Characterization of the Mitochondrial Genome of the Vietnamese Central Highland Wild Boar (Sus scrofa)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.2. De Novo Assembly
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. Phylogenetic Tree
3. Results
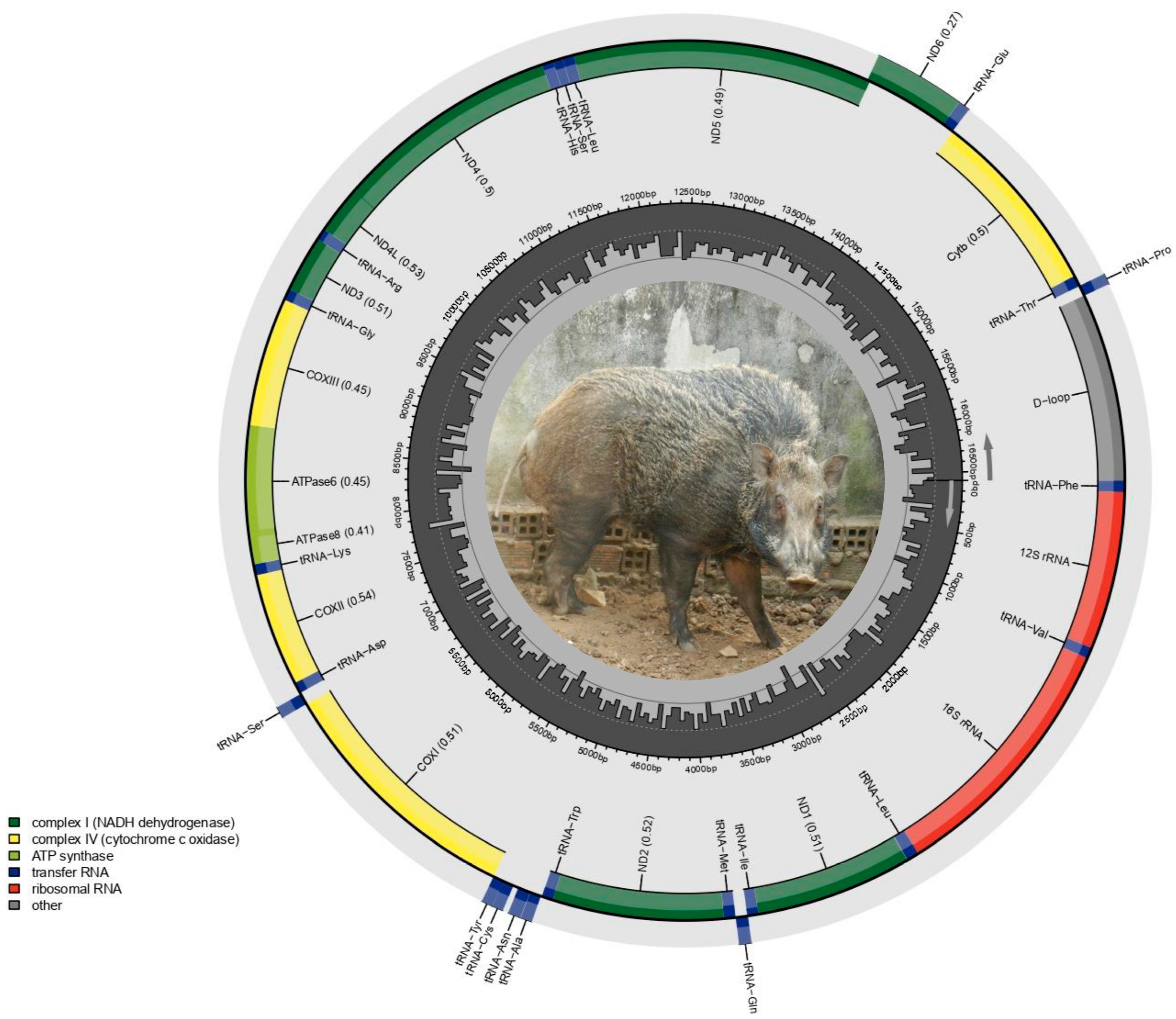
3.1. Complete Mitochondrial Genome Analysis
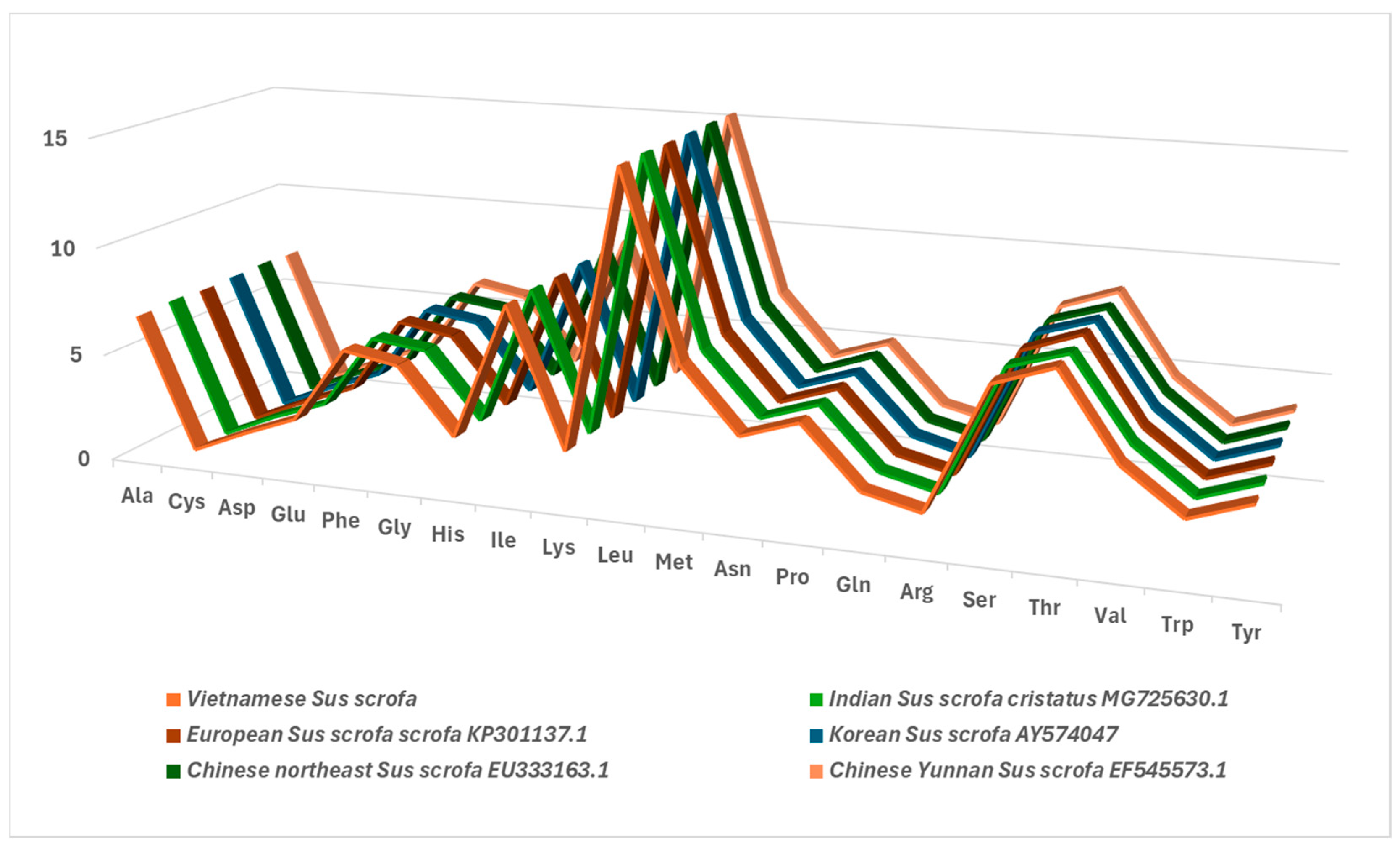
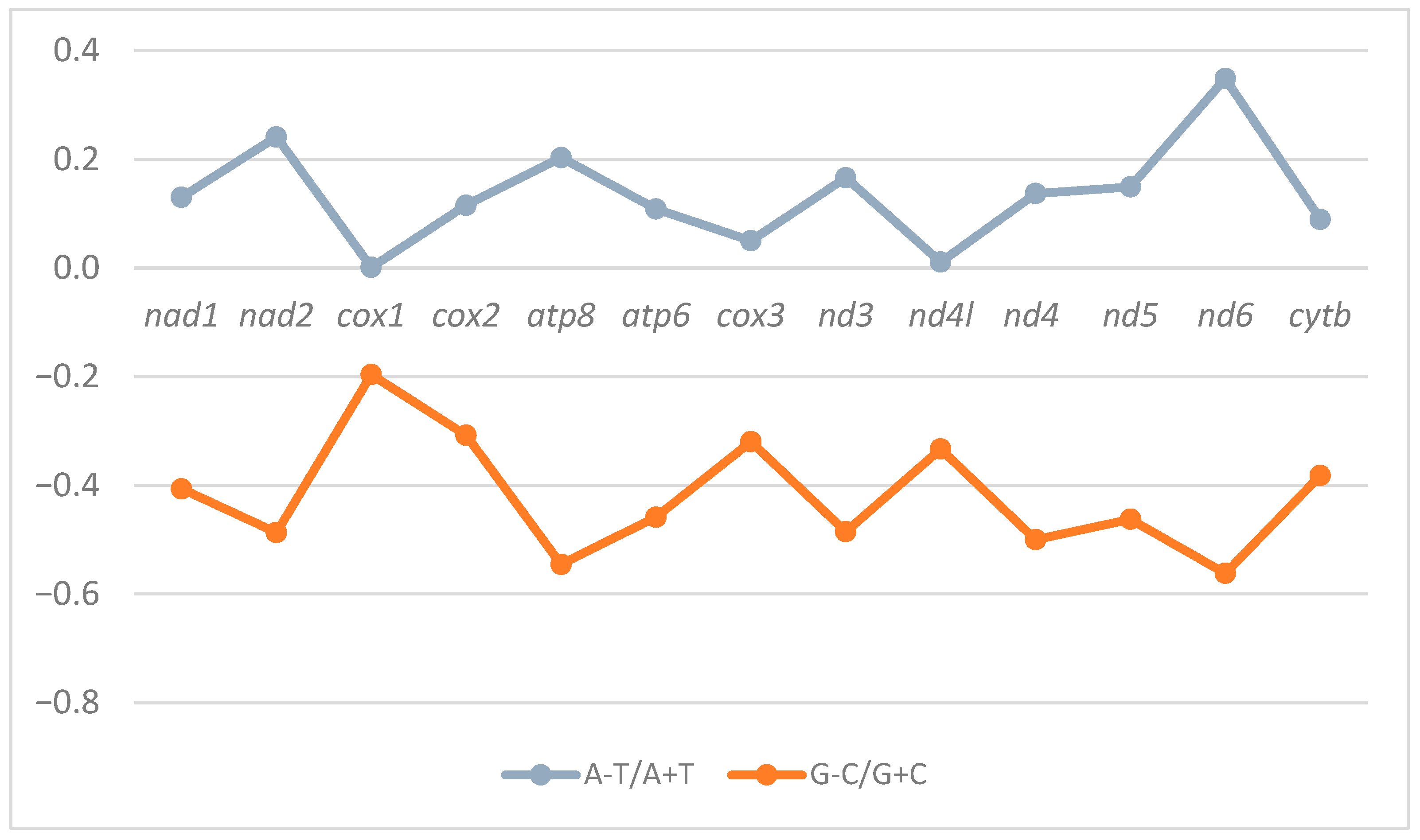
3.2. Nucleotide Composition Pattern
3.3. Protein-Coding Genes
3.4. Control Region
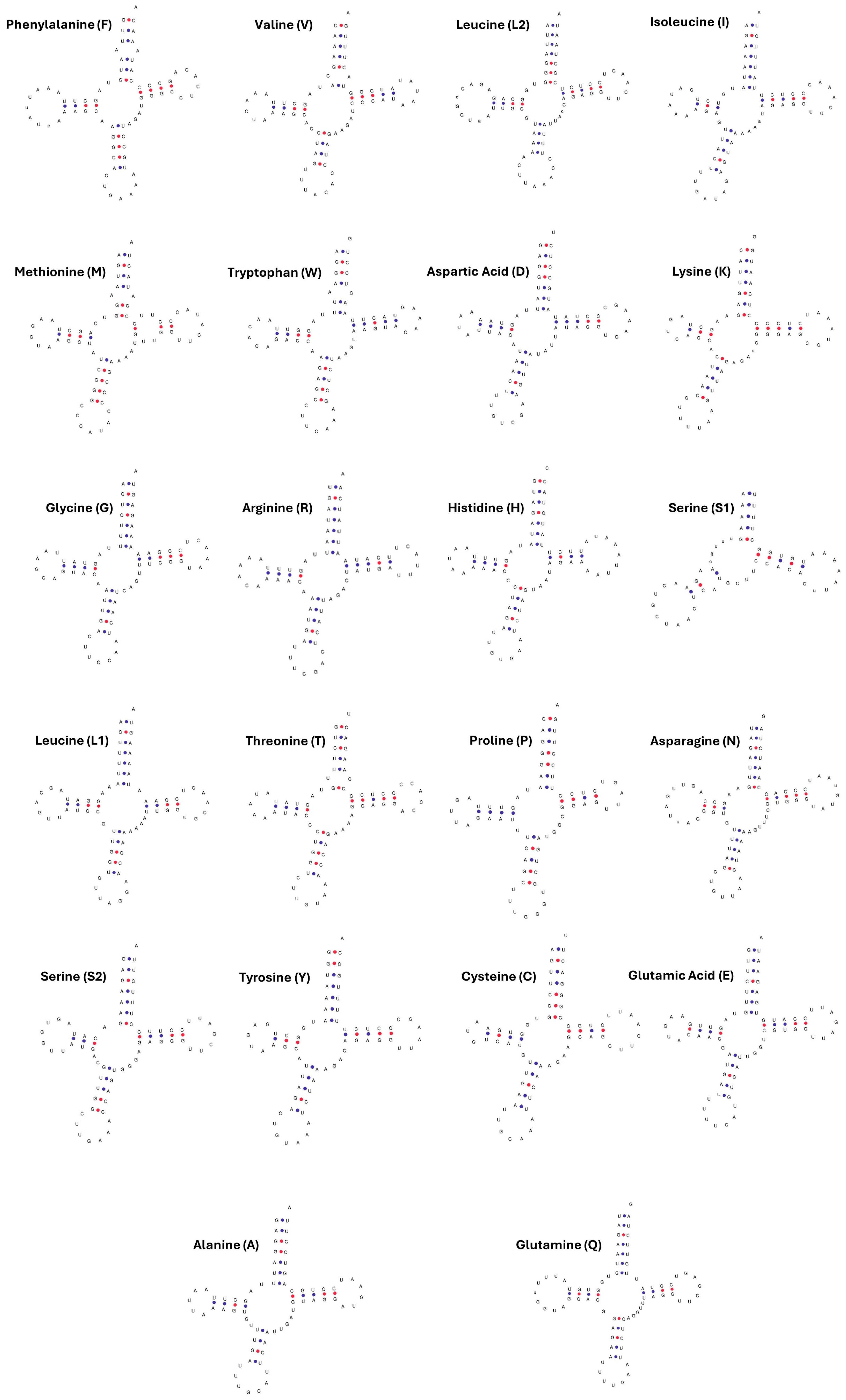
3.5. tRNA and rRNA Genes
3.6. Overlapping and Intergenic Regions
3.7. Mutations
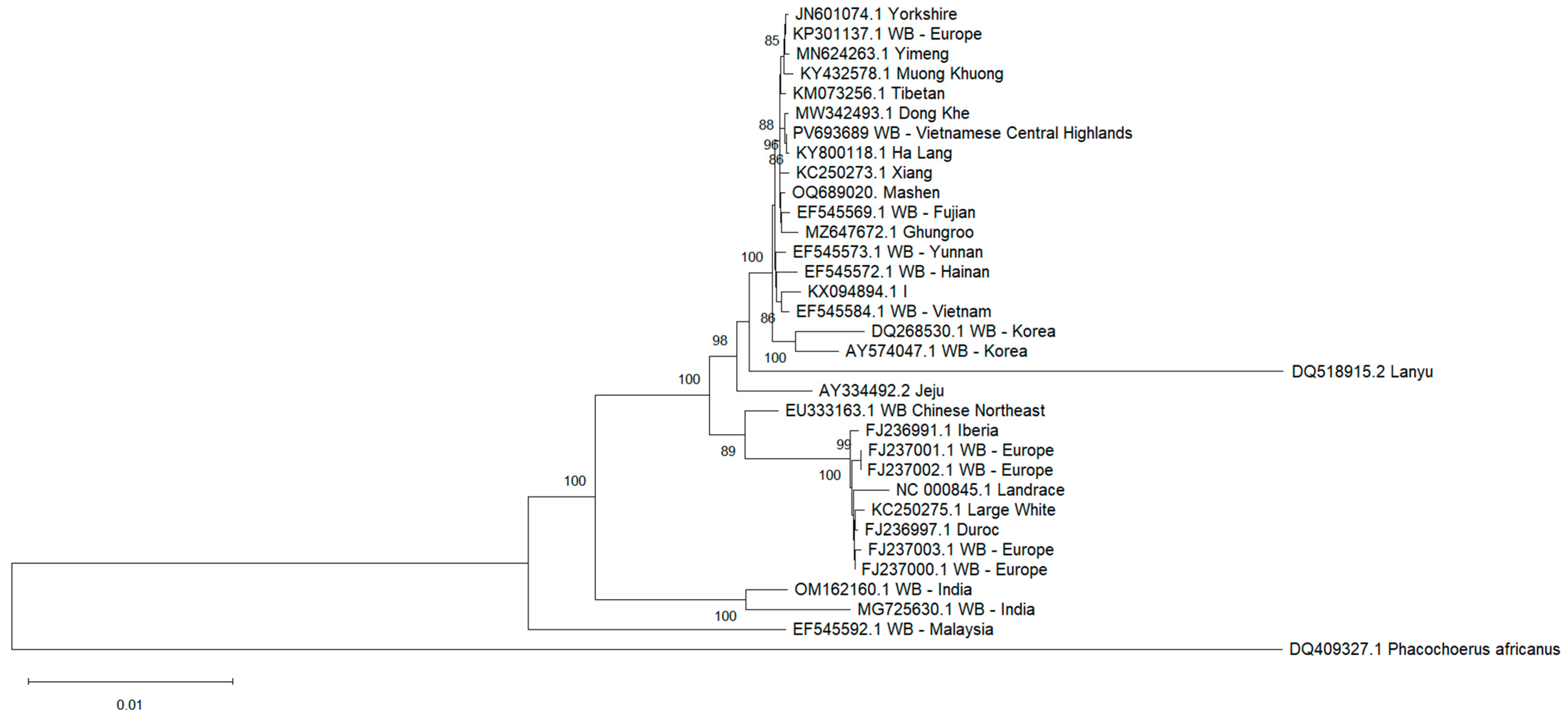
3.8. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Groves, C.P.; Schaller, G.B.; Amato, G.; Khounboline, K. Rediscovery of the wild pig Sus bucculentus. Nature 1997, 386, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.N.; Long, L.T.; Phuong Mai, N.T. Biological characterization of Vietnamese native wild boars in central highland (Sus scrofa). Acad. J. Biol. 2014, 36, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, C.; Meijaard, E. Sus bucculentus. In The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Goedbloed, D.J.; van Hooft, P.; Megens, H.J.; Langenbeck, K.; Lutz, W.; Crooijmans, R.P.; van Wieren, S.E.; Ydenberg, R.C.; Prins, H.H. Reintroductions and genetic introgression from domestic pigs have shaped the genetic population structure of Northwest European wild boar. BMC Genet. 2013, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allendorf, F.W.; Leary, R.F.; Spruell, P.; Wenburg, J.K. The problems with hybrids: Setting conservation guidelines. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2001, 16, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randi, E. Detecting hybridization between wild species and their domesticated relatives. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, F.B.; Dobney, K.; Denham, T.; Capriles, J.M. Evaluating the roles of directed breeding and gene flow in animal domestication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6153–6158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, N.T.P. Evaluation of Biological and Genetic Characteristics of Wild Boars Sus scrofa (Linnaeus, 1758) from Central Highlands. Ph.D. Thesis, Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology, Ha Noi, Vietnam, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Merheb, M.; Matar, R.; Hodeify, R.; Siddiqui, S.S.; Vazhappilly, C.G.; Marton, J.; Azharuddin, S.; Al Zouabi, H. Mitochondrial DNA, a Powerful Tool to Decipher Ancient Human Civilization from Domestication to Music, and to Uncover Historical Murder Cases. Cells 2019, 8, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Khan, M.Z.; Chai, W.; Ullah, Q.; Wang, C. Exploring Genetic Markers: Mitochondrial DNA and Genomic Screening for Biodiversity and Production Traits in Donkeys. Animals 2023, 13, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branicki, W.; Kupiec, T.; Pawlowski, R. Validation of cytochrome b sequence analysis as a method of species identification. J. Forensic Sci. 2003, 48, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clop, A.; Amills, M.; Noguera, J.L.; Fernández, A.; Capote, J.; Ramón, M.M.; Kelly, L.; Kijas, J.M.H.; Andersson, L.; Sànchez, A. Estimating the frequency of Asian cytochrome B haplotypes in standard European and local Spanish pig breeds. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2004, 36, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Kumar, A.; Hussain, S.A.; Vipin; Singh, L. Cytochrome b based genetic differentiation of Indian wild pig (Sus scrofa cristatus) and domestic pig (Sus scrofa domestica) and its use in wildlife forensics. Sci. Justice 2013, 53, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, C.A.; Paiva, S.R.; Pereira, R.W.; Guimarães, S.E.; Dutra, W.M., Jr.; Murata, L.S.; Mariante, A.S. Iberian origin of Brazilian local pig breeds based on Cytochrome b (MT-CYB) sequence. Anim. Genet. 2009, 40, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hongo, H.; Ishiguro, N.; Watanobe, T.; Shigehara, N.; Anezaki, T.; Long, V.T.; Binh, D.V.; Tien, N.T.; Nam, N.H. Variation in mitochondrial DNA of Vietnamese pigs: Relationships with Asian domestic pigs and Ryukyu wild boars. Zool. Sci 2002, 19, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, S.; Arakawa, A.; Ba, N.V.; Dinh, N.C.; Ninh, P.H.; Okamura, T.; Dang-Nguyen, T.Q.; Kikuchi, K.; Pham, L.D.; Taniguchi, M. Population structure of Vietnamese pigs using mitochondrial DNA. Anim. Sci. J. 2023, 94, e13875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, N.T.P.; Chung, D.C.; Chi, H.N.Q.; Son, H.N. The genetic relationship of Vietnamese pigs in central highlands assessed by cytochrome b. Open J. Genet. 2014, 4, 362–369. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Bui, T.A.; Nguyen, P.T.; Kim, O.T.P.; Vo, T.T.B. The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of the indigenous I pig (Sus scrofa) in Vietnam. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 30, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thom, B.T.; Van Phung, T.; Nga, C.T.T.; Khuyen, D.T.; Chiem, D.T.H.; Duc, N.M. Morphological and mitochondrial genome characterization of indigenous Dong Khe pig in rural areas of Northeast Vietnam. Livest. Res. Rural Dev. 2021, 33, e84. Available online: http://www.lrrd.org/lrrd33/6/3384ducng.html (accessed on 6 July 2025).
- Bui, T.A.; Nguyen, H.D.; Vo, T.T.B. Complete mitochondrial genome sequence and phylogenetic status of Halang Pig (Sus scrofa). Asian J. Biol. 2018, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaña-Lozano, P.; Moreno-Carmona, M.; Ochoa-Capera, M.; Medina, N.S.; Boore, J.L.; Prada, C.F. Comparative genomic analysis of vertebrate mitochondrial reveals a differential of rearrangements rate between taxonomic class. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.-J.; Yu, W.-B.; Yang, J.-B.; Song, Y.; dePamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.-S.; Li, D.-Z. GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, W.; Fukunaga, T.; Isagozawa, R.; Yamada, K.; Maeda, Y.; Satoh, T.P.; Sado, T.; Mabuchi, K.; Takeshima, H.; Miya, M.; et al. MitoFish and MitoAnnotator: A Mitochondrial Genome Database of Fish with an Accurate and Automatic Annotation Pipeline. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Externbrink, F.; Florentz, C.; Fritzsch, G.; Pütz, J.; Middendorf, M.; Stadler, P.F. MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Suleski, M.; Sanderford, M.; Sharma, S.; Tamura, K. MEGA12: Molecular Evolutionary Genetic Analysis Version 12 for Adaptive and Green Computing. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2024, 41, msae263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, N.T.; Kocher, T.D. Patterns of nucleotide composition at fourfold degenerate sites of animal mitochondrial genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 41, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, T.M.; Eddy, S.R. tRNAscan-SE: A program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Xiang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X. The phylogenetic status of typical Chinese native pigs: Analyzed by Asian and European pig mitochondrial genome sequences. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.J.; Kumar, S.; Choudhury, M.; Pegu, S.R.; Meera, K.; Deb, R.; Kumar, S.; Banik, S.; Gupta, V.K. Complete mitochondrial genome sequence analysis revealed double matrilineal components in Indian Ghoongroo pigs. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadel, G.S.; Clayton, D.A. Mitochondrial DNA maintenance in vertebrates. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1997, 66, 409–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojala, D.; Montoya, J.; Attardi, G. tRNA punctuation model of RNA processing in human mitochondria. Nature 1981, 290, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Li, C.; Fang, W.Y.; Yu, X.P. The Complete Mitochondrial Genome of two Tetragnatha Spiders (Araneae: Tetragnathidae): Severe Truncation of tRNAs and Novel Gene Rearrangements in Araneae. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigurðardóttir, S.; Helgason, A.; Gulcher, J.R.; Stefansson, K.; Donnelly, P. The mutation rate in the human mtDNA control region. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2000, 66, 1599–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buroker, N.E.; Brown, J.R.; Gilbert, T.A.; O’Hara, P.J.; Beckenbach, A.T.; Thomas, W.K.; Smith, M.J. Length heteroplasmy of sturgeon mitochondrial DNA: An illegitimate elongation model. Genetics 1990, 124, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, T.P.; Miya, M.; Endo, H.; Nishida, M. Round and pointed-head grenadier fishes (Actinopterygii: Gadiformes) represent a single sister group: Evidence from the complete mitochondrial genome sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 40, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.L.; Mohapatra, B. Intergenic. In Encyclopedia of Animal Cognition and Behavior; Vonk, J., Shackelford, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Castresana, J. Cytochrome b Phylogeny and the Taxonomy of Great Apes and Mammals. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuffra, E.; Kijas, J.M.; Amarger, V.; Carlborg, O.; Jeon, J.T.; Andersson, L. The origin of the domestic pig: Independent domestication and subsequent introgression. Genetics 2000, 154, 1785–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G. Genetic aspects of domestication, common breeds and their origin. In Genetic Aspects of Domestication, Common Breeds and Their Origin; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Schleimer, A.; Richart, L.; Drygala, F.; Casabianca, F.; Maestrini, O.; Weigand, H.; Schwartz, C.; Mittelbronn, M.; Frantz, A.C. Introgressive hybridisation between domestic pigs (Sus scrofa domesticus) and endemic Corsican wild boars (S. s. meridionalis): Effects of human-mediated interventions. Heredity 2022, 128, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, A.C.; Massei, G.; Burke, T. Genetic evidence for past hybridisation between domestic pigs and English wild boars. Conserv. Genet. 2012, 13, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, L.A.; Haile, J.; Lin, A.T.; Scheu, A.; Geörg, C.; Benecke, N.; Alexander, M.; Linderholm, A.; Mullin, V.E.; Daly, K.G. Correction for Frantz et al., Ancient pigs reveal a near-complete genomic turnover following their introduction to Europe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 14610–14611. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, G.; Dobney, K.; Albarella, U.; Fang, M.; Matisoo-Smith, E.; Robins, J.; Lowden, S.; Finlayson, H.; Brand, T.; Willerslev, E. Worldwide phylogeography of wild boar reveals multiple centers of pig domestication. Science 2005, 307, 1618–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, G.; Albarella, U.; Dobney, K.; Rowley-Conwy, P.; Schibler, J.; Tresset, A.; Vigne, J.-D.; Edwards, C.J.; Schlumbaum, A.; Dinu, A. Ancient DNA, pig domestication, and the spread of the Neolithic into Europe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15276–15281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, S. From globalized pig breeds to capitalist pigs: A study in animal cultures and evolutionary history. Environ. Hist. 2011, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Shi, L. The origin and genetic differentiation of native breeds of pigs in southwest China: An approach from mitochondrial DNA polymorphism. Biochem. Genet. 1993, 31, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | Start | Stop | Strand | Length | Intergenic Nucleotides |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| trnF(gaa) | 345 | 414 | + | 70 | 0 |
| rrnS | 415 | 1376 | + | 962 | 0 |
| trnV(tac) | 1376 | 1443 | + | 68 | −1 |
| rrnL | 1442 | 3013 | + | 1572 | −2 |
| trnL2(taa) | 3014 | 3088 | + | 75 | 0 |
| nad1 | 3091 | 4045 | + | 955 | 2 |
| trnI(gat) | 4046 | 4114 | + | 1042 | 0 |
| trnQ(ttg) | 4112 | 4184 | − | 73 | −3 |
| trnM(cat) | 4186 | 4255 | + | 70 | 1 |
| nad2 | 4256 | 5297 | + | 1042 | 0 |
| trnW(tca) | 5298 | 5365 | + | 68 | 0 |
| trnA(tgc) | 5372 | 5439 | − | 68 | 6 |
| trnN(gtt) | 5441 | 5515 | − | 75 | 1 |
| trnC(gca) | 5548 | 5613 | − | 66 | 32 |
| trnY(gta) | 5613 | 5678 | − | 66 | −1 |
| cox1 | 5680 | 7224 | + | 1545 | 1 |
| trnS2(tga) | 7228 | 7296 | − | 69 | 3 |
| trnD(gtc) | 7304 | 7371 | + | 68 | 7 |
| cox2 | 7372 | 8059 | + | 688 | 0 |
| trnK(ttt) | 8060 | 8126 | + | 67 | 0 |
| atp8 | 8128 | 8331 | + | 204 | 1 |
| atp6 | 8289 | 8969 | + | 681 | −43 |
| cox3 | 8969 | 9752 | + | 784 | −1 |
| trnG(tcc) | 9753 | 9821 | + | 69 | 0 |
| nad3 | 9822 | 10,168 | + | 347 | 0 |
| trnR(tcg) | 10,169 | 10,237 | + | 69 | 0 |
| nad4l | 10,238 | 10,534 | + | 297 | 0 |
| nad4 | 10,528 | 11,905 | + | 1378 | −7 |
| trnH(gtg) | 11,906 | 11,974 | + | 69 | 0 |
| trnS1(gct) | 11,975 | 12,033 | + | 59 | 0 |
| trnL1(tag) | 12,034 | 12,103 | + | 70 | 0 |
| nad5 | 12,104 | 13,924 | + | 1821 | 0 |
| nad6 | 13,908 | 14,435 | − | 528 | −17 |
| trnE(ttc) | 14,436 | 14,504 | − | 69 | 0 |
| cob | 14,509 | 15,648 | + | 1140 | 4 |
| trnT(tgt) | 15,649 | 15,716 | + | 68 | 0 |
| trnP(tgg) | 15,716 | 15,780 | − | 65 | −1 |
| Accession Number | Whole | Protein-Coding Genes (PCGs) | Large Ribosomal RNA (rrnL) | Small Ribosomal RNA (rrnS) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length | %AT | Length | %AT | Length | %AT | Length | %AT | ||
| Vietnamese Central Highland Sus scrofa | PV693689 | 16,581 | 60.6 | 11,342 | 60.3 | 1572 | 62.7 | 962 | 59.4 |
| Indian Sus scrofa cristatus | MG725630.1 | 16,738 | 60.46 | 11,348 | 60.4 | 1570 | 62.4 | 958 | 59.2 |
| European Sus scrofa scrofa | KP301137.1 | 16,770 | 60.41 | 11,342 | 60.4 | 1570 | 62.8 | 960 | 59.5 |
| Korean Sus scrofa | AY574047.1 | 16,651 | 60.57 | 11,345 | 60.4 | 1570 | 62.7 | 962 | 59.6 |
| Chinese northeast Sus scrofa | EU333163.1 | 16,581 | 60.60 | 11,341 | 60.3 | 1569 | 62.6 | 962 | 59.5 |
| Chinese Yunnan Sus scrofa | EF545573.1 | 16,620 | 60.48 | 11,341 | 60.3 | 1570 | 62.7 | 961 | 59.4 |
| Sus scrofa domestica | AP003428.1 | 16,770 | 60.33 | 11,354 | 60.2 | 1571 | 62.6 | 962 | 59.5 |
| Sus scrofa breed Yorkshire | JN601074.1 | 16,770 | 60.41 | 11,354 | 60.3 | 1571 | 62.8 | 962 | 59.4 |
| Sus scrofa breed Tibetan | KM073256.1 | 16,710 | 60.47 | 11,341 | 60.3 | 1570 | 62.8 | 961 | 59.4 |
| Sus scrofa breed Iberian | FJ236991.1 | 16,941 | 60.15 | 11,369 | 60.3 | 1571 | 62.6 | 962 | 59.5 |
| Sus scrofa breed Lanyu | DQ518915.2 | 16,747 | 60.44 | 11,345 | 60.3 | 1563 | 62.8 | 956 | 58.9 |
| Sus scrofa breed Large White | KC250275.1 | 16,610 | 60.55 | 11,341 | 60.3 | 1570 | 62.5 | 960 | 59.5 |
| Sus scrofa breed Dong Khe | MW342493.1 | 16,708 | 60.46 | 11,342 | 60.3 | 1570 | 62.7 | 962 | 59.4 |
| Sus scrofa breed Ha Lang | KY800118.1 | 16,717 | 60.47 | 11,338 | 60.3 | 1572 | 62.7 | 962 | 59.5 |
| Sus scrofa breed I | KX094894.1 | 16,724 | 60.42 | 11,337 | 60.3 | 1570 | 62.7 | 960 | 59.5 |
| Sus verrucosus | NC_023536.1 | 16,479 | 60.98 | 11,335 | 60.5 | 1570 | 62.6 | 959 | 60 |
| Phacochoerus africanus | DQ409327.1 | 16,719 | 60.75 | 11,361 | 60.6 | 1572 | 63.2 | 963 | 59.9 |
| Accession Number | T (U) | C | A | G | Total | AT Skew | GC Skew | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vietnamese Central Highland Sus scrofa | PV693689 | 26.3 | 27.8 | 34.0 | 11.9 | 11,342 | 0.127156 | −0.40089 |
| Indian Sus scrofa cristatus | MG725630.1 | 26.4 | 27.7 | 34.0 | 11.9 | 11,348 | 0.12542 | −0.39942 |
| European Sus scrofa scrofa | KP301137.1 | 26.3 | 27.8 | 34.0 | 11.9 | 11,342 | 0.127246 | −0.40093 |
| Korean Sus scrofa | AY574047.1 | 26.3 | 27.7 | 34.0 | 12.0 | 11,345 | 0.127793 | −0.39618 |
| Chinese northeast Sus scrofa | EU333163.1 | 26.3 | 27.8 | 34.0 | 11.9 | 11,341 | 0.128603 | −0.40124 |
| Chinese Yunnan Sus scrofa | EF545573.1 | 26.3 | 27.8 | 34.0 | 11.9 | 11,341 | 0.126901 | −0.40013 |
| Sus scrofa domestica | AP003428.1 | 26.2 | 27.8 | 34.0 | 11.9 | 11,354 | 0.12957 | −0.40035 |
| Sus scrofa breed Yorkshire | JN601074.1 | 26.3 | 27.7 | 34.0 | 11.9 | 11,354 | 0.127262 | −0.39938 |
| Sus scrofa breed Tibetan | KM073256.1 | 26.3 | 27.8 | 34.0 | 11.9 | 11,341 | 0.126991 | −0.40062 |
| Sus scrofa breed Iberian | FJ236991.1 | 26.3 | 27.8 | 34.0 | 11.9 | 11,369 | 0.128228 | −0.40142 |
| Sus scrofa breed Lanyu | DQ518915.2 | 27.4 | 26.9 | 32.9 | 12.8 | 11,345 | 0.091732 | −0.35586 |
| Sus scrofa breed Large White | KC250275.1 | 26.2 | 27.9 | 34.0 | 11.9 | 11,341 | 0.12864 | −0.40151 |
| Sus scrofa breed Dong Khe | MW342493.1 | 26.3 | 27.8 | 34.0 | 11.9 | 11,342 | 0.127448 | −0.40133 |
| Sus scrofa breed Ha Lang | KY800118.1 | 26.3 | 27.8 | 34.0 | 11.9 | 11,338 | 0.127358 | −0.4012 |
| Sus scrofa breed I | KX094894.1 | 26.3 | 27.8 | 34.0 | 11.9 | 11,337 | 0.12714 | −0.40027 |
| Sus verrucosus | NC_023536.1 | 26.5 | 27.6 | 34.0 | 11.8 | 11,335 | 0.124454 | −0.4004 |
| Phacochoerus africanus | DQ409327.1 | 26.6 | 27.5 | 34.0 | 12.0 | 11,361 | 0.122802 | −0.39375 |
| tRNA | Mismatched Base Pairs | Stem | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Methionine CAT | U-U A-A | T-arm AA | 2 1 |
| Phenylalanine GAA | A-A | AA | 1 |
| Serine GCT | A-A | AC | 1 |
| Threonine TGT | U-C | AA | 1 |
| Tryptophan TCA | A-C | AA | 1 |
| Valine TAC | C-A | AA | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran, M.T.; Vo, A.L.H.; Ho, C.N.Q.; Vu, M.Q.; To, Q.M.; Nguyen, M.T.P.; Dang, L.T.T.; Phan, N.L.C.; Doan, C.C.; Hoang, H.N.Q.; et al. Characterization of the Mitochondrial Genome of the Vietnamese Central Highland Wild Boar (Sus scrofa). Animals 2025, 15, 2029. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142029
Tran MT, Vo ALH, Ho CNQ, Vu MQ, To QM, Nguyen MTP, Dang LTT, Phan NLC, Doan CC, Hoang HNQ, et al. Characterization of the Mitochondrial Genome of the Vietnamese Central Highland Wild Boar (Sus scrofa). Animals. 2025; 15(14):2029. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142029
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran, Minh Thi, Anh Le Hong Vo, Chi Nguyen Quynh Ho, Manh Quang Vu, Quan Minh To, Mai Thi Phuong Nguyen, Loan Thi Tung Dang, Nhan Lu Chinh Phan, Chung Chinh Doan, Huy Nghia Quang Hoang, and et al. 2025. "Characterization of the Mitochondrial Genome of the Vietnamese Central Highland Wild Boar (Sus scrofa)" Animals 15, no. 14: 2029. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142029
APA StyleTran, M. T., Vo, A. L. H., Ho, C. N. Q., Vu, M. Q., To, Q. M., Nguyen, M. T. P., Dang, L. T. T., Phan, N. L. C., Doan, C. C., Hoang, H. N. Q., Le, C. P. M., Hoang, S. N., Nguyen, H. T. M., & Le, L. T. (2025). Characterization of the Mitochondrial Genome of the Vietnamese Central Highland Wild Boar (Sus scrofa). Animals, 15(14), 2029. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142029





