Simple Summary
CRISPR/Cas9 driven multiplex genome editing may induce genotoxicity and chromosomal rearrangements due to DNA double-strand breaks at multiple loci simultaneously. To overcome this problem in porcine cells we utilized Target-AID, a base editing system, to edit multiple loci in the porcine genome. We showed that the Target-AID system works well in porcine fibroblasts with up to 63.15% efficiency. This is the first report demonstrating that the Target-AID system works well in porcine cells and can be used to generate genome-edited pigs.
Abstract
Multiplex genome editing may induce genotoxicity and chromosomal rearrangements due to double-strand DNA breaks at multiple loci simultaneously induced by programmable nucleases, including CRISPR/Cas9. However, recently developed base-editing systems can directly substitute target sequences without double-strand breaks. Thus, the base-editing system is expected to be a safer method for multiplex genome-editing platforms for livestock. Target-AID is a base editing system composed of PmCDA1, a cytidine deaminase from sea lampreys, fused to Cas9 nickase. It can be used to substitute cytosine for thymine in 3–5 base editing windows 18 bases upstream of the protospacer-adjacent motif site. In the current study, we demonstrated Target-AID-mediated base editing in porcine cells for the first time. We targeted multiple loci in the porcine genome using the Target-AID system and successfully induced target-specific base substitutions with up to 63.15% efficiency. This system can be used for the further production of various genome-engineered pigs.
1. Introduction
The development of programmable nucleases, including the clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated protein (Cas) system, has significantly increased the efficiency of genetic engineering of livestock and has ushered in a new era in animal biotechnology. This technology can be used to enhance livestock traits, such as improved meat production [1] or disease resistance [2], generate precise disease models of human diseases [3], produce donor organs for xenotransplantation [4], and improve animal welfare [5].
Conventional genome-editing systems, such as CRISPR/Cas9, rely on DNA repair mechanisms after target-specific double-strand breaks (DSBs) in DNA. Although these systems are very efficient, they are limited in their use as a multiplex genome engineering tools because simultaneous DSBs at multiple loci induce genotoxicity and chromosomal rearrangements [6]. This disadvantage of conventional genome-editing systems for multiplex genome engineering can be overcome using the base-editing system. The base editing system involves the fusion of the CRISPR/Cas nickase with a deaminase, such as rAPOBEC [7] or PmCDA1 [8], which can substitute DNA base pairs at target sites without DSBs. Thus, base editing is expected to be a safer method for multiplex genome-editing platforms for livestock. However, base editing also has limitations. The base-editing system can only substitute a target base within the “editing window”, which is specified by the Cas or deaminase enzymes used in the system. To overcome this limitation, several different base editors with different editing windows have been developed to expand the available target sites for base editing [9].
Target-AID is a base-editing system composed of PmCDA1 and a cytidine deaminase from sea lampreys fused to Cas9 nickase [8]. The Target-AID system can substitute cytosine for thymine in 3–5 base editing windows at 18 bases upstream of the protospacer-adjacent motif (PAM) of Cas9 nickase. The Target-AID system was first developed and validated in CHO cells [8] and was then validated in plants [10,11,12,13], fungi [14], yeast [15,16], bacteria [17], and zebrafish [18,19] cells. However, to the best of our knowledge, there are no reports describing the use of the Target-AID system in livestock, particularly in pigs.
In the current study, we demonstrated Target-AID-mediated base editing in porcine cells for the first time. We targeted multiple loci in the gag and pol genes of porcine endogenous retrovirus (PERV) in the porcine genome using the Target-AID system and successfully induced target-specific base substitution.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of Guide RNA Sequences
The complete genome sequences for PERV-A, PERV-B, and PERV-C were obtained from GenBank (accession numbers KY484771, AY099324, and HM159246, respectively). All of the guide RNA (gRNA) sequences for the Target-AID systems were designed using BE-Designer tools on the CRISPR RGEN Tools website (http://www.rgenome.net/be-designer/, accessed on 12 December 2021). First, we designed a series of gRNAs targeting the gag, pol, and env genes for each of PERV-A, PERV-B, and PERV-C. We then selected gRNAs that induced a premature stop codon for each gene. Next, we selected single gRNAs that could target the same region on all the PERV-A, PERV-B, and PERV-C genes simultaneously. Finally, we selected the gRNA sequences, 5′-ttcaggttaagaagggacct-3′ for gag and 5′-acagtaccccttgagtagag-3′ for pol, to use for further experiments (Table 1).

Table 1.
Design of target gRNA sequences used in the study. Among the potential targets, the orange-highlighted gRNAs were selected for use in this study. PERV = porcine endogenous retrovirus. Cytosines in Editing Window marked in red letters indicate target sequences of Target-AID.
2.2. Vector Construction
The vector for the Target-AID system was obtained from Addgene (#79620; Watertown, MA, USA) and cloned into the piggyBac vector used in our previous studies [20,21] using MluI and NotI restriction enzymes. In addition, we added two U6 promoter-driven single guide RNA sequences targeting the gag and pol genes, using the In-Fusion HD Cloning Kit (Takara Bio, Kusatsu, Japan). The scheme for the vector used in this study, PB-CMV-Target-AID-PERV(pol-gag), is shown in Figure 1a.
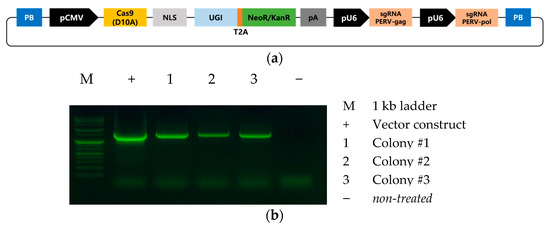
Figure 1.
Target-AID vector system used in the study. (a) Scheme of the PB-CMV-Target-AID-PERV(pol-gag) vector used in this study. (b) PCR analysis of the target AID vector integration in porcine fibroblasts.
2.3. In Vitro Culture of Porcine Fibroblasts and Transfection
Immortalized porcine fibroblasts [22] were cultured in DMEM (Gibco, Waltham, MA, USA) supplemented with 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Gibco), 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco), 100 mM β-mercaptoethanol (Sigma, St Louis, MO, USA), and 1% nonessential amino acids (Gibco) at 37 °C with 5% CO2. We transfected 3 × 105 cells using the Neon Nucleofection system (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Briefly, 500 ng of the PB-CMV-Target-AID-PERV(pol-gag) vector and 500 ng of the transposase vector (pCy43, provided by the Sanger Institute) were transfected at 1400 V for 20 ms, with a pulse number of 2. After 2 d of transfection, the fibroblasts were treated with 2 µg/mL neomycin (Sigma) for 10 d for antibiotic selection. After selection, single cells were subcultured in each well of 96-well plates and then expanded. Cell colonies from each single cell were analyzed by PCR to confirm the integration of the vector. The primer sequences are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Primer sequences used in the study.
2.4. Targeted Deep Sequencing
The on-target regions of the gRNAs were PCR-amplified from genomic DNA extracted from transfected cells using Phusion polymerase (New England BioLabs, Ipswich, MA, USA). The resulting amplicons were subjected to paired-end deep sequencing using a Mi-Seq instrument (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). Deep sequencing data were analyzed using the online BE-Analyzer tool (http://www.rgenome.net/be-analyzer/, accessed on 12 December 2021). C-to-T base substitutions in the editing window, 16 to 19 bp upstream of the PAM sequence, were considered to result from the Target-AID system. The primers used in this study are listed in Table 2.
3. Results and Discussion
In the current study, we selected PERV integrated into the porcine genome as a target for base editing. PERV is a retrovirus that is found in most pig genomes in multiple copies. It is a potential risk in pig-to-human xenotransplantation, because most related retroviruses, such as human immunodeficiency virus, induce severe diseases, including immunodeficiencies [23] in host animals. However, because PERV is integrated into the porcine genome, it is impossible to remove this virus from pigs even when they are maintained in a microorganism-barrier facility. In 2015, Yang et al. [24] reported the inactivation of 62 copies of PERV pol genes in the porcine genome using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. However, 2 years later, the same group reported genotoxicity and chromosomal abnormalities induced by simultaneous DNA cleavage at multiple PERV sites [25]. To avoid the risk of genotoxicity induced by multiplex DSBs we used a Target-AID-based base-editing system to inactivate PERV in the porcine genome. We followed the CRISPR-STOP strategy used in a previous study [26], with slight modifications. Since the Target-AID system substitutes cytosine for thymine we carefully selected in-frame CAG, CAA, or CGA sequences in the open reading frame and designed gRNAs to change the sequences into the stop codons, TAG, TAA, or TGA, respectively. As a result of base editing, the target gene was knocked out due to the introduction of a premature stop codon.
Three PERV subtypes (PERV-A, PERV-B, and PERV-C) have been identified. Each PERV genome is composed of three core genes, gag, pol, and env. In this study, we attempted to design a single gRNA to simultaneously target all three PERV subtypes. As shown in Table 1, we designed two gRNAs simultaneously targeting the gag and pol genes of all three PERV subtypes. A gRNA for env was not used because we could not find a single gRNA targeting this gene in all PERV subtypes.
We constructed a piggyBac-based vector containing the Target-AID system with two sgRNAs targeting the gag and pol genes (Figure 1a). We transfected the vector into porcine fibroblasts and confirmed the integration of the vector by PCR analysis after 10 days of antibiotic selection. As expected, the transfected vector was successfully integrated into the genome of all tested cells (Figure 1b). To confirm the base-editing events mediated by the Target-AID system, targeted deep sequencing analysis was performed at the gRNA target site. We found successful C-to-T substitutions at the gag (Figure 2a) and pol genes (Figure 2b) in all tested cell colonies, whereas nontreated wild-type cells showed no substitutions (Table 3). Colonies #1 and #3 showed high substitution rates; however, colony #2 showed a relatively lower substitution rate (Figure 1b). A previous study in which the pol gene of PERV was targeted using a BE3 base editor [27] also failed to achieve 100% efficient removal of active PERV. This may be related to the integration site or the copy number of the Target-AID vector in the transgenic cells. Further studies are required to improve the efficiency of base editing in porcine cells. On the other hand, it might be possible that our PCR result for colony #2 is false positive due to plasmid DNA contamination. For this reason, we are focusing on sequencing data from colonies #1 and #3. Interestingly, we found that substitution at gag (63.15% and 52.12% for colonies #1 and #3, respectively) showed slightly higher efficiencies than substitution at pol (54.60% and 47.83% for colonies #1 and #3, respectively). Because both gRNAs were expressed from the same integrated vector, this result indicated that gRNA design also influences the efficiency of Target-AID-mediated base substitutions.
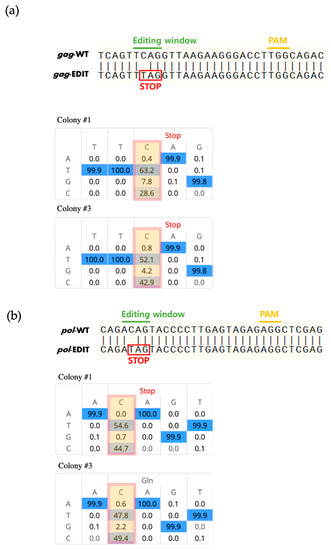
Figure 2.
Base edited results at the target locus of Target-AID. (a) Sequence alignment of gag from wild-type and edited cell lines. (b) Sequence alignment of pol from wild-type and edited cell lines.

Table 3.
C-to-T substitution mediated by the Target-AID system in porcine fibroblasts.
There are some previous reports of base editing in porcine cells using another base editing system, BE [27,28,29,30]. As the “editing windows” of the Target-AID and BE systems are different, these two base-editing systems may be used complementarily for complex porcine genome engineering. Furthermore, in combination with zygote electroporation [31] or somatic cell nuclear transfer [32], it is expected that base-edited pigs can be generated using the Target-AID system. Particularly, for generating PERV inactivated pigs, ribonucleoprotein (RNP) based Target-AID is recommended to avoid safety issue in clinical xenotransplantation. Genome-wide off-target studies for the Target-AID system are also recommended for the same reason. Further studies are required for adopting Target-AID based system in clinical conditions.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, the current study showed, for the first time, that the Target-AID system can be used for base editing of multiple loci in porcine fibroblasts. We confirmed that the Target-AID system successfully induced a C-to-T substitution at the target site of the porcine genome with up to 63.15% efficiency. This system can be used for the further production of multiplex genome-engineered pigs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.-Y.Y. and O.K.; investigation, S.-Y.Y. and O.K.; formal analysis, S.-Y.Y., G.J. and O.K.; writing—original draft preparation, O.K.; writing—review and editing, S.-Y.Y., G.J. and O.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by Gyeongsangbuk-do government (grant for biomedical company), Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2021R1F1A1051953) and ToolGen, Inc.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Min-Ju Kim, Jihee Han and Yein Jeon for technical support for experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
S.-Y.Y. and O.K. are employees of the genome-editing company, ToolGen Inc. The funder had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
| AID | Activation-Induced Cytidine Deaminase |
| APOBEC | Apolipoprotein B mRNA Editing, Catalytic Polypeptide-like |
| BE | Base Editors |
| Cas9 | CRISPR-associated protein 9 |
| CHO | Chinese Hamster Ovary |
| CRISPR | Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| DSB | Double Strand Breaks |
| PAM | Protospacer Adjacent Motif |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PERV | Porcine Endogenous Retrovirus |
| PmCDA1 | Petromyzon marinus Cytidine Deaminase 1 |
| RNA | Ribonucleic Acid |
References
- Kang, J.D.; Kim, S.; Zhu, H.Y.; Jin, L.; Guo, Q.; Li, X.C.; Zhang, Y.C.; Xing, X.X.; Xuan, M.F.; Zhang, G.L.; et al. Generation of Cloned Adult Muscular Pigs with Myostatin Gene Mutation by Genetic Engineering. Rsc Adv. 2017, 7, 12541–12549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitworth, K.M.; Prather, R.S. Gene Editing as Applied to Prevention of Reproductive Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome. Mol. Reprod Dev. 2017, 84, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, T.; Liu, J.; Fang, B.; Geng, X.; Xiong, Q.; Zhang, L.; Jin, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; et al. A Bama Miniature Pig Model of Monoallelic TSC1 Mutation for Human Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. J. Genet. Genom. 2020, 47, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Xu, W.; Kan, Y.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; Song, X.; Wu, J.; Xiong, J.; Goswami, D.; Yang, M.; et al. Extensive Germline Genome Engineering in Pigs. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Carlson, D.F.; Lancto, C.A.; Garbe, J.R.; Webster, D.A.; Hackett, P.B.; Fahrenkrug, S.C. Efficient Nonmeiotic Allele Introgression in Livestock Using Custom Endonucleases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16526–16531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, B.R.; Lonetree, C.; Kluesner, M.G.; Johnson, M.J.; Pomeroy, E.J.; Diers, M.D.; Lahr, W.S.; Draper, G.M.; Slipek, N.J.; Smeester, B.A.; et al. Highly Efficient Multiplex Human T Cell Engineering without Double-Strand Breaks Using Cas9 Base Editors. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komor, A.C.; Kim, Y.B.; Packer, M.S.; Zuris, J.A.; Liu, D.R. Programmable Editing of a Target Base in Genomic DNA without Double-Stranded DNA Cleavage. Nature 2016, 533, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, K.; Arazoe, T.; Yachie, N.; Banno, S.; Kakimoto, M.; Tabata, M.; Mochizuki, M.; Miyabe, A.; Araki, M.; Hara, K.Y.; et al. Targeted Nucleotide Editing Using Hybrid Prokaryotic and Vertebrate Adaptive Immune Systems. Science 2016, 353, aaf8729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komor, A.C.; Zhao, K.T.; Packer, M.S.; Gaudelli, N.M.; Waterbury, A.L.; Koblan, L.W.; Kim, Y.B.; Badran, A.H.; Liu, D.R. Improved Base Excision Repair Inhibition and Bacteriophage Mu Gam Protein Yields C:G-to-T:A Base Editors with Higher Efficiency and Product Purity. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, eaao4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sretenovic, S.; Pan, C.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, Y. Rice Genome Engineering and Gene Editing, Methods and Protocols. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2238, 95–113. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.T.; Cheng, Y.J.; Yuan, Y.H.; Hung, W.F.; Cheng, Q.W.; Wu, F.H.; Lee, L.Y.; Gelvin, S.B.; Lin, C.S. Application of Cas12a and NCas9-Activation-Induced Cytidine Deaminase for Genome Editing and as a Non-Sexual Strategy to Generate Homozygous/Multiplex Edited Plants in the Allotetraploid Genome of Tobacco. Plant Mol. Biol. 2019, 101, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimatani, Z.; Ariizumi, T.; Fujikura, U.; Kondo, A.; Ezura, H.; Nishida, K. Plant Genome Editing with CRISPR Systems, Methods and Protocols. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1917, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shimatani, Z.; Fujikura, U.; Ishii, H.; Terada, R.; Nishida, K.; Kondo, A. Herbicide Tolerance-Assisted Multiplex Targeted Nucleotide Substitution in Rice. Data Brief 2018, 20, 1325–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.; Park, B.G.; Kim, B.; Hahn, J. Multiplex Gene Disruption by Targeted Base Editing of Yarrowia Lipolytica Genome Using Cytidine Deaminase Combined with the CRISPR/Cas9 System. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 15, 1900238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Després, P.C.; Dubé, A.K.; Nielly-Thibault, L.; Yachie, N.; Landry, C.R. Double Selection Enhances the Efficiency of Target-AID and Cas9-Based Genome Editing in Yeast. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2018, 8, 3163–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambu-Nishida, Y.; Nishida, K.; Hasunuma, T.; Kondo, A. Development of a Comprehensive Set of Tools for Genome Engineering in a Cold- and Thermo-Tolerant Kluyveromyces Marxianus Yeast Strain. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banno, S.; Nishida, K.; Arazoe, T.; Mitsunobu, H.; Kondo, A. Deaminase-Mediated Multiplex Genome Editing in Escherichia Coli. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Yoshioka, S.; Nishida, K.; Hosokawa, H.; Kakizuka, A.; Maegawa, S. In Vivo Targeted Single-Nucleotide Editing in Zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, Y.; Yan, G.; Li, S.; Qin, W.; Lin, S. Optimized Target-AID System Efficiently Induces Single Base Changes in Zebrafish. J. Genet. Genom. 2018, 45, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Kwon, H.S.; Kwon, D.; Koo, O.J.; Moon, J.H.; Park, E.J.; Yum, S.Y.; Lee, B.C.; Jang, G. Production of Transgenic Porcine Embryos Reconstructed with Induced Pluripotent Stem-Like Cells Derived from Porcine Endogenous Factors Using PiggyBac System. Cell Reprogram 2019, 21, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Yum, S.; Lee, S.; Lee, W.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Koo, O.; Lee, B.; Jang, G. Disruption of Exogenous EGFP Gene Using RNA-Guided Endonuclease in Bovine Transgenic Somatic Cells. Zygote 2015, 23, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Lee, C.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, B.C.; Kim, J.S.; Jang, G. Production of CMAH Knockout Preimplantation Embryos Derived from Immortalized Porcine Cells Via TALE Nucleases. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Ma, X.; Yuan, T.; Niu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Ping, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; et al. Porcine Genome Engineering for Xenotransplantation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 168, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Güell, M.; Niu, D.; George, H.; Lesha, E.; Grishin, D.; Aach, J.; Shrock, E.; Xu, W.; Poci, J.; et al. Genome-Wide Inactivation of Porcine Endogenous Retroviruses (PERVs). Science 2015, 350, 1101–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, D.; Wei, H.-J.; Lin, L.; George, H.; Wang, T.; Lee, I.-H.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Kan, Y.; Shrock, E.; et al. Inactivation of Porcine Endogenous Retrovirus in Pigs Using CRISPR-Cas9. Science 2017, 357, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuscu, C.; Parlak, M.; Tufan, T.; Yang, J.; Szlachta, K.; Wei, X.; Mammadov, R.; Adli, M. CRISPR-STOP: Gene Silencing through Base-Editing-Induced Nonsense Mutations. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Ge, W.; Li, N.; Liu, Q.; Chen, F.; Yang, X.; Huang, X.; Ouyang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Efficient Base Editing for Multiple Genes and Loci in Pigs Using Base Editors. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bi, D.; Qin, G.; Song, R.; Yao, J.; Cao, C.; Zheng, Q.; Hou, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J. Cytosine Base Editor (HA3A-BE3-NG)-Mediated Multiple Gene Editing for Pyramid Breeding in Pigs. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 592623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Chen, W.; Cai, Q.; Liang, P.; Chen, Y.; Cong, P.; Huang, J. Effective Generation of Maternal Genome Point Mutated Porcine Embryos by Injection of Cytosine Base Editor into Germinal Vesicle Oocytes. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Yu, T.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, M.; Tang, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. Efficient Base Editing by RNA-Guided Cytidine Base Editors (CBEs) in Pigs. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, M.; Wittayarat, M.; Tanihara, F.; Sato, Y.; Namula, Z.; Le, Q.A.; Lin, Q.; Takebayashi, K.; Otoi, T. One-Step Genome Editing of Porcine Zygotes through the Electroporation of a CRISPR/Cas9 System with Two Guide RNAs. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol.-Anim. 2020, 56, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, O.J.; Park, S.J.; Lee, C.; Kang, J.T.; Kim, S.; Moon, J.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Jang, G.; Kim, J.S.; et al. Production of Mutated Porcine Embryos Using Zinc Finger Nucleases and a Reporter-Based Cell Enrichment System. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 27, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).