of Mycobacterium avium subspecies Paratuberculosis infections in dairy herds: The value of precise field data. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RH Whitlock Environment of the adult cow. In Proceedings of the the 2nd New Horizons in Johne’s Disease Control Workshop, 10th International Colloquium on Paratuberculosis, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 9–14 August 2009; University of Minnesota: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2009.
- Smith, R.L.; Schukken, Y.H.; Pradhan, A.K.; Smith, J.M.; Whitlock, R.H.; Van Kessel, J.S.; Wolfgang, D.R.; Grohn, Y.T. Environmental contamination with Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in endemically infected dairy herds. Prev. Vet. Med. 2011, 102, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orloski, K.; Robbe-Austerman, S.; Stuber, T.; Hench, B.; Schoenbaum, M. Whole genome sequencing of Mycobacterium bovis isolated from livestock in the United States, 1989–2018. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| qPCR | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | MAY 2023 | (b) | NOVEMBER 2023 | |||||||
| Pos (%) | Neg (%) | Inc 1 (%) | Total | Pos (%) | Neg (%) | Inc (%) | Total | |||
| ELISA | Pos | 33 (42.3) | 26 (33.3) | 19 (24.4) | 78 | 14 (31.1) | 23 (51.1) | 8 (17.8) | 45 | |
| Neg | 33 (3.5) | 753 (80.0) | 155 (16.5) | 941 | 13 (1.4) | 883 (95.5) | 29 (3.1) | 925 | ||
| Total | 66 (6.5) | 779 (76.4) | 174 (17.1) | 1019 | 27 (2.8) | 906 (93.4) | 37 (3.8) | 970 | ||
| (a) | MAY 2023 | (b) | NOVEMBER 2023 | (c) | JUNE 2024 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COW_ID | CULT | SHED_CLASS | COPIES/g | COW_ID | CULT | SHED_CLASS | COPIES/g | COW_ID | CULT | SHED_CLASS | COPIES/g | COW_ID | CULT | SHED_CLASS | COPIES/g | |||
| 81 | + | N.A. | 674 | + | 1.84 × 104 | 27 | - | 5.84 × 104 | 52 | + | HS | 7.89 × 106 | ||||||
| 100 | + | 1.99 × 104 | 677 | - | 2.10 × 104 | 81 | + | N.A. | 147 | + | HS | 4.16 × 106 | ||||||
| 131 | - | HS * | 5.37 × 106 | 706 | + | 2.09 × 104 | 147 | + | 2.01 × 104 | 207 | + | HS | 1.46 × 106 | |||||
| 147 | + | HS | 4.18 × 105 | 736 | + | N.A. | 187 | + | 2.09 × 104 | 332 | + | N.A. | ||||||
| 157 | + | HS | 3.05 × 106 | 737 | + | HS | 1.00 × 105 | 260 | + | 6.01 × 104 | 339 | + | 3.75 × 104 | |||||
| 161 | - | HS | 1.43 × 105 | 740 | + | HS | 2.63 × 105 | 287 | + | N.A. | 397 | + | HS | 3.70 × 106 | ||||
| 163 | - | HS | 1.41 × 105 | 741 | + | SS | 6.32 × 107 | 365 | + | HS | 1.08 × 106 | 428 | + | N.A. | ||||
| 217 | + | HS | 5.09 × 105 | 747 | + | 3.97 × 104 | 433 | + | N.A. | 459 | + | 3.67 × 104 | ||||||
| 236 | - | 5.96 × 104 | 748 | - | N.A. | 453 | - | 2.05 × 104 | 506 | - | N.A. | |||||||
| 252 | + | N.A. | 752 | + | 2.13 × 104 | 488 | + | HS | 2.95 × 106 | 515 | - | 1.87 × 104 | ||||||
| 351 | - | 8.15 × 104 | 753 | - | HS | 1.69 × 105 | 603 | + | N.A. | 570 | + | N.A. | ||||||
| 357 | + | HS | 2.44 × 106 | 754 | - | 4.25 × 104 | 651 | - | 6.23 × 104 | 1191 | - | 5.56 × 104 | ||||||
| 471 | + | HS | 1.03 × 105 | 759 | + | 1.87 × 104 | 706 | + | HS | 2.08 × 105 | 1195 | + | 8.03 × 104 | |||||
| 473 | + | N.A. | 769 | + | HS | 5.05 × 105 | 715 | - | 2.03 × 104 | |||||||||
| 485 | + | SS ** | 7.65 × 107 | 775 | + | HS | 5.84 × 105 | 791 | - | N.A. | ||||||||
| 487 | + | HS | 3.17 × 105 | 776 | + | HS | 1.11 × 105 | 810 | + | N.A. | ||||||||
| 490 | + | HS | 1.80 × 105 | 782 | - | N.A. | 839 | + | N.A. | |||||||||
| 492 | + | 1.75 × 104 | 783 | - | N.A. | 841 | + | HS | 1.80 × 105 | |||||||||
| 493 | - | 2.08 × 104 | 800 | + | 4.30 × 104 | 877 | - | 2.15 × 104 | ||||||||||
| 494 | + | HS | 2.45 × 106 | 808 | + | 2.15 × 104 | 906 | - | 5.98 × 104 | |||||||||
| 495 | + | HS | 1.04 × 105 | 810 | - | N.A. | 1005 | + | HS | 1.60 × 105 | ||||||||
| 496 | - | 2.08 × 104 | 813 | + | HS | 6.15 × 105 | 1038 | - | HS | 5.89 × 105 | ||||||||
| 499 | + | 2.06 × 104 | 836 | + | SS | 1.17 × 107 | 1053 | + | N.A. | |||||||||
| 559 | + | N.A. | 837 | + | SS | 5.93 × 107 | 1066 | + | 4.07 × 104 | |||||||||
| 571 | - | 4.00 × 104 | 846 | + | HS | 4.30 × 105 | 1074 | + | HS | 1.03 × 105 | ||||||||
| 591 | - | N.A. | 849 | + | N.A. | 1130 | - | N.A. | ||||||||||
| 600 | + | SS | 2.76 × 107 | 850 | + | N.A. | 1133 | + | N.A. | |||||||||
| 608 | + | 3.67 × 104 | 851 | + | 5.53 × 104 | |||||||||||||
| 644 | + | 4.16 × 104 | 892 | - | 2.12 × 104 | |||||||||||||
| 651 | - | N.A. | 928 | + | 2.08 × 104 | |||||||||||||
| 657 | - | N.A. | 944 | - | HS | 2.40 × 105 | ||||||||||||
| 668 | + | HS | 1.59 × 105 | 981 | - | N.A. | ||||||||||||
| 670 | + | 6.30 × 104 | 987 | + | SS | 1.33t × 107 | ||||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Filippi, A.; Ventura, G.; Lamontanara, A.; Orrù, L.; Ostanello, F.; Frontoni, R.; Mazzera, L.; Tuccia, E.; Ricchi, M.; Garbarino, C. The Results After One Year of an Experimental Protocol Aimed at Reducing Paratuberculosis in an Intensive Dairy Herd. Animals 2025, 15, 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182695
Filippi A, Ventura G, Lamontanara A, Orrù L, Ostanello F, Frontoni R, Mazzera L, Tuccia E, Ricchi M, Garbarino C. The Results After One Year of an Experimental Protocol Aimed at Reducing Paratuberculosis in an Intensive Dairy Herd. Animals. 2025; 15(18):2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182695
Chicago/Turabian StyleFilippi, Anita, Giordano Ventura, Antonella Lamontanara, Luigi Orrù, Fabio Ostanello, Riccardo Frontoni, Laura Mazzera, Edoardo Tuccia, Matteo Ricchi, and Chiara Garbarino. 2025. "The Results After One Year of an Experimental Protocol Aimed at Reducing Paratuberculosis in an Intensive Dairy Herd" Animals 15, no. 18: 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182695
APA StyleFilippi, A., Ventura, G., Lamontanara, A., Orrù, L., Ostanello, F., Frontoni, R., Mazzera, L., Tuccia, E., Ricchi, M., & Garbarino, C. (2025). The Results After One Year of an Experimental Protocol Aimed at Reducing Paratuberculosis in an Intensive Dairy Herd. Animals, 15(18), 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182695





