Functional Metabolic Diversity of Bacterioplankton in Maritime Antarctic Lakes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. FAPROTAX Analisys, Functional Prediction, and Metabolic Indices
2.3. Community Level Physiological Profiling
- ni: average qualitative color value of the three wells,
- c: average qualitative color value of control wells.
2.4. Clustering and Multivariate Ordination Analyses
2.5. Co-Occurrence Network Analysis
3. Results
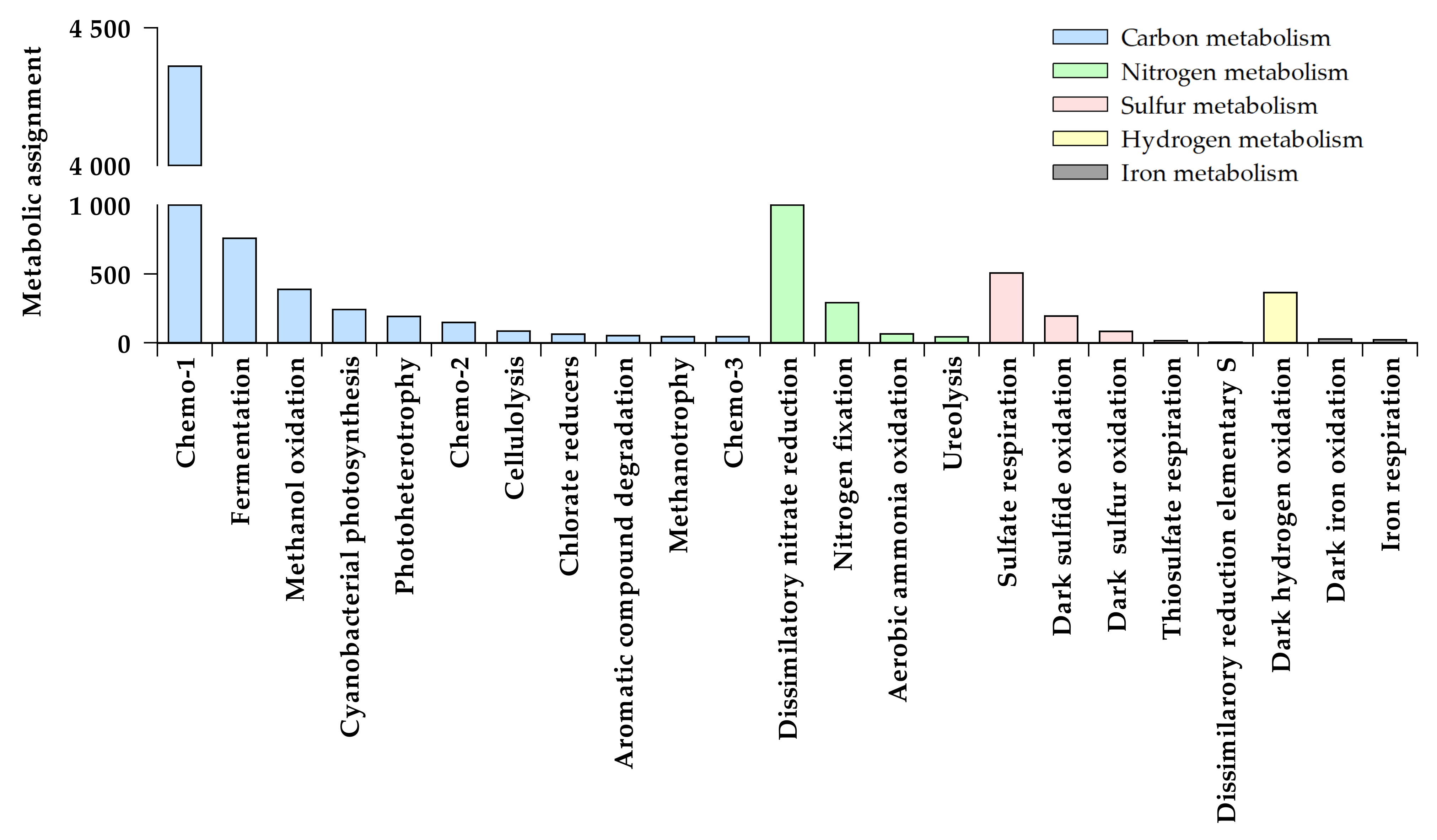
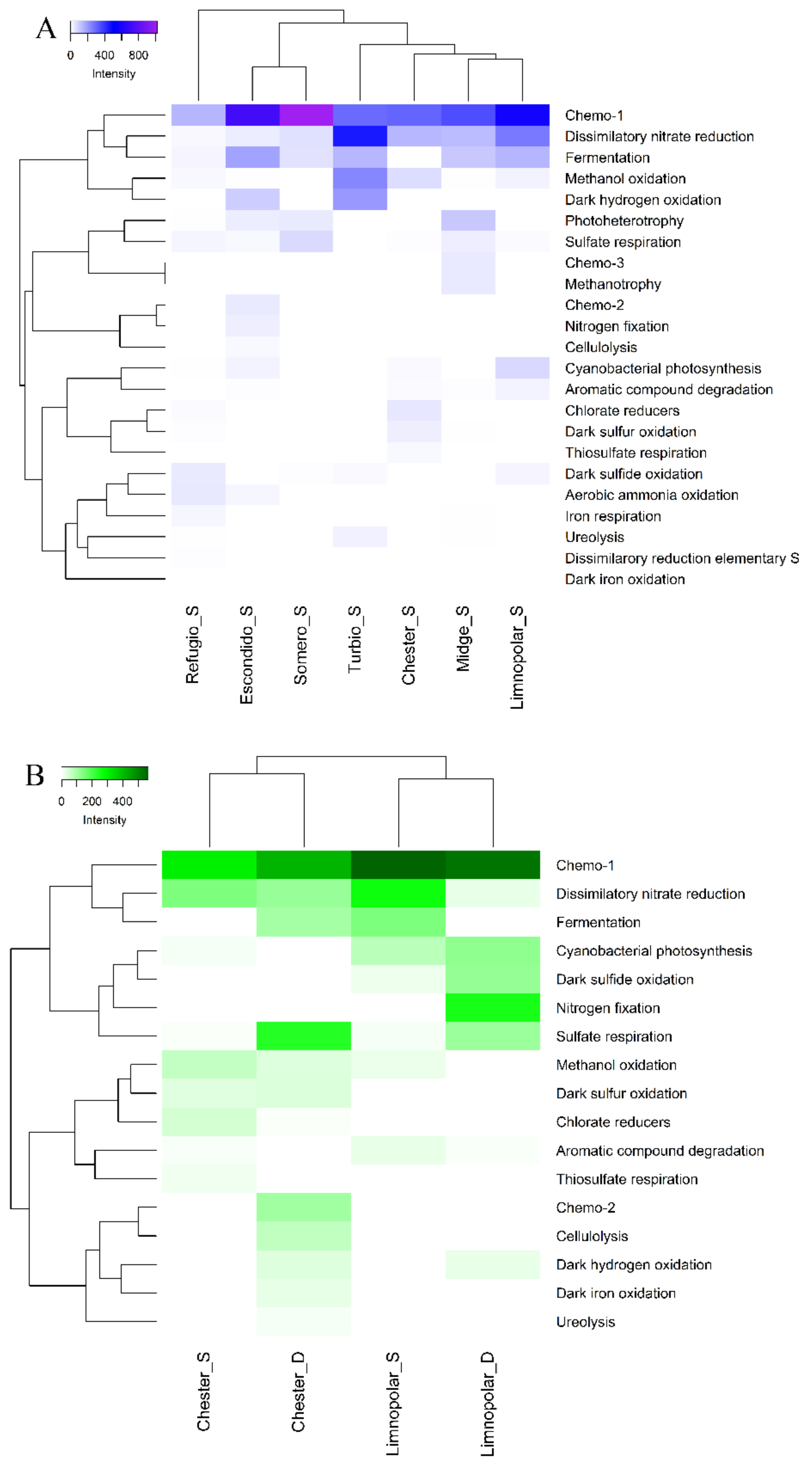
3.1. Functional Structure of Bacterioplankton Communities
3.1.1. Heterotrophic Metabolisms
3.1.2. Autotrophic Metabolisms
3.1.3. Other Respiratory Metabolisms
3.1.4. Assimilation of Nitrogen Compounds
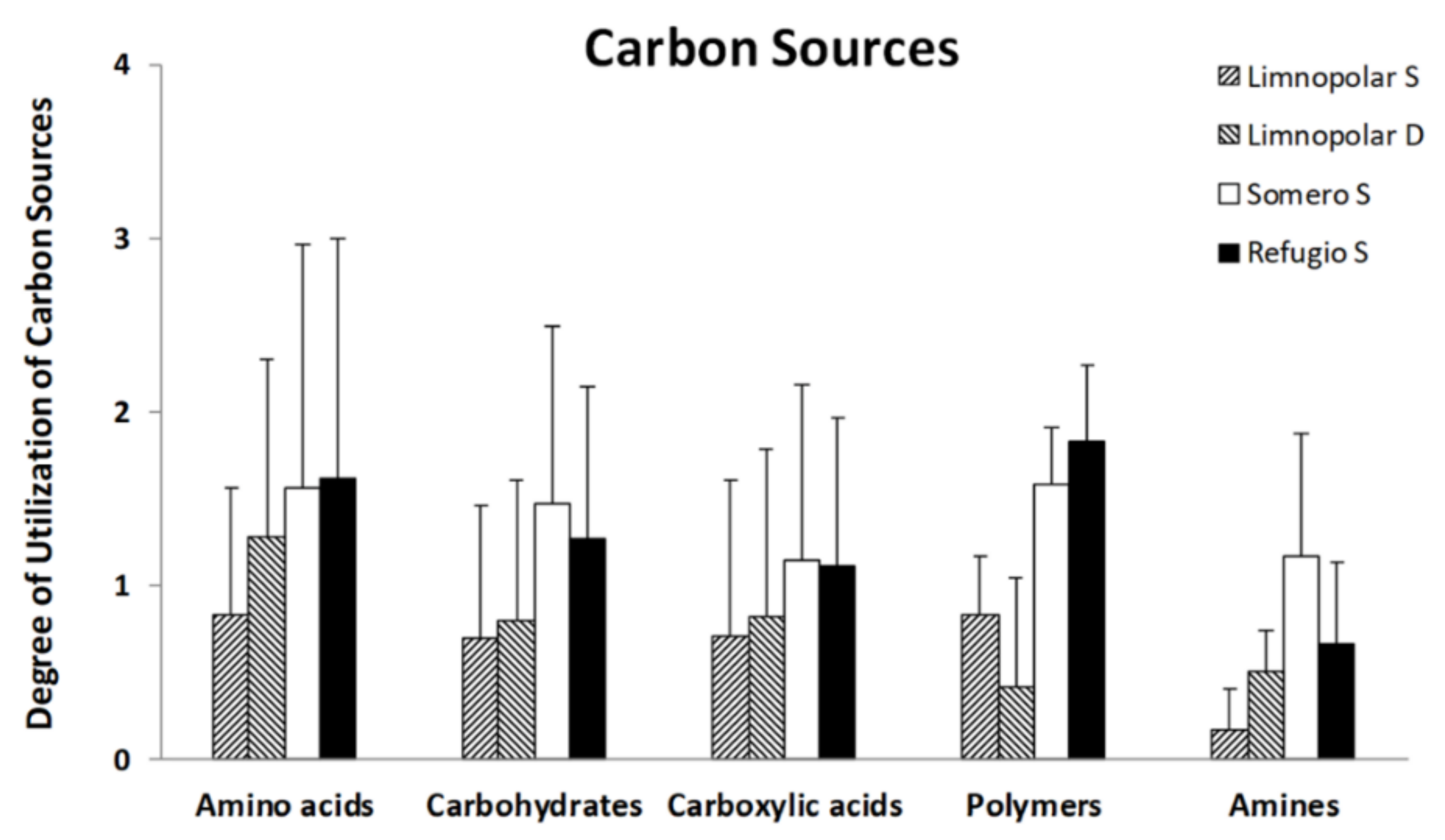
3.2. Carbon-Substrate Utilization Profiles
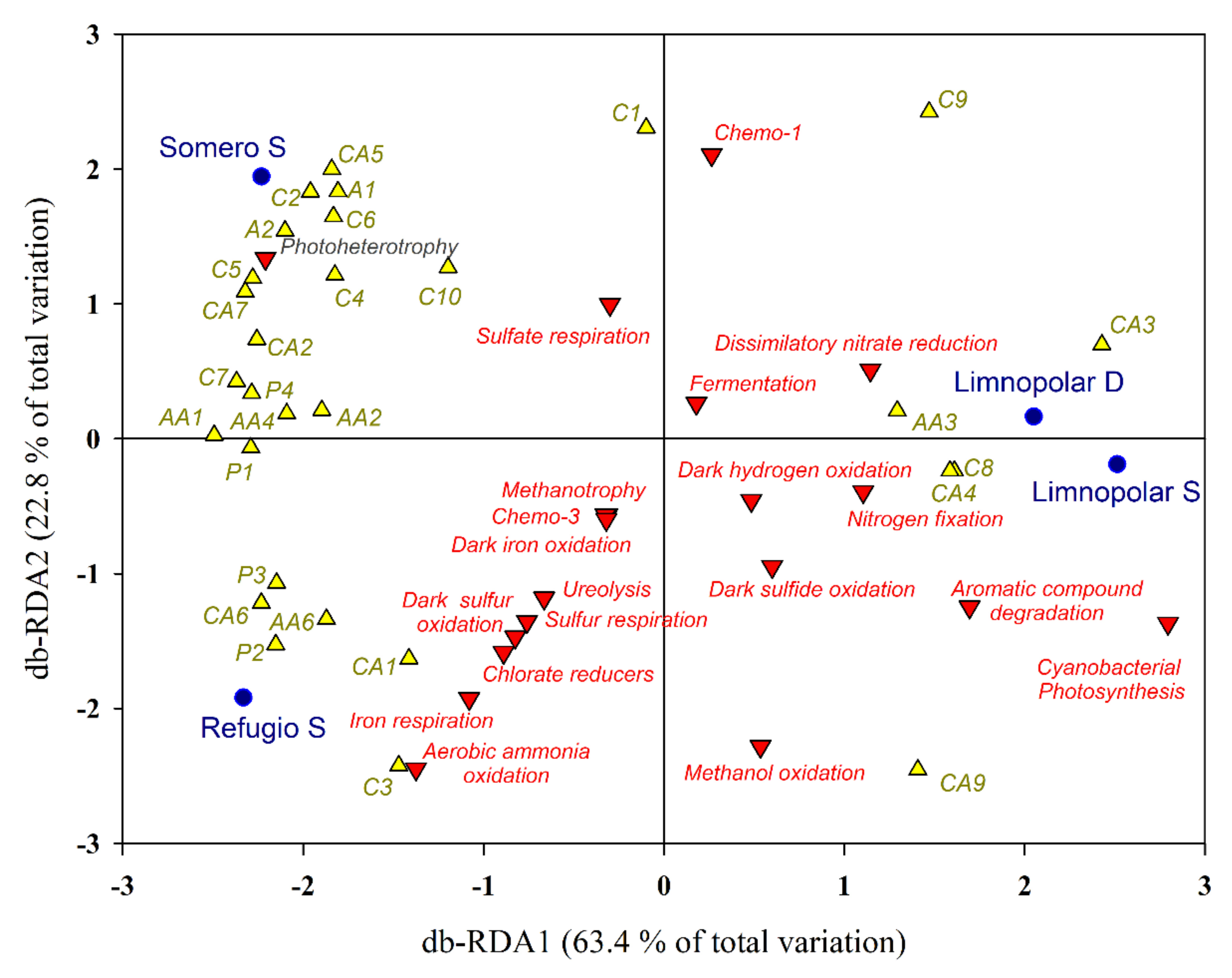
3.3. Statistical Analyses and Diversity Parameters
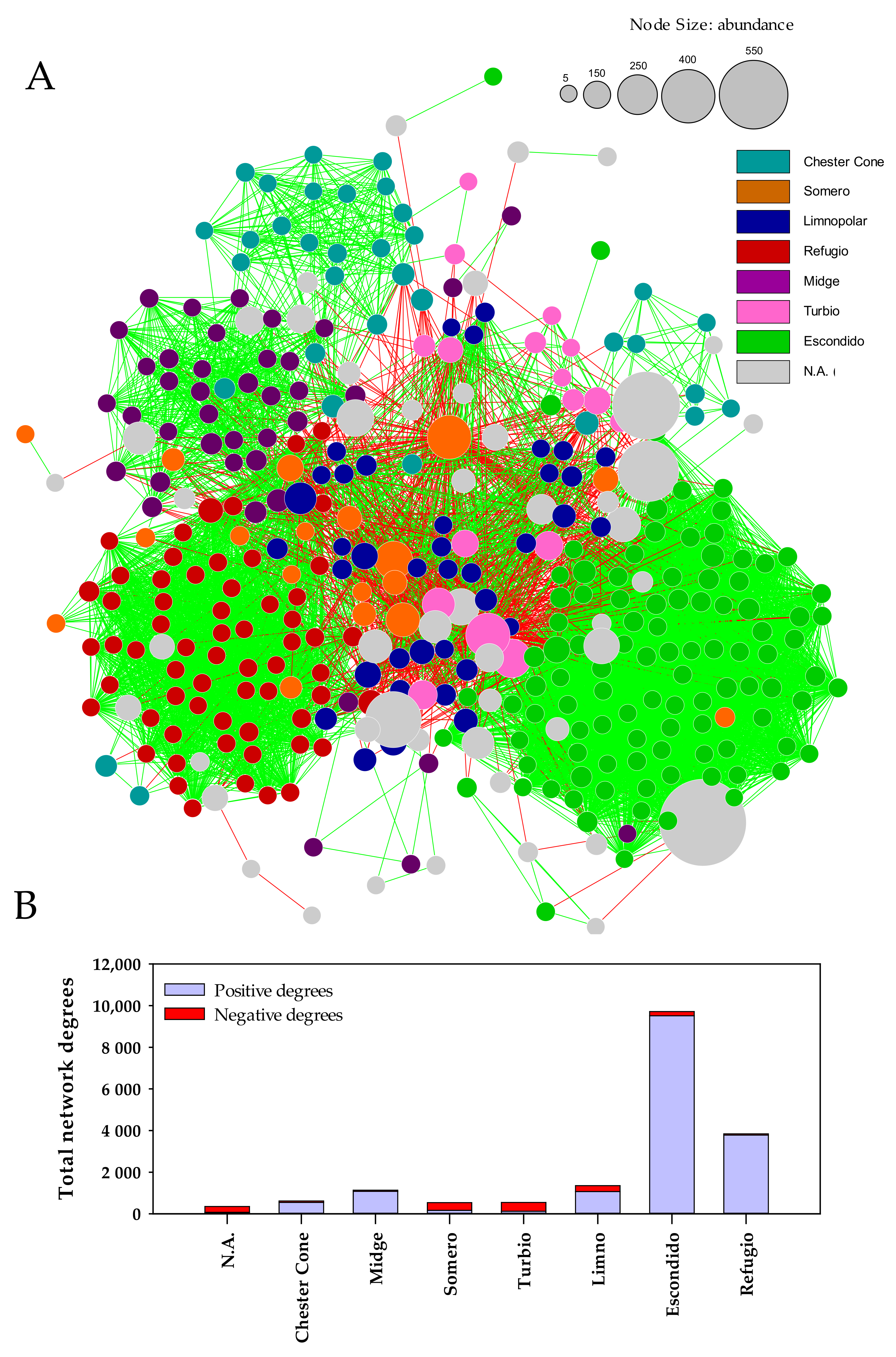
3.4. Co-Occurrence Network of Bacterioplankton Communities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pearce, D.; Van Der Gast, C.; Lawley, B.; Ellis-Evans, J. Bacterioplankton community diversity in a maritime Antarctic lake, determined by culture-dependent and culture-independent techniques. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2003, 45, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reche, I.; Pulido, E.; Baquero, R.M.; Casamayor, E.O. Does ecosystem size determine aquatic bacterial richness? Ecology 2005, 86, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiaffino, M.R.; Unrein, F.; Gasol, J.M.; Farias, M.E.; Estevez, C.; Balagué, V.; Izaguirre, I. Comparative analysis of bacterioplankton assemblages from maritime Antarctic freshwater lakes with contrasting trophic status. Polar Biol. 2009, 32, 923–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picazo, A.; Rochera, C.; Villaescusa, J.A.; Miralles-Lorenzo, J.; Velázquez, D.; Quesada, A.; Camacho, A. Bacterioplankton community composition along environmental gradients in lakes from Byers Peninsula (Maritime Antarctica) as determined by next-generation sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochera, C.; Camacho, A. Limnology and aquatic microbial ecology of Byers Peninsula: A Main freshwater biodiversity hotspot in Maritime Antarctica. Diversity 2019, 11, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis-Evans, J.C. Microbial diversity and function in Antarctic freshwater ecosystems. Biodivers. Conserv. 1996, 5, 1395–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laybourn-Parry, J.; Quayle, W.C.; Henshaw, T.; Ruddell, A.; Marchant, H.J. Life on the edge: The plankton and chemistry of Beaver Lake, an ultra-oligotrophic epishelf lake, Antarctica. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laybourn-Parry, J. Survival mechanisms in Antarctic lakes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2002, 357, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laybourn-Parry, J. No place too cold. Science 2009, 324, 1521–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaud, L.; Caruso, C.; Mangano, S.; Interdonato, F.; Bruni, V.; Giudice, A.L. Predominance of Flavobacterium, Pseudomonas, and Polaromonas within the prokaryotic community of freshwater shallow lakes in the northern Victoria Land, East Antarctica. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 82, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, A. Planktonic microbial assemblages and the potential effects of metazooplankton predation on the food web of lakes from the maritime Antarctica and sub-Antarctic islands. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2006, 5, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loreau, M.; Naeem, S.; Inchausti, P.; Bengtsson, J.; Grime, J.P.; Hector, A.; Hooper, D.U.; Raffaelli, D.; Schmid, B.; Tilman, D.; et al. Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: Current knowledge and future challenges. Science 2001, 294, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, B.J.; Srivastava, D.S.; Duffy, J.E.; Wright, J.P.; Downing, A.L.; Sankaran, M.; Jouseau, C. Effects of biodiversity on the functioning of trophic groups and ecosystems. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 443, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louca, S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Doebeli, M. Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science 2016, 353, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louca, S.; Jacques, S.M.; Pires, A.P.F.; Leal, J.S.; Srivastava, D.S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Farjalla, V.; Doebeli, M. High taxonomic variability despite stable functional structure across microbial communities. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G. PIC-RUSt2: An improved and customizable approach for metagenome inference. bioRxiv 2020, 672295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aßhauer, K.P.; Wemheuer, B.; Daniel, R.; Meinicke, P. Tax4Fun: Predicting functional profiles from metagenomic 16S rRNA data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2882–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, T.; Larson, J.; Meulemans, J.; Hillmann, B.; Lynch, J.; Sidiropoulos, D.; Spear, J.R.; Caporaso, G.; Blekhman, R.; Knight, R.; et al. BugBase predicts organism-level microbiome phenotypes. bioRxiv 2017, 133462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberán, A.; Velazquez, H.C.; Jones, S.; Fierer, N. Hiding in plain sight: Mining bacterial species records for phenotypic trait information. mSphere 2017, 2, e00237-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galand, P.E.; Pereira, O.; Hochart, C.; Auguet, J.C.; Debroas, D. A strong link between marine microbial community composition and function challenges the idea of functional redundancy. ISME J. 2018, 12, 2470–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Xia, P.; Song, X.; Lin, T.; Cao, H. Community structure and functional diversity of epiphytic bacteria and planktonic bacteria on submerged macrophytes in Caohai Lake, southwest of China. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jiang, H.; Sun, X.; Huang, J.; Han, M.; Wang, B. Distinct co-occurrence patterns of prokaryotic community between the waters and sediments in lakes with different salinity. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 97, fiaa234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garland, J.L.; Mills, A.L. Classification and characterization of heterotrophic microbial communities on the basis of patterns of community-level sole-carbon-source utilization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1991, 57, 2351–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Ge, Z.; Poudel, D.R. Application and optimization of Biolog EcoPlates in functional diversity studies of soil microbial communities. MATEC Web Conf. 2015, 22, 04015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chróst, R.J.; Münster, U.; Rai, H.; Albrecht, D.; Witzel, P.K.; Overbeck, J. Photosynthetic production and exoenzymatic degradation of organic matter in the euphotic zone of a eutrophic lake. J. Plankton Res. 1989, 11, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jãrgensen, N.O.; Jensen, R.E.; Jørgensen, N.O. Microbial fluxes of free monosaccharides and total carbohydrates in freshwater determined by PAD-HPLC. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1994, 14, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.-H.; Dobbs, F.C. Comparison of two kinds of Biolog microplates (GN and ECO) in their ability to distinguish among aquatic microbial communities. J. Microbiol. Methods 1999, 36, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzesiak, J.; Zdanowski, M.K.; Górniak, D.; Świątecki, A.; Aleksandrzak-Piekarczyk, T.; Szatraj, K.; Sasin-Kurowska, J.; Nieckarz, M. Microbial community changes along the Ecology Glacier ablation zone (King George Island, Antarctica). Polar Biol. 2015, 38, 2069–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Martínez, J.; Serrano, E.; Schmid, T.; Mink, S.; Linés, C. Periglacial processes and landforms in the South Shetland Islands (northern Antarctic Peninsula region). Geomorphology 2012, 155, 62–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochera, C.; Justel, A.; Fernández-Valiente, E.; Bañón, M.; Rico, E.; Toro, M.; Camacho, A.; Quesada, A. Interannual meteorological variability and its effects on a lake from maritime Antarctica. Polar Biol. 2010, 33, 1615–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bañón, M.; Justel, A.; Velázquez, D.; Quesada, A. Regional weather survey on Byers Peninsula, Livingston Island, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Antarct. Sci. 2013, 25, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lipzig, N.P.M.; King, J.C.; Lachlan-Cope, T.A.; Broeke, M.R. Precipitation, sublimation, and snow drift in the Antarctic Peninsula region from a regional atmospheric model. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2004, 109, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, M.; Camacho, A.; Rochera, C.; Rico, E.; Bañón, M.; Fernández-Valiente, E.; Marco, E.; Justel, A.; Avendaño, M.C.; Ariosa, Y.; et al. Limnological characteristics of the freshwater ecosystems of Byers Peninsula, Livingston Island, in maritime Antarctica. Polar Biol. 2007, 30, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, M.; Hrbáček, F.; Ruiz-Fernández, J.; de Pablo, M.Á.; Vieira, G.; Ramos, M.; Antoniades, D. Active layer dynamics in three topographically distinct lake catchments in Byers Peninsula (Livingston Island, Antarctica). Catena 2017, 149, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochera, C.; Toro, M.; Rico, E.; Fernández-Valiente, E.; Villaescusa, J.A.; Picazo, A.; Quesada, A.; Camacho, A. Structure of planktonic microbial communities along a trophic gradient in lakes of Byers Peninsula, South Shetland Islands. Antarct. Sci. 2013, 25, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaescusa, J.A.; Casamayor, E.O.; Rochera, C.; Velázquez, D.; Chicote, A.; Quesada, A.; Camacho, A. A close link between bacterial community composition and environmental heterogeneity in maritime Antarctic lakes. Int. Microbiol. 2010, 13, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Delgado, J.A.; Villaescusa, J.A.; Diazmacip, M.E.; Velazquez, D.; Rico, E.; Toro, M.; Quesada, A.; Camacho, A. Minimum population size estimates demonstrate an increase in southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) on Livingston Island, maritime Antarctica. Polar Biol. 2012, 36, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, P.A.; Francelino, M.R.; Schaefer, C.E.G.; Simas, F.N.; de Mendonça, B.A. Distribution and characterization of soils and landform relationships in Byers Peninsula, Livingston Island, Maritime Antarctica. Geomorphology 2012, 155, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamans, A.C.; Boluda, R.; Picazo, A.; Gil, C.; Ramos-Miras, J.J.; Tejedo, P.; Pertierra, L.R.; Benayas, J.; Camacho, A. Soil features in rookeries of Antarctic penguins reveal sea to land biotransport of chemical pollutants. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2015; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Shannon, C.E.; Weaver, W. The Measurement Theory of Communication; University of Illinois Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker, R.H. Evolution of species diversity in land communities. Evol. Biol. 1977, 10, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A. Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand. J. Stat. 1984, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Christian, B.W.; Lind, O.T. Multiple carbon substrate utilization by bacteria at the sediment–water interface: Seasonal patterns in a stratified eutrophic reservoir. Hydrobiologia 2007, 586, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Gallagher, E.D. Ecologically meaningful transformations for ordination of species data. Oecologia 2001, 129, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faust, K.; Raes, J. Conet app: Inference of biological association networks using cytoscape. F1000Research 2016, 5, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, C.T.; Franz, M.; Kazi, F.; Donaldson, S.L.; Morris, Q.; Bader, G.D. Cytoscape Web: An interactive web-based network browser. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2347–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, R.J.; Jones, S.E.; Eiler, A.; McMahon, K.D.; Bertilsson, S. A guide to the natural history of freshwater lake bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 14–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackey, T.J.; Sumner, D.Y.; Hawes, I.; Jungblut, A.D.; Andersen, D. Growth of modern branched columnar stromatolites in Lake Joyce, Antarctica. Geobiology 2015, 13, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, H.; Mojib, N.; Hakim, J.A.; Hawes, I.; Tanabe, Y.; Andersen, D.T.; Bej, A.K. Microbial communities and their predicted metabolic functions in growth laminae of a unique large conical mat from Lake Untersee, East Antarctica. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mao, G.; Gao, G.; Wang, Y. Impact of planktonic low nucleic acid-content bacteria to bacterial community structure and associated ecological functions in a shallow lake. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 658, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, A. Sulfur bacteria. In Encyclopedia of Inland Waters; Likens, G.E., Ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: Oxford, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Valiente, E.; Camacho, A.; Rochera, C.; Rico, E.; Vincent, W.; Quesada, A. Community structure and physiological characterization of microbial mats in Byers Peninsula, Livingston Island (South Shetland Islands, Antarctica). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 59, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velazquez, D.; Jungblut, A.D.; Rochera, C.; Rico, E.; Camacho, A.; Quesada, A. Trophic interactions in microbial mats on Byers Peninsula, maritime Antarctica. Polar Biol. 2016, 40, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaro, E.; Zangrando, R.; Vecchiato, M.; Turetta, C.; Barbante, C.; Gambaro, A. D- and l-amino acids in Antarctic lakes: Assessment of a very sensitive HPLC-MS method. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 5259–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villaescusa, J.A.; O’ Casamayor, E.; Rochera, C.; Quesada, A.; Michaud, L.; Camacho, A. Heterogeneous vertical structure of the bacterioplankton community in a non-stratified Antarctic Lake. Antarct. Sci. 2013, 25, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellenberger, S.; Drake, H.L.; Kolb, S. Functionally Redundant cellobiose-degrading soil bacteria respond differentially to oxygen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6043–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nichols, D.; Bowman, J.; Sanderson, K.; Nichols, C.M.; Lewis, T.; McMeekin, T.; Nichols, P.D. Developments with Antarctic microorganisms: Culture collections, bioactivity screening, taxonomy, PUFA production and cold-adapted enzymes. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1999, 10, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budnick, W.R.; Mruzek, J.L.; Larson, C.A.; Passy, S.I. The impacts of nutrient supply and imbalance on subcontinental co-occurrence networks and metacommunity composition of stream algae. Ecography 2021, 44, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Shen, F.; Zeng, J.; Huang, R.; Yu, Z.; Wu, Q.L. Network analysis reveals seasonal variation of co-occurrence correlations between Cyanobacteria and other bacterioplankton. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Lake | X-UTM | Y-UTM | Catchment Size (km2) | Lake Surface (km2) | Maximum Depth (m) | Analyses Conducted | Trophic Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refugio | 602200 | 3050550 | 0.12 | 0.016 | 0.5 | F, B | Eutrophic |
| Turbio | 598000 | 3051800 | 0.58 | 0.021 | 7.8 | F | Oligotrophic |
| Escondido | 599475 | 3052650 | 0.08 | 0.022 | 4.5 | F | Ultra-oligotrophic |
| Somero | 596800 | 3052150 | 0.06 | 0.011 | 0.5 | F, B | Mesotrophic |
| Midge | 597700 | 3054150 | 0.27 | 0.054 | 8.2 | F | Ultra-oligotrophic |
| Chester | 597500 | 3053550 | 0.09 | 0.039 | 5.0 | F | Ultra-oligotrophic |
| Limnopolar | 597100 | 3052200 | 0.58 | 0.023 | 5.5 | F, B | Oligotrophic |
| Refugio S | Turbio S | Escondido S | Somero S | Midge S | Chester S | Chester D | Limnopolar S | Limnopolar D | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAPROTAX | Chao-1 | 20 | 8 | 15 | 6 | 15 | 12 | 14 | 8 | 9 |
| Shannon H | 2.00 | 1.64 | 1.53 | 0.75 | 1.75 | 1.55 | 1.97 | 1.41 | 1.56 | |
| Evenness J | 0.67 | 0.790 | 0.56 | 0.42 | 0.65 | 0.62 | 0.750 | 0.68 | 0.71 | |
| Menhinick | 1.07 | 0.22 | 0.43 | 0.17 | 0.52 | 0.47 | 0.40 | 0.240 | 0.26 | |
| C:N:S ratio | 3:0.9:1 | 60:41:1 | 65:6:1 | 15:0.8:1 | 18:4:1 | 8:3:1 | 3:0.4:1 | 30:10:1 | 3:1:1 | |
| BIOLOG | Richness S | 25 | - | - | 23 | - | - | - | 23 | 23 |
| Shannon H | 3.12 | - | - | 3.09 | - | - | - | 2.93 | 2.89 | |
| Evenness J | 0.97 | - | - | 0.99 | - | - | - | 0.93 | 0.92 | |
| AWCD | 1.32 | - | - | 1.39 | - | - | - | 0.71 | 0.83 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Picazo, A.; Villaescusa, J.A.; Rochera, C.; Miralles-Lorenzo, J.; Quesada, A.; Camacho, A. Functional Metabolic Diversity of Bacterioplankton in Maritime Antarctic Lakes. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9102077
Picazo A, Villaescusa JA, Rochera C, Miralles-Lorenzo J, Quesada A, Camacho A. Functional Metabolic Diversity of Bacterioplankton in Maritime Antarctic Lakes. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(10):2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9102077
Chicago/Turabian StylePicazo, Antonio, Juan Antonio Villaescusa, Carlos Rochera, Javier Miralles-Lorenzo, Antonio Quesada, and Antonio Camacho. 2021. "Functional Metabolic Diversity of Bacterioplankton in Maritime Antarctic Lakes" Microorganisms 9, no. 10: 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9102077
APA StylePicazo, A., Villaescusa, J. A., Rochera, C., Miralles-Lorenzo, J., Quesada, A., & Camacho, A. (2021). Functional Metabolic Diversity of Bacterioplankton in Maritime Antarctic Lakes. Microorganisms, 9(10), 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9102077






