Evaluation of the Effectiveness of a Matrix of Exogenous Proteases in the Nutrition of Shrimp Penaeus vannamei
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Units
2.2. Experimental Design, Diets, and Management
2.3. Zootechnical Performance
2.4. Yield of Headless and Shell-Less Shrimp
2.5. Analysis of Centesimal Composition
2.6. Meat Quality Analysis
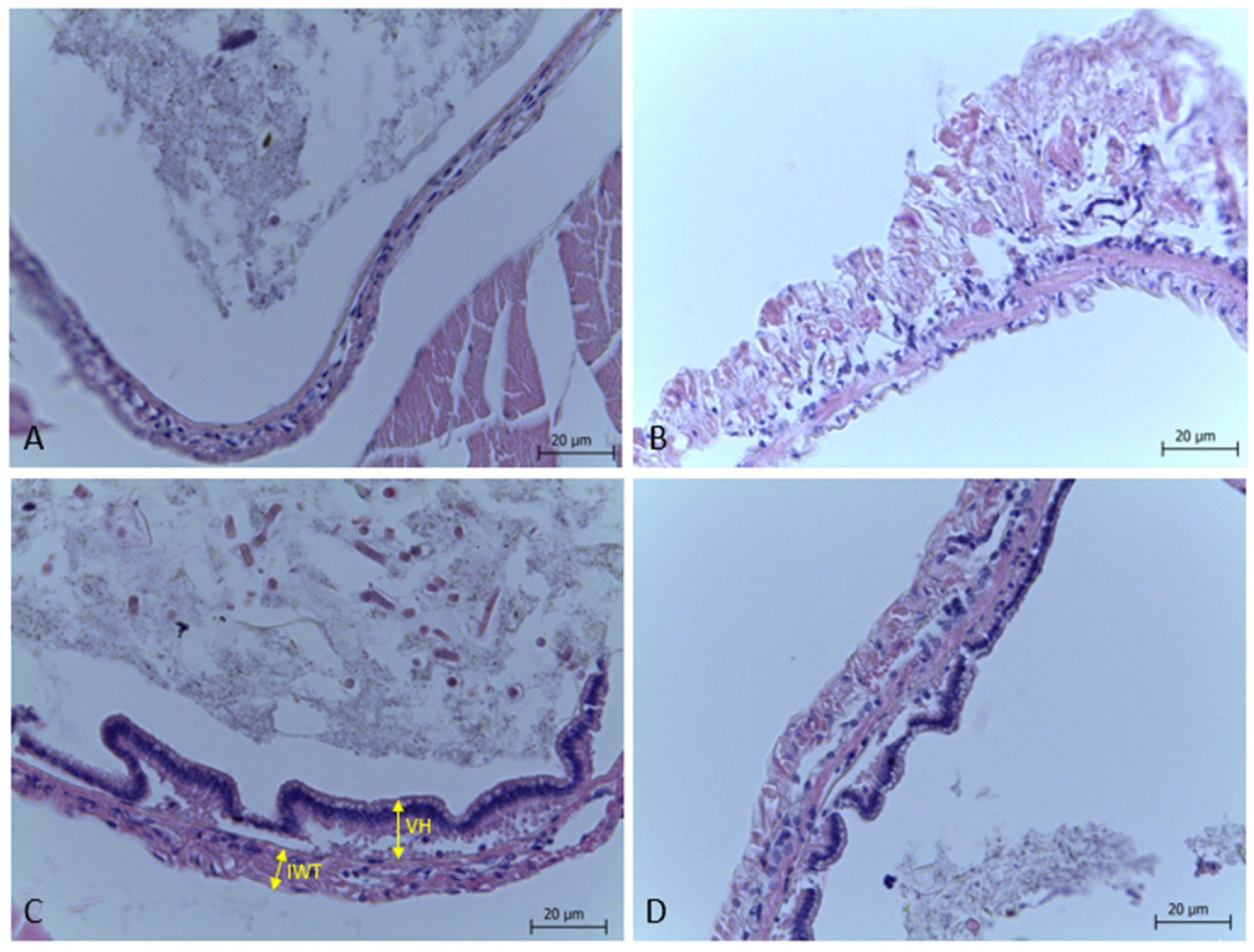
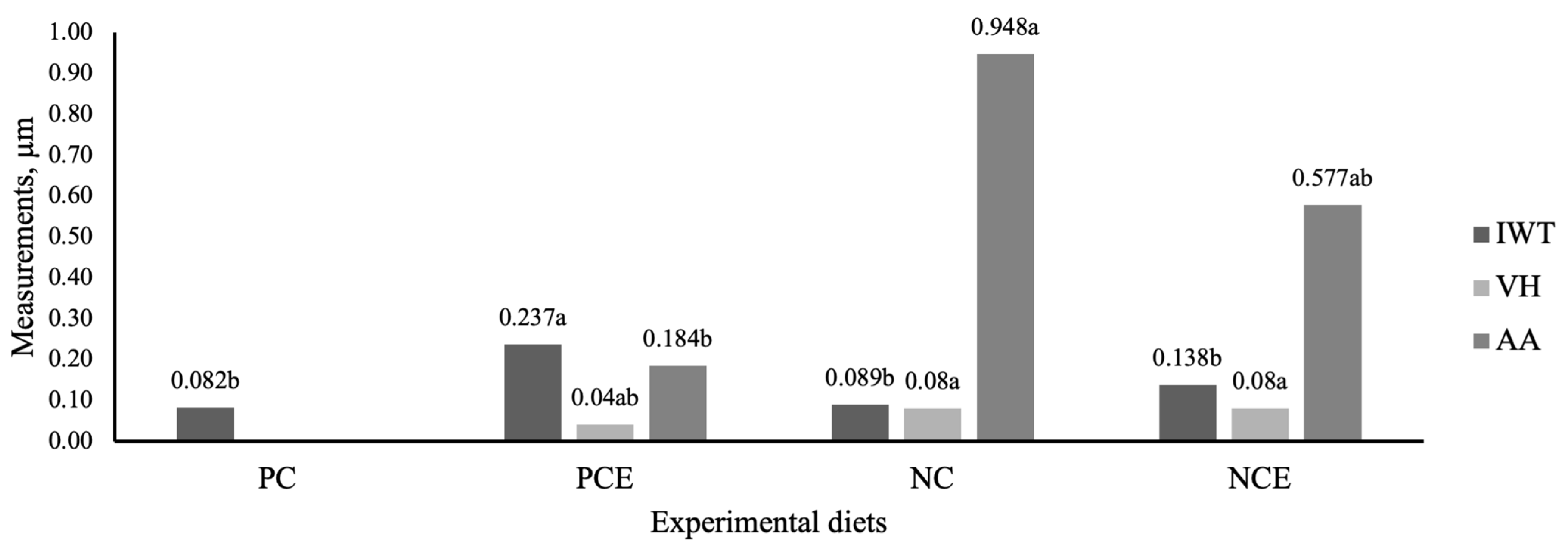
2.7. Histological Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarker, P.K. Microorganisms in Fish Feeds, Technological Innovations, and Key Strategies for Sustainable Aquaculture. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamborain-Mason, J.; Viana, D.; Nicholas, K.; Jackson, E.D.; Koehn, J.Z.; Passarelli, S.; Yoo, S.-H.; Zhang, A.W.; Davin, H.C.; Duggan, C.P.; et al. A Decision Framework for Selecting Critically Important Nutrients from Aquatic Foods. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2023, 10, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garibay-Valdez, E.; Cicala, F.; Martinez-Porchas, M.; Gómez-Reyes, R.; Vargas-Albores, F.; Gollas-Galván, T.; Martínez-Córdova, L.R.; Calderón, K. Longitudinal Variations in the Gastrointestinal Microbiome of the White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Z.; Yao, D.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Aweya, J.J. Functional Characterization of Arginine Metabolic Pathway Enzymes in the Antibacterial Immune Response of Penaeid shrimp. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2022, 127, 104293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buarque, D.S.; Castro, P.F.; Santos, F.M.S.; Lemos, D.; Júnior, L.B.C.; Bezerra, R.S. Digestive Peptidases and Proteinases in the Midgut Gland of the Pink Shrimp Farfantepenaeus paulensis (Crustacea, Decapoda, Penaeidae). Aquac. Res. 2009, 40, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klahan, R.; Deevong, P.; Wiboonsirikul, J.; Yuangsoi, B. Growth Performance, Feed Utilisation, Endogenous Digestive Enzymes, Intestinal Morphology, and Antimicrobial Effect of Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Fed with Feed Supplemented with Pineapple Waste Crude Extract as a Functional Feed Additive. Aquac. Nutr. 2023, 2023, 1160015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez-De Lucio, B.S.; Hernández-Domínguez, E.M.; Villa-García, M.; Díaz-Godínez, G.; Mandujano-Gonzalez, V.; Mendoza-Mendoza, B.; Álvarez-Cervantes, J. Exogenous Enzymes as Zootechnical Additives in Animal Feed: A Review. Catalysts 2021, 11, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Liu, Y.; Fu, S.; Zhuo, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, S.; Tu, Y.; Shan, T. Effect of a Novel Alkaline Protease from Bacillus Licheniformis on Growth Performance, Carcass Characteristics, Meat Quality, Antioxidant Capacity, and Intestinal Morphology of White Feather Broilers. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 5176–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Oh, H.; Kim, Y.; Song, D.; An, J.; Chang, S.; Go, Y.; Cho, H.; Lee, B.; Kim, W.K.; et al. Effects of Exogenous Protease on Performance, Economic Evaluation, Nutrient Digestibility, Fecal Score, Intestinal Morphology, Blood Profile, Carcass Trait, and Meat Quality in Broilers Fed Normal Diets and Diets Considered with Matrix Value. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureshkumar, S.; Song, J.; Sampath, V.; Kim, I. Exogenous Enzymes as Zootechnical Additives in Monogastric Animal Feed: A Review. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.M.; Hong, J.S.; Kim, Y.B.; Nawarathne, S.R.; Choi, I.; Yi, Y.-J.; Wu, D.; Lee, H.; Han, S.E.; Nam, K.T.; et al. Responses in Growth Performance and Nutrient Digestibility to a Multi-Protease Supplementation in Amino Acid-Deficient Broiler Diets. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2020, 62, 840–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Q.; Chai, X.Q.; Liu, D.Y.; Kabir Chowdhury, M.A.; Leng, X.J. Effects of Temperature and Feed Processing on Protease Activity and Dietary Protease on Growths of White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, and Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus × O. aureus. Aquac. Nutr. 2016, 22, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.-L.; Tan, B.-P.; Chi, S.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Chowdhury, M.A.K.; Dong, X.-H. The Effects of a Dietary Protease-complex on Performance, Digestive and Immune Enzyme Activity, and Disease Resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei Fed High Plant Protein Diets. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 2550–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryam; Shah, S.Z.H.; Fatima, M.; Nadeem, H.; Ashraf, S.; Hussain, M. Roles of Dietary Supplementation of Exogenous Protease in Low Fishmeal Aquafeed—A Mini Review. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2024, 24, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.L.S.; Lazzari, R. Nutritional implications of exogenous proteases in fish feeding. Pesqui. Agropecuária Gaúcha 2022, 28, 70–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipps-Wiemann, P. Proteases—Animal Feed. In Enzymes in Human and Animal Nutrition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 279–297. ISBN 9780128054192. [Google Scholar]
- Dalsgaard, J.; Verlhac, V.; Hjermitslev, N.H.; Ekmann, K.S.; Fischer, M.; Klausen, M.; Pedersen, P.B. Effects of Exogenous Enzymes on Apparent Nutrient Digestibility in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Fed Diets with High Inclusion of Plant-Based Protein. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2012, 171, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanthi, M.; Chotikachinda, R.; Medagoda, N.; Lee, K.-J. Exogenous Protease Supplementation in High or Low Fish Meal Diets for Pacific White shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei: Comparative Effect on Growth, Innate Immunity, Nutrient Digestibility, Gut Microbiome and Intestinal Morphology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, R.; Tacon, A.G.J.; Lemos, D. Effect of Dietary Phytase and Protease Supplementation on the Growth Performance and Apparent Nutrient Digestibility in Juvenile Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Fed Fish Meal–Free and Phosphorus Limiting Diets. Aquac. Int. 2024, 32, 6053–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Maulu, S.; Wang, J.; Xie, X.; Liang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Xue, M. The Application of Protease in Aquaculture: Prospects for Enhancing the Aquafeed Industry. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 16, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-J.; Liu, W.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.-M.; Wen, H.; Liu, H. Beneficial Effects of Dietary Exogenous Protease on the Growth, Intestinal Health and Immunity of GIFT (Oreochromis niloticus) Fed Plant-based Diets. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 1822–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.S.; Mohammady, E.Y.; Adnan, A.M.; Abd Elnabi, H.E.; Ayman, M.F.; Soltan, M.A.; El-Haroun, E.R. Effect of Dietary Protease at Different Levels of Malic Acid on Growth, Digestive Enzymes and Haemato-Immunological Responses of Nile Tilapia, Fed Fish Meal Free Diets. Aquaculture 2020, 522, 735124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlophe-Ginindza, S.N.; Moyo, N.A.G.; Ngambi, J.W.; Ncube, I. The Effect of Exogenous Enzyme Supplementation on Growth Performance and Digestive Enzyme Activities in Oreochromis mossambicus Fed Kikuyu-Based Diets. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 3777–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, Y.E.; Pereira, N.A.; Laitano, M.V.; Moreno, P.; Fernández-Gimenez, A.V. Exogenous Proteases from Seafood Processing Waste as Functional Additives in Rainbow Trout Aquaculture. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 4350–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.C.; Wu, J.W.; Jin, Z.H.; Ye, Z.F.; Yang, S.; Sun, Y.Q.; Fei, H. Exogenous Enzymes as Functional Additives in Finfish Aquaculture. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeoye, A.A.; Jaramillo-Torres, A.; Fox, S.W.; Merrifield, D.L.; Davies, S.J. Supplementation of Formulated Diets for Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) with Selected Exogenous Enzymes: Overall Performance and Effects on Intestinal Histology and Microbiota. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2016, 215, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRC. Nutrient Requirements of Fish and Shrimp; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; ISBN 9780309163385.
- Instituto Adolfo Lutz (São Paulo). Métodos físico-químicos para análise de alimentos. In Coordenadores Odair Zenebon, Neus Sadocco Pascuet e Paulo Tiglea; Instituto Adolfo Lutz: São Paulo, Brazil, 2008; p. 1020. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International; Cunniff, P.A., Ed.; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2000; ISBN 9780935584677. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, A.A.; Rech, B.T.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Pucci, D.M.T. Quality evaluation of frozen seafood (Genypterus brasiliensis, Prionotus punctatus, Pleoticus muelleri, and Perna perna) previously treated with phosphates. Pan-Am. J. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 3, 248–258. [Google Scholar]
- Hamm, R. Biochemistry of Meat Hydration. Adv. Food Res. 1960, 10, 355–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osório, J.C.S.; Osório, M.T.M.; Jardim, P.O.C.; PimenteL, M.A.; Pouey, J.L.O.; Lüder, W.E.; Cordellino, R.A.; Oliveira, N.M.; Gularte, M.A.; Borba, M.F.; et al. Métodos para Avaliação de Carne Ovina “In Vivo”, Na carcaça e na Carne; Pelotas Editora Universitária/UFPEL: Santiago, Chile, 1998; 107p. [Google Scholar]
- Humason, G.L. Animal Tissue Techniques, 3rd ed.; W.H. Freeman and Company: São Francisco, CA, USA, 1972; 641p. [Google Scholar]
- Tolosa, E.M.C.; Rodrigues, C.J.; Behmer, O.A.; de Freitas Neto, A.G. Manual de Técnicas para Histologia Normal e Patológica; Manole: São Paulo, Brazil, 2003; ISBN 9788520414408. [Google Scholar]
- Schleder, D.D.; Peruch, L.G.B.; Poli, M.A.; Ferreira, T.H.; Silva, C.P.; Andreatta, E.R.; Hayashi, L.; do Nascimento Vieira, F. Effect of Brown Seaweeds on Pacific White Shrimp Growth Performance, Gut Morphology, Digestive Enzymes Activity and Resistance to White Spot Virus. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes-Blackburn, D.; Greiner, R. Enzymes used in animal feed: Leading technologies and forthcoming developments. In Functional Polymers in Food Science; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 47–73. ISBN 9781119108580. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Li, X.-Q.; Chowdhury, M.A.K.; Chen, J.-N.; Leng, X.-J. Effects of protease supplementation in low fish meal pelleted and extruded diets on growth, nutrient retention and digestibility of gibel carp, Carassius auratus gibelio. Aquaculture 2016, 460, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, E.S.E.; Tawfeek, S.S.; Abdel-Fadeel, A.A.A.; Abdel-Daim, A.S.A.; Abdel-Razik, A.-R.H.; Youssef, I.M.I. Effect of Dietary Protease Supplementation on Growth Performance, Water Quality, Blood Parameters and Intestinal Morphology of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 106, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Li, X.; Kabir Chowdhury, M.A.; Wang, J.; Leng, X. Dietary Protease, Carbohydrase and Micro-Encapsulated Organic Acid Salts Individually or in Combination Improved Growth, Feed Utilization and Intestinal Histology of Pacific White Shrimp. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Yin, M.; Qi, X.; Li, Z.; Yu, Z.; Chen, M.; Xiao, T.; Wang, X. Freezing and storage on aquatic food: Underlying mechanisms and implications on quality deterioration. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e91322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, M.S. Chemical and Physical Characteristics of Meat|water-holding capacity. In Encyclopedia of Meat Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 274–282. ISBN 9780123847348. [Google Scholar]
- Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento (MAPA). Instrução Normativa nº 23 de 20 de agosto de 2019. In Estabelece Regulamento Técnico e Requisitos de Qualidade para Camarão; Diário Oficial da União: Brasília, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chouljenko, A.; Chotiko, A.; Bonilla, F.; Moncada, M.; Reyes, V.; Sathivel, S. Effects of Vacuum Tumbling with Chitosan Nanoparticles on the Quality Characteristics of Cryogenically Frozen Shrimp. Lebenson. Wiss. Technol. 2017, 75, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chande, N.S.; Patange, S.B.; Chavan, D.R.; Bhujbal, P.K.; Dalavi, P.D. Effect of individual quick freezing on performance, storage and frozen storage characteristics of white-leg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Pharma Innov. 2023, 12, 2071–2077. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.; Wu, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, F.; Xu, Y.; Xia, W. Recent Advances in Quality Retention of Non-Frozen Fish and Fishery Products: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1747–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Silva, d.A.; da Silva Campelo, M.C.; de Oliveira Soares Rebouças, L.; de Oliveira Vitoriano, J.; Alves, C., Jr.; Alves da Silva, J.B.; de Oliveira Lima, P. Use of Cold Atmospheric Plasma to Preserve the Quality of White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, J.; Rasco, B.; Sablani, S.S.; Ovissipour, M.; Qu, Z. Kinetics of Quality Changes of Shrimp (Litopenaeus setiferus) during Pasteurization. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroga, I.M.B.N.; da Silva, J.A.; Cavalheiro, J.M.O.; Queiroga, R.d.C.R.E.; Batista, A.S.M.; Barreto, T.A. Qualidade sensorial do camarão Litopenaeus vannamei congelado. Semin. Cienc. Agrar. 2014, 35, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, K.D.; Mishkind, D.; Riddle, M.R.; Tabin, C.J.; Gumucio, D.L. Blueprint for an Intestinal Villus: Species-specific Assembly Required. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2018, 7, e317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Ji, D.; Yao, J.; Zou, Y.; Yan, M. Comparative Analysis of Intestinal Characteristics of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) and Intestinal Flora with Different Growth Rates. Fishes 2022, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Tan, B.; Yang, Q.; Mao, M.; Lin, Y.; Chi, S. Growth, Nonspecific Immunity, Intestinal Flora, Hepatopancreas, and Intestinal Histological Results for Litopenaeus vannamei Fed with Diets Supplement with Different Animal by-Products. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 29, 101521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Alcade, M.C.; García-Ulloa, M.; Montaño, E.M.; Castro-Martínez, C.; Álvarez-Ruiz, P.; Rodríguez González, H. Use of Enzyme Mixtures in Diets Based on Animal and Plant Ingredients for Litopenaeus vannamei: Effect on Digestibility, Growth, and Enzyme Activity. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2023, 23, TRJFAS21999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Liu, Y.; Fu, S.; Zhuo, J.; Wang, J.; Shan, T. Dietary novel alkaline protease from Bacillus licheniformis improves broiler meat nutritional value and modulates intestinal microbiota and metabolites. Anim. Microbiome 2024, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Zamorano, M.; Navarrete del Toro, M.A.; García-Carreño, F. Exogenous proteinases as feed supplement for shrimp: In vitro evaluation. Aquac. Nutr. 2013, 19, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Description | PC | PCE | NC | NCE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean meal 45% | 41.446 | 41.446 | 41.604 | 41.604 |
| Corn 8% | 31.421 | 31.421 | 32.080 | 32.080 |
| Fishmeal 53% | 9.788 | 9.788 | 9.528 | 9.528 |
| Fish oil | 3.500 | 3.500 | 3.074 | 3.074 |
| Artemia biomass | 4.075 | 4.075 | 4.075 | 4.075 |
| Common salt | 1.251 | 1.251 | 1.251 | 1.251 |
| Premix | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Vitamin C | 0.600 | 0.600 | 0.600 | 0.600 |
| L-Lysine HCl | 0.380 | 0.380 | 0.255 | 0.255 |
| L-Threonine | 0.288 | 0.288 | 0.284 | 0.284 |
| DL-Methionine | 0.258 | 0.258 | 0.255 | 0.255 |
| Seaweed | 2.000 | 2.000 | 2.000 | 2.000 |
| Soy lecithin | 1.500 | 1.500 | 1.500 | 1.500 |
| Potassium | 1.200 | 1.200 | 1.200 | 1.200 |
| Lactic acid | 0.750 | 0.750 | 0.750 | 0.750 |
| Sodium lactate | 0.325 | 0.325 | 0.325 | 0.325 |
| Adsorbent | 0.100 | 0.100 | 0.100 | 0.100 |
| Binder | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.035 |
| Antioxidant | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.030 |
| Antifungal | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.030 |
| Inert | 0.025 | 0.000 | 0.025 | 0.000 |
| Protease blend | 0.000 | 0.025 | 0.000 | 0.025 |
| Total | 100.000 | 100.000 | 100.000 | 100.000 |
| Calculated chemical composition | ||||
| Moisture (%) | 10.237 | 10.237 | ||
| Dry matter (%) | 83.763 | 83.763 | ||
| Ashes (%) | 7.513 | 7.513 | ||
| TDN (%) | 56.208 | 56.208 | ||
| Gross energy (kcal/kg) | 4200.000 | 4162.500 | ||
| Crude protein (%) | 35.000 | 34.000 | ||
| Crude fiber (%) | 4.768 | 4.768 | ||
| Acid detergent fiber (%) | 6.983 | 6.983 | ||
| Neutral detergent fiber (%) | 10.499 | 10.499 | ||
| Methionine (%) | 0.800 | 0.775 | ||
| Met + Cys (%) | 1.263 | 1.225 | ||
| Lysine (%) | 2.400 | 2.335 | ||
| Threonine (%) | 1.600 | 1.553 | ||
| Tryptophan (%) | 0.426 | 0.426 | ||
| Arginine (%) | 2.369 | 2.369 | ||
| Isoleucine (%) | 1.473 | 1.473 | ||
| Valine (%) | 1.610 | 1.610 | ||
| Aspartic acid (%) | 3.709 | 3.709 | ||
| Glutamic acid (%) | 5.721 | 5.721 | ||
| Grease (%) | 5.676 | 5.676 | ||
| Linoleic acid (%) | 0.684 | 0.684 | ||
| Linolenic acid (%) | 0.097 | 0.097 | ||
| Arachidonic acid (%) | 0.688 | 0.688 | ||
| Calcium (%) | 0.760 | 0.760 | ||
| Phosphorus (%) | 0.733 | 0.733 | ||
| Sodium (%) | 0.600 | 0.600 | ||
| Potassium (%) | 1.316 | 1.316 | ||
| Chlorine (%) | 1.002 | 1.002 | ||
| Main Effects | IBW (g) | BW (g) | FI (g) | BWG (g) | SGDAY (%) | SGWEEK (%) | FE (%) | FCR (g/g) | Survival (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | 0.57 ± 0.01 | 13.2 ± 1.33 | 25.8 ± 0.52 | 12.6 ± 1.33 | 15.0 ± 1.52 | 104.9 ± 11.1 | 48.9 ± 5.57 | 2.07 ± 0.22 | 78.1 ± 4.15 |
| NC | 0.56 ± 0.02 | 12.9 ± 1.76 | 25.5 ± 0.70 | 12.4 ± 1.76 | 14.7 ± 2.09 | 103.0 ± 14.7 | 48.4 ± 6.82 | 2.09 ± 0.28 | 78.9 ± 7.08 |
| 0 g/t protease | 0.56 ± 0.02 | 11.9 b ± 0.57 | 25.8 ± 0.56 | 11.3 b ± 0.57 | 13.5 b ± 0.69 | 94.6 b ± 4.82 | 44.0 b ± 2.06 | 2.28 a ± 0.11 | 77.± 7.30 |
| 250 g/t protease | 0.57 ± 0.02 | 14.5 a ± 1.00 | 25.5 ± 0.67 | 13.9 a ± 1.01 | 16.6 a ± 1.202 | 116.0 a ± 8.41 | 54.7 a ± 3.66 | 1.84 b ± 0.12 | 80.6 ± 3.41 |
| Interaction | |||||||||
| PC | 0.57 ± 0.02 | 12.1 b ± 0.63 | 26.0 ± 0.53 | 11.6 b ± 0.64 | 13.8 b ± 0.76 | 96.4 b ± 5.33 | 44.5 b ± 2.15 | 2.25 A ± 0.11 | 76.9 ± 3.95 |
| PCE | 0.57 ± 0.02 | 14.2 a ± 1.01 | 25.6 ± 0.43 | 13.6 a ± 1.02 | 16.2 a ± 1.21 | 113.4 a ± 8.52 | 53.3 a ± 4.23 | 1.89 b ± 0.15 | 79.4 ± 4.22 |
| NC | 0.56 ± 0.02 | 11.7 B ± 0.43 | 25.5 ± 0.52 | 11.1 B ± 0.44 | 13.2 B ± 0.52 | 92.7 B ± 3.66 | 43.6 B ± 1.99 | 2.30 A ± 0.10 | 78.4 ± 9.86 |
| NCE | 0.57 ± 0.02 | 14.8 A ± 0.94 | 25.4 ± 0.87 | 14.2 A ± 0.95 | 16.9 A ± 1.13 | 118.6 A ± 7.96 | 56.1 A ± 2.52 | 1.79 B ± 0.08 | 81.9 ± 1.89 |
| Nutrition | 0.30 | 0.78 | 0.16 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.37 | 0.52 | 0.33 |
| Protease | 0.54 | <0.001 | 0.17 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.16 |
| Interaction | 0.54 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.82 |
| C.V. (%) | 3.630 | 6.01 | 2.41 | 6.34 | 6.34 | 6.34 | 5.82 | 5.55 | 7.32 |
| Main Effects | YieldSC (%) | YieldSCC (%) | Moisture (%) | Protein (%) | Lipids (%) | Ash (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | 62.2 ± 2.25 | 51.2 b ± 1.56 | 75.9 ± 2.20 | 19.3 ± 1.47 | 0.26 ± 0.03 | 4.5 ± 0.41 |
| NC | 62.4 ± 2.23 | 52.2 a ± 1.51 | 76.4 ± 1.13 | 18.6 ± 1.46 | 0.27 ± 0.05 | 4.5 ± 0.22 |
| 0 g/t protease | 60.5 b ± 0.91 | 50.8 b ± 1.37 | 75.9 ± 2.29 | 19.1 ± 1.82 | 0.28 ± 0.04 | 4.4 ± 0.37 |
| 250 g/t protease | 64.0 a ± 1.73 | 52.6 a ± 1.29 | 76.4 ± 0.92 | 18.7 ± 1.07 | 0.25 ± 0.04 | 4.6 ± 0.26 |
| Interaction | ||||||
| PC | 60.5 b ± 0.83 | 50.3 bY ± 1.32 | 74.9 ± 2.97 | 20.1 ± 1.80 | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 4.2 ± 0.43 |
| PCE | 63.9 a ± 1.96 | 52.2 ay ± 1.12 | 76.8 ± 0.83 | 18.4 ± 0.22 | 0.27 ± 0.03 | 4.8 ± 0.10 |
| NC | 60.5 B ± 1.00 | 51.4 BX ± 1.20 | 76.8 ± 1.36 | 18.2 ± 1.51 | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 4.7 ± 0.16 |
| NCE | 64.2 A ± 1.49 | 53.0 Ax ± 1.33 | 76.0 ± 0.97 | 19.0 ± 1.50 | 0.23 ± 0.03 | 4.4 ± 0.21 |
| Nutrition | 0.481 | 0.00 | 0.62 | 0.43 | 0.73 | 0.90 |
| Protease | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.60 | 0.62 | 0.14 | 0.37 |
| Interaction | 0.52 | 0.56 | 0.23 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| C.V. (%) | 2.23 | 2.41 | 2.31 | 7.53 | 12.0 | 5.69 |
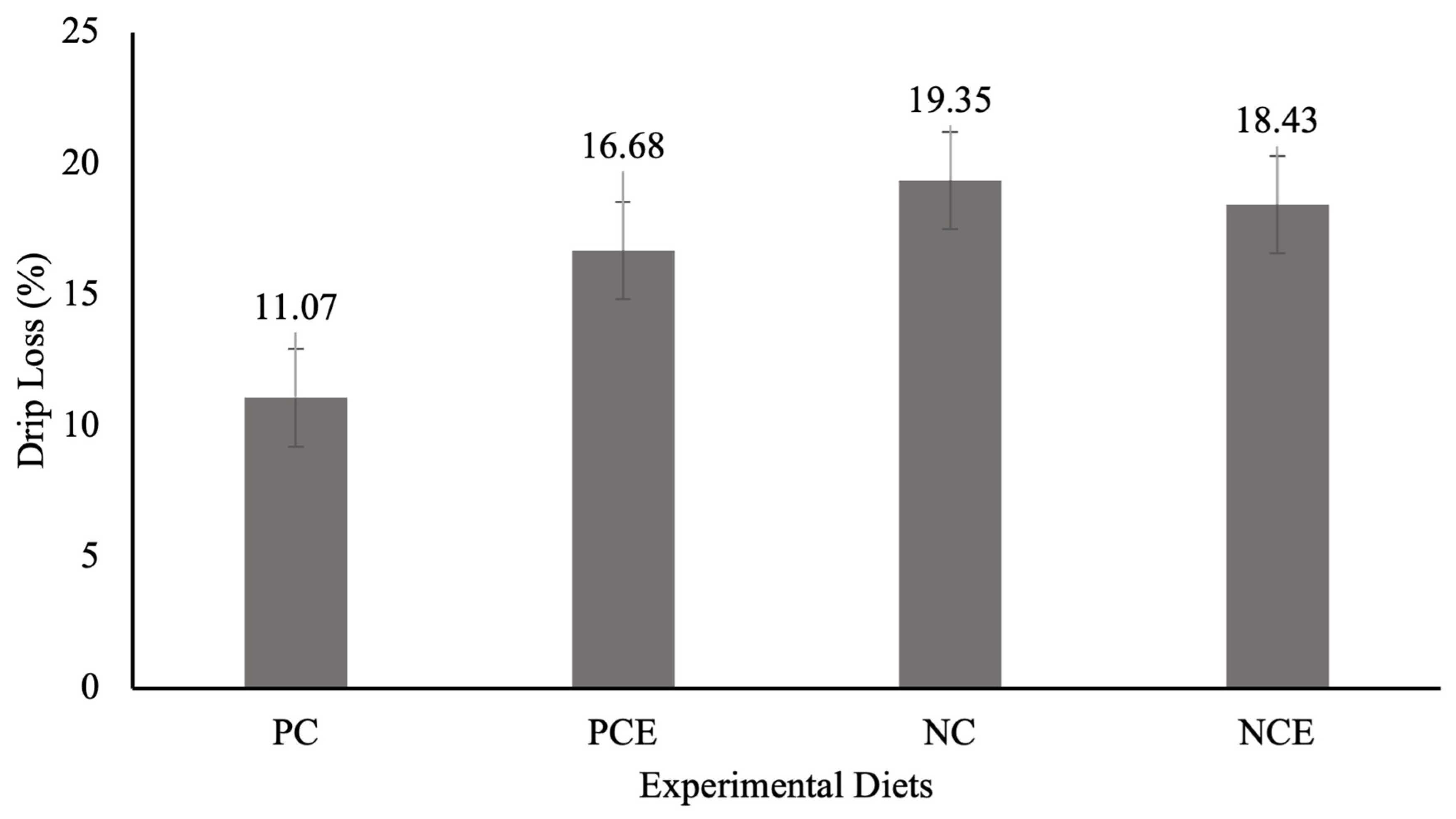
| Main Effects | pH | Moisture (%) | Protein (%) | WRC (%) | WCL (%) | SF (kgf) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | 6.57 a ± 0.37 | 76.1 a ± 1.29 | 23.4 a ± 3.05 | 70.78 a ± 3.69 | 60.1 a ± 2.23 | 2.05 a ± 0.94 |
| NC | 6.42 a ± 0.24 | 76.7 a ± 1.23 | 22.5 a ± 2.47 | 72.5 a ± 3.80 | 58.9 a ± 2.01 | 2.11 a ± 0.88 |
| 0 g/t protease | 6.54 A ± 0.35 | 76.4 A ± 1.11 | 22.8 A ± 2.65 | 70.2 B ± 4.26 | 59.8 A ± 2.00 | 2.05 A ± 0.91 |
| 250 g/t protease | 6.45 A ± 0.25 | 76.4 A ± 1.42 | 23.1 A ± 2.86 | 73.1 A ± 3.57 | 59.2 A ± 2.36 | 2.11 A ± 0.88 |
| Interaction | ||||||
| PC | 6.67 a ± 0.49 | 75.6 b ± 1.42 | 24.0 a ± 3.28 | 72.0 a ± 3.12 | 61.6 a ± 1.67 | 1.95 a ± 0.84 |
| PCE | 6.48 a ± 0.27 | 76.1 a ± 0.97 | 22.9 a ± 2.85 | 73.0 a ± 4.62 | 58.6 b ± 2.09 | 2.16 a ± 1.06 |
| NC | 6.41 A ± 0.24 | 77.22 A ± 1.27 | 21.6 A ± 1.95 | 68.4 B ± 4.31 | 57.9 B ± 1.41 | 2.15 A ± 0.96 |
| NCE | 6.42 A ± 0.24 | 76.59 A ± 1.20 | 23.4 A ± 2.84 | 73.1 A ± 2.54 | 59.9 A ± 2.60 | 2.06 A ± 0.80 |
| Nutrition | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.33 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.93 |
| Protease | 0.39 | 0.91 | 0.72 | 0.02 | 0.45 | 0.90 |
| Interaction | 0.37 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.000 | 0.59 |
| C.V. (%) | 6.48 | 2.05 | 16.16 | 6.79 | 4.43 | 58.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Souza, J.T.; da Silva Oliveira, M.É.; da Cunha, A.E.; da Silva, V.M.F.; de Araújo, R.A.N.; Silva, M.A.M.; Júnior, R.A.H.; de Assunção, M.A.V.; Lopes, A.C.A.; Monteiro, D.P.; et al. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of a Matrix of Exogenous Proteases in the Nutrition of Shrimp Penaeus vannamei. Animals 2025, 15, 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101410
Souza JT, da Silva Oliveira MÉ, da Cunha AE, da Silva VMF, de Araújo RAN, Silva MAM, Júnior RAH, de Assunção MAV, Lopes ACA, Monteiro DP, et al. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of a Matrix of Exogenous Proteases in the Nutrition of Shrimp Penaeus vannamei. Animals. 2025; 15(10):1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101410
Chicago/Turabian StyleSouza, Joice Teixeira, Maria Érica da Silva Oliveira, Ana Elidarly da Cunha, Vanessa Maria Freitas da Silva, Ruan Arthur Nunes de Araújo, Mário Augusto Monteiro Silva, Raimundo Audei Henrique Júnior, Marcos Aurelio Victor de Assunção, Ana Cecília Araújo Lopes, Daniel Pigatto Monteiro, and et al. 2025. "Evaluation of the Effectiveness of a Matrix of Exogenous Proteases in the Nutrition of Shrimp Penaeus vannamei" Animals 15, no. 10: 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101410
APA StyleSouza, J. T., da Silva Oliveira, M. É., da Cunha, A. E., da Silva, V. M. F., de Araújo, R. A. N., Silva, M. A. M., Júnior, R. A. H., de Assunção, M. A. V., Lopes, A. C. A., Monteiro, D. P., Ribeiro, T. P., de Oliveira, M. F., & de Lima, M. R. (2025). Evaluation of the Effectiveness of a Matrix of Exogenous Proteases in the Nutrition of Shrimp Penaeus vannamei. Animals, 15(10), 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101410







