The Effects of Fungal Feed Additives in Animals: A Review
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Edible Fungi and Their Potential Uses
3. Hazardous Fungi Species
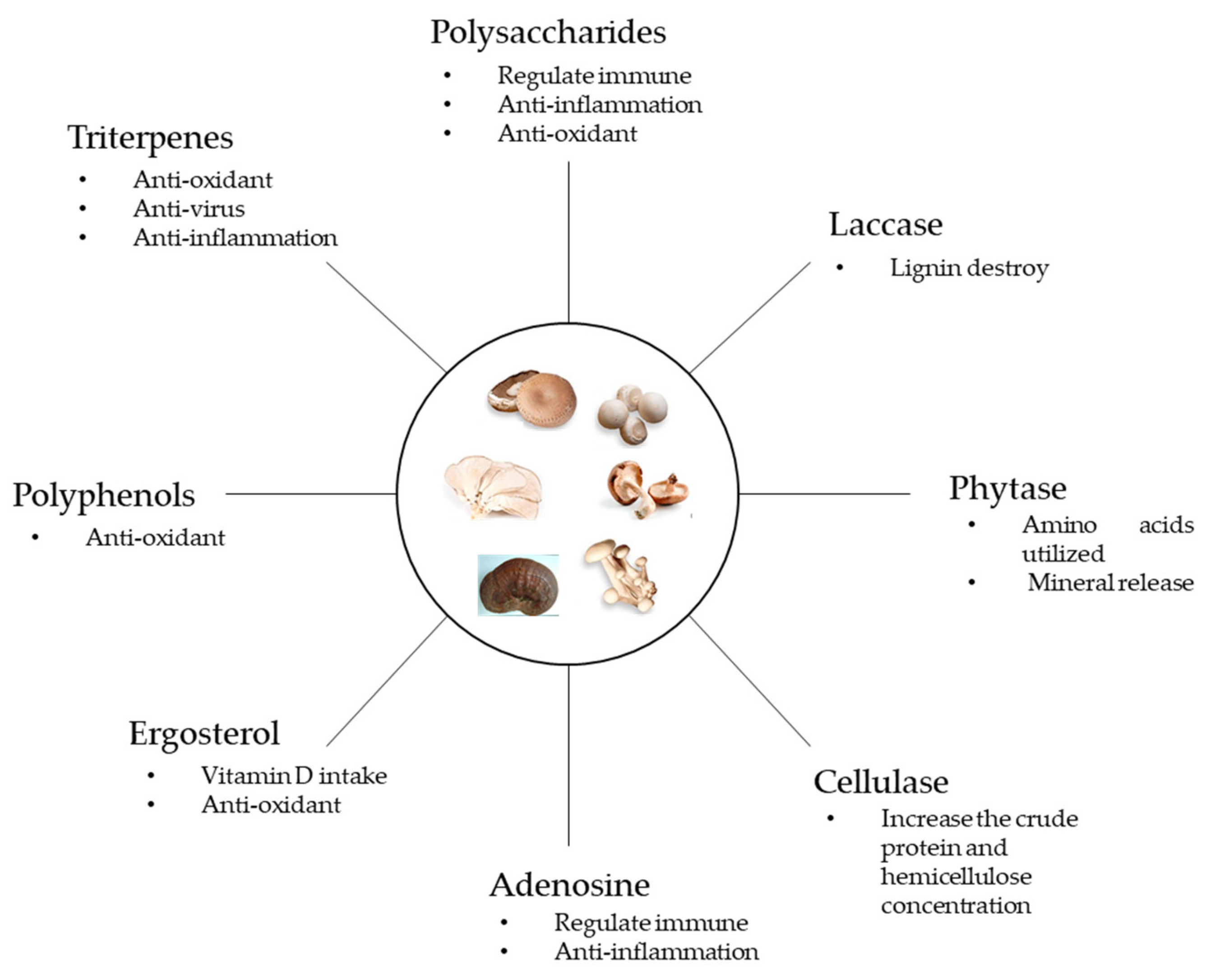
4. The Functional Components of Fungi
4.1. Triterpenes
4.2. Polyphenols and Flavonoids
4.3. Ergosterol
4.4. Adenosine
4.5. Fungal Cell Wall and Polysaccharides
4.6. Enzymes
5. The Potential Use of Fungal Feed Additives
6. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| Gpx | Glutathione peroxidase |
| SOD | Superoxidase dismutase |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| MyD88 | Myeloid differentiation primary response 88 |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| CAT | Catalase |
| NFκB | Nuclear factor kappa B p 65 |
| iNOS | Inducible nitric oxide synthases |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-γ |
| IL-1ß | Interleukin-1ß |
| Nrf-2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 |
| GCLC | Glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic |
| KCTD-15 | Potassium channel tetramerization domain-containing 15 |
| CEBPα | CCAAT-enhancer-binding proteins-alpha |
| CPT-1 | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I |
| PPAR-γ | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
References
- Bengtson, S.; Rasmussen, B.; Ivarsson, M.; Muhling, J.; Broman, C.; Marone, F.; Stampanoni, M.; Bekker, A. Fungus-like mycelial fossils in 2.4-billion-year-old vesicular basalt. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, G.M.; Schmit, J.P. Fungal biodiversity: What do we know? What can we predict? Biodivers. Conserv. 2006, 16, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleko, D.; Mwilawa, A.; Msalya, G.; Pasape, L.; Mtei, K. Forage growth, yield and nutritional characteristics of four varieties of napier grass (Pennisetum purpureum Schumach) in the west Usambara highlands. Afr. Crop Sci. J. 2019, 6, e00214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, W.Y.; Liu, C.L.; Tsai, C.F.; Lin, W.C.; Chang, S.C.; Shih, H.D.; Shy, Y.M.; Lee, T.T. Evaluation of waste mushroom compost as a feed supplement and its effects on the fat metabolism and anti-oxidant capacity of broilers. Animals 2020, 10, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finimundy, T.C.; Barros, L.; Calhelha, R.C.; Alves, M.J.; Prieto, M.A.; Abreu, R.M.V.; Dilon, A.J.P.; Henriques, J.A.P.; Roesch, M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Multifunctions of pleurotus sajor-caju (fr.) singer: A highly nutritious food and a source for bioactive compounds. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.C.; Lin, L.J.; Chao, Y.P.; Chiang, C.J.; Lee, M.T.; Chang, S.C.; Yu, B.; Lee, T.T. Anti-oxidant molecular targets of wheat bran fermented by white rot fungi and its potential modulation of antioxidative status in broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2017, 58, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, W.Y.; Lin, W.C.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Huang, C.M.; Chang, S.C.; Lee, T.T. Evaluation of the combined use of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Aspergillus Oryzae with phytase fermentation products on growth, inflammatory, and intestinal morphology in broilers. Animals 2019, 9, E1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khempaka, S.; Thongkratok, R.; Okrathok, S.; Molee, W. An evaluation of cassava pulp feedstuff fermented with A. oryzae, on growth performance, nutrient digestibility and carcass quality of broilers. J. Poult. Sci. 2013, 51, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.C.; Lin, W.C.; Chuang, W.Y.; Chen, M.H.; Chang, S.C.; Lee, T.T. Effects of mushroom waster medium and stalk residues on the growth performance and oxidative status in broilers. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciorowski, K.G.; Herrera, P.; Jones, F.T.; Pillai, S.D.; Ricke, S. C Effects on poultry and livestock of feed contamination with bacteria and fungi. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2007, 133, 109–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkvold, G.P.; Arias, S.; Taschl, I.; Gruber-Dorninger, C. Chapter 9—Mycotoxins in corn: Occurrence, impacts, and management. In Corn; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 235–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, M.; Fanelli, F.; Cimmarusti, M.T.; Mirabelli, V.; Haidukowski, M.; Logrieco, A.F.; Caliandro, R.; Mule, G. In vitro single and combined mycotoxins degradation by Ery4 laccase from Pleurotus eryngii and redox mediators. Food Control 2018, 90, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Li, X.; Saleemi, M.K.; He, C. Mycotoxin contamination and control strategy in human, domestic animal and poultry: A review. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 142, 104095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, L.P.; Lee, M.T.; Chen, C.S.; Yu, B.; Lee, T.T. Effects of co-fermented Pleurotus eryngii stalk residues and soybean hulls by Aureobasidium pullulans on performance and intestinal morphology in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 2959–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.L.; Chiang, C.J.; Chao, Y.P.; Yu, B.; Lee, T.T. Effect of Cordyceps Militaris waster medium on production performance, egg traits and egg yolk cholesterol of laying hens. J. Poult. Sci. 2015, 52, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.C.; Lin, M.J.; Chao, Y.P.; Chiang, C.J.; Jea, Y.S.; Lee, T.T. Effects of spent mushroom compost meal on growth performance and meat characteristics of grower geese. R. Bras. Zootec. 2016, 45, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.T.; Lo, C.T.; Chang, S.C.; Lee, T.T. Effects of Trichoderma fermented wheat bran on growth performance, intestinal morphology and histological findings in broiler chickens. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 16, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.C.; Lee, M.T.; Lo, C.T.; Chang, S.C.; Lee, T.T. Effects of dietary supplementation of Trichoderma pseudokoningii fermented enzyme powder on growth performance, intestinal morphology, microflora and serum anti-oxidantive status in broiler chickens. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 17, 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, P.Y.; Chang, C.L.; Huang, C.M.; Chang, S.C.; Lee, T.T. Effects of solid-state fermented wheat bran by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Saccharomyces cerevisiae on growth performance and intestinal microbiota in broiler chickens. Ital. J. Poult. Sci. 2017, 54, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.T.; Lin, W.C.; Wang, S.Y.; Lin, L.J.; Yu, B.; Lee, T.T. Evaluation of potential anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Antrodia cinnamomea powder and the underlying molecular mechanisms via Nrf2- and NF-κB-dominated pathways in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2419–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.T.; Lin, W.C.; Lin, L.J.; Wang, S.Y.; Chang, S.C.; Lee, T.T. Effects of dietary Antrodia cinnamomea fermented product supplementation on antioxidation, anti-inflammation, and lipid metabolism in broiler chickens. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019. In press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Sun, H.; Hao, Y.; Zheng, X.; Song, Q.; Dai, S.; Zhu, Z. Chemical structure and inhibition on α-glucosidase of the polysaccharides from Cordyceps militaris with different developmental stages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, T.B.; Wang, H.X. Pharmacological actions of cordyceps, a prized folk medicine. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2005, 57, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wu, G.; Huang, Z. Structural analysis and anti-oxidant activities of polysaccharides from cultured Cordyceps militaris. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 58, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Meng, X.Y.; Yang, R.L.; Qin, T.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, K.Y.; Fei, C.Z.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.L.; Xue, F.Q. Cordyceps militaris polysaccharides can enhance the immunity and antioxidation activity in immunosuppressed mice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.Y.; Park, E.H. Anti-inflammatory and related pharmacological activities of cultured mycelia and fruiting bodies of cordyceps militaris. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 96, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Chu, F.H.; Chien, S.C.; Liao, J.W.; Hsieh, H.W.; Li, W.H.; Lin, C.C.; Shaw, J.F.; Kuo, Y.H.; Wang, S.Y. Establishment of the metabolite profile for an Antrodia cinnamomea health food product and investigation of its chemoprevention activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8556–8564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.C.; Yang, Y.H.; Lu, H.C. Enhanced anti-oxidant and antitumor activities of Antrodia cinnamomea cultured with cereal substrates in solid state fermentation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 78, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.H.; Huang, R.L.; Chen, C.T.; Chen, H.C.; Hsu, W.C.; Lu, M.K. Antrodia camphorate polysaccharides exhibit anti-hepatitis B virus effects. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 209, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Pan, C.L.; Yao, Y.C.; Chang, S.S.; Li, S.L.; Wu, T.F. Proteomic analysis of the effect of Antrodia camphorate extract on human lung cancer A549 cell. Proteomics 2006, 6, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Shah, N.P. Anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative activities of natural and sulphonated polysaccharides from Pleurotus eryngii. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 23, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Hu, C.; Che, G.; Zhou, M.; Jia, L. anti-oxidant and hepatoprotective activities of intracellular polysaccharide from Pleurotus eryngii si-04. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duru, M.E.; Cayan, G.T. Biologically active terpenoids from mushroom origin: A review. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2015, 9, 456–483. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Hu, Q.; Ma, G.; Su, A.; Xie, M.; Li, X.; Chen, G.; Zhao, L. Effects of Flammulina velutipes polysaccharide on immune response and intestinal microbiota in mice. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 56, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Hoo, P.C.; Tan, L.T.; Pusparajah, P.; Khan, T.M.; Lee, L.H.; Goh, B.H.; Chan, K.G. Golden Needle Mushroom: A culinary medicine with evidenced-based biological activities and health promoting properties. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 474–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yu, J.; Zhao, L.; Ma, N.; Fang, Y.; Pei, F.; Mariga, M.; Hu, Q. Polysaccharides from Flammulina velutipes improve scopolamine-induced impairment of learning and memory of rats. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Q.; Xu, N.; Zhou, M.; Gao, B.; Wang, C.; Shi, Y. Fermenting liquid vinegar with higher taste, flavor and healthy value by using discarded Cordyceps militaris solid culture medium. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 98, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfuz, S.; Song, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Diao, Z.; Ren, G.; Guo, Z.; Cui, Y. Effect of golden needle mushroom (Flammulina velutipes) stem waste on laying performance, calcium utilization, immune response and serum immunity at early phase of production. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitlow, L.W.; Hagler, W.M.J. Mycotoxins in Dairy Cattle: Occurrence, Toxicity, Prevention and Treatment. Proc. Southwest Nutr. Conf. 2005, 124–138. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, W.X.; Marchal, J.L.M.; vanderPoel, A.F.B. Strategies to prevent and reduce mycotoxins for compound feed manufacturing. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2018, 237, 129–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Masuda, M.; Sakurai, A.; Sakakibara, M. Medicinal uses of the mushroom Cordyceps militaris: Current state and prospects. Fitote 2010, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Zhu, F.; Xu, B. An insight into the anti-inflammatory properties of edible and medicinal mushrooms. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 47, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Yang, W.; Zhao, L.; Pei, F.; Fang, D.; Hu, Q. A critical review on the health promoting effects of mushrooms nutraceuticals. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2018, 7, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Q.; Zhao, J.; Chen, L.X.; Wang, S.F.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.P. Lanostane triterpenes from the mushroom Ganoderma resinaceum and their inhibitory activities against a-glucosidase. Phytochemistry 2018, 149, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.M.; Chatterjee, K.; De, D.; Jana, K.; Bera, T.K.; Ghosh, D. Inhibitory effect of hydro-methanolic extract of seed of Holarrhena antidysenterica on alpha-glucosidase activity and postprandial blood glucose level in normoglycemic rat. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 135, 194–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Du, R.; Xiu, L.; Bian, Z.; Ma, C.; Sato, N.; Hattori, M.; Zhang, H.; Liang, Y.; Yu, S.; et al. Protective effect of triterpenes of Ganoderma lucidum on lipopolysaccharide induced inflammatory responses and acute liver injury. Cytokine 2020, 127, 154917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudhgaonkar, S.; Thyagarajan, A.; Sliva, D. Suppression of the inflammatory response by triterpenes isolated from the mushroom Ganoderma lucidum. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Nguyen, V.T.; Tae, N.; Lee, S.; Ryoo, S.; Min, B.S.; Lee, J.H. Anti-inflammatory and heme oxygenase-1 inducing activities of lanostane triterpenes isolated from mushroom Ganoderma lucidum in RAW264.7 cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 280, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, R. Are pleuromutilin antibiotics finally fit for human use? Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1241, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.M.; Chuang, D.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Guo, Y.H.; Tsai, P.W.; Shyur, L.F. Metabolite profiling and chemopreventive bioactivity of plant extracts from Bidens Pilosa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 95, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, I.; Lozano, M.; Moro, C.; Arrigo, M.D.; Rostagno, M.A.; Martinez, J.A.; GarciaLafuente, A.; Guillamon, E.; Villares, A. Anti-oxidant properties of phenolic compounds occurring in edible mushrooms. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Ramírez, A.; Pavo-Caballero, C.; Baeza, E.; Baenas, N.; Garcia-Viguera, C.; Marín, F.R.; Soler-Rivas, C. Mushrooms do not contain flavonoids. J. Funct. Food 2016, 25, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, T.K. Fungi contain genes associated with flavonoid biosynthesis pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 68, 103910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, J.A.; Barros, L.; Martins, A.; Morais, J.S.; Vasconcelos, M.H.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Phenolic profile of seventeen Portuguese wild mushrooms. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 56Gasecka, M.; Mleczek, M.; Siwulski, M.; Niedzielski, P. Phenolic composition and anti-oxidant properties of Pleurotus ostreatus and Pleurotus eryngii enriched with selenium and zinc. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2016, 242, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, M.; Fang, Z. Efficient physical extraction of active constituents from edible fungi and their potential bioactivities: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019. In press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Suo, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, B. Green tea catechins ameliorate adipose insulin resistance by improving oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 1648–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Saravanakumar, K.; Wang, M.H. Total phenolic, flavonoid contents and free radical scavenging capacity of extracts from tubers of Stachys affinis. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 15, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starčević, K.; Krstulović, L.; Brozić, D.; Maurić, M.; Stojević, Z.; Mikulec, Ž.; Bajić, M.; Mašek, T. Production performance, meat composition and oxidative susceptibility in broiler chicken fed with different phenolic compounds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.T.; Lai, L.P.; Lin, W.C.; Ciou, J.Y.; Chang, S.C.; Yu, B.; Lee, T.T. Improving nutrition utilization and meat Quality of broiler chickens through solid-state fermentation of agricultural by-products by Aureobasidium Pullulans. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Avic. 2017, 19, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.F.; Hsieh, C.H.; Lin, W.Y. Proteomic response of LAP-activated RAW 264.7 macrophages to the anti-inflammatory property of fungal ergosterol. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoutsis, K.; Grasso, S.; Menon, A.; Brunton, N.P.; Lyng, J.G.; Jacquier, J.C.; Bhuyan, D.J. Recovery of ergosterol and vitamin D2 from mushroom waste - Potential valorization by food and pharmaceutical industries. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, A.C.; Kühn, J.; Brandsch, C.; Hirche, F.; Stangl, G.I. Intake of ergosterol increases the vitamin D concentrations in serum and liver of mice. J. Steroid Biochem. 2019, 194, 105435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caiazzo, E.; Maione, F.; Morello, S.; Lapucci, A.; Paccosi, S.; Steckel, B.; Lavecchia, A.; Parenti, A.; Iuvone, T.; Schrader, J.; et al. Adenosine signaling mediates the anti-inflammatory effects of the COX-2 inhibitor nimesulide. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 112, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.P.; Hwang, T.L.; Chan, Y.; El-Shazly, M.; Wug, T.Y.; Lo, I.W.; Hsu, Y.M.; Lai, K.H.; Houh, M.F.; Yuani, S.S.; et al. Research and development of Cordyceps in Taiwan. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2016, 5, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskó, G.; Antonioli, L.; Cronstein, B.N. Adenosine metabolism, immunity and joint health. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 151, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Shinozuka, K.; Yoshikawa, N. Anticancer and antimetastatic effects of cordycepin, an active component of Cordyceps sinensis. J. Pharma. Sci. 2014, 127, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaicharoenaudomrung, N.; Jaroonwitchawan, T.; Noisa, P. Cordycepin induces apoptotic cell death of human brain cancer through the modulation of autophagy. Toxicol. In Vitro 2018, 46, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Cuesta, A.; Ortunño, J.; Esteban, M.A.; Meseguer, J. Immunostimulant properties of a cell wall-modified whole Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain administered by diet to seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2003, 96, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awaad, M.; Atta, A.M.; El-Ghany, W.A.; Elmenawey, M.; Ahmed, A.; Hassan, A.A.; Nada, A.; Abdelaleem, G.A.; Kawkab, A.A. Effect of a specific combination of mannan-oligosaccharides and β-glucans extracted from yeast cell wall on the health status and growth performance of ochratoxicated broiler chickens. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 7, 82–96. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khalaifah, H.S. Benefits of probiotics and/or prebiotics for antibiotic-reduced poultry. Poult. Sci. 2018, 11, 3807–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-González, J.A.; Serna-Saldívar, S.O.; Gutierrez-Uribe, J.A. Mycochemical changes induced by selenium enrichment in P. ostreatus fruiting bodies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4074–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penney, J.; Lu, Y.; Pan, B.; Feng, Y.; Walk, C.; Li, J. Pure yeast beta-glucan and two types of yeast cell wall extracts enhance cell migration in porcine intestine model. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 59, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.H.; Cheng, L.; Kang, K.; Tian, G.; Mohammad, A.M.; Xue, B.; Wang, L.Z.; Zou, H.W.; Mathew, G.G.; Wang, Z.S. Effects of yeast and yeast cell wall polysaccharides supplementation on beef cattle growth performance, rumen microbial populations and lipopolysaccharides production. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Cui, S.; Xie, M. Bioactive polysaccharides from Cordyceps sinensis: Isolation, structure features and bioactivities. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre. 2017, 1, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Duan, X.; Tang, T.; Shen, Y.; Hu, B.; Liu, A.; Chen, H.; Li, C.; Liu, Y. Characterization and anti-oxidant activities of polysaccharides from thirteen boletus mushrooms. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Ren, Z.; Wang, X.; Jia, L.; Zhang, C. Anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and renoprotective effects of acidichydrolytic polysaccharides by spent mushroom compost (Lentinula edodes) on LPS-induced kidney injury. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhu, L.; Qu, Y.; Qu, X.; Mu, M.; Zhang, M.; Muneer, G.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, L. Analyses of active anti-oxidant polysaccharides from four edible mushrooms. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyama, V.; Keawsompong, S.; LeBlanc, J.G.; deLeBlanc, A.M.; Chatel, J.M.; Chanput, W. Action modes of the immune modulating activities of crude mushroom polysaccharide from Phallus atrovolvatus. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre. 2020, 23, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettin, F.; Cousseau, F.; Martins, K.; Boff, N.A.; Zaccaria, S.; daSilveira, M.M.; Dillon, A.J.P. Phenol removal by laccases and other phenol oxidases of Pleurotus sajor-caju PS-2001 in submerged cultivations and aqueous mixtures. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, J.A.; Vieira, Y.A.; Cruz, I.A.; Vilar, D.S.; Aguiar, M.M.; Torres, N.H.; Bharagava, R.N.; Lima, Á.S.; deSouza, R.L.; Ferreira, L.F.R. Sequential degradation of raw vinasse by a laccase enzyme producing fungus Pleurotus sajor-caju and its ATPS purification. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 25, e00411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hamid, A.M.; Solbiati, J.O.; Cann, I.K.O. Chapter One—Insights into lignin degradation and its potential industrial applications. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 82, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; van Lier, J.B.; Spanjers, H. White rot fungi pretreatment to advance volatile fatty acid production from solid-state fermentation of solid digestate: Efficiency and mechanisms. Energy 2018, 162, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Wang, X.; Zhen, L.; Gu, J.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Q.; Ma, J.; Peng, H.; Lei, L.; Zhao, W. Effects of inoculating with lignocellulose-degrading consortium on cellulose degrading genes and fungal community during co-composting of spent mushroom substrate with swine manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 291, 121876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowieson, A.J.; Ruckebusch, J.P.; Sorbara, J.O.B.; Wilson, J.W.; Guggenbuhl, P.; Roos, F.F. A systematic view on the effect of phytase on ileal amino acid digestibility in broilers. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 225, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes-Blackburn, D.; Jorquera, M.; Gianfreda, L.; Rao, M.; Greiner, R.; Garrido, E.; Mora, M.L. Activity stabilization of Aspergillus niger and Escherichia coli phytases immobilized on allophanic synthetic compounds and montmorillonite nanoclays. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9360–9367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanzenbock, E.; Apprich, S.; Tirpanalan, O.; Zitz, U.; Kracher, D.; Schedle, K.; Kneifel, W. Wheat bran biodegradation by edible Pleurotus fungi e A sustainable perspective for food and feed. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 86, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, M.; Perez, J.F.; L´etourneau-Montminy, M.P.; Franco-Rossell’o, R.; Aligue, R.; Sol‘a-Oriol, D. The effects of microbisal phytase and dietary calcium and phosphorus levels on the productive performance and bone mineralization of broilers. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2018, 243, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndrepepa, G. Uric acid and cardiovascular disease. Eur. Caediol. 2018, 484, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhya, C.; Alagarsamy, S.; Szakacs, G.; Pandey, A. Comparative evaluation of neutral protease production by Aspergillus oryzae in submerged and solid-state fermentation. Process. Biochem. 2005, 40, 2689–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mihalcioiu, M.; Li, L.; Zakikhani, M.; Camirand, A.; Kremer, R. Vitamin D prevents lipid accumulation in murine muscle through regulation of PPARγ and perilipin-2 expression. J. Steroid Biochem. 2018, 177, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegari, M.; Sarbakhsh, P.; Mobasseri, M.; Noshad, H.; Esfandiari, A.; Khodadadi, B.; Gargari, B.P. The effects of vitamin D supplementation on lipid profiles and oxidative indices among diabetic nephropathy patients with marginal vitamin D status. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2019, 13, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asbaghi, O.; Kashkooli, S.; Choghakhori, R.; Hasanvand, A.; Abbasnezhad, A. Effect of calcium and vitamin D co-supplementation on lipid profile of overweight/obese subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the randomized clinical trials. Obes. Med. 2019, 15, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindhu, J.; Arunava, D. An edible fungi Pleurotus ostreatus inhibits adipogenesis via suppressing expression of PPAR γ and C/EBP α in 3T3-L1 cells: In vitro validation of gene knock out of RNAs in PPAR γ using CRISPR spcas9. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 116, 109030. [Google Scholar]
| Animal Type | Treatment | Rearing Period | Body (Egg) Weight | Feed Conversion Rate | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broilers | 0.5% A. pullulans fermentation 2 | 22–35 d | +12% * | −4% | [14] |
| 1–35 d | +8% * | −3% | |||
| Hendrix laying hens | 2% C. militaris wastes residue | 5–8 weeks | +4% * | −10% * | [15] |
| 9–12 weeks | +3% * | −5% * | |||
| 0–12 weeks | +7% * | −6% * | |||
| White Roman geese | 5% mushroom waste compost | 5–8 weeks | +2% | 0% | [16] |
| 9–12 weeks | −1% | +31% | |||
| Male broilers | 0.1% T. pseudokoningii powder | 1–21 d | +10% * | −4% | [18] |
| 22–35 d | +6% | −3% | |||
| Broilers | 10% P. eryngii mushroom compost fermented wheat bran | 1–21 d | +2% | −8% | [6] |
| 22–35 d | +3% | 0% | |||
| 1–35 d | +2% | −3% | |||
| Male broilers | 0.1% A. cinnamomea | 1–21 d | +14% * | −1% | [20] |
| 22–35 d | +10% * | −5% | |||
| 1–35 d | +11% * | −7% | |||
| Male broilers | 10% A. cinnamomea fermented wheat bran | 1–21 d | +7% * | −5% * | [21] |
| 22–35 d | −1% | +1% | |||
| 1–35 d | −2% | +2% | |||
| Male broilers | 0.5% mushroom waste compost | 1–21 d | +3% | −6% * | [4] |
| 22–35 d | +5% | +5% | |||
| 1–35 d | +4% | −7% |
| Animal Type | Treatment | Functional Components | Functions | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broilers | 0.5% A. pullulans ferment 1 | - 2 | Increased SOD and CAT activities, ileum villus height and lactic acid bacteria number in cecum | [14] |
| Hendrix laying hens | 2% C. militaris waste residue | Cordycepin, cordycepic acid, crude polysaccharides, flavonoid, adenosine, and crude triterpenoid | Increased egg mass and eggshell strength; improved feed conversion rate throughout the entire experimental period; decreased cholesterol content in egg yolk | [15] |
| White Roman geese | 5% mushroom waste compost | - | Increased SOD activities and decreased MDA content in serum; improved flavor, color, and acceptability on sensory evaluation | [16] |
| Male broilers | 10% T. pseudokoningii fermented wheat bran | Cellulase, xylanase, and reducing sugar | Decreased coliform count and increased villus height in ileum | [17] |
| Male broilers | 0.1% T. pseudokoningii powder | Phenols, xylanase, and cellulase | Increased SOD and CAT activities, jejunum villus height, and lactic acid bacteria levels in cecum | [18] |
| Broilers | 10% S. cerevisiae fermented wheat bran | - | Increased villus height and lactic acid content in ileum | [19] |
| Male broilers | 0.4% A. cinnamomea addition | Crude triterpenoids, crude polysaccharides, and phenols | Enhanced Nrf-2, GCLC, SOD, CAT and HO-1 mRNA expression and decreased NF-κB and IL-1β mRNA expression | [20] |
| Male broilers | 10% A. cinnamomea fermented wheat bran | Crude triterpenoids, crude polysaccharides, and phenols | Enhanced SOD and CAT activities and decreased total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein content in serum | [21] |
| Male broilers | 0.1% S. cerevisiae or A. oryzae powder | Xylanase, protease, cellulase, and ß-glucanase | Decreased the number of Clostridium perfringens in ileum and suppressed inflammation-related mRNA expression | [7] |
| Male broilers | 0.5% mushroom waste compost | Crude triterpenes, phenols, flavonoids, gallocatechin, and epigallocatechin | Increased antioxidant capacity, adipolysis, and gut barrier expression | [4] |
| Female broilers | 1% C. militaris waste residue | Polysaccharides, triterpenes, phenols, and flavonoids | Enhanced antioxidant-related mRNA expression | [9] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chuang, W.Y.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Lee, T.-T. The Effects of Fungal Feed Additives in Animals: A Review. Animals 2020, 10, 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10050805
Chuang WY, Hsieh YC, Lee T-T. The Effects of Fungal Feed Additives in Animals: A Review. Animals. 2020; 10(5):805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10050805
Chicago/Turabian StyleChuang, Wen Yang, Yun Chen Hsieh, and Tzu-Tai Lee. 2020. "The Effects of Fungal Feed Additives in Animals: A Review" Animals 10, no. 5: 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10050805
APA StyleChuang, W. Y., Hsieh, Y. C., & Lee, T.-T. (2020). The Effects of Fungal Feed Additives in Animals: A Review. Animals, 10(5), 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10050805





