Impacts of Milking and Housing Environment on Milk Microbiota
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Treatment and Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. 16S rRNA Genes Sequencing
3. Results
3.1. Alpha and Beta Diversities of Microbiota from Raw Milk and Environmental Samples
3.2. Bacterial Group Analysis of Raw Milk, Cow Trough Water, Teat Dip Cup, Teat, Teat Liner, Dairy Hall Air, Cowshed Air, Feces, Feed and Bedding Samples
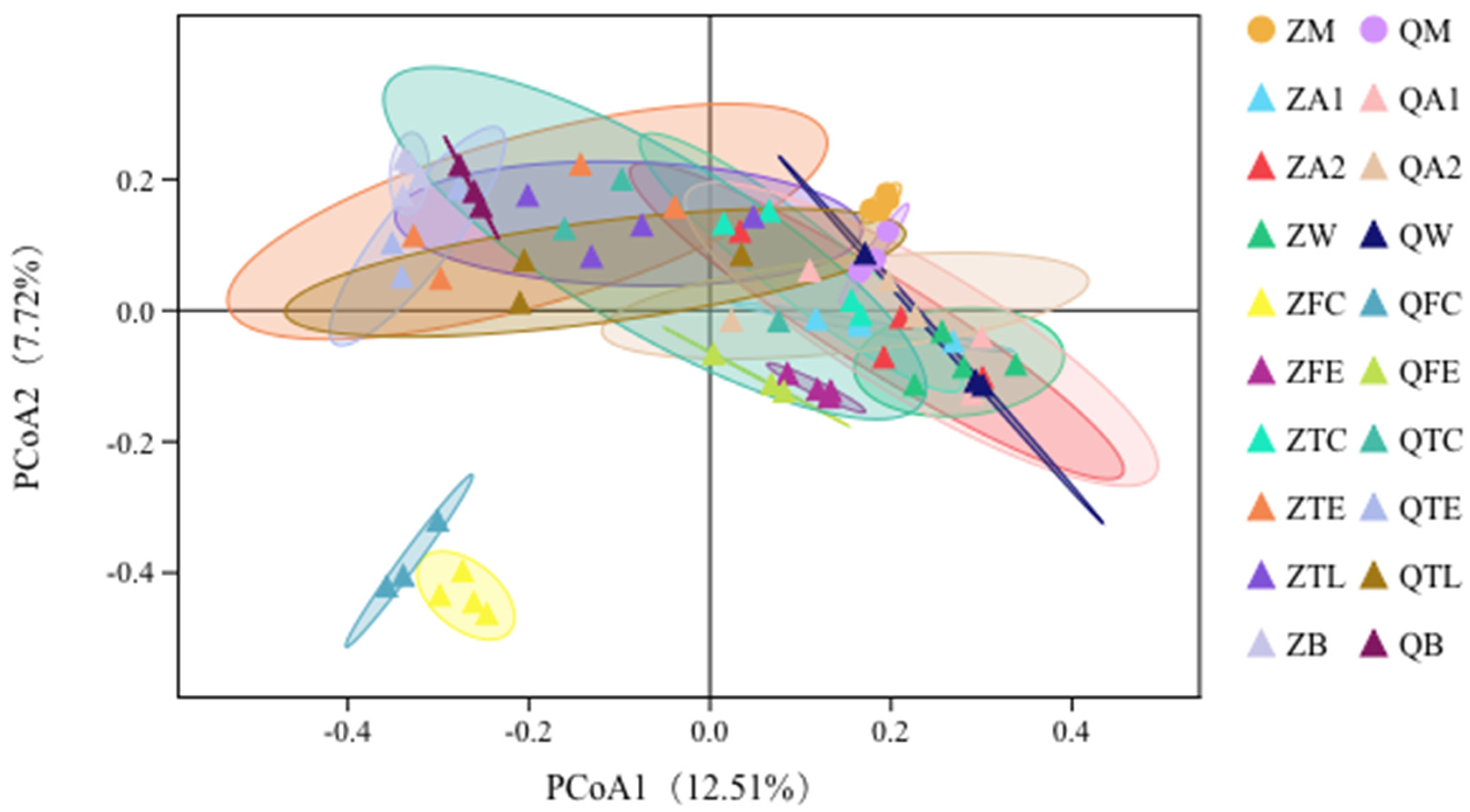
3.3. Principal Coordinates Analysis (PCoA) Shows Relationships between Raw Milk and Environmental Samples
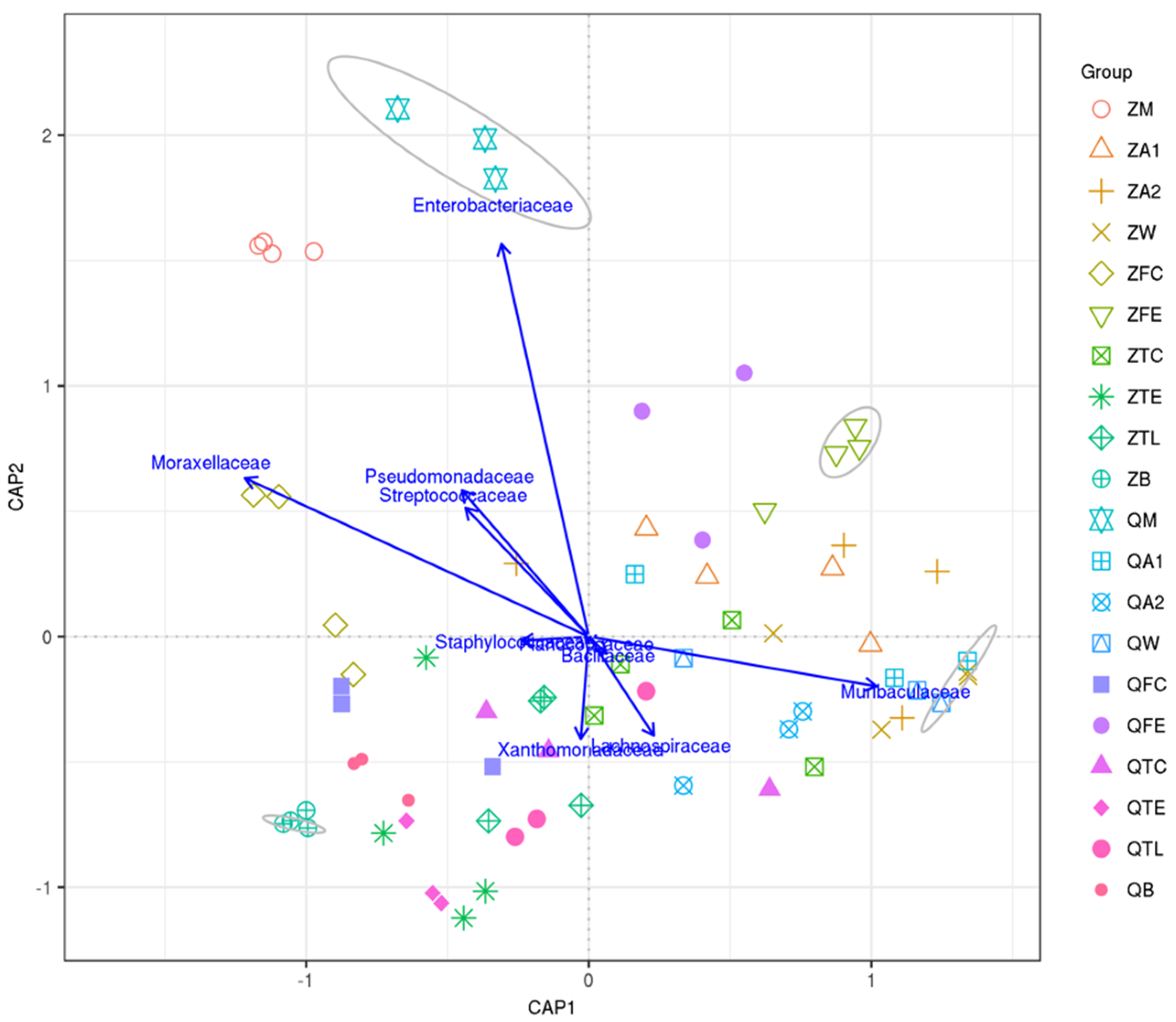
3.4. Canonical Analysis of Principal Coordinates (CAP) Shows Relationships between Raw Milk and Environmental Samples
3.5. Source Tracker Model Further Evaluates the Contribution of Environmental Sample Sources to the Raw Milk Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dehghan, M.; Mente, A.; Rangarajan, S.; Sheridan, P.; Mohan, V.; Iqbal, R.; Gupta, R.; Lear, S.; Wentzel-Viljoen, E.; Avezum, A.; et al. Association of dairy intake with cardiovascular disease and mortality in 21 countries from five continents (PURE): A prospective cohort study. Lancet 2018, 392, 2288–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.F.; Uniacke-Lowe, T.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; O’Mahony, J.A. Dairy Chemistry and Biochemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Qu, X.; Zheng, N.; Su, C.; Wang, J.; Soyeurt, H. Large scale study of the within and between spatial variability of lead, arsenic, and cadmium contamination of cow milk in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 3054–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppel, K.; Golebiewski, M.; Konopka, K.; Kunowska-Slosarz, M.; Slosarz, J.; Grodkowski, G.; Przysucha, T.; Balcerak, M.; Madras-Majewska, B.; Sakowski, T. Relationship between the Quality of Colostrum and the Formation of Microflora in the Digestive Tract of Calves. Animals 2020, 10, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigouette, J.P.; Bethel, J.W.; Bovbjerg, M.L.; Waite-Cusic, J.G.; Häse, C.C.; Poulsen, K.P. Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices Regarding Raw Milk Consumption in the Pacific Northwest. Int. Assoc. Food Prot. 2018, 38, 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- Capodifoglio, E.; Centola Vidal, A.M.; Lima, J.A.S.; Bortoletto, F.; D’Abreu, L.F.; Siqueira Goncalves, A.C.; Nakashima Vaz, A.C.; de Carvalho Balieiro, J.C.; Netto, A.S. Lipolytic and proteolytic activity of Pseudomonas spp. isolated during milking and storage of refrigerated raw milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 5214–5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friman, M.J.; Eklund, M.H.; Pitkälä, A.H.; Rajala-Schultz, P.J.; Rantala, M.H.J. Description of two Serratia marcescens associated mastitis outbreaks in Finnish dairy farms and a review of literature. Acta Veter Scand. 2019, 61, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, V.; Quero, G.M. Culture-Dependent and Culture-Independent Nucleic-Acid-Based Methods Used in the Microbial Safety Assessment of Milk and Dairy Products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 493–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.A.; Kent, D.J.; Boor, K.J.; Martin, N.H.; Wiedmann, M. Different management practices are associated with mesophilic and thermophilic spore levels in bulk tank raw milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, A.J.; Feehily, C.; Fenelon, M.A.; Gleeson, D.; Hill, C.; Cotter, P.D. Tracking the Dairy Microbiota from Farm Bulk Tank to Skimmed Milk Powder. mSystems 2020, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vacheyrou, M.; Normand, A.-C.; Guyot, P.; Cassagne, C.; Piarroux, R.; Bouton, Y. Cultivable microbial communities in raw cow milk and potential transfers from stables of sixteen French farms. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 146, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves Dos Santos, M.T.P.; Jose Benito, M.; de Guia Cordoba, M.; Alvarenga, N.; Seco de Herrera, S.R.-M. Yeast community in traditional Portuguese Serpa cheese by culture-dependent and -independent DNA approaches. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 262, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichler, S.J.; Trmcic, A.; Martin, N.H.; Boor, K.J.; Wiedmann, M. Pseudomonas fluorescens group bacterial strains are responsible for repeat and sporadic postpasteurization contamination and reduced fluid milk shelf life. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 7780–7800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andre, M.C.D.P.B.; Hidalgo Campos, M.R.; Borges, L.J.; Kipnis, A.; Pimenta, F.C.; Serafini, A.B. Comparison of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from food handlers, raw bovine milk and Minas Frescal cheese by antibiogram and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis following SmaI digestion. Food Control 2008, 19, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, A.R.; Perea, J.M.; Garcia-Bejar, B.; Jimenez, L.; Garzon, A.; Arias, R. Dominant Yeast Community in Raw Sheep’s Milk and Potential Transfers of Yeast Species in Relation to Farming Practices. Animals 2020, 10, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bava, L.; Colombini, S.; Zucali, M.; Decimo, M.; Morandi, S.; Silvetti, T.; Brasca, M.; Tamburini, A.; Crovetto, G.M.; Sandrucci, A. Efficient milking hygiene reduces bacterial spore contamination in milk. J. Dairy Res. 2017, 84, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, C.J.; Gleeson, D.; O’Toole, P.W.; Cottera, P.D. Impacts of Seasonal Housing and Teat Preparation on Raw Milk Microbiota: A High-Throughput Sequencing Study. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehmeti, I.; Muji, S.; Diep, D.B.; Nes, I.F. High frequency of the potential pathogen Lactococcus garvieae in raw milk from Kosovo. Food Control 2015, 53, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, Y.; You, C.; Ren, J.; Chen, W.; Zheng, H.; Liu, Z. Variation in Raw Milk Microbiota Throughout 12 Months and the Impact of Weather Conditions. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skeie, S.B.; Haland, M.; Thorsen, I.M.; Narvhus, J.; Porcellato, D. Bulk tank raw milk microbiota differs within and between farms: A moving goalpost challenging quality control. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1959–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Palmer, J.; Teh, K.H.; Biggs, P.; Flint, S. 16S rDNA high-throughput sequencing and MALDI-TOF MS are complementary when studying psychrotrophic bacterial diversity of raw cows’ milk. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 97, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoc, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Knittel, K.; Fuchs, B.M.; Ludwig, W.; Peplies, J.; Gloeckner, F.O. SILVA: A comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7188–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Wu, H.; Nishino, N. An investigation of seasonal variations in the microbiota of milk, feces, bedding, and airborne dust. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 33, 1858–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Knights, D.; Kuczynski, J.; Charlson, E.S.; Zaneveld, J.; Mozer, M.C.; Collman, R.G.; Bushman, F.D.; Knight, R.T.; Kelley, S.T. Bayesian community-wide culture-independent microbial source tracking. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verhegghe, M.; De Block, J.; Van Weyenberg, S.; Herman, L.; Heyndrickx, M.; Van Coillie, E. Effect of a pre-milking teat foam and a liner disinfectant on the presence of mesophilic and (proteolytic) psychrotrophic bacteria prior to milking. J. Dairy Res. 2019, 86, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, M.; Liu, D. A systematic characterization of the distribution, biofilm-forming potential and the resistance of the biofilms to the CIP processes of the bacteria in a milk powder processing factory. Food Res. Int. 2018, 113, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skowron, K.; Sekowska, A.; Kaczmarek, A.; Grudlewska, K.; Budzynska, A.; Bialucha, A.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E. Comparison of the effectiveness of dipping agents on bacteria causing mastitis in cattle. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2019, 26, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, A.; Pereira, J.M.; Amiama, C.; Bueno, J. Mastitis diagnosis in ten Galician dairy herds (NW Spain) with automatic milking systems. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2015, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, B.; Meng, L.; Liu, H.; Zheng, N.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhao, S.; Li, F.; Wang, J. Impacts of Milking and Housing Environment on Milk Microbiota. Animals 2020, 10, 2339. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10122339
Du B, Meng L, Liu H, Zheng N, Zhang Y, Guo X, Zhao S, Li F, Wang J. Impacts of Milking and Housing Environment on Milk Microbiota. Animals. 2020; 10(12):2339. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10122339
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Bingyao, Lu Meng, Huimin Liu, Nan Zheng, Yangdong Zhang, Xiaodong Guo, Shengguo Zhao, Fadi Li, and Jiaqi Wang. 2020. "Impacts of Milking and Housing Environment on Milk Microbiota" Animals 10, no. 12: 2339. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10122339
APA StyleDu, B., Meng, L., Liu, H., Zheng, N., Zhang, Y., Guo, X., Zhao, S., Li, F., & Wang, J. (2020). Impacts of Milking and Housing Environment on Milk Microbiota. Animals, 10(12), 2339. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10122339






