Different Responses of Bacterial and Archaeal Communities in River Sediments to Water Diversion and Seasonal Changes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
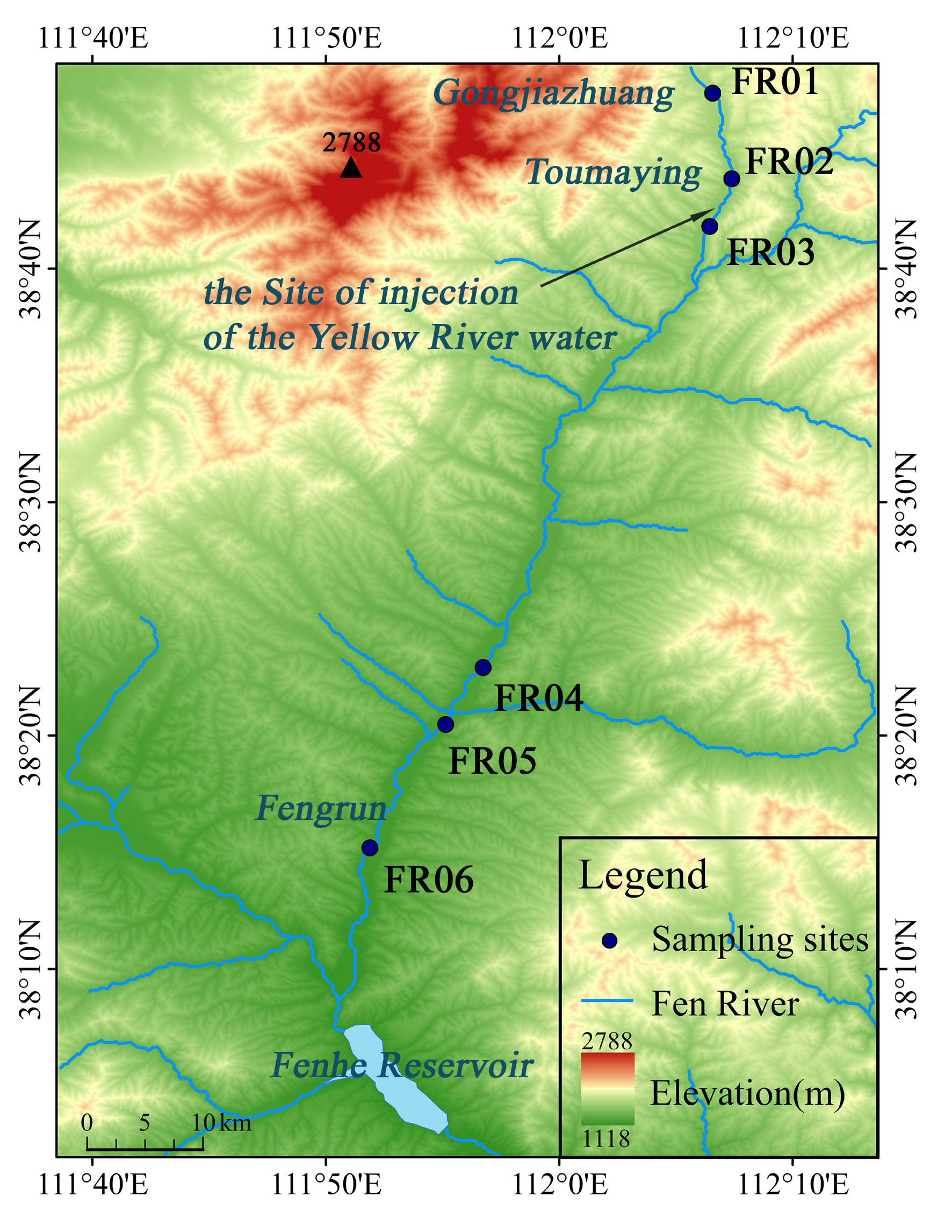
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Site
2.2. Sample Collection and Measurements
2.3. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
2.4. Illumina MiSeq Sequencing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Features of River Water and Sediment
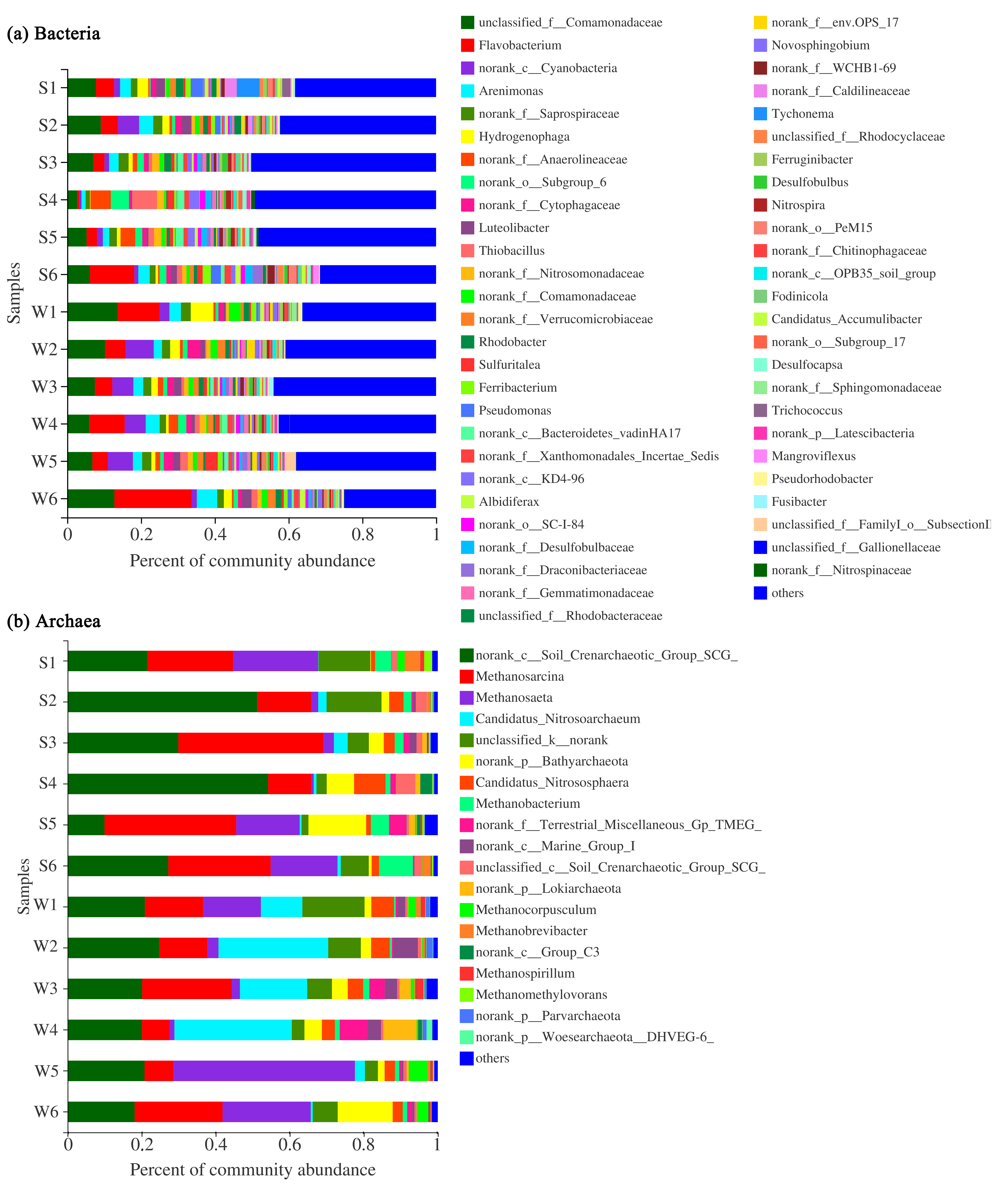
3.2. Overview of Bacterial and Archaeal Communities
3.3. Different Responses of Bacterial and Archaeal Core Floras to Water Diversion
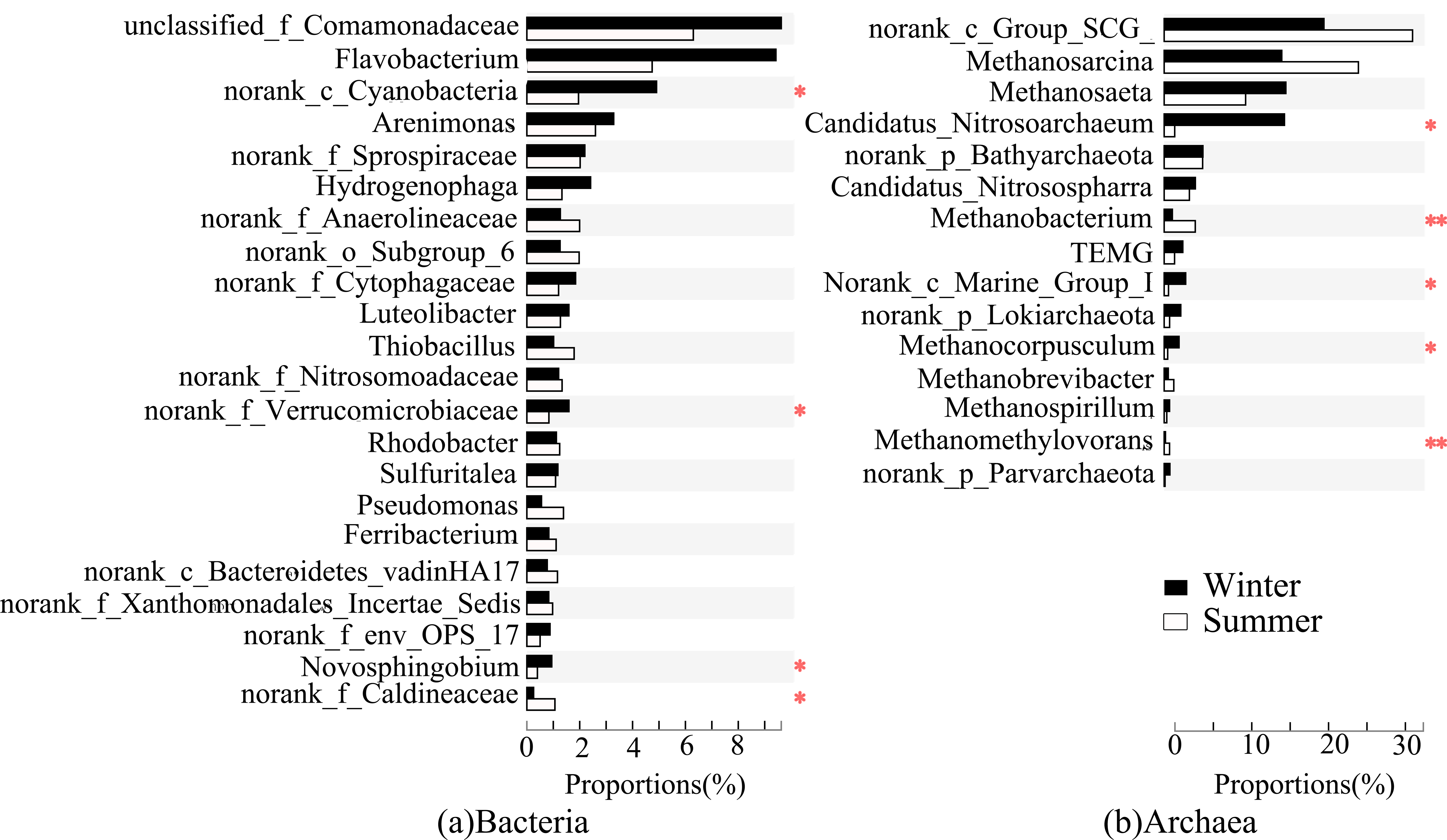
3.4. Different Responses of Bacterial and Archaeal Core Floras to Seasonal Variations
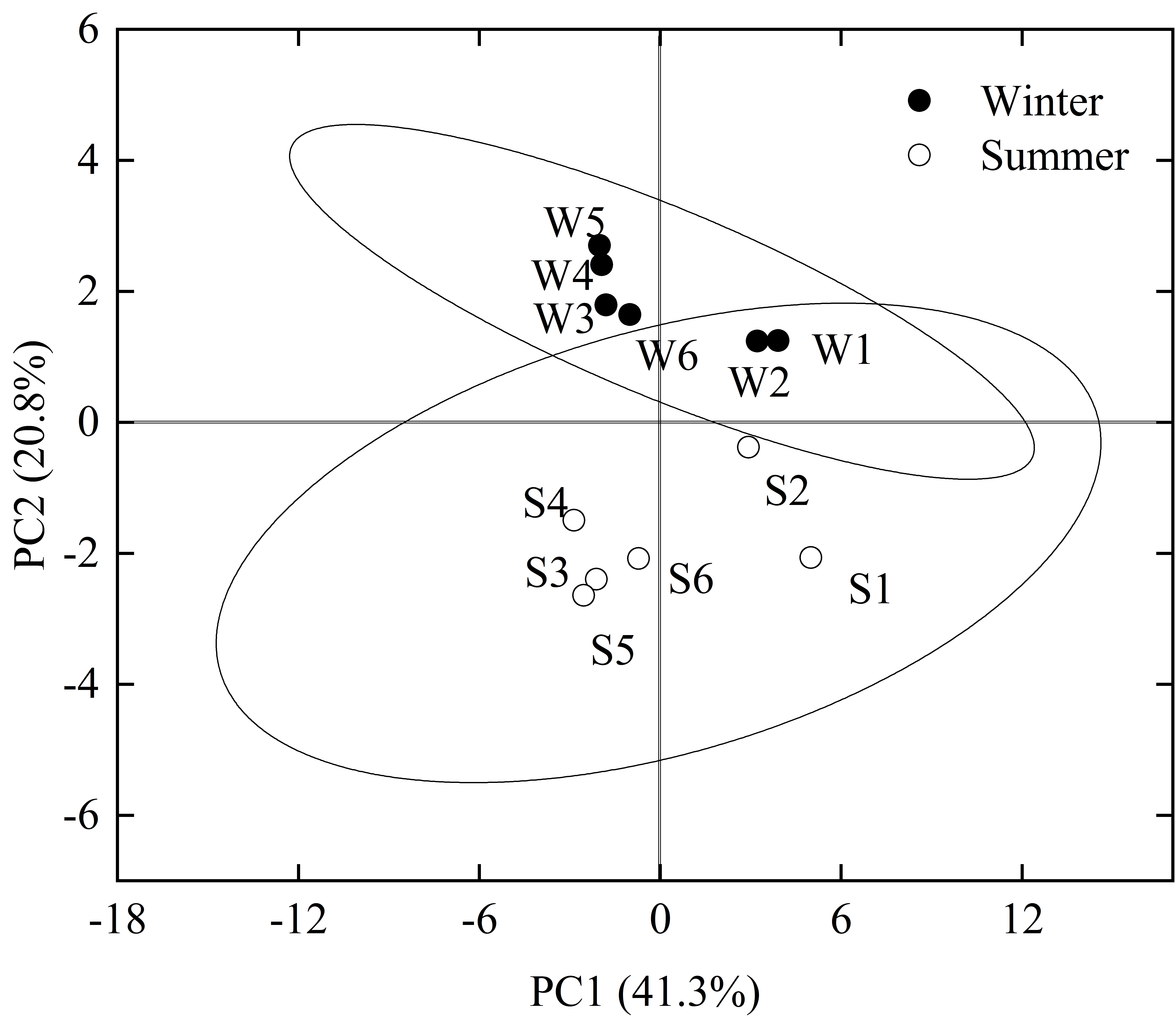
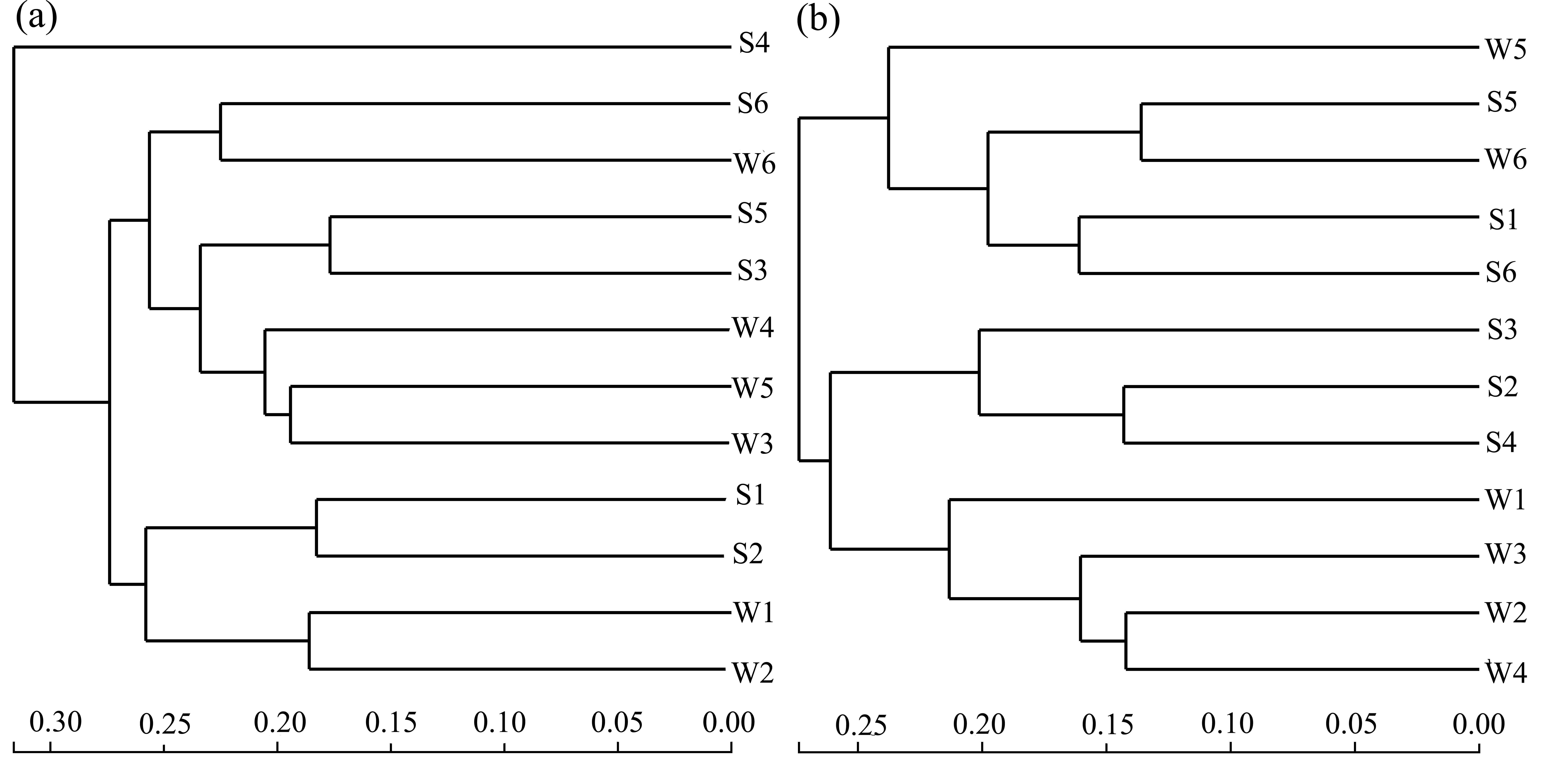
3.5. Differences in Changes of Microbial Diversity and Community Structure
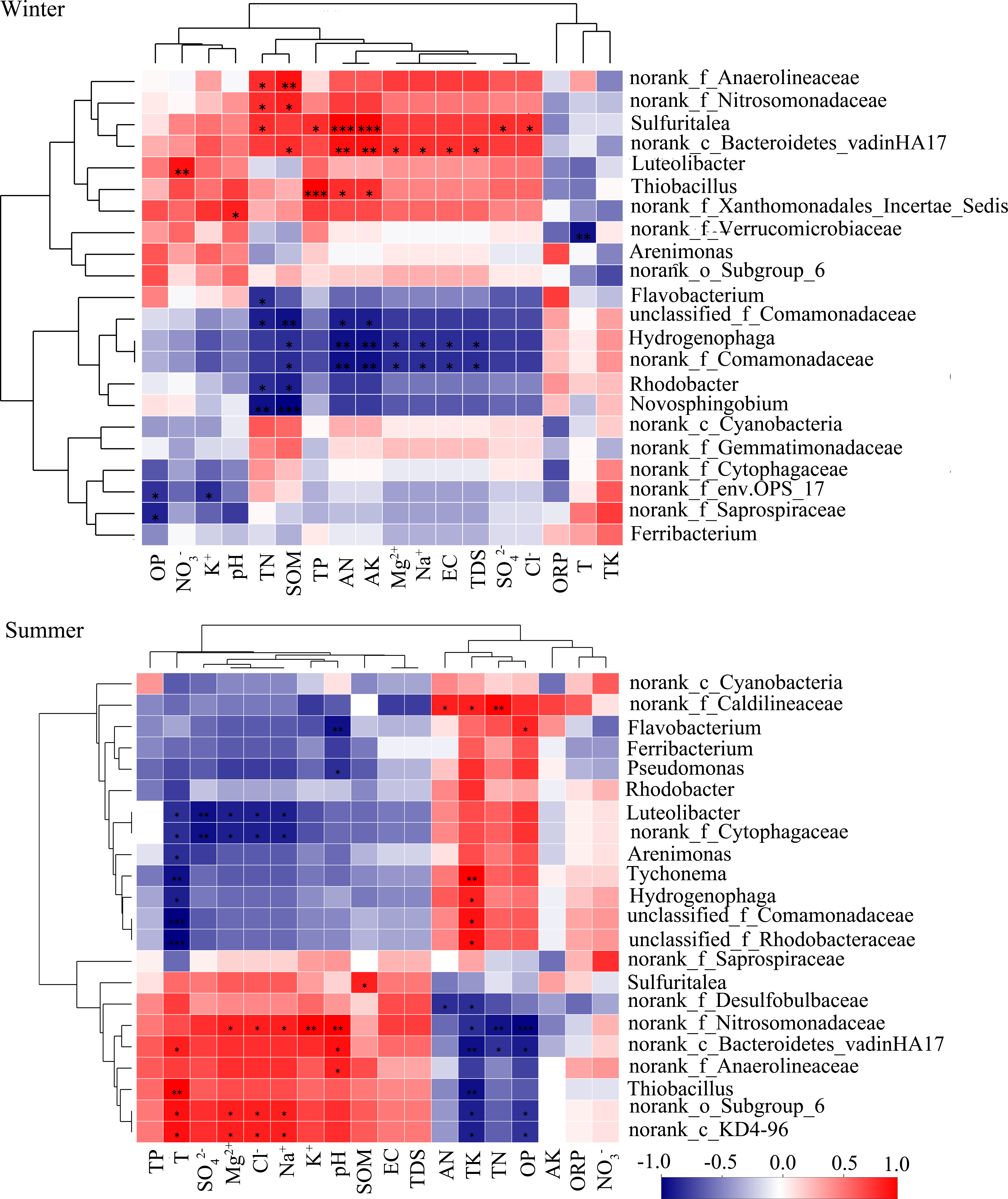
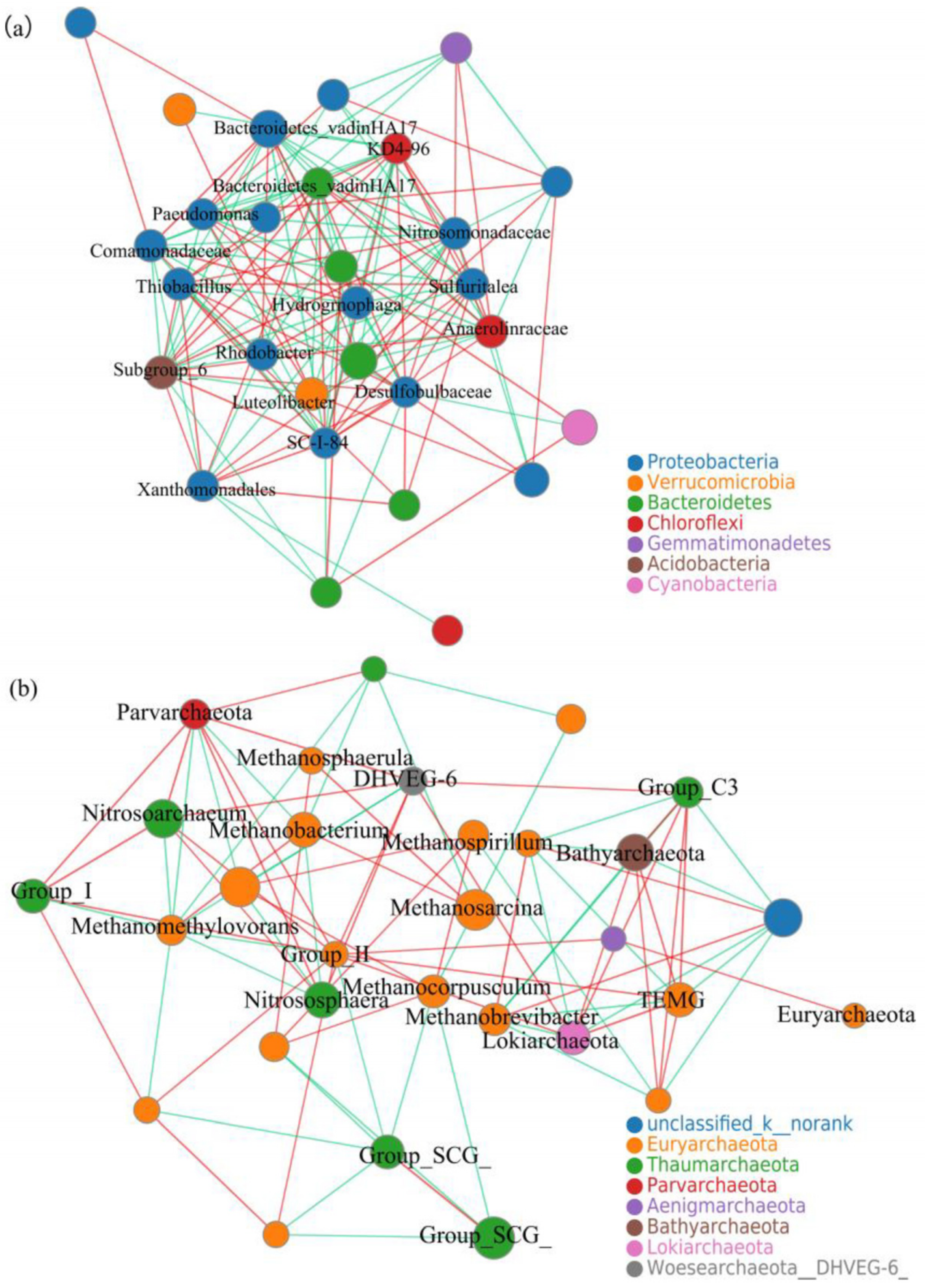
3.6. Microbial Interaction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flemming, H.; Wuertz, S. Bacteria and archaea on earth and their abundance in biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, M.O.; Thion, C.; Gubry-Rangin, C.; Prosser, J.I. Differential sensitivity of ammonia oxidising archaea and bacteria to matric and osmotic potential. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 129, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, W.; Dam, B. Biochemistry and molecular biology of lithotrophic sulfur oxidation by taxonomically and ecologically diverse bacteria and archaea. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 999–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Xia, C.; Xu, M.; Guo, J.; Sun, G.; Wang, A. Community structure and distribution of planktonic ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in the Dongjiang river, China. Res. Microbiol. 2014, 165, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wei, G.; Shi, W.; Sun, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Gao, Z. Distinct distribution patterns of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in sediment and water column of the yellow river estuary. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, Z.; He, Z. Diversity, abundance and community structure of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in riparian sediment of zhenjiang ancient canal. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 90, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsodi, A.K.; Anda, D.; Makk, J.; Krett, G.; Dobosy, P.; Büki, G.; Erőss, A.; Mádl-Szőnyi, J. Biofilm forming bacteria and archaea in thermal karst springs of gellért hill discharge area (Hungary). J. Basic Microb. 2018, 58, 928–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Maza-Márquez, P.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Vahala, R. Performance and microbial community structure of a polar arctic circle aerobic granular sludge system operating at low temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 256, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albright, M.B.N.; Timalsina, B.; Martiny, J.B.H.; Dunbar, J. Comparative genomics of nitrogen cycling pathways in bacteria and archaea. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 77, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, A.J. Polyamine function in archaea and bacteria. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 18693–18701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.; Liu, W.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, M.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Q.; Ni, J. Dominant role of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in nitrification due to ammonia accumulation in sediments of danjiangkou reservoir, china. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2018, 102, 3399–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Norton, J.M.; Stark, J.M.; Reeve, J.R.; Habteselassie, M.Y. Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria are more responsive than archaea to nitrogen source in an agricultural soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 96, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Li, M.; Hong, Y.; Gu, J. Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in polluted mangrove sediment. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 34, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, T.; Pan, G.; Crowley, D.; Li, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. Abundance, composition and activity of ammonia oxidizer and denitrifier communities in metal polluted rice paddies from south China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Wang, H.; Chen, F.; Fu, X.; Fang, X.; Sun, X.; Yu, G. Impacts of nitrogen and phosphorus additions on the abundance and community structure of ammonia oxidizers and denitrifying bacteria in chinese fir plantations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muema, E.K.; Cadisch, G.; Röhl, C.; Vanlauwe, B.; Rasche, F. Response of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea to biochemical quality of organic inputs combined with mineral nitrogen fertilizer in an arable soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 95, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A. Thermodynamic limits to microbial life at high salt concentrations. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1908–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, G.; Yang, X.; Wu, F.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X. Microbial community structure and diversity in cellar water by 16s rrna high-throughput sequencing. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 1704–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A. Bioenergetic aspects of halophilism. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1999, 63, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, A.; Gajaraj, S.; Hu, Z. Seasonal population changes of ammonia-oxidizing organisms and their relationship to water quality in a constructed wetland. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 40, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, A.; Horton, J.; Gajaraj, S.; McIntosh, S.; Miles, R.J.; Mueller, R.; Reed, R.; Hu, Z. Temporal and spatial distributions of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria and their ratio as an indicator of oligotrophic conditions in natural wetlands. Water Res. 2012, 46, 4121–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, B.; Vojvoda, J.; Reinthaler, T.; Reyes, C.; Pinto, M.; Herndl, G.J. Nitrosopumilus adriaticus sp. nov. and Nitrosopumilus piranensis sp. nov., Two ammonia-oxidizing archaea from the adriatic sea and members of the class Nitrososphaeria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 1892, 69, 1892–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Song, C.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Y. Shifts between ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in relation to nitrification potential across trophic gradients in two large chinese lakes (lake Taihu and lake Chaohu). Water Res. 2013, 47, 2285–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Dong, H.; Yu, B.; Lv, G.; Deng, S.; Berzins, N.; Dai, M. Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in Qinghai lake, northwestern China. Geomicrobiol. J. 2009, 26, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, W.; Gu, J.; Gu, J. Community structure and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria after conversion from soybean to rice paddy in albic soils of northeast China. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2014, 98, 2765–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gannes, V.; Eudoxie, G.; Dyer, D.H.; Hickey, W.J. Diversity and abundance of ammonia oxidizing archaea in tropical compost systems. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhao, D.; Luo, J.; Luo, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Huang, R.; Huang, R.; Guo, K.; Guo, K.; et al. The influence of land use on the abundance and diversity of ammonia oxidizers. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 70, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.; Tragin, M.; Lozano, J.; Ghiglione, J.; Vaulot, D.; Bouget, F.; Galand, P.E. Rhythmicity of coastal marine picoeukaryotes, bacteria and archaea despite irregular environmental perturbations. ISME J. 2019, 13, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, M.K.; Wong, C.K.; Chu, K.H.; Kwan, H.S. Community structure, dynamics and interactions of bacteria, archaea and fungi in subtropical coastal wetland sediments. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitschuler, C.; Hofmann, K.; Illmer, P. Abundances, diversity and seasonality of (non-extremophilic) archaea in alpine freshwaters. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2016, 109, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genderjahn, S.; Alawi, M.; Mangelsdorf, K.; Horn, F.; Wagner, D. Desiccation- and saline-tolerant bacteria and archaea in kalahari pan sediments. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasternak, Z.; Al-Ashhab, A.; Gatica, J.; Gafny, R.; Avraham, S.; Minz, D.; Gillor, O.; Jurkevitch, E. Spatial and temporal biogeography of soil microbial communities in arid and semiarid regions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Wu, F.; Yang, W.; Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Tan, B. Abundance and composition dynamics of soil ammonia-oxidizing archaea in an alpine fir forest on the eastern tibetan plateau of China. Can. J. Microbiol. 2012, 58, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, R.; Jin, W.; Han, S.; Zhou, X.; Wang, T.; Gao, S.; Wang, Q.; Chen, C.; Xie, G.; Wang, Q. Rapid enrichment and ammonia oxidation performance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea from an urban polluted river of China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Dong, R.M.; Dong, C.Z.; Huang, L.; Jiang, H.; Wei, Y.; Feng, L.; Liu, D.; Yang, G.; Zhang, C.; et al. Diversity of microbial plankton across the three gorges dam of the Yangtze river, China. Geosci. Front. 2012, 3, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, M.G.; Henry, R.; Maricatto, F.E. Spatial and temporal heterogeneity in the jurumirim reservoir, Sao Paulo, Brazil. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 1999, 4, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Li, B.; Cai, Q.; Han, Q.; Gu, Y.; Qu, Y. Phytoplankton functional groups in a high spatial heterogeneity subtropical reservoir in China. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Jia, C.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Yang, M.; Zhao, M.; Li, W.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q. Dynamics of bacterial community diversity and structure in the terminal reservoir of the south-to-north water diversion project in China. Water 2018, 10, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Wu, S.; Wu, X.; Lv, X.; Sivakumar, B.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Gao, A.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Impacts of a large river-to-lake water diversion project on lacustrine phytoplankton communities. J. Hydrol. 2020, 587, 124938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wu, S.; Dai, J.; Wu, X.; Xue, W.; Liu, F. Effects of short-term water diversion in summer on water quality and algae in gonghu bay, lake Taihu. J. Lake Sci. 2018, 30, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhao, M.; Liu, P.; Yang, M.; Jia, C.; Zhang, Q. Niche analysis of microbial community reveals the south-to-north water diversion impacts in miyun reservoir. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 170, 52037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, J.; Schulz, C.; Childers, G. Impact of freshwater diversion projects on diversity and activity of methanotrophic communities in freshwater wetlands. AGU Fall Meet. Abstr. 2009, 2009, B11A–B480A. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Jin, B.; Tang, L.; Tong, C. Temporal variation of nutrients fluxes across the sediment-water interface of shrimp ponds and influencing factors in the Jiulong river estuary. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- ZENG, M.F.D.S. The grain-size distribution of the suspended particulate matter in the huanghe estuary and its adjacent sea area in winter. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2011, 30, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akama, A. Balance sheet of nitrogen applied to japanese red pine (Pinus densiflora sieb. Et zucc.) Seedlings-a pot experiment. J. Jpn. For. Soc. 1986, 68, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.F.L.; Bain, D.C. A sodium hydroxide fusion method for the determination of total phosphate in soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan. 2008, 13, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otabbong, E.; Leinweber, P.; Schlichting, A.; Meissner, R.; Shenker, M.; Litaor, I.; Sapek, A.; Robinson, S.; Niedermeier, A.; Hacin, H.; et al. Comparison of ammonium lactate, sodium bicarbonate and double calcium lactate methods for extraction of phosphorus from wetland peat soils. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 2004, 54, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaitanya, T.; Padmaja, G.; Rao, P.C. Improving the efficiency of ammonium acetate extraction of soil potassium by saturation extract method. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2020, 26, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.M.; Jenkinson, D.S. Determination of organic carbon in soil: I. Oxidation by dichromate of organic matter in soil and plant materials. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 11, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Tan, G.; Wang, H.; Gai, X. Effect of biochar additions to soil on nitrogen leaching, microbial biomass and bacterial community structure. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2016, 74, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Si, D.; Chen, Q. Evolution of microbial community along with increasing solid concentration during high-solids anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the miseq illumina sequencing platform. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one fastq preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoc, T.; Salzberg, S.L. Flash: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Uparse: Highly accurate otu sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. Qiime allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.; Rhoads, W.J.; Edwards, M.A.; Pruden, A. Impact of water heater temperature setting and water use frequency on the building plumbing microbiome. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1318–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Joseph, S.D.; Ji, M.; Nielsen, S.; Mitchell, D.R.G.; Donne, S.; Horvat, J.; Wang, J.; Munroe, P.; Thomas, T. Chemolithotrophic processes in the bacterial communities on the surface of mineral-enriched biochars. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1087–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boix-Amorós, A.; Collado, M.C.; Mira, A. Relationship between milk microbiota, bacterial load, macronutrients, and human cells during lactation. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mar, J.S.; LaMere, B.J.; Lin, D.L.; Levan, S.; Nazareth, M.; Mahadevan, U.; Lynch, S.V. Disease severity and immune activity relate to distinct interkingdom gut microbiome states in ethnically distinct ulcerative colitis patients. mBio 2016, 7, e1016–e1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Teh, B.; Sun, C.; Hu, S.; Lu, X.; Boland, W.; Shao, Y. Biodiversity and activity of the gut microbiota across the life history of the insect herbivore spodoptera littoralis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramayo-Caldas, Y.; Mach, N.; Lepage, P.; Levenez, F.; Denis, C.; Lemonnier, G.; Leplat, J.; Billon, Y.; Berri, M.; Doré, J.; et al. Phylogenetic network analysis applied to pig gut microbiota identifies an ecosystem structure linked with growth traits. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2973–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comte, J.; Jacquet, S.; Viboud, S.; Fontvieille, D.; Millery, A.; Paolini, G.; Domaizon, I. Microbial community structure and dynamics in the largest natural french lake (lake Bourget). Microb. Ecol. 2006, 52, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, D.B.; Brunelle, B.W.; Trachsel, J.; Allen, H.K. Meta-analysis to define a core microbiota in the swine gut. mSystems 2017, 2, e4–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudi, K.; Angell, I.L.; Pope, P.B.; Vik, J.O.; Sandve, S.R.; Snipen, L. Stable core gut microbiota across the freshwater-to-saltwater transition for farmed atlantic salmon. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2018, 84, e1917–e1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Yan, J.; Zuo, B.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Cui, Z. Full-scale of composting process of biogas residues from corn stover anaerobic digestion: Physical-chemical, biology parameters and maturity indexes during whole process. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Li, Z.; Hou, X.; Jin, C. The performance and microbial community identification in mesophilic and atmospheric anaerobic membrane bioreactor for municipal wastewater treatment associated with different hydraulic retention times. Water 2019, 11, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, C.; Deng, Y. Effect of potassium on nitrate removal from groundwater in agricultural waste-based heterotrophic denitrification system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jiang, B.; Kong, Z.; Yang, C.; Li, L.; Feng, B.; Luo, Z.; Xu, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Li, Y. Improved stability of up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor treating starch wastewater by pre-acidification: Impact on microbial community and metabolic dynamics. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 326, 124781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, D.B.; Vesth, T.C.; Hallin, P.F.; Pedersen, A.G.; Ussery, D.W. Bayesian prediction of bacterial growth temperature range based on genome sequences. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Jiao, Y.; Lee, D. A lab-scale anoxic/oxic-bioelectrochemical reactor for leachate treatments. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 186, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Jiang, T.; Zeng, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, B. Oxygen availability affects the synthesis of quorum sensing signal in the facultative anaerobe Novosphingobium pentaromativorans us6-1. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2021, 105, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.K.; Jung, M.Y.; Yu, D.S.; Park, S.J.; Oh, T.K.; Rhee, S.K.; Kim, J.F. Genome sequence of an ammonia-oxidizing soil archaeon, “Candidatus Nitrosoarchaeum koreensis” my1. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 5539–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, I.S.; Alves, A.; Tacão, M.; Almeida, A.; Cunha, Â.; Correia, A. Seasonal and spatial variability of free-living bacterial community composition along an estuarine gradient (Ria de Aveiro, Portugal). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 68, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laque, T.; Farjalla, V.F.; Rosado, A.S.; Esteves, F.A. Spatiotemporal variation of bacterial community composition and possible controlling factors in tropical shallow lagoons. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 59, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.; Kim, J.; Lee, T.; Oh, Y.; Nguyen, V.K.; Cho, S. Correlation of microbial community with salinity and nitrogen removal in an anammox-based denitrification system. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puyol, D.; Batstone, D.J.; Hülsen, T.; Astals, S.; Peces, M.; Krömer, J.O. Resource recovery from wastewater by biological technologies: Opportunities, challenges, and prospects. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Qiu, S.; Li, B.; Peng, Y. Detection of nitrifiers and evaluation of partial nitrification for wastewater treatment: A review. Chemosphere 2015, 140, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.; Amin, S.A.; Martens-Habbena, W.; Walker, C.B.; Urakawa, H.; Devol, A.H.; Ingalls, A.E.; Moffett, J.W.; Armbrust, E.V.; Stahl, D.A. Marine ammonia-oxidizing archaeal isolates display obligate mixotrophy and wide ecotypic variation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12504–12509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Bu, F.; Zhu, W.; Luo, G.; Xie, L. Microbial consortiums of hydrogenotrophic methanogenic mixed cultures in lab-scale ex-situ biogas upgrading systems under different conditions of temperature, PH and CO. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Jiao, N.; Zhang, R.; Yang, Z. Niche partitioning of marine group i crenarchaeota in the euphotic and upper mesopelagic zones of the east China sea. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2011, 77, 7469–7478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chang, Y.; Chen, Q. Community structure analysis of archaea and bacteria in sediments of liaohe estuary (in China). Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołębiewski, M.; Całkiewicz, J.; Creer, S.; Piwosz, K. Tideless estuaries in brackish seas as possible freshwater-marine transition zones for bacteria: The case study of the vistula river estuary. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2017, 9, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korlević, M.; Šupraha, L.; Ljubešić, Z.; Henderiks, J.; Ciglenečki, I.; Dautović, J.; Orlić, S. Bacterial diversity across a highly stratified ecosystem: A salt-wedge mediterranean estuary. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 39, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Liang, Q.; Niu, M.; Yu, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F. The diversity and richness of archaea in the northern continental slope of south China sea. Microbiol. China 2017, 44, 1589–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, L.A.; Baker, B.J.; Anantharaman, K.; Brown, C.T.; Probst, A.J.; Castelle, C.J.; Butterfield, C.N.; Hernsdorf, A.W.; Amano, Y.; Ise, K.; et al. A new view of the tree of life. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, K.G.; May, M.K.; Kevorkian, R.T.; Steen, A.D. Meta-analysis of quantification methods shows that archaea and bacteria have similar abundances in the subseafloor. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2013, 79, 7790–7799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievert, S.M.; Ziebis, W.; Kuever, J.; Sahm, K. Relative abundance of archaea and bacteria along a thermal gradient of a shallow-water hydrothermal vent quantified by rrna slot-blot hybridization. Microbiology 2000, 146, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelle, C.J.; Hug, L.A.; Wrighton, K.C.; Thomas, B.C.; Williams, K.H.; Wu, D.; Tringe, S.G.; Singer, S.W.; Eisen, J.A.; Banfield, J.F. Extraordinary phylogenetic diversity and metabolic versatility in aquifer sediment. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, C.; Dollive, S.; Grunberg, S.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Wu, G.D.; Lewis, J.D.; Bushman, F.D. Archaea and fungi of the human gut microbiome: Correlations with diet and bacterial residents. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Wen, H.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, G. Comparison of archaeal community composition between qinghai lake and other salt lakes in china. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2017, 57, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Guo, Y.; Wu, S.; Chen, L.; Tao, H.; Liu, S. Metabolomics uncovers the regulatory pathway of acyl-homoserine lactones based quorum sensing in anammox consortia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2206–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, C.M.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing: Cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005, 21, 319–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarova, K.S.; Wolf, Y.I.; Karamycheva, S.; Zhang, D.; Aravind, L.; Koonin, E.V. Antimicrobial peptides, polymorphic toxins, and self-nonself recognition systems in archaea: An untapped armory for intermicrobial conflicts. mBio 2019, 10, e715–e719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, A.; Kumar, M. Computational exploration of putative luxr solos in archaea and their functional implications in quorum sensing. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorob’Eva, L.I.; Khodzhaev, E.; Novikova, T.M.; Chudinova, E.M. Antistress cross-effects of extracellular metabolites of bacteria, archaea, and yeasts: A review. Prikl. Biokhim. Mikrobiol. 2013, 49, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| January | June | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal River Reach | Water-Receiving Reach | Normal River Reach | Water-Receiving Reach | ||
| Water | T (°C) | 1.4 ± 1.0 | 1.2 ± 0.5 | 19.6 ± 0.1 * | 21.9 ± 0.6 * |
| EC (μs/cm) | 535.0 ± 28.0 ** | 1257.0 ± 27.0 ** | 436.0 ± 34.0 ** | 1205.0 ± 32.0 ** | |
| ORP (mv) | 410.0 ± 55.2 | 366.0 ± 15.0 | 209.4 ± 26.3 | 199.2 ± 22.5 | |
| TDS (g/L) | 0.3 ± 0.0 ** | 0.8 ± 0.0 ** | 0.3 ± 0.2 ** | 0.8 ± 0.0 ** | |
| NO3− (mg/L) | 12.0 ± 1.7 * | 19.7 ± 0.5 * | 12.4 ± 2.6 | 11.4 ± 1.7 | |
| SO42− (mg/L) | 70.1 ± 6.7** | 205.5 ± 3.7 ** | 121.6 ± 0.9 * | 400.9 ± 116.3 * | |
| Cl− (mg/L) | 6.6 ± 0.8 ** | 132.3 ± 3.8 ** | 7.0 ± 0.4 ** | 150.9 ± 67.6 ** | |
| Na+ (mg/L) | 6.7 ± 0.6 ** | 121.1 ± 3.8 ** | 8.4 ± 1.2 ** | 152.2 ± 3.9 ** | |
| K+ (mg/L) | 1.8 ± 0.0 | 3.9 ± 0.0 | 2.4 ± 0.3 | 4.9 ± 0.6 | |
| Mg2+ (mg/L) | 15.5 ± 0.7 ** | 37.0 ± 0.6 ** | 16.8 ± 1.5 * | 41.0 ± 0.6 * | |
| Ca2+ (mg/L) | 63.7 ± 0.2 | 67.6 ± 1.6 | 76.3 ± 7.0 | 65.2 ± 3.7 | |
| Sediment | PS (μm) | 105.0 ± 33.0 | 53.0 ± 18.0 | 247.0 ± 147.0 | 116.0 ± 61.0 |
| pH | 7.8 ± 0.0 | 8.1 ± 0.2 | 8.4 ± 0.4 | 8.9 ± 0.1 | |
| SOM (g/kg) | 14.7 ± 1.9 | 23.2 ± 8.3 | 11.9 ± 3.7 | 16.0 ± 4.2 | |
| TN (g/kg) | 4.4 ± 0.0 | 8.3 ± 0.1 | 11.3 ± 0.0 * | 6.4 ± 0.0 * | |
| AN (mg/kg) | 33.0 ± 2.0 * | 84.3 ± 23.1 * | 160.0 ± 29.0 * | 73.0 ± 8.5 * | |
| TP (mg/kg) | 464.5 ± 36.5 | 578.5 ± 45.3 | 530.0 ± 50.0 | 589.3 ± 44.4 | |
| OP (mg/kg) | 5.5 ± 0.5 | 10. 3 ± 3.9 | 17.0 ± 4.0 | 7.8 ± 1.8 | |
| TK (g/kg) | 28.3 ± 0.0 | 27.0 ± 0.2 | 28.2 ± 0.2 | 23.5 ± 0.1 | |
| AK (mg/kg) | 48.5 ± 6.5 * | 109.8 ± 24.3 * | 69.0 ± 1.0 | 78.0 ± 15.5 | |
| Sample | Season | OTUs | Shannon Index | Chao Index | Coverage Index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | Archaea | Bacteria | Archaea | Bacteria | Archaea | Bacteria | Archaea | ||
| FR01 | Winter | 2822 | 590 | 6.06 | 3.56 | 3768.44 | 733.13 | 0.98 | 0.99 |
| Summer | 2149 | 504 | 5.94 | 3.32 | 2859.82 | 602.89 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| FR02 | Winter | 3146 | 512 | 6.51 | 3.10 | 4103.01 | 610.25 | 0.98 | 0.99 |
| Summer | 2884 | 456 | 6.42 | 3.17 | 3857.02 | 619.43 | 0.98 | 0.99 | |
| FR03 | Winter | 3631 | 582 | 6.76 | 3.26 | 4722.66 | 789.59 | 0.97 | 0.99 |
| Summer | 3549 | 392 | 6.86 | 2.95 | 4470.78 | 553.25 | 0.98 | 0.99 | |
| FR04 | Winter | 3659 | 363 | 6.77 | 3.08 | 4717.44 | 462.13 | 0.98 | 0.99 |
| Summer | 3602 | 237 | 6.92 | 3.03 | 4479.15 | 326.44 | 0.98 | 0.99 | |
| FR05 | Winter | 3441 | 288 | 6.51 | 2.42 | 4513.04 | 380.57 | 0.98 | 0.99 |
| Summer | 3737 | 298 | 7.01 | 2.94 | 4746.85 | 385.15 | 0.98 | 0.99 | |
| FR06 | Winter | 2708 | 335 | 5.79 | 2.89 | 4044.36 | 450.93 | 0.98 | 0.99 |
| Summer | 2303 | 348 | 5.76 | 3.06 | 3261.68 | 461.56 | 0.98 | 0.99 | |
| Average | Winter | 3234.5 | 445 | 6.40 | 3.05 | 4311.49 | 580.51 | 0.98 | 0.99 |
| Summer | 3037.3 | 372.5 | 6.48 | 3.08 | 3945.88 | 491.45 | 0.98 | 0.99 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, J.; Niu, Y.; Yuan, R.; Wang, S. Different Responses of Bacterial and Archaeal Communities in River Sediments to Water Diversion and Seasonal Changes. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040782
Lv J, Niu Y, Yuan R, Wang S. Different Responses of Bacterial and Archaeal Communities in River Sediments to Water Diversion and Seasonal Changes. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(4):782. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040782
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Jiali, Yangdan Niu, Ruiqiang Yuan, and Shiqin Wang. 2021. "Different Responses of Bacterial and Archaeal Communities in River Sediments to Water Diversion and Seasonal Changes" Microorganisms 9, no. 4: 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040782
APA StyleLv, J., Niu, Y., Yuan, R., & Wang, S. (2021). Different Responses of Bacterial and Archaeal Communities in River Sediments to Water Diversion and Seasonal Changes. Microorganisms, 9(4), 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040782








