Administration of Protein Hydrolysates from Anchovy (Engraulis Encrasicolus) Waste for Twelve Weeks Decreases Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Severity in ApoE–/–Mice
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
2.2. Anchovy Protein Hydrolysates
2.3. Histopathological Examination
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
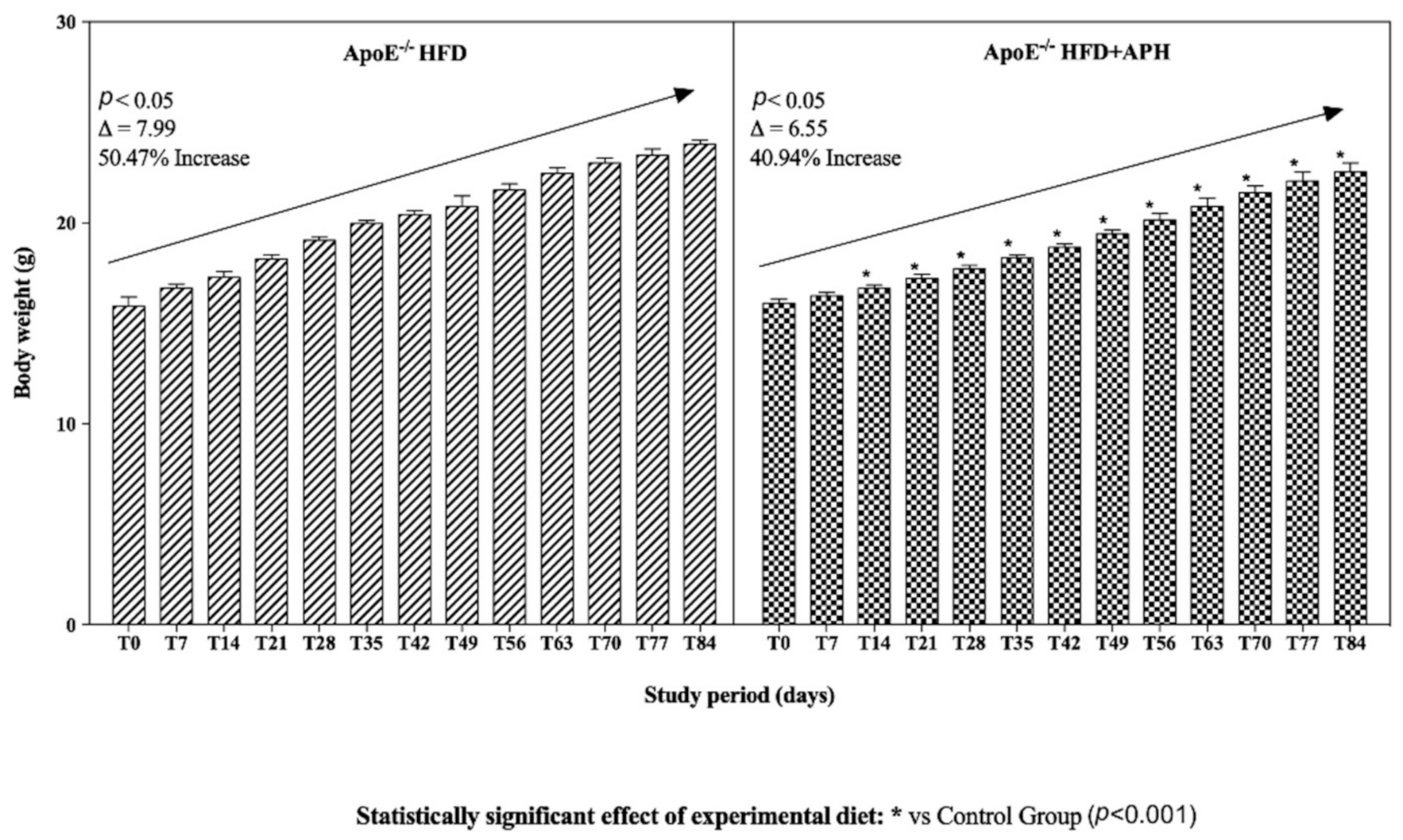
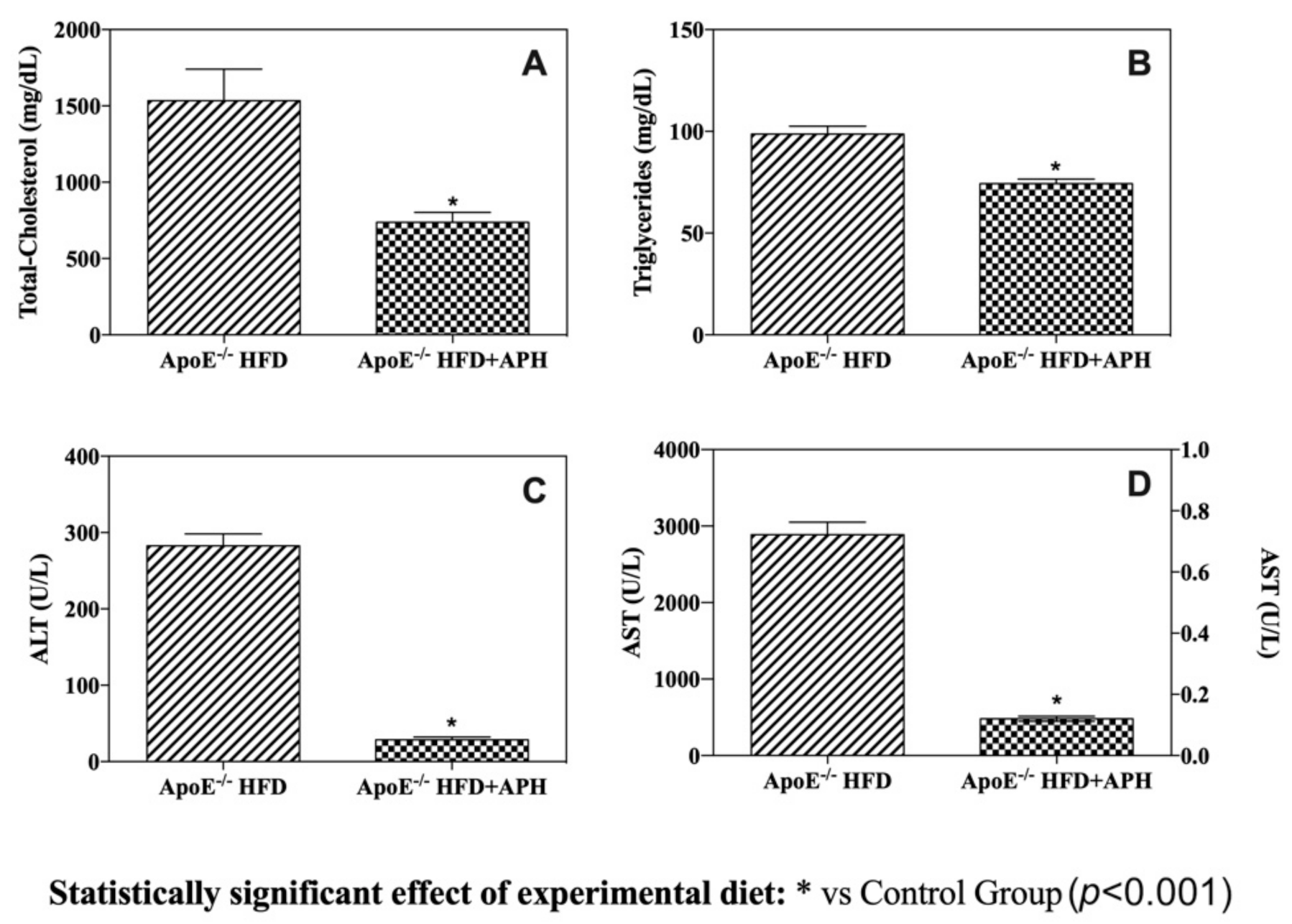
3.1. Animals
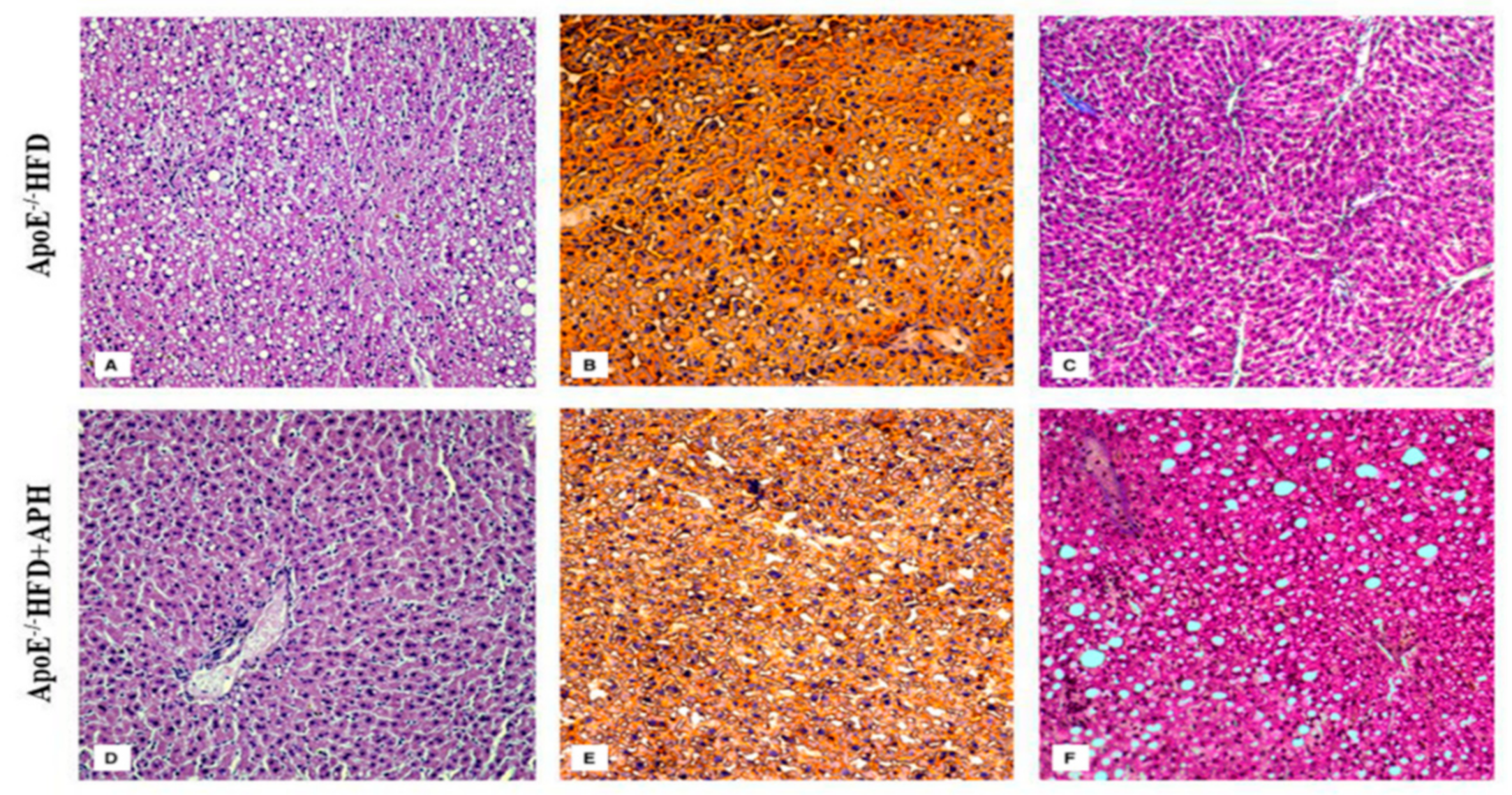
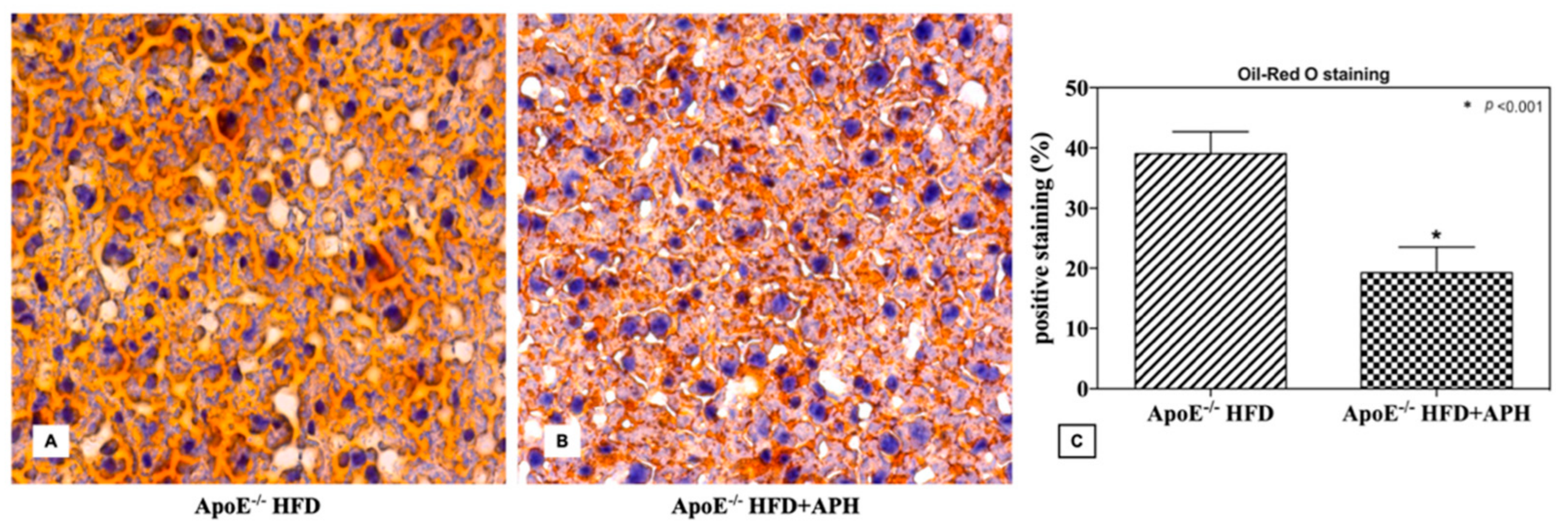
3.2. Macroscopic and Histological Evaluation
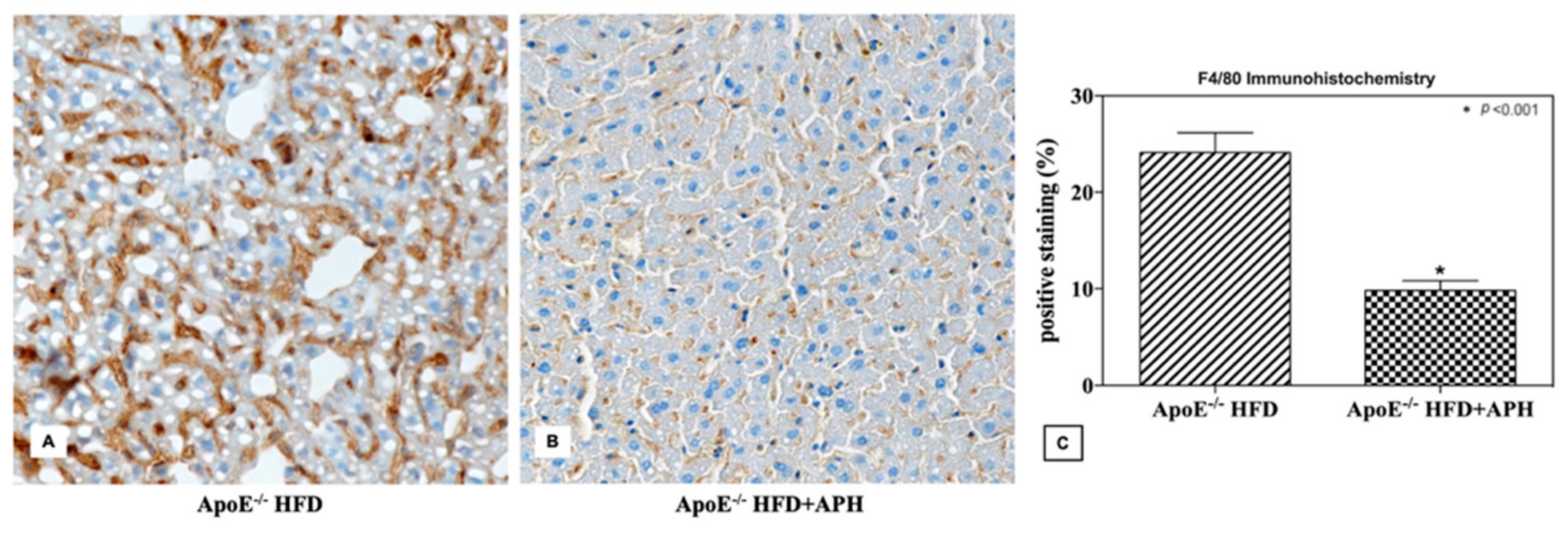
3.3. Immunohistochemical Evaluation
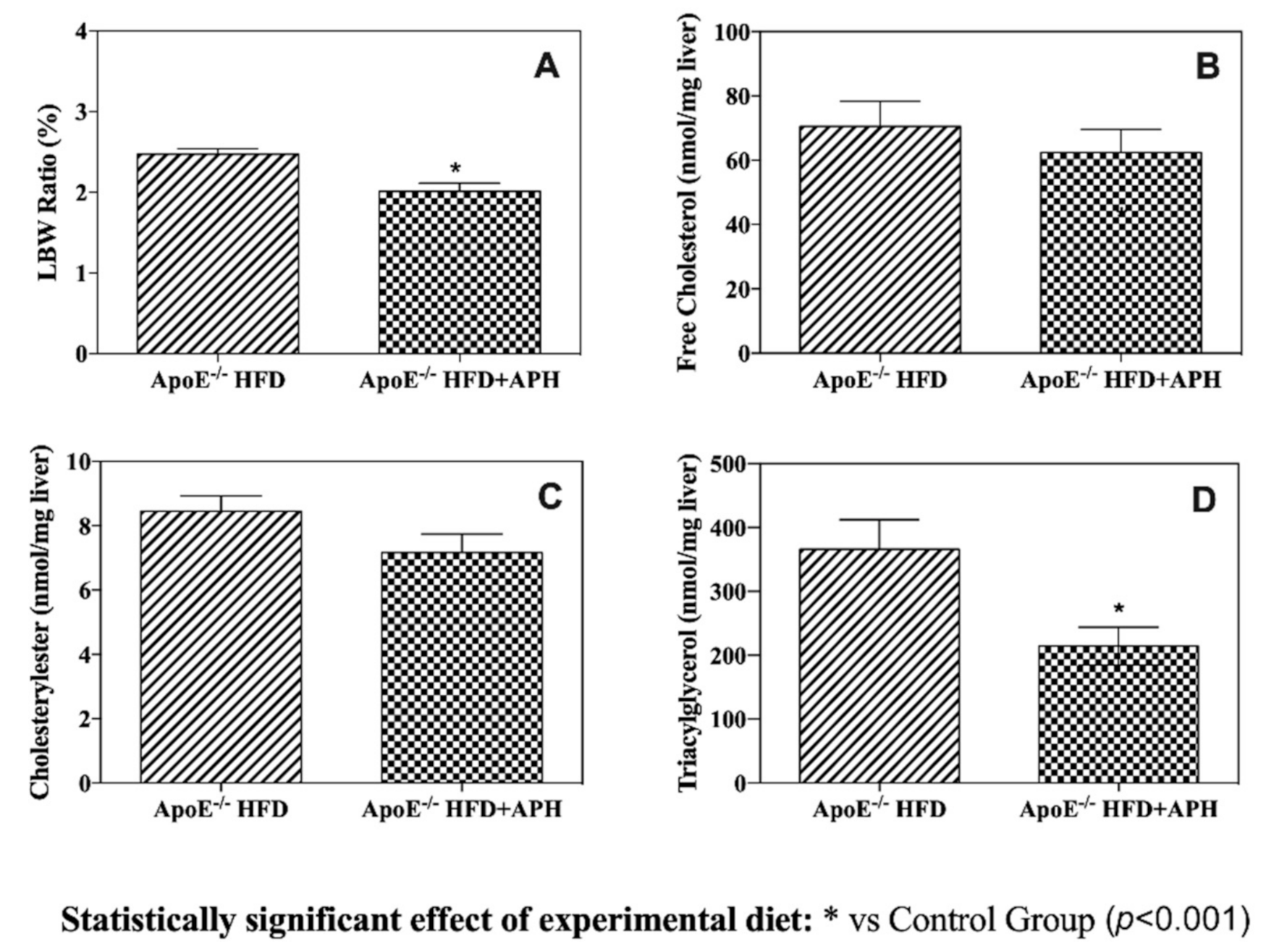
3.4. Hepatic Lipid Content
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; George, J.; International Consensus Panel. MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanwal, F.; Kramer, J.R.; Duan, Z.; Yu, X.; White, D.; El-Serag, H.B. Trends in the burden of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a United States cohort of veterans. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marjot, T.; Moolla, A.; Cobbold, J.F.; Hodson, L.; Tomlinson, J.W. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Adults: Current Concepts in Etiology, Outcomes, and Management. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, bnz009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clapper, J.R.; Hendricks, M.D.; Gu, G.; Wittmer, C.; Dolman, C.S.; Herich, J.; Athanacio, J.; Villescaz, C.; Ghosh, S.S.; Heilig, J.S. Diet-induced mouse model of fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis reflecting clinical disease progression and methods of assessment. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 305, G483–G495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szczepaniak, L.S.; Nurenberg, P.; Leonard, D.; Browning, J.D.; Reingold, J.S.; Grundy, S.; Hobbs, H.H.; Dobbins, R.L. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy to measure hepatic triglyceride content: Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in the general population. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2005, 288, E462–E468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borges-Canha, M.; Neves, J.S.; Libânio, D.; Von-Hafe, M.; Vale, C.; Araújo-Martins, M.; Leite, A.R.; Pimentel-Nunes, P.; Carvalho, D.; Leite-Moreira, A. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiac function and structure—A meta-analysis. Endocrine 2019, 66, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowman, J.K.; Armstrong, M.J.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Newsome, P.N. Current therapeutic strategies in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowman, J.K.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Newsome, P.N. Pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. QJM Int. J. Med. 2010, 103, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eslam, M.; Valenti, L.; Romeo, S. Genetics and epigenetics of NAFLD and NASH: Clinical impact. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petta, S.; Muratore, C.; Craxi, A. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease pathogenesis: The present and the future. Dig. Liver Dis. 2009, 41, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.P. From fat to inflammation. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schierwagen, R.; Maybüchen, L.; Zimmer, S.; Hittatiya, K.; Bäck, C.; Klein, S.; Uschner, F.E.; Reul, W.; Boor, P.; Nickenig, G.; et al. Seven weeks of Western diet in apolipoprotein-E-deficient mice induce metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with liver fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larter, C.Z.; Yeh, M.M. Animal models of NASH: Getting both pathology and metabolic context right. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 1635–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hatters, D.M.; Peters-Libeu, C.A.; Weisgraber, K.H. Apolipoprotein E structure: Insights into function. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006, 31, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, Y.; Tian, H.; Yao, S.; Li, G.; Qin, S. Simvastatin reduces atherogenesis and promotes the expression of hepatic genes associated with reverse cholesterol transport in apoE-knockout mice fed high-fat diet. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Katagiri, H.; Ishigaki, Y.; Yamada, T.; Ogihara, T.; Imai, J.; Uno, K.; Hasegawa, Y.; Kanzaki, M.; Yamamoto, T.T. Involvement of apolipoprotein E in excess fat accumulation and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddick, R.L.; Zhang, S.H.; Maeda, N. Atherosclerosis in mice lacking apo E. Evaluation of lesional development and progression. Arter. Thromb. J. Vasc. Biol. 1994, 14, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalafati, I.P.; Borsa, D.; Dimitriou, M.; Revenas, K.; Kokkinos, A.; Dedoussis, G.V. Dietary patterns and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a Greek case–control study. Nutrition 2019, 61, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddy, W.H.; Herbison, C.E.; Jacoby, P.; Ambrosini, G.L.; O’Sullivan, T.A.; Ayonrinde, O.T.; Olynyk, J.K.; Black, L.J.; Beilin, L.J.; Mori, T.A.; et al. The Western Dietary Pattern Is Prospectively Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Adolescence. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kechagias, S.; Ernersson, A.; Dahlqvist, O.; Lundberg, P.; Lindstrom, T.; Nystrom, F.H.; for the Fast Food Study Group. Fast-food-based hyper-alimentation can induce rapid and profound elevation of serum alanine aminotransferase in healthy subjects. Gut 2008, 57, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anania, C.; Perla, F.M.; Olivero, F.; Pacifico, L.; Chiesa, C. Mediterranean diet and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 2083–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aller, R.; Izaola, O.; de la Fuente, B.; De Luis Román, D.A. Mediterranean diet is associated with liver histology in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 32, 2518–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, H.M.; Johnson, N.A.; Burdon, C.A.; Cohn, J.S.; O’Connor, H.T.; George, J. Omega-3 supplementation and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, F.; Wang, H.; Tian, Y.; Li, Q.; He, L.; Li, N.; Liu, Z. Fish oil alleviated high-fat diet–induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via regulating hepatic lipids metabolism and metaflammation: A transcriptomic study. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, N.; Sano, K.; Horiuchi, A.; Tanaka, E.; Kiyosawa, K.; Aoyama, T. Highly purified eicosapentaenoic acid treatment improves nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2008, 42, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harnedy, P.A.; FitzGerald, R.J. Bioactive peptides from marine processing waste and shellfish: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wergedahl, H.; Liaset, B.; Gudbrandsen, O.A.; Lied, E.; Espe, M.; Muna, Z.; Mørk, S.; Berge, R.K. Fish protein hydrolysate reduces plasma total cholesterol, increases the proportion of HDL cholesterol, and lowers acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase activity in liver of Zucker rats. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 1320–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sirtori, C.R.; Galli, C.; Anderson, J.W.; Arnoldi, A. Nutritional and nutraceutical approaches to dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis prevention: Focus on dietary proteins. Atherosclerosis 2009, 203, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Beynen, A.C. Influence of dietary fish proteins on plasma and liver cholesterol concentrations in rats. Br. J. Nutr. 1993, 69, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalamaiah, M.; Dinesh kumar, B.; Hemalatha, R.; Jyothirmayi, T. Fish protein hydrolysates: Proximate composition, amino acid composition, antioxidant activities and applications: A review. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 3020–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villamil, O.; Váquiro, H.; Solanilla, J.F. Fish viscera protein hydrolysates: Production, potential applications and functional and bioactive properties. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halim, N.R.A.; Yusof, H.M.; Sarbon, N.M. Functional and bioactive properties of fish protein hydolysates and peptides: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drotningsvik, A.; Mjøs, S.A.; Pampanin, D.M.; Slizyte, R.; Carvajal, A.; Remman, T.; Høgøy, I.; Gudbrandsen, O.A. Dietary fish protein hydrolysates containing bioactive motifs affect serum and adipose tissue fatty acid compositions, serum lipids, postprandial glucose regulation and growth in obese Zucker fa/fa rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parolini, C.; Vik, R.; Busnelli, M.; Bjørndal, B.; Holm, S.; Brattelid, T.; Manzini, S.; Ganzetti, G.S.; Dellera, F.; Halvorsen, B.; et al. A Salmon Protein Hydrolysate Exerts Lipid-Independent Anti-Atherosclerotic Activity in ApoE-Deficient Mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giannetto, A.; Esposito, E.; Lanza, M.; Oliva, S.; Riolo, K.; Di Pietro, S.; Abbate, J.M.; Briguglio, G.; Cassata, G.; Cicero, L.; et al. Protein Hydrolysates from Anchovy (Engraulis encrasicolus) Waste: In Vitro and In Vivo Biological Activities. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørndal, B.; Berge, C.; Ramsvik, M.S.; Svardal, A.; Bohov, P.; Skorve, J.; Berge, R.K. A fish protein hydrolysate alters fatty acid composition in liver and adipose tissue and increases plasma carnitine levels in a mouse model of chronic inflammation. Lipids Health Dis. 2013, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mangano, V.; Gervasi, T.; Rotondo, A.; De Pasquale, P.; Dugo, G.; Macrì, F.; Salvo, A. Protein hydrolysates from anchovy waste: Purification and chemical characterization. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.-C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaria, C.; Ieni, A.; Corti, I.; Puleio, R.; Brachelente, C.; Mazzullo, G.; Lanteri, G. Immunohistochemical Study of Four Fish Tumors. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2019, 31, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotondo, A.; Salvo, A.; Gallo, V.; Rastrelli, L.; Dugo, G. Quick unreferenced NMR quantification of Squalene in vegetable oils: 1 H-NMR quantification of squalene in oils without reference. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1700151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvo, A.; Rotondo, A.; La Torre, G.L.; Cicero, N.; Dugo, G. Determination of 1,2/1,3-diglycerides in Sicilian extra-virgin olive oils by 1 H-NMR over a one-year storage period. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, V.L.; Hatch, N.W.; Chan, H.-W.; de Beer, M.C.; de Beer, F.C.; Tannock, L.R. A murine model of obesity with accelerated atherosclerosis. Obesity 2010, 18, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferré, N.; Martínez-Clemente, M.; López-Parra, M.; González-Périz, A.; Horrillo, R.; Planagumà, A.; Camps, J.; Joven, J.; Tres, A.; Guardiola, F.; et al. Increased susceptibility to exacerbated liver injury in hypercholesterolemic ApoE-deficient mice: Potential involvement of oxysterols. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 296, G553–G562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.H.; Christensen, M.S.; Dyerberg, J.; Schmidt, E.B. Heart rate variability and fatty acid content of blood cell membranes: A dose-response study with n-3 fatty acids. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 70, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fickova, M.; Hubert, P.; Crémel, G.; Leray, C. Dietary (n-3) and (n-6) polyunsaturated fatty acids rapidly modify fatty acid composition and insulin effects in rat adipocytes. J. Nutr. 1998, 128, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccione, G.; Arfuso, F.; Fazio, F.; Bazzano, M.; Giannetto, C. Serum lipid modification related to exercise and polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation in jumpers and thoroughbred horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2014, 34, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surette, M.E.; Whelan, J.; Broughton, K.S.; Kinsella, J.E. Evidence for mechanisms of the hypotriglyceridemic effect of n − 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Lipids Lipid Metab. 1992, 1126, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, H.-G.; Lee, J.K.; Park, H.G.; Jeon, J.-K.; Kim, S.-K. Antioxidant peptides isolated from the marine rotifer, Brachionus rotundiformis. Process. Biochem. 2009, 44, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, T.; Ishigami, M.; Luo, F.; Lingyun, M.; Ishizu, Y.; Kuzuya, T.; Hayashi, K.; Nakano, I.; Ishikawa, T.; Feng, G.-G.; et al. Branched-chain amino acids alleviate hepatic steatosis and liver injury in choline-deficient high-fat diet induced NASH mice. Metabolism 2017, 69, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagner, A.; Polizzi, A.; Fouché, E.; Ducheix, S.; Lippi, Y.; Lasserre, F.; Barquissau, V.; Régnier, M.; Lukowicz, C.; Benhamed, F.; et al. Liver PPARα is crucial for whole-body fatty acid homeostasis and is protective against NAFLD. Gut 2016, 65, 1202–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbate, J.M.; Macrì, F.; Capparucci, F.; Iaria, C.; Briguglio, G.; Cicero, L.; Salvo, A.; Arfuso, F.; Ieni, A.; Piccione, G.; et al. Administration of Protein Hydrolysates from Anchovy (Engraulis Encrasicolus) Waste for Twelve Weeks Decreases Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Severity in ApoE–/–Mice. Animals 2020, 10, 2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10122303
Abbate JM, Macrì F, Capparucci F, Iaria C, Briguglio G, Cicero L, Salvo A, Arfuso F, Ieni A, Piccione G, et al. Administration of Protein Hydrolysates from Anchovy (Engraulis Encrasicolus) Waste for Twelve Weeks Decreases Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Severity in ApoE–/–Mice. Animals. 2020; 10(12):2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10122303
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbate, Jessica M., Francesco Macrì, Fabiano Capparucci, Carmelo Iaria, Giovanni Briguglio, Luca Cicero, Andrea Salvo, Francesca Arfuso, Antonio Ieni, Giuseppe Piccione, and et al. 2020. "Administration of Protein Hydrolysates from Anchovy (Engraulis Encrasicolus) Waste for Twelve Weeks Decreases Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Severity in ApoE–/–Mice" Animals 10, no. 12: 2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10122303
APA StyleAbbate, J. M., Macrì, F., Capparucci, F., Iaria, C., Briguglio, G., Cicero, L., Salvo, A., Arfuso, F., Ieni, A., Piccione, G., & Lanteri, G. (2020). Administration of Protein Hydrolysates from Anchovy (Engraulis Encrasicolus) Waste for Twelve Weeks Decreases Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Severity in ApoE–/–Mice. Animals, 10(12), 2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10122303







