Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Pro-Inflammatory Mediator Expression in Pelteobagrus vachelli During Ichthyophthiriasis: A 40-Day Longitudinal Study of IL-1β, IL-6, and SAA
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics and Legislation
2.2. Fish
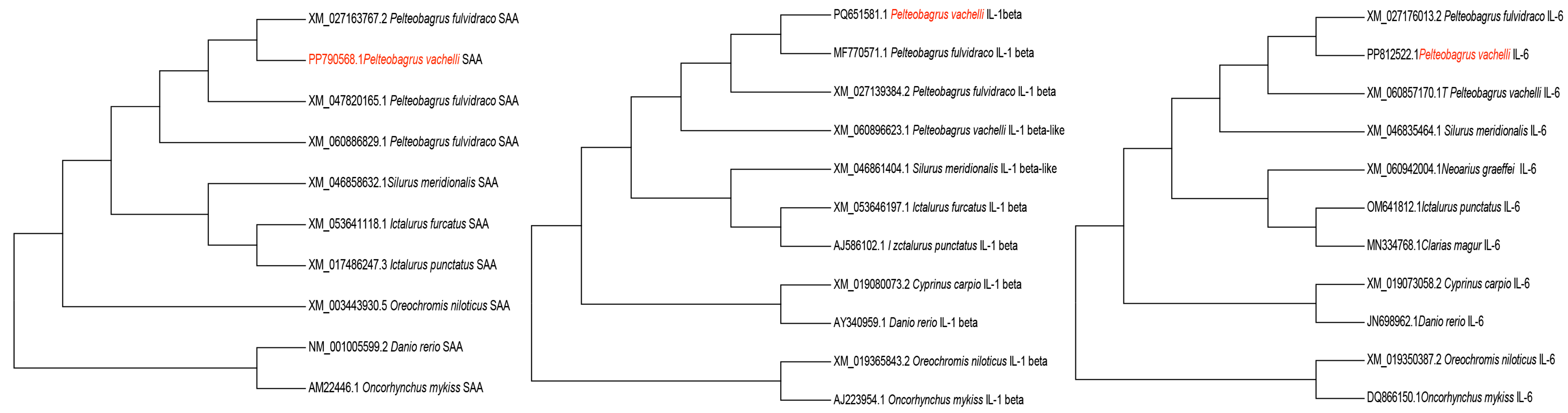
2.3. Gene Cloning and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. Infection
2.4.1. Parasites
2.4.2. Experimental Grouping
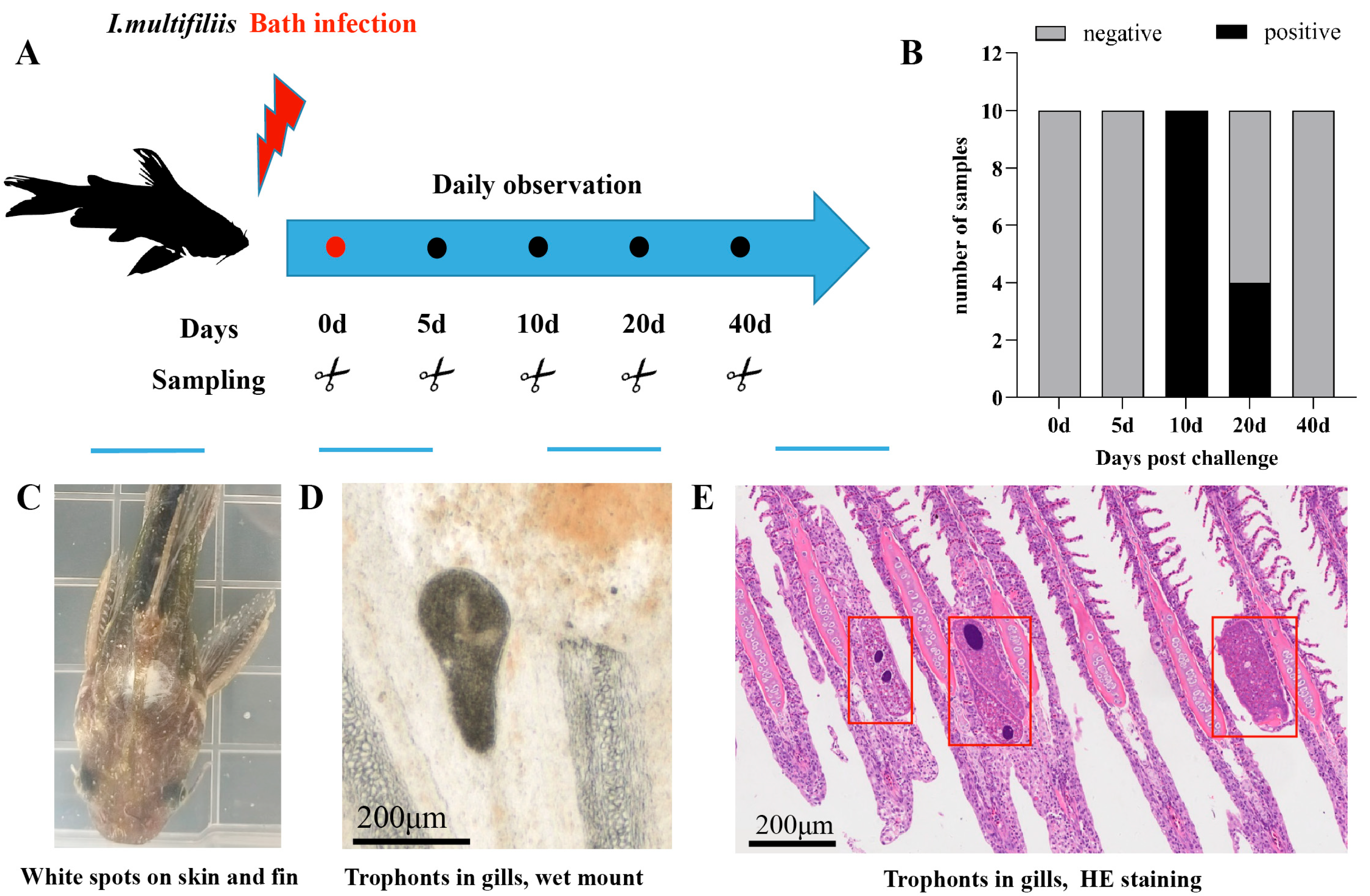
2.4.3. Ich Challenge and Sampling
2.5. Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CDS Cloning and Phylogenetic Analysis
3.2. Symptoms of Infected Fish
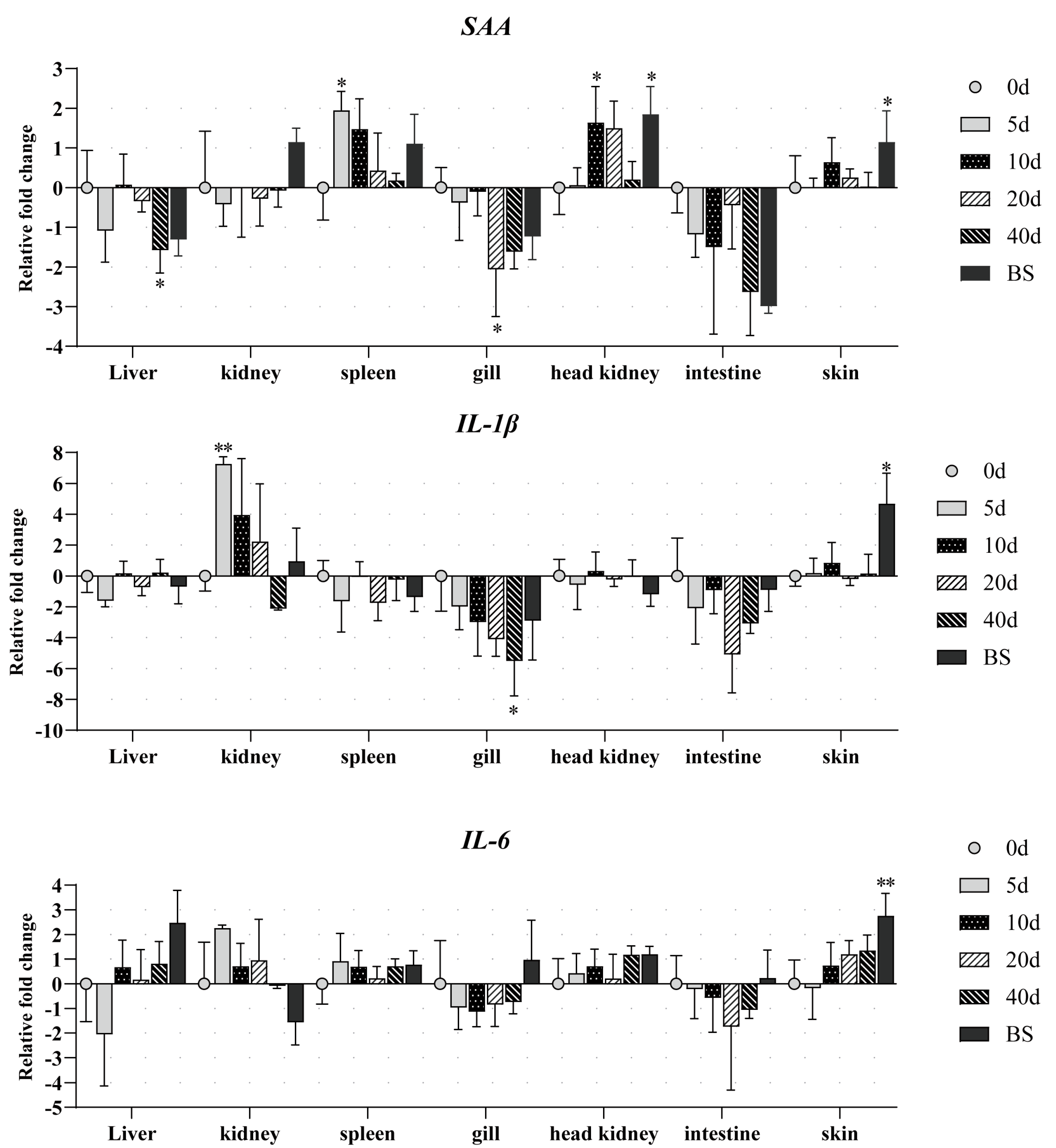
3.3. Expression of SAA, IL-1β, and IL-6
- SAA. Significant upregulation of SAA was observed in the spleen, head kidney, and skin. In the spleen, SAA exhibited the earliest expression surge, with a 4-fold increase compared to uninfected controls at 5 dpi, followed by a gradual decline. The head kidney displayed parallel kinetics to the spleen, with SAA levels peaking at 10 dpi (3-fold increase). Notably, moribund fish showed a further elevation to 3.9-fold. Upregulation was observed in skin during the terminal stages, reaching 2.5-fold in moribund specimens. In contrast, downregulation patterns were detected in the liver, gills, intestine, and kidney. Significant suppression emerged in gills by 20 dpi and in the liver by 40 dpi. No statistically significant changes were observed in the intestine or kidney throughout the observation period.
- IL-1β. Significant upregulation of IL-1β was observed in the kidney and skin. IL-1β expression peaked at 5 dpi with a 150-fold increase compared to uninfected controls, followed by a rapid return to baseline levels. The skin of moribund fish exhibited marked induction (52.8-fold elevation vs. control fish). Pronounced downregulation emerged at 40 dpi in the gills, showing 15.4-fold suppression relative to uninfected darkbarbel catfish.
- IL-6. Significant changes were only found in the skin of moribund fish, showing a 7.8-fold increase compared to the uninfected controls.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ich | Ichthyophthirius multifiliis |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| SAA | Serum Amyloid A |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
References
- Matthews, R.A. Ichthyophthirius multifiliis Fouquet and ichthyophthiriosis in freshwater teleosts. Adv. Parasitol. 2005, 59, 159–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traxler, G.S.; Richard, J.; McDonald, T.E. Ichthyophthirius multifiliis (Ich) epizootics in spawning sockeye salmon in British Columbia, Canada. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1998, 10, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, R.S.; Hannick, L.; Shanmugam, D.; Hostetler, J.B.; Brami, D.; Joardar, V.S.; Johnson, J.; Radune, D.; Singh, I.; Badger, J.H.; et al. Comparative genomics of the pathogenic ciliate Ichthyophthirius multifiliis, its free-living relatives and a host species provide insights into adoption of a parasitic lifestyle and prospects for disease control. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Hafez, G.; Lahnsteiner, F.; Mansour, N.; Licek, E. Pathophysiology of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis infection in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and chub (Leuciscus cephalus). J. Comp. Pathol. 2014, 151, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Gersdorff Jørgensen, L. The fish parasite Ichthyophthirius multifiliis-host immunology, vaccines and novel treatments. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 67, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Liang, X.; Wang, T.; Yin, S. A high-density SNP-based genetic map and several economic traits-related loci in Pelteobagrus vachelli. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Chen, S.; Correa, S.B.; Ye, S.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J. Longitudinal habitat gradient affects diet and body condition of riverine fish: A case study of Pelteobagrus catfishes in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. River Res. Appl. 2022, 38, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, A. Examination of the Population Structure of Darkbarbel Catfish (Pelteobagrus vachelli) in the Upper Yangtze River, China, Using Novel Microsatellite Markers. Master’s Thesis, Queen’s University, Kingston, ON, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, G.; Ke, W.; Liao, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Hu, J.; Mei, J. A chromosome-level genome assembly of the darkbarbel catfish Pelteobagrus vachelli. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs; Bureau of Fisheries and Fishing Administration; National Fisheries Technology Extension Center; China Society of Fisheries. China Fishery Statistical Yearbook 2024; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Fan, W.; Chen, J.; Liao, B.; Qin, C.; Wang, J. Histopathological observation of Pelteobagrus vachelli infected with Ichthyophthirius multifillis. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2020, 35, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. Proinflammatory cytokines. Chest 2000, 118, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigh, J.; Lindenstrøm, T.; Buchmann, K. Expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) during an infection with Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2004, 17, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinecke, R.D.; Buchmann, K. inflammatory response of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum, 1792) larvae against Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, S.F.; Buchmann, K.; Nielsen, M.E. Real-time gene expression analysis in carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) skin: Inflammatory responses caused by the ectoparasite Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 22, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, B.K.; Dhar, S.; Kumar, V.; Parida, P.K.; Hoque, F.; Parida, S.N.; Bisai, K.; Devnath, S.; Jana, A.K.; Mistri, A.; et al. Molecular approach and techniques used in the diagnosis of fish parasites. Agric. Assoc. Text. Chem. Crit. Rev. J. 2022, 34–54. [Google Scholar]
- Samiappan, S.C.; Palanisamy, S.; Ravichandran, M.; Balasubramanian, B.; Issara, U.; Arumugam, V.A. Common Bacterial Fish Diseases and Approaches on Molecular Techniques for Characterization and Early Detection of Pathogens. In Aquaculture Science and Engineering; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xue, M.; Yang, T.; Li, Y.; Jiang, N.; Fan, Y.; Meng, Y.; Luo, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, L. Characterization of a novel RNA virus causing massive mortality in yellow catfish, Pelteobagrus fulvidraco, as an emerging genus in Caliciviridae (Picornavirales). Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e00624-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Feng, Y.; Qin, Z.; Yu, Z.; Tian, Z.; Peng, K.; OuYang, P.; Chen, D.; Huang, X.; Geng, Y. Vibrio misgurnus sp. nov., a new pathogen of cultured loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus), closely related to Vibrio cholerae. Aquaculture 2024, 586, 740799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jaafar, R.; He, Y.; Wu, B.; Kania, P.; Buchmann, K. Effects of a Pseudomonas H6 surfactant on rainbow trout and Ichthyophthirius multifiliis: In vivo exposure. Aquaculture 2022, 547, 737479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnichsen, R.; Nielsen, G.G.B.; Dam, J.S.; Schrøder-Petersen, D.; Buchmann, K. AI-Driven Realtime Monitoring of Early Indicators for Ichthyophthirius multifiliis Infection of Rainbow Trout. J. Fish Dis. 2025, 48, e14027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Lyu, X.M.; Nie, P.; Liu, Y. Morphological, histopathological and molecular characterization of parasitic ciliate Ichthyophthirius multifiliis infecting an indigenous and endangered fish, Schizothorax macropogon (Cyprinidae: Schizothoracinae) in high plateau, Tibet, China. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 25, 101192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 22−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.M.; Barreda, D.R. The acute inflammatory response of teleost fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2023, 146, 104731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaafar, R.; Ødegård, J.; Mathiessen, H.; Karami, A.M.; Marana, M.H.; Jørgensen, L.v.G.; Zuo, S.; Nielsen, T.; Kania, P.W.; Buchmann, K. Quantitative trait loci (QTL) associated with resistance of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss against the parasitic ciliate Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Wang, S.; Dan, C.; Zhang, Y.B.; Mei, J. The role of antimicrobial peptide HBβ-C in ichthyophthirius multifillis resistance in all-male and hybrid yellow catfish. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2021, 45, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kania, P.W.; Chettri, J.K.; Buchmann, K. Characterization of serum amyloid A (SAA) in rainbow trout using a new monoclonal antibody. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 40, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlar, C.M.; Whitehead, A.S. Serum amyloid A, the major vertebrate acute-phase reactant. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 265, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, J.B.; Lunde, H.; Jensen, L.; Whitehead, A.S.; Robertsen, B. Serum amyloid A transcription in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) hepatocytes is enhanced by stimulation with macrophage factors, recombinant human IL-1β, IL-6 and TNFα or bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2000, 24, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E Jensen, L.; Hiney, M.P.; Shields, D.C.; Uhlar, C.M.; Lindsay, A.J.; Whitehead, A.S. Acute phase proteins in salmonids: Evolutionary analyses and acute phase response. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, M.; Silva-Álvarez, V.; Aversa-Marnai, M.; Lamas-Bervejillo, M.; Quartiani, I.; Perretta, A.; Villarino, A.; Ferreira, A.M. Serum amyloid A is a positive acute phase protein in Russian sturgeon challenged with Aeromonas hydrophila. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadiso, T.M.; Krasnov, A.; Skugor, S.; Afanasyev, S.; Hordvik, I.; Nilsen, F. Gene expression analyses of immune responses in Atlantic salmon during early stages of infection by salmon louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) revealed bi-phasic responses coinciding with the copepod-chalimus transition. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiki, K.; Shin, D.H.; Nakao, M.; Yano, T. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of carp (Cyprinus carpio) interleukin-1β, high affinity immunoglobulin E Fc receptor γ subunit and serum amyloid A. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2000, 10, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Tang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Yu, F.; Yu, W.; He, F.; Fu, C.; Mao, S. Cloning, expression analysis, and antibacterial properties of three serum amyloid A in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 65, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, S.F.; Buchmann, K.; Nielsen, M.E. Ichthyophthirius multifiliis infection induces massive up-regulation of serum amyloid A in carp (Cyprinus carpio). Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2007, 115, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.A.; Zou, J.; Houlihan, D.F.; Secombes, C.J. Directional responses following recombinant cytokine stimulation of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) RTS-11 macrophage cells as revealed by transcriptome profiling. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoffersen, T.B.; Kania, P.W.; von Gersdorff Jørgensen, L.; Buchmann, K. Zebrafish Danio rerio as a model to study the immune response against infection with Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 40, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosten, L.A.B.; Netea, M.G.; Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-1β in innate inflammation, autophagy and immunity. Semin. Immunol. Acad. Press 2013, 25, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandevyver, S.; Dejager, L.; E Vandenbroucke, R.; Libert, C. An acute phase protein ready to go therapeutic for sepsis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6 signaling in health and disease. F1000Research 2020, 9, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teachey, D.T.; Lacey, S.F.; Shaw, P.A.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Maude, S.L.; Frey, N.; Pequignot, E.; Gonzalez, V.E.; Chen, F.; Finklestein, J.; et al. Identification of predictive biomarkers for cytokine release syndrome after chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 664–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhsin, M.; Ajendra, J.; Gentil, K.; Berbudi, A.; Neumann, A.-L.; Klaas, L.; Schmidt, K.E.; Hoerauf, A.; Hübner, M.P. IL-6 is required for protective immune responses against early filarial infection. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 48, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primer | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | GenBank Accession No. | Length (bp) | Experiment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β F | ATGGCTGGCGAAGATTTT | XM_060895816.1 | 729 | Gene cloning |
| IL-1β R | TCAGAACTCATTCTGAGAGACTACT | |||
| q-IL-1β F | ACCAGGACCTCTTCACTATCT | PQ651581 | 98 | RT-qPCR |
| q-IL-1β R | GTCCTGCATGCTGTAACTCT | |||
| IL-6 F | ATGGATTTCTATGAAACATCTGGA | XM_027176013.2 | 597 | Gene cloning |
| IL-6 R | TCATTGCTGGTGTTTTGAGATCCA | |||
| q-IL-6 F | AGATGCCGATCCTCAACAAT | PP812522 | 100 | RT-qPCR |
| q-IL-6 R | ACCTGGTACACCCGCAAACC | |||
| SAA F | ATGTTTATGGACTCACCACAGATG | XM_060886829.1 | 1404 | Gene cloning |
| SAA R | TTACACTGGCTCTGGTTTAGGCTC | |||
| SAA F | GTACAGCAGCCTCCAGT | PP790568 | 111 | RT-qPCR |
| SAA R | ATGAGGAATTGATGAAGAGC | |||
| β-actin F | GATTCGCTGGAGATGATGCT | EU161066.1 | 162 | RT-qPCR |
| β-actin R | CGTGCTCAATGGGGTACTTC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Pi, X.; Wang, Q.; Fu, Y.; Fan, W.; Yang, Q. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Pro-Inflammatory Mediator Expression in Pelteobagrus vachelli During Ichthyophthiriasis: A 40-Day Longitudinal Study of IL-1β, IL-6, and SAA. Animals 2025, 15, 1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111577
He Y, Wang M, Wang J, Wang Y, Pi X, Wang Q, Fu Y, Fan W, Yang Q. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Pro-Inflammatory Mediator Expression in Pelteobagrus vachelli During Ichthyophthiriasis: A 40-Day Longitudinal Study of IL-1β, IL-6, and SAA. Animals. 2025; 15(11):1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111577
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Yang, Miaomiao Wang, Jun Wang, Yadong Wang, Xiaolan Pi, Qi Wang, Yan Fu, Wei Fan, and Qian Yang. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Pro-Inflammatory Mediator Expression in Pelteobagrus vachelli During Ichthyophthiriasis: A 40-Day Longitudinal Study of IL-1β, IL-6, and SAA" Animals 15, no. 11: 1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111577
APA StyleHe, Y., Wang, M., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Pi, X., Wang, Q., Fu, Y., Fan, W., & Yang, Q. (2025). Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Pro-Inflammatory Mediator Expression in Pelteobagrus vachelli During Ichthyophthiriasis: A 40-Day Longitudinal Study of IL-1β, IL-6, and SAA. Animals, 15(11), 1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111577







