Molecular Detection and Characterization of Coronaviruses in Migratory Ducks from Portugal Show the Circulation of Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
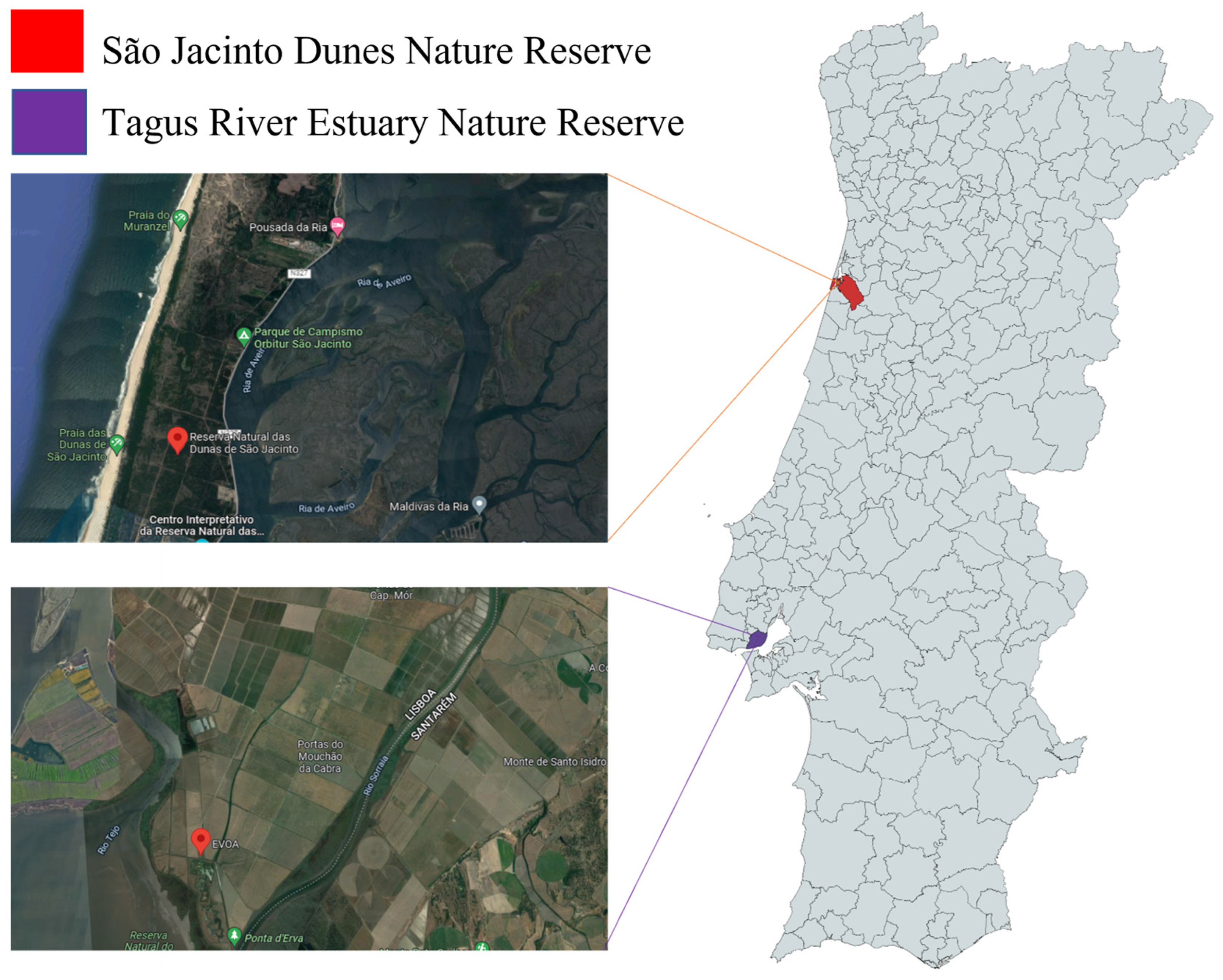
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Screening for Coronaviruses
2.3. Sanger Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
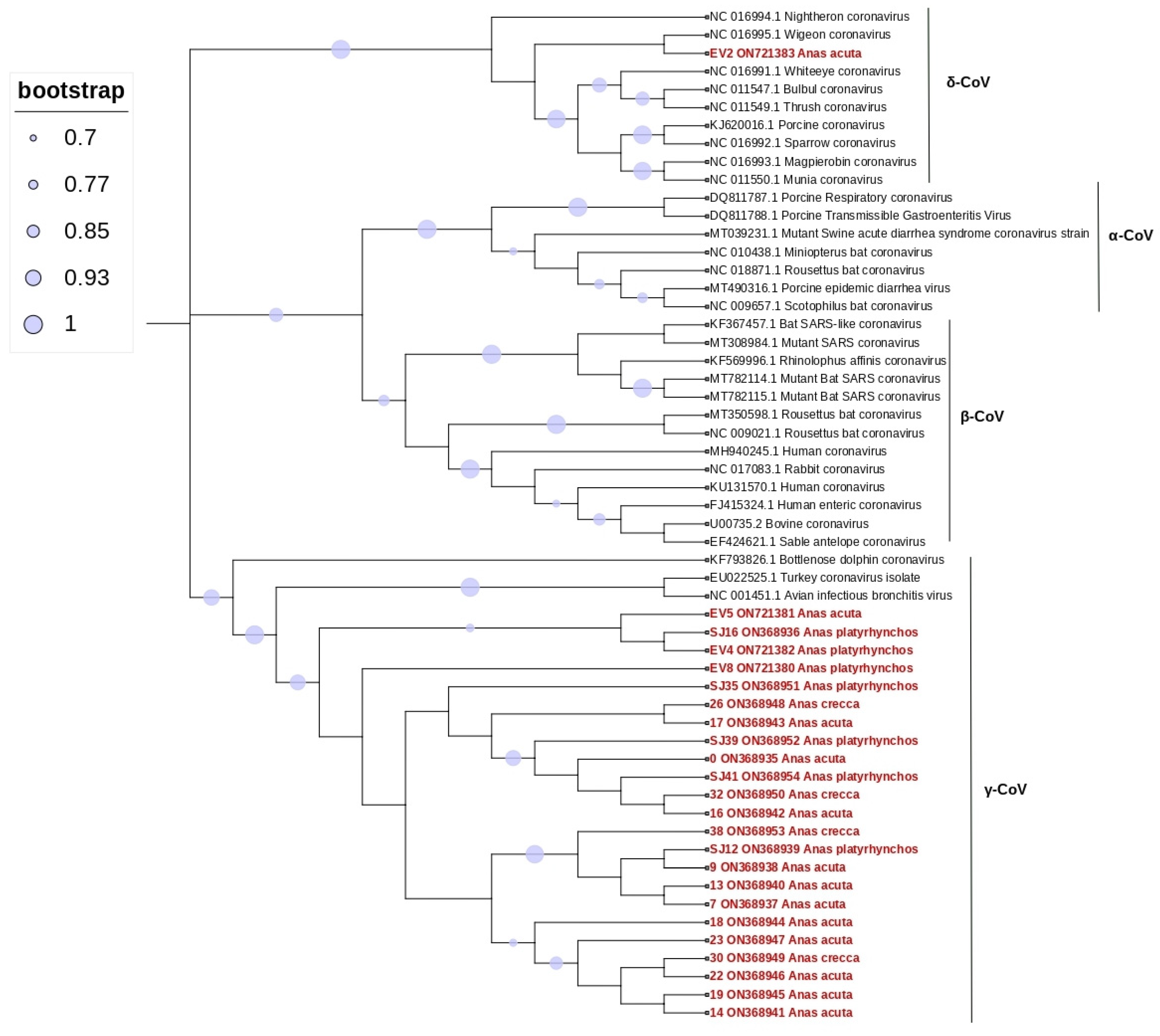
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Domańska-Blicharz, K.; Miłek-Krupa, J.; Pikuła, A. Diversity of Coronaviruses in Wild Representatives of the Aves Class in Poland. Viruses 2021, 13, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hepojoki, S.; Lindh, E.; Vapalahti, O.; Huovilainen, A. Prevalence and genetic diversity of coronaviruses in wild birds, Finland. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2017, 7, 1408360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackwood, M.W.; Hall, D.; Handel, A. Molecular evolution and emergence of avian gammacoronaviruses. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Du, J.; Su, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Z.; Jin, Q. Identification of Diverse Bat Alphacoronaviruses and Betacoronaviruses in China Provides New Insights Into the Evolution and Origin of Coronavirus-Related Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monchatre-Leroy, E.; Boué, F.; Boucher, J.-M.; Renault, C.; Moutou, F.; Gouilh, M.A.; Umhang, G. Identification of Alpha and Beta Coronavirus in Wildlife Species in France: Bats, Rodents, Rabbits, and Hedgehogs. Viruses 2017, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alluwaimi, A.M.; Alshubaith, I.H.; Al-Ali, A.M.; Abohelaika, S. The Coronaviruses of Animals and Birds: Their Zoonosis, Vaccines, and Models for SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV2. Front. Veter- Sci. 2020, 7, 582287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-N.; Chan, K.; Ooi, E.; Chiou, M.-T.; Hoang, M.; Hsueh, P.-R.; Ooi, P. Animal Coronavirus Diseases: Parallels with COVID-19 in Humans. Viruses 2021, 13, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Lam, C.S.F.; Lau, C.C.Y.; Tsang, A.K.L.; Lau, J.H.N.; Bai, R.; Teng, J.L.L.; Tsang, C.C.C.; Wang, M.; et al. Discovery of Seven Novel Mammalian and Avian Coronaviruses in the Genus Deltacoronavirus Supports Bat Coronaviruses as the Gene Source of Alphacoronavirus and Betacoronavirus and Avian Coronaviruses as the Gene Source of Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3995–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Z.-L. Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muradrasoli, S.; Bálint, Á.; Wahlgren, J.; Waldenström, J.; Belák, S.; Blomberg, J.; Olsen, B. Prevalence and Phylogeny of Coronaviruses in Wild Birds from the Bering Strait Area (Beringia). PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, D.K.W.; Leung, C.Y.H.; Gilbert, M.; Joyner, P.H.; Ng, E.M.; Tse, T.M.; Guan, Y.; Peiris, J.S.M.; Poon, L.L.M. Avian Coronavirus in Wild Aquatic Birds. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 12815–12820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honkavuori, K.S.; Briese, T.; Krauss, S.; Sanchez, M.D.; Jain, K.; Hutchison, S.K.; Webster, R.G.; Lipkin, W.I. Novel Coronavirus and Astrovirus in Delaware Bay Shorebirds. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Lam, C.S.F.; Lai, K.K.Y.; Huang, Y.; Lee, P.; Luk, G.S.M.; Dyrting, K.C.; Chan, K.-H.; Yuen, K.-Y. Comparative Analysis of Complete Genome Sequences of Three Avian Coronaviruses Reveals a Novel Group 3c Coronavirus. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Ji, L.; Ming, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, T.; He, G. Co-circulation of coronavirus and avian influenza virus in wild birds in Shanghai, 2020–2021. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihindukulasuriya, K.; Wu, G.; Leger, J.S.; Nordhausen, R.W.; Wang, D. Identification of a Novel Coronavirus from a Beluga Whale by Using a Panviral Microarray. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 5084–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Lam, C.S.F.; Tsang, A.K.L.; Hui, S.-W.; Fan, R.Y.Y.; Martelli, P.; Yuen, K.-Y. Discovery of a Novel Bottlenose Dolphin Coronavirus Reveals a Distinct Species of Marine Mammal Coronavirus in Gammacoronavirus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1318–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Han, F.; Shu, X.; Li, Q.; Ding, Q.; Hao, C.; Yan, X.; Xu, M.; Hu, H. Co-infection of porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus and porcine deltacoronavirus enhances the disease severity in piglets. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łukaszuk, E.; Dziewulska, D.; Stenzel, T. Occurrence and Phylogenetic Analysis of Avian Coronaviruses in Domestic Pigeons (Columba livia domestica) in Poland between 2016 and 2020. Pathogens 2022, 11, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubálek, Z. An annotated checklist of pathogenic microorganisms associated with migratory birds. J. Wildl. Dis. 2004, 40, 639–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wille, M.; Lindqvist, K.; Muradrasoli, S.; Olsen, B.; Järhult, J.D. Urbanization and the dynamics of RNA viruses in Mallards (Anas platyrhynchos). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 51, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohaim, M.A.; El Naggar, R.F.; Helal, A.M.; Bayoumi, M.M.; El-Saied, M.A.; Ahmed, K.A.; Shabbir, M.Z.; Munir, M. Genetic Diversity and Phylodynamics of Avian Coronaviruses in Egyptian Wild Birds. Viruses 2019, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Q.-Y.; Wang, K.-C.; Liu, S.; Hou, G.-Y.; Jiang, W.-M.; Wang, S.-C.; Li, J.-P.; Yu, J.-M.; Chen, J.-M. Genomic Analysis and Surveillance of the Coronavirus Dominant in Ducks in China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drzewnioková, P.; Festa, F.; Panzarin, V.; Lelli, D.; Moreno, A.; Zecchin, B.; De Benedictis, P.; Leopardi, S. Best Molecular Tools to Investigate Coronavirus Diversity in Mammals: A Comparison. Viruses 2021, 13, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Kan, X.; Huss, S.E.; Jiang, L.; Chen, L.-Q.; Hu, Y. Using Phylogenetic Analysis to Investigate Eukaryotic Gene Origin. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 2018, e56684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v4: Recent updates and new developments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miłek, J.; Blicharz-Domańska, K. Coronaviruses in avian species—Review with focus on epidemiology and diagnosis in wild birds. J. Veter- Res. 2018, 62, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erasmus Medical Centre (NL); Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale delle Venezie (IT); Richard, M.; Fouchier, R.; Monne, I.; Kuiken, T. Mechanisms and risk factors for mutation from low to highly pathogenic avian influenza virus. EFSA Support. Publ. 2017, 14, 1287E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, D. Coronavirus avian infectious bronchitis virus. Veter- Res. 2007, 38, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wille, M.; Holmes, E.C. Wild birds as reservoirs for diverse and abundant gamma- and deltacoronaviruses. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domanska-Blicharz, K.; Sajewicz-Krukowska, J. Recombinant turkey coronavirus: Are some S gene structures of gammacoronaviruses especially prone to exchange? Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decaro, N.; Lorusso, A. Novel human coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): A lesson from animal coronaviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 244, 108693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şekercioğlu, H.; Daily, G.C.; Ehrlich, P.R. Ecosystem consequences of bird declines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 18042–18047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurice, M.E.; Fuashi, N.A.; Mbua, R.L.; Mendzen, N.S.; Okon, O.-A.; Ayamba, N.S. The Environmental Influence on the Social Activity of Birds in Buea University Campus, Southwest Region, Cameroon. Interdiscip. J. Environ. Sci. Educ. 2020, 16, e2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somveille, M.; Rodrigues, A.S.L.; Manica, A. Why do birds migrate? A macroecological perspective. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2015, 24, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wille, M.; Muradrasoli, S.; Nilsson, A.; Järhult, J.D. High Prevalence and Putative Lineage Maintenance of Avian Coronaviruses in Scandinavian Waterfowl. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonassen, C.M.; Kofstad, T.; Larsen, I.-L.; Løvland, A.; Handeland, K.; Follestad, A.; Lillehaug, A. Molecular identification and characterization of novel coronaviruses infecting graylag geese (Anser anser), feral pigeons (Columbia livia) and mallards (Anas platyrhynchos). J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, L.A.; Savage, C.; Naylor, C.; Bennett, M.; Chantrey, J.; Jones, R. Genetically Diverse Coronaviruses in Wild Bird Populations of Northern England. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1091–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-R.; Oem, J.-K. Surveillance of Avian Coronaviruses in Wild Bird Populations of Korea. J. Wildl. Dis. 2014, 50, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamings, A.; Nelson, T.; Vibin, J.; Wille, M.; Klaassen, M.; Alexandersen, S. Detection and characterisation of coronaviruses in migratory and non-migratory Australian wild birds. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, G.; Waldenström, J.; Fransson, T. Direct and indirect effects of winter harshness on the survival of Mallards Anas platyrhynchos in northwest Europe. Ibis 2012, 154, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagodatski, A.; Trutneva, K.; Glazova, O.; Mityaeva, O.; Shevkova, L.; Kegeles, E.; Onyanov, N.; Fede, K.; Maznina, A.; Khavina, E.; et al. Avian Influenza in Wild Birds and Poultry: Dissemination Pathways, Monitoring Methods, and Virus Ecology. Pathogens 2021, 10, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryaman, G.K.; Soejoedono, R.D.; Setiyono, A.; Poetri, O.N.; Handharyani, E. Isolation and characterization of avian coronavirus from healthy Eclectus parrots (Eclectus roratus) from Indonesia. Veter-World 2019, 12, 1797–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Collection Site | Sample ID | Host Species | Accession Number | CoV Genera |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evoa | #0 | Anas acuta | ON368935 | Gammacoronavirus |
| #7 | Anas acuta | ON368937 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| #9 | Anas acuta | ON368938 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| #13 | Anas acuta | ON368940 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| #14 | Anas acuta | ON368941 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| #16 | Anas acuta | ON368942 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| #17 | Anas acuta | ON368943 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| #18 | Anas acuta | ON368944 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| #19 | Anas acuta | ON368945 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| #22 | Anas acuta | ON368946 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| #23 | Anas acuta | ON368947 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| #26 | Anas crecca | ON368948 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| #30 | Anas crecca | ON368949 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| #32 | Anas crecca | ON368950 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| #38 | Anas crecca | ON368953 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| #EV2 | Anas acuta | ON721383 | Deltacoronavirus | |
| #EV4 | Anas platyrhynchos | ON721382 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| #EV5 | Anas acuta | ON721381 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| S São Jacinto Dunes Nature Reserve | ##EV8 | Anas platyrhynchos | ON721380 | Gammacoronavirus |
| #SJ12 | Anas platyrhynchos | ON368939 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| #SJ16 | Anas platyrhynchos | ON368936 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| #SJ35 | Anas platyrhynchos | ON368951 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| #SJ39 | Anas platyrhynchos | ON368952 | Gammacoronavirus | |
| #SJ41 | Anas platyrhynchos | ON368954 | Gammacoronavirus |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hemnani, M.; Rodrigues, D.; Santos, N.; Santos-Silva, S.; Figueiredo, M.E.; Henriques, P.; Ferreira-e-Silva, J.; Rebelo, H.; Poeta, P.; Thompson, G.; et al. Molecular Detection and Characterization of Coronaviruses in Migratory Ducks from Portugal Show the Circulation of Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus. Animals 2022, 12, 3283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12233283
Hemnani M, Rodrigues D, Santos N, Santos-Silva S, Figueiredo ME, Henriques P, Ferreira-e-Silva J, Rebelo H, Poeta P, Thompson G, et al. Molecular Detection and Characterization of Coronaviruses in Migratory Ducks from Portugal Show the Circulation of Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus. Animals. 2022; 12(23):3283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12233283
Chicago/Turabian StyleHemnani, Mahima, David Rodrigues, Nuno Santos, Sergio Santos-Silva, Maria Ester Figueiredo, Pedro Henriques, Joana Ferreira-e-Silva, Hugo Rebelo, Patricia Poeta, Gertrude Thompson, and et al. 2022. "Molecular Detection and Characterization of Coronaviruses in Migratory Ducks from Portugal Show the Circulation of Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus" Animals 12, no. 23: 3283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12233283
APA StyleHemnani, M., Rodrigues, D., Santos, N., Santos-Silva, S., Figueiredo, M. E., Henriques, P., Ferreira-e-Silva, J., Rebelo, H., Poeta, P., Thompson, G., & Mesquita, J. R. (2022). Molecular Detection and Characterization of Coronaviruses in Migratory Ducks from Portugal Show the Circulation of Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus. Animals, 12(23), 3283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12233283








