Cross-Modal Complementarity Learning for Fish Feeding Intensity Recognition via Audio–Visual Fusion
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset Acquisition and Materials
2.2. Audio and Visual Preprocessing
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Overall Architecture
2.3.2. Feature Extraction
2.3.3. Cross-Modal Enhancement via Low-Rank Bilinear Pooling
2.3.4. Adaptive Attention Fusion
2.3.5. Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Overall Performance Comparison
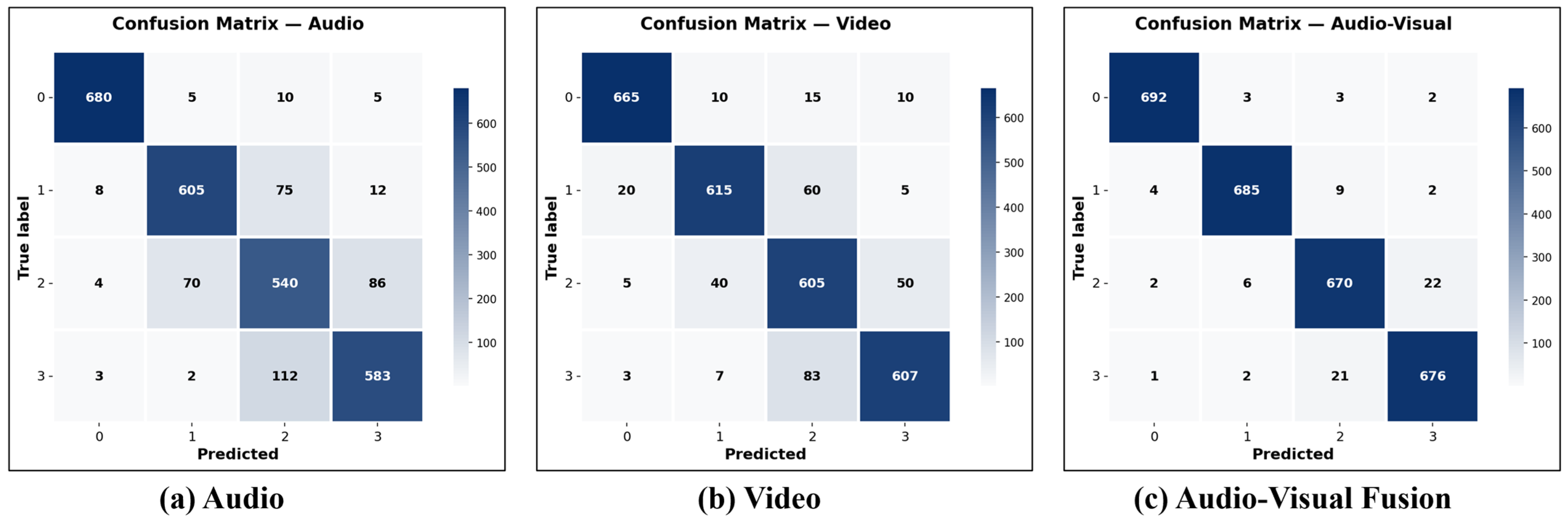
3.2.1. Audio-Based Method Performance
3.2.2. Video-Based Method Performance
3.2.3. Audio–Visual-Based Method Performance
3.2.4. Ablation Study
4. Discussion
4.1. Key Findings and Technical Contributions
4.2. Limitations and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mandal, A.; Ghosh, A.R. Role of artificial intelligence (AI) in fish growth and health status monitoring: A review on sustainable aquaculture. Aquac. Int. 2024, 32, 2791–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Shao, W.H.; Yi, W.J.; Zhang, E. A review of conservation status of freshwater fish diversity in China. J. Fish Biol. 2024, 104, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljehani, F.; N’Doye, I.; Laleg-Kirati, T.M. Feeding control and water quality monitoring on bioenergetic fish growth modeling: Opportunities and challenges. Aquac. Eng. 2024, 109, 102511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, D.; Wang, W. Fish Tracking, Counting, and Behaviour Analysis in Digital Aquaculture: A Comprehensive Survey. Rev. Aquac. 2025, 17, e13001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, Z.; Wu, S.; Miao, Z.; Du, L.; Duan, Y. Automatic recognition methods of fish feeding behavior in aquaculture: A review. Aquaculture 2020, 528, 735508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Hao, J.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X. Application of computer vision in fish intelligent feeding system—A review. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, B.; Sun, X.; Hong, Q.; Duan, Q. Intelligent fish feeding based on machine vision: A review. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 231, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Xu, D.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Sun, C.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y. Evaluation of fish feeding intensity in aquaculture using a convolutional neural network and machine vision. Aquaculture 2019, 507, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Mei, S.; Duan, Y.; Li, D.; Chen, Y. A dual attention network based on efficientNet-B2 for short-term fish school feeding behavior analysis in aquaculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 187, 106316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Liu, J.; An, D.; Wei, Y. Dynamic feeding method for aquaculture fish using multi-task neural network. Aquaculture 2022, 551, 737913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Fang, X.; Song, L.; Li, D.; Chen, Y. Computer vision models in intelligent aquaculture with emphasis on fish detection and behavior analysis: A review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 2785–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Du, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Du, L. Recent advances in acoustic technology for aquaculture: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2024, 16, 357–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, U.; Li, D.; Du, Z.; Akhter, M.; Mushtaq, Z.; Qureshi, M.F.; Rehman, H.A.U. Augmenting aquaculture efficiency through involutional neural networks and self-attention for oplegnathus punctatus feeding intensity classification from log mel spectrograms. Animals 2024, 14, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Sun, J.; Lian, G.; Chen, T.; Plumbley, M.D.; Li, D.; Wang, W. Fish feeding intensity recognition in aquaculture: A new audio dataset AFFIA3K and a deep learning algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 32nd International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing (MLSP), Xi’an, China, 22–25 August 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.; Cui, M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Bai, Z.; Sun, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Li, D. Feeding intensity recognition of aquaculture fish using Mel Spectrogram and deep learning algorithms. Aquac. Eng. 2023, 102, 102345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voellmy, I.K.; Purser, J.; Flynn, D.; Kennedy, P.; Simpson, S.D.; Radford, A.N. Acoustic noise reduces foraging success in two sympatric fish species via different mechanisms. Anim. Behav. 2014, 89, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Du, Z.; Xu, X.; Bai, Z.; Han, J.; Cui, M.; Li, D. A review of aquaculture: From single modality analysis to multimodality fusion. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 226, 109367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Du, Z.; Chen, T.; Lian, G.; Li, D.; Wang, W. Multimodal Fish Feeding Intensity Recognition in Aquaculture. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024, 22, 9485–9497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Cui, M.; Xu, X.; Bai, Z.; Han, J.; Li, W.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Li, D. Harnessing multimodal data fusion to advance accurate identification of fish feeding intensity. Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 246, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhao, S.; Duan, Y.; Meng, Y.; Li, D.; Zhao, R. MMFINet: A multimodal fusion network for accurate fish feeding intensity recognition in recirculating aquaculture systems. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 232, 110138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, S.; Durand, F. A fast approximation of the bilateral filter using a signal processing approach. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Graz, Austria, 7–13 May 2006; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 568–580. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Q.; Cao, Y.; Iqbal, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Plumbley, M.D. Panns: Large-scale pretrained audio neural networks for audio pattern recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2020, 28, 2880–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Ahn, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, S. Blind deep S3D image quality evaluation via local to global feature aggregation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 4923–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemmeke, J.F.; Ellis, D.P.; Freedman, D.; Jansen, A.; Lawrence, W.; Moore, R.C.; Plakal, M.; Ritter, M. Audio set: An ontology and human-labeled dataset for audio events. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 776–780. [Google Scholar]
- Carreira, J.; Zisserman, A. Quo vadis, action recognition? a new model and the kinetics dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6299–6308. [Google Scholar]
- Subaar, C.; Addai, F.T.; Addison, E.C.; Christos, O.; Adom, J.; Owusu-Mensah, M.; Appiah-Agyei, N.; Abbey, S. Investigating the detection of breast cancer with deep transfer learning using ResNet18 and ResNet34. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2024, 10, 035029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theckedath, D.; Sedamkar, R.R. Detecting affect states using VGG16, ResNet50 and SE-ResNet50 networks. SN Comput. Sci. 2020, 1, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UÇan, M.; Kaya, B.; Kaya, M. Multi-class gastrointestinal images classification using EfficientNet-B0 CNN model. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Data Analytics for Business and Industry (ICDABI), Sakhir, Bahrain, 25–26 October 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M. Mobilevit: Light-weight, general-purpose, and mobile-friendly vision transformer. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.02178. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Ni, J.; Gao, J.; Han, Z.; Luan, T. A novel method for peanut variety identification and classification by Improved VGG16. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijwil, M.M.; Doshi, R.; Hiran, K.K.; Unogwu, O.J.; Bala, I. MobileNetV1-based deep learning model for accurate brain tumor classification. Mesopotamian J. Comput. Sci. 2023, 2023, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolarik, M.; Sarnovský, M.; Paralič, J. Detecting the absence of lung sliding in ultrasound videos using 3D convolutional neural networks. Acta Polytech. Hung. 2023, 20, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Lee, J.; Watanabe, S. I3D: Transformer architectures with input-dependent dynamic depth for speech recognition. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, D.; Liu, Y. Video-based emotion recognition using CNN-RNN and C3D hybrid networks. In Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Tokyo, Japan, 12–16 November 2016; pp. 445–450. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, T.; Kim, K. Two-stream mixed convolutional neural network for American sign language recognition. Sensors 2022, 22, 5959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feichtenhofer, C.; Fan, H.; Malik, J.; He, K. Slowfast networks for video recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6202–6211. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Z.; Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, L. Videomae: Masked autoencoders are data-efficient learners for self-supervised video pre-training. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 10078–10093. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, M.; Yue, X.; Qian, X.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Li, D.; Wang, W. Audio-Visual Class-Incremental Learning for Fish Feeding intensity Assessment in Aquaculture. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.15171. [Google Scholar]





| FFI | Description |
|---|---|
| None | Fish do not respond to food |
| Weak | Fish eat only pellets that fall directly |
| in front of them but do not move to take food | |
| Medium | Fish move to take the food, but return to |
| their original positions | |
| Strong | Fish move freely between food items and |
| consume all the available food |
| Audio Method | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | Parameters (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet18 [26] | 82.3 | 81.8 | 82.1 | 81.9 | 11.2 |
| ResNet50 [27] | 84.1 | 83.7 | 83.9 | 83.8 | 23.5 |
| EfficientNet-B0 [28] | 83.6 | 83.2 | 83.4 | 83.3 | 4.0 |
| MobileViT [29] | 85.4 | 85.1 | 85.3 | 85.2 | 5.7 |
| VGG16 [30] | 81.7 | 81.2 | 81.5 | 81.3 | 134.3 |
| MobileNetV1 [31] | 84.8 | 84.3 | 84.6 | 84.4 | 3.2 |
| MobileNetV2 | 86.0 | 85.8 | 85.9 | 85.7 | 2.2 |
| Video Method | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | Parameters (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet3D-18 [32] | 85.4 | 85.1 | 85.3 | 85.2 | 33.2 |
| I3D [33] | 87.2 | 86.8 | 87.0 | 86.9 | 12.3 |
| C3D [34] | 84.6 | 84.2 | 84.4 | 84.3 | 78.4 |
| TSM-ResNet50 [35] | 87.8 | 87.4 | 87.6 | 87.5 | 24.3 |
| SlowFast [36] | 88.3 | 87.9 | 88.1 | 88.0 | 34.6 |
| VideoMAE [37] | 86.5 | 86.1 | 86.3 | 86.2 | 87.1 |
| S3D | 89.0 | 88.7 | 89.2 | 88.8 | 7.8 |
| Fusion Method | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | Parameters (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element-Wise Addition | 90.5 | 90.1 | 90.3 | 90.2 | 11.0 |
| Feature Concatenation | 91.2 | 90.8 | 91.0 | 90.9 | 11.2 |
| Score Averaging | 92.1 | 91.6 | 91.8 | 91.7 | 11.0 |
| Cross-Attention | 93.4 | 92.9 | 93.2 | 93.0 | 12.8 |
| MMFINet [20] | 93.6 | 93.1 | 93.4 | 93.2 | 15.2 |
| MFFFI [19] | 92.8 | 92.3 | 92.6 | 92.4 | 13.5 |
| ACAF-Net (Ours) | 95.4 | 95.1 | 95.3 | 95.2 | 11.8 |
| Models | LBP | BF | AAF | Acc. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | X | X | X | 91.2 |
| +BF | X | X | 92.3 | |
| +LBP | X | X | 93.1 | |
| + | X | 93.8 | ||
| +AAF | X | X | 94.1 | |
| +BF+AAF | X | 94.6 | ||
| +LBP+AAF | X | 94.9 | ||
| ACAF-Net (Full) | 95.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Wei, Y.; Ma, W.; Wang, T. Cross-Modal Complementarity Learning for Fish Feeding Intensity Recognition via Audio–Visual Fusion. Animals 2025, 15, 2245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15152245
Li J, Wei Y, Ma W, Wang T. Cross-Modal Complementarity Learning for Fish Feeding Intensity Recognition via Audio–Visual Fusion. Animals. 2025; 15(15):2245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15152245
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jian, Yanan Wei, Wenkai Ma, and Tan Wang. 2025. "Cross-Modal Complementarity Learning for Fish Feeding Intensity Recognition via Audio–Visual Fusion" Animals 15, no. 15: 2245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15152245
APA StyleLi, J., Wei, Y., Ma, W., & Wang, T. (2025). Cross-Modal Complementarity Learning for Fish Feeding Intensity Recognition via Audio–Visual Fusion. Animals, 15(15), 2245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15152245






